- How can I start a DRL lamp without a throttle?
- Purchase of a special model DRL 250
- Using a Capacitor
- Using an incandescent lamp
- Technical characteristics of DRL and its analogues
- Low pressure sodium lamps
- Types of gas discharge lamps.
- Low pressure gas discharge lamps.
- High pressure gas discharge lamps.
- Requirements for the disposal of mercury devices
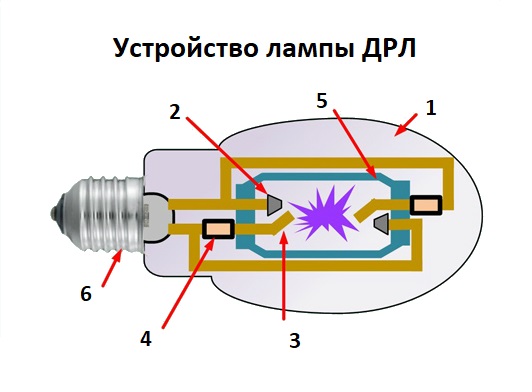
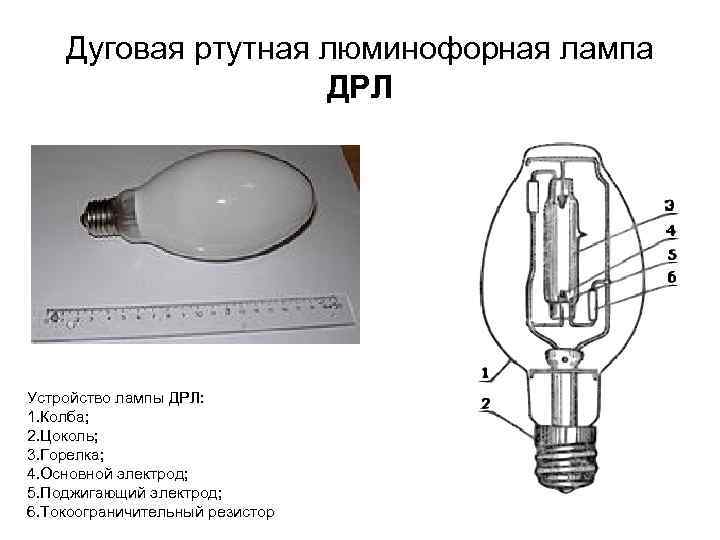
- Operating principle
- Types of DRL lamps
- Life time
- Application specifics: pros and cons of lamps
How can I start a DRL lamp without a throttle?
To operate an arc lamp without an additional device, you can go in several directions:
- Use a light source with a special design (DRV type lamp). A feature of lamps that can work without a choke is the presence of an additional tungsten filament, which acts as a starter. The parameters of the spiral are selected according to the characteristics of the burner.
- Starting a standard DRL lamp using a voltage pulse supplied by a capacitor.
- Ignition of the DRL lamp by connecting an incandescent lamp or other load in series.
Ignition of the lamp by connecting the boiler in series is presented in a video filmed for the channel "Little by little".
Purchase of a special model DRL 250
Direct switching lamps are available in the product lines of a number of companies:
- TDM Electric (DRV series);
- Lisma, Iskra (DRV series);
- Philips (ML series);
- Osram (HWL series).
The characteristics of some direct lamps are shown in the table.
| Parameter | DRV 160 | DRV 750 |
| Power, W | 160 | 750 |
| Flux, lm | 8000 | 37500 |
| plinth | E27 | E40 |
| Resource, hours | 5000 | 5000 |
| Color temperature, K | 4000 | 4000 |
| Length, mm | 127 | 358 |
| Diameter, mm | 77 | 152 |
The principle of operation of the DRV lamp:
- At the initial stage of ignition of the lamp, the spiral provides a voltage on the cathodes within 20 V.
- As the arc ignites, the voltage begins to rise, which reaches 70 V. In parallel, the voltage on the spiral decreases, causing a decrease in the glow. During operation, the spiral is an active ballast, which reduces the efficiency of the main burner. Therefore, there is a decrease in the luminous flux with equal power consumption.
Advantages of DRV lamps:
- the ability to work in AC networks 50 Hz with a voltage of 220-230 V without additional devices for starting and supporting discharge burning;
- the possibility of using instead of incandescent lamps;
- short time to reach full power mode (within 3-7 minutes).
Lamps have several disadvantages:
- reduced luminous efficiency (compared to conventional DRL lamps);
- resource reduced to 4000 hours, determined by the life of the tungsten filament.
Due to shortcomings, DRV lamps are used in household lamps or in old industrial installations designed for mounting powerful incandescent lamps. In this case, the devices allow you to improve illumination while reducing power consumption.
Using a Capacitor
When using lamps of the DRI type, the start is carried out through the IZU - a special device that gives an ignition impulse. It consists of a series-connected diode D and a resistance R, as well as a capacitor C.When voltage is applied to the capacitor, a charge is formed, which is fed through the thyristor K to the primary winding of the transformer T. An increased voltage pulse is formed on the secondary winding, which ensures the ignition of the discharge.
Condenser ignition circuit
The use of elements allows you to reduce energy consumption by 50%. The connection diagram is identical, a dry-type capacitor is installed in parallel, designed to operate in circuits with a voltage of 250 V.
The capacitance of the capacitor depends on the operating current of the inductors:
- 35 uF at 3A current;
- 45 microfarads at a current of 4.4A.
Using an incandescent lamp
For ignition of the DRL, an incandescent lamp with a power equal to a gas discharge lamp can be connected. It is possible to turn on the lamp by using a ballast with a similar power (for example, a boiler or an iron). Such methods do not provide stable operation and do not meet safety requirements, therefore they are not recommended for use.
The ignition of the DRL 250 using an incandescent lamp with a power of 500 watts is demonstrated by the author Andrey Ivanchuk.
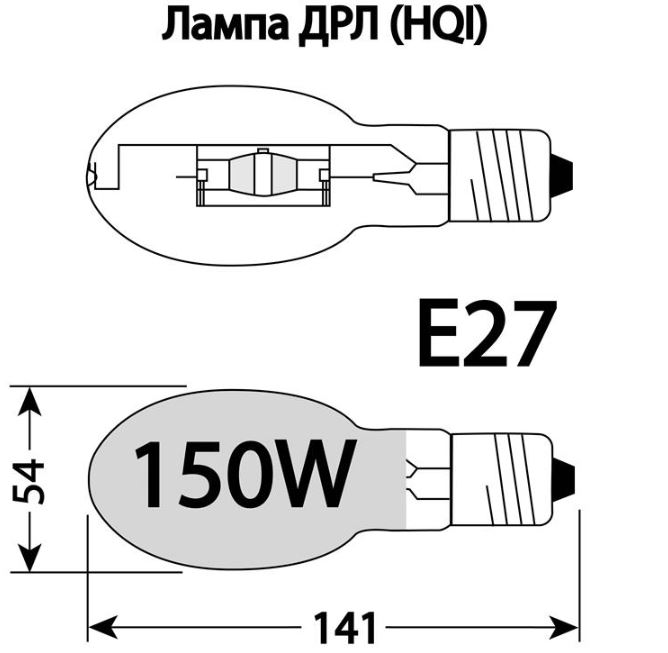
Technical characteristics of DRL and its analogues
The main technical characteristic of the light source - its power - is reflected in the marking of the DRL lamps. The rest of the indicators that determine the operating conditions, you need to familiarize yourself additionally. To do this, you should study the accompanying documents.
Other indicators include the following specifications:
- luminous flux - it determines the need for a certain number of light sources to create the required illumination per unit area;
- service life - determines the guaranteed period of operation of a particular model;
- socle standard size - sets the parameters of fixtures with which it is possible to use a particular lamp;
- dimensions - also determine the possibility of using lamps with a particular lamp.
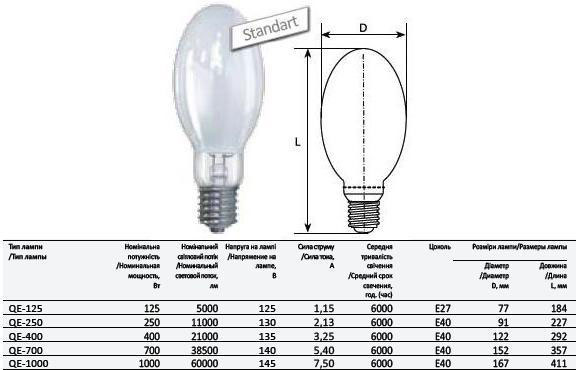
The main technical characteristics of DRL series lamps are given in the following table:
| Model | Electric power, Tue | Light flow, Lm | Lifetime, hours | Dimensions, mm (length × diameter) | Plinth type |
| DRL-50 | 50 | 1900 | 10000 | 130 × 56 | E27 |
| DRL-80 | 80 | 3600 | 12000 | 166 × 71 | E27 |
| DRL-125 | 125 | 6300 | 12000 | 178 × 76 | E27 |
| DRL-250 | 250 | 13000 | 12000 | 228 × 91 | E40 |
| DRL-400 | 400 | 24000 | 15000 | 292 × 122 | E40 |
| DRL-700 | 700 | 40000 | 18000 | 357 × 152 | E40 |
| DRL-1000 | 1000 | 55000 | 10000 | 411 × 157 | E40 |
| DRV-160 | 160 | 2500 | 3000 | 178 × 76 | E27 |
| DRV-250 | 250 | 4600 | 3000 | 228 × 91 | E40 |
| DRV-500 | 500 | 12250 | 3000 | 292 × 122 | E40 |
| DRV-750 | 750 | 22000 | 3000 | 372 × 152 | E40 |
 Device for street lighting of the ZhKU12 series, working with DRL lamps
Device for street lighting of the ZhKU12 series, working with DRL lamps
Low pressure sodium lamps
The tube is filled with an appropriate amount of metallic sodium and inert gases - neon and argon. The discharge tube is placed in a transparent glass protective jacket, which provides thermal insulation of the discharge tube from the outside air and maintains the optimum temperature at which heat losses are negligible. A high vacuum must be created in the protective jacket, since the efficiency of the lamp depends on the magnitude and maintenance of the vacuum during the operation of the lamp. At the end of the outer tube, a plinth is fixed, usually a pin, for connecting to the network.
Connection diagrams for high pressure sodium lamps.
First, when the sodium lamp is ignited, a discharge occurs in the neon, and the lamp begins to glow red. Under the influence of a discharge in neon, the discharge tube heats up and sodium begins to melt (the melting point of sodium is 98°C).Part of the molten sodium evaporates, and as the sodium vapor pressure in the discharge tube rises, the lamp begins to glow yellow. The process of flaring up the lamp lasts 10-15 minutes.
Sodium lamps are among the most economical of existing light sources. The efficiency of the lamp is influenced by a number of factors: the temperature of the discharge tube, the heat-insulating properties of the protective jacket, the pressure of the filler gases, etc. To obtain the highest efficiency of the lamp, the temperature of the discharge tube must be maintained within the range of 270-280 ° C. In this case, the sodium vapor pressure is 4 * 10-3 mmHg Art. Increasing and decreasing the temperature against the optimum leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the lamp.
To keep the temperature of the discharge tube at an optimum level, it is necessary to better isolate the discharge tube from the surrounding atmosphere. Removable protective tubes used in domestic lamps do not provide sufficient thermal insulation, therefore, a lamp of the DNA-140 type, manufactured by our industry, with a power of 140 W, has a luminous efficiency of 80-85 lm / W. Sodium lamps are now being developed, in which the protective tube is integral with the discharge tube. This design of the lamp provides good thermal insulation and, together with the improvement of the discharge tube by making dents on it, makes it possible to raise the luminous efficiency of the lamps to 110-130 lm / W.
The pressure of neon or argon should be no more than 10 mm Hg. Art., since at their higher pressure, sodium vapor can move to one side of the tube. This leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the lamp. To prevent the movement of sodium in the lamp, dents are provided on the tube.
The service life of the lamp is determined by the quality of the glass, the pressure of the filling gases, the design and materials of the electrodes, etc. Under the influence of hot sodium, especially its vapor, the glass is severely eroded.
Comparative scale of lamp temperatures.
Sodium is a strong chemical reducing agent, therefore, when combined with silicic acid, which is the basis of glass, it reduces it to silicon, and the glass turns black. In addition, glass absorbs argon. In the end, only neon remains in the discharge tube, and the lamp stops lighting. The average lamp life is from 2 to 5 thousand hours.
The lamp is connected to the network using a high-dissipation autotransformer, which provides the high open circuit voltage necessary for ignition of the lamp and stabilization of the discharge.
The main disadvantage of low-pressure sodium lamps is the uniform color of the radiation, which does not allow
use them for general lighting purposes in a production environment, due to significant color distortion of objects. Very effective application sodium lamps for lighting, transport sidings, freeways and, in some cases, outdoor architectural lighting in cities. The domestic industry produces sodium lamps in limited quantities.
Types of gas discharge lamps.
According to pressure, there are:
- GRL low pressure
- GRL high pressure
Low pressure gas discharge lamps.
Fluorescent lamps (LL) - designed for lighting. They are a tube coated from the inside with a phosphor layer. A high voltage pulse is applied to the electrodes (usually six hundred volts or more). The electrodes are heated, a glow discharge occurs between them. Under the influence of the discharge, the phosphor begins to emit light.What we see is the glow of the phosphor, and not the glow discharge itself. They operate at low pressure.
Read more about fluorescent lamps - here
Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are fundamentally no different from LLs. The difference is only in the size, shape of the flask. The start-up electronics board is usually built into the base itself. Everything is geared towards miniaturization.
More about the CFL device - here
Display backlight lamps also do not have fundamental differences. Powered by an inverter.
Induction lamps. This type of illuminator does not have any electrodes in its bulb. The flask is traditionally filled with an inert gas (argon) and mercury vapor, and the walls are covered with a layer of phosphor. Gas ionization occurs under the action of a high-frequency (from 25 kHz) alternating magnetic field. The generator itself and the gas flask can make up one whole device, but there are also options for spaced manufacturing.
High pressure gas discharge lamps.
There are also high pressure devices. The pressure inside the flask is greater than atmospheric pressure.
Arc mercury lamps (abbreviated DRL) were previously used for outdoor street lighting. Nowadays they are used less and less. They are being replaced by metal halide and sodium light sources. The reason is low efficiency.
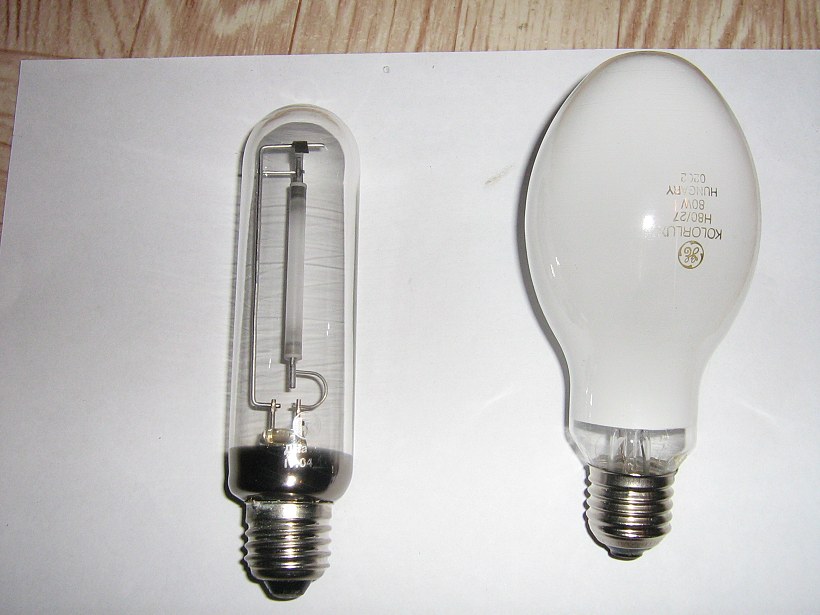
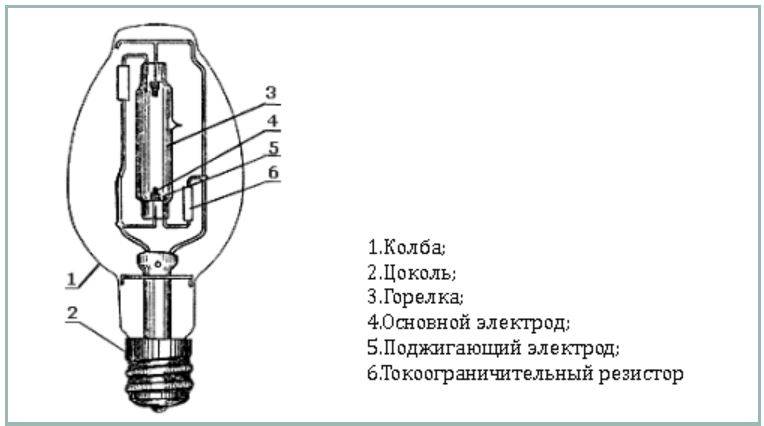
The appearance of the DRL lamp
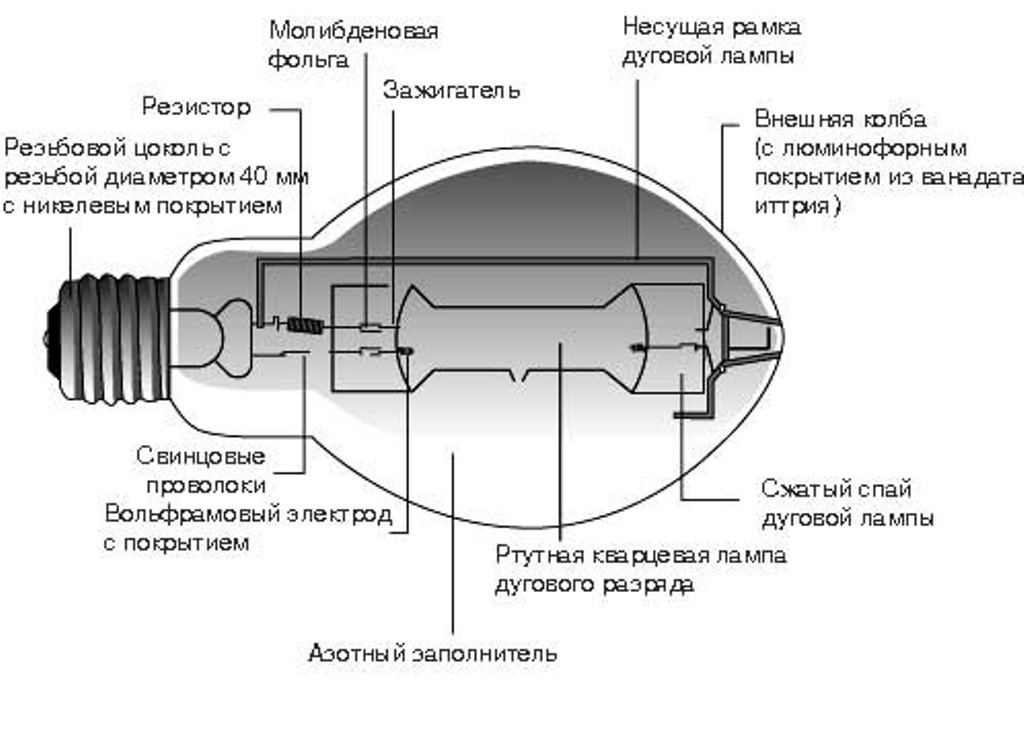
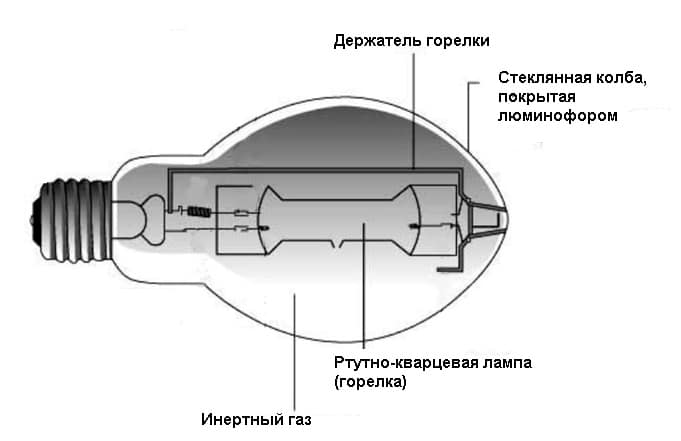
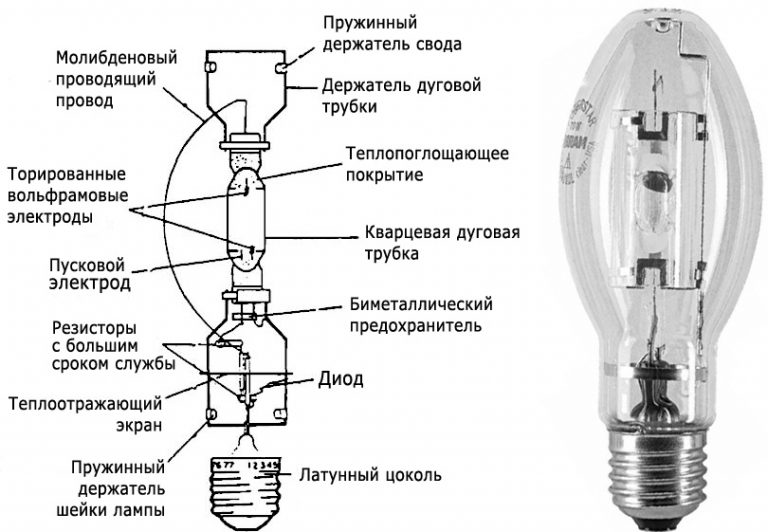
Arc mercury iodide lamps (HID) contain a burner in the form of a tube of fused quartz glass. It contains electrodes. The burner itself is filled with argon, an inert gas with impurities of mercury and rare earth metal iodides. May contain cesium. The burner itself is placed inside a heat-resistant glass flask. Air is pumped out of the flask, practically the burner is in a vacuum. More modern ones are equipped with a ceramic burner - it does not darken.Used to illuminate large areas. Typical powers are from 250 to 3500 watts.
Arc sodium tubular lamps (HSS) have twice the light output compared to DRL at the same power consumption. This variety is designed for street lighting. The burner contains an inert gas - xenon and vapors of mercury and sodium. This lamp can be immediately recognized by the glow - the light has an orange-yellow or golden hue. They differ in a rather long transition time to the off state (about 10 minutes).
Arc xenon tubular light sources are characterized by bright white light, spectrally close to daylight. The power of lamps can reach 18 kW. Modern options are made of quartz glass. The pressure can reach 25 atm. The electrodes are made of tungsten doped with thorium. Sometimes sapphire glass is used. This solution ensures the predominance of ultraviolet in the spectrum.
The light flux is created by the plasma near the negative electrode. If mercury is included in the composition of the vapor, then the glow occurs near the anode and cathode. Flashes are also of this type. A typical example is IFC-120. They can be identified by an additional third electrode. Due to their range, they are great for photography.
Metal halide discharge lamps (MHL) are characterized by compactness, power and efficiency. Often used in lighting fixtures. Structurally, they are a burner placed in a vacuum flask. The burner is made of ceramic or quartz glass and filled with mercury vapor and metal halides. This is necessary to correct the spectrum.Light is emitted by the plasma between the electrodes in the burner. Power can reach 3.5 kW. Depending on impurities in mercury vapor, a different color of the light flux is possible. They have good light output. The service life can reach 12 thousand hours. It also has good color reproduction. Long goes to the operating mode - about 10 minutes.
Requirements for the disposal of mercury devices
It is impossible to throw away waste or defective mercury-containing light bulbs thoughtlessly. Devices with a damaged flask are a serious threat to human health and the environment in general, and therefore require specific disposal.
The question of how to dispose of unsafe waste is relevant for both business owners and ordinary residents. The recycling of mercury lamps is carried out by organizations that have received the appropriate license.
The company enters into a service contract with such a firm. Upon request, a representative of the recycling company visits the facility, collects and removes the lamps for subsequent disinfection and recycling. The estimated cost of the service is 0.5 USD for one lighting device.
Reception points have been organized to collect mercury-containing light bulbs from the population. People living in small towns can hand over hazardous waste for recycling through the "ecomobile"
If the emission of mercury-containing lamps by enterprises is somehow controlled by supervisory authorities, then compliance with the rules for disposal by the population is the personal responsibility of citizens.
Unfortunately, due to low awareness, not every user of mercury lamps is aware of the possible consequences of mercury vapor entering the environment.
All types of energy-saving lamps are described in detail in the following article, which discusses the principles of operation, compares devices, and provides a simplified economic assessment.
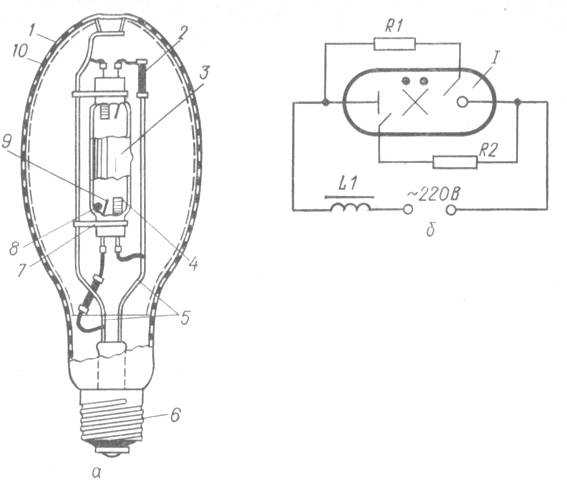
Operating principle
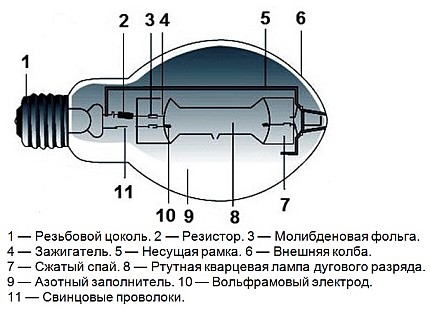
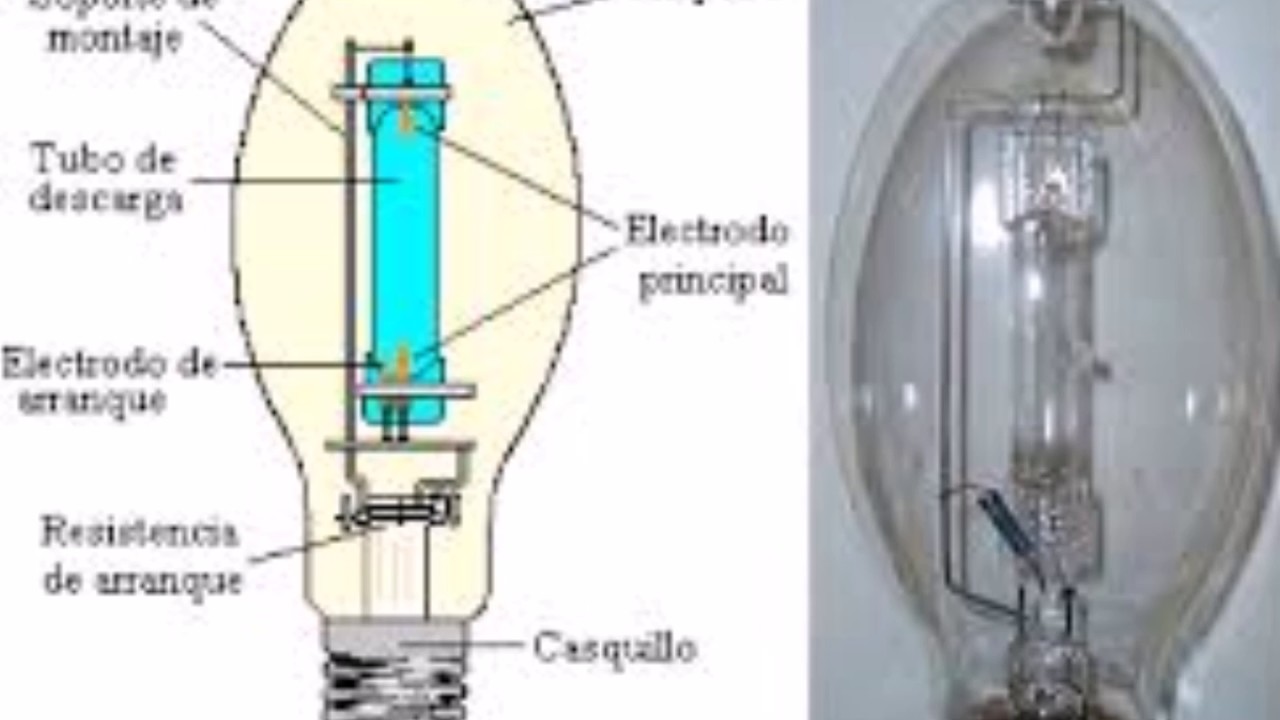
The burner (RT) of the lamp is made of a refractory and chemically resistant transparent material (quartz glass or special ceramics), and is filled with strictly metered portions of inert gases. In addition, metallic mercury is introduced into the burner, which in a cold lamp has the form of a compact ball, or settles in the form of a coating on the walls of the flask and (or) electrodes. The luminous body of the RLVD is a column of arc electric discharge.
Scheme 3. Transformer input.
The ignition process of a lamp equipped with ignition electrodes is as follows. When a supply voltage is applied to the lamp, a glow discharge occurs between the closely spaced main and ignition electrodes, which is facilitated by a small distance between them, which is significantly less than the distance between the main electrodes, therefore, the breakdown voltage of this gap is also lower. The appearance in the RT cavity of a sufficiently large number of charge carriers (free electrons and positive ions) contributes to the breakdown of the gap between the main electrodes and the ignition of a glow discharge between them, which almost instantly turns into an arc discharge.
Stabilization of the electrical and light parameters of the lamp occurs 10 - 15 minutes after switching on. During this time, the lamp current significantly exceeds the rated current and is limited only by the resistance of the ballast. The duration of the starting mode is highly dependent on the ambient temperature: the colder, the longer the lamp will flare up.
The electrical discharge in the burner of a mercury arc lamp produces visible blue or violet radiation, as well as intense ultraviolet radiation. The latter excites the glow of the phosphor deposited on the inner wall of the outer bulb of the lamp. The reddish glow of the phosphor, mixing with the white-greenish radiation of the burner, gives a bright light close to white.
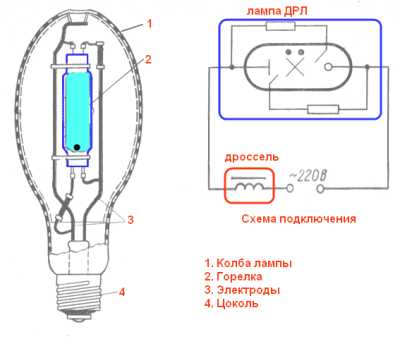
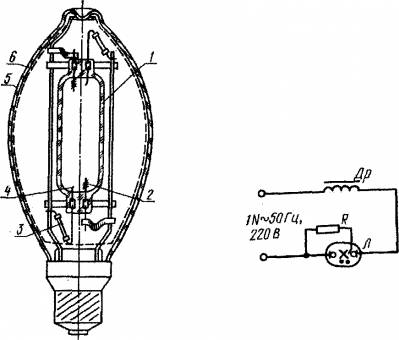
Scheme of switching on the DRL lamp.
A change in the mains voltage up or down causes a corresponding change in the luminous flux. A deviation of the supply voltage by 10 - 15% is permissible and is accompanied by a change in the luminous flux of the lamp by 25 - 30%. When the supply voltage drops below 80% of the rated voltage, the lamp may not light up, and the burning one may go out.
When burning, the lamp becomes very hot. This requires the use of heat-resistant wires in lighting devices with mercury arc lamps, and imposes serious requirements on the quality of cartridge contacts. Since the pressure in the burner of a hot lamp increases significantly, its breakdown voltage also increases. The voltage of the supply network is insufficient to ignite a hot lamp. Therefore, before re-ignition, the lamp must cool down. This effect is a significant drawback of high-pressure mercury arc lamps, since even a very short interruption of the power supply extinguishes them, and a long cooling pause is required for re-ignition.
General information: DRL lamps have a high light output. They are resistant to atmospheric influences, their ignition does not depend on the ambient temperature.
- DRL type lamps are available with a power of 80, 125, 250, 400, 700, 1000 W;
- average service life of 10,000 hours.
An important disadvantage of DRL lamps is the intense formation of ozone during their combustion. If for bactericidal installations this phenomenon usually turns out to be useful, then in other cases the ozone concentration near the light device can significantly exceed the permissible value according to sanitary standards. Therefore, rooms where DRL lamps are used must have adequate ventilation to remove excess ozone.
O0Dr-main winding of the inductor, D0Dr-additional inductor winding, C3-interference suppression capacitor, SV-selenium rectifier, R-charging resistor, L-two-electrode lamp DRL, P-discharger.
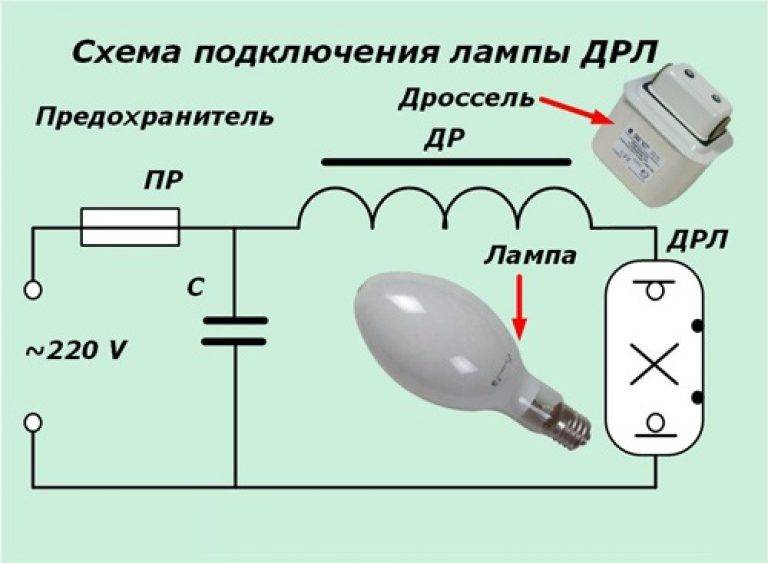
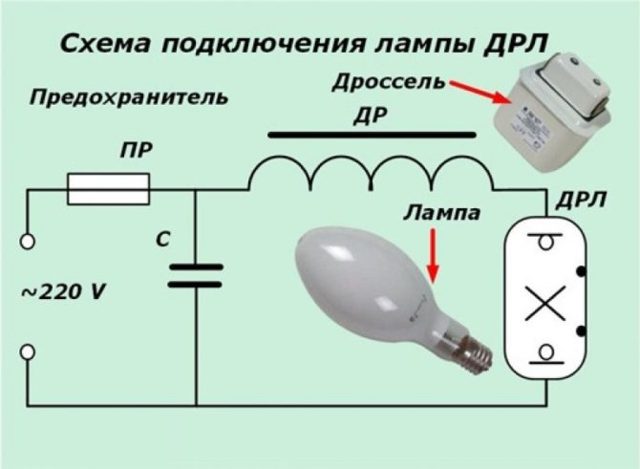
Turning on: Turning on the lamps in the network is carried out using the control gear (start-control equipment). Under normal conditions, a choke is connected in series with the lamp (scheme 2), at very low temperatures (below -25 ° C), an autotransformer is introduced into the circuit (scheme 3).
When the DRL lamps are turned on, a large starting current is observed (up to 2.5 Inom). The lamp ignition process lasts up to 7 minutes or more, the lamp can be turned on again only after it has cooled down (10-15 minutes).
- technical data of the lamp DRL 250 Power, W - 250;
- lamp current, A - 4.5;
- base type - E40;
- luminous flux, Lm - 13000;
- light output, Lm / W - 52;
- color temperature, K - 3800;
- burning time, h - 10000;
- color rendering index, Ra - 42.
Types of DRL lamps
This type of illuminator is classified according to the vapor pressure inside the burner:
- Low pressure - RLND, not more than 100 Pa.
- High pressure - RVD, about 100 kPa.
- Ultra-high pressure - RLSVD, about 1 MPa.
DRL has several varieties:
- DRI - Arc Mercury with radiating additives.The difference is only in the materials used and the filling with gas.
- DRIZ - DRI with the addition of a mirror layer.
- DRSH - Arc Mercury Ball.
- DRT - Arc Mercury tubular.
- PRK - Direct Mercury-Quartz.
Western labeling is different from Russian. This type is marked as QE (if you follow ILCOS - generally accepted international marking), you can find out the manufacturer from the further part:
HSB\HSL - Sylvania,
HPL-Philips,
HRL - Radium,
MBF-GE,
HQL Osram.
Life time
Such a light source, according to manufacturers, is capable of burning for at least 12,000 hours. It all depends on such a characteristic as power - the more powerful the lamp, the longer it lasts.
Popular models and how many hours of service they are designed for:
- DRL 125 - 12000 hours;
- 250 - 12000 hours;
- 400 - 15000 hours;
- 700 - 20000 hours.
Note! In practice, there may be other numbers. The fact is that the electrodes, like the phosphor, are able to fail faster.
As a rule, light bulbs are not repaired, they are easier to replace, since a worn-out product shines 50% worse.
Designed for at least 12,000 hours of operation
There are several varieties of DRL (decoding - an arc mercury lamp), which are applicable both in everyday life and in production conditions. Products are classified by power, where the most popular models are 250 and 500 watts. Using them, they still create street lighting systems. Mercury appliances are good due to their availability and powerful light output. However, more innovative designs are emerging, safer and with better glow quality.
Application specifics: pros and cons of lamps
DRL-type illuminators are mainly installed on poles for lighting streets, driveways, park areas, adjacent territories and non-residential buildings. This is due to the technical and operational features of the lamps.
The main advantage of mercury-arc devices is their high power, which provides high-quality illumination of spacious areas and large objects.
It is worth noting that the DRL passport data for luminous flux are relevant for new lamps. After a quarter, the brightness deteriorates by 15%, after a year - by 30%
Additional benefits include:
- Durability. The average life, declared by manufacturers, is 12 thousand hours. Moreover, the more powerful the lamp, the longer it will last.
- Work at low temperatures. This is a decisive parameter when choosing a lighting device for the street. Discharge lamps are frost-resistant and retain their performance at sub-zero temperatures.
- Good brightness and lighting angle. The light output of DRL devices, depending on their power, ranges from 45-60 Lm / V. Thanks to the operation of the quartz burner and the phosphor coating of the bulb, a uniform distribution of light with a wide scattering angle is achieved.
- Compactness. The lamps are relatively small, the length of the product for 125 W is about 18 cm, the device for 145 W is 41 cm. The diameter is 76 and 167 mm, respectively.
One of the features of using DRL illuminators is the need to connect to the network through a choke. The role of the intermediary is to limit the current that feeds the light bulb. If you connect a lighting device bypassing the throttle, then it will burn out due to the large electric current.
Schematically, the connection is represented by a serial connection of a mercury phosphor lamp through a choke to the power supply.A ballast is already built into many modern DRL illuminators - such models are more expensive than conventional lamps
A number of disadvantages limit the use of DRL lamps in everyday life.
Significant cons:
- Ignition duration. Exit to full illumination - up to 15 minutes. Mercury takes time to heat up, which is very inconvenient at home.
- Sensitivity to the quality of power supply. When the voltage drops by 20% or more from the nominal value, it will not work to turn on the mercury lamp, and the luminous device will go out. With a decrease in the indicator by 10-15%, the brightness of the light deteriorates by 25-30%.
- Noise at work. The DRL-lamp makes a buzzing sound, not noticeable on the street, but noticeable indoors.
- Pulsation. Despite the use of a stabilizer, the bulbs flicker - it is undesirable to perform long-term work in such lighting.
- Low color reproduction. The parameter characterizes the reality of perception of surrounding colors. The recommended color rendering index for residential premises is at least 80, optimally 90-97. For DRL lamps, the value of the indicator does not reach 50. Under such lighting, it is impossible to clearly distinguish shades and colors.
- Unsafe application. During operation, ozone is released, therefore, when operating the lamp indoors, the organization of a high-quality ventilation system is required.
In addition, the presence of mercury in the flask itself is a potential hazard. Such light bulbs after use cannot simply be thrown away. In order not to pollute the environment, they are disposed of properly.
Another limitation of the use of discharge lamps in everyday life is the need to install them at a considerable height. Models with a power of 125 W - suspension in 4 m, 250 W - 6 m, 400 W and more powerful - 8 m
A significant minus of DRL illuminators is the impossibility of switching on again until the lamp has completely cooled down. During operation of the device, the gas pressure inside the glass flask increases greatly (up to 100 kPa). Until the lamp cools down, it is impossible to break through the spark gap with the start voltage. Re-enabling occurs after about a quarter of an hour.