- Options for manufacturing protective cases
- Purpose
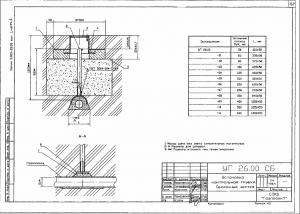
- GAS PIPE CONTROL PIPE DN50
- Purpose of the protective case
- Making a case
- Features of support-guiding products
- Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
- Purpose of the protective case
- Making a case
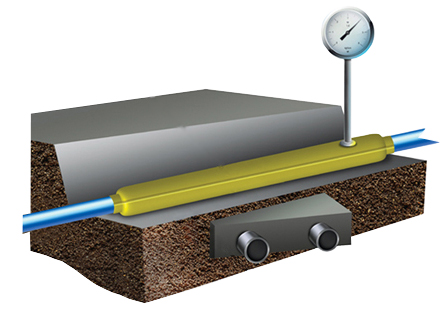
- Control tube on the gas pipeline: purpose + installation rules on the case
- Gas pipe protective case (ZFGT)
- How is the protective case installed?
- What SNIPs regulate the laying of pipelines and the use of cases
- The purpose of monitoring the condition of an underground gas pipeline
- Placement of the gas pipeline in the case
- Bituminous VUS
- Purpose of the protective case
- Making a case
- The control tube diameter must be at least 32 mm
Options for manufacturing protective cases
Detachable case fixed length 6 meters
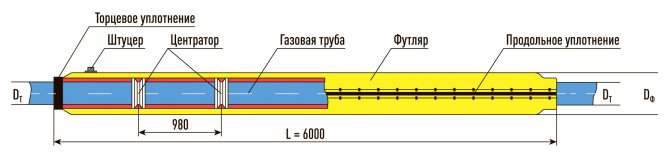
Case fixed length - 6000 mm. Designed for installation on existing gas pipelines at the intersection with utilities in a limited space and does not have the ability to increase or decrease the length.
Detachable case composite sectional on end flanges
The maximum length of one section is 5500 mm, the minimum is 2000 mm. A special rubber seal is installed between the flanges.The flange connection is mounted on stainless steel M10 bolts and allows the production of protective cases of any length according to the customer's dimensions.
Purpose

The water drainage system in most cases is mounted from polyethylene pipes. Despite the strength of this material, deformation of the pipeline may occur under the pressure of the soil or water mass. Especially often such situations arise when laying sewers under highways, railways, in canals or technical tunnels.
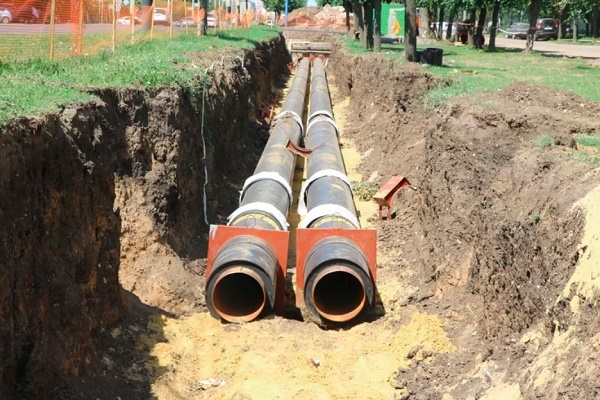
The case is an additional shell of the pipeline. The purpose of the sewer case is to protect underground pipes made of polyethylene and similar materials from negative impacts from the outside. In particular, we are talking about pressure from the soil, soil water and other factors that significantly reduce the service life of all elements of the sewer system.
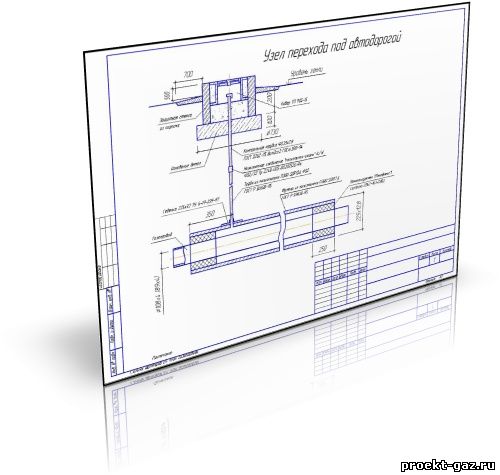
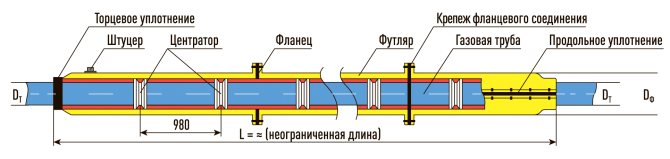
GAS PIPE CONTROL PIPE DN50
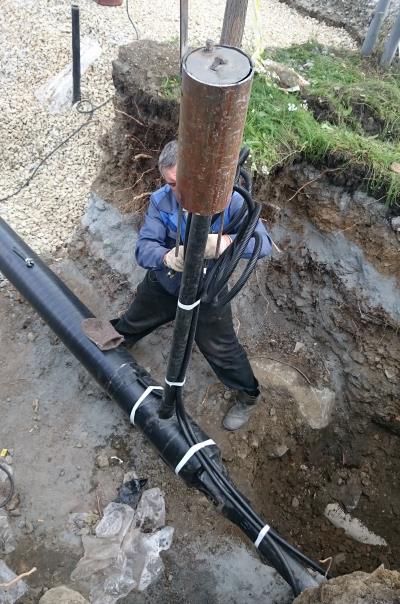
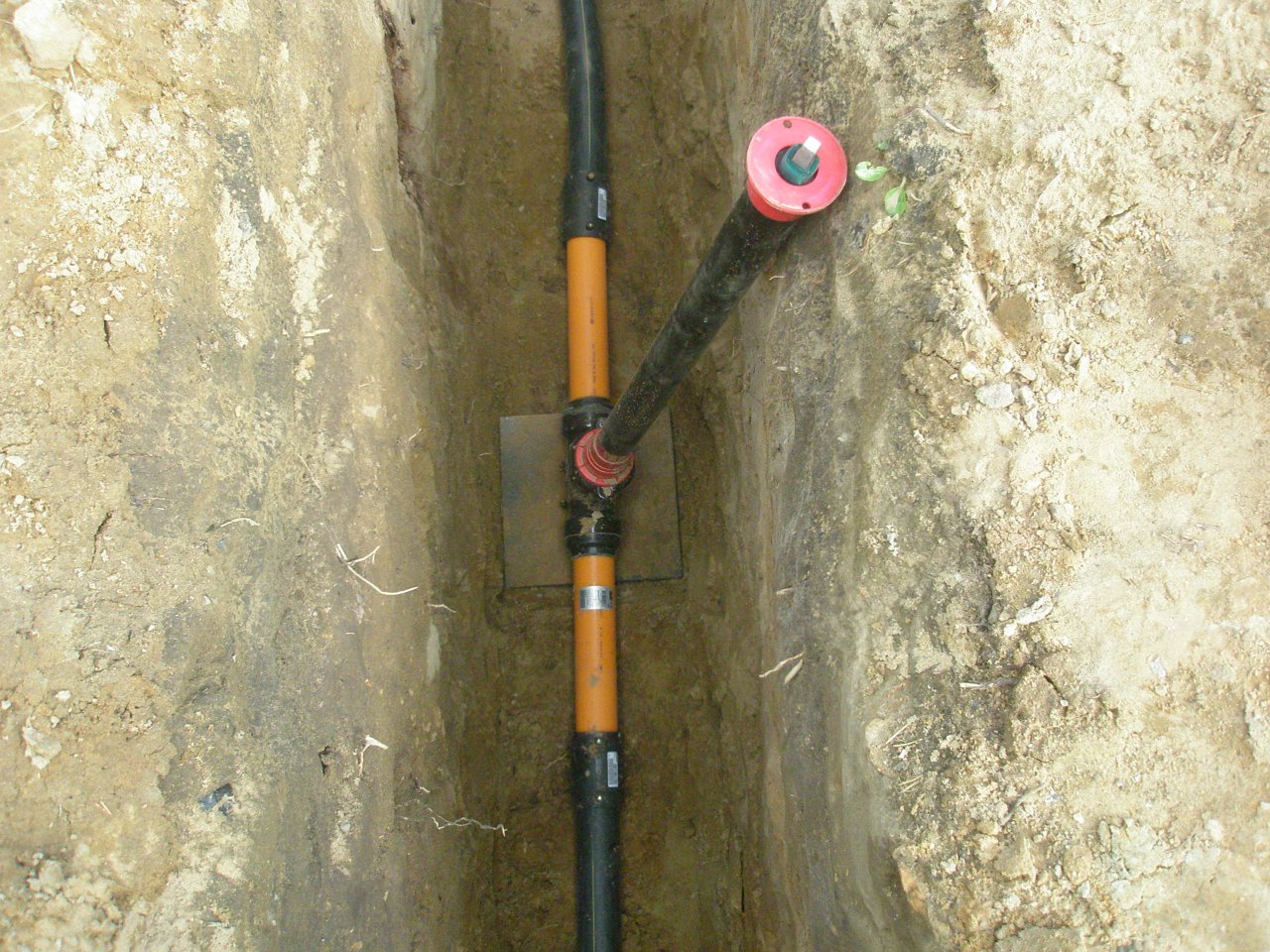
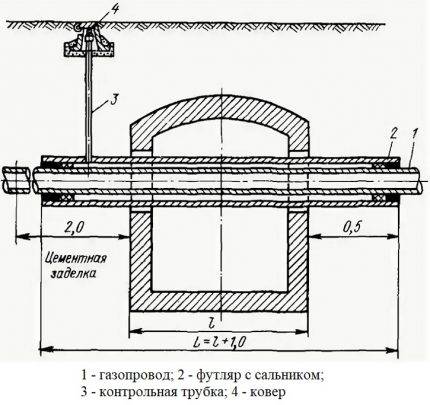
The control tube on the gas pipeline is designed to quickly detect gas leaks in the underground gas pipeline, in the most critical places for connecting bends, and also where the gas pipeline is difficult to access for inspection. Most effective on gas pipelines located above the groundwater level. The free end of the control tube is brought to the surface under a protective device - a carpet.
We manufacture control tubes in series, incl. according to drawings
UG 14.01.00 s.5.905-25.05, UG 11.01.00 s.5.905-30.07, UG 16.01.00 s.5.905-15.
It is possible to manufacture other standard sizes, CT with a cork, as well as products according to the drawings of the Customer.
The control tube is used for systematic monitoring and detection of gas leaks on underground gas pipelines without opening the road surface.They are usually installed at certain distances along the gas pipeline route, most often above the gas pipeline points for which periodic operational control is important.
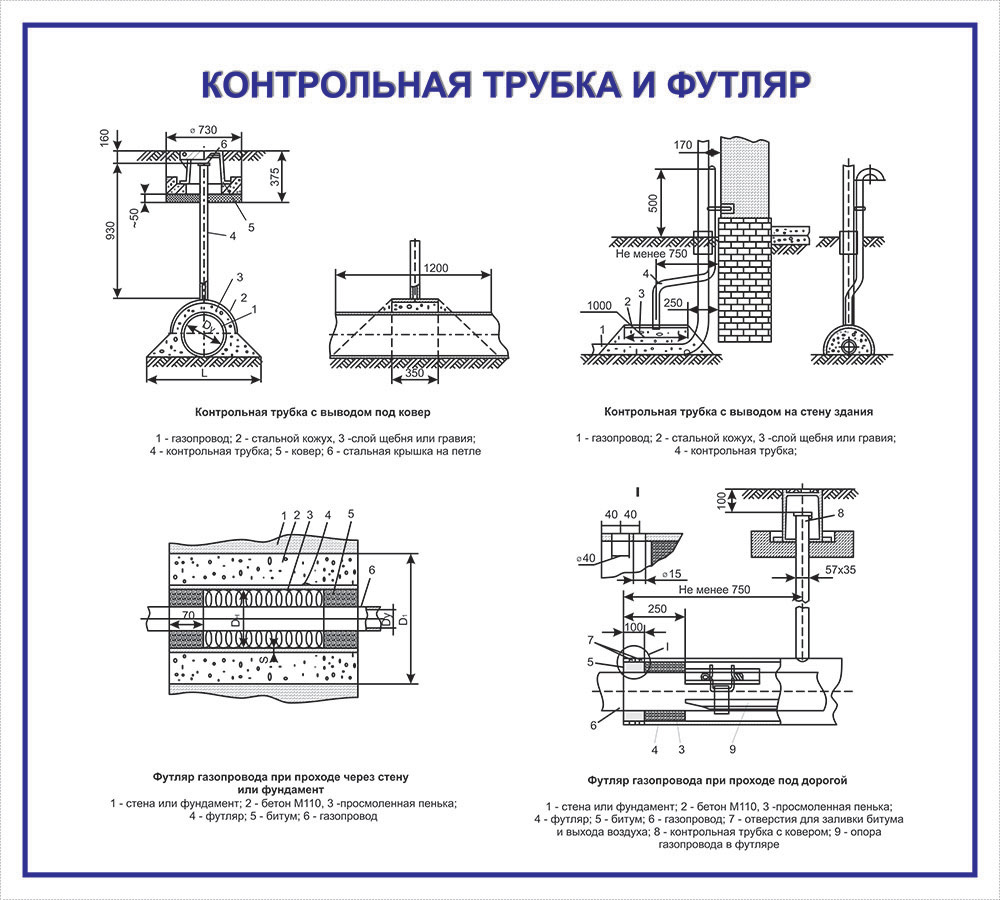
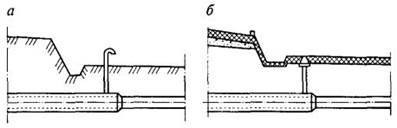
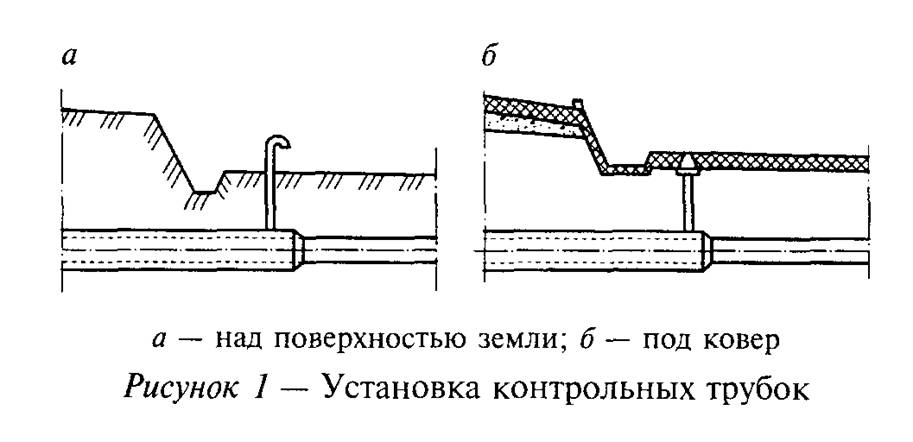
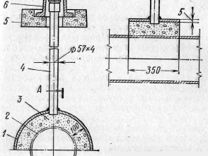
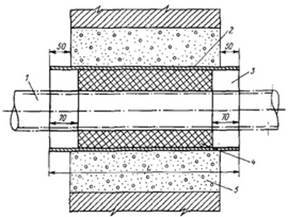
The control tube is made of a 2-inch pipe, the lower end of which is welded to the gas pipeline case, the area between the gas pipeline and the case is covered with a layer of crushed stone or fine gravel 100 mm high and covered with a steel casing about 350 mm long, bent in the form of a semicircle and usually installed above the gas pipeline joint. From above, the control tube is closed with a steel cap mounted on a hinge. To determine the gas leakage, the cover of the control tube is folded back and the gas sampling tube of the gas indicator is inserted into the pipe. In the absence of an indicator, a gas leak is detected by smell.
On polyethylene gas pipelines, control tubes are installed at the locations of permanent polyethylene-steel joints, at the intersection of gas pipelines with railways, heating networks, highways, tram tracks, collectors and tunnels, canals; in places where polyethylene pipes come out of the ground on above-ground vertical sections of the gas pipeline when using detachable connections in a case; as well as in places without a well location of detachable connections. If the length of the gas pipeline section is not more than 150 m and the pipe is installed without welded joints, it is allowed not to install a control tube.
It is more efficient to install control tubes on a gas pipeline located above the groundwater level. In some cases, devices are installed that make it easier to detect a gas leak and block its movement into the danger zone. The loosened soil contributes to the release of gas to the outside in the direction of basements and buildings.To control such leaks and vent gas in the desired direction, in some cases, permanently open drains are arranged,
Purpose of the protective case
The use of the case is due not only to the protection of the gas pipeline itself from the effects of an aggressive environment and various damages, but also to ensure safety for others. Everyone knows that a gas leak is a very dangerous phenomenon, so additional protection, in this case, is not a luxury, but a necessary condition.
Pipe laying using a protective case is strictly regulated, in accordance with regulatory documents - SNiP 42-01 and SNiP 32-01. According to the requirements specified in the last document, not only the pipe laying process itself is regulated, but also the distance at which the ends of the protective case should be located.
In particular, if we are talking about railway tracks, then the protective case must pass through them and have a length of at least 50 meters from the exit. Such great importance is justified by the fact that natural gas is very explosive, and trains have a very high mass. As for roads, the cases should protrude from the exit 3.5 meters from them. In addition, there are precise instructions for the depth of laying the pipeline, which is about one and a half meters.
Making a case
In accordance with the same regulations, the cases must be made of steel pipes. The diameter may be different, because it all depends on the parameters of the diameter of the gas pipeline, but, in general, the diameter will not differ much, the spread will be within 10 cm.
Features of support-guiding products
Conventional supports for pipeline communications perform a number of functions.Their main “duty” is to fix the structure. In addition, thanks to the sliding bearings, the linear expansion of the pipeline has no consequences. And the support-guide rings make it possible to pull the inner pipeline through the outer communication part (case) without causing any harm to it.
Based on this, we can distinguish several main functions that are carried out thanks to just such a support:
- protection of the pipeline from various damages;
- protection of sleeve joints and welds;
- simple and quick pulling of the pipeline through the case;
- support for the supply pipe;
- cathodic protection against corrosive influences (due to this detail, the possibility of contact between the metal frames of the two pipes is excluded).
The installation of these rings is carried out at the stage of assembling the pipeline itself. Their installation does not require the use of special equipment, since the support ring is fixed using electric arc welding. The most common materials for such supports are high-quality polypropylene, steel.
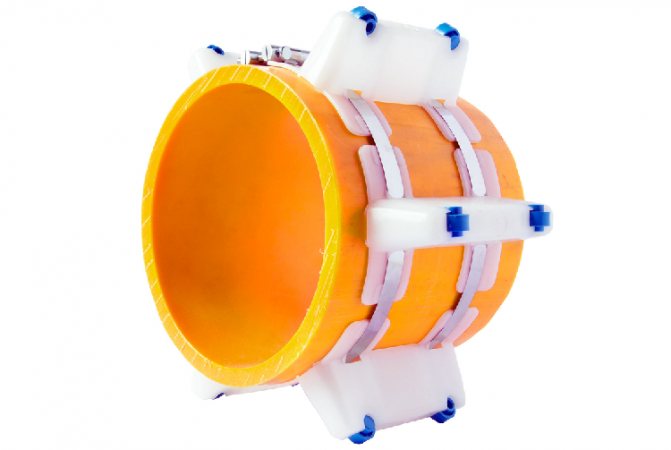

The design feature of the supports makes it easier and faster to pull the inner pipe into the outer
Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
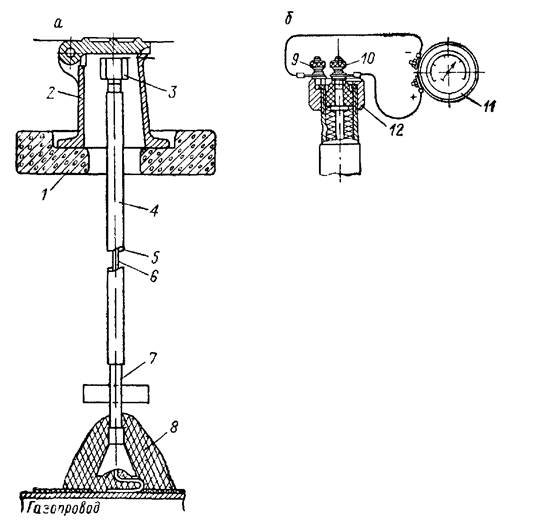
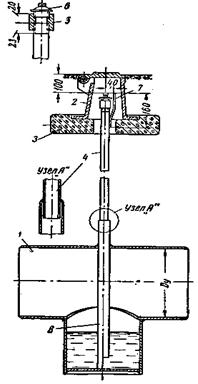
The control tube (Fig. 20) is a two-inch pipe, the lower part of which is welded to the case, and the space between the case and the gas pipeline is filled with fine gravel or a layer of crushed stone.
The control tube is a U-shaped tube filled with soda lime and calcium chloride in approximately equal amounts.The layers of calcium chloride and soda lime should be separated at the bottom with a small piece of cotton wool (Fig.
45), and at the top should not reach 6 mm to the side outlet tubes; from above they are covered with pieces of cotton wool; the tube is closed with stoppers and filled with Mendeleev putty.
note
Rubber tubes are also put on the side tubes, closed with scraps of a glass rod.
The control tube (Fig. III-7, a) makes it possible to quickly determine the presence of gas leaks from an underground gas pipeline. The controlled section of the gas pipeline is covered with a layer of crushed stone or gravel 100 mm high and covered with a steel semicircular casing, the length of which is assumed to be 350 mm.
From the casing to the surface of the earth under the carpet, a tube is diverted, through which the gas from the place of a possible leak rises. From above, the outlet tube is covered with a light steel cap on a hinge. To determine the presence of gas, the cover is folded back and a gas indicator hose is inserted into the tube.
In the absence of an indicator, the presence of gas is detected by smell.
The control tube (Fig. 13) consists of an iron casing, usually installed above the seam (joint) of the gas pipeline, a steel pipe with a diameter of 2 (inches) extends from the casing to the surface of the earth, at the upper end of which there is a coupling with a plug. Gravel is laid between the casing and the gas pipeline to facilitate the passage of gas into the pipe in the event of a leak.
In order to avoid the scattering of metal fragments for the manufacture of control tubes, CDs from paper sleeves are used.
Control tubes are used when blasting on an open surface in the event of a significant removal of charges from one another. In underground conditions, a control segment of the igniter cord is used.
Control tube (Fig.5.6) makes it possible to quickly determine the presence of gas leaks from an underground gas pipeline. The controlled section of the gas pipeline / is covered with a layer of crushed stone or gravel 3 100 mm high and covered with a steel semicircular casing 2 about 350 mm long.
Important
From the casing to the surface of the earth under the carpet 5, a tube 4 is taken away, along which the gas rises up from the place of a possible leak. From above, the outlet tube is covered with a light steel cover 6 on a loop.
To determine the presence of gas, the cover is thrown back and a gas indicator hose is inserted into the tube.
Control tubes on polyethylene gas pipelines should be installed at the locations of permanent connections of plastic pipes with steel pipes, at the intersection of gas pipelines with heating networks.
Control tubes 3 indicate the presence of water in the mixer. One of them is used to release air from the system when the bundle is filled with water.
The control tube is a U-shaped tube filled with soda lime and calcium chloride in approximately equal amounts. The layers of calcium chloride and soda lime should be separated at the bottom with a small piece of cotton wool (Fig.
45), and at the top should not reach 6 mm to the side outlet tubes; from above they are covered with pieces of cotton wool; the tube is closed with stoppers and filled with Mendeleev putty.
Rubber tubes are also put on the side tubes, closed with scraps of a glass rod.
Control tubes on polyethylene gas pipelines should be provided at one end of metal cases when the gas pipeline crosses railways, tramways, highways, canals, collectors and tunnels, as well as on vertical above-ground sections at the places where polyethylene pipes come out of the ground when using detachable connections in the case, in places where detachable connections are located without a well and at one of the ends of the section in which a polyethylene gas pipeline is pulled. When pulling a pipe without welded joints and a section length of not more than 150 m, it is allowed not to install a control tube.
Advice
The control tube is used to systematically monitor and locate gas leaks in underground gas networks without opening road surfaces.
The control tubes should be brought to the surface of the earth under the carpet.
Control tubes are installed at both ends of the case.
The free end of the control tubes is lowered into the tank to different depths and ends at levels corresponding to the controlled volumes. Shut-off needle valves are screwed onto the outer ends of the tubes, by opening which it is determined by the outgoing gas stream whether it is a gas or a liquid.
Pages: 1 2 3 4
Purpose of the protective case
The use of the case is due not only to the protection of the gas pipeline itself from the effects of an aggressive environment and various damages, but also to ensure safety for others. Everyone knows that a gas leak is a very dangerous phenomenon, so additional protection, in this case, is not a luxury, but a necessary condition.
Pipe laying using a protective case is strictly regulated, in accordance with regulatory documents - SNiP 42-01 and SNiP 32-01.According to the requirements specified in the last document, not only the pipe laying process itself is regulated, but also the distance at which the ends of the protective case should be located.

In particular, if we are talking about railway tracks, then the protective case must pass through them and have a length of at least 50 meters from the exit. Such great importance is justified by the fact that natural gas is very explosive, and trains have a very high mass. As for roads, the cases should protrude from the exit 3.5 meters from them. In addition, there are precise instructions for the depth of laying the pipeline, which is about one and a half meters.
Making a case
In accordance with the same regulations, the cases must be made of steel pipes. The diameter may be different, because it all depends on the parameters of the diameter of the gas pipeline, but, in general, the diameter will not differ much, the spread will be within 10 cm.
Control tube on the gas pipeline: purpose + installation rules on the case
The underground laying of gas pipelines has a lot of advantages. They do not spoil the exterior of city buildings and the countryside, do not interfere with the movement of vehicles, do not force the existing buildings to be displaced. But they have a significant drawback - the difficulty of monitoring both the pipe itself and the medium moving through it.
We will tell you how the control tube on the gas pipeline helps to monitor the status of the system. Let's get acquainted with the design features of this device. We will analyze the location options and installation rules.
From the article presented by us, you will learn where and in what sequence control tubes are installed on the gas pipeline system. Familiarize yourself with the features of attaching them to cases and semicircular casings. You will understand how necessary it is to monitor the technical condition of an underground pipeline.
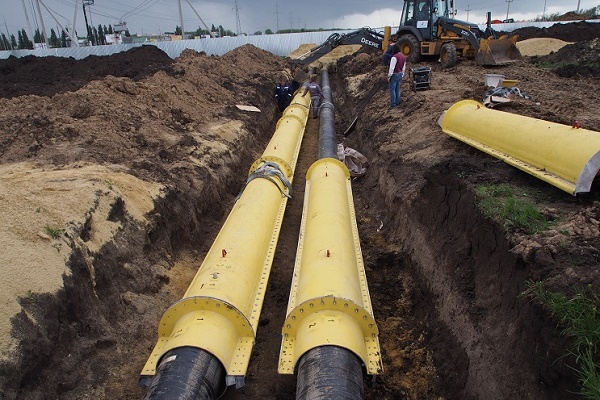
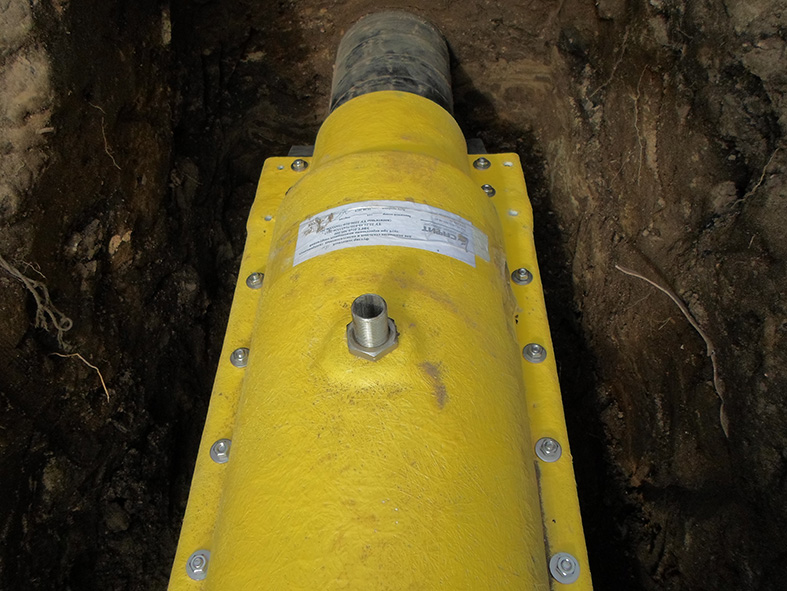
Gas pipe protective case (ZFGT)
Manufacture of casings from high quality composite materials for underground pipelines - gas pipelines and oil pipelines according to TU 2296-056-38276489-2017 Dimensions FT150; TF200; FT250; FT300; FT350 FT400; FT500; FT600; FT800; FT1000; FT1200; FT1400
The products have been tested and have a GAZCERT certificate.
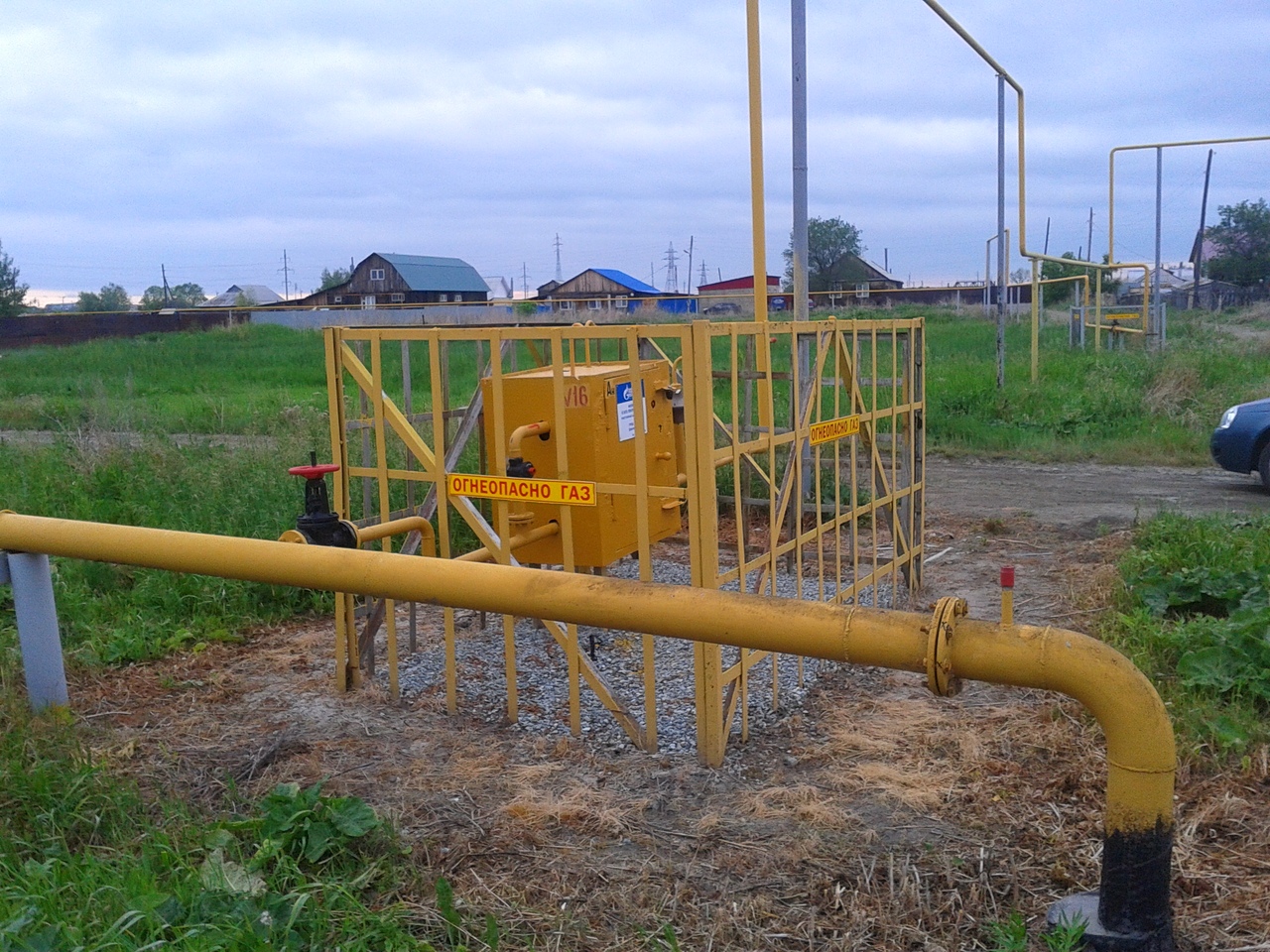
The composite protective case is used to protect pipes from external loads and mechanical damage at the intersections with underground structures, roads, railways and trams, as well as for the possible detection and removal of gas in case of damage to the gas pipeline within the protective case.
Advantages
The case protects the pipes from vibrations, friction and mechanical damage.
Particular attention should be paid if pipes are laid next to other communications. Fiberglass cases have a number of advantages over steel ones:
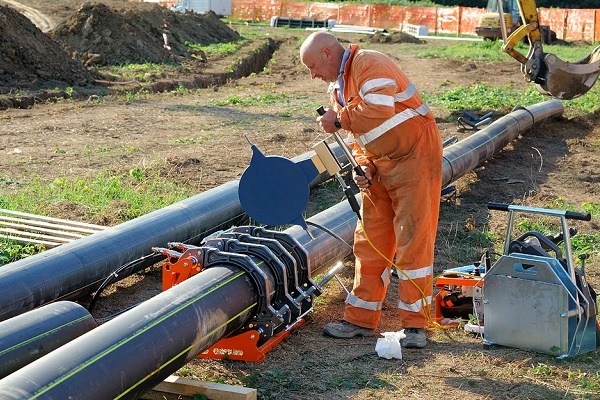
- Quick assembly that does not require highly qualified specialists and long installation
- No welding
- No corrosion
- Stray current protection
- Assembly versatility
- Service life up to 30 years
- tightness
- Strength
- Maintenance Free
- Meets all safety requirements
- No additional security measures required
Working temperature from -50 to +100
Development, production, testing of protective elements of pipelines according to the TOR
Development of rem.sets for the gas pipeline according to the Customer's specification.
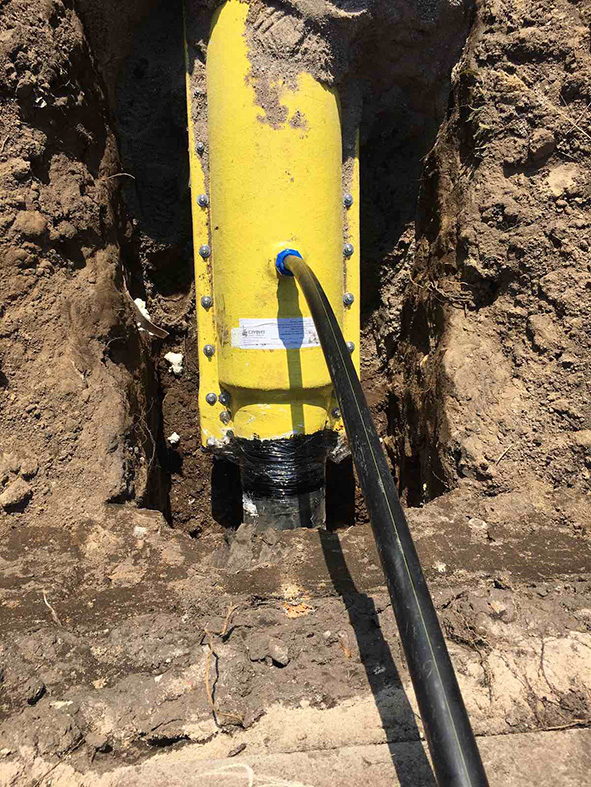
How is the protective case installed?
When laying a gas pipeline and an oil pipeline, the protective case is assembled from the upper and lower casings. These casings are tightened with stainless steel bolts and sealed with rubber seals.
What SNIPs regulate the laying of pipelines and the use of cases
5.2.1 Laying of gas pipelines should be carried out at a depth of at least 0.8 m to the top of the gas pipeline or case. In places where the movement of vehicles and agricultural machinery is not provided, the depth of laying steel gas pipelines can be at least 0.6 m.
SP 42-101-2003 "General provisions for the design and construction of gas distribution systems from metal and polyethylene pipes"
4.53 Cases for gas pipelines should be provided to protect the gas pipeline from external loads, from damage at the intersection with underground structures and communications, as well as to enable repair and replacement, detection and removal of gas in case of leakage. The connections of the components of the case must ensure its tightness and straightness.
SNiP 32-01-95 "1520 mm gauge railways"
8.12 When laying underground at the intersection, pipelines are enclosed in a protective pipe (channel, tunnel), the ends of which, at intersections with pipelines transporting explosive and flammable products (oil, gas, etc.), are located on each side at least 50 m from the foot of the slope of the embankment or the edge of the slope of the excavation, and in the presence of drainage structures - from the outermost drainage structure; at intersections with water pipes, sewerage lines, heating networks, etc. - not less than 10 m.
The purpose of monitoring the condition of an underground gas pipeline
Gas pipelines laid in trenches need regular inspection no less than ground routes. Of course, they are not threatened with purely mechanical damage, as happens with open communications. However, gas workers have no less reason to worry about their condition.
If the pipe transporting blue fuel is immersed in the ground:
- It is difficult to monitor the mechanical condition of the gas pipeline, but its walls are affected by ground pressure, the weight of structures and pedestrians, as well as passing vehicles if the pipeline passes under a highway or a railway line.
- It is impossible to detect corrosion in a timely manner. It is caused by aggressive groundwater, directly the soil, which contains active components. The loss of initial technical characteristics is facilitated by technical fluids penetrating to the depth of the route.
- It is difficult to determine the loss of tightness due to a violation of the integrity of the pipe or welded assembly. The reason for the loss of tightness is usually the oxidation and rusting of metal pipelines, the banal wear of polymer structures, or a violation of assembly technology.
Despite the fact that the laying of gas pipelines in trenches provides for the complete replacement of aggressive soil with soil with neutral properties, and the device in places of possible spillage of technical liquids is completely prohibited, without special devices they cannot be considered completely protected from chemical aggression.
source
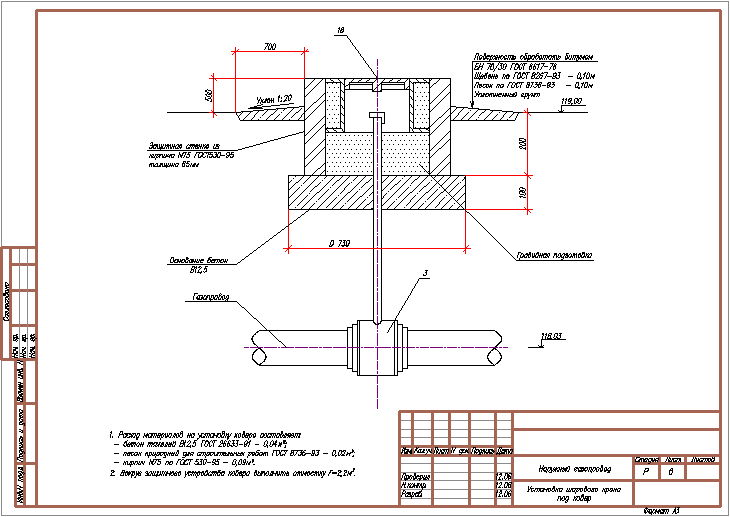
Placement of the gas pipeline in the case
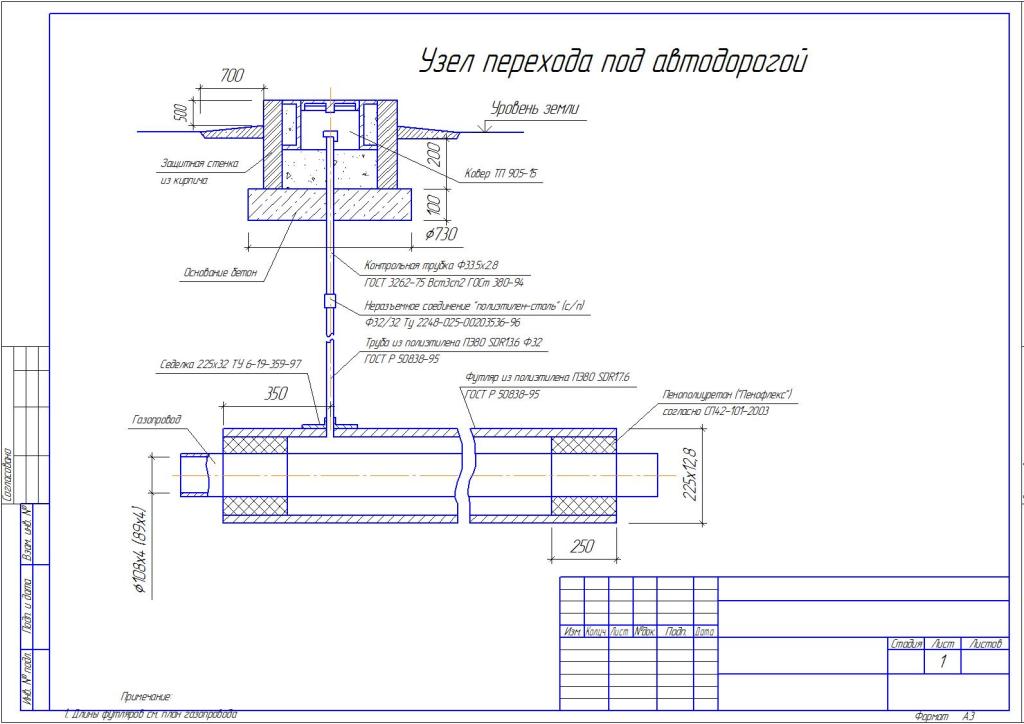
As soon as the check of gas pipelines is over, they can be placed in protective cases, inside of which there are special dielectric stands.It is on them that gas pipes are placed, after which the structure is sealed on both sides. In addition, special seals are installed, and the bitumen mixture is also sealed.
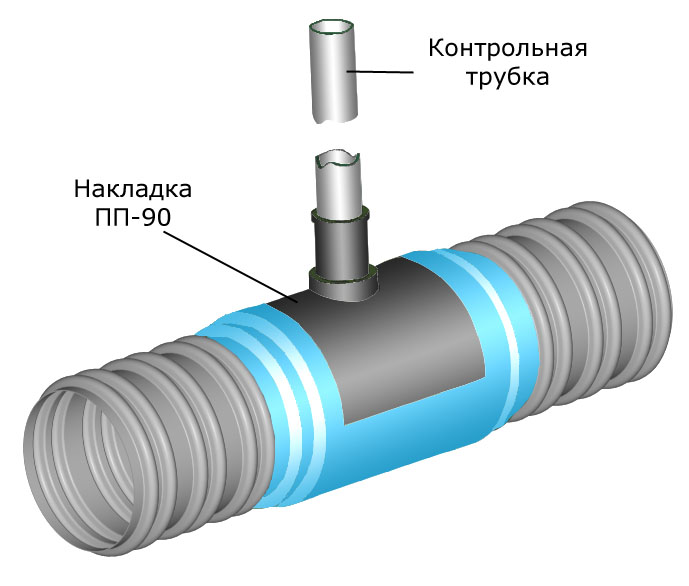
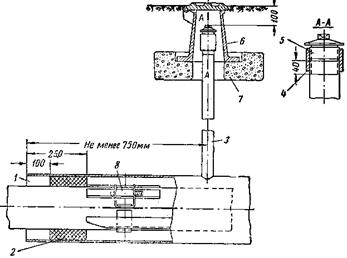
Then, at one end of the structure, at a distance of 750 mm from the edge, a hole is drilled. Then a control tube is mounted in it, the end of which, during the installation of the structure, will be brought out, i.e. to the surface of the earth. There will be a special device - a carpet, into which the control tube will be stuck.
This is necessary in order to find out about the presence or absence of gas in the case, and the control tube is a kind of conductor. According to regulatory documents, a tube with a diameter of at least 32 mm is a mandatory component of this design.
Laying a pipe with a protective case across the road will be carried out in exactly the same way as the usual sealing of pipes into the ground. Directly, they can be opened from the outside, but this will lead to a temporary stop of all traffic.
In such cases, it is necessary to organize additional detours, which in itself is very disadvantageous in terms of finances. In addition, such an opportunity may not be available at all in some settlements, and laying across railway tracks is generally strictly prohibited. In this case, one has to resort to finding other solutions that can help solve the problem with minimal financial costs.
If there is no possibility of laying through the roadway, a closed method is used. Its meaning is that a hole is made under the roads or railway tracks, the diameter of which will depend on the dimensions of the gas pipelines.
There are several ways to implement this method:
- Horizontal drilling. This method is used quite rarely, because it is quite aggressive and can damage the road surface.
- Punching or piercing the earth. This method is more preferable, because it uses mainly manual labor, which in itself is more accurate and precise than using technology. The remains of the earth are not compacted here, but are thrown out.
In general, there are special instructions according to which the development of the land is carried out. This takes into account the diameter of the pipes themselves, and some properties of the earth itself in a particular area. But, as practice shows, the method and the equipment that is available to the contractor who is laying the pipes are used.
Protective cases play an important role in the process of gasification of the territory. First of all, this is to ensure human safety, because a gas leak through a pipe wall can cause irreparable consequences. A person, often, himself is the cause of these events, performing earthwork near or through the intersection of gas pipelines.
Such irresponsibility can lead to catastrophic consequences, but protective cases significantly reduce these risks.
Bituminous VUS

Highly reinforced bituminous insulation is used as a waterproofing and a way to prevent corrosion manifestations on steel pipes in channelless types of laying water mains and industrial pipelines.
The main area of use of existing coatings is the prevention of corrosive formations in a network of pipes of small diameter, which operate at normal temperatures.
The multilayer structure of bitumen-mastic processing consists of:
- primer on the surface of the pipes;
- the first layer is reinforced fiberglass;
- the second layer consists of bituminous mastic, which is made up of hydrophobic materials;
- the next reinforcing layer consists of fiberglass;
- a pair or a single layer of coating consisting of kraft paper.
Video
Highly reinforced bitumen-polymer insulation has the following advantages:
- Ease of application.
- Great level of strength.
- Resistance to the influence of mechanical damage.
- Resistant to cathodic spalling.
- Excellent adhesion characteristics to steel parts.
- Minimum permeability of oxygen and water.
- Resistance to formations of corrosion.
- Tolerance to temperature changes.
Purpose of the protective case
The use of the case is due not only to the protection of the gas pipeline itself from the effects of an aggressive environment and various damages, but also to ensure safety for others. Everyone knows that a gas leak is a very dangerous phenomenon, so additional protection, in this case, is not a luxury, but a necessary condition.
Pipe laying using a protective case is strictly regulated, in accordance with regulatory documents - SNiP 42-01 and SNiP 32-01. According to the requirements specified in the last document, not only the pipe laying process itself is regulated, but also the distance at which the ends of the protective case should be located.
In particular, if we are talking about railway tracks, then the protective case must pass through them and have a length of at least 50 meters from the exit. Such great importance is justified by the fact that natural gas is very explosive, and trains have a very high mass. As for roads, the cases should protrude from the exit 3.5 meters from them. In addition, there are precise instructions for the depth of laying the pipeline, which is about one and a half meters.
Making a case
In accordance with the same regulations, the cases must be made of steel pipes. The diameter may be different, because it all depends on the parameters of the diameter of the gas pipeline, but, in general, the diameter will not differ much, the spread will be within 10 cm.
The control tube diameter must be at least 32 mm
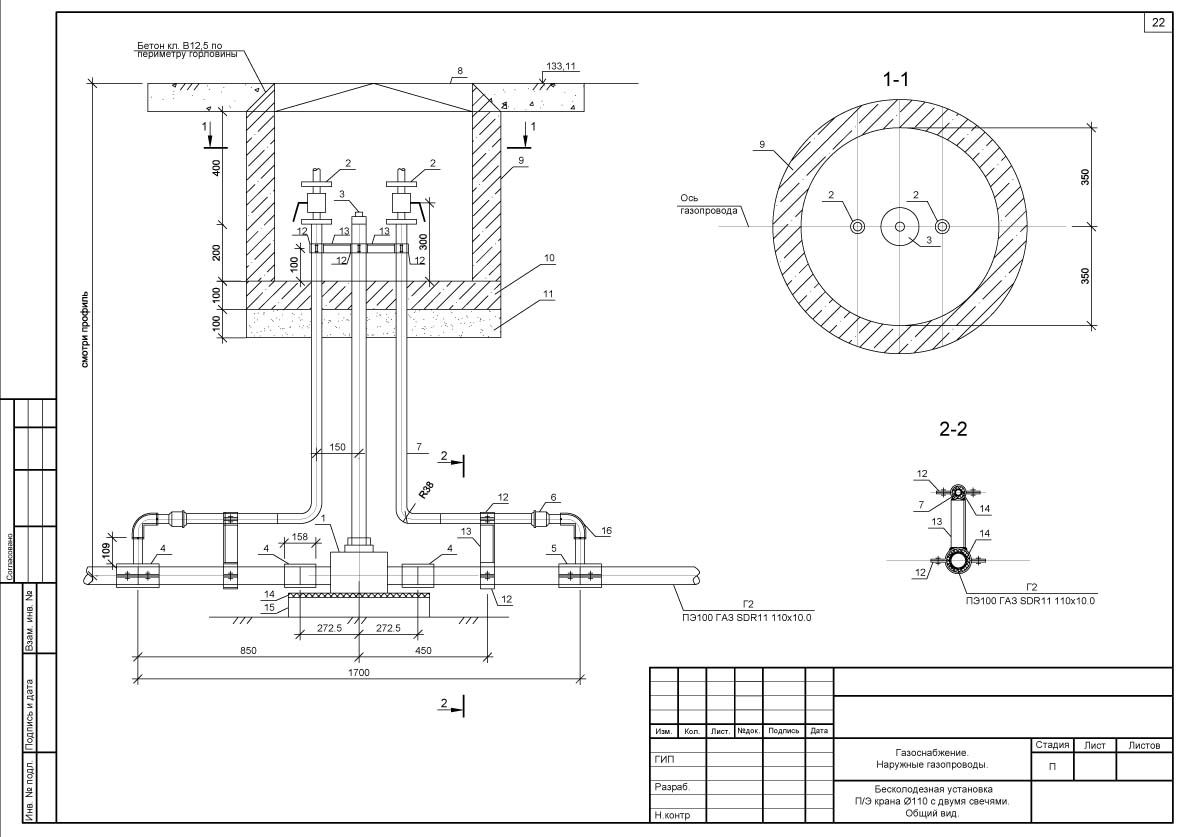
- Control tubes are installed in the most responsible. places of the gas pipeline (above the joints at the points of connection of branches at enterprises), brought to the surface under the carpet, they are designed to quickly detect gas leaks from an underground gas pipeline. To protect gas pipelines from large dynamic and static. loads at the intersection of railways and highways, collectors and wells, walls and foundations of buildings or when laying gas pipelines at shallow depths, they are enclosed in cases, which are a piece of steel pipe, the diameter of which is larger than the diameter of the gas pipeline. The gap between the case and the gas pipeline is sealed. The case is equipped with a control tube led out under the carpet.
- In some places, control tubes are installed above the welded joints of gas pipelines. This device consists of a metal casing 350 mm long, semi-cylindrical, with a diameter larger than the pipe diameter by 200 mm.From the casing, laid on a layer of crushed stone or gravel, a pipe with a diameter of 60 mm is diverted to the surface of the pipe, in which gas accumulates in case of leaks in a controlled place.
- When laying a gas pipeline under a carriageway with an improved road surface, the marks of the well covers and the carpet must correspond to the mark of the road surface, in places where there is no traffic and people pass, they must be at least 0.5 m above ground level.
In the absence of an improved road surface around wells and carpets, a blind area of at least 0.7 m wide with a slope of 50 ° / 00 is provided, which excludes the penetration of surface water into the soil near the well (carpet).
The control tube diameter must be at least 32 mm.
When removing the control tube above ground level, its end must be bent by 180 °.
Installation options for control tubes are shown in Figure 1.
For sampling from cases, an exhaust candle made of steel pipes is provided, installed on a foundation or other support.
The installation option for the exhaust candle is shown in Figure 2.
Cases for gas pipelines should be provided to protect the gas pipeline from external loads, from damage at the intersection with underground structures and communications, as well as for the possibility of repair and replacement, detection and removal of gas in the event of a leak. The connections of the components of the case must ensure its tightness and straightness.
The control tube diameter must be at least 32 mm
15.79kb.
1 page
Tourist's note Before departure
60.08kb.
1 page
Memo to a tourist in Serbia Visas
63.09kb.
1 page
one.Foreign passport, (original) with a validity period of at least 3 months after the end date of the trip, if you have 2 valid international passports, it is also required
77.97kb.
1 page
Educational program 5B011100 Informatics
848.29kb.
12 p.
31.31kb.
1 page
Letter about changing the password under the agreement (for an individual)
31.09kb.
1 page
What should be a child who lived with people who hated him? And what should a child feel when he finds out that the greatest light wizard Albus Dumbledore himself sent him to these people
4716.05kb.
20 pp.
Graphical analysis in real life
4950.95kb.
35 pages
This is a result pre-programmed by the teacher, which must be achieved by the teacher and students at the end of the lesson.
70.38kb.
1 page
1. On the computer monitor, the image is formed from
35.49kb.
1 page
Documents required to open a UAE visa
27.33kb.
1 page