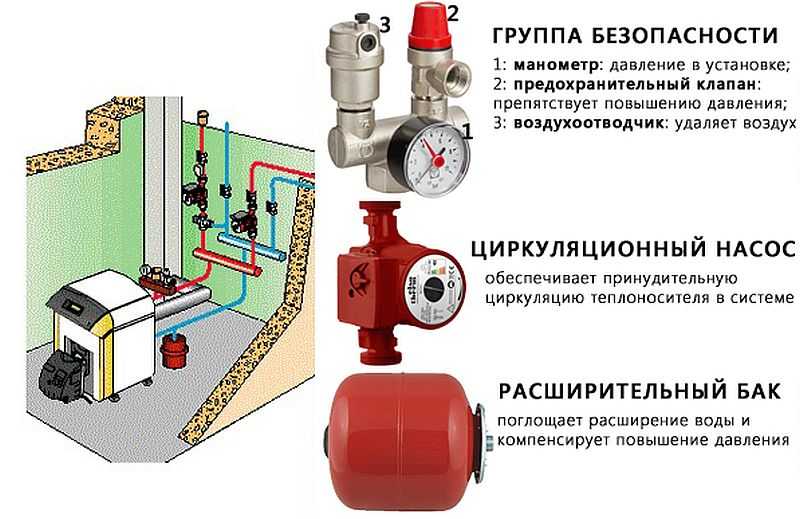
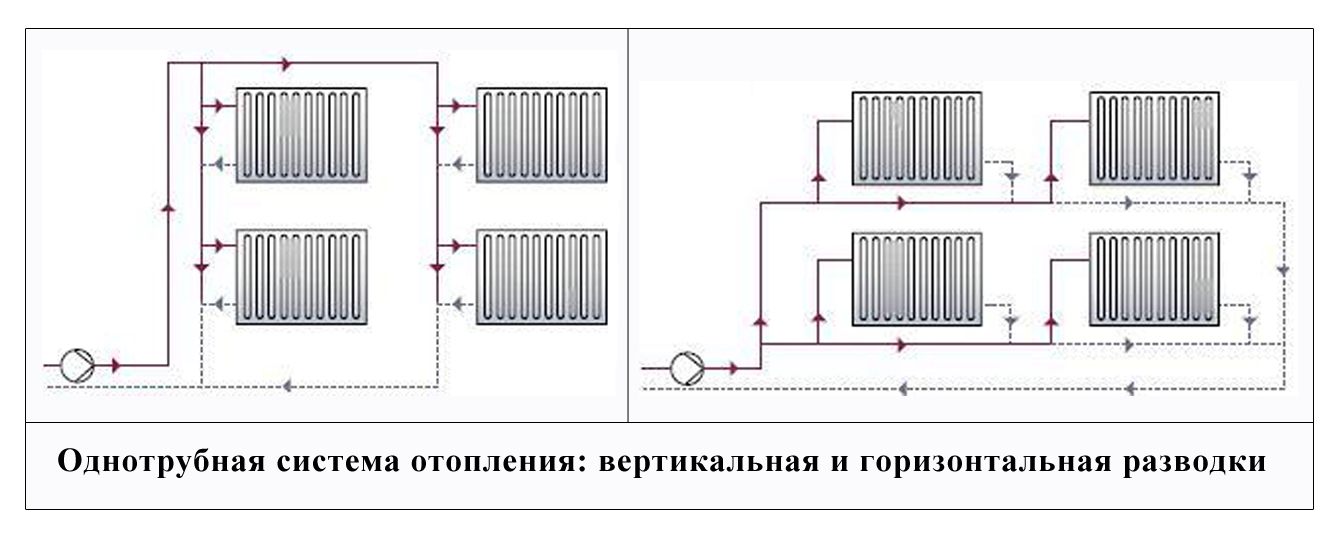
- Diaphragm expansion tank - calculation principles
- Increase in pressure
- Types of pressure in the heating system
- Working value
- Minimum value
- Control mechanisms
- Reasons for the increase in power
- Why is it falling
- Leakage with and without cracks
- Release of air from the coolant
- The presence of an aluminum radiator
- Common Causes
- Pressure in the heating system of a private house
- Causes of pressure drop in the heating system
- Why does pressure drop
- There is air in the system
- Air comes out of the expansion tank
- Flow
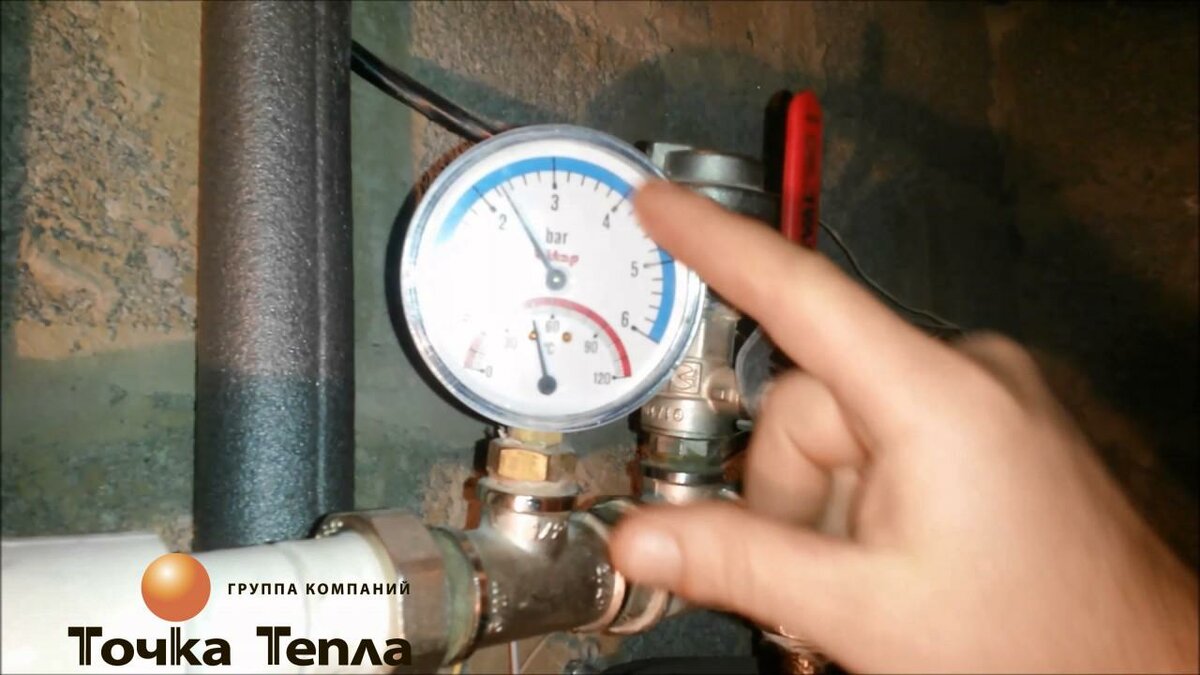
- What should be the pressure in the heating system
- Pressure in an open heating system
- Pressure in a closed heating system
- What to do with pressure drops
- A bit of theory
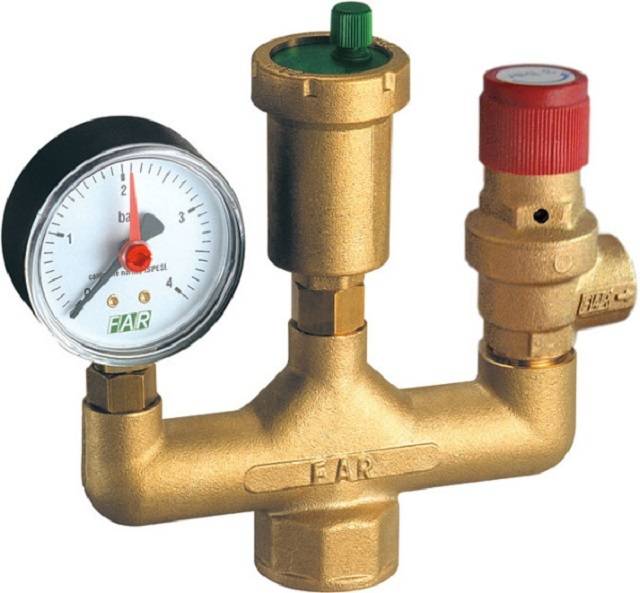
- Purpose of the device
- Defining concepts
- Device and principle of operation
- Pressure in the heating of high-rise buildings
Diaphragm expansion tank - calculation principles
Often the reason why pressure loss occurs in the heating system is the wrong choice of a double-circuit heating boiler.
That is, the calculation takes into account the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises in which heating will be performed. This parameter affects the choice of the area of heating radiators - and they use a relatively small amount of coolant
However, sometimes after the calculation, the radiators are replaced with pipes for which a much larger amount of water is used (and this fact is not taken into account). Accordingly, it is precisely such an error in the calculation that leads to an insufficient level of pressure in the system.
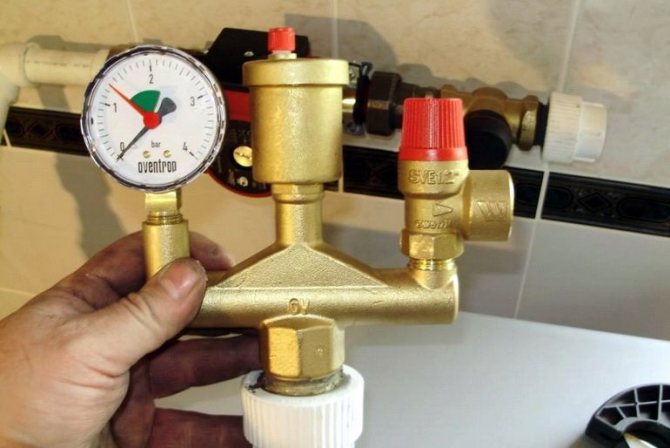
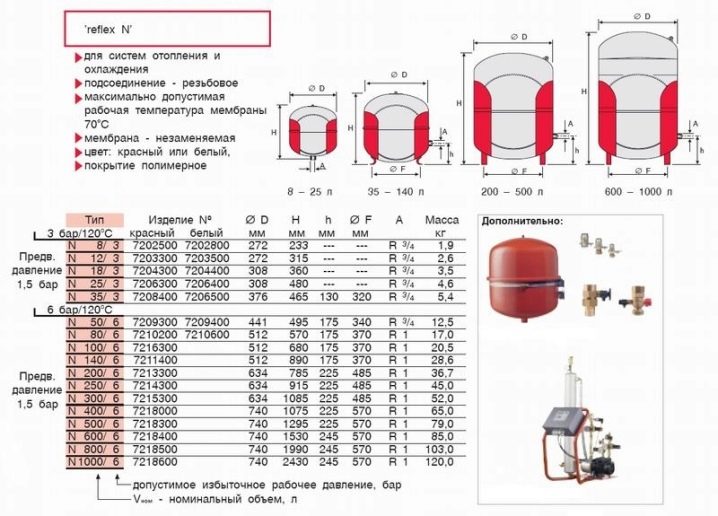
 Expansion tanks come in a variety of sizes.
Expansion tanks come in a variety of sizes.
For the normal functioning of a two-circuit system with 120 liters of coolant, an expansion tank with a volume of 6-8 liters is quite enough. However, this number is based on a system that uses heatsinks. When using pipes instead of radiators, there is more water in the system. Accordingly, it expands more, thus filling the expansion tank completely. This situation leads to an emergency descent of excess fluid using a special valve. This causes the system to shut down. Water gradually cools, its volume decreases. And it turns out that there is not enough liquid in the system to maintain pressure at a normal level.
In order to avoid such an unpleasant situation (it is unlikely that anyone will be happy about the breakdown of the heating system in the cold season), it is necessary to carefully calculate the volume of the required expansion tank. In closed systems, supplemented by a circulation pump, the most rational is the use of a membrane expansion tank, which performs the function of such an element as a heating pressure regulator.
Table for determining the maximum volume of liquid that the tank can hold
Of course, it is quite difficult to calculate the exact amount of water in the pipes of the heating system. However, an approximate indicator can be obtained by multiplying the boiler power by 15.That is, if a boiler with a capacity of 17 kW is installed in the system, then the approximate volume of coolant in the system will be 255 liters. This indicator is useful for calculating the appropriate volume of the expansion tank.
The volume of the expansion tank can be found using the formula (V * E) / D. In this case, V is an indicator of the volume of the coolant in the system, E is the expansion coefficient of the coolant, and D is the level of tank efficiency.
D is calculated in this way:
D = (Pmax-Ps)/(Pmax +1).
Here Pmax is the maximum pressure level allowed during system operation. In most cases - 2.5 bar. But Ps is the tank charging pressure coefficient, usually 0.5 bar. Accordingly, substituting all the values, we get: D \u003d (2.5-0.5) / (2.5 +1) \u003d 0.57. Further, taking into account that we have a boiler with a capacity of 17 kW, we calculate the most suitable tank volume - (255 * 0.0359) / 0.57 \u003d 16.06 liters.
Be sure to pay attention to the technical documentation of the boiler. In particular, a 17 kW boiler has a built-in expansion tank, the volume of which is 6.5 liters
Thus, in order for the system to function properly and to prevent cases such as pressure drops in the heating system, it is necessary to supplement it with an auxiliary tank with a volume of 10 liters. Such a pressure regulator in the heating system is able to normalize it.
Increase in pressure
The reasons for the spontaneous increase in pressure in the heating circuit, leading to the operation of the safety valve, may be as follows:
- Breakage of the valve on the jumper with the cold water supply system. Screw valves and plug valves have one common problem - they are not able to provide absolute tightness when tightly closed.Leaks are usually caused by worn screw valve gaskets or scale trapped between it and the seat. This can also be provoked by a scratch on the body and the stopper of the tap. When the pressure in a closed heating system is exceeded by a cold one (this happens very often), water gradually seeps into the circuit. It is further discharged into the drainage through a safety valve.
- There is not enough expansion tank. The heating of the coolant and the subsequent increase in its volume cannot be fully compensated due to the lack of space in the tank. Signs of this problem are an increase in pressure directly when the boiler is fired up or turned on.
To eliminate the first malfunction, it is better to replace the valve with a modern ball valve. This type of valves is characterized by stable tightness in the closed position and a huge service life. Frequent maintenance is also not needed here. It usually comes down to tightening the gland nut under the handle after a few hundred closing cycles.

To solve the second problem, you will have to replace the expansion tank by choosing a larger tank. There is also an option with equipping the circuit with an additional expansion tank. In order for the systems to work without failures, the volume of the expansion tank should be approximately 1/10 of the total amount of coolant.
Sometimes it happens that an increase in pressure provokes a circulation pump. This is typical for the filling section after the impeller, if the pipeline has a high hydraulic resistance. The usual reason is an underestimated diameter.There is no need to panic in such a situation: this problem is solved by simply installing a security group (at a sufficient distance from the pump). Replacing the filling with a pipe of a larger diameter is justified only if there is a large temperature difference between the first radiators from the boiler and the last radiators in the direction of circulation of the coolant.
Types of pressure in the heating system
There are three indicators:
- Static, which is taken equal to one atmosphere or 10 kPa / m.
- Dynamic, taken into account when using a circulation pump.
- Working, emerging from the previous ones.
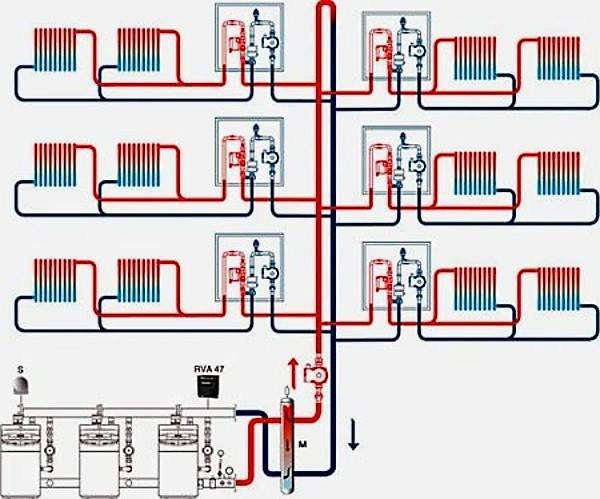
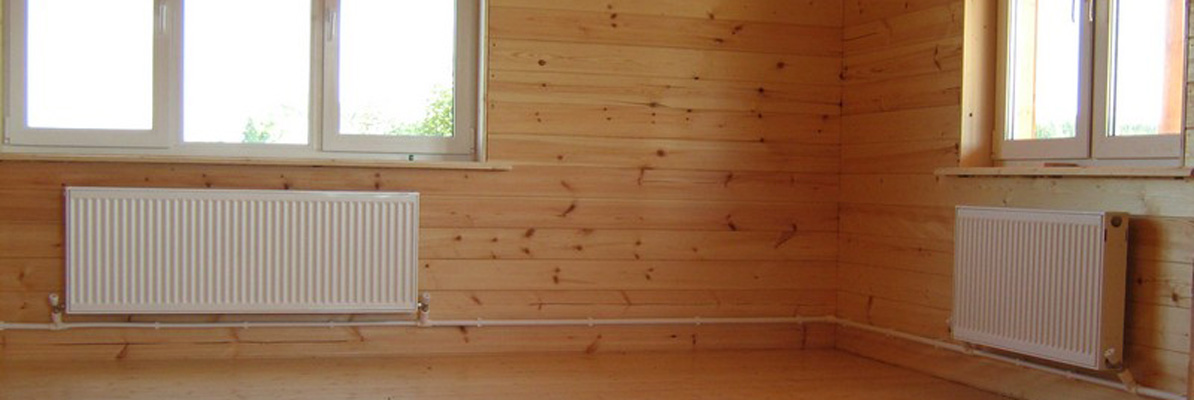
Photo 1. An example of a strapping scheme for an apartment building. Hot coolant flows through red pipes, cold coolant flows through blue pipes.
The first indicator is responsible for the pressure in the batteries and the pipeline. Depends on the length of the strap. The second occurs in the case of forced movement of the fluid. Correct calculation will allow the system to work safely.
Working value
It is characterized by regulatory documents and is the sum of two components. One of them is dynamic pressure. It exists only in systems with a circulation pump, which is not often found in apartment buildings. Therefore, in most cases, a value equal to 0.01 MPa for each meter of pipeline is taken as a working one.
Minimum value
It is chosen as the number of atmospheres at which water does not boil if heated above 100 °C.
| Temperature, °C | Pressure, atm |
| 130 | 1,8 |
| 140 | 2,7 |
| 150 | 3,9 |
The calculation is made as follows:
- determine the height of the house;
- add a margin of 8 m, which will prevent problems.
So, for a house with 5 floors of 3 meters each, the pressure will be: 15 + 8 = 23 m = 2.3 atm.
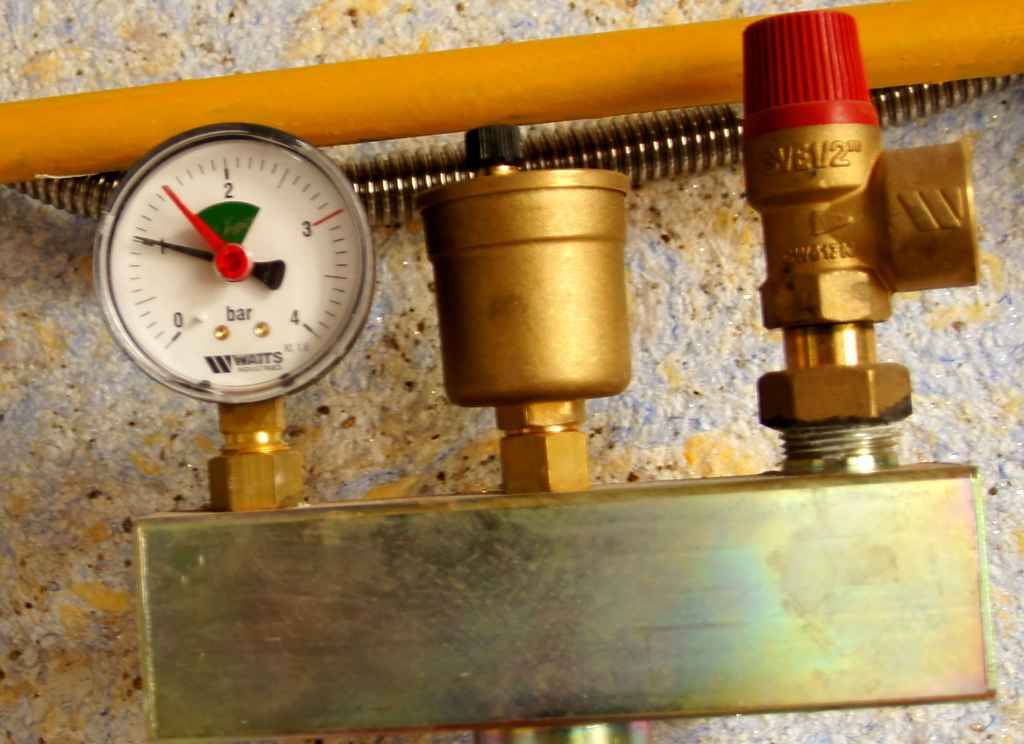
Control mechanisms
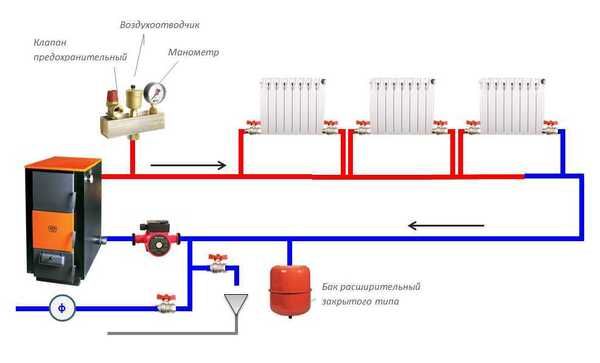
To prevent emergency situations in closed systems, relief and bypass valves are used.
Reset. Installed with access to the sewer for emergency descent of excess energy from the system, protecting it from destruction.
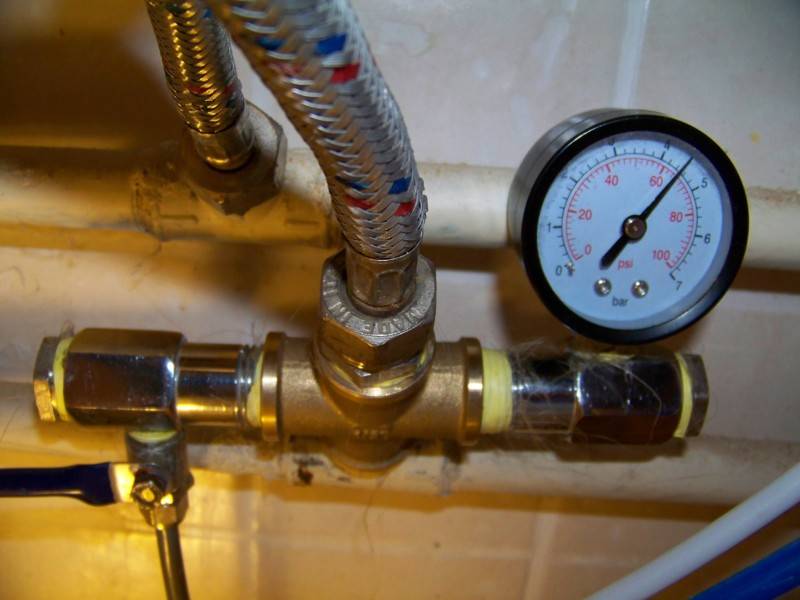
Photo 4. Relief valve for the heating system. Used to drain excess coolant.
bypass. Installed with access to an alternative circuit. Regulates the differential pressure by sending excess water into it to eliminate the increase in the following sections of the main circuit.
Modern manufacturers of heating fittings produce "smart" fuses equipped with temperature sensors that respond not to an increase in pressure, but to the temperature of the coolant.
Reference. It is not uncommon for pressure relief valves to stick. Make sure that their design has a rod for manually retracting the spring.
Do not forget that any problem in the heating system of the house is fraught not only with loss of comfort and costs. Emergencies in the heating network threaten the safety of residents and the building. Therefore, care and competence are needed in the control of heating.
Reasons for the increase in power
An uncontrolled increase in pressure is an emergency.
May be due to:
- faulty automatic control of the fuel supply process;
- the boiler operates in manual high combustion mode and is not switched to medium or low combustion;
- battery tank malfunction;
- feed faucet failure.
The main reason is overheating of the coolant. What can be done?
- The operation of the boiler and automation should be checked.In manual mode, reduce the fuel supply.
- If the pressure gauge reading is critically high, drain some of the water until the reading drops into the working area. Next, check the readings.
- If there are no boiler malfunctions, check the condition of the storage tank. It accepts the volume of water that increases when heated. If the damping rubber cuff of the tank is damaged, or there is no air in the air chamber, it will completely fill with water. When heated, the coolant will have nowhere to be displaced, and the increase in water pressure will be significant.
Checking the tank is easy. You need to press the nipple in the valve to fill the tank with air. If there is no air hiss, then the cause is a loss of air pressure. If water appears, the membrane is damaged.
A dangerous increase in power can lead to the following consequences:
- damage to heating elements, up to rupture;
- overheating of water, when a crack appears in the boiler structure, instantaneous vaporization will occur, with the release of energy equal in power to an explosion;
- irreversible deformation of the elements of the boiler, heating and bringing them into an unusable state.
The most dangerous is the explosion of the boiler. At high pressure, water can be heated to a temperature of 140 C without boiling. When the slightest crack appears in the boiler heat exchanger jacket or even in the heating system next to the boiler, the pressure drops sharply.
Superheated water, with a sharp decrease in pressure, instantly boils with the formation of steam throughout the volume. The pressure instantly rises from vaporization, and this can lead to an explosion.
At high pressure and water temperature above 100 C, power must not be abruptly reduced near the boiler. Do not fill the firebox with water: cracks may appear from a strong temperature drop.
It is necessary to take measures to reduce the temperature and smoothly reduce the pressure by draining the coolant in small portions at a far point from the boiler.
If the water temperature is below 95 C, corrected for the error of the thermometer, then the pressure is reduced by the discharge of part of the water from the system. In this case, vaporization will not occur.
Why is it falling
Problems of this type quite often arise against the background of various kinds of reasons.
Leakage with and without cracks
The reasons for its formation are:
- the appearance of a violation in the structure of the expansion tank due to the formation of cracks in its membrane;
Reference! The problem is identified by pinching the spool with a finger. If there is a problem, coolant will flow from it.
- the coolant exits through the coil or heat exchanger of the DHW circuit, normalization of the system can only be achieved by replacing these elements;
- the occurrence of microcracks and loose fixation of heating system devices, such leaks are easy to detect during visual inspection and are easy to eliminate on their own.
If all of the above reasons are not present, the standard boiling of the liquid in the boiler is possible, and its exit through the safety valve.
Release of air from the coolant
This type of problem occurs immediately after the system is filled with liquid.
To avoid the formation of air pockets, such a process should be carried out from its lower part.
Attention! This procedure requires only cold water. Air masses dissolved in the coolant could appear during the heating process
Air masses dissolved in the coolant could appear during the heating process.
To normalize the operation of the system, deaeration is used using a Mayevsky crane.
The presence of an aluminum radiator
Batteries made of this material have an unpleasant feature: the coolant reacts with aluminum after they are filled. Oxygen and hydrogen are produced.
The first creates an oxide film from inside the radiator, and the water supply is removed by Mayevsky's taps.
Important! The formation of an oxide film contributes to the further preservation of the system and the problem disappears after a couple of days
Common Causes
These include 2 main cases:

-
Breakdown of the circulation pump. If you stop it and the automatic control, then the preservation of stable values of the pressure gauge indicate precisely this reason.
When the pressure gauge readings decrease, it is necessary to look for a coolant leak.
- Regulator defect. When it is checked for serviceability and the subsequent detection of breakdowns, it is necessary to replace such a device.
Pressure in the heating system of a private house
Everything is clear when an open system is installed in the house, communicating with the atmosphere through an expansion tank. Even if a circulation pump is involved in it, the pressure in the expansion tank will be identical to atmospheric pressure, and the pressure gauge will show 0 bar. In the pipeline immediately after the pump, the pressure will be equal to the pressure that this unit can develop.
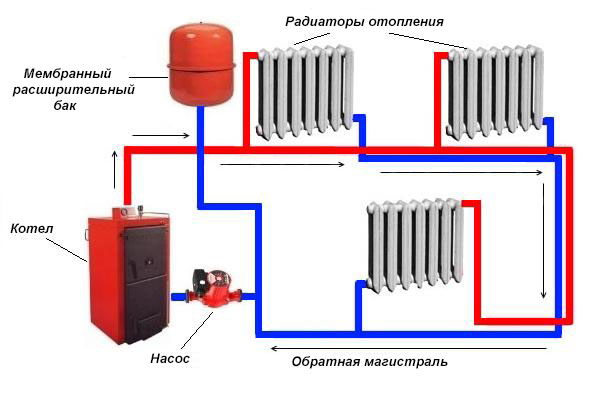
Everything is more complicated if a pressurized (closed) heating system is used. The static component in it is artificially increased in order to increase the efficiency of work and prevent air from entering the coolant. In order not to go deep into the theory, we want to immediately offer a simplified way to calculate the pressure in a closed system. You need to take the height difference between the lowest and highest points of the heating network in meters and multiply it by 0.1.We get the static pressure in Bars, and then add another 0.5 Bar to it, this will be the theoretically necessary pressure in the system.

In real life, an addition of 0.5 bar may not be enough. Therefore, it is generally accepted that in a closed system with a cold coolant, the pressure should be 1.5 bar, then during operation it will increase to 1.8–2 bar.
Causes of pressure drop in the heating system
In the heating system of a private house, the pressure can drop for a number of reasons. For example, in the event of a coolant leakage, which can occur in such situations:
- Through a crack in the diaphragm of the expansion tank. The leaked coolant is stored in the tank, so in this case the leak is considered hidden. To check the performance, you need to press the spool with your finger, through which air is pumped into the expansion tank. If water starts to flow, then this place is really damaged.
- Through the safety valve when the coolant boils in the boiler heat exchanger.
- Through small cracks in the devices, most often this occurs in those places that are affected by corrosion.
Another reason for the pressure drop in the heating system is the release of air, which was then removed using an air vent.
Air vent
In this situation, the pressure drops after a short period of time after the system is filled. In order to avoid such negative consequences, before pouring water into the circuit, oxygen and other gases must be removed from it.
Filling must be done gradually, from below and with cold water only.
Also, pressure drops may be due to the fact that aluminum radiators are provided in the heating system.
Water interacts with aluminum, is divided into components: the reaction of oxygen and metal, as a result of which an oxide film is formed and hydrogen is released, which is then removed by an automatic air vent.
Usually this phenomenon is typical only for new models of radiators: as soon as the entire aluminum surface is oxidized, the water will cease to decompose. It will be enough for you to make up for the missing amount of coolant.
Why does pressure drop
A decrease in pressure in the heating structure is observed very often. The most common causes of deviations are: the discharge of excess air, the release of air from the expansion tank, the leakage of the coolant.
There is air in the system
Air has entered the heating circuit or air pockets have appeared in the batteries. Reasons for the appearance of air gaps:
- non-compliance with technical standards when filling the structure;
- excess air is not forcibly removed from the water supplied to the heating circuit;
- enrichment of the coolant with air due to leakage of connections;
- malfunction of the air bleed valve.
If there are air cushions in the heat carriers, noises appear. This phenomenon causes damage to the components of the heating mechanism. In addition, the presence of air in the units of the heating circuit entails more serious consequences:
- vibration of the pipeline contributes to the weakening of welds and the displacement of threaded connections;
- the heating circuit is not vented, which leads to stagnation in isolated areas;
- the efficiency of the heating system decreases;
- there is a risk of "defrosting";
- there is a risk of damage to the pump impeller if air enters it.
To exclude the possibility of air entering the heating circuit, it is necessary to correctly start the circuit into operation by checking all the elements for operability.
Initially, test with increased pressure is carried out. When pressure testing, the pressure in the system should not fall within 20 minutes.
For the first time, the circuit is filled with cold water, with the taps for draining the water open and the valves for de-airing open. The mains pump is turned on at the very end. After eliminating air, the amount of coolant necessary for operation is added to the circuit.
During operation, air may appear in the pipes, to get rid of it you need:
- find an area with an air gap (in this place the pipe or battery is much colder);
- having previously turned on the make-up of the structure, open the valve or tap further downstream of the water and get rid of the air.
Air comes out of the expansion tank
The causes of problems with the expansion tank are as follows:
- installation error;
- incorrectly selected volume;
- nipple damage;
- membrane rupture.
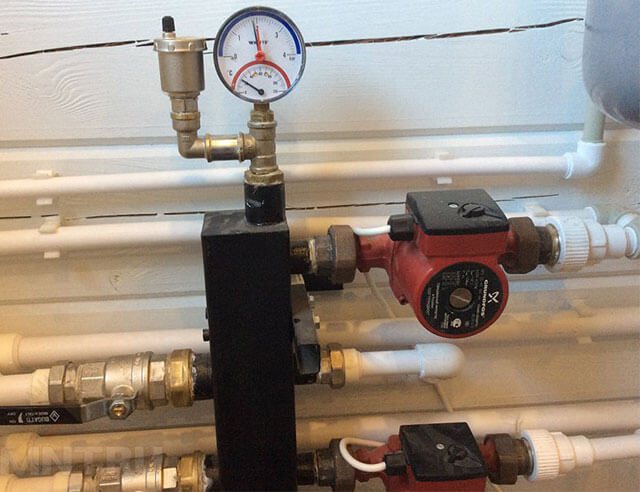
Photo 3. Scheme of the expansion tank device. The appliance may release air, causing the pressure in the heating system to drop.
All manipulations with the tank are carried out after disconnecting from the circuit. For repair, it is required to completely remove water from the tank. Next, you should pump it up and bleed a little air. Then, using a pump with a pressure gauge, bring the pressure level in the expansion tank to the required level, check the tightness and install it back on the circuit.
If the heating equipment is incorrectly configured, the following will be observed:
- increased pressure in the heating circuit and expansion tank;
- pressure drop to a critical level at which the boiler does not start;
- emergency releases of coolant with a constant need for make-up.
Important! On sale there are samples of expansion tanks that do not have devices for adjusting pressure. It is better to refuse to purchase such models.
Flow
A leak in the heating circuit leads to a decrease in pressure and the need for constant replenishment. Leakage of liquid from the heating circuit most often occurs from connecting joints and places affected by rust. It is not uncommon for fluid to escape through a torn expansion tank membrane.
You can determine the leak by pressing on the nipple, which should only allow air to pass through. If a place of loss of coolant is detected, it is necessary to eliminate the problem as soon as possible in order to avoid serious accidents.
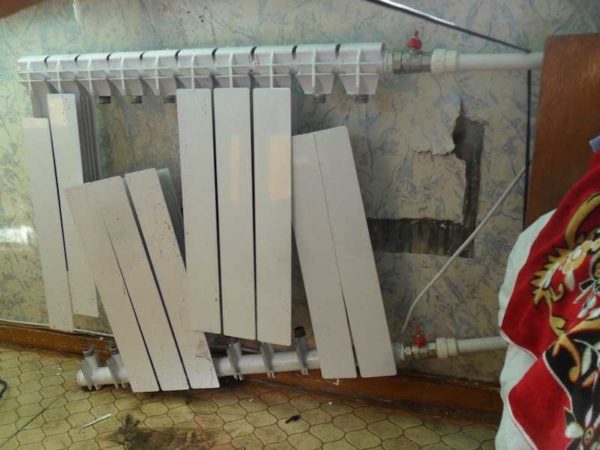
Photo 4. Leak in the pipes of the heating system. Due to this problem, the pressure may drop.
What should be the pressure in the heating system
Pressure indicators in the heating system are calculated individually, depending on the number of storeys of the building, the design of the system and the specified temperature parameters. When the height of the coolant rises by 1 meter, in the system filling mode (without temperature effects), the pressure rise is 0.1 BAR. This is called static exposure. The maximum pressure must be calculated in accordance with the technical characteristics of the weakest section of the pipeline.
Pressure in an open heating system
The pressure in a system of this kind is calculated according to static parameters. The highest value is 1.52 BAR.
Pressure in a closed heating system
A closed heating system has its advantages. The main one is the possibility of supplying the coolant over long distances by means of pumping equipment, and lifting the coolant through pipes by creating the appropriate pressure. Regardless of the design solutions, the average pressure of the heat-carrying mass on the pipe walls should not exceed 2.53 BAR.
What to do with pressure drops
The main causes of pressure drop in the pipes of the heating system are:
- wear of equipment and pipes;
- long-term operation in high pressure modes;
- differences in the cross-section of pipes in the system;
- sharp turn of valves;
- the occurrence of an air lock, the opposite flow;
- violation of the tightness of the system;
- wear of valves and flanges;
- excess volume of the heat-carrying medium.
To prevent pressure drops in the heating system, it is recommended to operate it without exceeding the technical specifications. Pumping equipment for closed heating system, as a rule, already in the factory is equipped with auxiliary equipment for pressure control.
To regulate the pressure parameters, the installation of additional equipment is used: expansion tanks, pressure gauges, safety and control valves, air vents. With a sharp increase in pressure in the system, the explosive valve allows you to drain a certain amount of heat-carrying mass and the pressure will return to normal. If the pressure drops in the system in the event of a coolant leakage, it is necessary to set the leak point, eliminate the malfunction, and press the pressure relief valve.
In addition, there are preventive measures to stabilize the pressure in the heating system:
- the use of pipes of large or equal diameter;
- slow rotation of corrective fittings;
- use of shock-absorbing devices and compensatory equipment;
- establishment of reserve (emergency) sources of power supply for pumping equipment powered by the mains;
- installation of bypass channels (for pressure relief);
- installation of a membrane hydraulic shock absorber;
- the use of dampers (elastic pipe sections) in critical sections of the heating system;
- Use of pipes with reinforced wall thickness.
Read also:
A bit of theory
In order to understand well what the working pressure is in the heating system of a private house or high-rise building and what it consists of, we will give some theoretical information. So, the working (total) pressure is the sum:
- static (manometric) pressure of the coolant;
- dynamic pressure that causes it to move.

Static refers to the pressure of the water column and the expansion of water as a result of its heating. If a heating system with a highest point at a level of 5 m is filled with a coolant, then a pressure equal to 0.5 bar (5 m of water column) will appear at the lowest point. As a rule, thermal equipment is located below, that is, a boiler, whose water jacket takes on this load. An exception is the water pressure in the heating system of an apartment building with a boiler house located on the roof, here the lowest part of the pipeline network bears the greatest load.
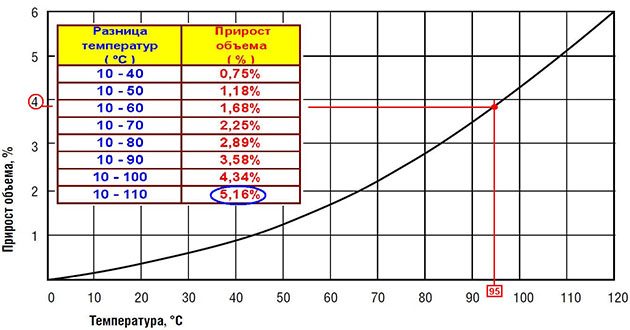
Now let's heat the coolant, which is at rest. Depending on the heating temperature, the volume of water will increase in accordance with the table:
When the heating system is open, part of the liquid will freely flow into the atmospheric expansion tank and there will be no increase in pressure in the network. With a closed circuit, the membrane tank will also accept part of the coolant, but the pressure in the pipes will increase. The highest pressure will occur if the circulation pump is used in the network, then the dynamic pressure developed by the unit will be added to the static one. The energy of this pressure is spent on forcing water to circulate and overcoming friction on the walls of pipes and local resistances.

Purpose of the device

The physical properties of the liquid - to increase in volume when heated and the impossibility of compression at low pressures - suggest the mandatory installation of expansion tanks in heating systems.
When heated from 10 to 100 degrees, water increases in volume by 4%, and glycol liquids (antifreeze) by 7%.
Heating built using a boiler, pipelines and radiators has a finite internal volume. The water heated in the boiler, increasing in volume, does not find a place to exit. The pressure in the pipes, radiator, heat exchanger rises to critical values that can break the structural elements, squeeze out the gaskets.
Private heating systems withstand, depending on the type of pipes and radiators, up to 5 atm. Safety valves in safety groups or in boiler protection equipment operate at 3 Atm. This pressure occurs when water is heated in a closed container to 110 degrees. The working limits are considered to be 1.5 - 2 Atm.
To accumulate excess coolant, expansion tanks are installed.
After cooling, the volume of the coolant returns to its previous values. To prevent the radiators from airing, water is returned to the system.
Defining concepts
First of all, let's deal with the basic concepts that owners of private houses or apartments with autonomous heating should know:
- Working pressure is measured in bar, atmosphere or megapascals.
- The static pressure in the circuit is a constant value, that is, it does not change when the heating boiler is turned off. Static pressure in the heating system is created by the coolant circulating through the pipeline.
- The forces that drive the coolant form a dynamic pressure that affects all components of the heating system from the inside.
- The permissible pressure level is the value at which the heating system can operate without breakdowns and accidents. Knowing what pressure should be in the heating boiler, you can maintain it at a given level. But exceeding this level threatens with unpleasant consequences.
- In the event of uncontrolled pressure surges in the autonomous heating system, the boiler radiator is the first to be damaged. As a rule, it can withstand no more than 3 atmospheres. As for batteries and pipes, depending on the material they are made of, they can handle heavy loads. Therefore, the choice of battery must be made based on the type of system.

It is impossible to say unequivocally what is the value of the working pressure in the heating boiler, since this indicator is influenced by several more factors. In particular, this is the length of the heating circuit, the number of floors in the building, the power and the number of batteries connected to a single system.The exact value of the working pressure is calculated during the creation of the project, taking into account the equipment and materials used.
So, the norm of pressure in the boiler for heating houses on two or three floors is approximately 1.5-2 atmospheres. In higher residential buildings, an increase in working pressure up to 2-4 atmospheres is allowed. For control, it is desirable to install pressure gauges.
Device and principle of operation
The body of the tank has a round, oval or rectangular shape. Made from alloy or stainless steel. Painted red to prevent corrosion. Blue-painted cisterns are used for water supply.
Sectional tank
Important. Colored expanders are not interchangeable
Blue containers are used at pressures up to 10 bar and temperatures up to +70 degrees. Red tanks are designed for pressure up to 4 bar and temperatures up to +120 degrees.
According to the design features, the tanks are produced:
- using a replaceable pear;
- with membrane;
- without separation of liquid and gas.
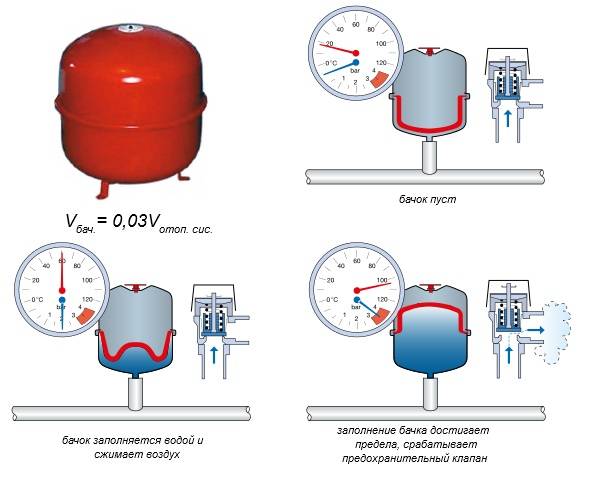
Models assembled according to the first variant have a body, inside of which there is a rubber pear. Its mouth is fixed on the body with the help of a coupling and bolts. If necessary, the pear can be changed. The coupling is equipped with a threaded connection, this allows you to install the tank on the pipeline fitting. Between the pear and the body, air is pumped under low pressure. At the opposite end of the tank there is a bypass valve with a nipple, through which gas can be pumped in or, if necessary, released.
This device works as follows. After installing all the necessary fittings, water is pumped into the pipeline.The filling valve is installed on the return pipe at its lowest point. This is done so that the air in the system can freely rise and exit through the outlet valve, which, on the contrary, is installed at the highest point of the supply pipe.
In the expander, the bulb under air pressure is in a compressed state. As water enters, it fills, straightens and compresses the air in the housing. The tank is filled until the water pressure is equal to the air pressure. If the pumping of the system continues, the pressure will exceed the maximum, and the emergency valve will operate.
After the boiler starts to work, the water heats up and begins to expand. The pressure in the system increases, the liquid begins to flow into the expander pear, compressing the air even more. After the pressure of water and air in the tank comes into equilibrium, the flow of fluid will stop.
When the boiler stops working, the water begins to cool, its volume decreases, and the pressure also decreases. The gas in the tank pushes the excess water back into the system, squeezing the bulb until the pressure equalizes again. If the pressure in the system exceeds the maximum allowable, an emergency valve on the tank will open and release excess water, due to which the pressure will decrease.
In the second version, the membrane divides the container into two halves, air is pumped in on one side, and water is supplied on the other. Works in the same way as the first option. The case is non-separable, the membrane cannot be changed.
Pressure equalization
In the third variant, there is no separation between gas and liquid, so air is partially mixed with water. During operation, gas is periodically pumped up.This design is more reliable, since there are no rubber parts that break through over time.
Pressure in the heating of high-rise buildings
In the heating system of multi-storey buildings, pressure is a necessary component. Only under pressure, the coolant can be pumped to the floors. And, the higher the house, the higher the pressure in the heating system.
To find out the pressure in the radiators of your apartment, you will have to contact the local operating office, on the balance sheet of which your house is located. It is difficult to say approximately - connection schemes can be different, different distances to the boiler room, different pipe diameters, etc. Accordingly, the operating pressure may be different. For example, skyscrapers of 12 floors or more are often divided by height. Up to, say, the 6th floor there is one branch with a lower pressure, from the seventh and above - another, with a higher one. Therefore, an appeal to the housing cooperative (or another organization) is almost inevitable.

Consequences of water hammer. This happens infrequently, apparently radiators are not at all for high-rise buildings, but still ...
Why know the pressure in your heating system? In order to select equipment that is designed for such a load during its modernization (replacement of pipes, radiators and other heating fittings). For example, not all bimetallic or aluminum radiators can be used in high-rise buildings. You can install only some models in some well-known brands, and very expensive ones. And then, in apartment buildings not too large number of storeys. And one more thing - having installed such radiators, you have to block them (shut off the supply) for the test period (pressure testing before the heating season). Otherwise, they may "break". But you can’t escape from unexpected water hammers ...