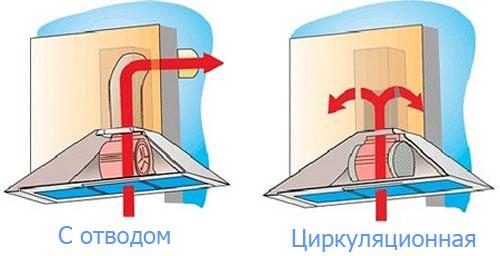
- Design errors
- Selection of industrial heaters
- Connecting a water heater
- 2 Mounting considerations
- Kinds
- Heat source
- materials
- non-standard version
- Features and nuances of the technological process of installation of supply ventilation with air heating
- Mounting Tips
- Calculation-online of electric heaters. Selection of electric heaters by power - T.S.T.
- 5 Selecting an electric ventilation heater
- Design features of the device
- Passive ventilation systems.
- On the wall
- Active ventilation systems
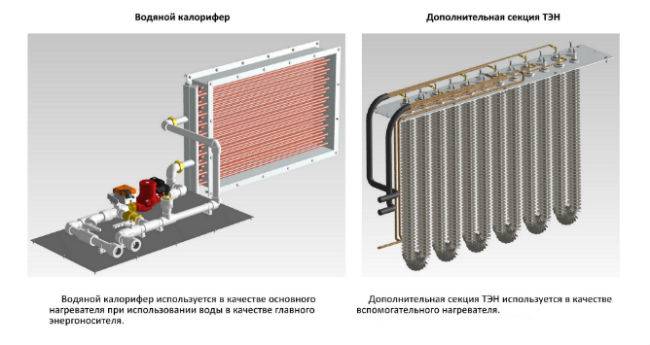
- Water heater
- Electric heater.
- breather
- Recuperation units for an apartment
- Do I need to focus on SNiP?
- Criteria for choosing heaters
- With or without fan
- Shape and material of tubes
- Minimum required power
- The principle of operation of the water heater
- Advantages and disadvantages
Design errors
At the stage of creating a project, errors and shortcomings are often encountered. This may be excessive noise background, reverse or insufficient draft, blowing (upper floors of multi-storey residential buildings) and other problems. Some of them can be solved even after the installation is completed, with the help of additional installations.
A vivid example of a low-skilled calculation is insufficient draft at the exhaust from the production room without particularly harmful emissions.Let's say the ventilation duct ends with a round shaft, rising above the roof by 2,000 - 2,500 mm. Raising it higher is not always possible and advisable, and in such cases the principle of flare emission is used. A tip with a smaller diameter of the working hole is installed in the upper part of the round ventilation shaft. An artificial narrowing of the cross section is created, which affects the rate of gas emission into the atmosphere - it increases many times over.
 Project example
Project example
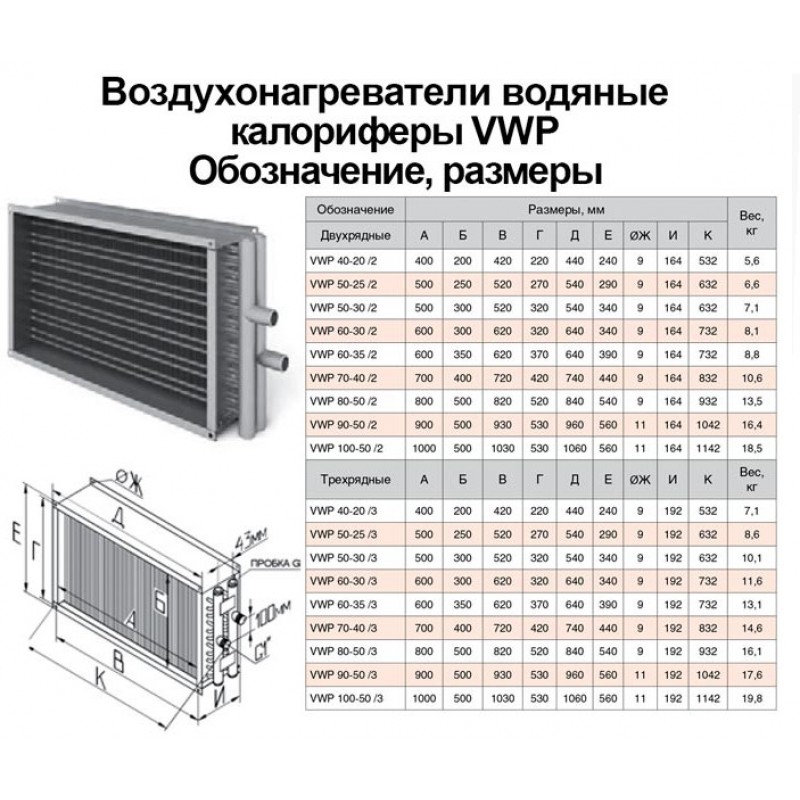
Selection of industrial heaters
Having decided on the primary source of heating, we select the type of air heater. The first question is under what conditions and within what temperature limits?
modes it will work. The second is the degree of contamination of the coolant and air.
If the heat exchangers are operated under poor
conditions with an air temperature of -20°C and below, it makes sense to opt for air heaters TVV, KP and KFB. It's bimetallic
heaters, in which a metal pipe with aluminum fins is used as a heat exchange element (similar to KSk and KPSk).
Their fundamental difference lies in the following:
1. Increased area for the passage of the coolant. Particularly important factor for operation at low outdoor temperatures.
The possibility of overgrowing with dirt, and in the case of steam air heaters, with scale is reduced. What, firstly, extends the total period
their services; secondly, with a contaminated coolant, it prevents complete overlapping of the internal section and, accordingly, freezing
heat exchanger; thirdly, the thermal performance is stable for a longer time.
2.The thickness of the aluminum fin of these air heaters is greater than that of KSK and KPSk, which contributes to less mechanical deformation.
heating element during transportation and operation. And the increased pitch of the aluminum fins contributes to less
clogging the intercostal space with dirt and dust, and, accordingly, reducing aerodynamic drag
This has a positive effect
during the operation of heaters in buildings with high dust content and air pollution, and, which is again important, during operation
at low temperatures, where the recommended mass velocity in the frontal section when selecting heaters is up to 3.5 kg/m2*s. 3
Less hydraulic resistance.
All of the above factors contribute to the fact that over the years, mining enterprises have chosen to create
process heat - water heaters TVV and steam KP, and for the layout of air heaters KFB 10 A4 heaters, which have significant
benefits under poor operating conditions in regions with low temperature regimes.


Delivery to buyers of purchased industrial air heaters is carried out both on a self-pickup basis and by our company's vehicles. Wide
it is practiced to send equipment by forwarding companies, while air heaters are delivered to local terminals of transport companies free of charge.
Connecting a water heater
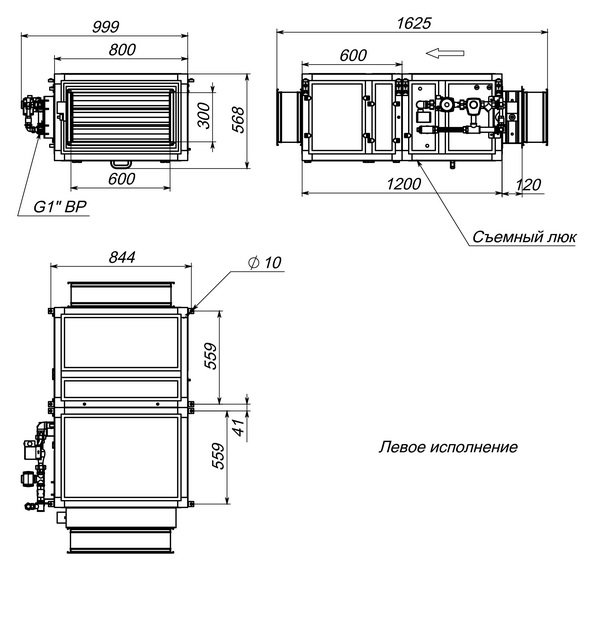
Air supply using a water heater can be performed in two versions, right and left. It depends on where the location of the mixing unit and the automation unit is located.When the air handling unit is viewed from the side of the air valve, then:
- The left execution implies that the automatic block and the mixing unit are located on the left side;
- The right execution implies that the automatic block and the mixing unit are located on the right side.
In each version, the connecting pipes are located on the air intake side, where the air damper is installed. Depending on the version, there are the following features:
- In the right versions, the supply tube is located at the bottom, and the return tube is at the top;
- In the left executions, everything is not so. The supply is at the top and the outflow is at the bottom.
Because in air handling units using water heaters, a mixing unit is required, the latter must contain a 2 or 3 way valve. The valve must be selected based on the parameters of the heat supply system. For individual circuits of autonomous heating systems, which can be a gas boiler, a three-way valve is required. If the air handling unit is connected to a central heating system, then a two-way valve is required. To summarize, the choice of valve depends on:
- System type;
- Water supply and return temperatures;
- Pressure drop between the supply and return pipes, if the system is central;
- Is there a separate pump on the ventilation inflow circuit, if the system is autonomous.
When installing a circuit with a water heater, installation is prohibited in that position if the inlet and outlet pipes are vertical. Also, installation should not be carried out if the air intake is at the top.This is due to the fact that snow can get into the inflow of the installation and melt there, which threatens the penetration of water into the automation. In order for the temperature controllers to work correctly, it is necessary to place the temperature sensor inside the duct outlet so that the area is even along a length of at least 50 cm from the inflow unit.
You should also be aware that:
- It is forbidden to carry out the installation of a supply unit 100 - 3500 m3/h, if the motor axis is vertical;
- It is forbidden to install air handling units where moisture or chemically active substances can get on them;
- It is forbidden to use the air handling unit where there is a direct impact of atmospheric precipitation on the unit;
- It is forbidden to block access for maintenance of installations;
- In order to install the air handling unit in a heated room and avoid condensation on the supply air duct, it is required to use only a thermally insulated air duct.
There is nothing particularly difficult in installing heaters, you just need to follow the rules and observe safety precautions. Sometimes it is better to entrust this matter to professionals and be sure that all work is done taking into account all requirements.
2 Mounting considerations
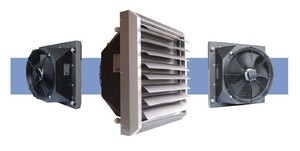
If natural air exchange works well in the room, the device can be mounted in the heating system directly at the air intake located in the basements of buildings. In the presence of forced ventilation, the equipment can be installed in any convenient place. To create a knot binding in this case, you will need:
- heater;
- pump;
- ball valve;
- thermomanometer;
- plug;
- Mayevsky's crane;
- detachable connection (in the form of a union nut);
- valve (three-way or two-way).
Today, ready-made models of strapping units in various designs are on sale. In some of them, in addition to the main set of parts, there are balancing and check valves, as well as cleaning filters that prevent clogging and quick breakdown of equipment.
Industrial hot water heaters with a fan are very large, so they are installed and connected by qualified specialists using the appropriate equipment. Appliances designed for domestic use are much smaller and lighter, so you can handle their installation yourself. It is only necessary to check in advance the strength of the ceiling or wall on which the heater will be mounted. Concrete and brick floors are characterized by the greatest strength, wooden structures are of medium strength, and plasterboard structures are characterized by minimum strength.
After choosing the optimal location, you can proceed to the installation. First you need to fix the bracket with holes, due to which the body of the device will be held. Then hang the heater and connect the pipes and the mixing unit (its partial installation can be carried out before installing the heater).
Insertion into the heating system is carried out by welding metal pipes or using connecting fittings. To avoid changing the position of the apparatus, it is necessary to eliminate the load on the nozzles, and replace the rigid parts with flexible ones. In order to isolate the system and prevent leakage, it is recommended to treat the joints with a sealant.
Kinds
On what grounds can heaters be classified?
Heat source
It can be used as:
- Electricity.
- Heat generated by an individual heating boiler, boiler house or CHP and delivered to the heater by a coolant.
Let's analyze both schemes in a little more detail.
An electric air heater for forced ventilation is, as a rule, several tubular electric heaters (heaters) with fins pressed onto them to increase the heat exchange area. The electric power of such devices can reach hundreds of kilowatts.
With a power of 3.5 kW or more, they are connected not to a socket, but directly to the shield with a separate cable; from 7 kW power supply from 380 volts is highly recommended.

In the photo - domestic electric heater ECO.
What are the advantages of an electric heater for ventilation against the background of a water one?
- Ease of installation. Agree that it is much easier to bring a cable to a heating device than to organize the circulation of a coolant in it.
- The absence of problems with the thermal insulation of the eyeliner. Losses in the power cable due to its own electrical resistance are two orders of magnitude less than heat losses in a pipeline with any coolant.
- Easy temperature setting. In order for the supply air temperature to be constant, it is enough to mount a simple control circuit with a temperature sensor in the power supply circuit of the heater. For comparison, a system of water heaters will force you to solve the problems of coordinating the air temperature, coolant and boiler power.
Does the power supply have disadvantages?
- The price of an electric device is slightly higher than a water one. For example, a 45-kilowatt electric heater can be bought for 10-11 thousand rubles; a water heater of the same power will cost only 6-7 thousand.
- More importantly, when using direct heating with electricity, the operating costs are outrageous. To heat the coolant that transfers heat to the air heating water system, the heat of combustion of gas, coal or pellets is used; this heat in terms of kilowatts is much cheaper than electricity.
| Thermal energy source | cost per kilowatt hour heat, rubles |
| main gas | 0,7 |
| Coal | 1,4 |
| Pellets | 1,8 |
| Electricity | 3,6 |
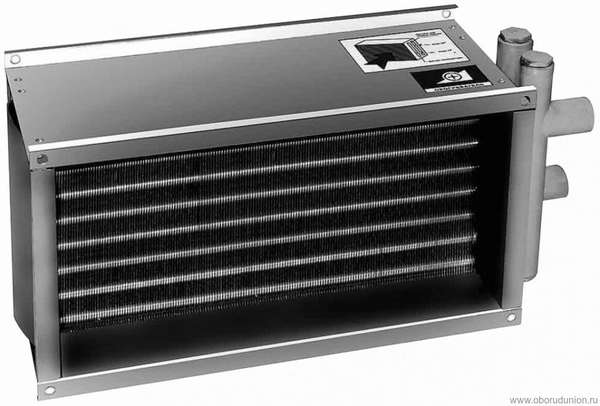
Water heaters for forced ventilation are, in general, ordinary heat exchangers with developed fins.

Water heater.
The water or other coolant circulating through them gives off heat to the air passing through the fins.
The advantages and disadvantages of the scheme mirror the features of the competing solution:
- The cost of the heater is minimal.
- Operating costs are determined by the type of fuel used and the quality of insulation of the coolant wiring.
- Air temperature control is relatively complex and requires a flexible circulation and/or boiler control system.
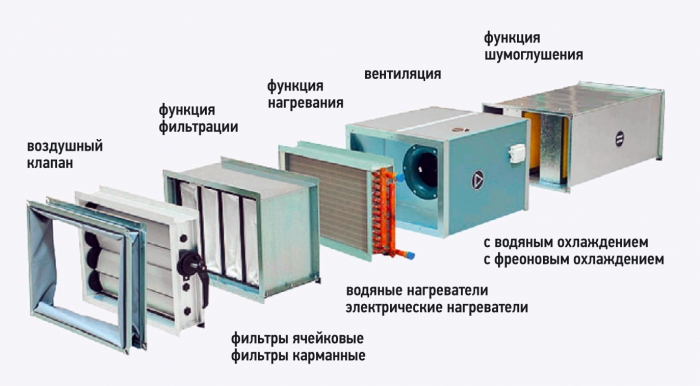
materials
For electric heaters, aluminum or steel fins are usually used on standard heating elements; somewhat less common heating scheme with an open tungsten coil.

Heating element with steel fins.
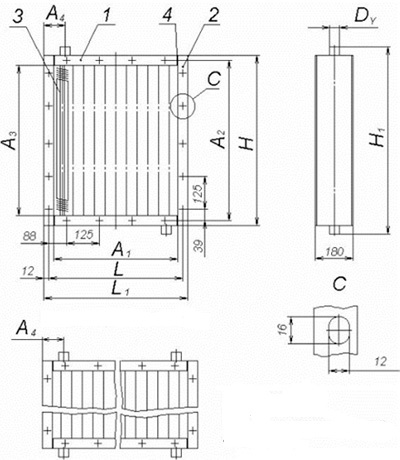
For water heaters, three versions are typical.
- Steel pipes with steel fins provide the lowest cost of construction.
- Steel pipes with aluminum fins, due to the higher thermal conductivity of aluminum, guarantee a slightly higher heat transfer.
- Finally, bimetallic heat exchangers made of copper tube with aluminum fins provide maximum heat transfer at the cost of a slightly lower resistance to hydraulic pressure.
non-standard version
A couple of solutions deserve special mention.
- Supply units are a heater with a pre-installed fan for air supply.
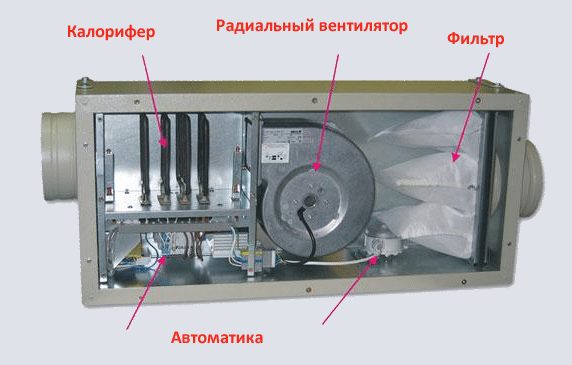
- In addition, the industry produces products with heat recuperators. Part of the thermal energy is taken from the air flow in the exhaust ventilation.
Features and nuances of the technological process of installation of supply ventilation with air heating
Installation of supply ventilation is not difficult for a professional. In principle, the technological process does not have a large number of difficulties. First of all, in order to prevent condensation, it is necessary to isolate the area before entering the device with a roll insulation.
Air ducts must be fixed to the wall or ceiling. To avoid unnecessary vibration, it is recommended to fix vibrating round inserts between the unit and the network. Supply ventilation with heating and cooling air should be located so that the ventilation grilles are directed to places of maximum concentration of people.
It is much easier to install equipment in a simple apartment or private house. For this, compact installations with small dimensions are used. If the room has plastic windows, it means that natural ventilation is impossible, and therefore it will be necessary to install a forced supply model.
The heated supply valve can be mounted both in the wall and in the ceiling, it all depends on the design of the room and the personal preferences of the owner.
Mounting Tips

Heaters with sensors in the greenhouse maintain the desired temperature
The water air heater is installed in rooms connected to the central heating main.When installing yourself, you should follow the recommendations of specialists:
- The diagonal of the heater depends on the characteristics of the bends of the channels, the type of damper and structural elements.
- To protect the heater from freezing, installation is carried out in rooms with a temperature of at least 0 degrees.
- Before starting installation, it is necessary to inspect the plates and tubes for integrity.
- Welded flanges are the easiest to connect end-to-end.
- Direct-flow air vent valves are located at the top of the outlet and supply manifolds.
- The joints of the device and the ventilation system are sealed.
- Wall models are installed by attaching the console with two self-tapping screws.
Calculation-online of electric heaters. Selection of electric heaters by power - T.S.T.
Skip to content This page of the site presents an online calculation of electric heaters. The following data can be determined online: - 1. the required output (heat output) of the electric air heater for the air handling unit. Basic parameters for calculation: volume (flow rate, performance) of the heated air flow, air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater, desired outlet temperature - 2. air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater. Basic parameters for calculation: consumption (volume) of the heated air flow, air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater, actual (installed) thermal power of the electrical module used
1. Online calculation of the power of the electric heater (heat consumption for heating the supply air)
The following indicators are entered into the fields: the volume of cold air passing through the electric heater (m3/h), the temperature of the incoming air, the required temperature at the outlet of the electric heater. At the output (according to the results of the online calculation of the calculator), the required power of the electric heating module is displayed to comply with the set conditions.
1 field. The volume of supply air passing through the electric heater (m3/h)2 field. Air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater (°С)
3 field. Required air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater
(°C) field (result). Required power of the electric heater (heat consumption for supply air heating) for the entered data
2. Online calculation of the air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater
The following indicators are entered into the fields: the volume (flow) of heated air (m3/h), the air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater, the power of the selected electric air heater. At the outlet (according to the results of the online calculation), the temperature of the outgoing heated air is displayed.
1 field. The volume of supply air passing through the heater (m3/h)2 field. Air temperature at the inlet to the electric heater (°С)
3 field. Thermal power of the selected air heater
(kW) field (result). Air temperature at the outlet of the electric heater (°С)
Online selection of an electric heater by the volume of heated air and heat output
Below is a table with the nomenclature of electric heaters produced by our company. According to the table, you can roughly select the electrical module suitable for your data.Initially, focusing on the indicators of the volume of heated air per hour (air productivity), you can choose an industrial electric heater for the most common thermal conditions. For each heating module of the SFO series, the most acceptable (for this model and number) range of heated air is presented, as well as some ranges of air temperature at the inlet and outlet of the heater. By clicking on the name of the selected electric air heater, you can go to the page with the thermal characteristics of this electric industrial air heater.
| Name of electric heater | Installed power, kW | Air performance range, m³/h | Inlet air temperature, °С | Outlet air temperature range, °C (depending on air volume) |
| SFO-16 | 15 | 800 — 1500 | -25 | +22 0 |
| -20 | +28 +6 | |||
| -15 | +34 +11 | |||
| -10 | +40 +17 | |||
| -5 | +46 +22 | |||
| +52 +28 | ||||
| SFO-25 | 22.5 | 1500 — 2300 | -25 | +13 0 |
| -20 | +18 +5 | |||
| -15 | +24 +11 | |||
| -10 | +30 +16 | |||
| -5 | +36 +22 | |||
| +41 +27 | ||||
| SFO-40 | 45 | 2300 — 3500 | -30 | +18 +2 |
| -25 | +24 +7 | |||
| -20 | +30 +13 | |||
| -10 | +42 +24 | |||
| -5 | +48 +30 | |||
| +54 +35 | ||||
| SFO-60 | 67.5 | 3500 — 5000 | -30 | +17 +3 |
| -25 | +23 +9 | |||
| -20 | +29 +15 | |||
| -15 | +35 +20 | |||
| -10 | +41 +26 | |||
| -5 | +47 +32 | |||
| SFO-100 | 90 | 5000 — 8000 | -25 | +20 +3 |
| -20 | +26 +9 | |||
| -15 | +32 +14 | |||
| -10 | +38 +20 | |||
| -5 | +44 +25 | |||
| +50 +31 | ||||
| SFO-160 | 157.5 | 8000 — 12000 | -30 | +18 +2 |
| -25 | +24 +8 | |||
| -20 | +30 +14 | |||
| -15 | +36 +19 | |||
| -10 | +42 +25 | |||
| -5 | +48 +31 | |||
| SFO-250 | 247.5 | 12000 — 20000 | -30 | +21 0 |
| -25 | +27 +6 | |||
| -20 | +33 +12 | |||
| -15 | +39 +17 | |||
| -10 | +45 +23 | |||
| -5 | +51 +29 |
5 Selecting an electric ventilation heater

Many users prefer to use an online calculator to calculate the heater, where all the nuances are provided. But even in such a situation, you need to be careful, since the power of the component nodes may be too large. When the unit has a performance indicator of 4 kW, then it can be powered from a conventional outlet. If the power of the heater is greater, then it will need a separate cable that will lead directly to the power panel. If the consumer decides to purchase a unit with an indicator of 8 kW, then 380 V power will be required for its operation.
Modern heaters are lightweight and quite compact in size, moreover, they are completely autonomous.For the stable operation of such units, it is not at all necessary to have a centralized hot water supply or steam. The only negative is that due to their low power, they are simply impractical to use over large areas. A secondary disadvantage is that they consume a lot of electricity.
Design features of the device
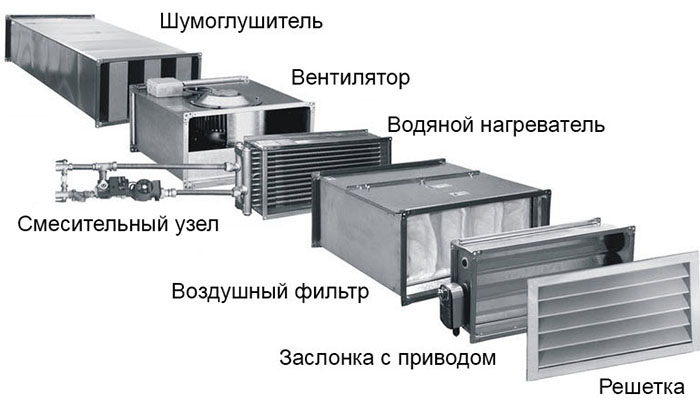
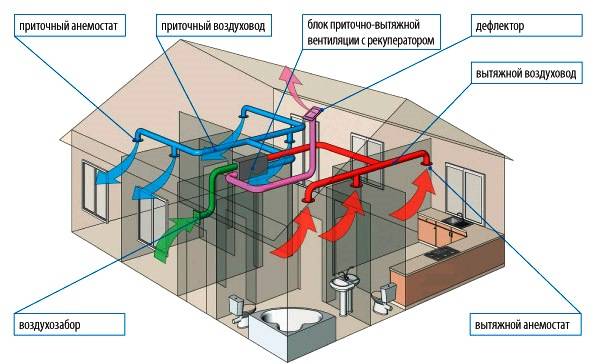
The main elements of supply ventilation
- Air intake grill. Acts as an aesthetic design, and a barrier that protects debris particles in the supply air masses.
- Supply ventilation valve. Its purpose is to block the passage of cold air from the outside in winter and hot air in summer. You can make it work automatically using an electric drive.
- Filters. Their purpose is to purify the incoming air. I need a replacement every 6 months.
- Water heater, electric heaters - designed to heat the incoming air masses.
- For rooms with a small area, it is recommended to use ventilation systems with electric heating elements, for large spaces - a water heater.
Elements of supply and exhaust ventilation
Additional elements
- Fans.
- Diffusers (contribute to the distribution of air masses).
- Noise suppressor.
- Recuperator.
The design of ventilation directly depends on the type and method of fixing the system. They are passive and active.
Passive ventilation systems.
Such a device is fresh air valve. The scooping of street air masses occurs due to the pressure drop. In cold weather, the temperature difference contributes to the injection, in the warm period - the exhaust fan. The regulation of such ventilation can be automatic and manual.
Automated regulation directly depends on:
- the flow rate of air masses passing through the ventilation;
- air humidity in the space.
The disadvantage of the system is that in the winter season such ventilation is not effective for heating the house, since a large temperature difference is created.
On the wall
Refers to the passive type of supply ventilation. Such an installation has a compact box that is mounted on the wall. To control the heating, it is equipped with an LCD display and a control panel. The principle of operation is to recuperate internal and external air masses. To heat the room, this device is placed near the heating radiator.
Active ventilation systems
Since in such systems it is possible to regulate the intensity of fresh air supply, such ventilation for heating and space heating is more in demand.
According to the principle of heating, such a supply heater can be water and electric.
Water heater
Powered by heating system. The principle of operation of this ventilation system is to circulate air through a system of channels and tubes, inside which there is hot water or a special liquid. In this case, heating takes place in a heat exchanger built into the centralized heating system.
Electric heater.
The principle of operation of the system is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy using an electric heating element.
breather
This is a compact device, small size for forced ventilation, heated. To supply fresh air, this device is attached to the wall of the room.
Breather Tion o2
Breezer construction o2:
- Channel consisting of an air intake and an air duct.This is a sealed and insulated tube, due to which the device draws air from outside.
- Air retention valve. This element is an air gap. It is designed to prevent the outflow of warm air while the device is turned off.
- Filtration system. It consists of three filters, which are installed in a certain sequence. The first two filters clean the air flow from visible contaminants. The third filter - deep cleaning - from bacteria and allergens. It cleans the incoming air from various odors and exhaust gases.
- Fan for air supply from the street.
- Ceramic heater, which is equipped with climate control. Responsible for heating the inflow of air flows and automatic temperature control.
Recuperation units for an apartment
The disadvantage of many supply ventilation systems is the high energy consumption for heating or cooling air entering the apartment. Recuperation units will help reduce energy consumption - they use the thermal energy of the exhausted air masses to heat fresh air from the street.
At high temperature difference outdoors and indoors the recovery unit will not be able to achieve the required parameters, and the air will have to be reheated, however, the energy consumption in this case will be much lower than for conventional supply air heating.
The higher the efficiency of the model, the less the need for additional air heating. On average, the efficiency of modern air handling units is 85-90%, which often makes it possible to completely abandon the use of a heater.
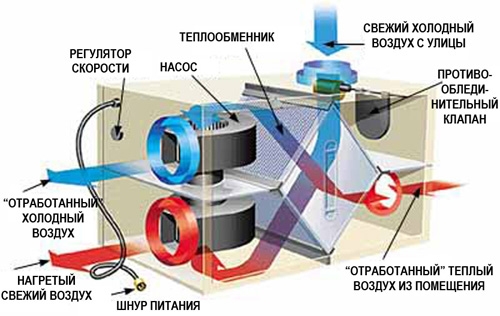
Monoblock air handling units with a heat exchanger take up relatively little space - they can be installed on a balcony or loggia. Among the products of leading manufacturers of climatic equipment, models with a capacity of 150 to 2000 m3 / h are widely used. For comparison, in a one-room superior apartment with an area of 60 m2 with two residents, air exchange is required on average from 300 to 500 m3/h.
Do I need to focus on SNiP?
In all calculations that we carried out, the recommendations of SNiP and MGSN were used. This regulatory documentation allows you to determine the minimum allowable ventilation performance that ensures a comfortable stay of people in the room. In other words, the requirements of SNiP are primarily aimed at minimizing the cost of the ventilation system and the cost of its operation, which is relevant when designing ventilation systems for administrative and public buildings.
In apartments and cottages, the situation is different, because you are designing ventilation for yourself, and not for the average resident, and no one forces you to adhere to the recommendations of SNiP. For this reason, the performance of the system can be either higher than the calculated value (for greater comfort) or lower (to reduce energy consumption and system cost). In addition, the subjective feeling of comfort is different for everyone: 30–40 m³ / h per person is enough for someone, and 60 m³ / h will not be enough for someone.
However, if you do not know what kind of air exchange you need to feel comfortable, it is better to follow the recommendations of SNiP.Since modern air handling units allow you to adjust the performance from the control panel, you can find a compromise between comfort and economy already during the operation of the ventilation system.
Criteria for choosing heaters
When choosing a heater, in addition to heating capacity, air volume capacity and heat exchange surface, it is necessary to determine the criteria listed below.
With or without fan
The main task of a heater with a fan is to create a warm air flow for heating a room. To drive air through the tube plates is the function of the fan. In the event of an emergency situation with a fan failure, the circulation of water through the tubes must be stopped.
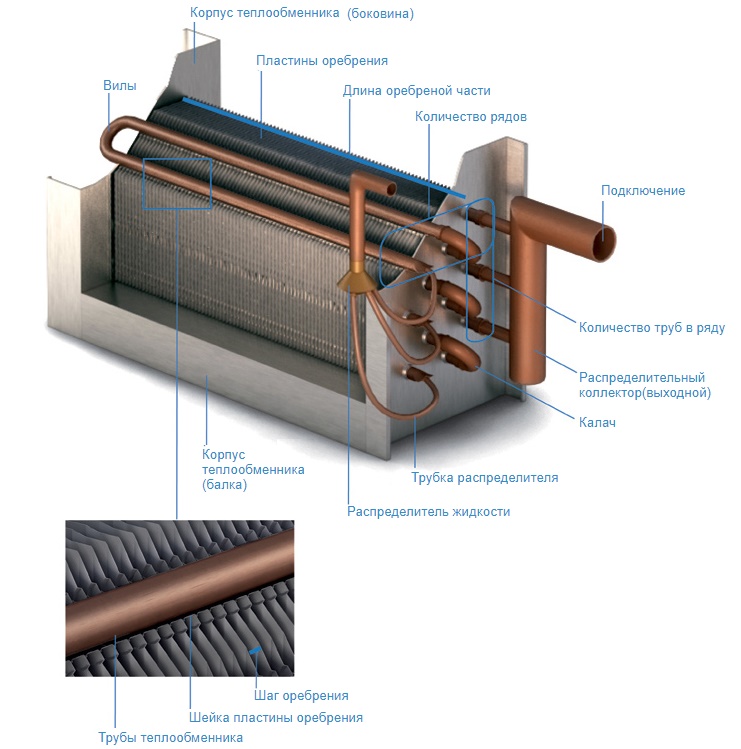
Shape and material of tubes
The basis of the heating element of the air heater is a steel tube from which the section grate is assembled. There are three tube designs:
- smooth-tube - ordinary tubes are located next to each other, the heat transfer is the lowest possible;
- lamellar - plates are pressed onto smooth tubes to increase the heat transfer area.
- bimetallic - steel or copper tubes with a wound aluminum tape of complex shape. Heat dissipation in this case is most efficient, copper tubes are more heat-conducting.
Minimum required power
To determine the minimum heating power, you can use a fairly simple calculation given in the comparative calculation between radiators and heaters earlier. But since heaters not only radiate thermal energy, but also circulate air with a fan, there is a more accurate way to determine the power, taking into account tabular coefficients. For a car dealership with dimensions of 50x20x6 m:
- Car dealership air volume V = 50 * 20 * 6 = 6,000 m3 (need to be heated in 1 hour).
- Outdoor temperature Tul = -20⁰C.
- Temperature in the cabin Tcom = +20⁰C.
- Air density, p = 1.293 kg / m3 at an average temperature (-20⁰C + 20⁰C) / 2 = 0. Air specific heat, s = 1009 J / (kg * K) at an outside temperature of -20⁰C - from the table.
- Air capacity G = L*p = 6,000*1.293 = 7,758 m3/h.
- Minimum power according to the formula: Q (kW) \u003d G / 3600 * c * (Tcom - Tul) \u003d 7758/3600 * 1009 * 40 \u003d 86.976 kW.
- With a power reserve of 15%, the minimum required heat output = 100.02 kW.
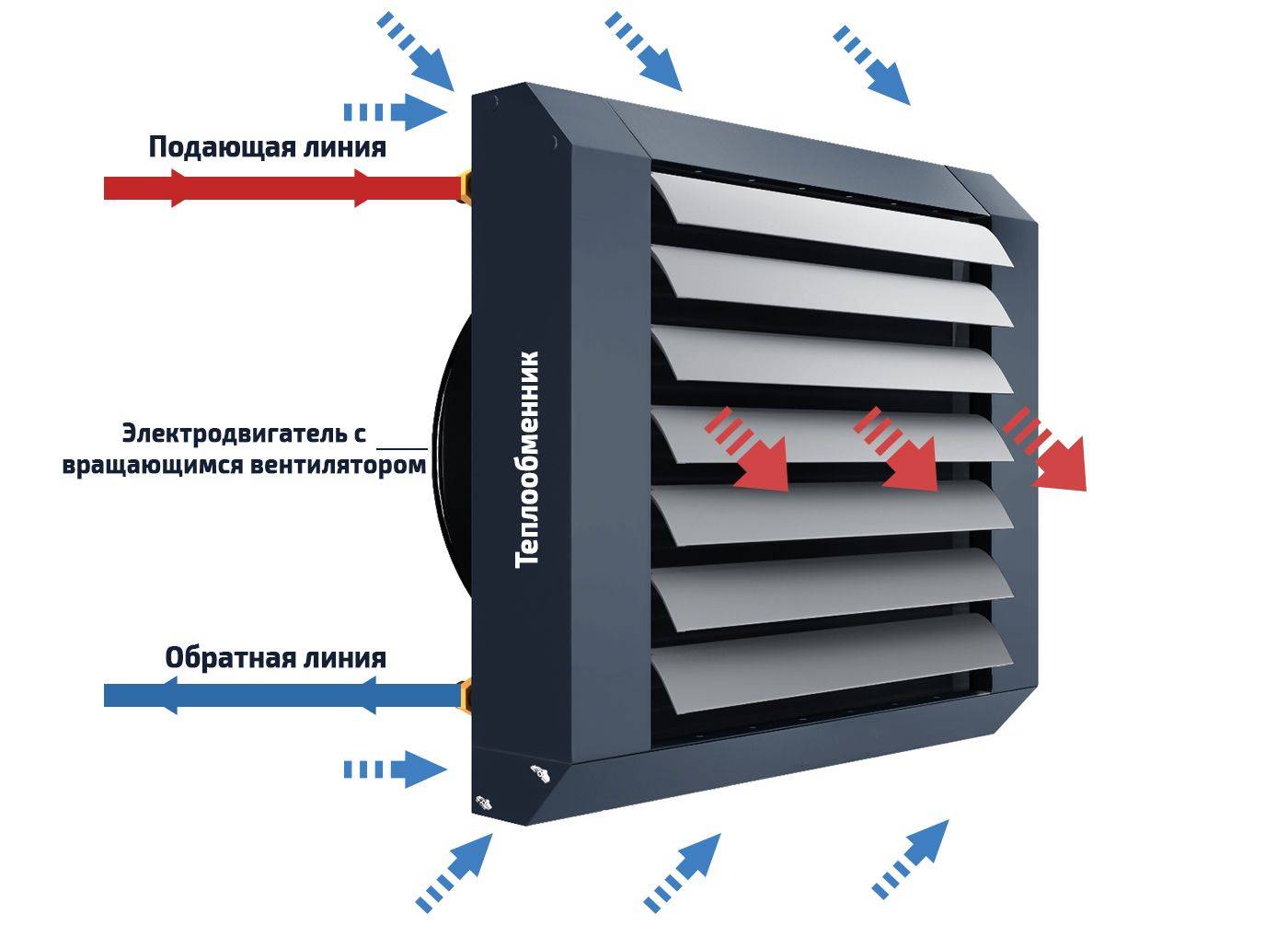
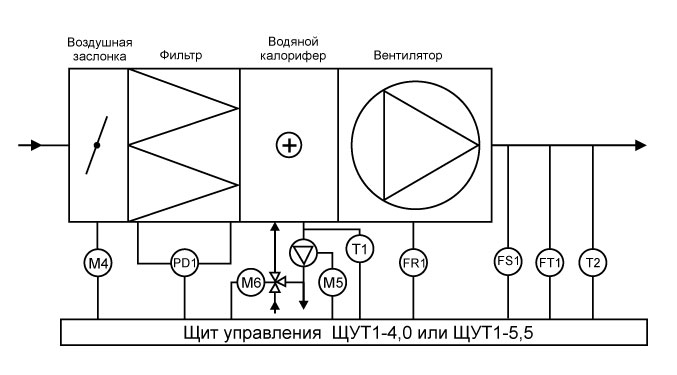
The principle of operation of the water heater
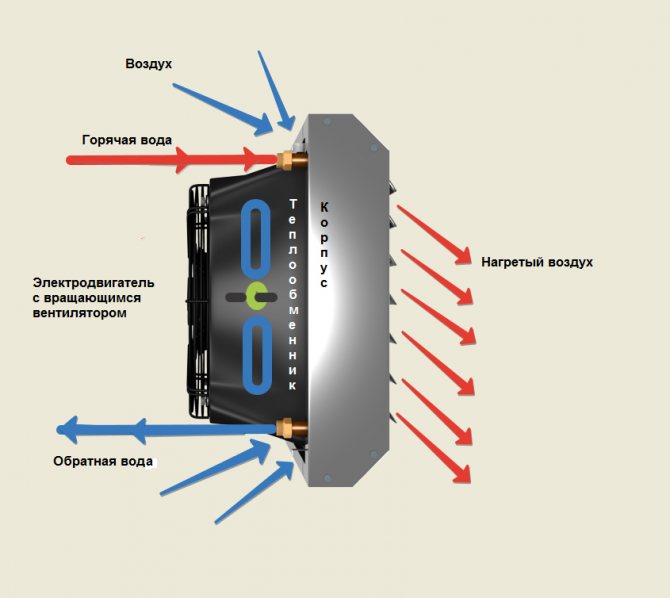
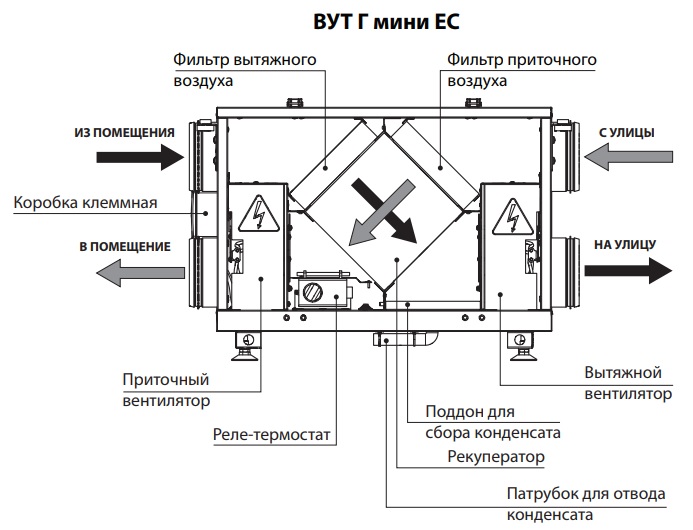
To begin with, let's look at the features of the ventilation system with water heaters, because the supply ventilation scheme with an electric heater is slightly different. The water heater consists of a heat exchanger and a fan.
The principle of its work is as follows:
- Through special air intake grilles installed at the outer end of the duct, air masses enter the ventilation ducts. Lattices are needed to protect against the penetration of small rodents, animals, birds and insects.
- After that, the air passes through filters, where it is cleaned of dust, plant pollen, harmful impurities and other pollutants.
- The heater receives heat from the water line. Thanks to this heat, the air masses are heated to the desired temperature.
- When passing through the heat exchanger, the incoming air flows are additionally heated due to the heat of the air removed from the room.
- The cleaned and heated masses are fed into the room with the help of a fan. Thanks to the installed diffuser, they are evenly distributed over the entire area.
- There is a lot of noise during operation of the unit. To reduce it, special noise absorbers are installed.
- If the system stops working, check valves are activated, which block the access of cold air masses to the room.
The design of the heater is characterized by the absence of its own heater. Its main constituent elements perform the following functions:
- the built-in fan directs the heated air masses into the room;
- the heat exchanger, consisting of metal tubes, receives water from the heating system.
In fact, the system of tubes performs the functions of a heating coil, as in an electric heater. A hot coolant from the heating system circulates through the pipes, having a temperature in the range of + 80 ... + 180 ° С. When air passes through the device, it heats up. to the desired temperature. The fan not only distributes heated air throughout the room, but also contributes to its reverse removal.
Advantages and disadvantages

The use of air heaters in supply ventilation is cost-effective for enterprises and institutions that have their own heat supply system. However, with a well-established operation of the ventilation system, proper piping, water heaters can be used to heat cottages.
The advantages of such devices include the following:
- Installation is quite simple. In terms of complexity, it does not differ from the installation of heating pipes.
- Due to the heating of air masses and their uniform distribution by means of a fan, the system is suitable for heating rooms of a large area and height.
- The absence of complex mechanisms ensures the safe operation of each component node.There are no wearing parts in the design, so breakdowns are rare.
- With the help of a fan, you can control the direction of the flow of warm air masses.
- The main advantage is that regular financial investments are not required for heating a large room. The costs will be only at first - for the purchase of equipment and installation of the system.
The main disadvantage of using water heaters is the impossibility of their use for domestic purposes, namely for heating city apartments. As an alternative, only electric heaters are suitable. Electric induction boiler for heating and his scheme