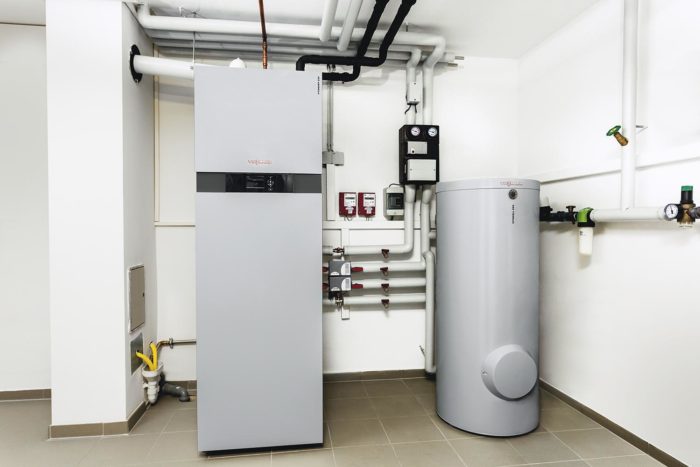
- Cons of application
- Types of condensing boilers
- Gas and more
- How is the equipment arranged?
- The real state of affairs
- Criterias of choice
- How to choose the right condensing boiler for your home?
- What is a condensing gas boiler?
- The principle of operation of the condensing gas heat generator
- Advantages and disadvantages of condensing boilers
- Benefits of condensing boilers
- Hardware deficiencies
- The principle of operation of gas condensing boilers
- Specifics of operation
- Requirements for the heating system
- Condensation
- Chimney
- What to consider when maintaining and operating
- The principle of operation of the condensing boiler
Cons of application
With a sufficiently large number of advantages, there are some features or, relatively speaking, disadvantages that should be considered when choosing, installing and maintaining condensing boilers:
- Insufficiently high temperature indicators of heating of air masses in a heated room. This feature is associated with the ratio of the temperature of the heat carrier for supply and return - 55 ° C to 35 ° C, which is very effective only when arranging the "warm floor" system.The use of a condensing boiler in a traditional heating system will require the mandatory installation of several additional radiators.
- During the operation of a condensing heater, it becomes necessary to ensure the disposal of all condensate released, which contains a certain amount of toxic acid. The chemical composition of such condensate does not allow the use of local sewer systems, represented by traditional septic tanks, for draining.
When arranging a heating system using a condensing boiler, at the design stage, a separate system is necessarily provided for, which makes it possible to effectively neutralize condensate.

Condensing boiler efficiency
The operation of equipment with a power of not more than 35W in the presence of a centralized sewer system will not require the installation of an additional bypass neutralizer.
One of the main disadvantages of any modern condensing boilers, according to the majority of domestic consumers, is still the rather high cost of such heating equipment.
Types of condensing boilers
Condensate boilers are classified according to the following criteria:
- by type of installation: floor or wall;
- by the number of circuits: single or double circuit.
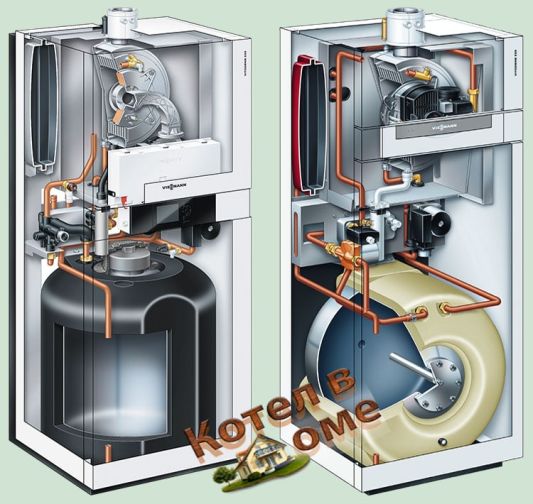
Condensing floor boilers are not only large in size, but can also be equipped with remote pumps and other equipment that requires a separate room for installation. They are usually single-circuit and are designed for heating large areas. Their advantages are maintainability and simplicity of design.
Condensing wall-mounted boilers differ from floor-standing boilers in their compact size and relatively low weight. All components and assemblies are located inside the case, there are no external elements. Available in single and double circuit design, easy to connect, unpretentious in operation.
 Condensing boiler single-circuit floor
Condensing boiler single-circuit floor
Single-circuit heating boilers for space heating can be used not only in heating systems, but also for hot water supply, subject to the presence of a boiler. They are characterized by simple design, low cost compared to a double-circuit boiler, high efficiency and heating power, economical fuel consumption.
A double-circuit condensing gas boiler is available with a storage boiler or with a flow-type heat exchanger. It can be used for heating or water heating without the need to purchase a separate boiler. Compact, easy to install and maintain, floor or wall mounting.
Gas and more
Despite the fact that methane is the most efficient type of fuel, gas condensing boilers can also be used with other gases, namely propane and butane, with a mixture of which gas tanks are filled. Since regular filling and maintenance of the gas tank requires constant expenses, the consumer subconsciously (or not) is always trying to save gas. A condensing boiler in this situation is convenient not only as a generator of albeit small, but additionally produced heat, but also as a device with a wide range of power modulation (regardless of the manufacturer). This saves gas because the consumer does not overheat the house.In addition, the reconfiguration of the burner to liquefied gas is carried out by switching the boiler settings without interfering with its design.
There are both liquid fuel and biofuel condensing boilers on the Russian market, which, unfortunately, are not widely used.
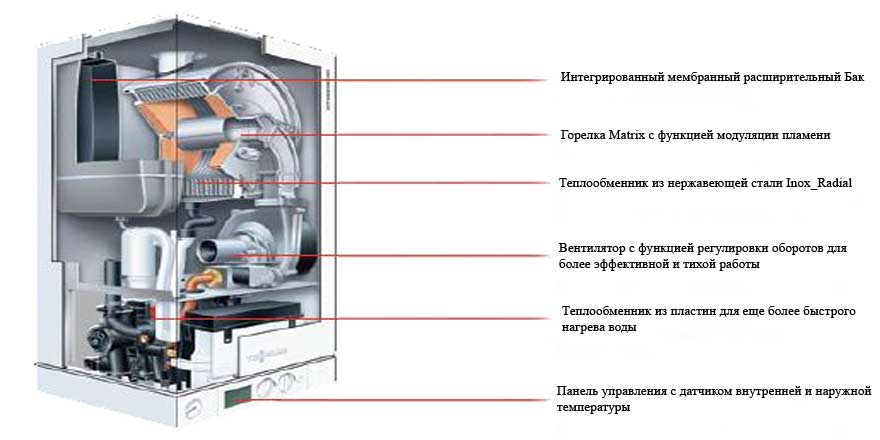
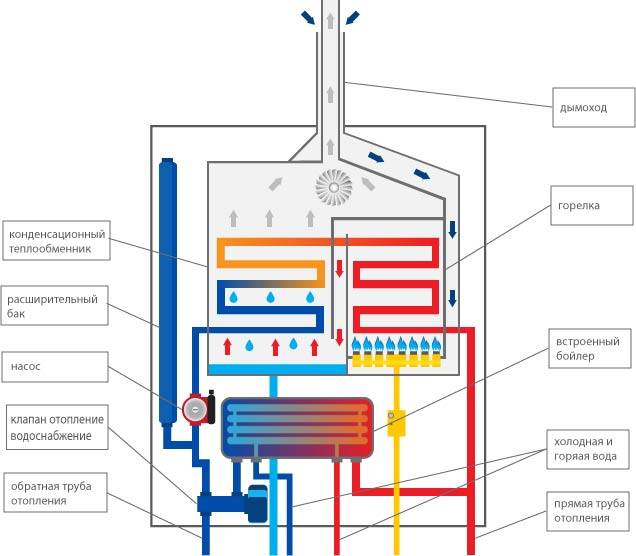
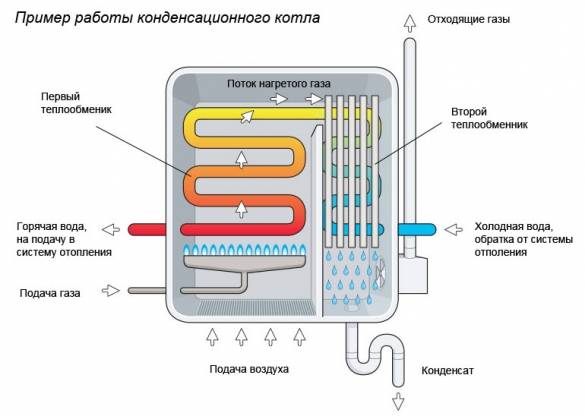
How is the equipment arranged?
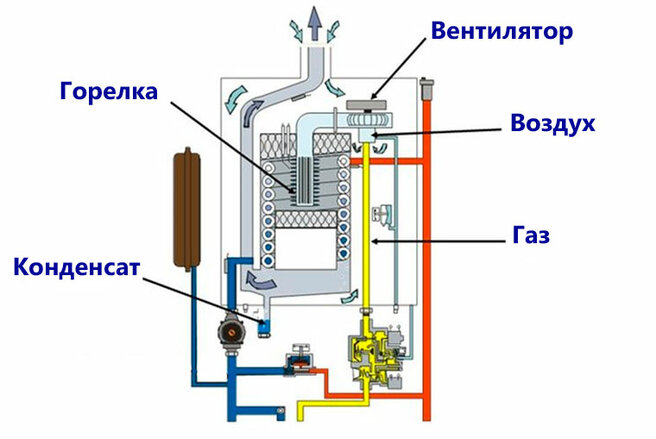
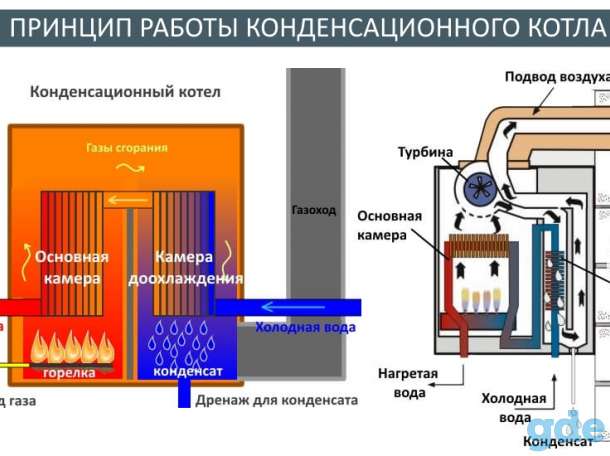
With the principle of operation of the heating system, it turns out that the design of the boiler has two heat exchangers: the main and additional (or secondary). The main unit functions normally and is heated by the gas used. The bulk of the heat is generated in this heat exchanger. As for the second - an additional heat exchanger, it works on the energy of air vapor that condenses on the equipment.
If everything is simple with the main device, then the condensing device has a complex structure. Since the temperature of the vapors is insignificant, and a sufficient amount of heat must be taken away.
There are a number of technical points that will achieve maximum effect:
- Spiral fins are attached to the heat exchanger in order to increase the temperature tapping surface.
- For intensive heat extraction, cavities with different cross-sectional diameters can be used.
- A secondary heat exchanger can be mounted on the return circuit of the boiler structure.
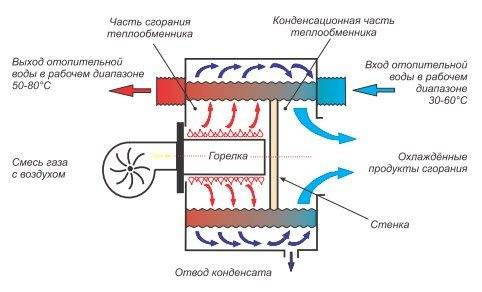
At the same time, manufacturers of condensing boilers equip only the best burners in their design, thanks to which gas and air interact optimally and efficiently.
The real state of affairs
Boiler device
So, condensing gas boilers are more economical - there is no doubt about it. But you still have to pay for this savings at least once. These models are one and a half times more expensive than traditional ones. This is the first.
Second
I would like to draw your attention to some positions that are not striking at first glance. And even some experts do not always pay attention to them.
For example, a condensing boiler is a wall-mounted option - in terms of power, it is in the range of 20–110 kW. Traditional wall-mounted units have more modest performance - up to a maximum of 36 kW.
Can you imagine that a small-sized double-circuit condensing apparatus is able to provide heat and hot water for household needs to a large private house? For example, a total area of 800 m². If you use a traditional heating unit, then only the floor type.
Based on this, you can compare the cost of the two models. It almost flattens out. But condensation models have much more advantages:
- Fuel economy.
- Reducing harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
- The efficiency of the equipment.
- In addition, under them there is no need to allocate a separate room for organizing a boiler room, as is usually the case with floor units.
Most importantly, the efficiency of the device depends on how intensively it is used. After all, the lower the temperature of the coolant in the return circuit, the more complete the condensation in the secondary heat exchanger, the more heat energy is released, and the higher the efficiency of the equipment becomes. That is why this type of heating device is more cost-effective in so-called low-temperature heating systems - underfloor heating as an example.
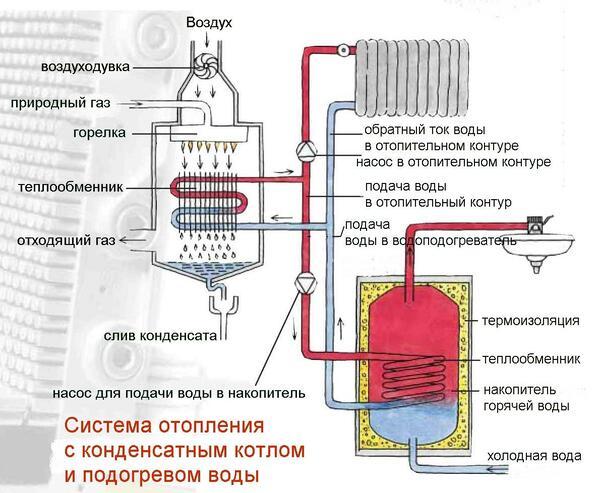
Scheme of a gas boiler
But in reality, Russian operating conditions are completely different than in the same Europe.For example, when the temperature outside the window is minus 20-50C, it is necessary to increase the temperature of the coolant. This can be done only by increasing the fuel consumption, because the main source of thermal energy is the burnt gas. And this means that the temperature of the coolant in the return circuit will not fall below 60C. With this indicator, it is impossible to talk about the condensation of wet vapors. That is, the condensing gas boiler you installed starts working like a normal one. So is it worth buying such an expensive device?
However, we will not belittle the advantages of condensation models. Even when operating in this mode, they are more economical than traditional ones. True, at first glance, the savings are not very large - up to 5%, but if you count on annual gas consumption, then the amount will be impressive. In addition, the design of the boiler is designed in such a way that even with a maximum drop in gas pressure in the pipe line, it will continue to work. Efficiency, if it falls, is negligible.
Criterias of choice
A condensing gas boiler, due to its high cost, must be selected most carefully based on the following criteria:
- it is recommended to purchase certified equipment from well-known brands that can guarantee full compliance with the declared characteristics, as well as provide a guarantee and service;
- heating power should be enough to heat a certain area of the room, taking into account the difference in temperatures inside and outside the buildings, as well as the length of communications with the coolant;
- installation method, depending on the amount of space and technical operating conditions of the boiler;
- complete set, which may not include expensive accessories or components, without which it is impossible to connect and operate the boiler;
- functionality, methods and ease of management;
- the possibility of connecting an additional heating circuit;
- gas and water consumption levels.
How to choose the right condensing boiler for your home?

An expensive purchase requires careful selection and a reasonable approach.
Boilers serve for many years, so it is better to pay attention to some selection rules:
- Power. In this case, more power is not required, as it will lead to rapid wear of the unit. To calculate the optimal indicator, a simple formula is suitable - 1 kW of heat is required per 10 m2. In houses with poor insulation, the presence of large windows and for regions with severe winters, the figure should be increased by 30-50%.
- The number of contours. If condensing boilers, the principle of operation of which differs little from conventional equipment, are equipped with two circuits, the owner gets the opportunity to heat and hot water. One circuit will work to heat the coolant, the second will be responsible for the distribution of hot water.
- Fuel consumption. This indicator depends on power, load on the system and efficiency. For example, boilers of 10 kW consume up to 1.12 m3 / h of gas, and 30 kW already 3.36 m3 / h. The largest indicator for units with a capacity of 60 kW - they require 6.72 m3 / hour of gas.
- What is the heat exchanger made of? If it is silumin (aluminum with silicon), then the device will be inert to chemicals, and stainless steel is cheaper, resistant to corrosion, thermal shock, but does not tolerate chemically aggressive substances.
- operating temperature. This parameter affects the efficiency.The lower the heating in the return, the faster the condensation process. For example, if the temperature of the direct/return circuit is 40/30 C, then the efficiency reaches 108%, and with the temperature of the direct/return circuit 90/75 C, the efficiency is only 98%.
- The presence of a control system, control, automation unit. The equipment is installed in all boilers, only the list of functions differs. Here the choice depends on the preferences of the owner, the desire to control the device remotely, set the night / day mode, warm up at minimum temperatures, and so on.
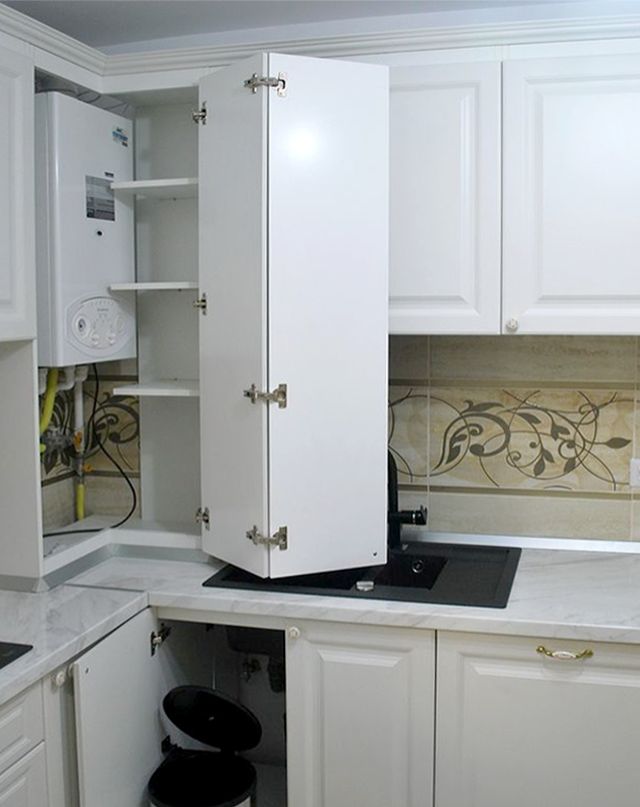
- Mounting. Boilers of floor and wall type are produced. Floor-standing - these are single-circuit units with increased power (from 100 kW), can be integrated into any heating system. Wall-mounted - devices with reduced power (up to 100 kW), double-circuit, do not require the arrangement of a full-fledged chimney, a pipe leading through the wall to the street is enough.
You can't get around the issue of price. The range of equipment is available in three price segments:
- Premium. This includes German manufacturers who offer units with a stylish design, with silent operation. The devices are made of high quality materials and with certificates of environmental safety.
- Average price. Comfortable and economical devices, including single-circuit, double-circuit, wall-mounted and floor-mounted. There is no difference with luxury models, except for a slightly less popular brand of the brand. An example is BAXI brand models.
- budget appliances. These are products from Korean, Slovak manufacturers, which are adapted to the conditions of our reality. The difference with elite models is only in simplified functionality and a minimal set of “smart” automation and control options.Such boilers perfectly tolerate pressure surges, power outages and support work where more expensive automation stops the functionality of the boiler.
When choosing a boiler, it will not be superfluous to pay attention to maintainability, the availability of spare parts in a wide sale and service centers with skilled employees.
What is a condensing gas boiler?
Gas condensing boilers are gaining market share more and more as they have proven to be very efficient devices. Condensing boilers have a fairly serious efficiency indicator. It is almost 96%. While in conventional boilers, the efficiency hardly reaches 85%. Condensing boilers are very economical. These boilers are very popular in Europe, because Europeans have a rather acute issue of fuel economy. Despite the slightly higher cost of a condensing boiler compared to a conventional boiler, condensing gas heating units pay for themselves quite quickly. Boilers of this type look confidently into the future, because the principle of their work is the most promising today.
The principle of operation of the condensing gas heat generator
Before we talk about the nuances of condensing technology, we note that an energy-efficient, and therefore comfortable and economical country house is a balanced building. This means that, in addition to a closed thermal insulation circuit, all elements of the cottage, including the engineering system, must be optimally matched to each other.
That is why it is so important to choose a boiler that works well with a low-temperature underfloor heating system, and will also reduce energy costs in the long run.

Sergey BugaevTechnician of Ariston company
In Russia, unlike European countries, condensing gas boilers are less common. In addition to environmental friendliness and greater comfort, this type of equipment allows you to reduce heating costs, because. such boilers work 15-20% more economically than conventional ones.
If you look at the technical characteristics of condensing gas boilers, you can pay attention to the efficiency of the equipment - 108-110%. This is contrary to the law of conservation of energy.
While, indicating the efficiency of a conventional convection boiler, manufacturers write that it is 92-95%. Questions arise: where do these numbers come from, and why does a condensing gas boiler work more efficiently than a traditional one?
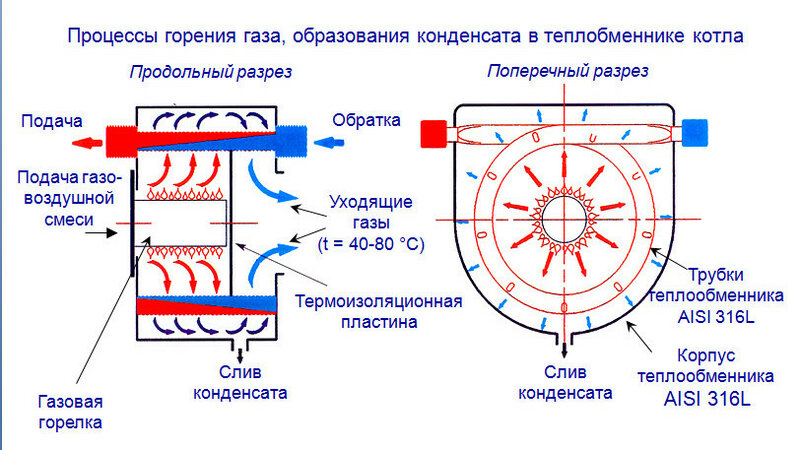
The fact is that such a result is obtained due to the method of heat engineering calculation used for conventional gas boilers, which does not take into account one important point, evaporation / condensation. As is known, during the combustion of fuel, for example, main gas (methane CH4), heat energy is released, and carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O) in the form of steam and a number of other chemical elements.
In a conventional boiler, the temperature of the flue gases after passing through the heat exchanger can reach up to 175-200 °C.
And water vapor in a convection (conventional) heat generator actually “flies into the pipe”, taking part of the heat (generated energy) with it into the atmosphere. Moreover, the value of this "lost" energy can reach up to 11%.
To increase the efficiency of the boiler, it is necessary to use this heat before it leaves, and transfer its energy through a special heat exchanger to the heat carrier. To do this, it is necessary to cool the flue gases to a temperature of the so-called. "dew point" (about 55 ° C), at which water vapor condenses with the release of useful heat. Those. - use the energy of the phase transition to maximize the use of the calorific value of the fuel.
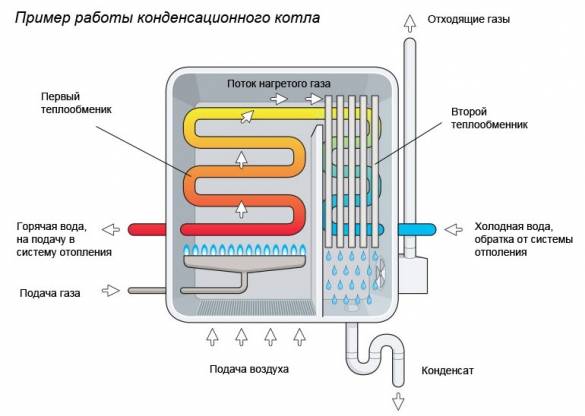
We return to the calculation method. Fuel has a lower and higher calorific value.
- The gross calorific value of a fuel is the amount of heat released during its combustion, taking into account the energy of water vapor contained in flue gases.
- The net calorific value of a fuel is the amount of heat released without taking into account the energy hidden in water vapor.
The efficiency of the boiler is expressed in the amount of thermal energy obtained from the combustion of fuel and transferred to the coolant. Moreover, indicating the efficiency of the heat generator, manufacturers can calculate it by default using the method using the net calorific value of the fuel. It turns out that the real efficiency of a convection heat generator is actually about 82-85%, and a condensing one (remember about 11% of the additional heat of combustion that it can "pick up" from water vapor) - 93 - 97%.
This is where the efficiency figures for a condensing boiler appear, exceeding 100%. Due to its high efficiency, such a heat generator consumes less gas than a conventional boiler.
Sergey Bugaev
Condensing boilers provide maximum efficiency if the return temperature of the coolant is less than 55 ° C, and these are low-temperature heating systems "warm floor", "warm walls" or systems with an increased number of radiator sections. In conventional high temperature systems, the boiler will operate in condensing mode. Only in severe frosts will we have to maintain a high temperature of the coolant, the rest of the time, with weather-dependent regulation, the temperature of the coolant will be lower, and due to this we will save 5-7% per year.
The maximum possible (theoretical) energy savings when using the heat of condensation is:
- when burning natural gas - 11%;
- when burning liquefied gas (propane-butane) - 9%;
- when burning diesel fuel (diesel fuel) - 6%.
Advantages and disadvantages of condensing boilers
A gas condensing boiler costs a little more than other types of equipment, but it's worth it. This type of equipment saves energy and is more economical in the long run. It is considered a more progressive type of heating apparatus.
A chimney is required for condensing equipment. Its installation will be quite cheap, since structures of this type can even use plastic structures. But, as a rule, no one takes risks, and stainless steel chimneys are installed. They are easy and quick to assemble. Have condensing gas boilers and pros and cons.
Benefits of condensing boilers
Advantages of condensing boilers The advantages include:
- profitability;
- high power;
- safety;
- high degree of automation;
- small dimensions;
- quick payback;
- noiselessness;
- resistance to corrosion;
- environmental friendliness.
Saving this equipment is considered the most significant plus. It is really significant in comparison with any other gas heating equipment.
Quiet operation is very important for small spaces. There are houses with a footage of only 30–40 sq.m. So for them, this indicator is vital for permanent residence. The security of the system is ensured by process automation. The system is self-configuring and does not require additional intervention or monitoring.
Corrosion resistance is important for those who use equipment for industrial purposes, in factories, etc.
The high cost of condensing-type gas boilers quickly pays off due to the economical use of energy.
The small size of the devices, even with significant power, allows the use of floor-standing boilers in any room without resorting to installation in a separate unit.
The power of the device may vary. There are boilers with low rates. This is due to its unique design and principle of operation, when the heated water vapor gives off its heat to the system again. For this equipment, there is no need to create a safety margin in reserve when buying. He's capable of more than what's listed in the docs.
Hardware deficiencies
Disadvantages of equipment The disadvantages of the installation include:
- the need to install a condensate drain system;
- compliance with installation requirements;
- getting permission to install.
The very need for additional installation is depressing, although in fact it is nothing complicated.Paperwork for gas equipment is a natural process that will have to go through in any case (if any type of gas heating equipment is used).
The requirements for installing such a device are a little tougher than for others. Here you will have to perfectly level the surface of the floor or wall, ideally observe the distances to objects, be sure to connect the chimney, etc.
But none of the shortcomings can be called significant. It is rather the hassle associated with the installation and does not depend on the features of the equipment itself.
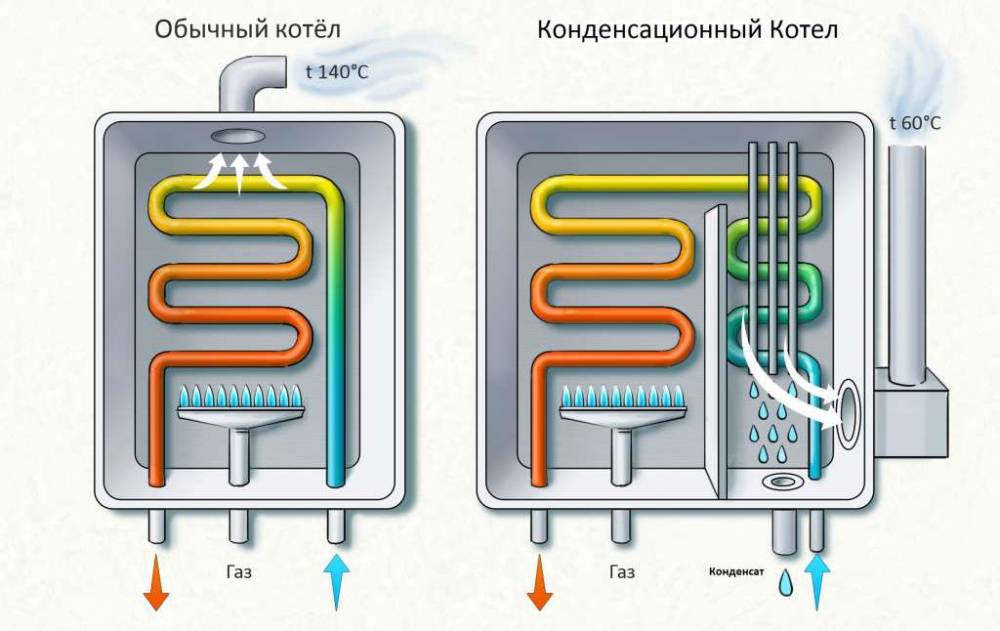
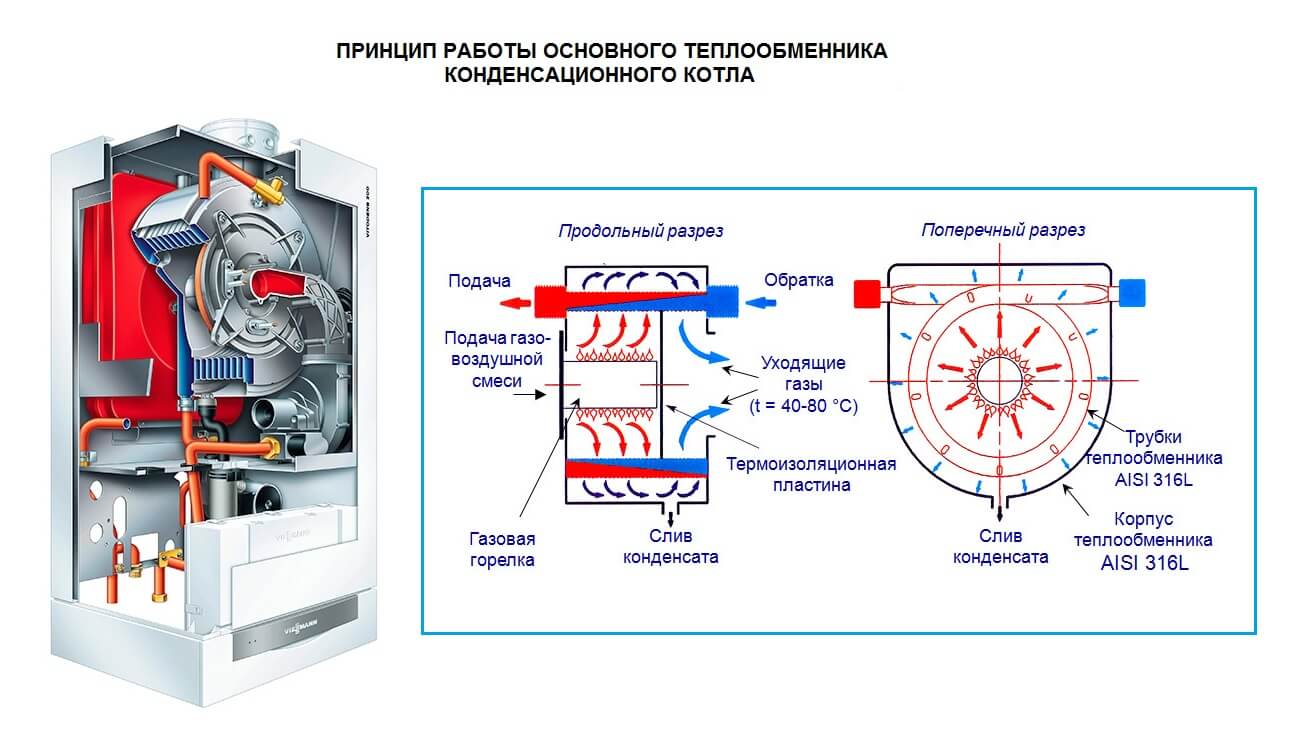
The principle of operation of gas condensing boilers
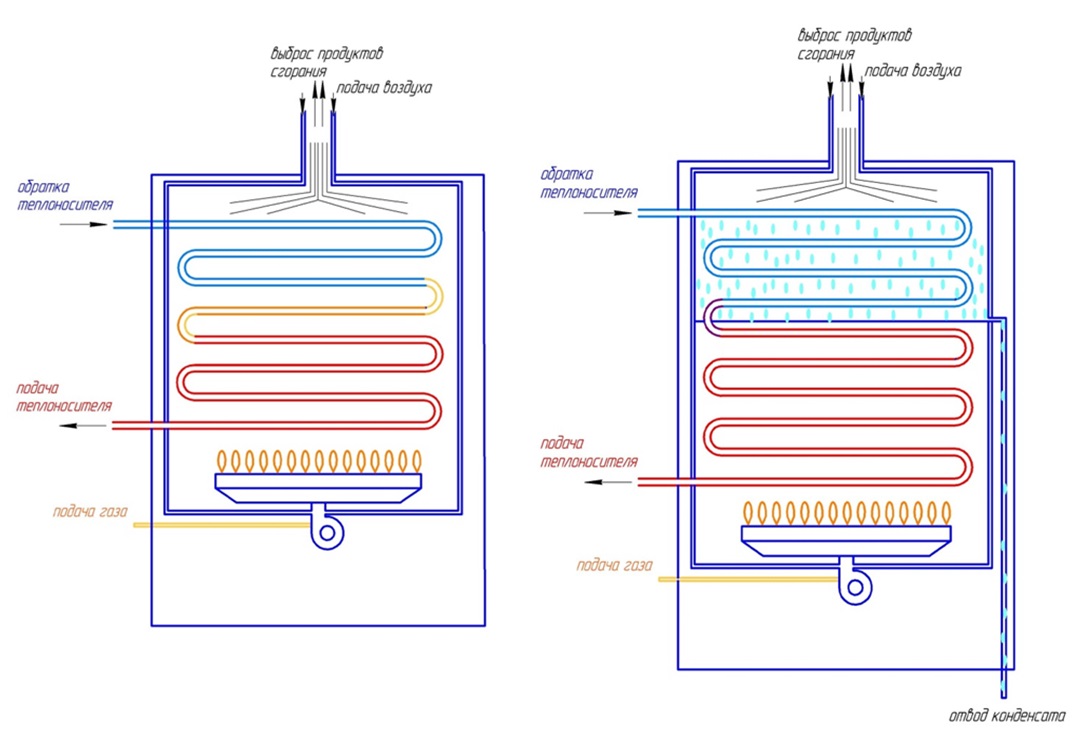
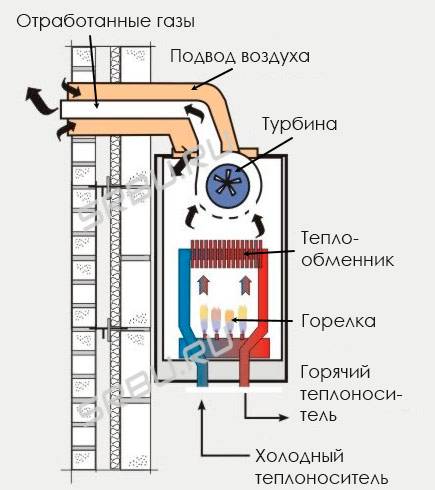
A conventional boiler releases rather hot combustion products into the chimney. Flue gas temperature ranges from 150-250 degrees. The condenser, after working out the main heat transfer process, cools down the gaseous products of combustion until a change in the state of aggregation begins to occur. That is, before the start of the condensation process. Due to this, the boiler increases the useful part of the heat transferred to the heated coolant. And it does it twice:
- first cooling the flue gases to 50-60 degrees
- and then taking away the heat released during the condensation process.
This is where an additional 15-20% of useful energy comes from. Below is a great illustration of how a condensing gas boiler works.
Specifics of operation
To transfer the heating system from a conventional boiler to a condensing boiler, simply connecting a new unit to the existing communications is not enough: in addition to the fact that you need to take permission to replace any gas equipment, the process of its operation itself will require compliance with certain rules.
Requirements for the heating system
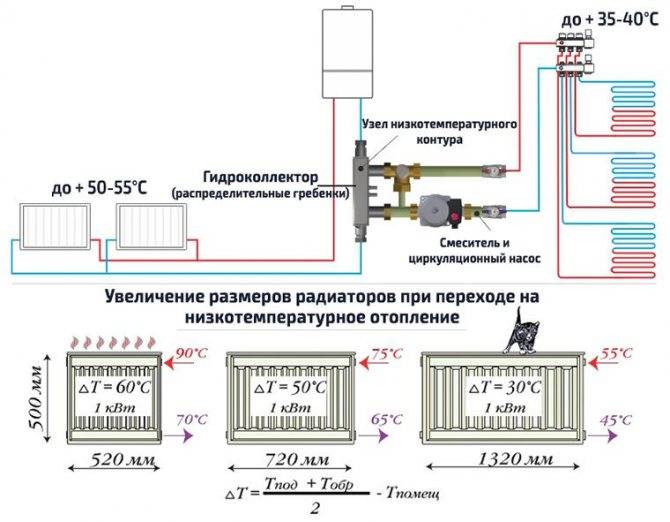
Low-temperature heating scheme Since a cooled (30–50 ° С) coolant that has already passed through the pipes is used to condense steam, such boilers will work with maximum efficiency only in low-temperature systems - these include underfloor heating, wall panels, capillary mats and batteries with an increased number sections.
In systems operating in high-temperature mode (60–80 °C), condensing units lose a significant part of their efficiency, up to 6–8%.
However, it is impossible to say that they are not at all suitable for standard radiator or radiant heating, because even in them it is simply not necessary to maintain too high a temperature (50-55 ° C) for heating a residential building most of the time - except for a few frosty weeks for a whole period.
Therefore, in the off-season, the condenser can fully service standard systems - just when a strong cold snap occurs (-25–30 ° C), it will switch to enhanced operation. The condensation process will stop and the efficiency will drop, but still it will be 3–5% higher than that of convection units.
Condensation
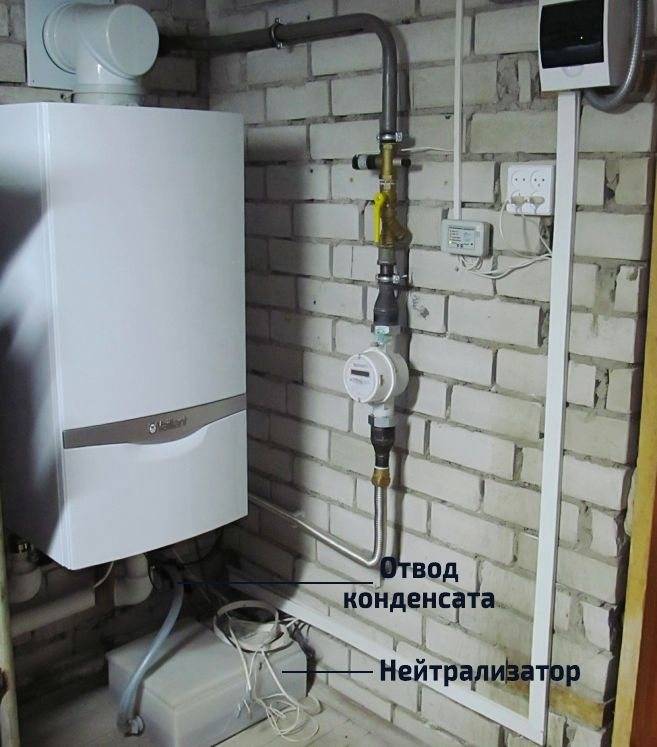

An example of the removal and neutralization of condensate. The next important nuance, which many users note as a drawback, is that the boiler needs daily disposal of waste condensate.
The amount of condensate can be determined at the rate of 0.14 kg per 1 kWh.So, for example, a unit with a capacity of 24 kW, which operates on average with a load of 40–50% (due to fine adjustment of parameters, based on weather conditions, a smaller part of the resource can also be used), allocates about 32–40 liters per day.
- central (village, city) sewage - condensate can simply be drained, provided that it is diluted in a ratio of at least 10: 1, and preferably 25: 1;
- local treatment plant (VOC) and septic tank - condensate must first pass through the acid neutralization procedure in a special tank.
The filler for the neutralizer, as a rule, is fine mineral chips with a total weight of 5 to 40 kg. You will have to change it manually every 1-2 months. There are also models with built-in neutralizers, getting into which, the condensate is automatically alkalized and drained by gravity into the sewer.
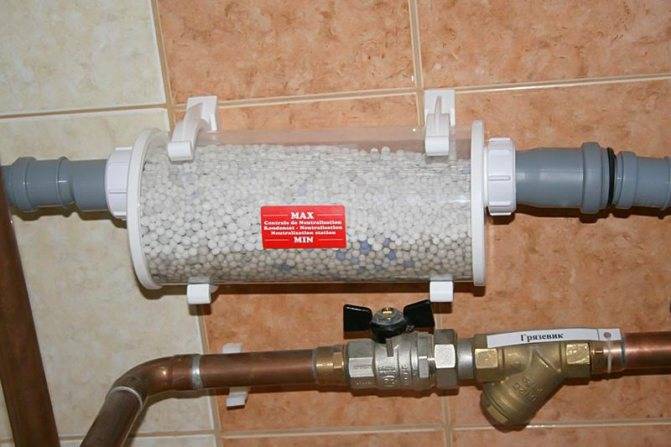

An example of the use of a compact neutralizer in the production of a small amount of condensate.
Chimney
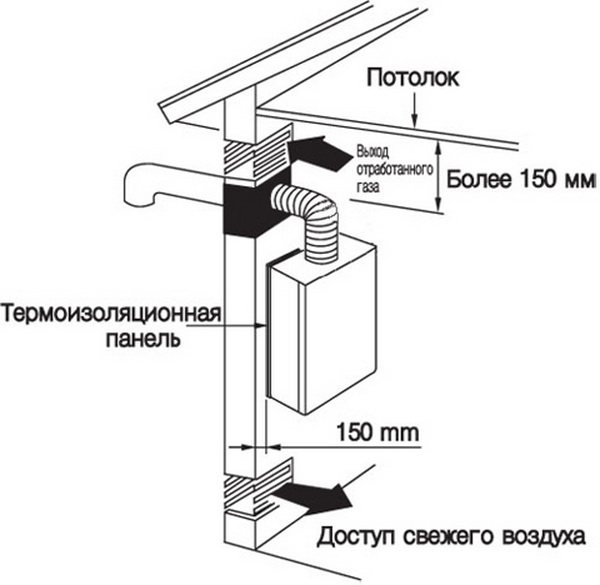
To remove combustion products, lightweight chimneys are installed on condensing boilers that do not require the construction of a more traditional counterpart. Usually, the term “lightweight” means coaxial chimneys - they are combined into a design according to the “pipe-in-pipe” principle.
The coaxial chimney is simultaneously used both for ejection of smoke (through the inner pipe) and for air supply (through the space between the inner and outer pipes). Due to this design, it does not take oxygen from the room, and also increases the efficiency of the boiler, since the air is heated even before it enters the burner.
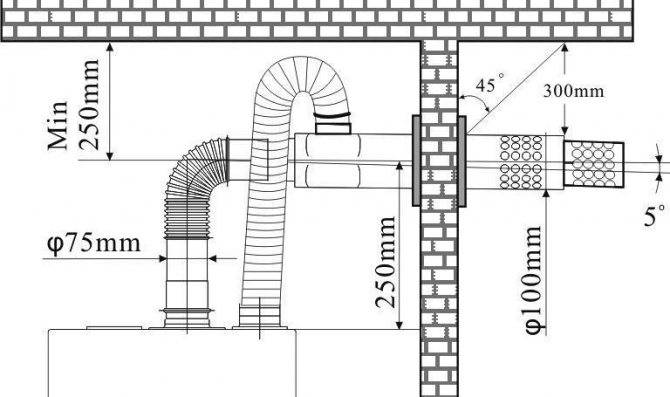
The installation of such a chimney is relatively simple: the only difficulty is the need to place it at a slight angle (3–5 °) to the street.This is done so that all the condensate that accumulates on the walls of the inner pipe does not fall back into the combustion chamber and onto the primary heat exchanger of the boiler, greatly reducing the service life of units vulnerable to acidity.
Chimney pipes for condensing units are made of lightweight anti-corrosion materials - stainless steel and hard polymers (plastic): at low temperatures of the exhaust gas, they do not deform, do not melt, and do not emit any pollutants into the atmosphere.
What to consider when maintaining and operating
Before purchasing and installing a condensing boiler, it must be taken into account that they have certain differences:
- flue gases can only be removed through a coaxial chimney;
- to remove condensate moisture into the city sewerage system, it is required to lay a specific anti-corrosion pipeline and equip a system to increase the pH of the condensate to 6.5;
- it is possible to connect an indirect heating boiler to condensing boilers;
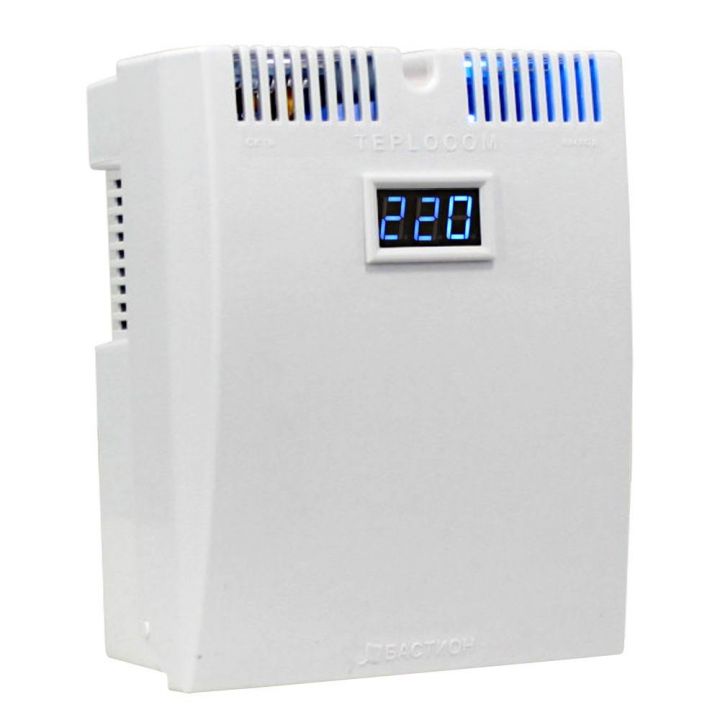
- in order to extend the life of the equipment, it is recommended to power the boiler through an electric stabilizer.
The condensing boiler is the most common type of heating boilers in Europe. In many states, the installation of other heating units is prohibited.
This is due to high emissions of harmful substances, and low efficiency of a traditional heating boiler.
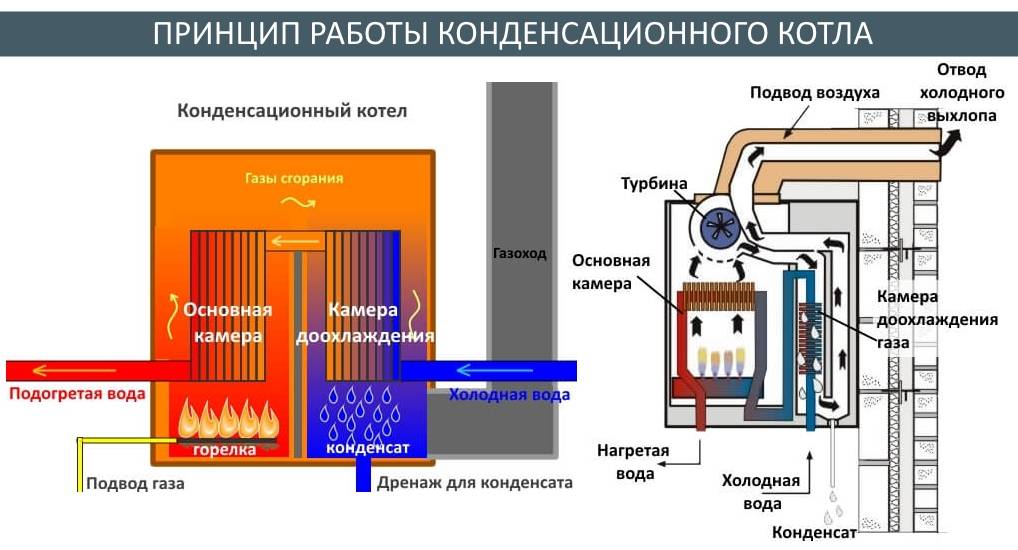
The principle of operation of the condensing boiler
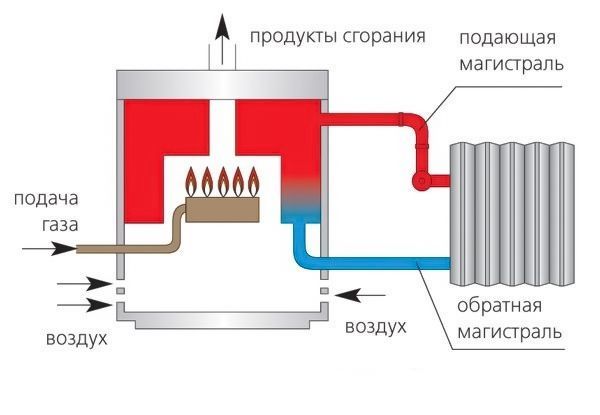
The condensing boiler is the little brother of the most common gas-fired convection boiler. The principle of operation of the latter is extremely simple, and therefore understandable even to people who are poorly versed in physics and technology.The fuel for a gas boiler, as its name implies, is natural (main) or liquefied (balloon) gas. During the combustion of blue fuel, as well as any other organic matter, carbon dioxide and water are formed and a large amount of energy is released. The released heat is used to heat the coolant - technical water circulating through the heating system of the house.
The efficiency of a gas convection boiler is ~90%. This is not so bad, at least higher than that of liquid and solid fuel heat generators. However, people have always sought to bring this figure as close as possible to the coveted 100%. In this regard, the question arises: where do the remaining 10% go? The answer, alas, is prosaic: they fly out into the chimney. Indeed, the products of gas combustion leaving the system through the chimney are heated to a very high temperature (150-250 ° C), which means that 10% of the energy we lost is spent on heating the air outside the house.
Scientists and engineers have been looking for the possibility of a more complete heat recovery for a long time, but the method of technological implementation of their theoretical developments was found only 10 years ago, when the condensing boiler was created.
What is its fundamental difference from the traditional convection gas-fuel heat generator? Having worked out the main process of fuel combustion and transfer of a significant part of the heat released in this case to the heat exchanger, the condenser cools down the combustion gases to 50-60°C, i.e. to the point where the process of water condensation begins. Already this is enough to significantly increase the efficiency, in this case, the amount of heat transferred to the coolant. However, this is not all.
Traditional gas boiler
Condensing gas boiler
At a temperature of 56°C - at the so-called dew point - water passes from a vaporous state to a liquid state, in other words, water vapor condenses. In this case, additional energy is released, which at one time was spent on the evaporation of water and in conventional gas boilers is lost along with the evaporating gas-vapor mixture. The condensing boiler is able to “pick up” the heat released during the condensation of water vapor and transfer it to the heat carrier.
Manufacturers of condensing type heat generators invariably draw the attention of their potential customers to the unusually high efficiency of their devices - above 100%. How is this possible? In fact, there is no contradiction to the canons of classical physics here.
Just in this case, a different system of calculations is used.
Often, when evaluating the efficiency of heating boilers, they calculate what part of the released heat is transferred to the coolant. The heat "taken away" in a conventional boiler and the heat from deep cooling of flue gases will give a total of 100% efficiency. But if we add here the heat released during the condensation of steam, we get ~ 108-110%.
From the point of view of physics, such calculations are not entirely correct. When calculating the efficiency, it is necessary to take into account not the released heat, but the total energy released during the combustion of a mixture of hydrocarbons of a given composition. This will include the energy spent on converting water into a gaseous state (subsequently released during the condensation process).
It follows from this that an efficiency factor exceeding 100% is just a tricky move by marketers exploiting the imperfection of an outdated calculation formula.Nevertheless, it should be recognized that the condenser, unlike a conventional convection boiler, manages to “squeeze out” everything or almost everything from the fuel combustion process. The positives are obvious - higher efficiency and reduced consumption of fossil resources.