- What is geotextile and dornite and why is it needed?
- What types of geotextiles are
- Geotextile for drainage (geotextile): technical characteristics and scope
- How to choose the density of geotextiles for drainage
- Technology of laying geotextiles for drainage
- Laying geotextiles in drainage tanks
- Which side to lay geotextile
- What it is
- How to choose geotextile? What is geotextile?
- SBNPs is applied:
- Benefits of SBNPs:
- SBNP-soil is applied:
- Non-woven geotextile AVTEX.
- Woven geotextile STABBUDTEX.
- Polyester geotextile Geomanit.
- The waterstop is a sealing tape
- Waterstops HydroContour.
- Waterstop Litaproof.
- Hydrostop AquaStop.
- Geotextile: do-it-yourself installation
- Tracks
- Video instruction for laying the track with step by step instructions
- Protecting beds from weeds
- Video instruction for protecting beds from weeds with geotextiles
- Ponds in the country
- Water pipes
- Geotextile for plumbing video guide
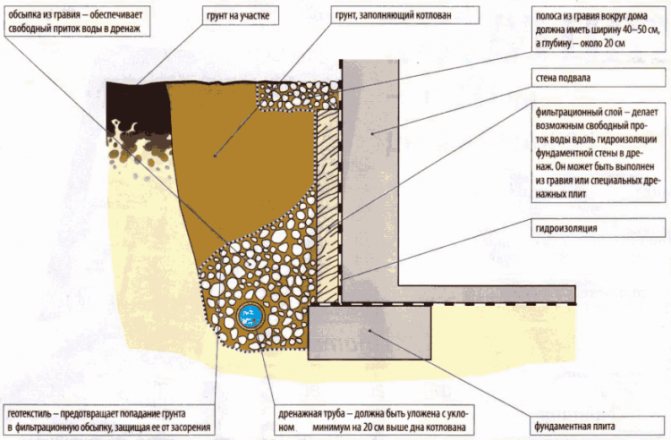
- Drainage around the house
- What is geotextile and how is it used, how to choose for drainage, laying in a photo
- Application
- Depending on the density
- Depending on raw material and production method
What is geotextile and dornite and why is it needed?
Geotextile - a non-woven, woven or knitted material, a fabric with high strength and other useful properties. Non-woven geotextiles are made from polypropylene or polyester (sometimes with the addition of fibers of plant or animal origin), by needle-punching or by thermal or chemical bonding of threads. Woven geotextiles (geotextile) - obtained by interlacing several threads (usually at right angles). Knitted geotextile (geo-knitwear) - loop weave. Depending on the method of production, the properties of geotextiles and the scope of its application change.
In general, all types of geotextiles have the following properties:
- elasticity - the material is resistant to stress and can perform a reinforcing function;
- elongation at break (up to 45%); tear and puncture resistance;
- filtering ability - the pores of the material are not silted up and are not clogged with soil particles;
- resistance to ultraviolet radiation, practically does not decompose, - environmentally friendly material.
In this regard, geotextiles are used where separation, partial reinforcement, drainage, and filtration are necessary. The areas of application of various geotextiles are very extensive - from medicine, household appliances, furniture production, packaging, to agriculture, construction of houses and roads.
Dornit is one of the varieties of geotextiles - domestic non-woven geotextiles. It is produced by a needle-punched method from polypropylene.
This material is characteristic in that it does not rot, mold and fungi, insects and rodents do not start in it, plant roots do not grow through it. It is chemically resistant, inert to the effects of chemical compounds in groundwater and soils.This material passes water well, but does not silt and is not clogged with soil particles. Dornit withstands heavy loads well; when used as a reinforcing material, it practically does not deform. Resistant to tearing and punctures. Isotropic - has equal properties in all directions. At breaks, it lengthens by 40-50%, that is, it continues to perform its functions. Its service life is at least 25 years. It retains its properties in the temperature range from - 60 to + 100 degrees C. Dornit can be fastened both mechanically and thermally.
Dornit is produced in rolls. 1.6-5.3 m wide, 50-150 m long, different density, from 90 to 800 g/sq.m.
Due to its special properties, dornit is used in the following areas:
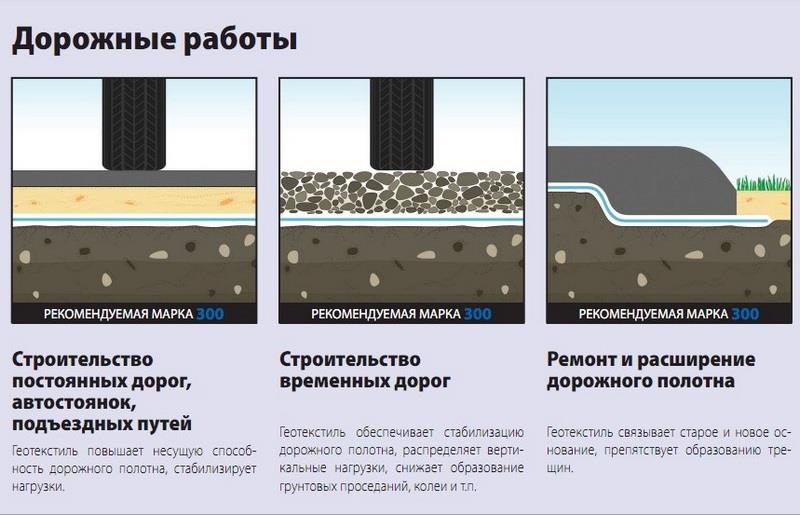
- In road construction, for separating layers. Its use can significantly reduce the cost of crushed stone and sand, which will be required much less. Dornit does not allow soil and bulk base to mix, increases the bearing capacity of the roadway, prevents the formation of ruts and cracking in the road surface. Compared to other geotextiles, dornite is more resistant to damage during installation.
- For strengthening slopes and slopes. Dornit, laid under the slabs, prevents soil from washing out at the junctions of the slabs, and also reduces tensile stress, stabilizing the slope.
- When arranging embankments - dornite separates the poured soil and the base.
- When creating decorative reservoirs or hydraulic structures, it prevents the mixing of soil and sand, the germination of roots, reinforces, redistributes the load.
- In drainage structures, drainage pipes are wrapped with dornite to prevent them from clogging.
- During the creation and operation of "green roofs". Dornit is laid under the soil layer for drainage, filtration and - to prevent the destruction of the fertile layer, allows the use of cheaper coarse-grained materials.
The material is easy to install, as the rolls are quite small. Therefore, transportation costs are also low. In the process of storage, transportation and laying, dornit does not absorb moisture, does not get moldy, it is not spoiled by rodents, etc.
When laying dornite, an overlap of 10-12 cm is made. The underlying surface is specially prepared (profiled and compacted, trees and shrubs are cut down at the same level with the surface) so that there are no irregularities of more than 5 cm. The rolls are rolled out manually in the longitudinal or transverse direction, periodically leveling and fastening to the ground with anchors (or in another way). If the canvases are pre-connected, this will reduce the amount of their overlap. When backfilling dornite, direct collision with the canvas should be avoided. Construction machinery can only pass after compaction of the minimum bulk layer.
What types of geotextiles are
Geotextiles can be of different types and, depending on the requirements of operation, are used in various conditions. Therefore, the main criterion for the classification of a geotextile is the material of its manufacture:
- polypropylene or polyester make it possible to produce the highest quality geofabric;
- from monofilament and staple raw materials, a product is obtained that has sufficient strength and quality suitable for use in most construction works;

The most popular geotextiles are dornit and non-woven geotextiles technonikol.
geotextiles made by thermal bonding cannot boast of special strength, as it is the thinnest of all the proposed options. However, it is he who has one of the best indicators when it comes to water resistance;
the use of blended yarns for the manufacture of geotextiles is not recommended, although such options are also commercially available. The thing is that cotton or woolen threads that get into the composition are very easy to rot. And this is a completely undesirable process when it comes to the construction or arrangement of drainage.
It is necessary to decide before choosing and buying geotextiles, where and in what works it will be used. Depending on this, the type of material from which it is made is selected. Which geotextile is better for drainage can be figured out by familiarizing yourself with its main technical characteristics.

Geotextile Dornit for drainage
Geotextile for drainage (geotextile): technical characteristics and scope
Geofabric for drainage or other systems is a material that has high performance:
- rigidity;
- elasticity;
- porosity.
It is these qualities that make it possible to use it for strengthening the soil, dividing the territory, filtering wastewater, protecting the slopes of the site, arranging drainage, etc.
The geofabric has gained particular popularity in Europe, where the construction of roads is indispensable without its use. The synthetic origin of the material allows it to maintain its characteristics for a long time, and its high strength allows it to withstand severe loads. Some manufacturers make geotextiles, the density of which is up to 250 kg per gap.

A characteristic feature of geotextiles is stiffness, elasticity and porosity.
When it comes to private or industrial construction, geotextile also has its place. It is widely used in urban sewer systems, in the construction of houses, railways, highways, gardening and drainage. What density of geotextiles is required for use in a particular area? For example, geofabric with a density of 200 g/m³ and higher is used for arranging drainage systems, about 100 g/m³ is enough for landscape work, and 800 g/m³ for the construction of runways for aircraft.
How this material works very simple: it is an interlayer that is used to separate two other layers from each other, while providing additional density. For example, it helps to significantly reduce the risk of failures on the road, and also prevents the erosion of the site by groundwater.
How to choose the density of geotextiles for drainage
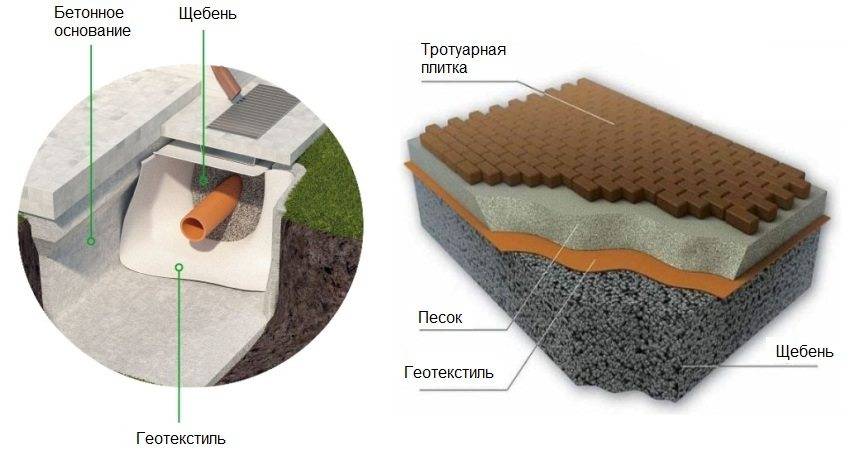
In drainage systems, geofabric plays a very important role - it prevents subsidence of the soil layer in the drainage system, and also prevents the process of crushed stone diffusion into the water. Geotextile acts as a filter that keeps the drainage pipe and materials from flooding.

Device drainage in the area
When thinking about which geotextile to choose for drainage, it is best to give preference to a material made from monofilament. It is easy to identify such material among others - it gives out a snow-white color. In this case, it is better if the fabric is made by thermal bonding.
If crushed stone is used as drainage, small stones can penetrate the material, creating damage in it.
It is worth paying attention to this when choosing a geofabric of the required density. The indicator for creating a drainage core will be at least 200 g / m³
If it is planned to wrap the drainage system, then geotextiles with a minimum density and thickness are suitable for this. At the same time, its water-repellent and other technical characteristics should be at the highest level.

Geotextile laying and preparation for installation of a drainage system
Technology of laying geotextiles for drainage
In order to understand how to use geotextiles in the process of arranging a drainage system, we will consider why it is needed and what types of it are. Based on the existing terrain, one of two drainage options is used:
- open;
- deep.
The first option is dug channels that are on the surface of the earth. They are easy to mount, but they have a rather unsightly appearance. If we are talking about arranging your own site, then this option can be called of little use.

Geotextile laying technology for drainage without crushed stone
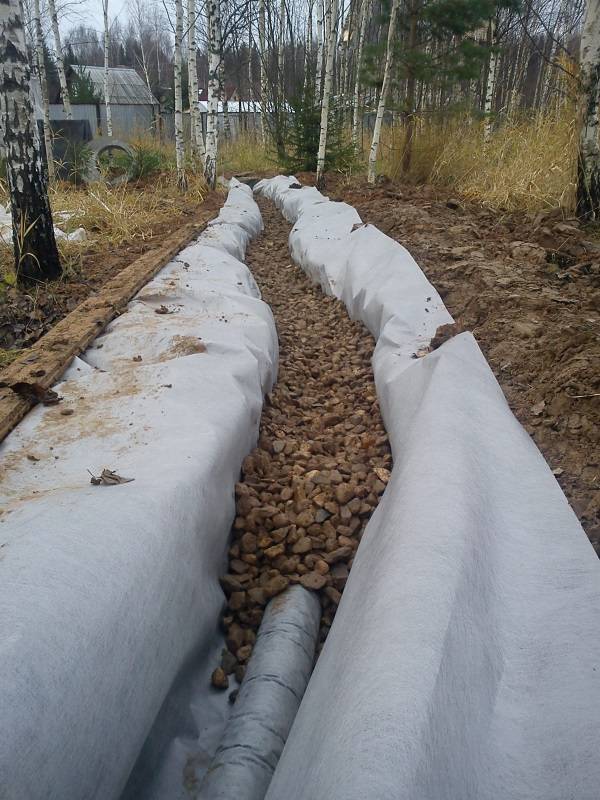
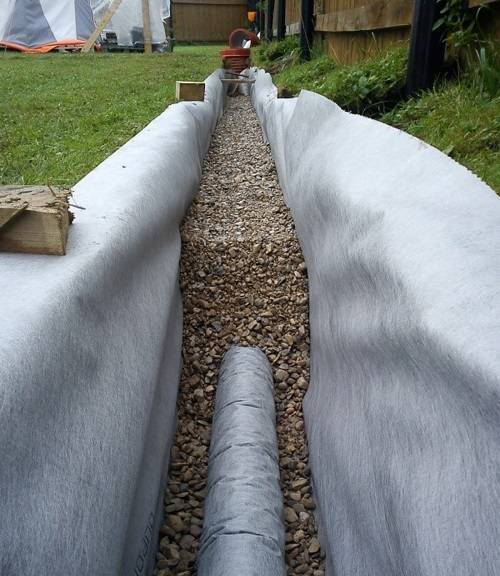
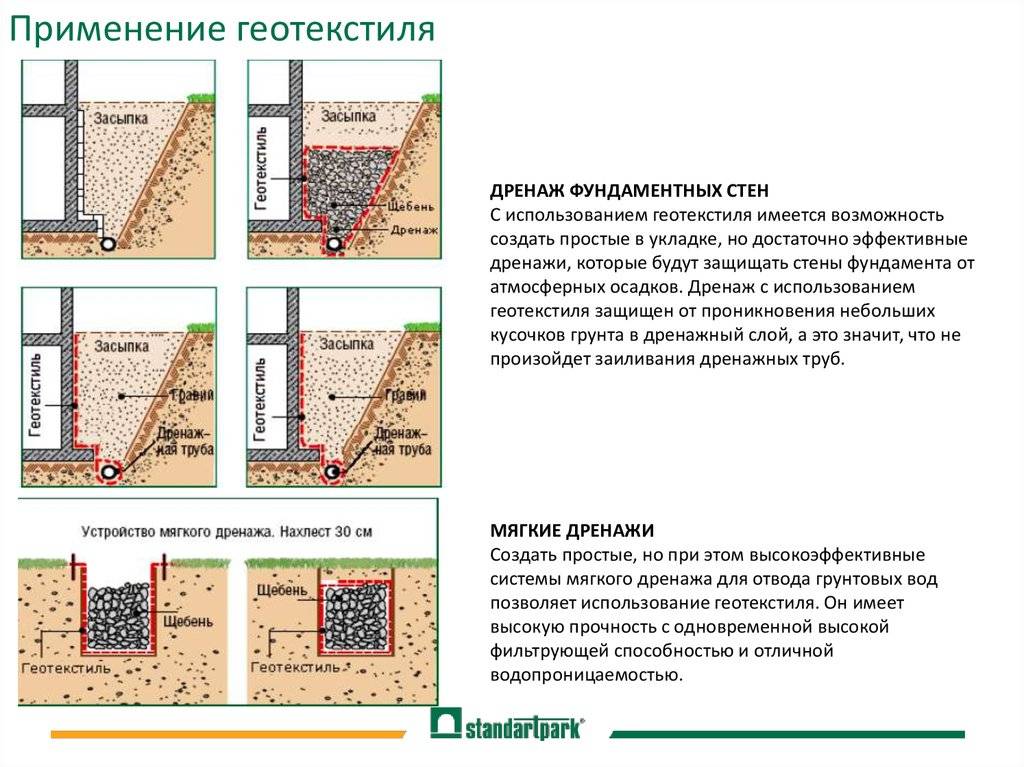
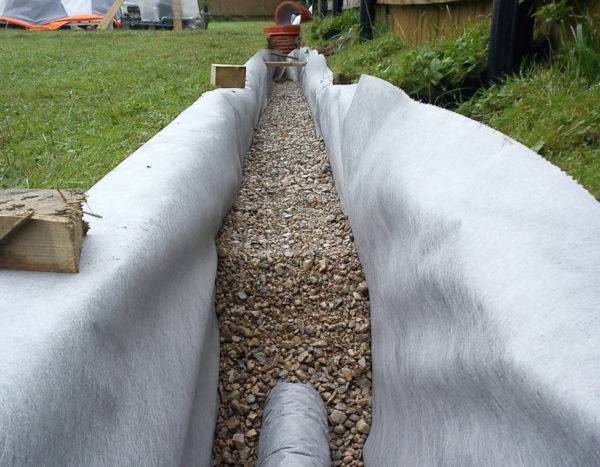
The deep system is not visible from the outside, as it is laid underground with the help of special pipes and deeply dug trenches. It is to ensure the safety of pipes, as well as to equip the inside of the tanks, that geotextiles are used.
As mentioned earlier, geofabric is widely used for arranging drainage systems in private plots and adjacent areas. Depending on the purpose and, accordingly, the density, the price of geotextiles for drainage will also vary.
Laying geotextiles in drainage tanks
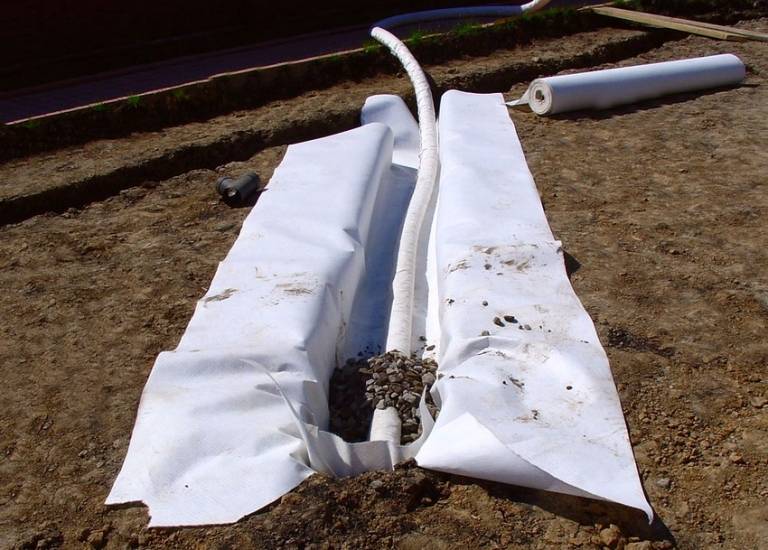
Another important condition that must be observed in order for the geotextile to fully fulfill its role is to properly lay it in the drainage system. To do this, there are rules, following which you can achieve the desired result:
- the bottom of the trench must be completely cleared of construction debris. The walls should be as even as possible;
- it is recommended to unpack the purchased geotextile immediately before laying, as the material is sensitive to sunlight;
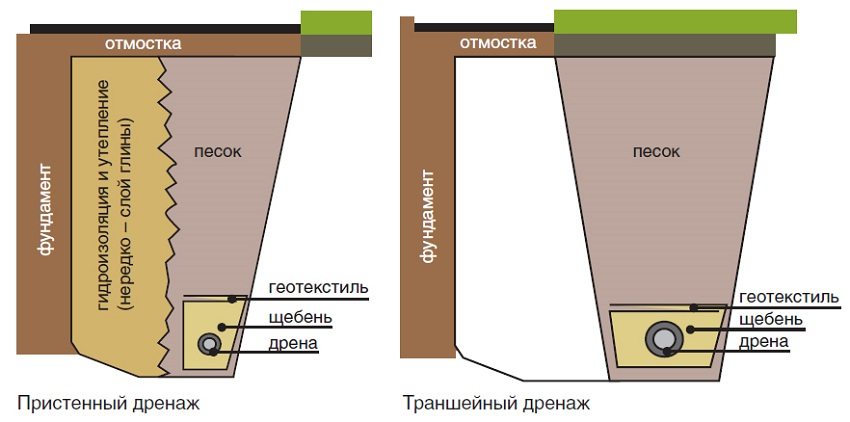
Scheme of laying attached and trench drainage
- if necessary, the canvas can be cut to the desired size before laying;
- geofabric must be overlapped;
- it is strictly forbidden to use those pieces of fabric that are damaged;
- laying should be done in such a way that the canvas is not stretched too tight. At the same time, the formation of waves and folds is also unacceptable;
- if we are talking about laying geotextiles for drainage on large surfaces, then at this time it is necessary to fix the already laid segments in order to avoid their displacement;
- in order to maintain integrity, as well as to minimize the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation, draining material should be poured into the trench immediately after laying;

A layer of crushed stone is laid on top of the canvas, preferably granite, which is not subject to erosion
- when the entire layer of drainage material is covered and compacted, the side edges of the geotextile should be wrapped inward. In this case, the free edges should have a length of at least 20 cm, this will help to avoid the possibility of contamination of the filler;
- when all the edges are wrapped as expected, you can fill the trench with earth.
Which side to lay geotextile
Another important question that arises in the process of work is which side to put geotextiles on? Even experts are divided here. Some of them argue that there is no significant difference, and the fact that one side is rough and the other smooth is just a cost of production. Reviews claim that no matter which side to lay the material, the characteristics of geotextiles remain unchanged.
Some manufacturers draw the attention of consumers to the fact that you need to lay the geofabric with the smooth side down. In this case, recommendations on which side to lay the geotextile in the drainage will necessarily be contained on the product packaging.

The use of geotextiles can increase the efficiency and durability of drainage systems
Another of the opinions on the question of which side to lay geotextiles suggests using a rough surface for better adhesion to the ground.
In any case, when deciding which side to put the geotextile on the ground, it is best to listen to the instructions of the manufacturer of the drainage geotextile you decide to buy.
What it is
 Most consumers under the terms "geofabric" and "geotextile" mean the same material.
Most consumers under the terms "geofabric" and "geotextile" mean the same material.
Indeed, these are two varieties of one geosynthetic.
They represent a canvas of polymer threads fastened by various methods.
For production use:
- polyolefins - polypropylene or polyethylene;
- polyester;
- polyamide;
- acrylic;
- occasionally, nylon and other polymers.
The most high-quality canvas is obtained from polypropylene and polyester fibers, materials based on them and are most widely used as rolled waterproofing for the foundation (technonikol).
The production technology allows the use of not only polymer monofilaments, but also the addition of textile waste - cotton and wool fibers - to the feedstock.
Material from mixed threads is cheaper, but inferior in quality to the canvas of their monofilaments.
The scope of mixed geotextile (geotextile) is limited due to the deterioration of performance.
How to choose geotextile? What is geotextile?

Nets for construction from basalt (SBNPs) are used in reinforcing cages of masonry walls and monolithic concrete when constructing a blind area for buildings and structures. Grids for road surfaces from basalt (SBNP) and grids (SBNP-soil) for strengthening subgrades and structures. Basalt fiber is the thinnest threads of durable basalt stone. Resistant to alkaline environment. It does not create a "cold bridge" in the wall. In asphalt concrete and soil, the loss of strength is 5% after 25 thaw cycles.
SBNPs is applied:
- reinforcement of brickwork in the wall;
- strengthening the concrete pavement of sidewalks and blind area;
- reinforcement of structures in earthquake-prone areas.
Benefits of SBNPs:
- resistance to aggressive environment;
- does not create a "cold bridge";
- adhesion with mortar and concrete;
- easy to process and cut;
- low cost.
SBNP-soil is applied:
- Reinforcement of the road subgrade;
- Strengthening of soils of the bases of the bases;
strengthening slopes with fertile soil with grass sowing.
Non-woven geotextile AVTEX.
Needle-punched fiber created from polyester threads. A multifunctional and versatile material that performs a reinforcing, drainage, filtering, strengthening function. Light weight, easy installation. It is applied at a temperature from-60 to +100 °.
Woven geotextile STABBUDTEX.
The fabric is woven from high-modulus polyester yarns with a strength of up to 220 kH/m. The width of the material is up to 10 m. It is not exposed to chemical and biological influences. It reinforces the structure of the roadbed of unpaved, concrete and asphalt concrete roads. Needle-punched non-woven polyester yarn. Designed to separate layers of pavement, filter and drain water. Serves as protection of loose surfaces from washouts and destructions. Ecological cleanliness and durability.
Polyester geotextile Geomanit.
Needle-punched from continuously interconnected threads of one hundred percent polypropylene. Due to its strength, resistance to biological and chemical influences, it is widely used in the construction of roads, reservoirs and engineering networks.
The waterstop is a sealing tape

Waterstops HydroContour.
Waterstops Hydrocontour are used for:
- Sealing of technological seams with PVC membranes;
- Waterproofing of external formwork joints no more than 25 mm;
- Formwork sealing of working joints, rubber, 196 mm;
- Central sealing of cold joints 250 mm wide.
Waterstop Litaproof.
The pro-thinned-out tape, is made of polyvinylchloride by an extrusion method.
- Internal for expansion joints.
- External for working seams.
- Combined with swellable hydrophilic cord.
- Angular and U-shaped.
Hydrostop AquaStop.
It consists of guides and a sealing profile made of rubber. Resistant to external influences. High strength and elasticity. Environmentally friendly.
Geotextile: do-it-yourself installation
So, geotextiles have several areas of application in the household:
- when laying underground water supply;
- as a material for greenhouses;
- the basis for an artificial reservoir in the country;
- weed protection;
- foundation laying;
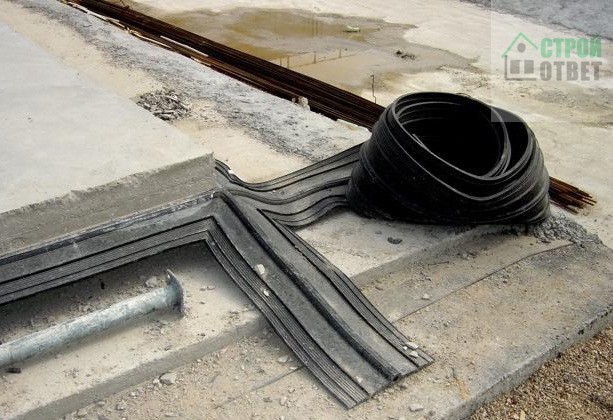
- laying paths from tiles.
The sequence of actions during the installation of geotextiles directly depends on the object of protection.
Tracks
Sidewalk paths to summer cottages are not subject to erosion, they look beautiful, but at the same time they need protection from subsidence.


To properly lay geotextiles for drainage, you need to perform the following steps:
- Mark the future track in length and width.
- Take out the soil level to a depth of 40-50 cm (if the earth is very humid, it is better up to 70 cm).
- Lay 1 layer of geofabric - it should completely cover the bottom, and the edges should protrude about 15 cm on each side.
- Next, a uniform layer of crushed stone is poured (4-5 cm)
- A 2nd layer of fabric is laid, and the overlap between the different parts should be at least 30-40 cm.
- Now a rather large (10-15 cm) layer of sand is filled up and also leveled.
- It is on this pillow that the tile itself is laid out.
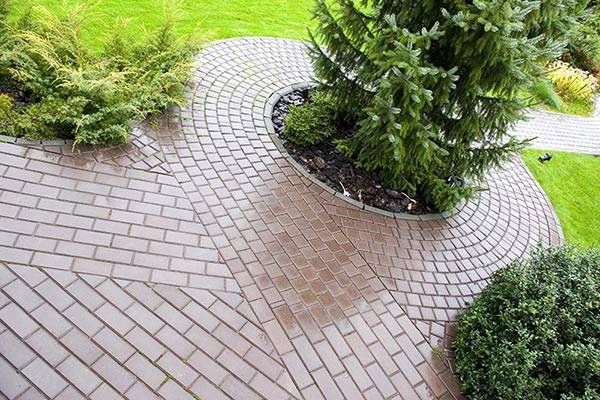

Strengthening with sand and gravel guarantees a long service life of the track even under constant loads. If the soil is swampy, then not 2, but 3-4 layers can be made using the same technology (alternating crushed stone and sand).
Video instruction for laying the track with step by step instructions
Protecting beds from weeds
To make life easier for yourself and not to engage in constant weeding of beds in the garden, you can lay a layer of geotextile directly on the soil before planting (preferably in early spring). The step-by-step algorithm in this case is as follows:
- A layer of geofabric with an overlap of at least 25-30 cm is placed on the surface of the future bed.
- At certain intervals, holes are cut (using ordinary sharp scissors) in accordance with the places where the crop will grow. For example, the interval for strawberries is about 20 cm, for bushes with tomatoes a little more - 25-30 cm.
- The fiber is attached to the bed using improvised methods - bricks, stones.
- Plants are planted in the hole.
Video instruction for protecting beds from weeds with geotextiles
- First, a small top layer of soil is removed.
- Then a layer of sand is poured (about 7-8 cm) and carefully leveled.
- Geofabric is laid on this layer, and black soil is poured on it.
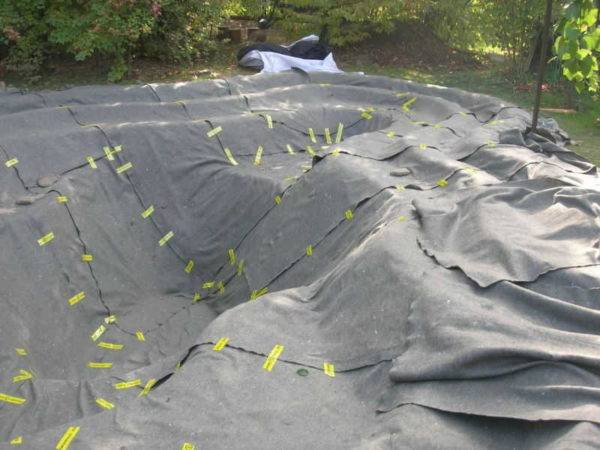
Ponds in the country
Having your own pond in the country is always relevant and beautiful.
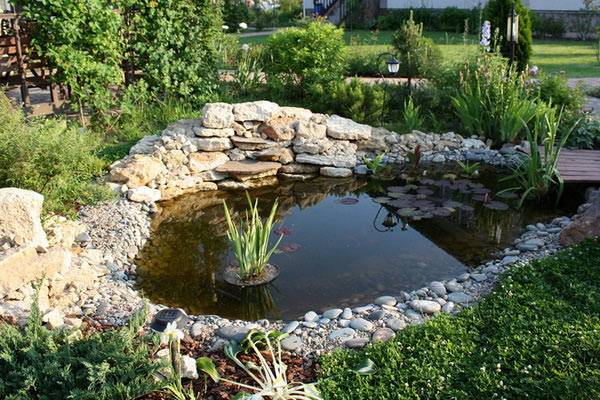


However, excess water can erode nearby soil layers. To avoid this, you need to act like this:
- In a pre-dug small pit, a layer of gravel and sand (5-6 cm each) is laid in succession.
- Next is the waterproofing.
- Geotextiles should be laid on it (standard overlap is about 30 cm).
- Geotextiles must be carefully fixed throughout (especially at the joints) with ordinary stones.
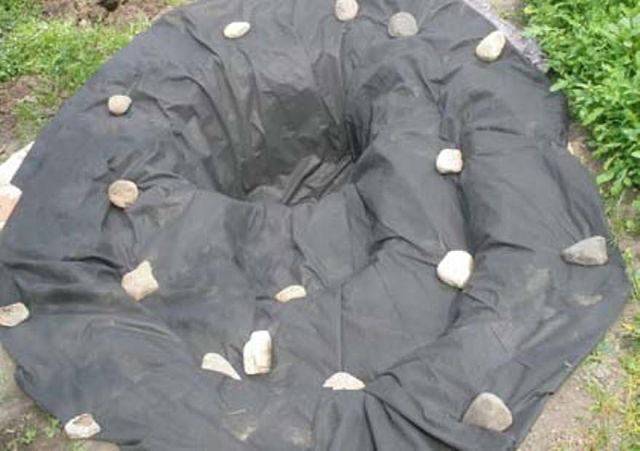

Water pipes
Finally, the use of geotextiles when laying underground water pipes in the country is an essential condition for its long-term trouble-free service.
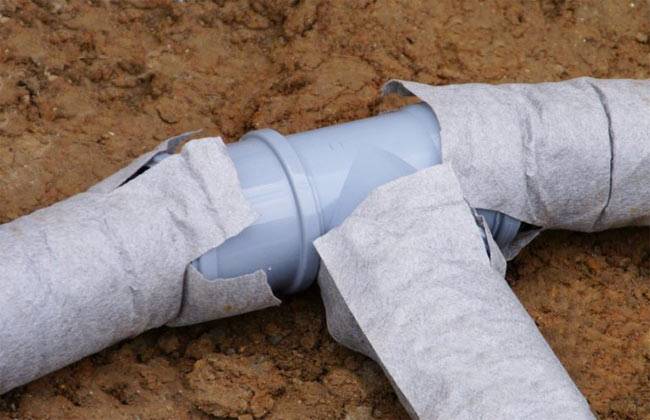

The fiber protects the pipe not only from moisture and rotting, but also from temperature changes, freezing, since the synthetic material creates a greenhouse effect, helping to retain heat.
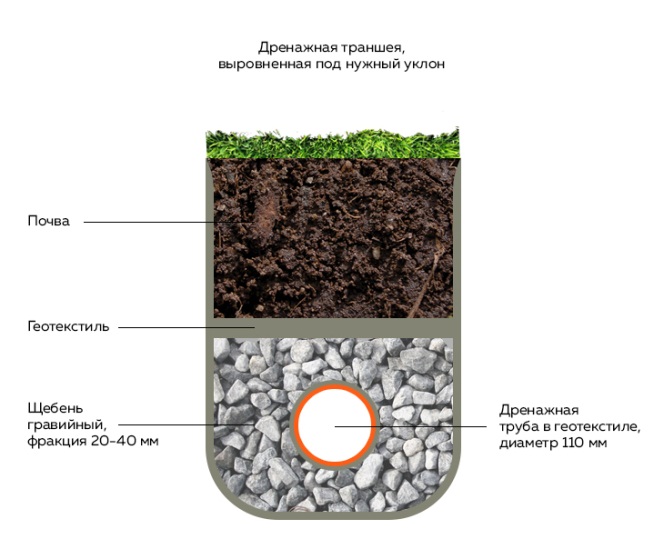
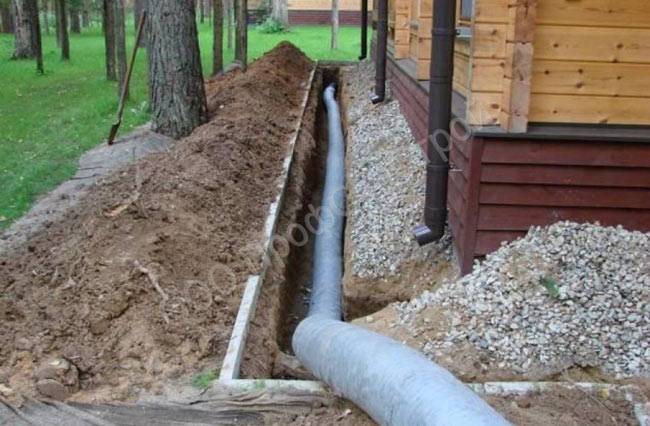
Drainage laying can be completely done with your own hands according to the following scheme:
- Agrofibre is lined in a previously dug trench.
- Crushed stone is laid on it in an even layer.
- Then the pipes themselves are mounted.
- As a result, the entire system is covered with geotextile, which is wrapped over and fixed at the edges with an overlap of at least 40 cm.
Geotextile for plumbing video guide
Drainage around the house
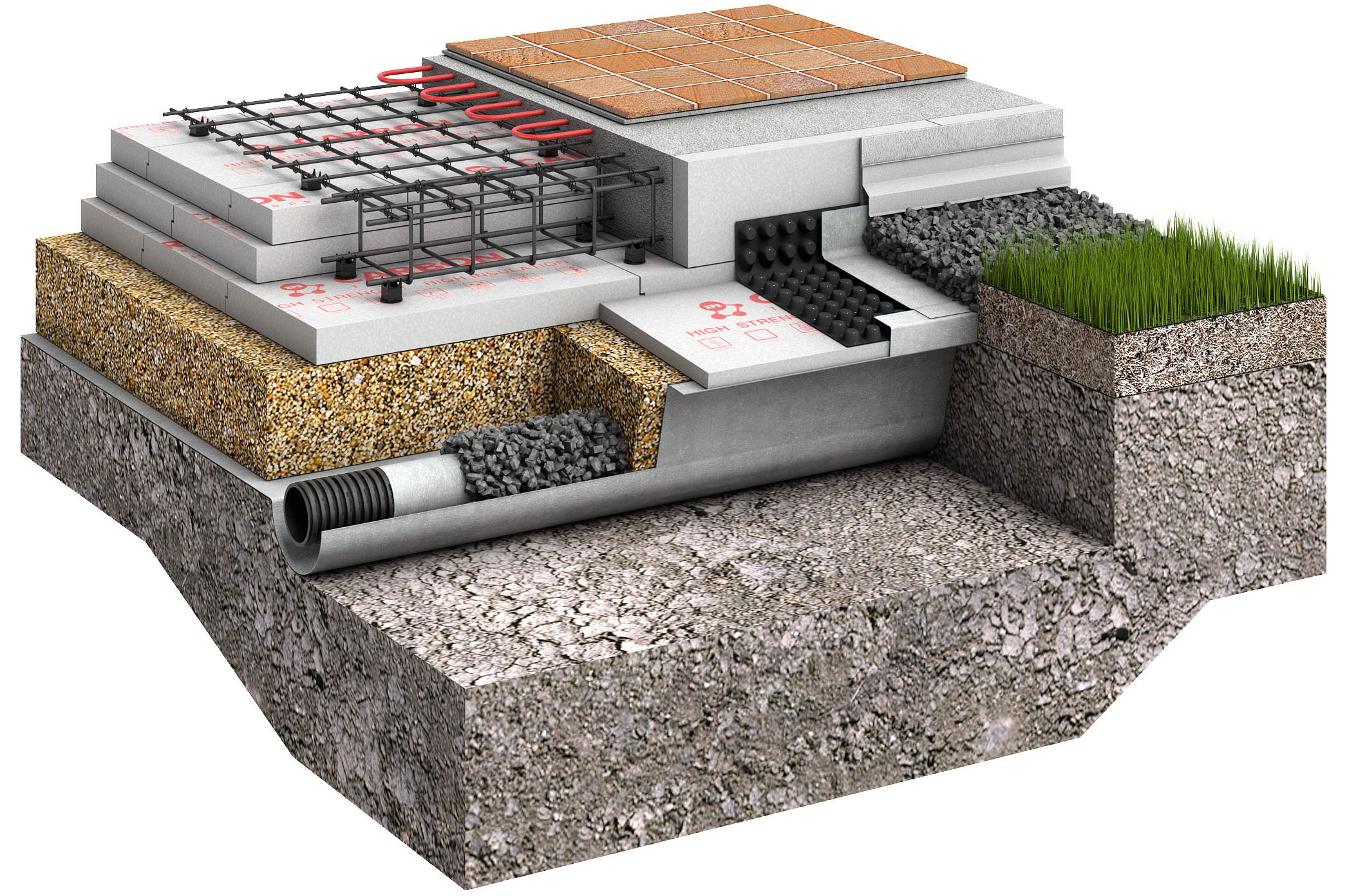
In places with high humidity, swampy soil, as well as in areas where groundwater passes nearby, the task of protecting a house or other buildings from water is very relevant. For this, a drainage system is made using high-density geotextiles around the building.

What is geotextile and how is it used, how to choose for drainage, laying in a photo
To answer this question, you need to understand the main types of material. This nonwoven fabric is classified according to the following criteria:
Basic properties and selection rules
How to choose a geotextile for drainage and which one is better to use in order for the system to work with maximum reliability? Here you need to take into account all the physical characteristics of the material, which will vary depending on the specific type of web. Among the main ones it is worth highlighting:
After the answer to the question of how geotextile is used and what it is, it remains only to decide which canvas should be chosen for the drainage system.

Laying drainage pipes using geotextiles
Experts recommend a material with the following characteristics:
Geotextile laying technology
Before laying geotextiles, it is necessary to clarify basic technological requirements for installation. In particular, it is believed that geotextiles are too susceptible to sunlight, so they are taken out of the package not in advance, but before direct installation. It is also recommended to cover the material with soil as soon as possible, without leaving it under the sun's rays. Proper preparation matters trenches - each of them must be with smooth slopes and without construction debris inside, because it can damage the coating.
The geotextile laying technology here involves the following steps:
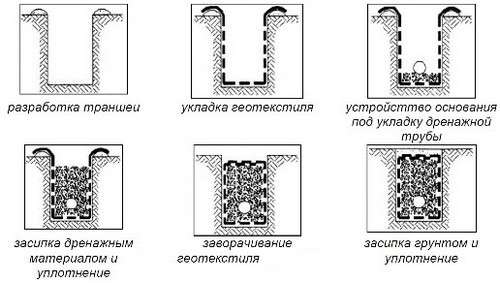
The photo shows the laying of geotextiles - step by step technology
All work on laying drainage pipes using geotextiles is carried out as quickly as possible. Thanks to the creation of such an effective system, silting of pipelines when draining the filtered liquid can be avoided.
Manufacturers and cost of geotextiles
Now, knowing the answer to the question, what is a geofabric and how it is laid, we will talk about how to choose a geotextile for drainage and which one is better to use. To determine the economic feasibility of using geotextiles, you need to choose the right material based on the cost factor. The price per square meter of geotextile will vary between 0.3-1 dollar and will depend on the brand, type of material and its performance characteristics.
Among the popular manufacturers are the Russian companies Dornit, Avantex, Geotex, Geopol, Gront, Montem, Nomotex.Foreign manufacturers are also widely represented on the market - the American company Typar, the Czech NETEX A, the English Terram, the Austrian Polifelt.
In general, the price of a geotextile suitable for use in drainage, low. You should not focus only on the cost or the country of origin. The advantages of geotextiles, suitable for the installation of high-quality drainage systems, are evaluated comprehensively - density and strength, manufacturing method and type of feedstock are taken into account. The selected material must correspond to the existing operating conditions and the functional purpose of the system, and the fame and popularity of the brand in this case fades into the background. Moreover, many domestic companies have successfully mastered the technology of low-cost production of high-quality geotextiles.
Overview Geotextile: what it is and how it is used, how to choose for drainage, laying.
Geotextile is a waterproof fabric characterized by high strength. Numerous 100% polypropylene fibers are used as a base.
The use of geotextiles has found distribution in various areas of construction. This became possible due to the high performance properties of the material. Geotextile is resistant to mold, fungi, it does not rot and rodents do not spoil it. The material does not lose its qualities when the temperature drops from -60 to +100 degrees. Geotextiles are characterized by high strength, resistance to chemicals and ultraviolet rays.

Application
Geotextiles have appeared recently, but are already used in various fields: in construction, landscape design, horticulture and horticulture, in the construction of footpaths, roads and runways. From the same material, only of low density, they make hygiene products, disposable medical clothing and underwear, and are used as rough upholstery for upholstered furniture. In general, the scope of geotextiles is very wide, and it is worth knowing which type is suitable for what purposes.
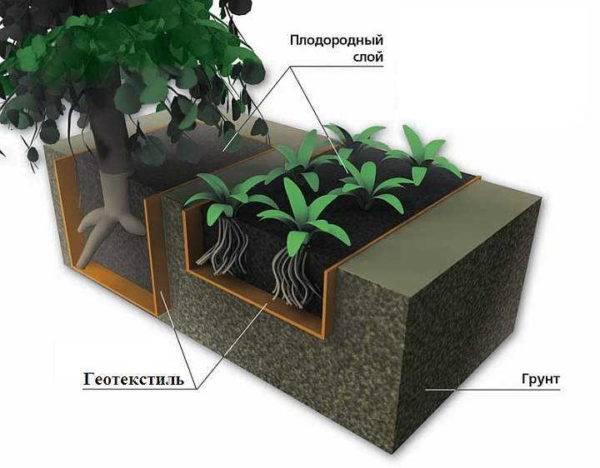
One of the types of application is in the arrangement of the site
Depending on the density
The cost of geotextiles can vary significantly. As you already understood, the price is formed depending on the material and method of production. But density also plays an important role. The same materials, but with different densities, have different prices. How to find out which geotextile is needed in a particular case? You can roughly navigate by this division by density:
- Up to 60-80 g / m2 - agrotextile or covering material. It can be used for protection against germination of weeds (geotextile against weeds). Usually used non-woven polyester. To avoid confusion, they usually write like this - agrotextiles.
- A density of about 100 g / m² is for drainage, but geofabric is undesirable, as it quickly “silts up”.
-
150 g/m² and above - for separation of fractions: sand and crushed stone. You can take denser ones, but less is not worth it.
- Geotextiles with a weight of 100 to 200 g / m² are used for arranging footpaths, under paving slabs, under lawns, to create alpine slides, etc.
- With a density of 200 to 300 g / m², they are placed under general roads, under a car parking area.
- Above 300 g/m² - for motorways, runways, etc.
These are just approximate boundaries.It is always worth choosing geotextiles, paying attention to specific conditions. For example, for hard and rocky soil, such a characteristic as elongation at break will be important. The better the material stretches, the less the possibility of rupture when "fitting" bumps and protrusions.

When constructing ponds, pools
When choosing geotextiles for construction work and under roads / paths, parking lots, sites, see that there is a high breaking load (tensile strength). This characteristic can be neglected if you form uneven terrain, but there will be no load on them.
Depending on raw material and production method
Thermally bonded geotextiles have high tensile strength but only wick water in the transverse direction. That is, it can be used in areas with low groundwater levels, on well-drained soils. It is good as a separator of different fractions and materials when arranging platforms, for footpaths made of various materials, and is suitable for changing the landscape. But all this - in areas with good drainage. It is not very suitable for drainage systems - water is not drained well enough.
Needle-punched is less durable, but water passes both in the longitudinal and transverse directions. It is suitable for laying on heavy soils that do not drain water well - loams, clays. The lack of strength can be compensated by laying a geogrid on the bottom - another type of geosynthetics. It will take on the main loads, and the geotextile will not allow fractions to mix. This type can be used in drainage. The optimal density of drainage geotextile in terms of price / quality ratio is 200 g / m².

Geotextile for drainage.Properties: elasticity and strength, resistance to heavy loads and mold, long shelf life, ease of installation, fire safety and non-toxicity, resistance to ultraviolet rays
Woven geotextile is very durable, has high tensile strength. It is ideal for creating embankments, changing the landscape, creating retaining walls. And the load withstands without question. It is not recommended to use it in drainage - the gaps between the threads are quickly clogged with small particles, which worsens the drainage of water.