- Coagulation and flocculation of sewage pollution
- Coagulation: more about the process
- Flocculation: more about the wastewater treatment process
- Water purification systems for an apartment: how to choose?
- When do you need a main cleaner?
- When is the faucet nozzle enough?
- When can you get by with a jug?
- When is a sorption flow system needed?
- When is a reverse osmosis system required?
- biological methods
- Test Equipment
- What it is?
- Conditions for the process
- Types of industrial pollution
- Comparison of coagulants with improvised means
- Such different pure water
- The difference between cleaning and disinfection
- Instructions on how to do an analysis in the laboratory
- Water intake and delivery
- Price
- Deciphering the results
- How to determine which method is needed?
- How coagulants work
- In what cases is it applied?
Coagulation and flocculation of sewage pollution
In comparison with biochemical methods, physicochemical methods have a number of advantages:
- complete removal of toxic, non-oxidizable organic pollutants from waters;
- the process allows to achieve an extremely deep and stable degree of purification of waste streams;
- compactness of treatment facilities in comparison with other treatment methods;
- reduced sensitivity to changes in load parameters;
- if desired, the process can be fully automated;
- a deeper understanding of the processes of kinetics, which allows for a clear and correct selection / calculation of the necessary equipment;
- the method is in no way connected with the control of the activity of living microorganisms, which means that it requires less intervention in the wastewater treatment process;
- the use of coagulation allows the recovery of substances.
Coagulation: more about the process
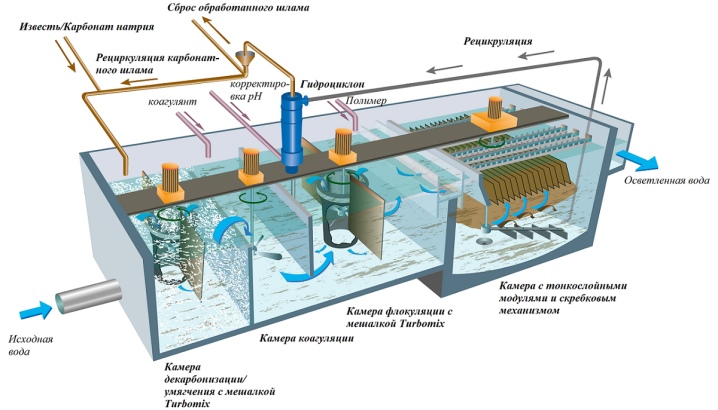
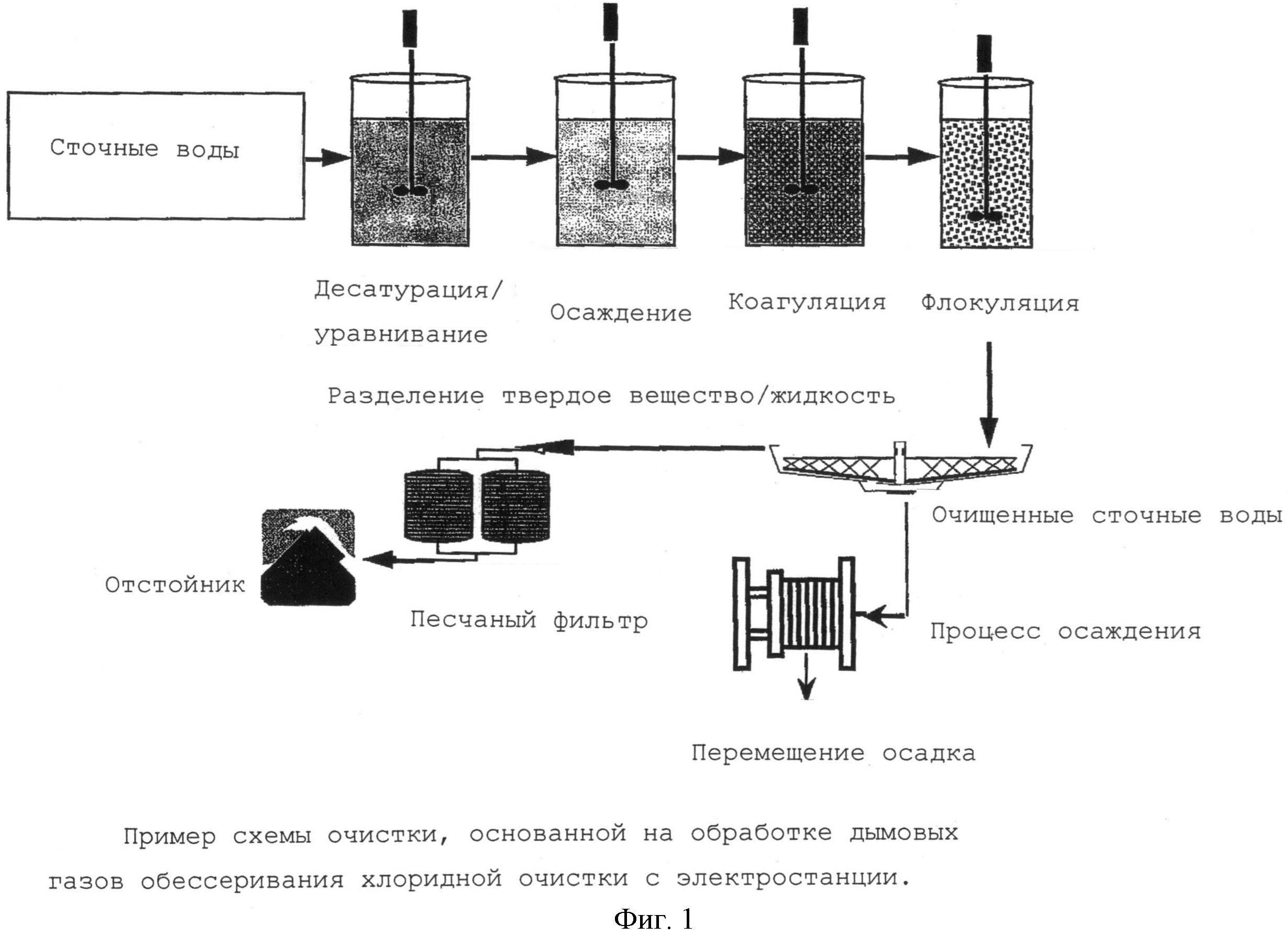
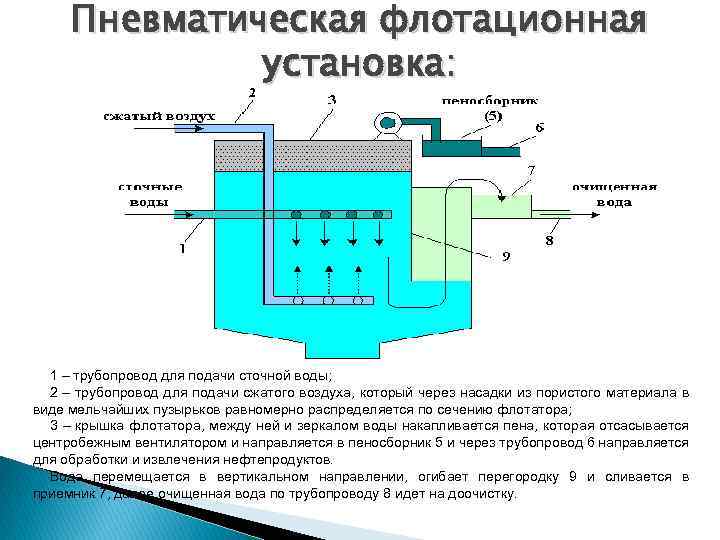
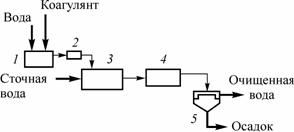
Before coagulation is carried out, a process of mechanical wastewater treatment is often applied. In this case, contaminants up to 10 microns and above are removed, but colloidal, fine particles remain. Therefore, wastewater is an aggregatively stable system, which is indicated for purification by coagulation - aggregative resistance is destroyed by the formation of larger particles that are removed mechanically or in another simple way.
The wastewater coagulation process is used to accelerate the settling process of fine particles and emulsified impurities. The method is most effective when there are particles up to 100 microns in size in the water stream, while the coagulation process sometimes occurs spontaneously, under the influence of physical interactions, to enhance which a special substance, a coagulant, is added to the wastewater stream. As a result, flakes are formed that settle under the influence of their gravity, but have the ability to seize colloidal/suspended inclusions and combine them (aggregate). Subsequently, there is a sorption of contaminants and sedimentation of flakes, followed by displacement and purification of wastewater.
As coagulants are used:
- bentonite;
- electrolytes;
- aluminum salts, soluble in water;
- iron salts or mixtures thereof;
- polyacrylamides during the hydrolysis of which flakes of metal oxide hydrates are formed.
Also, the wastewater treatment process, called coagulation, can be carried out using various clays, production wastes containing aluminum, pickling compounds, pastes, slag mixtures with a high content of silicon dioxide.
Flocculation: more about the wastewater treatment process

Flocculation is one of the types of coagulation, indicated for the formation of loose flocculent settlement structures from small particles, obtained under the influence of certain compositions. Unlike coagulation, aggregation is produced both by direct contact and by indirect interaction of molecules.
Functionally, flocculation is based on the adhesion of aggregated molecules through the formation of three-dimensional structures capable of rapid and complete separation from the liquid phase and transition to a flocculent state, due to which it is capable of settling to the bottom with subsequent removal from the tank. Thus, a wastewater treatment method is carried out.
Flocculation is performed to accelerate the capture of emulsified particles, the efficiency of sedimentation of accumulations, in addition, the method allows the use of a smaller amount of coagulants, and also reduces the time it takes for the process of flocculation.
For wastewater treatment, natural or synthesized flocculants are used:
- starch;
- dextrin;
- cellulose ethers;
- silicas;
- polyacrylamides.
Flocculation is a purification process, the speed of which depends on the intensity of the generated force field, the sequence and dose of the introduced flocculants and coagulants.
Water treatment methods are used for effluents from the chemical, petrochemical, pulp and paper industries and other industries where the flows contain a large amount of emulsified, suspended particles that are inseparable by other processing methods.
Water purification systems for an apartment: how to choose?
All well-known manufacturers offer an additional service: water analysis, after which experts select the best equipment. However, such a "gift" - an addition to the purchase - is not available to most people who live far from large cities. Therefore, to check the water, it is better to contact the city SES. Another option is a private laboratory.
When do you need a main cleaner?
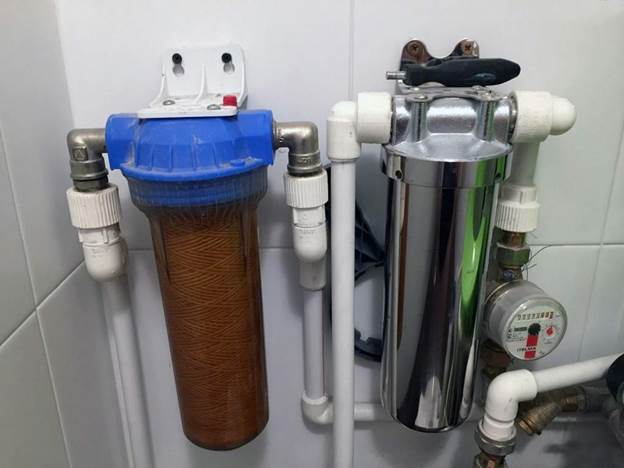

You can't do without this element if:
- there are large particles in the water that are visible without "weapons" - without glasses, a magnifying glass or a microscope;
- the liquid flowing from the tap is turbid, has a shade - brown or yellow;
- rusty plaque on the toilet, white marks on the tap, washing machine is not an emergency, but the norm;
- after thawing, sediment remains at the bottom of the container.
When is the faucet nozzle enough?

This compact replacement for a jug has some advantage over it: the modules for it have an increased resource (from 750 to 1000 liters). The cleaning quality is also good, and the filtration rate is 200-600 ml per minute.
The nozzle will be a very suitable device when:
- even for a jug it is difficult to find a place;
- it is not difficult for the owners to remove and put on the nozzle on the tap;
- they don't mind waiting for the "tap release" that is often required for other things.
When can you get by with a jug?
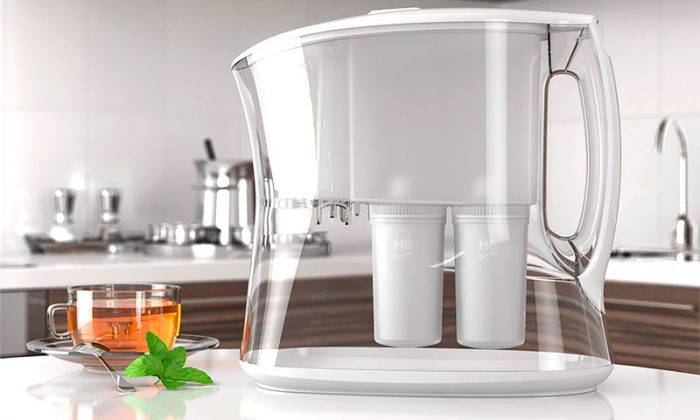

Each well-known manufacturer produces a large number of varieties of jugs and types of modules that are ideal for water purification from hardness, mechanical impurities, microorganisms, chlorine, and for mineralization.
You can get by with a jug if:
- the water in the apartment is of normal quality, and the owners just want to improve it a little;
- they are not upset by the need to regularly change cassettes every 1-3 months, in some regions - once every few weeks;
- the owners of the jars are not embarrassed that the water, which at the beginning of operation flowed in a cheerful trickle, after a certain period of time begins to flow rather slowly, or even drip in a spoon per hour;
- water consumption for drinking and cooking is small - up to 500 liters per month;
- there is no place for a multi-stage water purification system for the apartment;
- not satisfied with the "loss" of a large amount of money at once.
When is a sorption flow system needed?
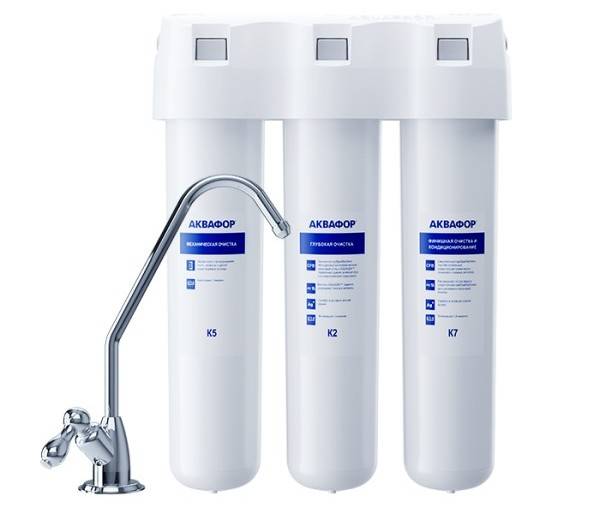

If the amount of chlorine, iron and mechanical particles in the liquid is within the normal range, and its hardness is from 4 to 8 mg-eq / l, then a standard three-stage (4-5) filter will cope with cleaning. The first module will remove large particles, after the second the liquid will be cleaned, softened and freed from iron. At the third stage, the smallest particles are removed, the water is conditioned.
This option is suitable if:
- owners are ready to buy and change modules every 3-12 months;
- moderate amount of impurities in water;
- there are at least two people in the family;
- there is space under the sink.
When is a reverse osmosis system required?
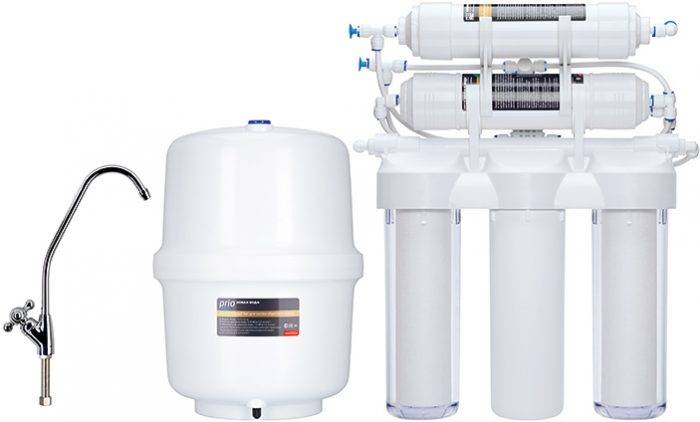

It is recommended to buy such an installation if the water hardness is from 8 to 12 meq / l. But serious requirements are imposed on the liquid supplied to the membrane.It should not contain organic impurities and an excess of other components. The limits are:
- suspensions - up to 0.56 mg/l;
- iron, chlorine - 0.1;
- manganese - 0.05;
- oxidizability is not more than 4 mgO2/l.
To achieve such a composition, preliminary cleaning with the help of sorbing, iron-removing modules is necessary.
A reverse osmosis system is ideal when:
- water is characterized by increased hardness;
- for her there is an opportunity to allocate a place under the sink;
- the pressure in the water supply is at least 3 atmospheres (otherwise you need to buy a pump);
- the owners are ready to install a main filter that frees water from large particles;
- they do not feel sorry for constantly "sacrificing" a sufficiently large amount of liquid, which will be sent straight to the sewer.
Water purification systems for an apartment are an urgent need, since it is difficult to find the area where crystal clear liquid would flow from the tap. Yes, utilities are cleaning it up, but, as always, there are not enough funds to replace obsolete equipment (corroded pipelines).
The best manufacturers of water treatment apartment devices: Aquaphor, Atoll, Barrier, Geyser, New Water. Maybe this video will help you choose a worthy candidate:
biological methods
Biological wastewater treatment is based on the introduction of special types of bacteria that contribute to the decomposition of organic substances into environmentally harmless elements.
In other words, oil and its derivatives are the basis of the diet for some microorganisms. Technologically, such processes take place in natural or artificially created biological filters.
For this use:
- biological ponds;
- filtering fields;
- irrigation fields.
Simplified, a biofilter is a tank filled with filter material (crushed stone, expanded clay, polymer chips, etc.), the surface of which is populated by active microorganisms.
Effluent passing through such a filter is cleaned of organic impurities and becomes suitable for further use.
Reference. In order to activate the purification process, artificial aeration is used - forced saturation of wastewater with oxygen in specialized facilities - aerotanks and oxygen tanks. The latter are improved versions of biological filters.
Test Equipment
 For wastewater research, modern laboratory equipment is used.
For wastewater research, modern laboratory equipment is used.
A complete set of instruments and installations that allows you to perform analyzes on the maximum number of points (for example, for compliance with SanPiN standards) has more than 30 units of laboratory equipment.
Most modern devices are capable of performing several tests (there are devices that do 7 or more procedures). Centrifuges and filtration units are used to separate solid particles and suspensions.
Chemical components are distinguished by various analyzers, instruments for spectral and photometry. The complete list of installations is too extensive, so it is inappropriate to give it.
In some laboratories, rapid analyzes are carried out, for which mini-laboratories are used (sets of instruments that can serve as field research centers). They are capable of performing full-fledged water tests, differing only in greater versatility and compactness.
What it is?

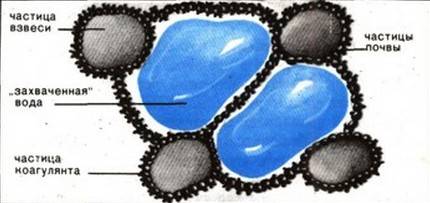
Coagulants (coagulating agents) - substances that cause coagulation, thickening, sticking, harmful particles and impurities in the liquid. In turn, coagulation of water is the process of its discoloration and clarification by chemical reagents - coagulants, which, interacting in water with hydrolates and soluble impurities, activate the processes of precipitation (precipitation).
In simple terms, when coagulants are added to water, the process of enlargement starts. Impurities, particles floating in the water and creating turbidity, begin to combine into large, visible accumulations.
This happens until they reach the size of flakes to settle. Suspended particles in a liquid medium can be so microscopic that any, even the most expensive multi-level filtration system, cannot cope with them. In some cases, it is necessary to increase the cost of purification, but this is not beneficial to anyone. For example, a person in the country has a swimming pool. From time to time, the water in it must be cleaned. The owner of the facility does not want to spend money on special expensive equipment, but the standard filter system cannot cope with pollution. Representatives of modern chemistry - coagulants - can help a simple budget filter.
Consider in detail the principle of their action:
-
a reagent is introduced into water contaminated with small colloidal particles that pass through the filter;
- particle properties begin to change;
- their charge is lost, with the help of which they could repel each other in a liquid under the action of electrostatic interaction forces;
- the suspension begins to stick together, forming large lumps;
- the action of attractive forces is activated - the particles begin to approach each other.
Important! Reagents do not change the chemical composition of water. They are needed in order to make the particles large for retention by the filter.
Most often, the presented special substances are used for cleansing:
- drinking water;
- industrial and domestic waste water;
- water attractions, swimming pools.
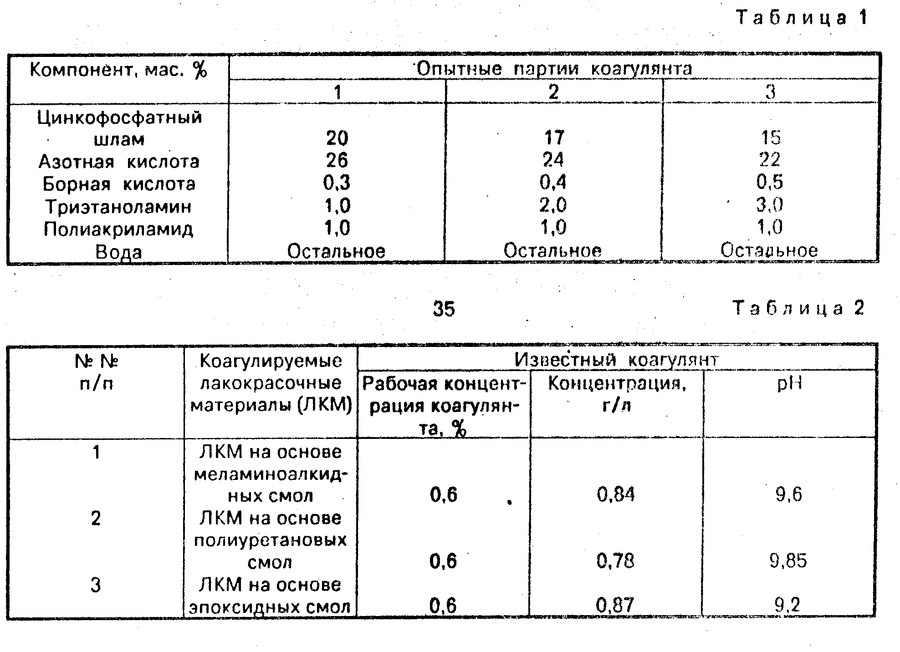
Water intended for further consumption, before and after treatment with coagulants, must be submitted for advanced chemical analysis. This will help to accurately calculate the dose of the substance.
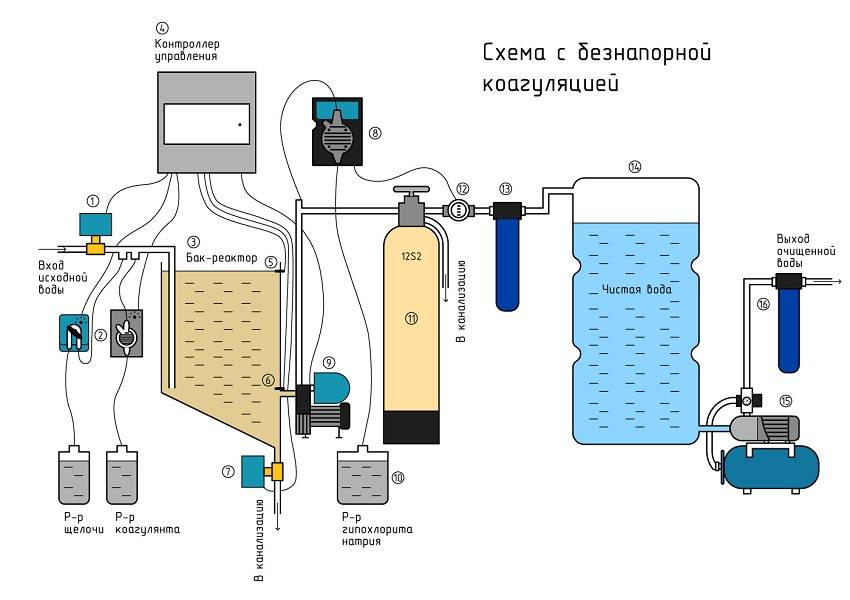
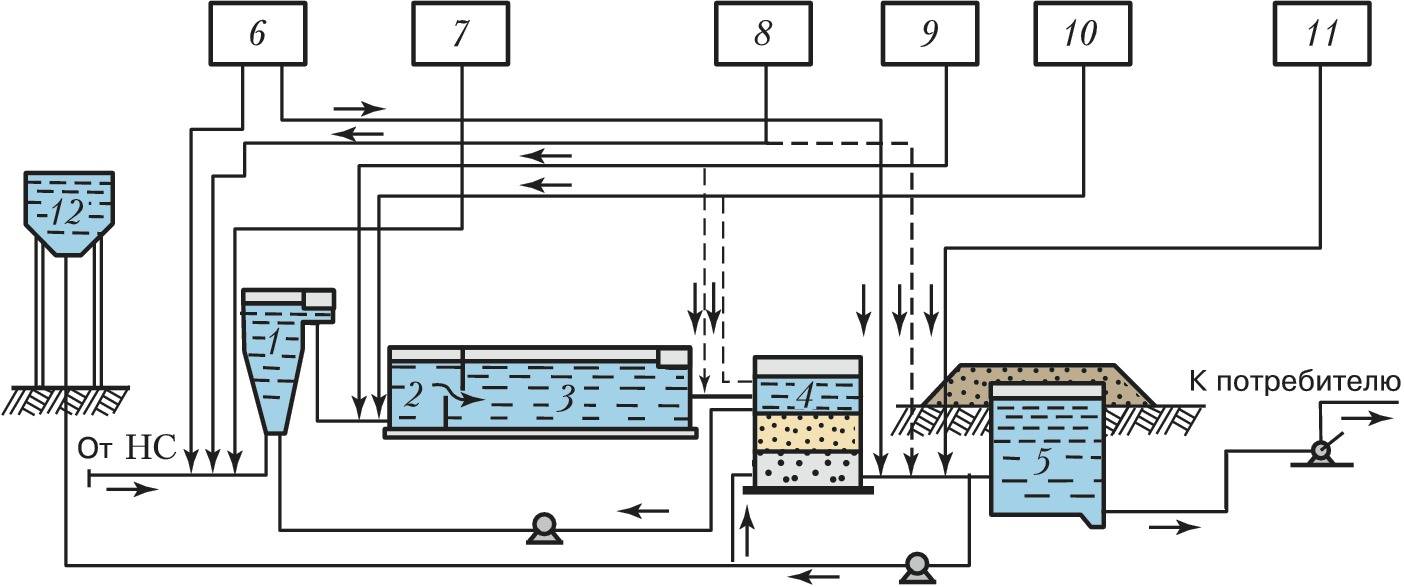
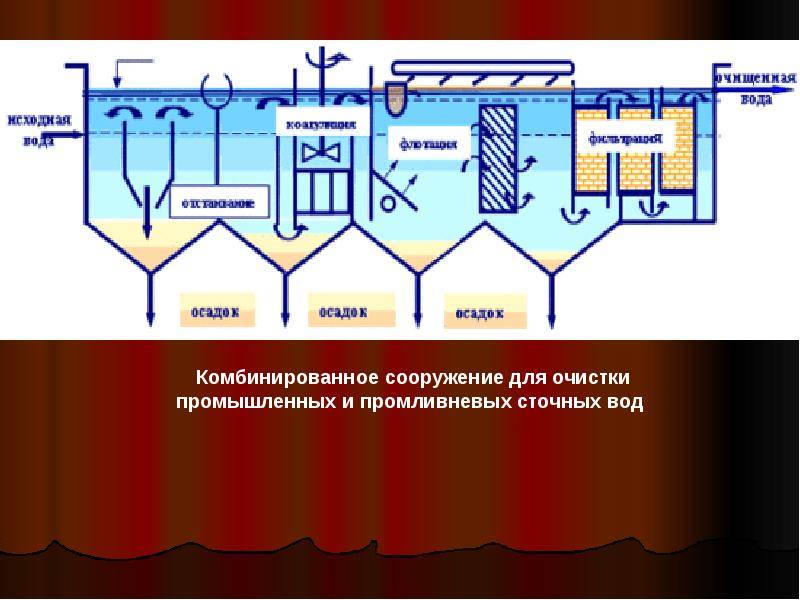
Conditions for the process
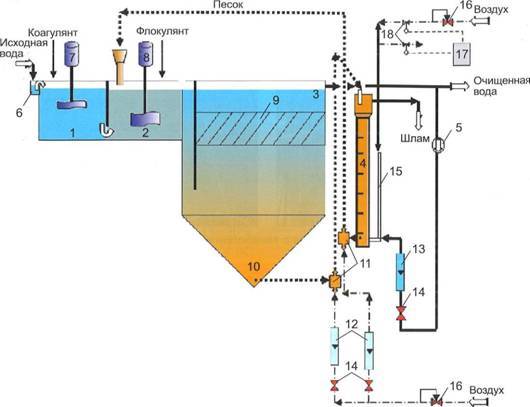
The maximum efficiency of wastewater treatment is achieved through an integrated approach to solving the problem. Therefore, when arranging autonomous treatment facilities, coagulation is used in combination with mechanical and biological treatment.
For this, structures are erected, consisting of vertical settling tanks, separated by partitions. Due to this, wastewater undergoes multi-stage treatment. First, they settle, then they are purified by processing by bacteria, after which they enter the chamber, where they enter the coagulation process and are filtered at the final stage.

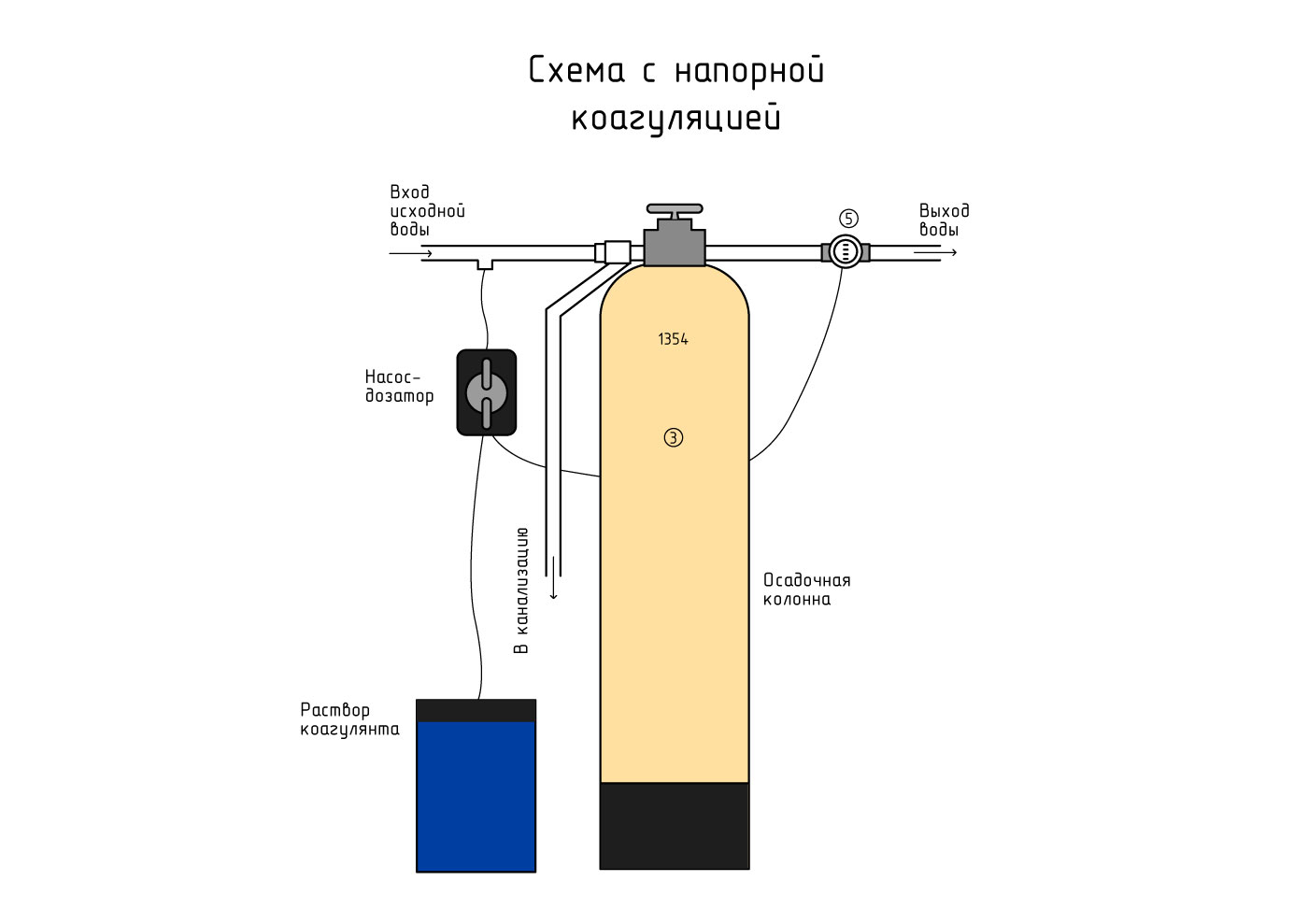
The coagulant can be located in a separate plastic container suspended in the toilet bowl, due to which, with each flush, particles of the reagent enter the system along with wastewater
It is better to entrust the installation of specialized equipment, the calculation of the approximate dose of consumables and the initial control at all stages of the wastewater treatment process to professionals.
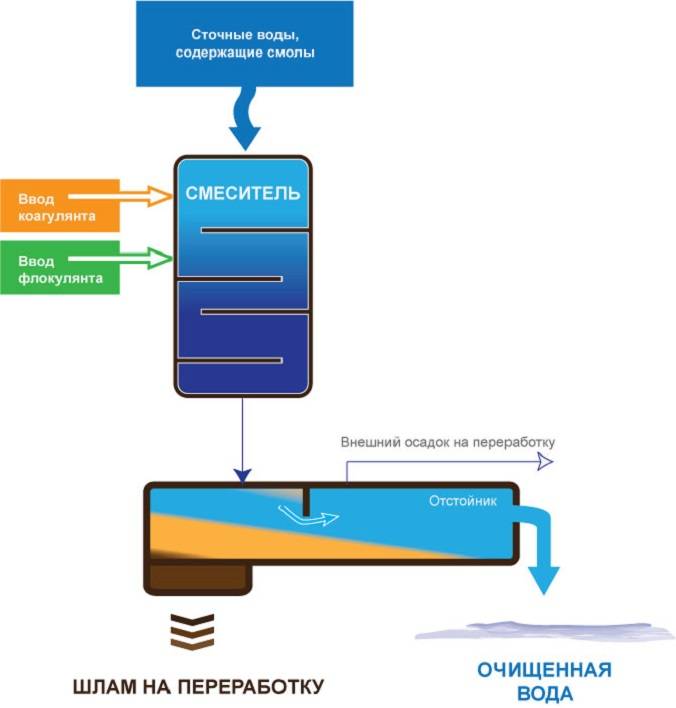
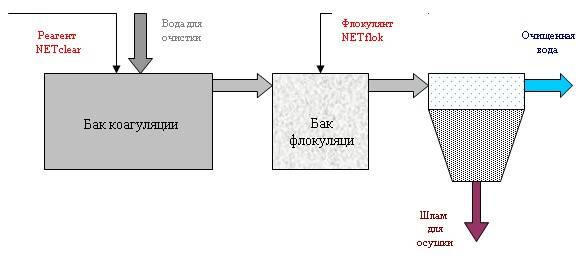
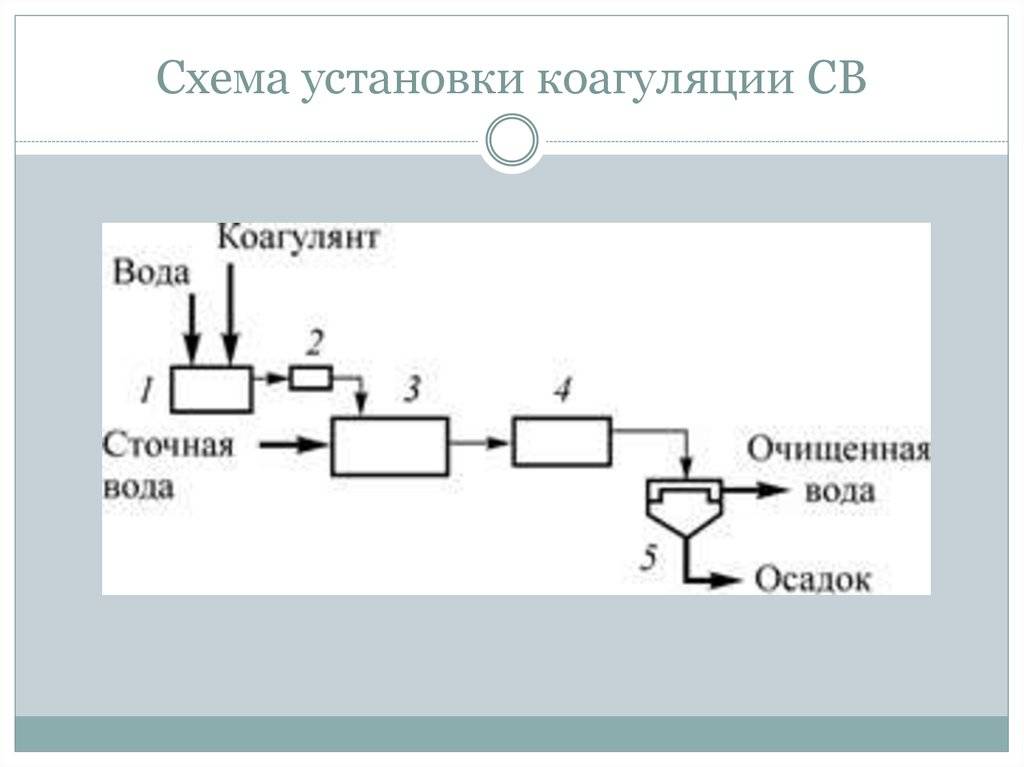
The coagulation scheme includes three main steps:
- Introduction of a coagulant into a contaminated liquid.
- Creation of conditions for maximum interaction of the active reagent with impurities.
- Sedimentation followed by filtration of settled particles.
A necessary condition for the occurrence of coagulation is the equality of particles with opposite charges
Therefore, in order to ensure that the desired result is achieved, obtaining the greatest reduction in turbidity of the effluents, it is so important to observe the concentration of the reagent used.
When using coagulants for wastewater treatment, it should be borne in mind that these substances work only at positive temperatures.
The working range of the reagents varies from 10 to 40°C, and if the temperature exceeds this indicator, the reaction starts to proceed much more slowly.
Therefore, it is so important to ensure the stability of the heating of the treated water. To accelerate the coagulation process, substances capable of forming colloidal dispersion systems - flocculants can be added to the water composition.
For this purpose, most often used: starch, polyacrylamide, activated silicate. They will be adsorbed on the coagulant flakes, turning them into stronger and larger aggregates.
To speed up the coagulation process, substances capable of forming colloidal dispersion systems - flocculants - can be added to the water composition. For this purpose, most often used: starch, polyacrylamide, activated silicate. They will be adsorbed on the coagulant flakes, turning them into stronger and larger aggregates.
The flocculant is introduced into the zone of the contact medium 1-3 minutes after the introduction of the coagulant. By this time, the processes of formation of microflakes and the subsequent sorption of precipitating substances are completed.
The amount of sediment deposited in the contact tanks depends on the type of reagent used and the degree of pre-treatment of the effluent to be treated.
On average, after mechanical cleaning, the volume of sediment per person per day is about 0.08 liters, after passing through biofilters - 0.05 liters, and after treatment in the aeration tank - 0.03 liters. It only needs to be removed in time as the tank is full.
Types of industrial pollution
An important characteristic of impurities entering the water is solubility:
- Some of them form true solutions, in which the particle sizes of foreign substances do not exceed 1 nm.
- Others form colloidal systems with larger grains. Their diameter can reach half a million nanometers.
- Still others do not dissolve in water at all, they form heterogeneous systems with impurities in suspension.
The condition of the water flow is of fundamental importance for choosing the right approaches to clean it.
Interesting. For wastewater with a large amount of insoluble contaminants, mechanical separation is the decisive step.
The composition of impurities is also fundamentally different. Foreign substances have the following character:
- inorganic (mineral components);
- organic (carbon-containing compounds);
- biological (microorganisms, viruses, some fungi).
At enterprises for the production of leather, wool, vitamins, and some drugs, biological pollutants prevail in the effluents; in mining complexes - mineral components.
The degree of aggressiveness of effluents varies from strong (concentrated acids and basic substances) to zero.
Comparison of coagulants with improvised means
In the absence of filters or their weak power, the problem of flowering water in the pool appears. The lack of necessary reagents forces the use of improvised substances. The most popular are hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate and a solution of brilliant green in alcohol. They have a disinfecting effect. The effect of their use lasts only temporarily and leads to consequences that need to be considered separately.
When hydrogen peroxide is added to the aquatic environment, the substance completely dissolves in it, decomposing into oxygen and water. The disinfecting effect will last until the peroxide is completely decomposed. During the active period, oxygen bubbles are released, and if a filter is installed in the pool, they will interfere with the cleaning process
After its application, flakes of dirty foam appear on the water surface. They are removed mechanically. Even after two days, the process of oxygen release will continue, which gives uncomfortable tactile sensations. When water with dissolved peroxide comes into contact with the skin, a slight tingling will begin.
This aqueous solution should not be swallowed or inhaled. This causes irritation of the mucous membranes. Peroxide allows water to cool more slowly, as it increases its density. However, peroxide cannot replace a full cleaning with a coagulant.
Potassium permanganate diluted in water has a disinfecting property until its color changes from pale pink to light brown or green.
It depends on the aggressiveness of the alkaline environment. After complete decomposition, the water takes on an unpresentable appearance, it will need to be replaced or cleaned with a coagulant
The composition of brilliant green includes alcohol and triphenylmethane dye.There is no exact data on how this coloring pigment affects a person when it enters the body. With prolonged contact of water, in which brilliant green is dissolved, with the walls of the pool, the material changes color.
Porous plastic and tiles acquire a greenish tint. Alcohol evaporates over time from the surface, and only paint remains in the water
These reagents cannot serve as a full-fledged replacement for coagulants, since they do not bind a fine suspension. They can only disinfect water for a short time, while dangerous heavy metals and substances invisible to the eye do not disappear. They remain in the container.
Such different pure water
- plumbing that has undergone standard multiple coarse cleaning and filtration in special sedimentation tanks;
- household, pre-softened to prevent the formation of scale in heating appliances, used for washing and washing;
- drinking, used exclusively for ingestion and cooking.
The ordinary water of the apartment is provided by the city water supply system. For self-treatment at home, various filters, structuring systems and some minerals recognized as useful (for example, shungite) are used. In addition, there are coagulants that disinfect water for home use.
The difference between cleaning and disinfection
Cleaning removes mechanical and chemical impurities.
Important. The purpose of disinfection is to remove living microorganisms that harm a person. Harmful microorganisms include pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria, their spores, viruses, fungi, helminths and their eggs.
Harmful microorganisms include pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria, their spores, viruses, fungi, helminths and their eggs.
Disinfection methods:
- Chemical: water treatment with ozone, chlorine dioxide, sodium hypochlorite, polymer antiseptics. These substances kill pathogens or make them unable to reproduce;
- Physical: water treatment with ultraviolet rays, ultrasound;
- Complex: a combination of chemical and physical methods.
Instructions on how to do an analysis in the laboratory
For the necessary research, it is better to contact large companies that have their own laboratories. In advance, they find out the list of proposed tests and conclude an agreement that specifies:
- the type of document to be issued;
- all tests carried out;
- cost of work;
- deadlines.
Water intake and delivery
In most cases, a laboratory specialist takes a sample for examination. Do it yourself like this:
- Prepare a container with a capacity of 1.5–2 liters, preferably a special one; a bottle of sweet, carbonated and alcoholic drinks will not work.
- If a sample is taken from a tap, the water should be allowed to drain for 10 minutes.
- Rinse the container from the source of the fence and, under low pressure, fill it to the brim, holding it at a distance of 1–2 cm from the tap.
- Close tightly with a lid so that there is no room for air.
The container is placed in a dark bag to protect it from sunlight during transportation, and delivered to the laboratory within 2-3 hours. Radiological analysis requires 10 liters of water.
Price
Average research prices:
- microbiological - 1–1.8 thousand rubles;
- standard - 3-4 thousand rubles;
- extended - up to 4.5-6 thousand rubles;
- full - 7-9 thousand rubles.
Services for sampling by a specialist and conservation (if necessary) will cost 1.5–2 thousand rubles, and the provision of consumables and instructions for preserving samples for testing for hydrogen sulfide will cost 0.4–0.6 thousand rubles. Radiological costs 10.5–11 thousand rubles. and is done longer than others - up to 2 weeks.
Deciphering the results
The protocol states:
- The number of identified substances and their maximum allowable concentration (MPC), specified in the regulatory documents (SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01, WHO recommendations).
- Hazard classes of elements (1K - extremely dangerous, 2K - highly dangerous; 3K - dangerous, 4K - moderately dangerous).
- Toxicity. Sanitary and toxicological indicators are designated “s-t”, organoleptic - depending on the ability of the element to change the smell, color, taste of water, cause foaming or opalescence, respectively, the first letters of the words that define these values (“zap”, “okr”, “privk” etc.).
Focusing on the results of the examination, they choose equipment to improve water quality.
 To remove mechanical contaminants, a mechanical cleaning filter is needed, a housing filter with a replaceable cartridge, and in case of high concentration, a column-type filter with a control valve and automatic flushing.
To remove mechanical contaminants, a mechanical cleaning filter is needed, a housing filter with a replaceable cartridge, and in case of high concentration, a column-type filter with a control valve and automatic flushing.
Ultraviolet immersion sterilizers (UV lamps) protect against viruses and bacteria, which operate in short wave mode and destroy microorganisms at the molecular level without affecting the natural properties of water. For a country house, it is enough to have a sterilizer with a capacity of 0.5–2 m³ / h.
The lamps have durable PTFE sockets.Wells serving cottage settlements, sanatoriums and enterprises require industrial sterilizers with a capacity of 8–60 m³/h.
The stationary filter removes chlorine, heavy metals, iron, oil products, mechanical particles and other undesirable impurities, and reduces hardness. Water is saturated with useful calcium in the form of aragonite. A free-standing faucet (keyboard or valve) is installed on the kitchen sink for clean liquid.
To introduce the necessary components and maintain their constant concentration, a dosing complex is used, which consists of a dosing pump, a pulse counter, suction and injection valves, and a container for dosing the reagent.

To remove iron compounds, non-reagent filters are installed, based on the principle of oxidation of iron with oxygen from a dissolved form to a solid state, followed by separation of the resulting suspension.
Carbon filters will help reduce the content of hydrogen sulfide in the well and well, cleaning occurs by adsorption.
How to determine which method is needed?
The choice of analysis methodology is determined by the origin of wastewater, the characteristics of the source:
- Domestic wastewater has a large amount of organic matter and surfactants that enter the drain as a result of domestic water procedures. They need a general determination of the composition of water, microbiological and chemical analysis.
- Industrial effluents are saturated with chemical solutions and carry solid mechanical particles. This requires physicochemical analysis using appropriate techniques.
- Stormwater runoff is characterized by the presence of oil products, salts of heavy metals, or emissions from nearby enterprises obtained as part of washouts from the upper layers of the soil.Physico-chemical, radiological methods are used here.
How coagulants work
Coagulation is a method of water purification by cohesion of dispersed pollutants for subsequent removal by a mechanical method, filtration. The association of polluting particles occurs due to the introduction of coagulating reagents, creating conditions for the simplest removal of associated pollutants from the treated water.
The term "coagulatio" in Latin means "thickening" or "clotting". The coagulants themselves are substances capable of creating insoluble and slightly soluble compounds due to a chemical reaction, which are easier and easier to remove from the composition of water than dispersed components.
Image gallery
Photo from
Coagulants belong to the group of liquid filters - substances that can purify water during a chemical reaction.
When coagulans are added to the dirty water to be treated, impurities of organic and inorganic origin are neutralized by the formation of a gel-like precipitate and precipitation to the bottom.
The introduction of coagulants into septic systems allows accelerating the process of sedimentation of impurities, increases the degree of water purification, so that effluents can be discharged without the use of underground post-treatment systems
Active use of coagulants was found at the enterprises of the chemical and food industries, where their introduction into the technological chain significantly reduces the cost of waste disposal
In addition to introducing independent sewage treatment plants, coagulants in everyday life are used to purify water in decorative ponds and fountains.
Water with added coagulant does not bloom under constant lighting, while it does not harm the environment and creates a threat to the ecological environment
Water treatment with a coagulant in the pool guarantees the possibility of discharging water to the relief without the use of a septic tank. The main thing is to remove the sediment in time
Coagulants can be used for the preparation of drinking water and water for filling aquariums, because. they neutralize only harmful substances, do not affect the beneficial composition
Substances for chemical filtration
The principle of operation of coagulants for water treatment
Use in independent treatment plants
Use in industrial plants
Scope of application in the domestic environment
Water bloom warning
Preparation of solution for the pool
Water treatment for aquariums
The principle of operation of substances is based on the fact that their molecular form has a positive charge, while most pollutants are negative. The presence of two negative charges in the structure of the atoms of dirty particles does not allow them to combine together. For this reason, dirty water always becomes cloudy.
At the moment a small portion of the coagulant is introduced into the liquid, the substance begins to pull the suspensions present in it towards itself. As a result: as the intensity of the scattered light increases, the liquid becomes more turbid for a short period of time. After all, one molecule of coagulant can easily attract several molecules of dirt to itself.
Coagulants provoke the formation of stable bonds between small particles of pollution and microbes present in the water.
The attracted dirt molecules begin to react with the coagulant, as a result of which they combine into large complex chemical compounds. Poorly soluble highly porous substances gradually settle to the bottom in the form of a white precipitate.
The task of the owner is only to remove the sediment in time, using any of the types of filtration available to him.
Molecules attracted to each other form large particles, which, due to their increased weight, settle and are then removed by filtration
The effectiveness of the drug can be judged by the formation of sediment at the bottom in the form of white flocculent formations - floccules. Due to this, the term "flocculation" is often used as a synonym for the concept of "coagulation".
The resulting flakes, the size of which can reach from 0.5 to 3.0 mm, have a large surface with a high sorption of precipitated substances
In what cases is it applied?
Quite often, coagulation is carried out for the purpose of wastewater treatment. There it helps to cope with dispersed and emulsified suspensions. Particles that are homogeneous and differ in chemical composition, according to the features of the physical plan, can stick together. To make coagulation more efficient, a lot of water:
- stir;
- warm up;
- exposed to electromagnetic fields.

In the vast majority of cases, mixing is done. This is quite an effective and, moreover, economical way to stimulate the process. How fast the adhesion will go depends on:
- particle type;
- their internal structure;
- degree of concentration;
- electrical characteristics;
- the variety of impurities present;
- pH indicator.
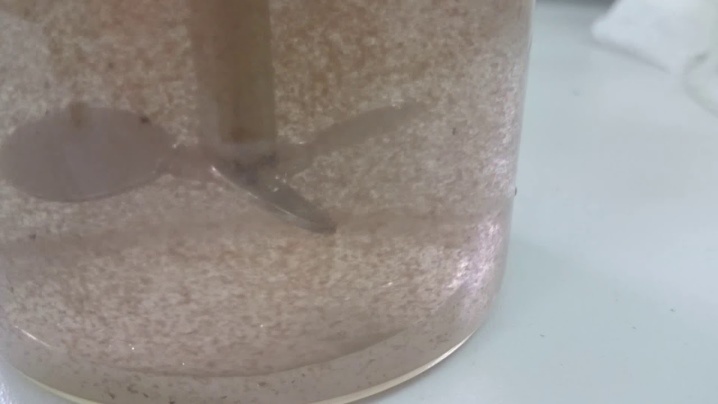

Coagulation is used to remove hazardous substances from wastewater discharged:
- the food industry;
- pulp and paper mills;
- production of medicines and their precursors;
- the chemical industry;
- the textile industry.

In some cases, the purpose of this procedure is the purification of drinking water from iron. It is curious that sulfate and chloride of iron itself help in this situation. Compounds of aluminum and sodium can also be used. However, iron-containing coagulants are even more effective and work faster. For the most complete result in a short time, alkalis can be additionally used when processing with precipitating substances.
At waterworks in Russia, aluminum sulfate crystalline hydrate is most often introduced into natural waters. It provokes the same processes that take place under the action of glandular compounds.