- Types of ventilation
- Centralized ventilation system with heat recovery and air conditioning
- Roof ventilation units
- Duct ventilation system
- The tasks of ventilation of yoga centers
- Accounting for temperature and humidity parameters
- Correct calculation is the basis of design
- Gym ventilation
- Gym ventilation survey
- Gym ventilation
- What should be taken into account when designing?
- Aeromass mobility standards
- Other Important Factors
- The supply of fresh air should be for every person
- Calculation and design
- Requirements for ventilation equipment
- Principles of organizing ventilation in sports facilities
- Ventilation of sports halls
- Air exchange rates in a fitness club
- Features of the ventilation system in the fitness club:
- Administrative and residential buildings
- Elements of the air exchange organization system
Types of ventilation
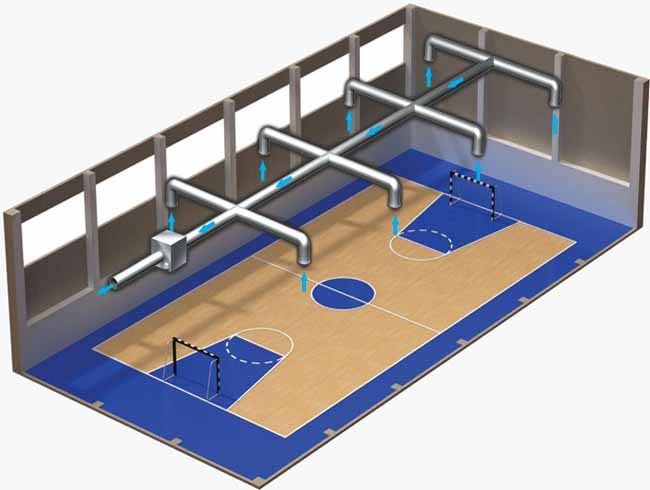
For ventilation of sports or gyms, a combined supply and exhaust system is used. An important condition for its creation is the same performance of supply and output of air flows, which makes it possible to exclude the appearance of drafts.Fresh air is supplied, as a rule, with the help of air diffusers that send compact supply jets in an inclined position from a height of about 3-4 m. Depending on the configuration and type of building, the number of floors and other features of the room, the following types of ventilation equipment can be used:
Centralized ventilation system with heat recovery and air conditioning
The operation of central air conditioners is based on the functioning of the central air conditioner, which provides the desired temperature and composition of the air. Heat recovery capability reduces space heating costs
Roof ventilation units
As an option - a monoblock roof unit, combined with an air conditioner. Used for ventilation of large halls, indoor stadiums. The system uses the principle of heat recovery. Air preparation and supply is carried out with the participation of a duct system that delivers a fresh supply stream to all rooms. The hood is made from ceiling lamps with the emission of exhaust air into the atmosphere
Duct ventilation system
Duct fans are used for relatively small rooms. The duct system distributes and transports fresh air, and the exhaust is done in the same way. Best option for small sports facilities with many separate rooms
The listed systems are not the only ones; other options are possible. Currently, there are many ready-made solutions on the market that provide ventilation for halls and rooms of various sizes and volumes.In order to choose the most suitable type of ventilation system, you should perform a careful calculation that provides information to find the right equipment.
The tasks of ventilation of yoga centers
In the yoga halls, people do physical exercises. With muscle loads, normal during exercise, the body needs to maintain oxygen balance. Therefore, visitors to the center will need more fresh air than under normal circumstances. For the comfort of those involved, the exhaust air must be removed from the room in a timely manner. With it, the negative consequences of classes will fly away - the smells of sweat and carbon dioxide. The airy atmosphere of the yoga center should meet the standards and give pleasure to all participants, without distracting them from the process of classes. For high-quality air exchange in the hall, it is necessary to develop a ventilation project.
An important part of design decisions is the correct selection of ventilation equipment. Natural ventilation methods are not used for gyms, as they cannot provide the necessary air exchange due to insufficient performance.
There are many mechanical ventilation options on the market. A proven and reliable solution for organizing air exchange in small gyms is the installation of a supply and exhaust unit in the form of a monoblock.
Accounting for temperature and humidity parameters
An important point in the design of systems of ventilation and heating complexes is the organization of the proper level of humidity, as well as the removal of excess heat from the building. This topic is especially relevant where the decoration of the room is exposed to increased exposure to steam and water.Engineering projects for shower rooms, toilets, pools should include:
- The layout of heating devices, excluding their contact with the bare skin of visitors. To prevent the risk of burns, it is forbidden to arrange niches in the walls, and place heating radiators in inaccessible places;
- In saunas, fire-fighting dry pipes;
- Required for solariums 4-fold air exchange.
It is believed that in gyms people emit more heat than in offices or apartments. To avoid overheating of visitors to the fitness center, be sure to take this circumstance into account when determining the temperature regime.
It is equally important to control the level of relative humidity.
Correct calculation is the basis of design
To create a properly functioning and economically justified climate system for a gym, careful planning and calculation is necessary, the result of which will be the data on the basis of which the design of this room will be carried out. It includes:
- Calculation of the required air exchange rate - how many times the air must be completely replaced in an hour.
- Calculation of the air flow rate of its movement speed and the required cross-section of the air ducts.
- Based on the previous data, the necessary equipment for ventilation of the premises is selected, the exact location of the air ducts and supply ventilation grilles is established.

Gym ventilation
- Details
- Published on Monday, 21 September 2015 19:52
- Hits: 11428
Gym ventilation survey
Examination and passportization of the ventilation of the sports hall is carried out before the design of ventilation and then usually during the reconstruction of the sports center or the need to extend the state certification and licensing of the stadium building complex with the issuance of the Ventilation Inspection Act or the passport of ventilation systems: ventilation examination; certification of ventilation. The cost of a ventilation inspection: 2,500 rubles for an inspection certificate for one ventilation system or a ventilation system passport, an engineer's visit to the site to measure air with an anemometer: 3,000 rubles. Attached is an anemometer verification certificate and a certificate of compliance with state measuring instruments, approval from Rostekhnadzor. The frequency of aerodynamic tests and certification of ventilation in sports halls is at least once every three years.
Upon arrival at the site, our engineer will inspect the ventilation and automation equipment, draw a diagram of the air ducts and photograph the general plan for the location of diffusers and grilles in the ceiling, measure the air flows in the main air ducts and at workplaces with an anemometer, which will allow us to draw a conclusion about the effectiveness of ventilation systems and compliance their norms in the Code of Rules SP-332.1325800.2017 “SPORTS FACILITIES. DESIGN RULES”, which will be displayed in the Ventilation Systems Inspection Act or in the Passports of Ventilation Units…
Examination and certification of ventilation systems is held in the gyms of preschool children's institutions and in schools, in the gyms of medical institutions and in swimming pool complexes once every three years.An SRO approval license is required when inspecting multi-storey sports centers and stadiums, a permit from Rostekhnadzor in the field of industrial safety is required for testing and examination of ventilation also at industrial facilities. The protocol of aerodynamic tests of ventilation systems is issued upon completion of the examination and certification in a single document with the main air measurements of all systems and with the signatures of all representatives. The certificate of completion of commissioning works is issued after comprehensive testing and balancing of ventilation units. Also, when checking, Rospotrebnazor is required to provide various documentation, an act of delivery of installation work, acts of individual testing of ventilation systems and a maintenance contract. The result of the work TECHNICAL REPORT of the examination of the ventilation of the premises of the sports center is issued upon completion with the attached working documentation.
Gym ventilation
The ventilation of the gym and the corresponding ventilation of the fitness club directly determines the class of the room and its attendance (and, of course, the profit of the organizer of sports events or training), which is why the design of the ventilation of fitness clubs must be carried out in accordance with the air exchange standards to ensure fresh air and a comfortable temperature in the rooms for those who train . The ventilation of the spa salon is designed with the required air exchange in accordance with SNiP 41-01-2003 "OVK" of supply air up to 4 times / hour and exhaust air up to 2.5 times / hour, taking into account the norm for people in the room, with mandatory air conditioning for automatic climate -control. Before designing the ventilation of a gym, a survey of existing ventilation systems is usually carried out and, if necessary, certification of the ventilation of the gym.According to the law, in order to commission a sports facility, it is necessary to have either a ventilation project or ventilation system passports, and at least once every three years, carry out aerodynamic tests of ventilation with the issuance of a Ventilation Inspection Act.
INSPECTION OF VENTILATION SYSTEMS AND CERTIFICATION OF VENTILATION

What should be taken into account when designing?
When designing, first of all, it is necessary to make calculations. We have already said above that for each athlete or trainee there should be at least 80 cubic meters of air per hour, and for each spectator another 20.
But here it is worth adding another category - staff. For each employee of the gym, 40 cubic meters of air must be circulated.
So the formula will look like this:
V=N1*L1+N2*L2+N3*L3, where
N1 is the number of trainees, L1 is the rate of air exchange for them. N2 is the number of spectators, L2 is the rate of air exchange for them. N3 is the number of workers, L3 is the rate of air exchange for them.
Aeromass mobility standards
When developing a project and choosing equipment, one more important factor must be taken into account - the movement of air masses. In simple terms, there should be no drafts in the gym.
 Making calculations and choosing equipment for arrangement of the ventilation system of the gym, it is also necessary to take into account the cross-section of the duct
Making calculations and choosing equipment for arrangement of the ventilation system of the gym, it is also necessary to take into account the cross-section of the duct
The aforementioned joint venture provides for this moment, the ventilation of sports halls has the following standards:
- swimming pools - no more than 0.2 m / s;
- halls for intensive training - no more than 0.3 m / s;
- halls for preparatory and recreational activities - no more than 0.5 m / s.
The situation is inversely proportional to the norms of the temperature regime. Directly for training grounds, air movement should be no more than 0.3 m / s. But, if we are talking about rooms for yoga, then the rules are softer.
Other Important Factors
Calculating the required power of the ventilation unit and the movement of air masses is far from all that needs to be taken into account when designing a gym. There are several important points.
First, a place to install equipment. It should not be located next to sports or any other equipment. It is desirable that the ventilation system has a remote control - this will eliminate many inconveniences.
Secondly, showers and changing rooms. Despite its small size in terms of area, one should not neglect the arrangement of ventilation in these rooms. With insufficient ventilation, condensation forms in them, and after it mold, which can spread to other rooms and halls.
 Do not forget to clean and change filters in ventilation systems in time. The accumulation of dust interferes with the full operation of the ventilation system and threatens the health of visitors
Do not forget to clean and change filters in ventilation systems in time. The accumulation of dust interferes with the full operation of the ventilation system and threatens the health of visitors
Thirdly, filters. As a rule, air is taken from the street. Equip the ventilation system with filters to ensure maximum comfort. This is especially true for large cities and halls located near the industrial zone.
Another recommendation that all experts give is to calculate the project with a margin. An emergency situation can always occur and part of the equipment will fail or the calculations for visitors will turn out to be incorrect, and more people will visit the hall. The recommended margin is 15-20% of the initial calculations.
The supply of fresh air should be for every person
The requirements for the ventilation of the gym are more serious than for living quarters. Since constant exercise leads to sweating and an increase in carbon dioxide, filtration should be carried out as often as possible. So, if in a living room the air should normally change every 10-20 minutes for an hour, then in the gym the required frequency is 7.5-10 minutes for the same period of time. This indicator allows you to determine the required power of the ventilation system. It is also necessary to take into account the intensity of the load on each person, but even if it is small, you should not abandon the oxygen exchange system.
Each gym is different from the other, even if their sizes are identical. For all the time, many architectural solutions have been developed, but they must also adhere to certain standards (especially with regard to height - at least 6 meters). So, each athlete should have at least 60 m3 of fresh oxygen. If the hall provides seats for spectators, then each of them should receive 20 m3 of ventilated oxygen.
When calculating, it is important not to forget about other, no less important premises:
- Locker room.
- Shower rooms.
- Warehouses.
- Coaches' offices.
- Massage rooms.
Here, the intensity of air exchange is calculated based on standard standards. It should be borne in mind that in the summer the gas should be cooled, and in the winter, on the contrary, it should be slightly warmed up. To achieve the maximum effect, air diffusers in private gyms must be installed at a height of 2.5-3 meters and in the region of 3-4 meters in public ones.
Calculation and design
When calculating the ventilation in the gym, it is necessary to determine the minimum performance of the system. To do this, you can use the following formula:
V = a*L
According to the formula, V is the performance, a is the number of people who are simultaneously engaged in the hall or are inside as spectators, L is the rate of air exchange. Also, when creating a ventilation project in a gym, one should take into account the norms. In this case, the formula will be:
V=n*S*H
According to this formula, V = performance, n is the air exchange rate established by building regulations, S is the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, and H is the height.
In addition, in the process of designing ventilation in the hall, the following points should be considered:
The room should have windows, it is desirable that they be equipped with a ventilation mode.
It is better to design the exhaust system with a margin: it is necessary to provide for the presence of shafts, calculate the number of fans and devices for forced air circulation.
If the air comes from the street, the system should be equipped with filters so that the atmosphere in the hall is as comfortable as possible.
It is important to take care of good ventilation not only in the hall, but also in showers and changing rooms, otherwise condensation may form in the building, which will lead to mold.
It is desirable that the project provides for the installation of equipment away from inventory storage areas, and the equipment itself can be controlled remotely.
Requirements for ventilation equipment
We assume that all norms and parameters correspond to the required ones.But at the same time, a huge air conditioner unit hangs above your bed, and to clean the system, you need to call a whole team with equipment that barely fits into the apartment.
Agree, in this situation, you will think a hundred times whether clean air is so important or you can get by with vents.
 The window leaf is the most popular method of natural ventilation of premises. However, not all rooms have them, and they are not relevant in any weather. For the cold season, in some cases, a heated supply duct ventilation system is more suitable.
The window leaf is the most popular method of natural ventilation of premises. However, not all rooms have them, and they are not relevant in any weather. For the cold season, in some cases, a heated supply duct ventilation system is more suitable.
Some residents of apartment buildings often complain about a massive ventilation system that runs through the entire room and of course this is wrong and should be corrected if technically possible.
Therefore, there are also architectural, external, as well as operational requirements.
For example:
- So, in some cases it is strictly forbidden to install air conditioner units on the front part.
- Equipment should not take up too much space, everything should be linked to a minimum.
- Small inertia of the system.
- Installation, assembly - the most simplified.
- Operation - devices should provide ease of operation and the least possible maintenance with repair and replacement of equipment.
- For fire safety, it is necessary to provide additional protection in the form of fireproof valves.
- For protection against vibrations and noise, additional protection is installed.
- Mutual installation of 2 air conditioners, so that in case of failure of 1, the second one can provide a minimum of 50% air exchange.
- In addition, ventilation and air conditioning systems must meet the economic possibilities both in terms of the equipment itself and in terms of the cost of their maintenance / operation.
The ventilation system can be natural, forced or mixed. If natural air exchange does not provide proper standards, it is developed with mechanical motivation.
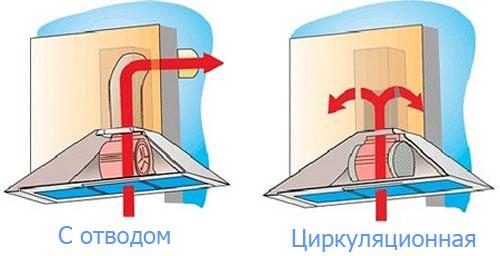
 Supply system - a design or type of ventilation air exchange, due to which there is an influx of fresh air. Exhaust system - a structure through which exhaust air exits
Supply system - a design or type of ventilation air exchange, due to which there is an influx of fresh air. Exhaust system - a structure through which exhaust air exits
Thanks to accurate calculations, you can already at the design stage find out which scheme you need for a particular room. In addition, it is regulated by separate regulations.
The choice of ventilation and air conditioning scheme depends on:
- type and purpose of the building/premises;
- the number of floors in the building;
- the possibility of the release of harmful substances;
- fire hazard.
The air exchange rate is set by the joint venture and VSN, and it is also determined by calculations.
Most often, for most types of buildings, natural ventilation without the use of mechanical stimulation meets all regulatory requirements.
However, if it does not cope, there is no way to establish ventilation or the coldest five-day period in the region bestows frosts below -40 degrees, artificial methods are provided.
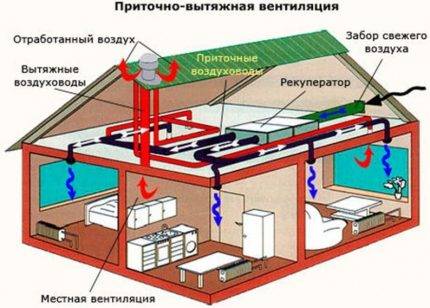
 The ventilation system is usually designed before the construction of the building, taking into account its purpose. However, if the building has a universal nature of use, such as rent for different offices, retail space, you have to adjust the system for a specific case.
The ventilation system is usually designed before the construction of the building, taking into account its purpose. However, if the building has a universal nature of use, such as rent for different offices, retail space, you have to adjust the system for a specific case.
In fact, ventilation is necessary to ensure a comfortable microclimate. What can we say about the buildings where people who need clean air live and work.
The following types of buildings are documented according to the quality of air exchange:
- residential and dormitories with premises for various purposes;
- administrative, research;
- educational, including school, preschool, boarding schools with accommodation;
- medical direction;
- consumer services;
- retail;
- various cultural and entertainment facilities - a circus, a cinema, a theater, a club.
Each has its own regulatory tables with a detailed indication of what kind of air exchange should provide high-quality ventilation.
But first, let's look at the regulations.
Principles of organizing ventilation in sports facilities
The air exchange requirements of fitness centers depend on the set of equipment used. The intensity of ventilation should take into account the purpose of the gym and is considered in conjunction with the installed equipment. The hall can be equipped with aerobics club accessories, yoga mats or sophisticated athletic equipment with treadmills. Each configuration option will require separate calculations of the need for air exchange. To get acquainted with the main standards of the regulatory framework, we will use the Soviet SNiP-th 2.08-02, dated 1989. It is accompanied by a reference manual, which lists the basic requirements for the air exchange of gyms. Consider the most important basic provisions of SNiP:
- The productivity of the supply of fitness clubs (gyms) should be at least 80 cubic meters per hour for a trained athlete, 20 cubic meters per hour for a passive spectator;
- In the halls, the directed movement of air masses and the appearance of drafts that cause colds are excluded;
- From the premises of the fitness club, an atmosphere saturated with carbon dioxide products of respiration, harmful fumes should be removed: - chlorine vapors from showers and pools, the smell of sweat and saunas;
- The microclimate system of gyms should take into account the intense heat dissipation of fitness center visitors, preventing stuffiness and overheating.
The project of ventilation of sports clubs should take into account the diversity of the set of sports and auxiliary facilities. For each of them, it is necessary to provide for the estimated rate of air exchange and temperature parameters of the air. For rooms where classes with heavy physical exertion are held, gyms, aerobics sections, sports dances, a temperature of 15 ° C is sufficient. The exercises of the yoga section can be classified as low-intensity exercises. So that the members of the section do not overcool, the recommended temperature for asana lovers is 18-19 ° C. Special microclimatic requirements are also imposed on other premises of sports centers:
- For wardrobes, massage rooms, utility rooms, a lower frequency of air mass renewal is allowed;
- The intensity of ventilation of showers and pools should provide for the timely removal of toxic fumes;
- Special ventilation conditions are created in places where chlorine-containing disinfectants, combustible and easily evaporating substances are stored;
- In solariums, saunas, climate control is necessary for the amount of heat release, the degree of air humidity, the concentration of ozone in it and other parameters.
The air exchange of gyms is calculated according to ventilation standards to the maximum in order to meet the needs of all premises. At the same time, it is necessary to observe other parameters of a healthy microclimate, to carry out air disinfection, and to maintain the necessary temperature and humidity conditions.
Ventilation of sports halls
The wrong air conditioning system in the gym can dramatically worsen your health.
If the management of the fitness club does not bother to install a flow-exhaust system based only on natural air exchange by ventilating the premises, a persistent unpleasant odor will inevitably appear in the gym. Vapors settling on the walls of the hall will promote the growth of pathogenic bacteria. When playing sports, a person consumes much more oxygen. If the training takes place in conditions of lack of oxygen, then very soon the general tone of the body, endurance and, as a result, sports results, will decrease.
Uneven circulation of air in the room entails the occurrence of drafts, zones in which the temperature is too low for training. This is fraught with colds, especially if not only adults, but also children are engaged in the hall.
 color solution for ventilation
color solution for ventilation
Air exchange rates in a fitness club
- for an athlete — 80 m3/h
- for the viewer - 20 m3 / h.
IMPORTANT! The calculation of the air volume is carried out according to two parameters: the frequency of air exchange or the amount of air per person. When choosing the performance of the ventilation system, the larger of the two air flow values is selected, calculated according to these parameters
- in the pool - 0.2 m/s;
- in sports halls for wrestling, table tennis and indoor skating rinks - 0.3 m/s;
- in other sports halls - 0.5 m/s.
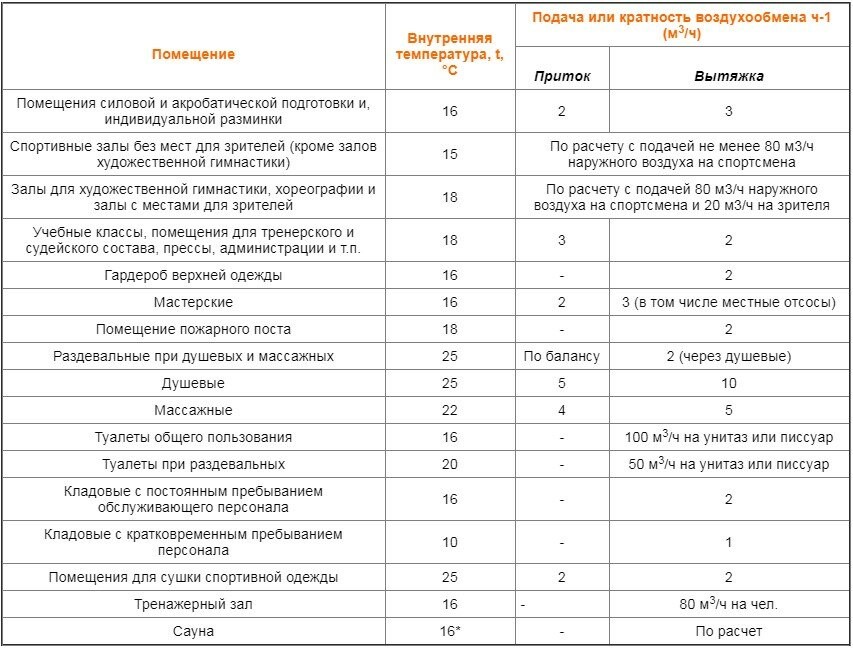
| room | Estimated air temperature, °C | Air exchange rate per 1 hour | |
| inflow | hood | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1. Gyms with seats St. 800 spectators, covered skating rinks with seats for spectators | 18* in the cold period of the year at a relative humidity of 30-45% and the design temperature of the outside air according to parameters B | According to the calculation, but not less than 80 m3/h of outdoor air per student and not less than 20 m3/h per spectator | |
| Not higher than 26 (on skating rinks - not higher than 25) in the warm season at a relative humidity of not more than 60% (on skating rinks - not more than 55%) and the design temperature of the outside air according to parameters B | |||
| 2. Sports halls with seats for 800 or less spectators | 18 * in the cold season. | ||
| Not more than 3 °C higher than the calculated outdoor air temperature according to parameters A in the warm period of the year (for the IV climatic region - according to paragraph 1 of this table) | |||
| 3. Sports halls without seats for spectators (except for rhythmic gymnastics halls) | 15* | According to the calculation, but not less than 80 m3/h of outdoor air per student | |
| 4. Indoor skating rinks without seats for spectators | 14* | Same | |
| 5. Halls for rhythmic gymnastics and choreographic classes | 18* | ||
| 6. Premises for individual strength and acrobatic training, for individual warm-up before competitions in athletics showrooms, workshops | 16* | 2 | 3 (in the workshop, local suctions according to the design assignment) |
| 7. Dressing room for outerwear for practitioners and spectators | 16 | — | 2 |
| 8. Dressing rooms (including massage rooms and dry heat baths) | 25 | According to the balance, taking into account showers | 2 (from showers) |
| 9. Showers | 25 | 5 | 10 |
| 10. Massage | 22 | 4 | 5 |
| 11. Dry heat bath chamber | 110** | — | 5 (intermittent action in the absence of people) |
| 12. Classrooms, methodological rooms, recreation rooms for students, rooms for instructors and coaches, for judges, the press, administrative and engineering staff | 18 | 3 | 2 |
| 13. Sanitary units: | |||
| general use, for spectators | 16 | — | 100 m3/h for 1 toilet or urinal |
| for those involved (in locker rooms) | 20 | — | 50 m3/h per 1 toilet or urinal |
| individual use | 16 | — | 25 m3/h per 1 toilet or urinal |
| 14. Washrooms at public sanitary facilities | 16 | — | Through sanitary facilities |
| 15. Inventory at the halls | 15 | — | 1 |
| 16. Parking area for ice care machines | 10 | According to the balance from the auditorium | 10 (1/3 from the top and 2/3 from the bottom zone) |
| 17. Welfare premises for workers, protection of public order | 18 | 2 | 3 |
| 18. Fire post room | 18 | — | 2 |
| 19. Premises (storerooms) for storing sports equipment and inventory, household supplies | 16 | — | 2 |
| 20. Room for refrigeration machines | 16 | 4 | 5 |
| 21. Drying room for sportswear | 22 | 2 | 3 |

Features of the ventilation system in the fitness club:
- Competent design of the ventilation system in the gym ensures the absence of drafts and a comfortable temperature for athletes;
- Air exchange in rooms with increased carbon dioxide emission should be increased by 6-8 times compared to ordinary rooms (the calculation is made based on the parameters of the table above);
- Ventilation equipment, as a rule, is located under the ceiling or on the roof so as not to take up space;
- If necessary, the system allows you to additionally heat or cool the air.Also, the supply air must be cleaned of contaminants using a filter system;
- The system is controlled by automation if it has pre-set air parameters that must be constantly maintained. In the absence of visitors, the control system can regulate the flow, temperature and supply of the required air flow. In automatic mode, this can be done using sensors for carbon dioxide, temperature, etc., or manually adjust the flow. This allows the ventilation system to operate in an economical mode;
- In addition to maintaining clean air, do not forget about the humidity, which should be at least 45% for gyms with wooden sports equipment. For other premises, the recommended range of relative humidity is 30-60%;
- To ensure the specified humidity parameters, it is possible to install a built-in humidification system in the ventilation.
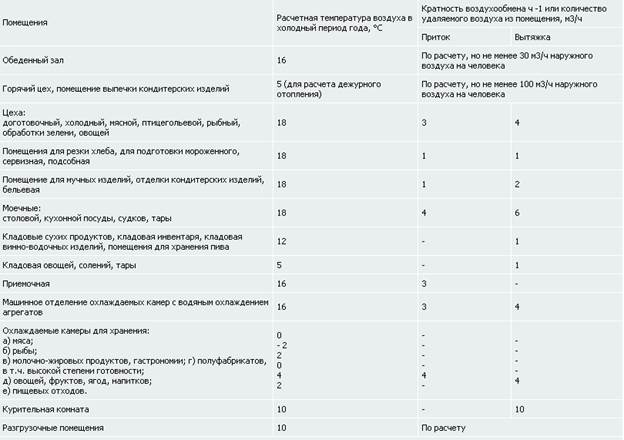
Administrative and residential buildings
As already mentioned, the multiplicity indicators have different values for different buildings, while in some cases the operation of systems for ensuring the rotation of air masses provides for the use of natural ventilation in the cold season. At the same time, in terms of used premises, for example, showers and latrines, the exhaust ventilation system should work more intensively than the fresh oxygen supply system in general rooms. Thus, the parameters of the shower air with steam removed from the premises every hour should be based on the calculation of 75 m³ / h per 1 mesh, and when organizing the removal of polluted air from the latrines at the rate of 25 m³ / h per 1 urinal and 50 m³ / h per 1 toilet bowl .
Multiplicity table for commercial premises.
When providing air change in a cafe, the organization of the ventilation and air conditioning system should ensure the frequency of air replacement in the supply system at the level of 3 units / h, for the exhaust system this figure should be 2 units / hour. The calculation of a complete air replacement system in the sales area depends on the type of ventilation used. So, if in the presence of ventilation of the supply and exhaust type, the frequency of air replacement is determined by calculation for all types of trading floors, then when equipping a building with an exhaust hood that does not provide air flow, the air exchange rate should be 1.5 units / h.
Multiplicity table for cafe premises
When using rooms with a large amount of steam, moisture, heat or gas, the calculation of air exchange can be based on the existing excess. In order to calculate air exchange by heat excess, formula (4) is used:
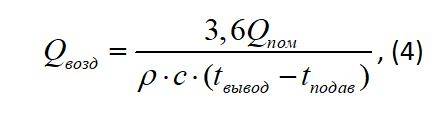
where Qpom - the amount of heat released into the room;
ρ is the air density;
c is the heat capacity of air;
t conclusion - the temperature of the air removed by ventilation;
t supply - the temperature of the air supplied to the room.
The organization of the air exchange system in the boiler room is based on the type of boiler used and should provide 1-3 times the replacement of the entire volume of oxygen within an hour.
Elements of the air exchange organization system
When choosing ventilation equipment, it is necessary to be guided by the calculated performance characteristics and dimensions of the device. Units that meet the requirements are selected from the range of air handling units offered on the market. The composition of the ventilation monoblock includes:
- Duct fans;
- Supply filtration unit;
- Heating elements for winter operation;
- Cooling devices for summer;
- Noise suppression systems;
- Heat exchangers.
The usual location of the monoblock is behind the false ceiling structures. If conditions permit, it is placed in a separate room. To evenly distribute the inflow, systems of air ducts and distribution ventilation grilles are used. Today, energy-saving recuperation PES from well-known European manufacturers are on sale. They use the energy of the exhaust air to heat the supply air. By installing a heat exchanger as a PES, you can count on reducing utility costs for heating. It gets too hot in yoga centers in summer. The situation can be corrected by installing an air conditioning system in the hall as an addition to ventilation. About the principle of the device, it can be cassette, wall or channel.