- Chemistry laboratory ventilation
- How to design an air exchange system?
- Ventilation standards in office premises
- Hot shop ventilation calculation
- Method of air exchange rates
- Suction rate method
- Equipment power method
- Equipment type method
- What should employees do in case of violations?
- Sanitary standards for the design of industrial enterprises
- Office ventilation standards
- The norm of air per person in the office
- General technical requirements
- How to check if ventilation is working?
- Hall ventilation
- Embryological laboratory
- Climate equipment for offices
- Office ventilation options
- natural ventilation
- Supply and exhaust ventilation system
- Supply and exhaust ventilation of the office
- Norms and requirements for ventilation in the office
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Chemistry laboratory ventilation
The ventilation of a chemical laboratory is an integrated approach to solving the tasks set, which includes a common system of air ducts with hoods located throughout the space of the premises, plus fume hoods in which experiments are carried out. General ventilation must meet the requirements of:
The volume of air in the laboratory should be changed 12-20 times in one hour. This takes into account the static volume when the entire system is not working.Based on this, ventilation equipment is also selected in terms of power and performance.
The exhaust part of the ventilation system is the central channel, from which local sections extend, distributed over the working areas.
Special filters are installed at the outlet, with the help of which chemicals are captured in the form of dust, vapors and condensate.
In chemical laboratories, both the exhaust system and the supply system can be used, working as separate parts
At the same time, it is important to achieve during installation that polluted air does not mix with clean air during the operation of the circuit.
How to design an air exchange system?
Office ventilation is thought out in advance. The design of ventilation is directly related to the characteristics of the rooms. Ventilation of office premises can be of several types:
- supply and exhaust;
- forced ventilation in the office.
The ventilation system in the office can be centralized and decentralized. In the first case, the system supplies air to the entire building, in the second, a separate system is installed for each room. To ensure normal air exchange in office premises, it is impossible to connect the ventilation systems of bathrooms with general exchange ones.
A decentralized system is equipped mainly in rooms where there are no large crowds of people. For each separate group of rooms, small supply or supply and exhaust structures are used.
They are mainly installed in warehouses, corridors. Electricity is used to increase the air temperature in the premises, because the supply of a heat pipeline from the boiler room significantly increases the cost of installation.
Ventilation standards in office premises
What ventilation standards are taken into account in office premises? The system project is created in accordance with the following building rules and regulations (SNiPam): No. 2.09.04.87, No. 2.08.02.89, No. 204.0591. Data such as the total working area, the number of employees, adjoining premises, and office equipment are important.
The company-designer of ventilation systems agrees in advance with the customer such nuances as:
- Place of installation of ventilation structures and elements
- Power, possible presence of water
- Installation of the drainage system
- Possible changes in the device
- Access to equipment after installation
At the same time, the components of the system are determined and project documentation is drawn up, taking into account all the wishes of the client. With correct and deliberate actions, the results of the fruitful work of the institution's employees will increase by more than 20%.
Hot shop ventilation calculation
The calculation is made taking into account the following criteria:
- type of installed cooking equipment;
- type of umbrella, placement height above the working surface;
- presence-absence of edge curtains;
- the type of food to be prepared;
- direction of air flow inside the kitchen.
Calculation methods:
Method of air exchange rates
It is used as an additional method, as it shows approximate results. Based on the German VDI52 method, according to which the air exchange rate depends on the height of the ceiling. Power, type of thermal equipment are not taken into account. In this case, the exhaust ratio is always greater than the air intake ratio.
For a kitchen with a height of 3-4 m, the inflow rate is 20 per hour, the hood is 30. With a ceiling height of 4-6 m, the inflow is 15, the hood is 20. Height is more than 6 m: inflow - 10, hood - 15.
Suction rate method
It takes into account the speed at which the exhaust air is drawn in with particles of fat, burning, odors. The calculation involves a hot flow between the top edge of the work surface (for example, stoves) and the bottom edge of the hood
Sides adjoining the wall are not taken into account.
The average speed of movement is 0.3 m/s (for food warmers - 0.2 m/s, fryers - 0.5 m/s). In this case, the exhaust edge should protrude 150-300 mm above the free edge of the working surface.
This method is used for standard hoods. It is a verification method when using other calculation schemes. Nevertheless, it is simple, with its help it is possible to calculate the effective heat, smoke removal, removal of burning.

Equipment power method
It is also determined by the German VDI 52 regulations. The calculation of ventilation in a hot shop is based on the specific heat release of the equipment (sensible and latent), which falls on 1 kW of power consumption.
The advantage of the technique is taking into account the characteristics of the type of equipment used. Minus - outdated data on the values of apparent-latent heat of kitchen appliances, which need to be additionally checked.
Based on the methodology, tables were compiled exhaust air flow for the types of equipment used in cooking, as well as a table of the coefficient of simultaneity, taking into account the non-synchronous operation of thermal equipment.
Calculations are made according to the data from the tables: the power consumption is multiplied by the specific heat index and by the simultaneity factor. Used most frequently.
Equipment type method
The exhaust air flow is determined for each equipment separately, then the indicators are summarized.The disadvantage is that only the area of the heat treatment technique is taken into account, and the power is not taken into account.
The last three methods allow you to calculate the air flow for standard hoods. For filtering ceilings, the indicators must be reduced by 20-25%, for supply and exhaust hoods - by 30-40%. An example of a calculation for the ventilation of any kitchen room will show that the multiplicity method is the most approximate of all, does not take into account factors directly related to technology.

What should employees do in case of violations?
If any violations are found, the employee is obliged to notify his supervisor in writing. If there was no response, and no positive changes are planned, it is necessary to write an application to the labor inspectorate or Rospotrebnadzor.
The application must include:
- Name and position of the applicant.
- The essence of the problem. It should be clear and concise, without carrying unnecessary information.
- Date and signature.
Download the application form to Rospotrebnadzor on violation of humidity and ventilation standards in the officeWe do not recommend filling out documents on your own. Save time - contact our lawyers by phone:
8 (800) 302-76-94
The head of the enterprise needs to pay great attention to the design and proper operation of ventilation systems in office premises. Compliance with all norms not only increases the safety of employees, but also increases their performance.
Violation of the norms entails not only administrative responsibility, but also the suspension of the organization's activities for an indefinite period.
Sanitary standards for the design of industrial enterprises
According to the rules of SNiP, any unfavorable elements emitted in the industrial premises, such as moisture and heat, are taken from the calculations of the technological part of the project documentation.
If such data are not available in the technological design standards, the amount of industrial harmful substances emitted in the room can be taken based on the natural facts collected from the study. Also, the desired value is indicated in the passport papers of the acquired specialized equipment.
Emissions of toxic substances into space occur through concentrated and dispersed devices of the general ventilation system.
The calculation of emitted substances should provide for their amount not exceeding:
- The maximum value for the city and settlements.
- Indicators of the maximum amount in the air that penetrates into residential buildings through windows according to the principle of natural ventilation (30% of the norm of the established limit for the amount of concentration of harmful, toxic substances in the working area).
Determination of the coefficient of dispersion into the working space of toxic elements that are in the system at the time of release, are part of the ventilation project of the enterprise. So, according to the standards, in industrial premises, provided that the volume of air per subject is 20 m3, it is necessary to take into account the process of supplying outside air. So in total, it should be up to 30 m3 / h for each subject in the room. If, however, there is more than 20 m3 per person, the amount of air supplied from outside should be at least 20 m3 / h for each subject.
When creating a project for a working area for industrial production purposes, in which there is no natural ventilation, while supplying outside air to them only through existing mechanical ventilation, the total amount of air should be at least 60 m3 / h per subject. The indicator may vary within the tabular data, but at the same time be at least one multiple of the air exchange flow per hour.
If the calculated air ratio is less than the tabular one, and at the same time recirculation is used, the external flow supply volume may be less than 60 m3 / h for one subject, but not less than 15-20% of the total air exchange flow in the system.
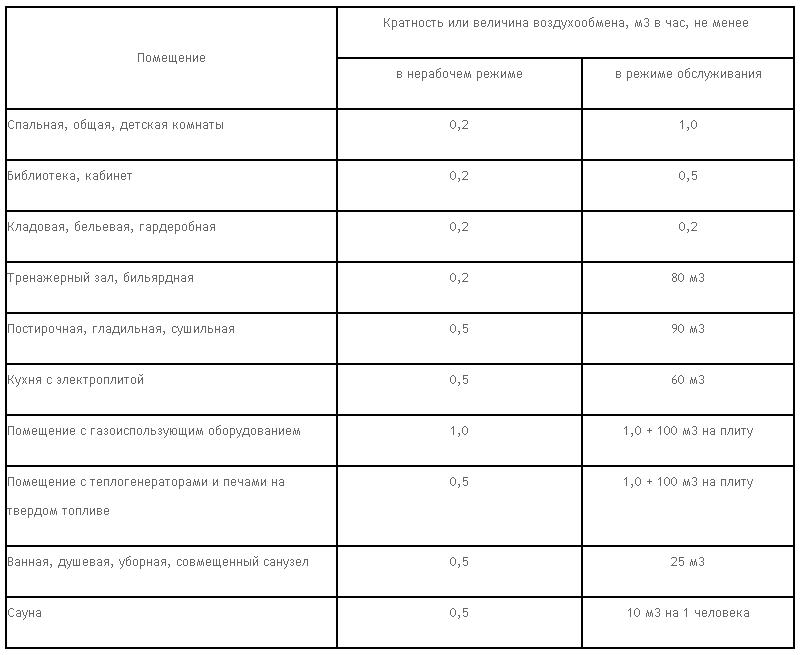
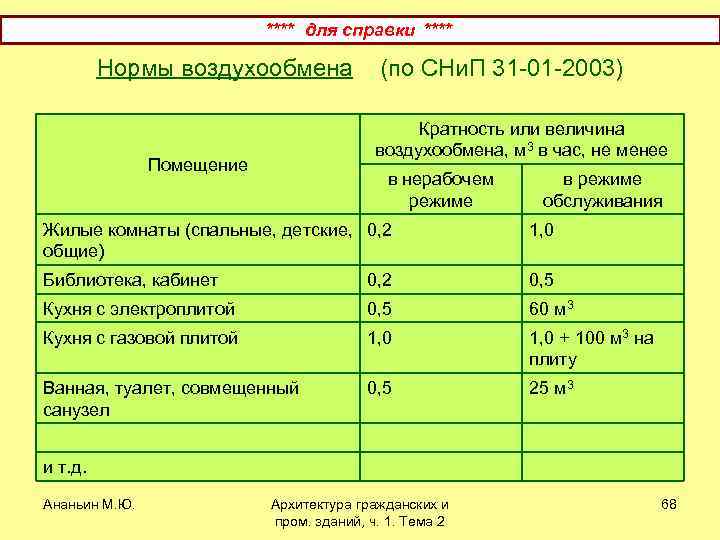
Office ventilation standards
The recommended exchange rate (according to GOST 30494-2011) is up to 1/10 meter per second, regardless of the season. It will not be difficult to calculate that in order to maintain the volume of air exchange at the required speed, it is impossible to do with window ventilation, because you need a very high-quality air input and output system, which will work almost always. In addition, office ventilation (since it is under heavy load) has special requirements.

Air ventilation scheme in the office
In SanPin 2.2.4, they present standards for the ventilation system in the office. Air microclimate characteristics are described below:
If the period is summer, then the optimum temperature is from 19 to 21 degrees Celsius. Humidity should be 30-45%, but not more than 60. The movement of the air flow should be equal to 0.2 - 0.3 m / s.
If the period is winter, then the optimal temperature is considered to be from 23 to 25 degrees Celsius. Humidity should not exceed 60%, but its ideal value is approximately 50.The movement of the air flow should be equal to 0.3-0.5 m / s.
SanPin also recommends the following humidity level depending on temperature:
- 40-60% at 22-24°C
- 70% at 25°C
- 65% at 26°C
- 60% at 27°C
Usually small offices are ventilated with a small number of devices. However, if the temperature cannot be brought down below 28 degrees, then additional resources must be connected.
The norm of air per person in the office
Calculating the required air exchange is not an easy task. Despite the fact that the problem has been known for a long time, domestic and Western calculations about the optimal value of air exchange are still contradictory and sometimes not fully substantiated.

The following is information on the air flow rates that a person needs in a room per employee:
- If the volume is up to 20 cubic meters per person, then the volumetric flow rate of the air supplied to the room will be at least 20 m ^ 3 per person per hour
- If the volume is 20-40 cubic meters per person, then the norm will be at least 30
- If the volume of the room per person is more than 40 meters, then natural ventilation can be dispensed with.
- If there are no windows in the room, then the norm will already be at least 60 m ^ 3 per person per hour.
Proper ventilation is extremely important. It is regulated by many documents, compliance with which is a prerequisite for productive work in the room.
General technical requirements
4.1.The minimum necessary air exchange, sufficient to maintain the required air quality in the serviced areas of the premises, should be provided by a system of natural or mechanical ventilation (air conditioning) by supplying outside air and removing air that has assimilated pollutants in the premises.
4.2. The required air quality in the serviced areas of the premises must be ensured under all modes of use of the premises and the corresponding modes of operation of the ventilation systems.
4.3. The supply of outside air to the premises is not necessary if the premises are not in use and there are no sources of pollution that are not related to the presence of people and their activities (for example, pollution from building materials, furnishings, etc.).
4.4. The scheme for organizing air exchange in the premises should ensure the distribution of supply air, excluding its flow through areas with high pollution to areas with less pollution.
4.5. Rooms equipped with exhaust systems (kitchens, bathrooms, toilets, smoking rooms, etc.) can use the air supplied through adjacent rooms to compensate for the exhaust air. The supply air quality must meet the requirements of Table 1.
Table 1 - Maximum permissible concentrations of pollutants in the air of settlements
| Substance | MPC in outdoor airqn MPC, mgm3 | |
| maximum single | average daily | |
| Nitrogen dioxide | 0,085 | 0,04 |
| Dust-toxic | 0,5 | 0,15 |
| Lead | 0,001 | 0,0003 |
| Sulphurous anhydride | 0,5 | 0,05 |
| Hydrocarbons (benzene) | 0,3 | 0,1 |
| carbon monoxide | 5 | 3 |
| Phenol | 0,01 | 0,003 |
| Carbon dioxide*: | ||
| in a populated area (village) | 650 | 650 |
| in small towns | 800 | 800 |
| in big cities | 1000 | 1000 |
| * MPC for carbon dioxide is not standardized, this value is for reference only. |
4.6. Stationary local sources of harmful emissions should, as a rule, be equipped with local exhausts.
4.7. The calculated air exchange in the premises should be taken as the largest of the supply and exhaust air costs for any mode of use of the premises.
4.8. Outdoor air intakes and exhaust air emissions should be arranged in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 41-01-2003.
4.9. The materials and design of ventilation ducts and chambers should minimize conditions that allow the growth and spread of microorganisms through the ventilation system. The design of the ventilation system must comply with the requirements of SNiP 41-01-2003.
How to check if ventilation is working?
 Checking the hood
Checking the hood
First, it is checked whether the hood is working, for this it is necessary to bring a sheet of paper or a flame from a lighter directly to the ventilation grill located in the bathroom or in the kitchen. The flame or leaf should bend towards the hood, if so, then it works, and if this does not happen, then the channel may be blocked, for example, clogged with leaves or for some other reason. Therefore, the main task is to eliminate the cause and provide traction in the channel.
In cases where the draft is unstable from neighbors, the air flow can pass to you, while bringing extraneous odors into your apartment, this is a sign of reverse draft. To eliminate it, it is necessary to mount special blinds that will close when reverse thrust appears.
Hall ventilation
In the dining and banquet hall, in addition to a good exhaust, there should also be fresh air.The inflow must exceed the outflow of exhaust air. It is also necessary to protect visitors from the penetration of smells from the kitchen and utility rooms. There must be a barrier.
Common mistakes in illiterate or independent design of restaurant ventilation in order to save money:
- Reduced air flow.
In expensive equipment, everything is calculated clearly. And any interference can lead to a deterioration in air quality or a malfunction of the device. The right decision: use recuperator. This is a device in the ventilation system that heats the flow coming from the outside due to the heat of the exhaust air. Mixing does not occur. And electricity is saved. - Combining the ventilation system of the kitchen and the hall.
Guaranteed penetration of odors from the kitchen. Expensive equipment will cease to perform its function. - Using only ducted air conditioner. It has high performance. The smells of different zones quickly mix. Waste of money for this system and guaranteed loss of customers.
Embryological laboratory
Embryological equipment is very sensitive, especially to changing operating conditions. Therefore, when developing ventilation, experts take into account this property of devices, focusing on compliance with certain strict requirements. Namely:
- Activated carbon filters must be installed in the ventilation system. These filter elements easily trap organic compounds that are present in the air in the form of light volatile suspensions. Installation is carried out both on the supply side and on the exhaust.
- Filters must be changed with a certain frequency, which depends on the volume of air driven through them, on the type of laboratory facilities, their purpose and other factors.
Filter elements are specially installed on two parts of the ventilation system. Because the air from the laboratory must leave the street clean, and it must also enter from the street clean, without bringing bacteria and viruses with it.
Climate equipment for offices
-
Supply ventilation unit for the office. Forces fresh air from the street directly into the office premises. The outflow of air occurs by forcing it into the corridors and lobbies. With an area of more than 40 sq. meters, the air is evacuated directly from it. Air handling units for ventilation of offices are used for areas up to 100 sq. meters;
- Supply and exhaust office ventilation systems. This is the most widely used type of equipment for the outflow, cleaning and delivery of air. The kit may include cooling or heating devices, humidifiers. The complete set is the most diverse, but the supply and exhaust ventilation of the office should be calculated and installed by professionals. Automatic control over functionality reduces power consumption and increases efficiency;
- Duct ventilation system in the office. Duct air conditioners with outside air mixed in are installed in small and medium-sized offices. It is combined with supply and exhaust equipment, bringing the temperature of the outdoor air to the required one. After which it is served in the rooms;
- Central air conditioning and ventilation in a large office. In large office buildings, the climate is controlled by chiller-fan coil systems and multi-zone VRF systems.The latter consist of many indoor units that provide different temperatures and humidity in the premises. Central air conditioners are supply and exhaust ventilation in offices with cooling and heating units. This type of climate systems is suitable for large offices that are not divided into separate rooms.
Office ventilation options

natural ventilation
Fresh air enters and leaves the room when windows and doors are opened. Installation of exhaust fans helps to remove exhaust air from bathrooms and kitchens. This option does not require installation costs, but there are many disadvantages: street noise, odors and dust, and in the cold season, opening windows can lead to colds and additional heating costs. With the help of natural ventilation, it is impossible to maintain the required temperature and humidity in the office.

Supply and exhaust ventilation system
In supply and exhaust ventilation systems, air is supplied and removed in the office through special installations. Air is preliminarily prepared, supplied and removed from the premises through a network of air ducts.
The unit includes a filter for cleaning the air from dust and excess moisture, a heater for heating the air in cold weather and a fan. The air can be cooled, humidified or dehumidified before being supplied.
The supply and exhaust system requires the allocation of free space under the ceiling or in the utility room, as well as complex installation work. Therefore, the best option is to plan the installation of the system at the design stage. repair or finishing work.
First you need to decide on design solutions. It is in the project that the optimal air exchange will be calculated, taking into account the characteristics of the office and the number of employees. You will understand what energy costs will be during the operation of this system, where the equipment will be located and the final cost of the project.
Advantages of a mechanically driven office ventilation system:
- Comfortable fresh air at any time of the year and under any weather conditions outside.
- Low noise level from the street. This is especially true if the office is located next to a construction site, a busy highway or a crowded street.
- Possibility of pre-treatment of air - you get clean air at the required temperature.
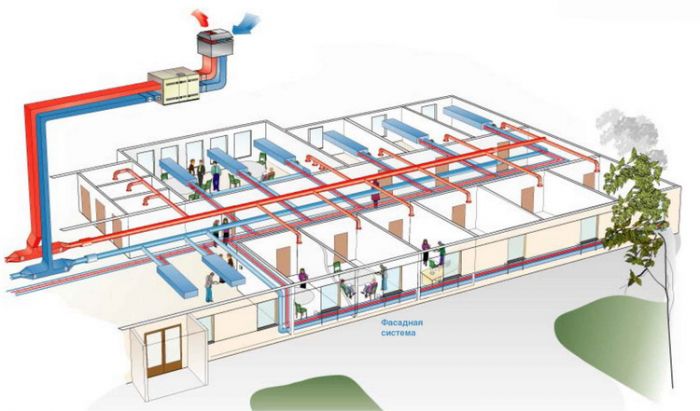
Supply and exhaust ventilation of the office
Duct ventilation of the supply-blowing system is used for rooms up to 600 sq. meters, since the productivity of the supply and exhaust ventilation of the office is up to 8 thousand cubic meters per hour.
SNiP ventilation of office premises requires air exchange:
- inflow 3.5 times per hour;
- outflow 2.8 times per hour.
The equipment is usually hidden behind the false ceiling of the utility room. Air is distributed through the offices by a system of ventilation ducts, the outlets of which are hidden behind diffusers or grilles.
The influx of air from the street with the supply ventilation of the office is carried out at a height of two meters above the soil surface. Air is passed through the cleaning system, if necessary, its temperature is lowered or increased (by an electric or water heater).
To reduce the power consumption, the supply air is heated by a heat exchanger. It is a heat exchanger in which heat from the exhaust air is transferred to fresh air.Recuperators for office ventilation are used rotary and lamellar. The first ones have an efficiency of more than 75%, they work in harsh frosts. But during operation, about 5% of the exhaust air gets back into the room.
Plate recuperators are inexpensive, their efficiency is not more than 65%. But they get icy, you have to provide them with heating.
All the necessary equipment for air treatment in the supply and exhaust system is located in one relatively small building. Duct ventilation of office premises is a combination of several modules.
To ensure the required air temperature in the office space, supply and exhaust ventilation is supplemented with air conditioners. Depending on the characteristics of the building, it can be several split systems or multi-splits.
Norms and requirements for ventilation in the office
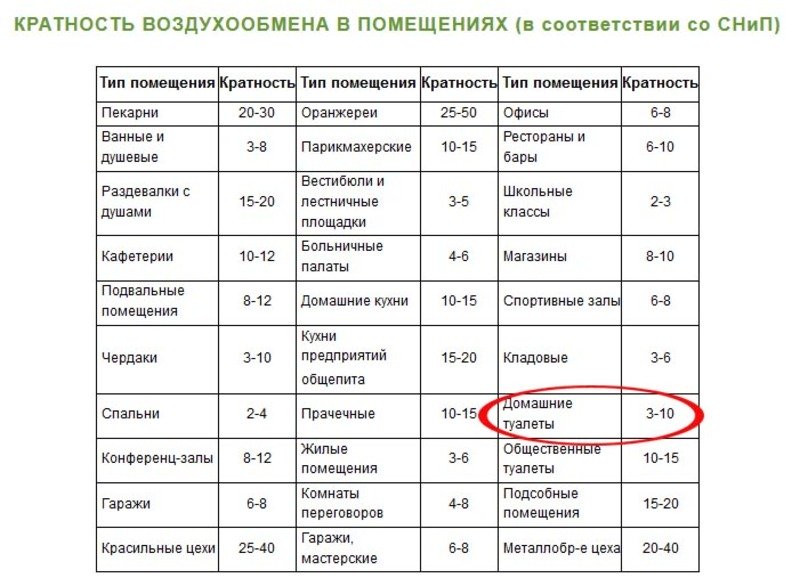
Ventilation in the office is a heterogeneous concept. There is a list of standards for each type of room, air exchange rates depend on the type of room and the number of people who are constantly in it. Accordingly, the exact rate is set based on one person and adapted to a specific room by multiplying the standard value by the number of employees.
Air exchange rates for office premises
| TYPE OF ROOM | AIR EXCHANGE RATE FOR 1 PERSON, M3 PER HOUR |
| Cabinet | 60 |
| The meeting room | 40 |
| The corridor | 11 |
| Meeting room | 30 |
| Reception | 40 |
| bathroom | 75 |
| smoking rooms | 100 |
The recommended air exchange rate according to GOST 30494-2011 is up to 0.1 meters per second, regardless of the season.It is easy to calculate that in order to maintain the volume of air exchange at the desired speed, window ventilation is not suitable, a high-quality air supply and exhaust system is needed, which will be almost constant.
In addition, since the load on office ventilation is higher than on ordinary household ventilation, higher requirements are also imposed on it:
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Air exchange rate for different store premises + drawing:
Application for calculation air exchange for various rooms:
Basic values for the ventilation system, air flow:
The air exchange rate reflects the need of the premises for the amount of air at which they function normally. The change of air is expressed in the number of times per hour or cubic meters for the same period. There are also specific values for 1 person and 1 square meter.
Hospitals, hazardous industries and public places need fresh air the most. Life sometimes depends on the indicator of the minimum air exchange rate, so use not only the standards, but also calculate everything yourself and invite specialists.
Do you have questions about the air exchange rate or related parameters? Ask them in the form below the article. You can also share valuable information with other readers. Perhaps someone will benefit from your personal experience in this matter.