- Types of RCD
- Electromechanical RCD
- Electronic RCD
- RCD portable and in the form of a socket
- RCD with overcurrent protection (difavtomat)
- Power calculation for RCD
- Calculating power for a simple single-level circuit
- We calculate the power for a single-level circuit with several protection devices
- We calculate the power for a two-level circuit
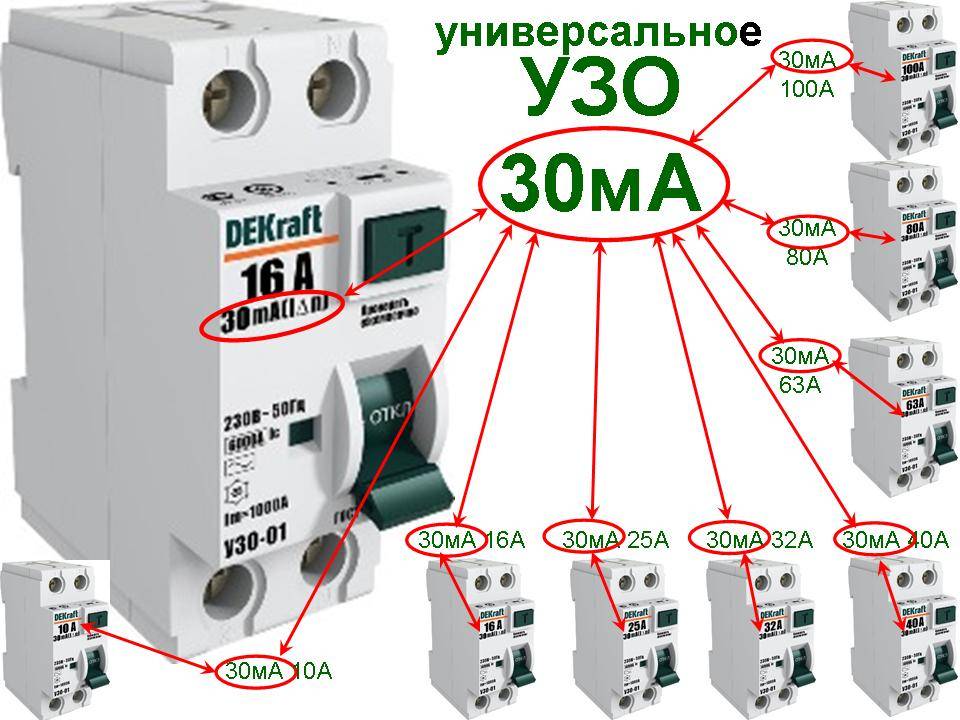
- RCD power table
- Purpose
- RCD selection criteria
- Rated current
- Leakage current
- Table: Dependence of the recommended RCD leakage current on the rated load current
- Varieties of residual current devices
- RCD design
- Residual current device manufacturers
- Protection options for a single-phase network
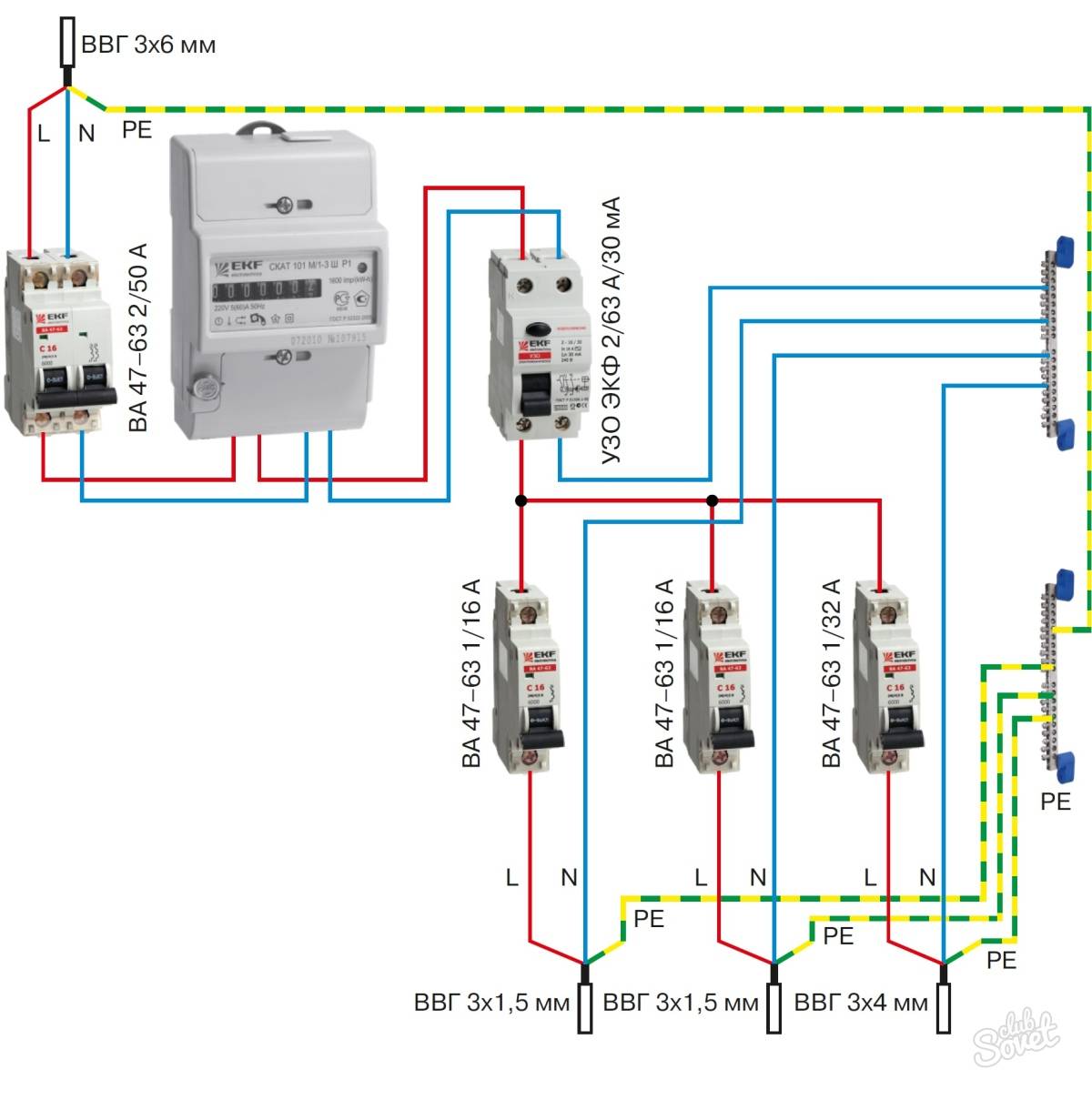
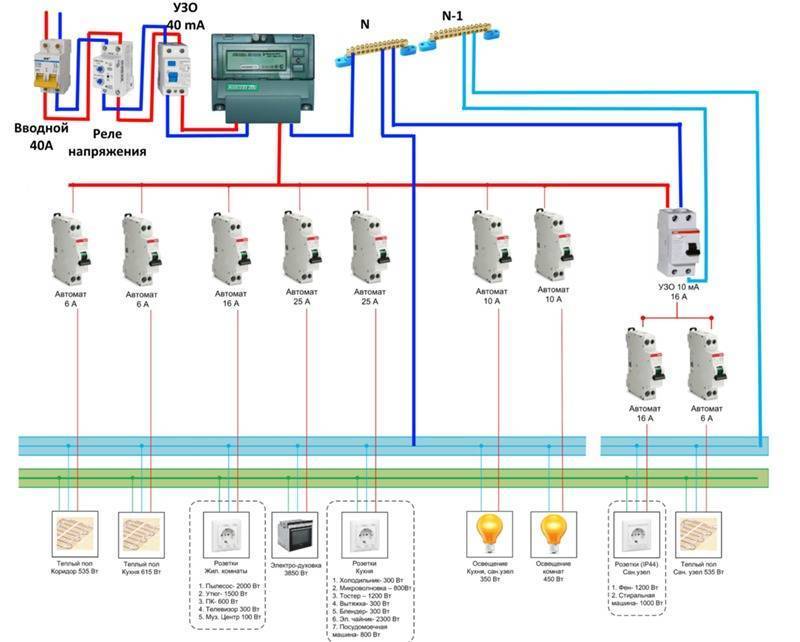
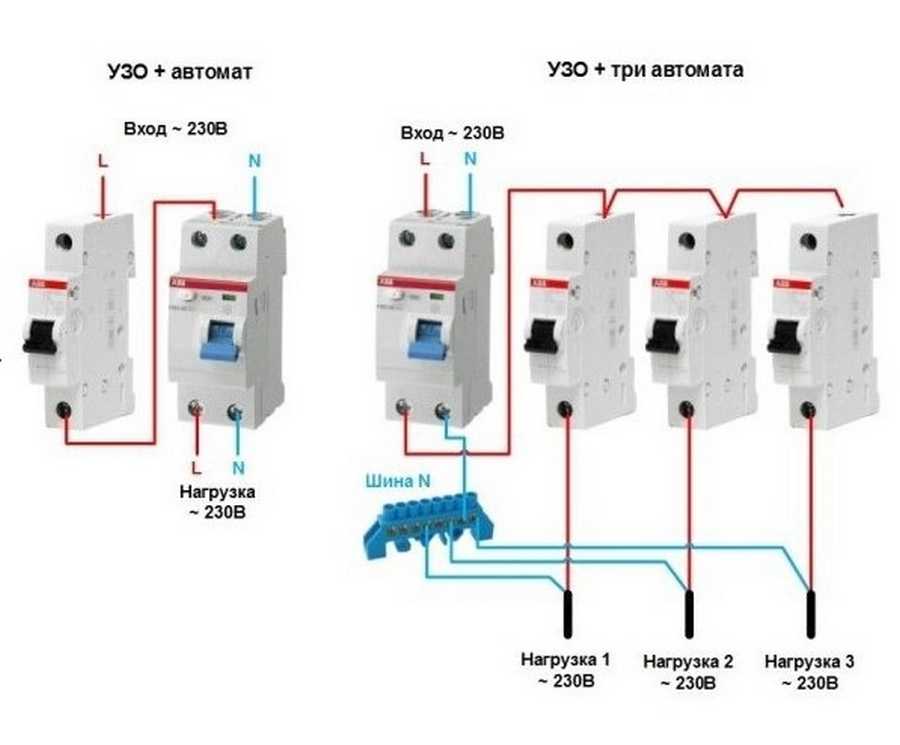
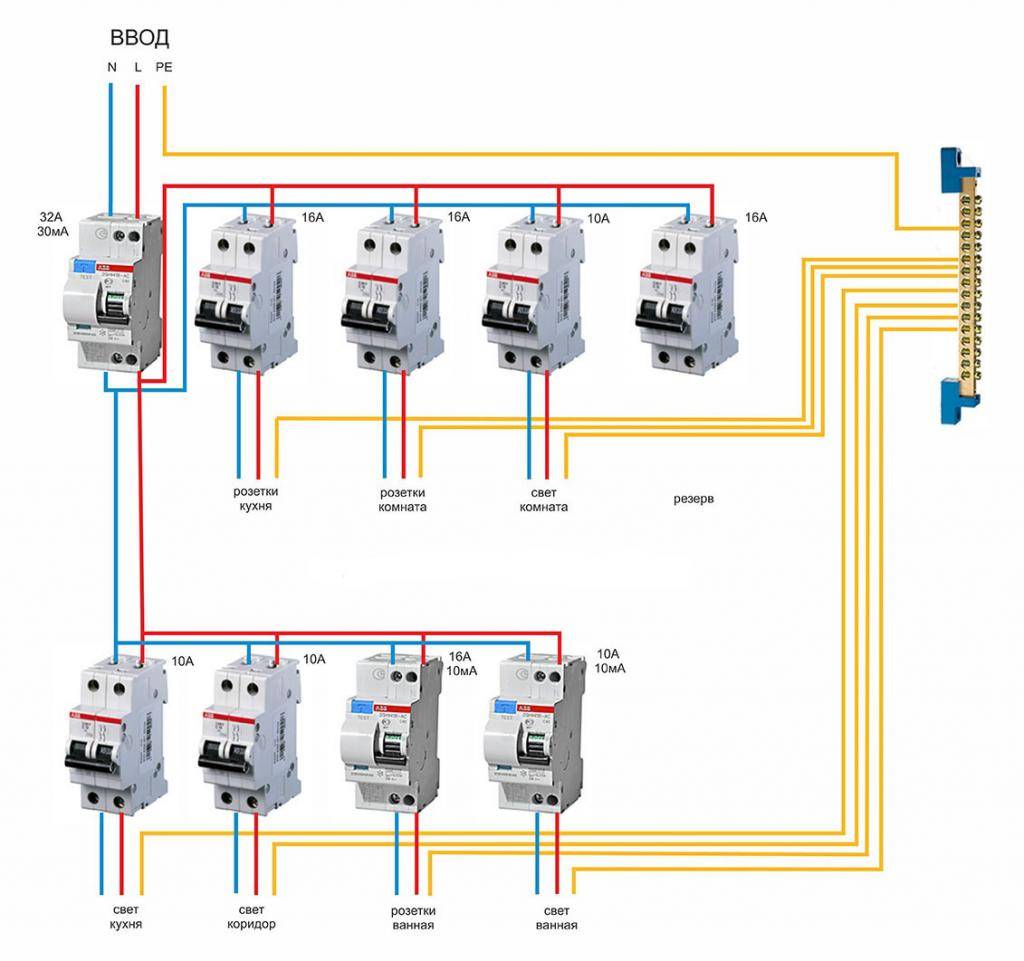
- Option #1 - common RCD for 1-phase network.
- Option #2 - common RCD for 1-phase network + meter.
- Option #3 - common RCD for 1-phase network + group RCD.
- Option #4 - 1-phase network + group RCDs.
- Trademark
- Leakage current and general protection circuit
- Calculation examples
- Selectivity
- Is it possible to install an RCD without grounding?
Types of RCD
Parameters by which protective devices can be subdivided:
- Control method - dependent and independent of voltage;
- Purpose - with built-in overcurrent protection and without it;
- Installation method - stationary and independent;
- The number of poles is two-pole (for a single-phase network) and four-pole (for a three-phase network).
Electromechanical RCD
Electromechanical RCD - "veteran" protection against current leakage. The device was patented back in 1928. In most European countries, it is the electromechanical safety device that is mandatory for use as protection against residual current.
The presence of voltage for the performance of an electromechanical RCD does not matter. The source of energy for performing protection functions is the leakage current, to which the circuit breaker reacts.
The basis of the device is the accuracy and reliability of mechanics. The magnetic core of the transformer has high sensitivity, as well as temperature and time stability. It is produced from nanocrystalline or amorphous alloys, which are characterized by high magnetic permeability.
Advantages:
- Reliability - a serviceable device guarantees 100% operation in case of current leakage, regardless of the presence of voltage in the network;
- Retains functionality even if the neutral conductor breaks;
- It has a simpler design, which increases the reliability of the switch;
- Does not require auxiliary power sources.
Flaws:
High price (depending on the brand, the price can be three times or even five times higher than the price of an electronic device).
Electronic RCD
Inside the device there is an amplifier on a microcircuit or a transistor, due to which the switch is triggered even if a slight current occurs in the secondary winding. The amplifier ramps it up to the pulse size needed to activate the relay. But for the operability of the elements of an electronic RCD, the presence of voltage in the network is necessary.
The question arises of the need for an RCD in the absence of voltage in the network.What to protect yourself from? If the voltage is lost due to a break in the neutral conductor in the circuit to the RCD, then a dangerous potential for humans continues to flow to the electrical installation through the phase conductor.
Advantages:
- Low price;
- Compactness.
Flaws:
- Operates only when voltage is present;
- Inoperable when the neutral is broken;
- A more complex design increases the likelihood of circuit breaker failure.
RCD portable and in the form of a socket
A simple solution that can protect against leakage current is portable RCDs and in the form of a socket. They are convenient when used in the bathroom and other rooms with high humidity, they can be connected to any of the rooms of the apartment, where necessary.
Most of the proposed models are made in the form of a power adapter with a socket hole for a plug. Even a child can use such a device - it is connected directly to the outlet, and then the appliance is turned on.
Easy to use and extension cords with RCD function, designed for several consumers.
There are models that are less versatile, they can be used after being installed on the cord of an electrical appliance instead of a plug, or they can be installed instead of a conventional electrical outlet.
Advantages:
- Installation does not require intervention in the wiring;
- Installation does not require the assistance of an electrician;
- The operation of automation allows you to determine in which consumer the insulation is damaged.
Flaws:
- Using the adapter in visible places brings disharmony to the design of the room;
- In a room that is cluttered with furniture and electrical appliances, and the space in front of the outlet is limited, there may not be free space for installing the adapter;
- High cost - a quality adapter will cost more than an RCD and socket purchased separately.
RCD with overcurrent protection (difavtomat)
The device combines the functions of an RCD and a circuit breaker, which is designed to protect against overcurrents (prevents wiring from overload and damage during a short circuit).
Advantages:
- Profitability - buying one device will cost less than two;
- Takes up less space in the dashboard;
- Saving time during the installation process.
Flaws:
- When the circuit breaker fails, the line will be unprotected both from leakage currents and from overcurrents;
- In the event of a device tripping, there is no way to determine what caused it - overcurrents or leakage current;
- False positives caused by office equipment. It is not recommended to install difavtomatov on the line to which computers and office equipment are connected.
Power calculation for RCD
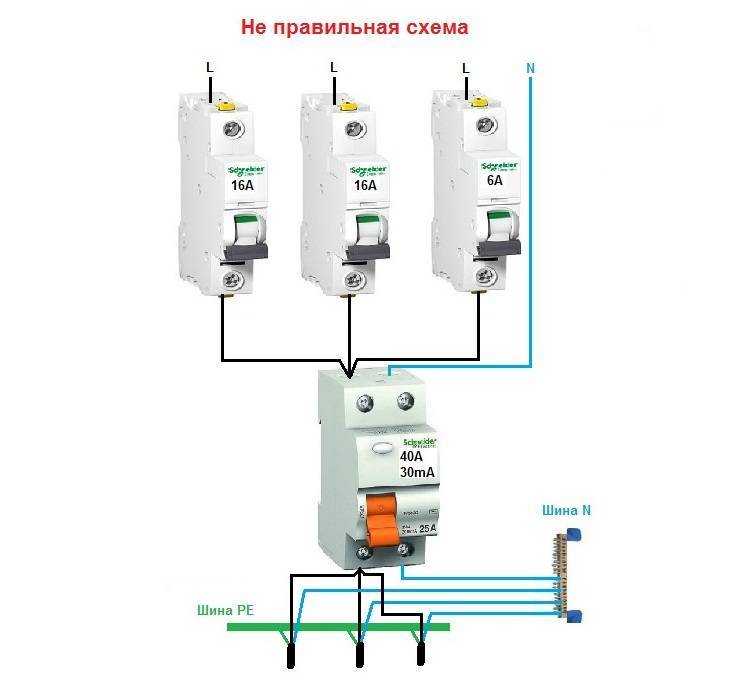
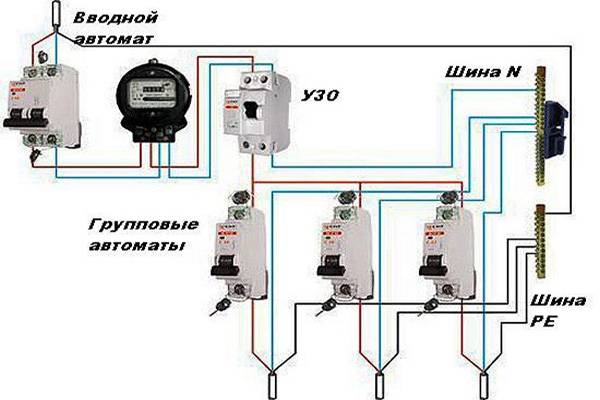
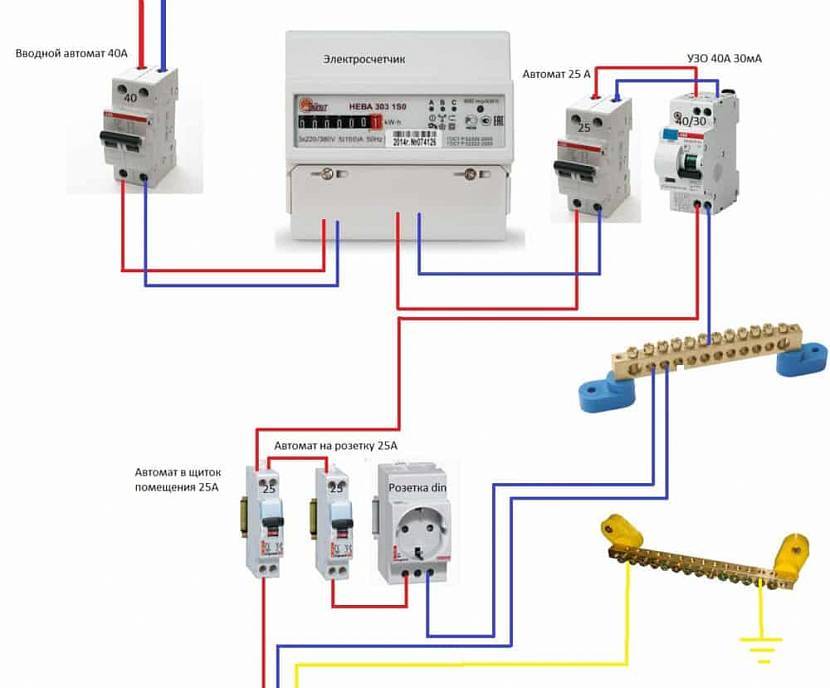
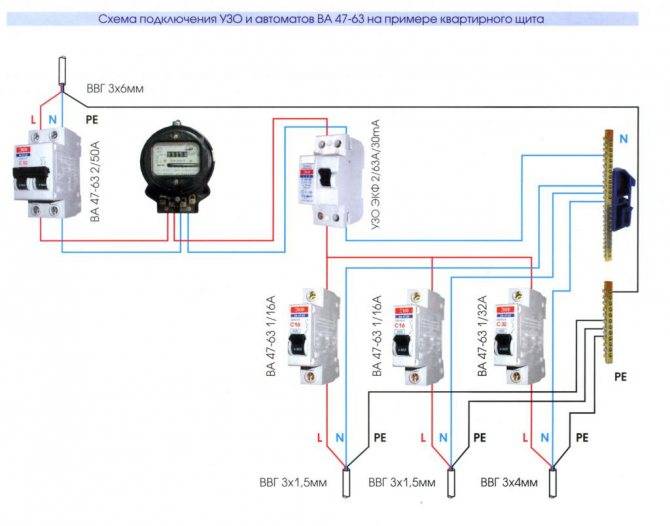
Each individual device has its own threshold current load, at which it will work normally and will not burn out. Naturally, it must be higher than the total current load of all devices connected to the RCD. There are three types of RCD connection schemes, for each of which the calculation of the power of the device is different:
- A simple single-level circuit with one protection device.
- Single-level scheme with several protection devices.
- Two-level trip protection circuit.
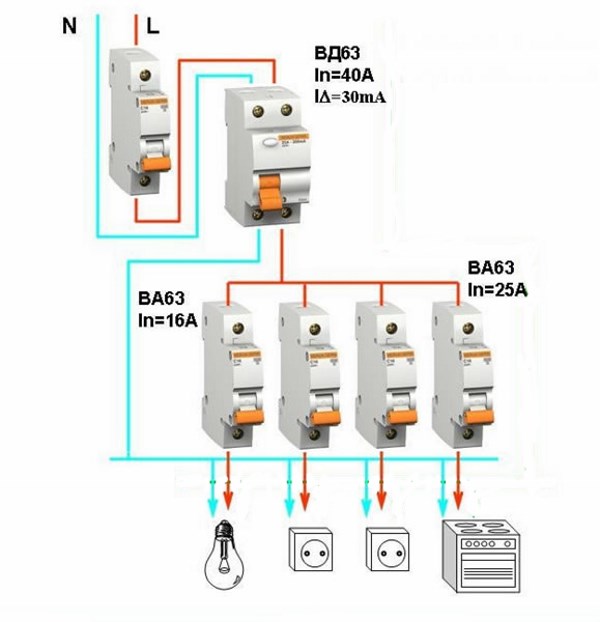
Calculating power for a simple single-level circuit
A simple single-level circuit is characterized by the presence of one RCD, which is installed after the counter. Its rated current load must be higher than the total current load of all consumers connected to it.Suppose the apartment has a boiler with a capacity of 1.6 kW, a washing machine for 2.3 kW, several light bulbs with a total of 0.5 kW and other electrical appliances for 2.5 kW. Then the calculation of the current load will be as follows:
(1600+2300+500+2500)/220 = 31.3 A
This means that for this apartment you will need a device with a current load of at least 31.3 A. The nearest RCD by power at 32 A. It will be enough even if all household appliances are turned on at the same time.
One such suitable device is the RCD ERA NO-902-126 VD63, designed for a rated current of 32 A and a leakage current of 30 mA.
We calculate the power for a single-level circuit with several protection devices
Such a branched single-level circuit assumes the presence of an additional bus in the meter device, from which wires depart, forming into separate groups for individual RCDs. Thanks to this, it is possible to install several devices on different groups of consumers or on different phases (with a three-phase network connection). Usually a separate RCD is installed on the washing machine, and the rest of the devices are mounted for consumers, which are formed into groups. Suppose you decide to install an RCD for a washing machine with a power of 2.3 kW, a separate device for a boiler with a power of 1.6 kW and an additional RCD for the rest of the equipment with a total power of 3 kW. Then the calculations will be as follows:
- For a washing machine - 2300/220 = 10.5 A
- For a boiler - 1600/220 = 7.3 A
- For the rest of the equipment - 3000/220 = 13.6 A
Given the calculations for this branched single-level circuit, three devices with a capacity of 8, 13 and 16 A will be required.For the most part, such connection schemes are applicable for apartments, garages, temporary buildings, etc.
By the way, if you don’t want to bother with installing such a circuit, then pay attention to portable RCD adapters that can be quickly switched between sockets. They are designed for one appliance.
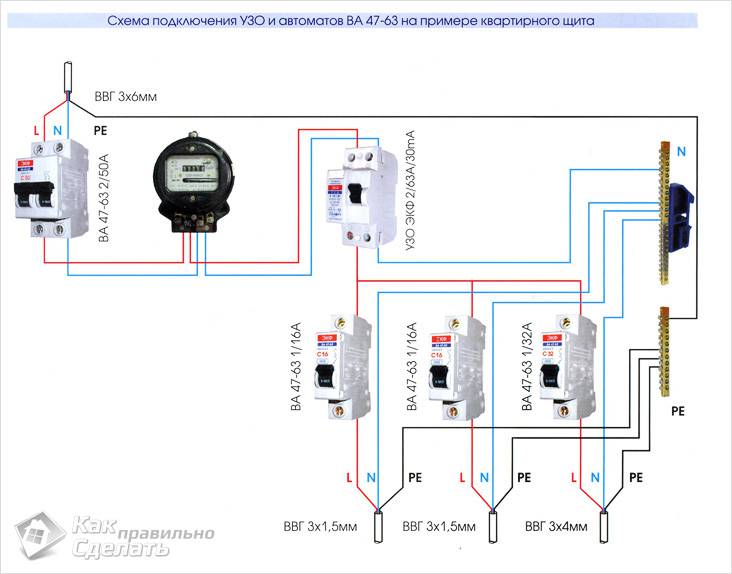
We calculate the power for a two-level circuit
The principle of calculating the power of a residual current device in a two-level circuit is the same as in a single-level one, with the only difference being the presence of an additional RCD located at the entrance to the apartment, up to the meter. Its rated current load must correspond to the total current load of all devices in the apartment, including the meter. We note the most common RCD indicators for current load: 4 A, 5 A, 6 A, 8 A, 10 A, 13 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A, etc.
The RCD at the input will protect the apartment from a fire, and the devices installed on individual groups of consumers will protect a person from electric shock. This scheme is the most convenient in terms of repairing electrical wiring, as it allows you to turn off a separate section without turning off the whole house. Also, if you need to repair cable systems at the enterprise, you will not have to turn off all office premises, which means there will be no massive downtime. The only drawback is the considerable cost of installing an RCD (depending on the number of devices).
If you need to choose an RCD for a group of machines for a single-phase network, then we can advise the ERA NO-902-129 VD63 model with a rated current load of 63 A - this is enough for all electrical appliances in the house.
RCD power table
If you are thinking about how to easily and quickly select an RCD by power, the table below will help you with this:
| Total load power kW | 2.2 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 7 | 8.8 | 13.8 | 17.6 | 22 |
| Type of RCD for 10-300 mA | 10 A | 16 A | 25 A | 32 A | 40 A | 64 A | 80 A | 100 A |
Purpose
The most important thing to understand is that the circuit breaker protects the electrical network from overcurrents, and the RCD provides human protection. If, as a result of an insulation breakdown, a potential has appeared on the body of an electrical appliance, when touching it, there is a possibility of receiving an electric shock. To prevent this from happening, immediately in the event of a current leakage, the residual current device will react and turn off the damaged section of the circuit.
It's important to know! RCD does not protect against overloads and short circuits, therefore, circuit breakers must be connected in series with them in the circuit.
RCD selection criteria
When looking for a suitable protective shutdown, the first thing to look at is the rated and residual current
After that, attention is focused on the type and design of the device, and they also find out which company produced the RCD.
Rated current
Masters specializing in working with electricity are advised to buy a residual current device with a rated current an order of magnitude higher than the calculated one. Thanks to this, it will be possible to achieve reliability in the operation of the differential current switch and for a long time not to repair or replace it. For example, for a 40 A machine, it is more expedient to choose an RCD for 63 A.
Leakage current
Nominal differential breaking current RCD must have a value of at least 3 times more current leaks in the circuit of electrical equipment protected from incidents, i.e., the condition IDn> = 3*ID must be met.
The total leakage current of the electrical installation ID is determined by a special device or calculated using certain data. If it is not possible to take measurements, it is recommended to determine the leakage current at the rate of 0.4 mA per 1 A of load current, and the circuit leakage current at the rate of 10 μA per 1 m of the length of the phase conductor.
Acceptable values of rated breaking current can be found in a special table.
Table: Dependence of the recommended RCD leakage current on the rated load current
| Rated load current in the protection zone, A | 16 | 25 | 40 | 63 | 80 |
| IDn when working in the protection zone of a single consumer, mA | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 100 |
| IDn when working in the consumer group protection zone, mA | 30 | 30 | 30(100) | 100 | 300 |
| IDn RCD for fire protection at ASU, mA | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
Varieties of residual current devices
The residual current circuit breaker can be one of the following types:
- AC. Such devices respond exclusively to alternating electric current, that is, they are designed to control the functioning of lighting, underfloor heating and small household appliances;
- A. RCDs of this class respond to both alternating and pulsating direct current that feeds household appliances such as refrigerators, computer system units and other electronically controlled devices;
- B. These residual current devices are used only in industrial plants.
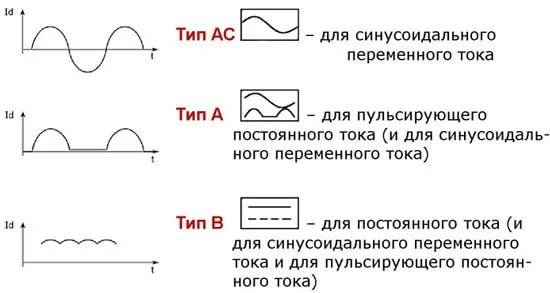 RCD type B is quite rare, on its case you can see the icon in the form of solid and dotted straight lines
RCD type B is quite rare, on its case you can see the icon in the form of solid and dotted straight lines
RCD design
If we consider the design of residual current devices, they are divided into the following types:
- electronic RCDs with a built-in board that instantly responds to any changes in the set parameters and turns off the power from the network, but is not able to work without power from an external source;
- electromechanical RCDs, which are reliable because they do not need power and are easily triggered in response to the appearance of a differential current.
Residual current device manufacturers
According to electricians, the most durable and reliable residual current devices produced under the following names:
- ABB is a product of a Swedish-Swiss company that has become a leader in the manufacture of electrical appliances, as it creates them with high quality and safety;
- Legrand is a French brand whose products are in no way inferior to ABB in quality, but are quite expensive;
- Schneider Electric is a French brand that has won the sympathy of many electrical service professionals;
- Siemens is a huge concern, the main specialization of which is the manufacture of appliances used in everyday life (it differs from other companies in less emphasis on product quality);
- Moeller - German products that meet all quality standards and are actively used in Russia;
- IEK - products whose quality is acceptable, and the price is low;
- Kontaktor is a company with a good reputation in the Russian market, since it produces devices at a plant owned by Legrand;
- DEKraft is a Russian company that has relatively recently begun to produce low-quality electrical appliances at a low price.
Protection options for a single-phase network
Manufacturers of powerful household appliances mention the need to install a set of protective devices.Often, the accompanying documentation for a washing machine, electric stove, dishwasher or boiler indicates which devices need to be additionally installed in the network.
However, more and more often several devices are used - for separate circuits or groups. In this case, the device in conjunction with the machine (s) is mounted in a panel and connected to a certain line
Considering the number of different circuits serving sockets, switches, equipment that loads the network to the maximum, we can say that there are an infinite number of RCD connection schemes. In domestic conditions, you can even install a socket with a built-in RCD.
Next, consider the popular connection options, which are the main ones.
Option #1 - common RCD for 1-phase network.
The place of the RCD is at the entrance of the power line to the apartment (house). It is installed between a common 2-pole machine and a set of machines for servicing various power lines - lighting and socket circuits, separate branches for household appliances, etc.
If a leakage current occurs on any of the outgoing electrical circuits, the protective device will immediately turn off all lines. This, of course, is its minus, since it will not be possible to determine exactly where the malfunction is.
Suppose that a current leakage has occurred due to the contact of a phase wire with a metal device connected to the network. The RCD trips, the voltage in the system disappears, and it will be quite difficult to find the cause of the shutdown.
The positive side concerns savings: one device costs less, and it takes up less space in the electrical panel.
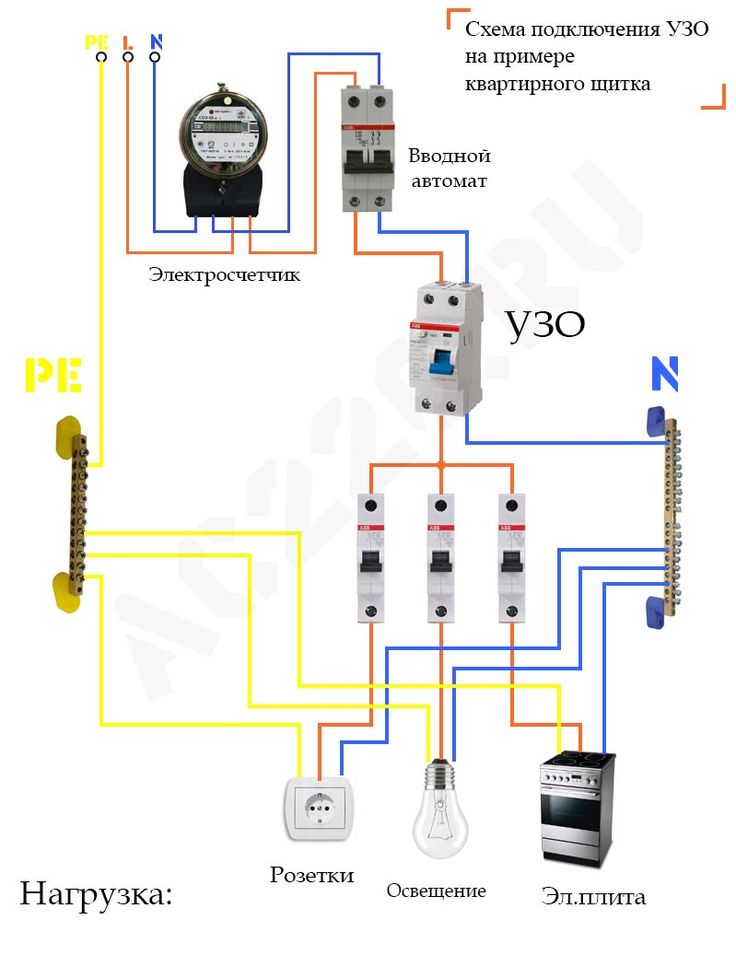
Option #2 - common RCD for 1-phase network + meter.
A distinctive feature of the scheme is the presence of an electricity meter, the installation of which is mandatory.
Current leakage protection is also connected to the machines, but a meter is connected to it on the incoming line.
If it is necessary to cut off the power supply to an apartment or house, they turn off the general machine, and not the RCD, although they are installed side by side and serve the same network
The advantages of this arrangement are the same as those of the previous solution - saving space on the electrical panel and money. The disadvantage is the difficulty of detecting the place of current leakage.
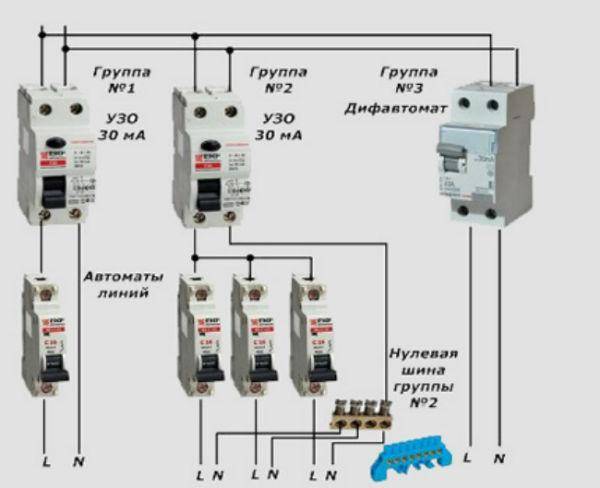
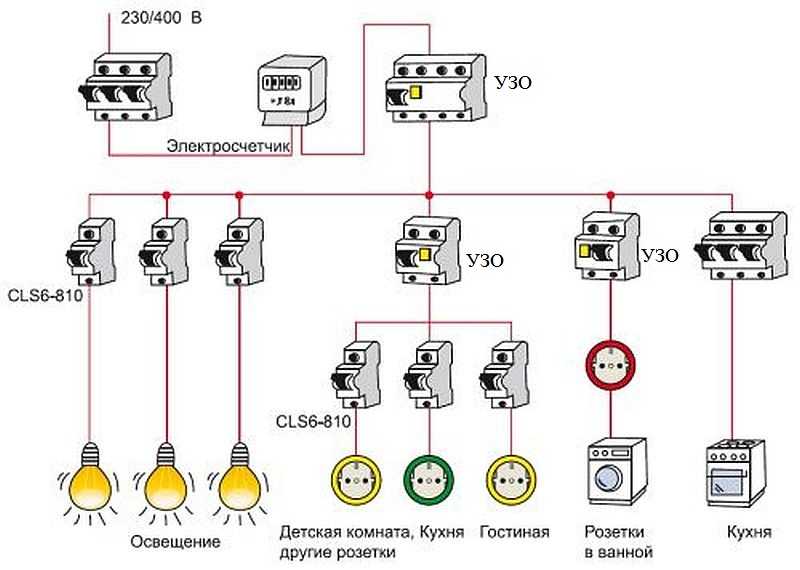
Option #3 - common RCD for 1-phase network + group RCD.
The scheme is one of the more complicated varieties of the previous version.
Thanks to the installation of additional devices for each working circuit, protection against leakage currents becomes double. From a security point of view, this is a great option.
Suppose an emergency current leakage occurred, and the connected RCD of the lighting circuit for some reason did not work. Then the common device reacts and disconnects all lines
So that both devices (private and common) do not immediately work, it is necessary to observe selectivity, that is, when installing, take into account both the response time and the current characteristics of the devices.
The positive side of the scheme is that in an emergency one circuit will turn off. It is extremely rare that the entire network goes down.
This can happen if the RCD installed on a particular line:
- defective;
- out of order;
- does not match the load.
To avoid such situations, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the methods for checking the RCD for performance.
Cons - the workload of the electrical panel with a lot of the same type of devices and additional expenses.
Option #4 - 1-phase network + group RCDs.
Practice has shown that the circuit without installing a common RCD also functions well.
Of course, there is no insurance against the failure of one protection, but this can be easily fixed by purchasing a more expensive device from a manufacturer you can trust.
The scheme resembles a variant with general protection, but without installing an RCD for each individual group. It has an important positive point - it is easier to determine the source of the leak here
From the point of view of economy, the wiring of several devices loses - one common one would cost much less.
If the electrical network in your apartment is not grounded, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the RCD connection diagrams without grounding.
Trademark
Speaking about the brand, we, in fact, will analyze the ratio of price and quality. The fact is that there is an unspoken classification of all RCD manufacturers according to their territorial location - European models, Asian and Russian.
One of the ways to distinguish a fake on a video:
Each product has its own characteristics:

- RCDs from Asian manufacturers are in the greatest demand in the world. Some manufacturers from Asia enter into contracts with a supplier of products to the Russian market and in this case produce devices under the Russian trademark.
Before choosing an RCD brand, decide what means you have for arranging protective automation in an apartment or in a private house. Most preferred firms:
- Swiss "ABV";
- French "Legrand" and "Schneider Electric";
- German "Siemens" and "Moeller".
Among domestic manufacturers, the most widely used products are:
- Kursk plant "KEAZ", the average price and quality, the company gives a guarantee for the manufactured RCDs for two years, which indicates the reliability of the products;
- The Moscow company "Interelectrokomplekt" ("IEK"), products do not always receive positive reviews, however, the demand for it is high due to its low cost;
- Ulyanovsk plant "Kontaktor", it is part of the Legrand group of companies, which affects the quality of products and, accordingly, the price;
- comparatively young Saint-Petersburg firm "DEKraft", in the Russian market it represents a company with a worldwide reputation "Schneider Electric".

As for Chinese manufacturers, the RCDs they produce are a direct competitor to the devices of the Russian company IEK. The price and quality are approximately at the same level, while the warranty period for the Chinese product is five years.
Leakage current and general protection circuit
For an apartment with TN-C-S wiring, it will not be a mistake to take an RCD for an unbalance of 30 mA without much thought. A separate section will be further devoted to the TN-C apartment system, but clear and final recommendations cannot be immediately given for private houses.
According to paragraph 7.1.83 of the PUE, the operating (natural) leakage current should not exceed 1/3 of the RCD unbalance current. But in a house with electric underfloor heating in the hallway, courtyard lighting and electric heating of the garage in winter, the operating leakage current can reach 20-25 mA with a living area of both 60 and 300 squares.
In general, if there is no greenhouse with electric heating of the soil, a heated water well, and the yard is illuminated by housekeepers, at the input after the meter it is enough to put a fire RCD with a rated current one step higher than the cut-off current of the machine, and for each consumer group - a protective RCD with the same rated current.But an accurate calculation can only be made by a specialist based on the results of electrical measurements of already finished wiring.
Calculation examples
How to calculate the RCD, we will analyze with examples for different cases.
The first is a new apartment with TN-C-S wiring; according to the data sheet, the power consumption limit is 6 kW (30 A). We check the machine - it costs 40 A, everything is OK
We take the RCD a step or two higher in terms of rated current - 50 or 63 A, it doesn’t matter - and for an unbalance current of 30 mA. We don’t think about the leakage current: builders should provide it within the normal range, but if not, let them fix it themselves for free
However, contractors do not allow such punctures - they know what the replacement of electrical wiring under warranty smells like.
Second. Khrushchev, plugs for 16 A. We put a washing machine for 3 kW; the current consumption is about 15 A. To protect it (and protect it from it), you need an RCD with a rating of 20 or 25 A for 30 mA of unbalance, but 20 A RCDs are rarely on sale. We take an RCD for 25 A, but in any case, it is MANDATORY to remove the plugs, and put a 32 A machine in their place, otherwise the situation described at the beginning is possible. If the wiring clearly cannot withstand a short-term surge of 32 A, nothing can be done, you need to change it.
In any case, you need to submit an application to the energy service for the replacement of the meter and the reconstruction of the electrical wiring, with or without replacement. This procedure is not very complicated and troublesome, and a new meter with an indication of the status of the wiring will serve in good stead in the future, see the section on alarms and malfunctions. And the RCD registered during the reconstruction will then allow free-of-charge calls for electricians for measurements, which is also very good for the future.
Third. A cottage with a consumption limit of 10 kW, which gives 50 A. The total leakage according to the results is 22 mA, with the house giving 2 mA, the garage 7, and the yard 13.We put a common difavtomat for 63 A cut-off and 100 mA imbalance, we power the house with a garage separately through an RCD for 80 A nominal and 30 mA imbalance. In this case, it is better to leave the yard without its own RCD at all, but take the lamps for it in waterproof cases with a ground terminal (industrial type), and lead their lands directly to the ground loop, it will be more reliable.
Selectivity
According to the selectivity of operation, residual current devices are of two types - "G" and "S".
These RCDs operate after a certain period of time, called exposure. They are used when several devices are connected in series in a circuit. To protect outgoing consumer branches, devices are installed without time delay, and RCDs of type “G” and “S” are installed at the input. If a current leakage occurs, and the outgoing RCD does not react, then after a certain time the input device should turn off.
For RCDs of type "S" the shutter speed is tuned in the range from 0.15 to 0.5 s, type "G" - from 0.06 to 0.08 s.
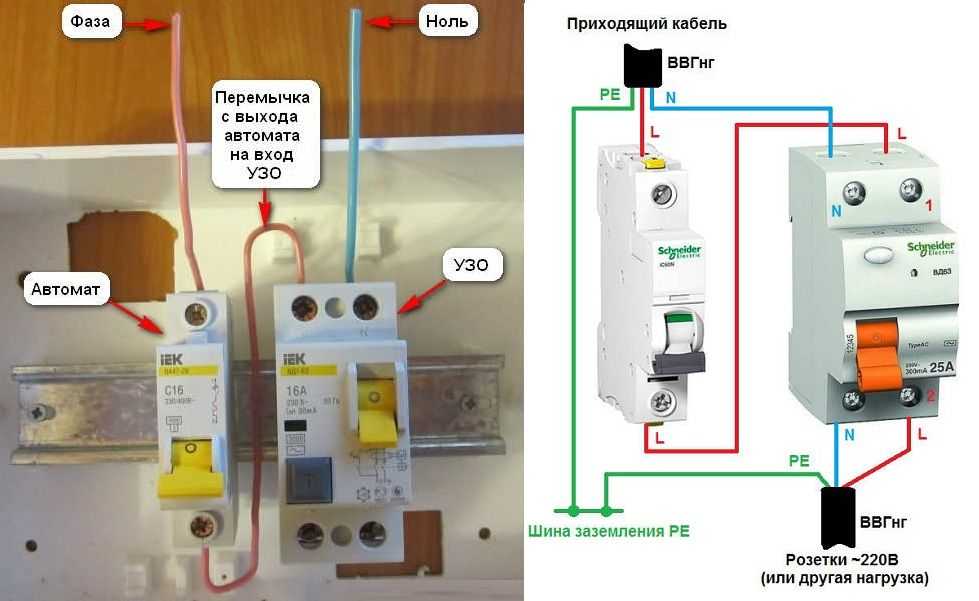
Is it possible to install an RCD without grounding?
Yes, a non-grounded installation reduces the protection potential of the wiring and people. But, even in the case of installing an RCD without earth, this is still a big plus. Because, in the event of a leak, the ground can simply be a puddle of water, through which the current will spread. Not to mention plumbing pipes and electrical appliances.
But when laying a separate line, with further protection of its RCD, it is best to lay a separate three-core cable, even if there is no ground in your house. Because even this option will increase the likelihood of disconnecting the device in the same way as if you had a ground.
Installation of RCD with zeroing