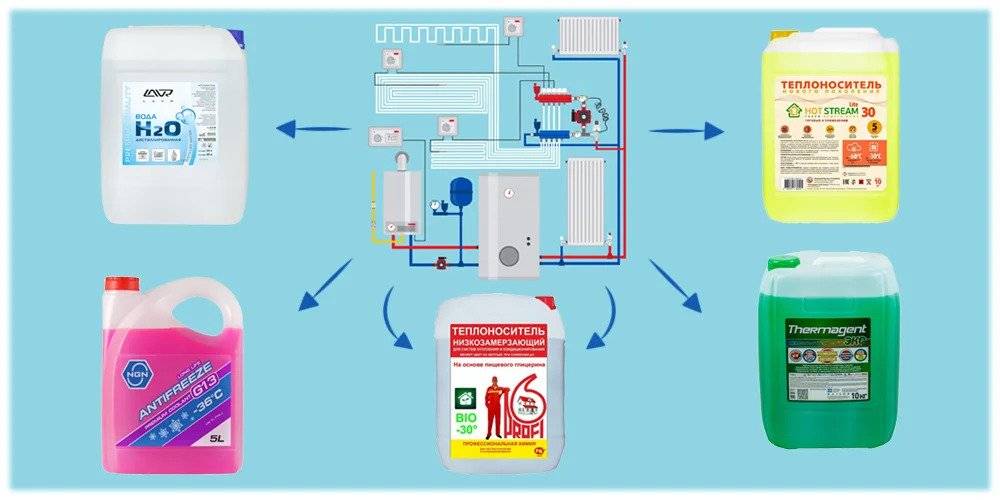
- Water is an available coolant
- Parameter control methods
- Way to reduce heat loss
- How to prevent a reduction in the service life of the coolant and avoid the formation of corrosion in the system?
- Installation of propylene heating
- Soldering
- Fitting
- Temperature norms
- Antifreeze as a coolant
- Responsible stage: calculation of the capacity of the expansion tank
- Heat supply of a multi-storey building
- Autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
- Centralized heating of a multi-storey building
- Types of electric boilers
- Heating boilers
- Induction boilers
- Electrode systems
- Antifreeze as a coolant
- Water use
- Main disadvantages
- Conclusions that can be drawn
Water is an available coolant
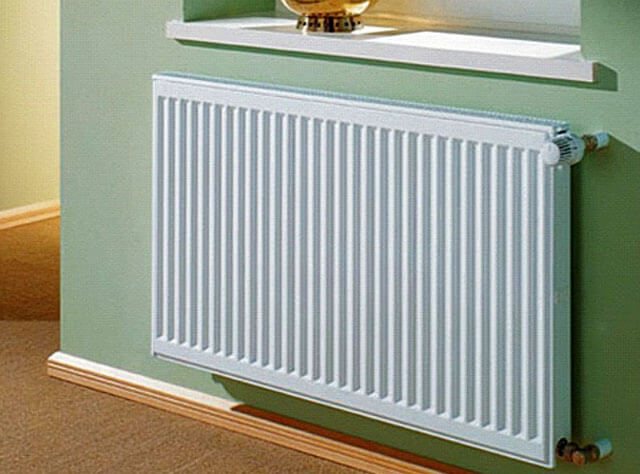
 Most consumers use plain water as a heat carrier. This is due to its low price, absolute availability, and good heat transfer performance. The great advantage of water is its safety for people and the environment. If for some reason a water leak occurs, its level can be easily replenished, and the leaked liquid can be eliminated in the usual way.
Most consumers use plain water as a heat carrier. This is due to its low price, absolute availability, and good heat transfer performance. The great advantage of water is its safety for people and the environment. If for some reason a water leak occurs, its level can be easily replenished, and the leaked liquid can be eliminated in the usual way.
The peculiarity of water is that it expands when it freezes, and can damage radiators and pipes.If you do not know which coolant to choose for the heating system in the house, consider the situations associated with the lack of heating. Water as a heat carrier can only be selected if the heating system operates smoothly and constantly.
 Do not fill out heating systems with coolant from the tap. Tap water contains too many impurities that will eventually settle in the pipes and cause them to break. Salt impurities and hydrogen are especially dangerous for heating systems. Salts react with metal surfaces and provoke the process of corrosion. In order to improve the quality of water, it is necessary to make it softer by eliminating impurities. This can be achieved in two ways: by exposure to temperature, or by a chemical reaction.
Do not fill out heating systems with coolant from the tap. Tap water contains too many impurities that will eventually settle in the pipes and cause them to break. Salt impurities and hydrogen are especially dangerous for heating systems. Salts react with metal surfaces and provoke the process of corrosion. In order to improve the quality of water, it is necessary to make it softer by eliminating impurities. This can be achieved in two ways: by exposure to temperature, or by a chemical reaction.
 The temperature effect assumes the usual boiling. You need to boil water in a metal container without a lid, preferably with a large bottom surface. During the heating process, carbon dioxide will be released into the air, and salts will settle to the bottom. Chemical elimination of impurities occurs due to the reaction with soda ash and slaked lime. These substances make the salts insoluble in water and they precipitate out. Before pouring the coolant into the heating system, it must be filtered so that the sediment does not interfere with its normal operation.
The temperature effect assumes the usual boiling. You need to boil water in a metal container without a lid, preferably with a large bottom surface. During the heating process, carbon dioxide will be released into the air, and salts will settle to the bottom. Chemical elimination of impurities occurs due to the reaction with soda ash and slaked lime. These substances make the salts insoluble in water and they precipitate out. Before pouring the coolant into the heating system, it must be filtered so that the sediment does not interfere with its normal operation.
 Ideal for heating systems distilled water. The distillate is devoid of any impurities and does not require additional processing. Such water must be bought in the store, as it is produced only in an industrial way.
Ideal for heating systems distilled water. The distillate is devoid of any impurities and does not require additional processing. Such water must be bought in the store, as it is produced only in an industrial way.
Parameter control methods
 System regulation
System regulation
Heating is adjustable. Methods:
- quantitative;
The parameters are changed by increasing, decreasing the amount of coolant supply. Pumps increase the pressure in the system, valves reduce the speed of the carrier.
- qualitative;
With a qualitative change in the parameters of the coolant, additives are added that change the characteristic indicators.
- mixed.
Uses both methods.
Way to reduce heat loss
The first, main condition for reducing heat loss is good thermal insulation.
The system needs to be optimized. Adjust the comfortable temperature inside the living rooms, follow the recommendations of the temperature regime in utility, non-residential premises.
 Comfort in home
Comfort in home
How to prevent a reduction in the service life of the coolant and avoid the formation of corrosion in the system?
First of all, this will be facilitated by the correct choice of the coolant intended for use in your particular system. Such indicators as the prevailing metal, approximate temperatures, type of equipment, etc. are of importance.
Preventive measures and compliance with operating rules are also important:
- Do not allow the system to overheat - high temperature contributes to the deposition of scale primarily on heat exchangers, namely, the efficiency of the heating system and hot water supply as a whole depends on them;
- Do not allow the system to be idle for a long time - even if you do not live in the house, carry out an annual heating start, avoiding fluid stagnation;
- Do not carry out self-service - dirt may enter the system, which will reduce performance;
- Do not add water to the antifreeze - this will also reduce the performance of the system, increase the risk of freezing, and increase the intensity of corrosion.
It is important to remember that the higher the density (content, concentration of propylene glycol) of the coolant, the less intensively the system will be polluted, and the less often flushing and complex cleaning of its elements will be required. Minimize emergency repair costs
Installation of propylene heating
Heating with polypropylene pipes is not mounted "in a plumbing" way: it is carried out mainly by fittings; soldering is permissible only for connecting straight pipe sections to size. Both soldering and fittings for heating pipes are also needed special, more on that below.
Such requirements are explained by considerations of reliability: any malfunction will be revealed at best when the system is pressure tested before the start of the heating season, or even in its midst in severe cold.
Soldering
Polypropylene soldering technology is described in detail in the relevant article.
To assemble the heating system, it is important to know that butt-soldered pipe joints are unacceptable. The ends of the pipe sections must be soldered into a special coupling: a larger diameter tube with a stepped inner profile. Accordingly, you need a suitable soldering iron, the usual “iron” will not work
Accordingly, you need a suitable soldering iron, an ordinary “iron” will not work.
Fitting

Heating pipe connection
All corners and tees of propylene heating are assembled only on fittings, and metal fittings are “American”, see fig. Shut-off valves are also exclusively metal. A pressed or fused metal clip in metal-plastic connectors with a constant long-term supply of hot water with a temperature above the maximum allowable for hot water supply of 70 degrees will gradually crawl out of the plastic frame, which can lead to a sudden breakthrough.
With hidden wiring, all detachable connections must be available for inspection and repair. That is, it is necessary that they can be unscrewed and tightened to the norm with a gas wrench of the appropriate size. In practice, this means that the minimum distance from any connection point to the wall of the recess under it was at least 15 cm, to the bottom of the recess - at least 2 cm, and to the top of the recess NOT MORE THAN 3 cm. fittings when immuring pipes into the floor.
Do-it-yourself reconstruction of the heating system in an apartment is not difficult, not difficult and does not require documentation, provided that the radiators are not transferred. The main task in its implementation is to carefully consider the choice of pipes, radiators and the possibility of combining it with the insulation of the apartment, and especially the floor.
Temperature norms

- DBN (B. 2.5-39 Heat networks);
- SNiP 2.04.05 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning".
For the calculated temperature of the water in the supply, the figure is taken that is equal to the temperature of the water at the outlet of the boiler, according to its passport data.
For individual heating, it is necessary to decide what the temperature of the coolant should be, taking into account such factors:
- 1 Beginning and end of the heating season according to the average daily temperature outside +8 °C for 3 days;
- 2 The average temperature inside heated premises of housing and communal and public importance should be 20 °C, and for industrial buildings 16 °C;
- 3 The average design temperature must comply with the requirements of DBN V.2.2-10, DBN V.2.2.-4, DSanPiN 5.5.2.008, SP No. 3231-85.
According to SNiP 2.04.05 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning" (clause 3.20), the limiting indicators of the coolant are as follows:
- 1 For a hospital - 85 °C (excluding psychiatric and drug departments, as well as administrative or domestic premises);
- 2 For residential, public, as well as domestic buildings (excluding halls for sports, trade, spectators and passengers) - 90 ° С;
- 3 For auditoriums, restaurants and production facilities of category A and B - 105 °C;
- 4 For catering establishments (excluding restaurants) - this is 115 °С;
- 5 For production premises (categories C, D and D), where combustible dust and aerosols are released - 130 ° C;
- 6 For stairwells, vestibules, pedestrian crossings, technical premises, residential buildings, industrial premises without flammable dust and aerosols - 150 °С.
Depending on external factors, the water temperature in the heating system can be from 30 to 90 °C. When heated above 90 ° C, dust and paintwork begin to decompose. For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit more heating.
To calculate the optimal indicators, special graphs and tables can be used, in which the norms are determined depending on the season:
- With an average value outside the window of 0 °С, the supply for radiators with different wiring is set at a level of 40 to 45 °С, and the return temperature is from 35 to 38 °С;
- At -20 °С, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °С, while the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °С;
- At -40 ° C outside the window for all heating devices set the maximum allowable values. At the supply it is from 95 to 105 ° C, and at the return - 70 ° C.
Antifreeze as a coolant
Higher characteristics for the efficient operation of the heating system have such a type of coolant as antifreeze. By pouring antifreeze into the heating system circuit, it is possible to reduce the risk of freezing of the heating system in the cold season to a minimum. Antifreeze is designed for lower temperatures than water, and they are not able to change its physical state. Antifreeze has many advantages, since it does not cause scale deposits and does not contribute to corrosive wear of the interior of the heating system elements.
Even if the antifreeze solidifies at very low temperatures, it will not expand like water, and this will not cause any damage to the heating system components. In the event of freezing, the antifreeze will turn into a gel-like composition, and the volume will remain the same. If, after freezing, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system rises, it will turn from a gel-like state into a liquid, and this will not cause any negative consequences for the heating circuit.
Such additives help to remove various deposits and scale from the elements of the heating system, as well as eliminate pockets of corrosion. When choosing antifreeze, you need to remember that such a coolant is not universal. The additives that it contains are only suitable for certain materials.
Existing coolants for heating systems-antifreezes can be divided into two categories based on their freezing point. Some are designed for temperatures up to -6 degrees, while others are up to -35 degrees.
Properties of various types of antifreeze
The composition of such a coolant as antifreeze is designed for a full five years of operation, or for 10 heating seasons.The calculation of the coolant in the heating system must be accurate.
Antifreeze also has its drawbacks:
- The heat capacity of antifreeze is 15% lower than that of water, which means that they will give off heat more slowly;
- They have a rather high viscosity, which means that a sufficiently powerful circulation pump will need to be installed in the system.
- When heated, antifreeze increases in volume more than water, which means that the heating system must include a closed-type expansion tank, and radiators must have a larger capacity than those used to organize a heating system in which water is the coolant.
- The speed of the coolant in the heating system - that is, the fluidity of antifreeze, is 50% higher than that of water, which means that all connectors of the heating system must be very carefully sealed.
- Antifreeze, which includes ethylene glycol, is toxic to humans, so it can only be used for single-circuit boilers.
In the case of using this type of coolant as antifreeze in the heating system, certain conditions must be taken into account:
- The system must be supplemented with a circulation pump with powerful parameters. If the circulation of the coolant in the heating system and the heating circuit is long, then the circulation pump must be outdoor installation.
- The volume of the expansion tank must be at least twice as large as the tank used for a coolant such as water.
- It is necessary to install volumetric radiators and pipes with a large diameter in the heating system.
- Do not use automatic air vents.For a heating system in which antifreeze is the coolant, only manual type taps can be used. A more popular manual type crane is the Mayevsky crane.
- If antifreeze is diluted, then only with distilled water. Melt, rain or well water will not work in any way.
- Before filling the heating system with coolant - antifreeze, it must be thoroughly rinsed with water, not forgetting about the boiler. Manufacturers of antifreezes recommend changing them in the heating system at least once every three years.
- If the boiler is cold, then it is not recommended to immediately set high standards for the temperature of the coolant to the heating system. It should rise gradually, the coolant needs some time to heat up.
If in winter a double-circuit boiler operating on antifreeze is turned off for a long period, then it is necessary to drain water from the hot water supply circuit. If it freezes, the water can expand and damage pipes or other parts of the heating system.
Responsible stage: calculation of the capacity of the expansion tank
In order to have a clear idea of the displacement of the entire heat system, you need to know how much water is placed in the boiler heat exchanger.
You can take averages. So, an average of 3-6 liters of water is included in a wall-mounted heating boiler, 10-30 liters in a floor or parapet boiler.
Now you can calculate the capacity of the expansion tank, which performs an important function. It compensates for the excess pressure that occurs when the coolant expands during heating.

Depending on the type of heating system, tanks are:
- closed;
- open.
For small rooms, an open type is suitable, but in large two-story cottages, closed expansion joints (membrane) are increasingly being installed.
If the reservoir capacity is less than required, the valve will depressurize too often. In this case, you have to change it, or put an additional tank in parallel.

For the formula for calculating the capacity of the expansion tank, the following indicators are needed:
- V(c) is the volume of the coolant in the system;
- K - coefficient of expansion of water (a value of 1.04 is taken, according to an indicator of water expansion of 4%);
- D is the expansion efficiency of the tank, which is calculated by the formula: (Pmax - Pb) / (Pmax + 1) = D, where Pmax is the maximum allowable pressure in the system, and Pb is the pre-inflating pressure of the compensator air chamber (the parameters are specified in the documentation for the tank );
- V (b) - the capacity of the expansion tank.
So, (V(c) x K)/D = V(b)
Heat supply of a multi-storey building

Distribution unit for heating an apartment building
The distribution of heating in a multi-storey building is important for the operational parameters of the system. However, in addition to this, the characteristics of heat supply should be taken into account. An important of them is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous.
An important of them is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous.
In overwhelming cases, they make a connection to the central heating system. This allows you to reduce the current costs in the estimate for heating a multi-storey building. But in practice, the level of quality of such services remains extremely low.Therefore, if there is a choice, preference is given to autonomous heating of a multi-storey building.
Autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
In modern multi-storey residential buildings, it is possible to organize an independent heat supply system. It can be of two types - apartment or common house. In the first case, an autonomous heating system of a multi-storey building is carried out in each apartment separately. To do this, they make an independent wiring of pipelines and install a boiler (most often a gas one). General house implies the installation of a boiler room, to which special requirements are imposed.
The principle of its organization is no different from a similar scheme for a private country house. However, there are a number of important points to consider:
- Installation of several heating boilers. One or more of them must necessarily perform a duplicate function. In case of failure of one boiler, another must replace it;
- Installation of a two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, as the most efficient;
- Drawing up a schedule for scheduled maintenance and preventive maintenance. This is especially true for heating heating equipment and security groups.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the heating scheme of a particular multi-storey building, it is necessary to organize an apartment heat metering system. To do this, for each incoming branch pipe from the central riser, you need to install energy meters. That is why the Leningrad heating system of a multi-storey building is not suitable for reducing current costs.
Centralized heating of a multi-storey building
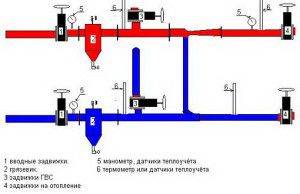
Scheme of the elevator node
How can the heating distribution in an apartment building change when it is connected to the central heating supply? The main element of this system is the elevator unit, which performs the functions of normalizing the coolant parameters to acceptable values.
The total length of the central heating mains is quite large. Therefore, in the heating point, such parameters of the coolant are created so that heat losses are minimal. To do this, increase the pressure to 20 atm. which leads to an increase in the temperature of hot water up to +120°C. However, given the characteristics of the heating system in an apartment building, the supply of hot water with such characteristics to consumers is not allowed. To normalize the parameters of the coolant, an elevator assembly is installed.
It can be calculated for both two-pipe and single-pipe heating systems of a multi-storey building. Its main functions are:
- Reducing pressure with an elevator. A special cone valve regulates the amount of coolant inflow into the distribution system;
- Lowering the temperature level to + 90-85 ° С. For this purpose, a mixing unit for hot and cooled water is designed;
- Coolant filtration and oxygen reduction.
In addition, the elevator unit performs the main balancing of the single-pipe heating system in the house. To do this, it provides shut-off and control valves, which in automatic or semi-automatic mode regulates pressure and temperature.
You also need to consider that the estimate for centralized heating of a multi-storey building will differ from the autonomous one. The table shows the comparative characteristics of these systems.
Types of electric boilers
Depending on the method of transferring thermal energy to the coolant, electric boilers are divided into three types:
- Tenovye.
- Induction.
- Electrode.
All these heating units are produced in two versions: 220 and 380 volts.
Heating boilers
Such electric boilers for home heating are the most popular. The principle of their action is as follows:
- The tubular element heats the water circulating in the closed system.
- Thanks to the circulation, fast and uniform heating of the entire system is ensured.
- The number of required heating elements depends on the power of the device and can vary from 1 to 6 heating elements.
Such boilers are equipped with a reliable automation system that allows you to monitor the temperature of the coolant and regulate it. The advantages of heating units for heating are:
- Simplicity and reliability of a design.
- Ease of installation.
- Cheap construction.
- The ability to use almost any liquid as a coolant.
- Such 380 volt boilers have a modern design and fit well into any interior.
Induction boilers
The principle of electromagnetic induction has long been successfully used for heating residential premises. Such a boiler has the following device:
- A metal core is inserted into a cylindrical body (usually a pipe section is used), on which a coil is wound.
- When voltage is applied to the coil and winding, vortex flows arise, as a result of which the pipe through which the coolant circulates heats up and transfers heat to the water.
- The circulation of water must be constant so that the coil and core do not overheat.
This electric heating system has the following advantages:
- High efficiency, reaching 98%.
- Such a 380 volt boiler is not subject to scale formation.
- Increased safety - no heating elements.
- Small dimensions and low weight ensure easy and quick installation of induction boilers.
Electrode systems
In its work, the 380 volt electrode boiler uses specially prepared water. The preparation of the coolant consists in dissolving a certain amount of salts in it to give the desired density. The general principle of operation of electrode heating devices is as follows:
- Two electrodes are inserted into a tube of suitable diameter.
- Due to the potential difference and the frequent change of polarity, the ions begin to move chaotically. So the coolant heats up quickly.
- Due to the rapid heating of the coolant, powerful convection flows are created, allowing you to quickly heat up a large volume without the use of a circulation pump.
The electrode boiler has obvious advantages, including:
- Small sizes.
- Fast access to rated power.
- Compact and simple design.
- No emergency, even if water flows out of the heating system.
Antifreeze as a coolant
Higher characteristics for the efficient operation of the heating system have such a type of coolant as antifreeze. By pouring antifreeze into the heating system circuit, it is possible to reduce the risk of freezing of the heating system in the cold season to a minimum. Antifreeze is designed for lower temperatures than water, and they are not able to change its physical state. Antifreeze has many advantages, since it does not cause scale deposits and does not contribute to corrosive wear of the interior of the heating system elements.
Even if the antifreeze solidifies at very low temperatures, it will not expand like water, and this will not cause any damage to the heating system components. In the event of freezing, the antifreeze will turn into a gel-like composition, and the volume will remain the same. If, after freezing, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system rises, it will turn from a gel-like state into a liquid, and this will not cause any negative consequences for the heating circuit.
Many manufacturers add various additives to antifreeze that can increase the life of the heating system.
Such additives help to remove various deposits and scale from the elements of the heating system, as well as eliminate pockets of corrosion. When choosing antifreeze, you need to remember that such a coolant is not universal. The additives that it contains are only suitable for certain materials.
Existing coolants for heating systems-antifreezes can be divided into two categories based on their freezing point. Some are designed for temperatures up to -6 degrees, while others are up to -35 degrees.
Properties of various types of antifreeze
The composition of such a coolant as antifreeze is designed for a full five years of operation, or for 10 heating seasons. The calculation of the coolant in the heating system must be accurate.
Antifreeze also has its drawbacks:
- The heat capacity of antifreeze is 15% lower than that of water, which means that they will give off heat more slowly;
- They have a rather high viscosity, which means that a sufficiently powerful circulation pump will need to be installed in the system.
- When heated, antifreeze increases in volume more than water, which means that the heating system must include a closed-type expansion tank, and radiators must have a larger capacity than those used to organize a heating system in which water is the coolant.
- The speed of the coolant in the heating system - that is, the fluidity of antifreeze, is 50% higher than that of water, which means that all connectors of the heating system must be very carefully sealed.
- Antifreeze, which includes ethylene glycol, is toxic to humans, so it can only be used for single-circuit boilers.
In the case of using this type of coolant as antifreeze in the heating system, certain conditions must be taken into account:
- The system must be supplemented with a circulation pump with powerful parameters. If the circulation of the coolant in the heating system and the heating circuit is long, then the circulation pump must be outdoor installation.
- The volume of the expansion tank must be at least twice as large as the tank used for a coolant such as water.
- It is necessary to install volumetric radiators and pipes with a large diameter in the heating system.
- Do not use automatic air vents. For a heating system in which antifreeze is the coolant, only manual type taps can be used. A more popular manual type crane is the Mayevsky crane.
- If antifreeze is diluted, then only with distilled water. Melt, rain or well water will not work in any way.
- Before filling the heating system with coolant - antifreeze, it must be thoroughly rinsed with water, not forgetting about the boiler. Manufacturers of antifreezes recommend changing them in the heating system at least once every three years.
- If the boiler is cold, then it is not recommended to immediately set high standards for the temperature of the coolant to the heating system. It should rise gradually, the coolant needs some time to heat up.
If in winter a double-circuit boiler operating on antifreeze is turned off for a long period, then it is necessary to drain water from the hot water supply circuit. If it freezes, the water can expand and damage pipes or other parts of the heating system.
Water use
The main advantage of water is its heat capacity and environmental friendliness. Everyone knows that water heats up for a long time, and it takes a lot of energy to bring it to a boil. This indicates a large amount of energy that the liquid accumulates in itself, and, therefore, it can transfer to the surrounding air when it cools in heating appliances.
Main disadvantages
A significant disadvantage of water is its ability to cause corrosion of metals, especially steel alloys. Over time, oxidized metal and scale formed from the precipitation of salts contained in water on the inner surface of pipes and equipment significantly impairs heat transfer.
The second serious drawback of water is its expansion when it freezes at temperatures below 0°C. That is, during a break in the supply of fuel or electricity in systems with electric pumps, freezing of water leads to a rupture of pipes and heating devices, completely disables the system.
Conclusions that can be drawn

The use of distilled water is the best option for a residential building where the owners live permanently. Antifreeze is a liquid that makes sense to purchase for periodic heating of buildings in which the owners visit from time to time. These are dachas, garages, temporary buildings on a site where a residential building is just being built.
When choosing antifreeze, the following recommendations may help:
- With a limited budget, it is advised to buy ethylene glycol products, but only proven, popular brands of well-known manufacturers (Warm House, Termagent, Bautherm, Dixis TOP).
- If there is a risk of liquid getting into domestic water (“thanks” to a double-circuit boiler, indirect heating boiler), then it is better to purchase a safe propylene glycol solution.
- Large heating systems are a sufficient reason to buy a higher quality coolant. For example, premium grade propylene glycol. Its service life is already impressive: it is 15 years.
- Glycerin solutions are not the best choice anyway. In addition to all the shortcomings of such antifreezes, there is another unpleasant moment. There is a "good chance" to purchase products made from technical glycerin.

For electrode boilers, special propylene glycol compounds are recommended, which contain additives that prevent foaming. For example, XNT-35. Before buying antifreeze for such equipment, it is better to consult with representatives of the coolant manufacturer.
Relatively numerous types of coolants and their parameters require the same different approach. The most elementary and economical option is to use ordinary water, an unpretentious and versatile liquid.Distilled water is the best choice, it's almost perfect. Abstainer owners may like the idea of using ethanol.
To equip a system with antifreeze, additional expenses will be required, and in the future - careful monitoring of the operation of the equipment. The choice of coolant depends on how the house or other building will be used, and on the desire of the owners to spend time and money on additional operations.
The opinion of a competent person can be heard in this video: