- The use of reagents: pros and cons
- How coagulation works
- Top 3 manufacturers of flocculation products
- Besfloc (Besflok)
- Zetag (Zetag)
- Praestol (Praestol)
- The main types of coagulants
- organic natural substances
- Synthetic coagulating compounds
- Top 3 manufacturers of flocculation agents
- Besfloc (Besflok)
- Zetag (Zetag)
- Praestol (Praestol)
- The use of reagents: pros and cons
- Norms for draining into the sewer
- How coagulants work
- Elimination of pollution containing oil by chemical methods
- Such different pure water
- Aluminum sulfate technical purified modified
- Advantages:
- Chemical processing
- pH control
- Algicides
- Disinfection
- coagulants
- Requirements and regulations
The use of reagents: pros and cons
The effectiveness of modern equipment for the neutralization of impurities in wastewater is not able to reach the maximum level without the use of reagents.
Modern coagulants can significantly increase the intensity and quality of the wastewater treatment process. The high cost of reagents pays off with a number of advantages that they have.
Among the indisputable advantages of using synthetic coagulants, it is worth highlighting:
- efficiency;
- affordable cost;
- high quality cleaning;
- versatility of application.
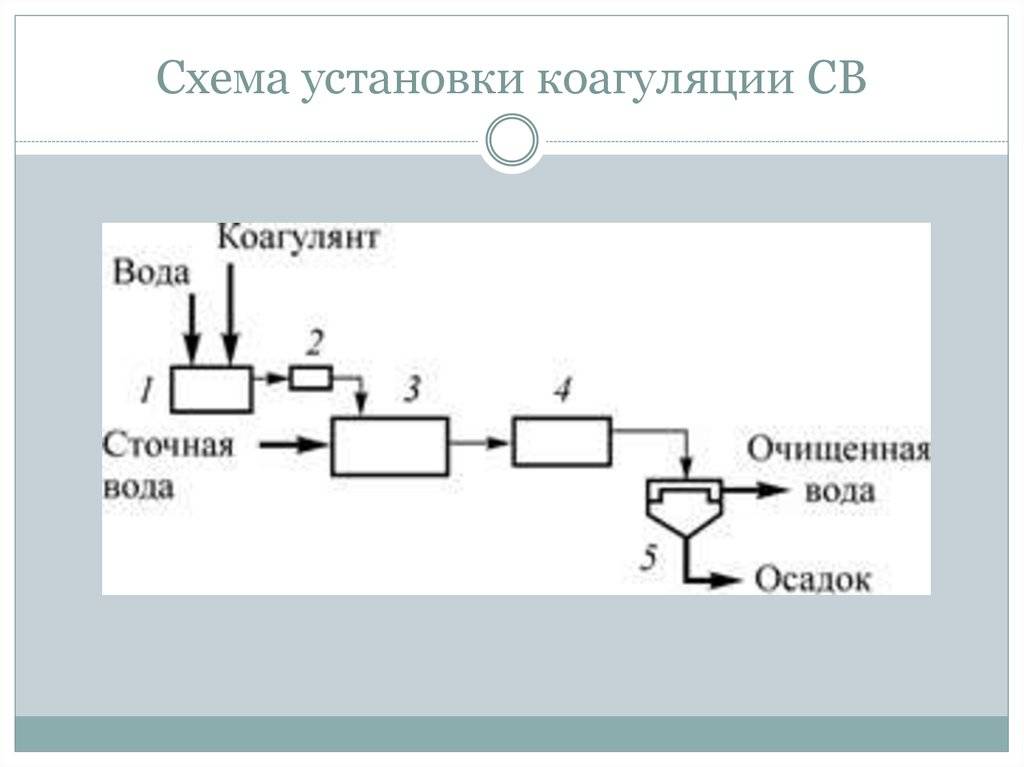
Wastewater is a stable aggressive system. And to destroy it, forming large particles in order to subsequently remove them by filtration, coagulation helps.
The use of reagents gives good results in removing suspended and colloidal particles from wastewater.

In fact, the particles of the coagulating phase, formed under the action of coagulants, are both the center of flocculation and the weighting agent.
But the precipitation method with the use of reagents is not without drawbacks. These should include:
- the need for strict adherence to the dosage;
- the formation of a large volume of secondary waste that needs additional filtration;
- the complexity of establishing the process on their own.
On an industrial scale, coagulation processes are used everywhere, they are put on stream. To establish a system at home, you will have to purchase special installations, the cost of which is quite high.
Most owners deal with this issue by using individual household-type coagulants, which are sold in small containers.
The active ingredients are simply added to the liquid, and then the precipitate that has fallen at the bottom is filtered out; but this process is quite laborious and therefore a lot of time is spent on its implementation
In some cases, coagulation can be carried out directly in a mechanical filtration system. To do this, the reagent is introduced into the section of the pipeline with the liquid to be processed before the place of its supply to the filter. And in this case, already foreign particles, “transformed” into flakes, enter the filtration system.
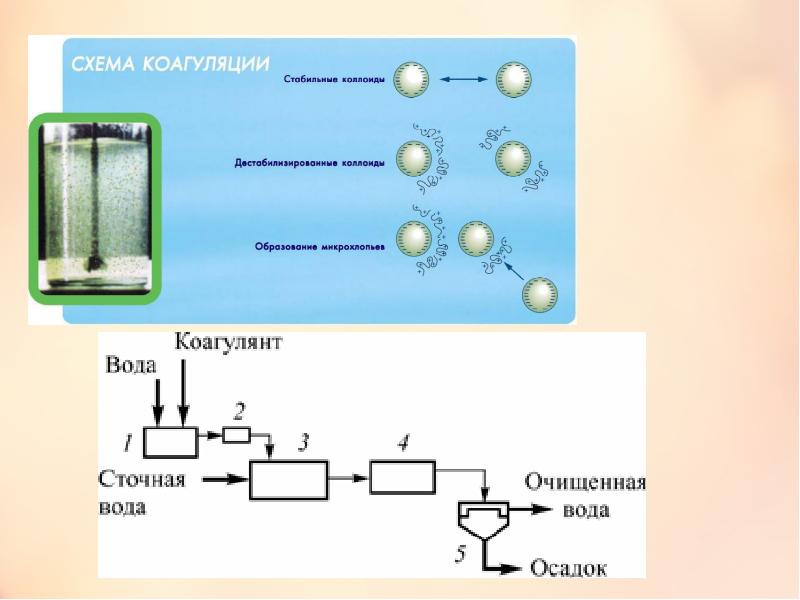
How coagulation works
Most water facilities have filters for water purification in the pool, which effectively remove various mechanical impurities of a certain fraction from the liquid medium. Small particles that the filtration system cannot catch gradually accumulate in the tank, the water becomes cloudy, then greenish and finally musty. Swimming in such a pool is dangerous for human health.
To restore purity and transparency to water, coagulants are used. These chemicals combine the smallest suspensions of heavy metals, biological grains, organic pollutants into a gel-like mass. The "jelly" then turns into flakes of debris that must be removed from the bottom and surface of the tank.
If the design is equipped with an automatic water purification system in the pool, then the flakes are retained by the filters. Grids of devices after such cleaning must be removed and washed under a water jet. As a result, the composition of the water in the pool is normalized, and you can again swim in it without fear.
If the pool is small and not equipped with an automatic filtration system, then the upper film is removed with an ordinary net. To clean the bottom, you will have to use a special water vacuum cleaner.
Top 3 manufacturers of flocculation agents
The leading companies involved in the development of equipment and technologies for the production of modern flocculants are France, Japan, Great Britain, South Korea, Finland, USA and Germany. There are 3 main leaders on the Russian market.
Besfloc (Besflok)

Release form: emulsions, granules, solutions and powdery substances.
They are mainly used as post-treatment after the use of coagulants.
- It has a high molecular weight, which contributes to the transformation of small particles into bulky flakes.
- Low consumption: 0.01-0.5 mg/l.
- It is applied in the mining, petrochemical industries, textile and paper and cellulose areas. It is often used to clean municipal drains.
- Due to the unique composition, it was possible to reduce the preliminary consumption of coagulants.
- Do not harm human health.
- Pass all stages of laboratory testing.
Zetag (Zetag)
Flocculant Zetag from the Swiss company Ciba Specialty Chemicals. It is used to accelerate the processes of water purification from organic compounds and solid suspensions.
Promotes the precipitation of the solid phase into a large-fraction precipitate. Used to prepare water from reservoirs for use in public water supply.
- The reagent is introduced with constant stirring, otherwise the reaction will not be complete.
- Minimization of turbulence is necessary, otherwise the probability of destruction of previously formed flakes is high.
- Increases the settling rate of polluting particles.
- Consumption is from 2 to 10 g/l.
Praestol (Praestol)
Flocculant created by joint technology of Russia and Germany. It appeared on the market in 1998 and quickly occupied its niche - the public utilities.
It is used for purification and disinfection of drinking water. It is also found in the petrochemical and chemical industries.
- Accelerates the cleaning process, promotes sediment compaction.
- Reduces the electrical activity of water molecules, which contributes to a more efficient association of pollutant particles.
- Flocculant Praestol is certified in Russia and complies with all hygienic norms and rules. It was recommended for use in the field of drinking water supply.
- Available as acrylamide-based granules and diluted in water to obtain a concentration of 0.1%. The manufacturer recommends for better storage to make a concentrated solution of 0.5%, and if necessary, bring it to the working composition.
- The solution is prepared at a water temperature of 15-20 degrees, settled for 60 minutes and only then is it ready for use.
The disadvantage of powdered and helium flocculants is the difficulty of their dilution. This requires appropriate equipment that can prepare a solution of the required concentration. Therefore, aqueous solutions and emulsions are the right choice.
The main types of coagulants
There are many types of coagulants. We will not list their formulas in detail in the article. Let us consider only two main groups, which, depending on the feedstock, are divided into organic and inorganic.
One category of coagulants is capable of deferrization of water and removing aluminum salts from it, the other is capable of raising or lowering the acidic pH, some reagents have a complex effect
Today, many domestic and foreign companies are engaged in the production of coagulants. The new generation reagents produced by them differ from the coagulants produced back in the Soviet Union by improved technical characteristics.
organic natural substances
They are specially designed reagents that, by accelerating the adhesion of aggressively unstable particles present in water, facilitate the processes associated with their separation and sedimentation. The organics help to encourage contaminants to combine into dense suspensions and emulsions, making it easier to remove them from the water.
High-molecular substances fight well with chlorine and effectively eliminate unpleasant "aromas" in the liquid, for example: the smell of hydrogen sulfide often present in a ferruginous liquid
When interacting with pollution molecules, organic coagulants significantly decrease in size. Upon completion of the reaction, they precipitate as a small amount of precipitate.
By minimizing the volume of sediment accumulated at the bottom of the tank, it is much easier and faster to filter. At the same time, the reduced amount of sediment in no way affects the quality of cleaning.
Due to the limited resource base, natural reagents have not found wide application in wastewater treatment on an industrial scale. But for domestic purposes they are often used.
Synthetic coagulating compounds
These types of reagents are based on mineral and synthetic elements. The polymers contribute to the formation of a high cationic charge, thereby stimulating the rapid appearance of flakes. They perfectly interact with water, having a complex effect on it: softening its structure, as well as getting rid of coarse impurities and salts.
The most widespread salts of polyvalent metals, created on the basis of iron or aluminum. Iron is used for rough cleaning.
Flocculants - secondary coagulants that turn suspensions and emulsions into flakes, are used in conjunction with primary coagulants. The tandem is able to clean both small portions of household waste and large volumes created by industrial enterprises
Among the iron compositions, the most popular are:
- ferric chloride - hygroscopic crystals with a dark metallic luster, perfectly eliminate large particles of pollution and easily remove the smell of hydrogen sulfide;
- ferrous sulfate - a crystalline hygroscopic product is highly soluble in water and is effective in sewage treatment.
Due to the low level of viscosity at a low molecular weight, such reagents are highly soluble in any type of liquid being treated.
Of the coagulants created on the basis of aluminum, the most widely used are:
- aluminum oxychloride (OXA) - used to treat water with a high content of organic natural substances;
- aluminum hydroxochlorosulfate (GSHA) - perfectly copes with natural sewage deposits;
- aluminum sulfate - a crude technical product in the form of gray-green pieces is used to purify drinking water.
In previous years, polymers were used only as an additive to inorganic coagulants, using them as stimulants that accelerate the formation of flocculation. Today, these reagents are increasingly used as the main ones, replacing inorganic ones with them.
If we compare organic and synthetic substances, then the former win in that they act much faster. In addition, they are able to function in almost any alkaline environment and do not interact with chlorine.
For the adsorption of salts, heavy metal ions and other suspensions dissolved in water, a portion of an organic reagent will be required several times less than a synthetic analogue (+)
Organic active compounds also benefit in that they do not change the pH in the water.This allows them to be used for water purification, where there are plankton colonies, algae and large microorganisms grow.
Top 3 manufacturers of flocculation agents
The leading companies involved in the development of equipment and technologies for the production of modern flocculants are France, Japan, Great Britain, South Korea, Finland, USA and Germany. There are 3 main leaders on the Russian market.
Besfloc (Besflok)
 Flocculant made in South Korea by KolonLifeScience, Inc. They produce a full range of reagents and are widely popular around the world.
Flocculant made in South Korea by KolonLifeScience, Inc. They produce a full range of reagents and are widely popular around the world.
Release form: emulsions, granules, solutions and powdery substances.
They are mainly used as post-treatment after the use of coagulants.
- It has a high molecular weight, which contributes to the transformation of small particles into bulky flakes.
- Low consumption: 0.01-0.5 mg/l.
- It is applied in the mining, petrochemical industries, textile and paper and cellulose areas. It is often used to clean municipal drains.
- Due to the unique composition, it was possible to reduce the preliminary consumption of coagulants.
- Do not harm human health.
- Pass all stages of laboratory testing.
Zetag (Zetag)
Flocculant Zetag from the Swiss company Ciba Specialty Chemicals. It is used to accelerate the processes of water purification from organic compounds and solid suspensions.
Promotes the precipitation of the solid phase into a large-fraction precipitate. Used to prepare water from reservoirs for use in public water supply.
- The reagent is introduced with constant stirring, otherwise the reaction will not be complete.
- Minimization of turbulence is necessary, otherwise the probability of destruction of previously formed flakes is high.
- Increases the settling rate of polluting particles.
- Consumption is from 2 to 10 g/l.
Praestol (Praestol)
Flocculant created by joint technology of Russia and Germany. It appeared on the market in 1998 and quickly occupied its niche - the public utilities.
It is used for purification and disinfection of drinking water. It is also found in the petrochemical and chemical industries.
- Accelerates the cleaning process, promotes sediment compaction.
- Reduces the electrical activity of water molecules, which contributes to a more efficient association of pollutant particles.
- Flocculant Praestol is certified in Russia and complies with all hygienic norms and rules. It was recommended for use in the field of drinking water supply.
- Available as acrylamide-based granules and diluted in water to obtain a concentration of 0.1%. The manufacturer recommends for better storage to make a concentrated solution of 0.5%, and if necessary, bring it to the working composition.
- The solution is prepared at a water temperature of 15-20 degrees, settled for 60 minutes and only then is it ready for use.
The disadvantage of powdered and helium flocculants is the difficulty of their dilution. This requires appropriate equipment that can prepare a solution of the required concentration. Therefore, aqueous solutions and emulsions are the right choice.
The use of reagents: pros and cons
The effectiveness of modern equipment for the neutralization of impurities in wastewater is not able to reach the maximum level without the use of reagents.
Modern coagulants can significantly increase the intensity and quality of the wastewater treatment process. The high cost of reagents pays off with a number of advantages that they have.
Among the indisputable advantages of using synthetic coagulants, it is worth highlighting:
- efficiency;
- affordable cost;
- high quality cleaning;
- versatility of application.
Wastewater is a stable aggressive system. And to destroy it, forming large particles in order to subsequently remove them by filtration, coagulation helps.
The use of reagents gives good results in removing suspended and colloidal particles from wastewater.

In fact, the particles of the coagulating phase, formed under the action of coagulants, are both the center of flocculation and the weighting agent.
But the precipitation method with the use of reagents is not without drawbacks. These should include:
- the need for strict adherence to the dosage;
- the formation of a large volume of secondary waste that needs additional filtration;
- the complexity of establishing the process on their own.
On an industrial scale, coagulation processes are used everywhere, they are put on stream. To establish a system at home, you will have to purchase special installations, the cost of which is quite high.
Most owners deal with this issue by using individual household-type coagulants, which are sold in small containers.
The active ingredients are simply added to the liquid, and then the precipitate that has fallen at the bottom is filtered out; but this process is quite laborious and therefore a lot of time is spent on its implementation
In some cases, coagulation can be carried out directly in a mechanical filtration system. To do this, the reagent is introduced into the section of the pipeline with the liquid to be processed before the place of its supply to the filter. And in this case, already foreign particles, “transformed” into flakes, enter the filtration system.
Norms for draining into the sewer
The standards provide uniform requirements for water discharged into the sewer, regardless of the nature of the enterprise. The regulatory documents stipulate the possibility of deviation of the pH value from the neutral value (7) by 1.5 units in both directions.
In addition, the following maximum allowable indicators are indicated:
- concentration of undissolved substances 500 mg/l;
- excess of chemical oxygen consumption in relation to biological within 5 days by 2.5 times;
- increase in the COD/BOD ratio within 20 days by 1.5 times.
Stocks must not contain:
- combustible;
- radioactive substances;
- compounds that decompose to form explosive gases.
The presence in the drain water of substances that can destroy the sewer is not allowed.
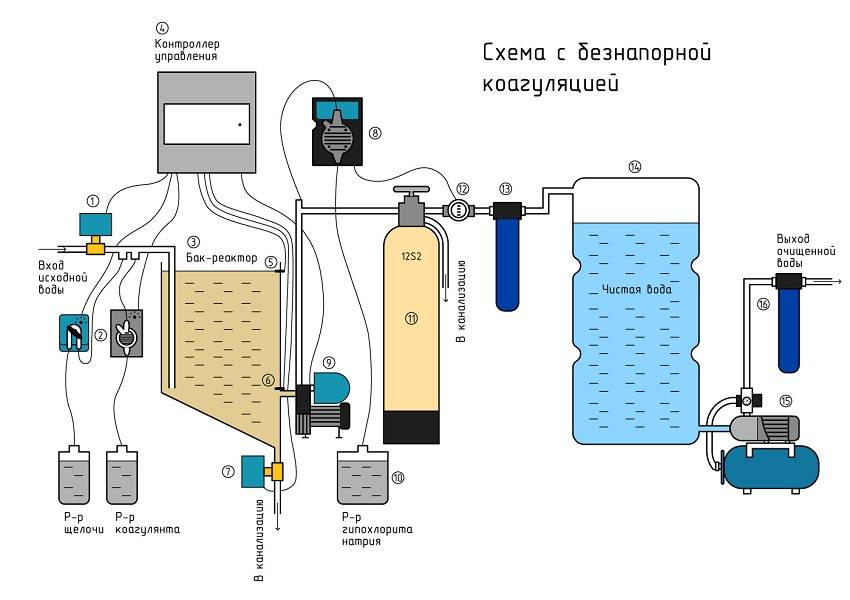
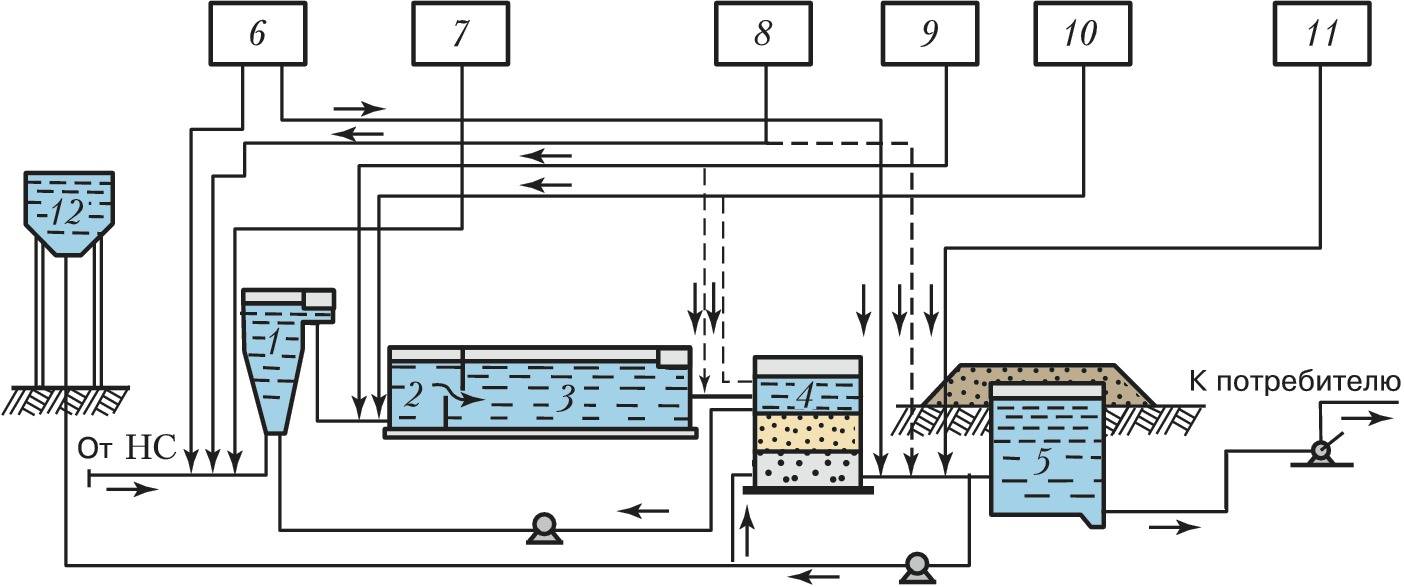
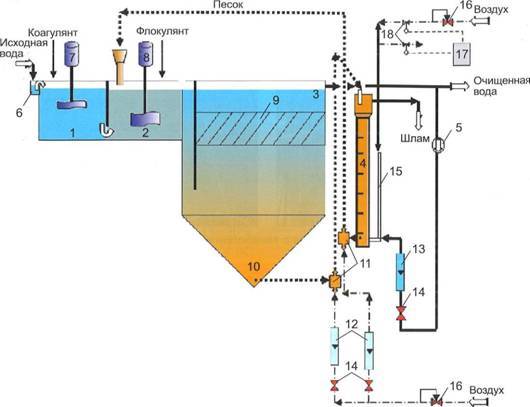
How coagulants work
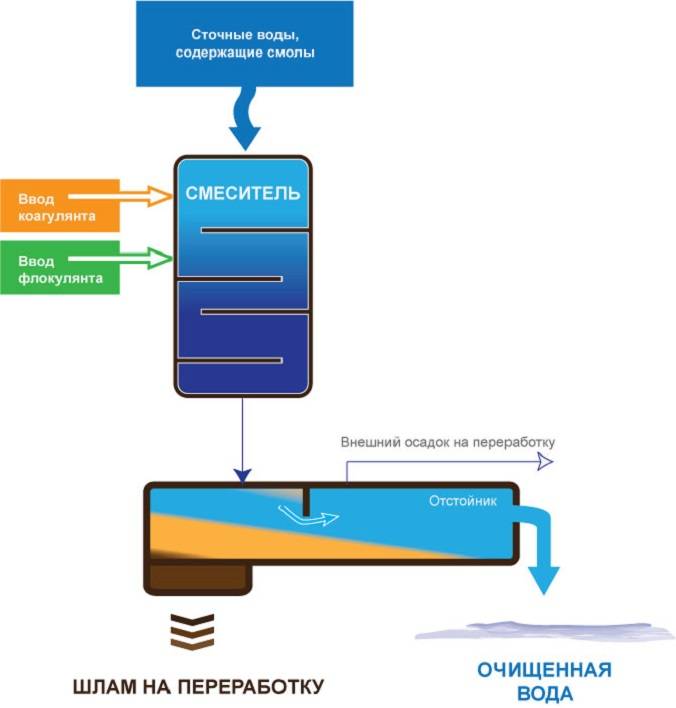
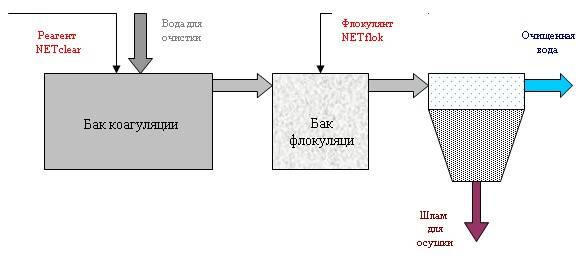
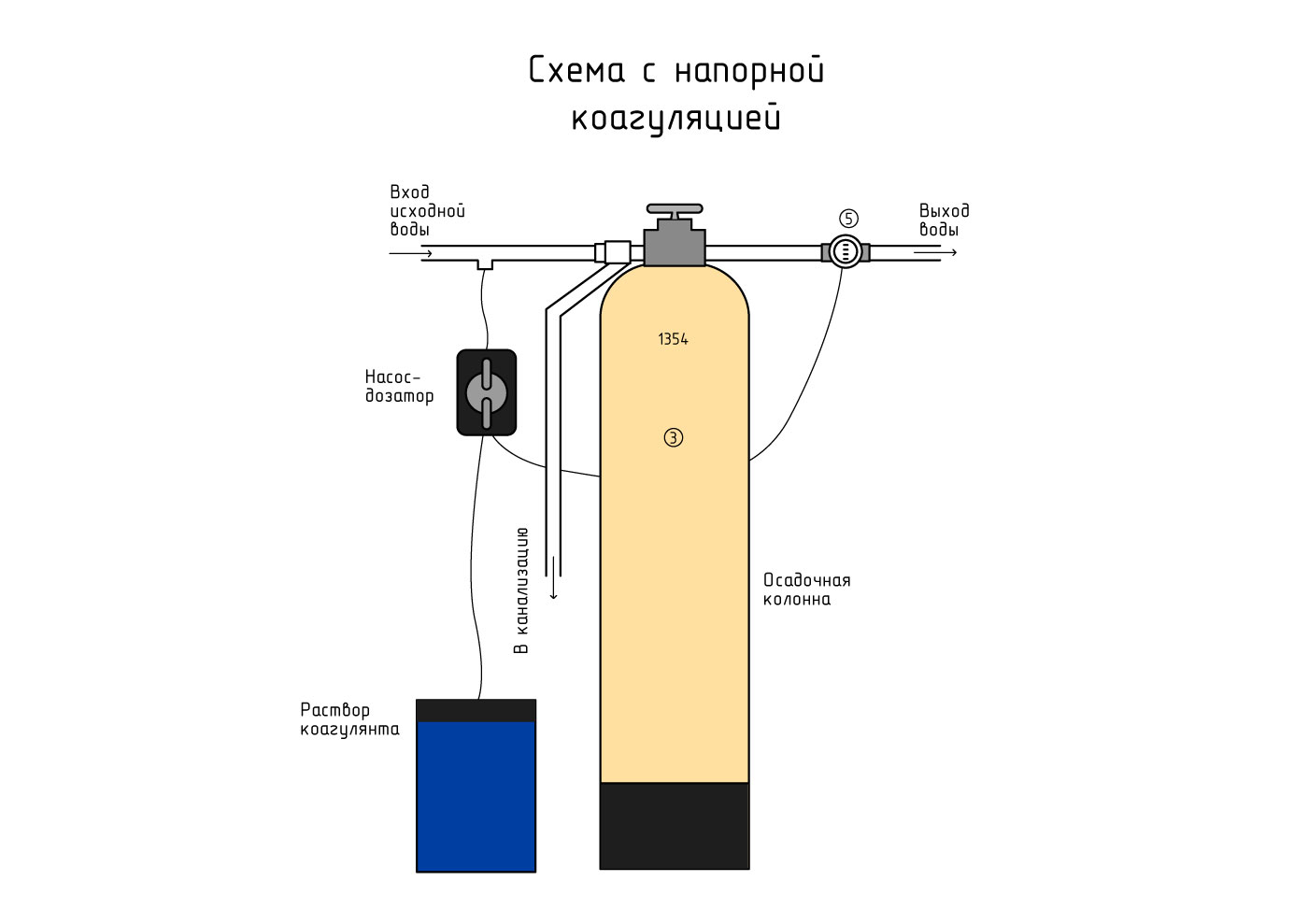
Coagulation is a method of water purification by cohesion of dispersed pollutants for subsequent removal by a mechanical method, filtration. The association of polluting particles occurs due to the introduction of coagulating reagents, creating conditions for the simplest removal of associated pollutants from the treated water.
The term "coagulatio" in Latin means "thickening" or "clotting". The coagulants themselves are substances capable of creating insoluble and slightly soluble compounds due to a chemical reaction, which are easier and easier to remove from the composition of water than dispersed components.
Image gallery
Photo from
Coagulants belong to the group of liquid filters - substances that can purify water during a chemical reaction.
When coagulans are added to the dirty water to be treated, impurities of organic and inorganic origin are neutralized by the formation of a gel-like precipitate and precipitation to the bottom.
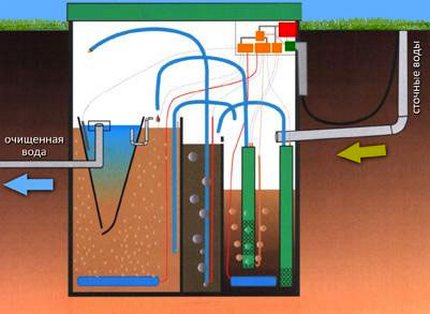
The introduction of coagulants into septic systems allows accelerating the process of sedimentation of impurities, increases the degree of water purification, so that effluents can be discharged without the use of underground post-treatment systems
Active use of coagulants was found at the enterprises of the chemical and food industries, where their introduction into the technological chain significantly reduces the cost of waste disposal
In addition to introducing independent sewage treatment plants, coagulants in everyday life are used to purify water in decorative ponds and fountains.
Water with added coagulant does not bloom under constant lighting, while it does not harm the environment and creates a threat to the ecological environment
Water treatment with a coagulant in the pool guarantees the possibility of discharging water to the relief without the use of a septic tank. The main thing is to remove the sediment in time
Coagulants can be used for the preparation of drinking water and water for filling aquariums, because. they neutralize only harmful substances, do not affect the beneficial composition
Substances for chemical filtration
The principle of operation of coagulants for water treatment
Use in independent treatment plants
Use in industrial plants
Scope of application in the domestic environment
Water bloom warning
Preparation of solution for the pool
Water treatment for aquariums
The principle of operation of substances is based on the fact that their molecular form has a positive charge, while most pollutants are negative. The presence of two negative charges in the structure of the atoms of dirty particles does not allow them to combine together. For this reason, dirty water always becomes cloudy.
At the moment a small portion of the coagulant is introduced into the liquid, the substance begins to pull the suspensions present in it towards itself. As a result: as the intensity of the scattered light increases, the liquid becomes more turbid for a short period of time. After all, one molecule of coagulant can easily attract several molecules of dirt to itself.
Coagulants provoke the formation of stable bonds between small particles of pollution and microbes present in the water.
The attracted dirt molecules begin to react with the coagulant, as a result of which they combine into large complex chemical compounds. Poorly soluble highly porous substances gradually settle to the bottom in the form of a white precipitate.
The task of the owner is only to remove the sediment in time, using any of the types of filtration available to him.
Molecules attracted to each other form large particles, which, due to their increased weight, settle and are then removed by filtration
The effectiveness of the drug can be judged by the formation of sediment at the bottom in the form of white flocculent formations - floccules.Due to this, the term "flocculation" is often used as a synonym for the concept of "coagulation".
The resulting flakes, the size of which can reach from 0.5 to 3.0 mm, have a large surface with a high sorption of precipitated substances
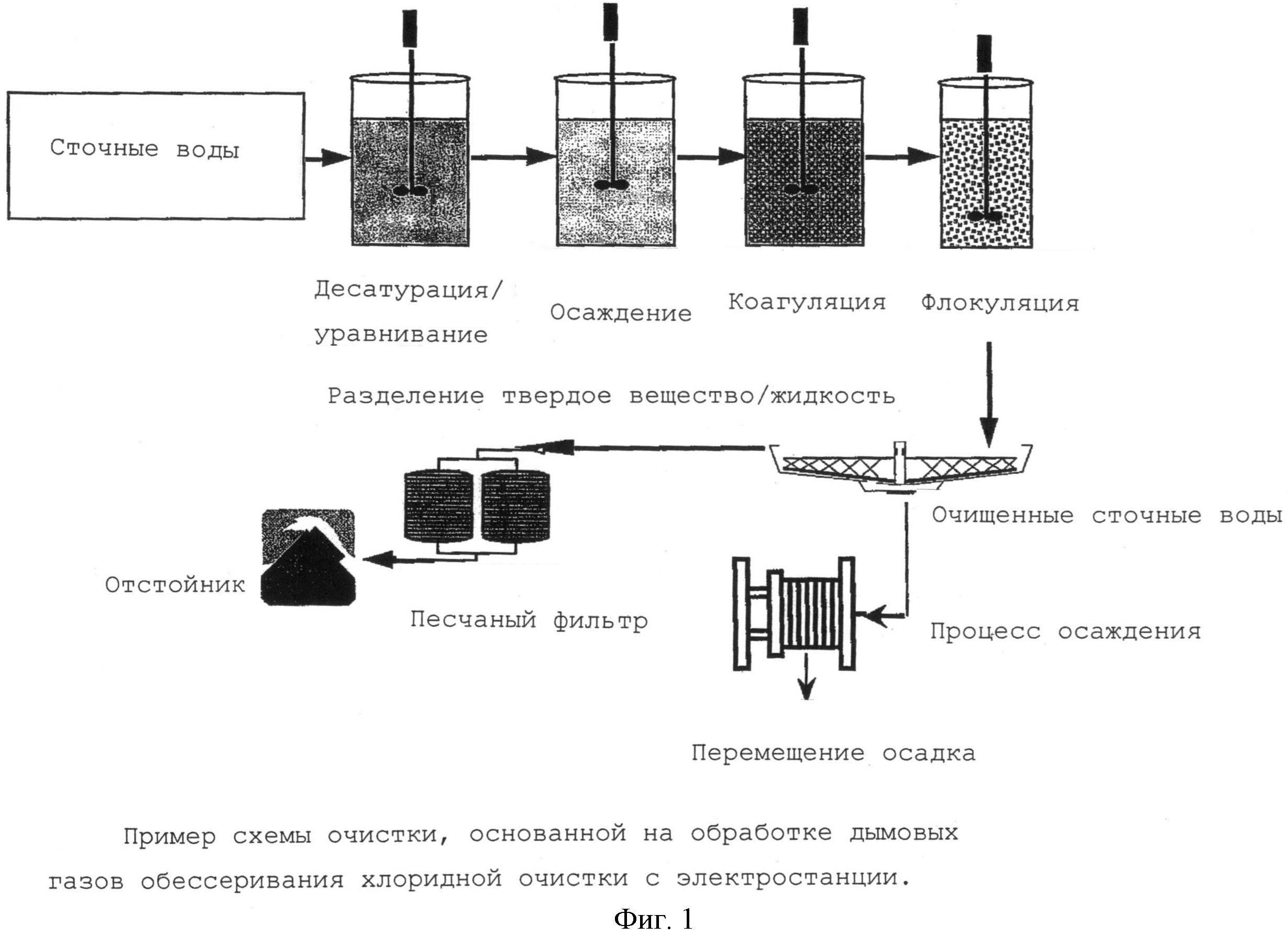
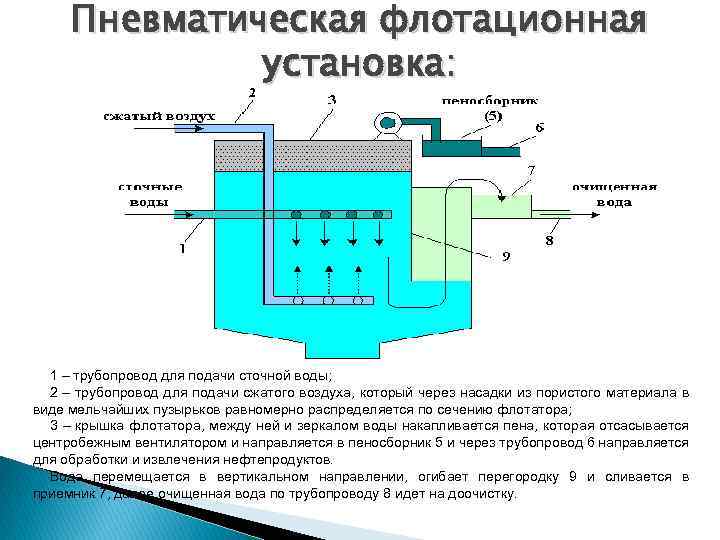
Elimination of pollution containing oil by chemical methods
The method of chemical cleaning is based on the ability of some chemicals and compounds to react with oil impurities, their derivatives, with their further decomposition into neutral components.
As a rule, the products of such reactions precipitate and are removed from the effluents mechanically.
The following chemical elements and compounds have received the greatest practical application:
- Oxygen, its derivative ozone.
- Chlorine-based reagents, bleach, ammonia solutions.
- Potassium, sodium salts of hypochlorous acid.
Reference. The use of chemical treatment methods makes it possible to extract from treated effluents up to 98% of the oil products contained in them.
The most widespread are two directions of chemical purification based on the reactions of neutralization and oxidation. In the first case, mutual neutralization is used to reduce acidity and alkalinity:
- adding solutions of soda ash, ammonia, lime;
- passing wastewater through neutralizing reagents - limestone, chalk, dolomite.
Oxidative reactions are used to remove toxic impurities represented by salts of heavy metals.
 Used as an oxidizing agent:
Used as an oxidizing agent:
- technical oxygen;
- ozone;
- compounds of chlorine, calcium and sodium.
In the context of wastewater treatment from petroleum products, chemical methods are designed to:
- weaken the corrosive load on the structures of water supply and treatment facilities;
- create favorable conditions for the implementation of biochemical processes in biological sedimentation tanks and oxidizers.
Such different pure water
- plumbing that has undergone standard multiple coarse cleaning and filtration in special sedimentation tanks;
- household, pre-softened to prevent the formation of scale in heating appliances, used for washing and washing;
- drinking, used exclusively for ingestion and cooking.
The ordinary water of the apartment is provided by the city water supply system. For self-treatment at home, various filters, structuring systems and some minerals recognized as useful (for example, shungite) are used. In addition, there are coagulants that disinfect water for home use.
Aluminum sulfate technical purified modified
TU 2163-173-05795731-2005
Purified modified technical aluminum sulfate is a non-caking plates, pieces of indefinite shape and different sizes, weighing no more than 3 kg, dark gray.
The coal introduced into aluminum sulfate is at the same time an opacifier, an accelerator of the aluminum hydrolysis process, and at the same time serves as an adsorbent for metals and organic substances, which is more pronounced when cleaning media during the cold season. The concentration of the sorbent on the surface of the filters forms an additional adsorption layer, which increases the degree of purification.
Purified modified technical aluminum sulfate is used as a coagulant in the purification of water for domestic and drinking and industrial purposes, as well as wastewater of various origins.
Specifications
Name of indicator
Norm
Mass fraction of aluminum oxide, %, not less than
14,0
Mass fraction of water-insoluble residue, %, max
1
Mass fraction of coal, %, no more
3
Hydrogen index (pH) of an aqueous solution with a mass fraction of the main substance of 0.5% in terms of aluminum oxide
3,2±0,3
Advantages:
-
increased flocculation rate;
-
additional sorption of metal salts, oil products and phenols
Shelf life: unlimited
Scope of coagulants:
-
Purification of water for household and drinking and industrial purposes;
-
Purification of natural waters in the process of water treatment;
-
Water purification for swimming pools;
-
Use in various industries as a binder, cellulose degumming, etc.)
Chemical processing
During chemical treatment, the impact on water occurs with the help of chemicals (chlorine, bromine), which prevent the development of bacteria and algae. Adding calcium and sodium salts to the pool helps to stabilize the biosphere and regulate the pH level.
pH control
The acid-base balance of pH is the main indicator of the ecosystem of the reservoir. If this indicator is below 7 units, then this indicates that the water has become acidic with a greenish tint.
If the pH level in the pool is above 7.5 units, then the water becomes alkaline and cloudy. The pH balance is easily checked with an electronic tester.
You can adjust the pH of water by adding sodium bisulfate (pH-) to lower it, and to increase using sodium bicarbonate (pH+). To stabilize by 0.1 units, 100 g of the substance is added per 10 m³ of water.
Algicides
Algicides are used to get rid of algae and plant microorganisms.For their correct use, you just need to look at the instructions. The dosage will depend on the capacity of the pool and the drug used.
Aqua Doctor is used to kill blue-green, black and brown algae. During primary processing:
- dilute 200 ml of the drug in 10 m³ of water;
- pour around the perimeter of the pool;
- turn on the filter.
Algicide Super Pool is used to combat algae and fungal vegetation:
- Dilute 100-150 ml of product per 10 m³ of water.
- Pour at the pool water supply point.
- Leave the pool for 8 hours with the filter on.
- Rinse the filter after the procedure.
Alba Super K is used to kill green, black and brown algae, as well as bacteria and various fungi:
- Dilute 150 mg of algicide in 10 m³ of water;
- pour near the water supply nozzles into an artificial reservoir.
When choosing drugs, it is necessary to pay attention to those that do not foam and have an effect on specific bacteria and plants present in the pond.
Disinfection
Chlorine-based disinfectants are among the most commonly used for water purification because they kill pathogens.
To maintain constant water chlorination in the norm (0.3-0.5 mg / l), you need to use one tablet of Super-tabs for 30 m³ of water 2 times a week and check the chlorine content with a tester.
To stabilize chlorine, you can increase its level with dichlor granules, and lower it with sodium sulfate, monitoring the pH balance.
In case of heavy contamination, shock chlorination is applied once every 2-3 weeks (once a week is possible):
- Adjust pH to 7.2.
- Add 3 tablets of Chlor-mini to 10 m³ of water (weekly dose).
- For cloudy and green water, add 10 tablets per 10 m³.
With such chlorination, the concentration of chlorine reaches 2.0-3.0 mg / l, and bathing is prohibited for 12 hours, so it is better to do it in the evening.
Do not throw tablets into the pool, as this may cause discoloration of the walls. Chemicals should be placed in the skimmer with the filter on. The high pH level of water neutralizes the effect of chlorine several times over.
coagulants
Coagulants serve to glue the smallest particles into larger compounds, which precipitate and are removed using a vacuum cleaner and filter system.
When purifying water with coagulants, the following steps must be taken:
- bring the pH level of water to normal (7.2-7.6 units);
- according to the instructions, dilute the required amount of the substance, based on the volume of water in the pool;
- add coagulant to the skimmer or pool with the pump turned on for several hours;
- after even distribution of the substance, turn off the pump and wait 8 hours for the coagulant to precipitate along with the debris;
- turn on the pump with filter and vacuum cleaner to collect sediment;
- clean the filter after coagulation.
Coagulants are used to better purify water from small elements and bacteria that the filter cannot remove. It takes 1-2 days to completely clean the pool with coagulant, while the flocculant works almost immediately.
All the most useful and important information on caring for water in a frame pool is here.
Requirements and regulations
 Wastewater should be treated to TAC or MPC levels, especially if they are returned to fishery water bodies. Such a rule is spelled out in SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00 "Hygienic requirements for the protection of surface waters."
Wastewater should be treated to TAC or MPC levels, especially if they are returned to fishery water bodies. Such a rule is spelled out in SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00 "Hygienic requirements for the protection of surface waters."
After biological treatment, BODp should decrease to 15 mg/l, and suspended solids to 70 mg/l.
After deep cleaning, the BODp index does not exceed 3-5 mg/l, and the concentration of suspended matter does not exceed 1-2 mg/l.
Other requirements and regulations:
- GN 2.1.5.689-98 “Maximum Permissible Concentrations (MPC) of Chemical Substances in the Water of Water Bodies for Domestic Drinking and Cultural and Domestic Water Use”;
- GN 2.1.5.690-98 "Tentative Permissible Levels (TAC) of Chemical Substances in Water of Water Bodies of Domestic Drinking and Cultural and Household Water Use".