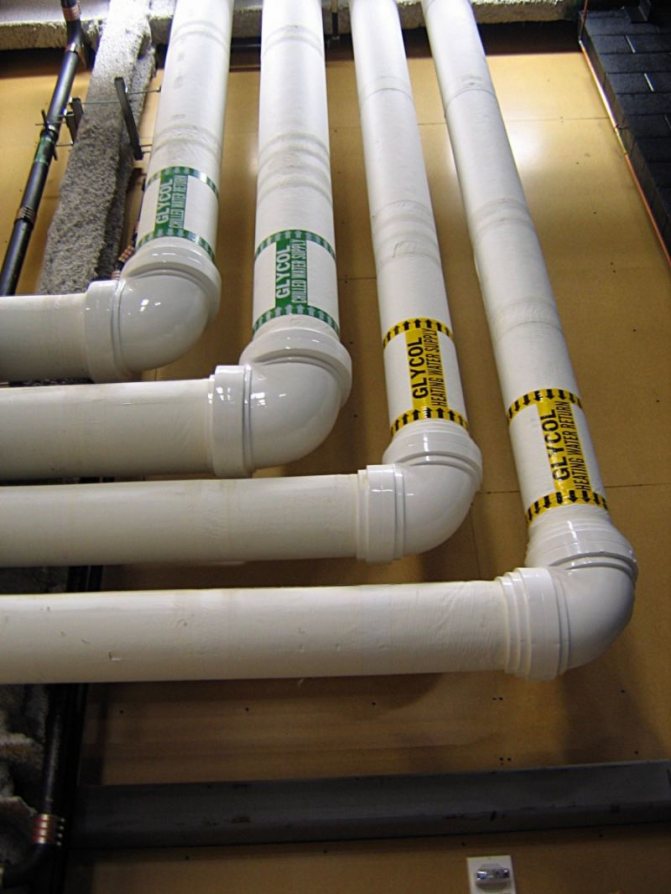
- Comparative table of pipes used for heating
- Comparative price overview
- Disadvantages of black steel heating pipes
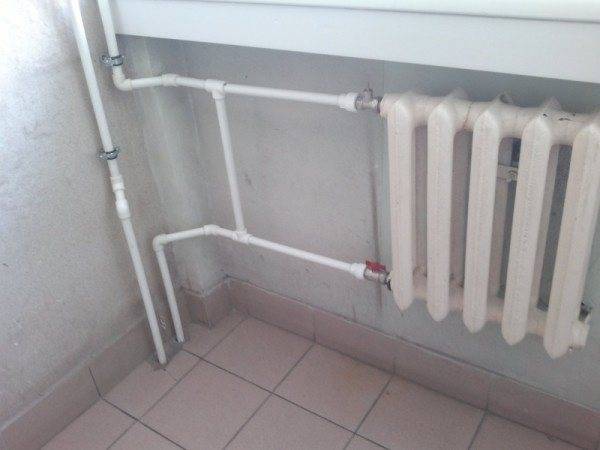
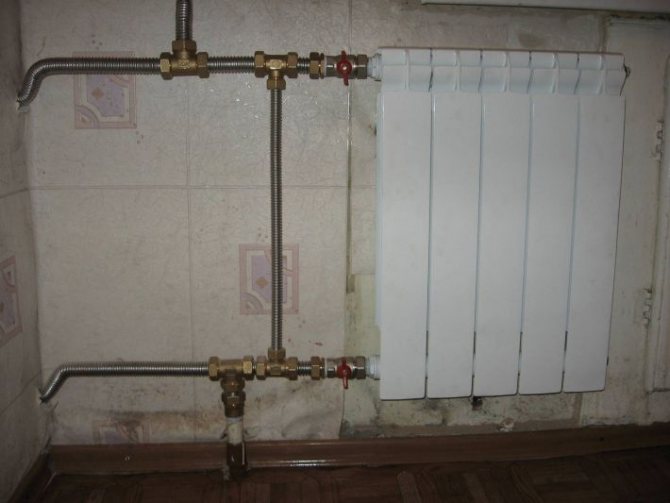
- Single pipe heating system
- Copper
- Choose the diameter for your heating
- Difficulties in choosing a pipeline diameter
- The dependence of the size on the speed of the coolant
- Coolant volume parameters
- Hydraulic losses
- How to make registers from round pipes with your own hands
- Influence of pipe diameter on efficiency for a heating system in a private house
- Pipe section selection: table
- How much heat should the pipeline supply
- Advantages and disadvantages of pipes from different materials
- Copper and brass
- Steel pipes
- metal-plastic
- Polyethylene
- Polypropylene
- Water heating devices
- Underfloor heating construction
- Skirting and floor convectors
- What materials can be used?
- Copper
- metal-plastic
- Made of cross-linked polyethylene
- Steel
- Polypropylene
- No. 6. Polypropylene pipes
- What pipes to put on heating. Central
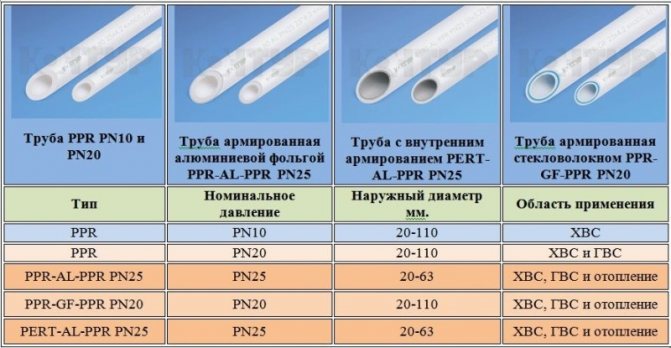
Comparative table of pipes used for heating
The main differences between polymer pipes used for the construction of heating systems can be conveniently presented in the form of a comparative table:
| XLPE pipes | Polypropylene pipes | Metal-plastic pipes | |
| The cost of pipes and fittings | The average cost of pipes and fittings.More expensive than polypropylene analogues, but cheaper than metal-plastic | The most budget option | The most expensive option, although its cost is more than compensated by reliability and practicality |
| Ease of installation | The connection is made by means of special sleeves. The sleeve is put on the end of the pipe, after which it expands and a fitting is inserted into it. Using a special tool, the sleeve is pushed onto the expanded end, ensuring a secure connection. | Installation is not possible without a special welding machine | Couplings are easy to install, but not very reliable. Non-separable press fittings are more reliable, but their installation requires a special tool |
| Range of sizes | For private heating networks, products with a diameter of 12 to 25 mm are used | A large number of pipe sizes are available, suitable for both private heating systems and main heating networks | For domestic projects of heating networks, it will not be difficult to choose the right diameter. Large-scale projects cannot be implemented, since the maximum pipe diameter is 50 mm |
| Linear extension | Depends on the heating of the pipe. Can reach up to 2 mm/m | Relatively high. An exception is pipes reinforced with fiberglass or aluminum. Here the coefficient is not more than 0.26-0.35 mm / m | The pipe is least subject to thermal expansion. The coefficient does not exceed 0.25 mm/m |
| High temperature resistance | The pipe is designed to operate in the temperature range from -50°C to 100°C. Products soften at temperatures above 130°C, melt after 200°C | Polypropylene begins to deform with prolonged exposure to temperatures above 120 ° C | Rated operating temperature - 95°C.Short-term heating up to 110°C is allowed |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, especially when heated | The pipe does not have sufficient flexibility. To pass corners and avoid obstacles, installation of corner joints is required | The pipe is easily bent without special tools and keeps its shape |
| Lifetime | Under recommended operating conditions (temperature 70°C, pressure 3 bar), the manufacturer guarantees performance for a period of at least 50 years | Most manufacturers claim a service life of at least 25 years | At least 15-25 years old. With proper installation and gentle operation, it reaches 50 years |
| Resistance to defrosting of the heating network | Easily withstands multiple freeze point transitions without affecting performance | It has good elasticity, allowing it to withstand repeated freezing cycles. | It can withstand up to three freezing cycles without loss of quality. Exceeding this threshold may be fraught with a violation of the integrity of the pipeline |
Comparative price overview
In construction, plumbing stores you can buy heating pipes that are made from different materials:
- Copper. The average price for 1 meter (diameter 20 mm) is 250 rubles. Permissible temperatures of the working fluid - up to 500 degrees Celsius. They transmit stray currents, which is a disadvantage.
- Polypropylene. The average price for 1 meter is 50 rubles. Suitable for liquid temperatures up to 95 degrees. They don't oxidize. Cannot withstand strong water hammer.
- Metal-plastic. The average price for 1 meter is 40 rubles. The temperature maximum is up to 150 degrees. The term of active operation is 15 years.
Prices vary depending on the diameter, wall thickness, fame of the manufacturer.
Copper pipes for heating
Disadvantages of black steel heating pipes
Black steel pipes have long been used for heating installations, since such products are strong enough and resistant to high pressures and temperatures.
There are two types of steel black pipes - seam and seamless or seamless. Products with seams are obtained by bending and welding sheet iron.
Although both types of products can be used for one purpose or another, the strength indicators for seamless pipes are higher.

However, black metal pipes have a number of imperfections. They are prone to oxidation and corrosion, so they begin to overgrow from the inside over time, especially if the pipeline is empty in the summer. The inner surface of the pipes is not too smooth, and the installation is carried out only by welding.
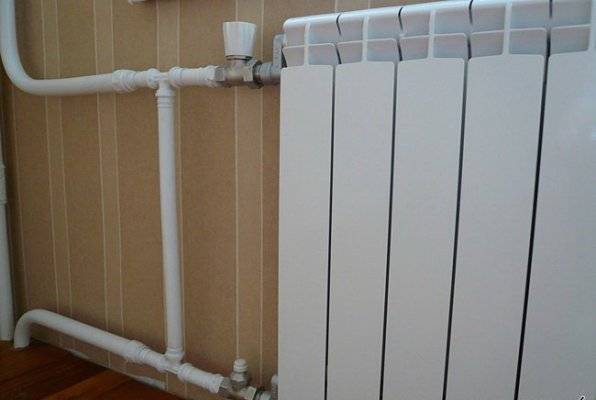
Single pipe heating system
This version of the distribution of heating pipes is also called sequential.
Peculiarities:
- You can make a self-accurate contour;
- A fairly economical option, its implementation requires a minimum of materials;
- Compatible with open systems;
- Depending on the distance of the sources, the temperature of the radiators changes, the nearest one will be the warmest, the extreme one the coldest;
- It is necessary to install bypasses, otherwise, if any battery is clogged, the system stops working;
- Forced fluid flow requires a powerful pump;
- Strict restrictions on the number of radiators in the riser.

In a horizontal system, the main pipe is usually masked in a screed, branch pipes to the batteries depart from it. The coolant is supplied from above, and leaves from below.

Features of installation of single-pipe wiring:
- From the very beginning, in any case, the boiler is installed.
- If you are using a natural circulation vertical design, then a large diameter supply pipe must be selected. This approach will allow the hot stream to create the necessary pressure, passing through the entire line.
- If you use a horizontal design, be sure to remember about the circulation pump when calculating. It must be installed in the return pipe. Also, the pump can be used in a vertical version, but the connection must be through a bypass. Otherwise, when de-energized, it will interfere with natural circulation.
- We must not forget about the slope of the supply pipe heading towards the radiators or from the main boiler. It is advisable to leave 3-5 degrees per meter of length.
- It is preferable to locate the boiler at the lowest point of the pipeline.
- It is recommended to use "Leningradka" - a system of jumpers and bypasses with thermoregulation. This approach will allow you to set the temperature on each radiator separately.
- Don't forget battery thermostatic heads.
- Experts advise using a Mayevsky crane for each battery. This approach will not allow airing to occur, which could interfere with the circulation of the coolant.
- In a vertical system, an expansion tank must be used.
- At the lowest point of the wiring, there must be a tap designed to fill and empty the system.
- The boiler is recommended to be purchased with a small margin of power. In this case, the system will be able to effectively heat the room even in severe frosts.
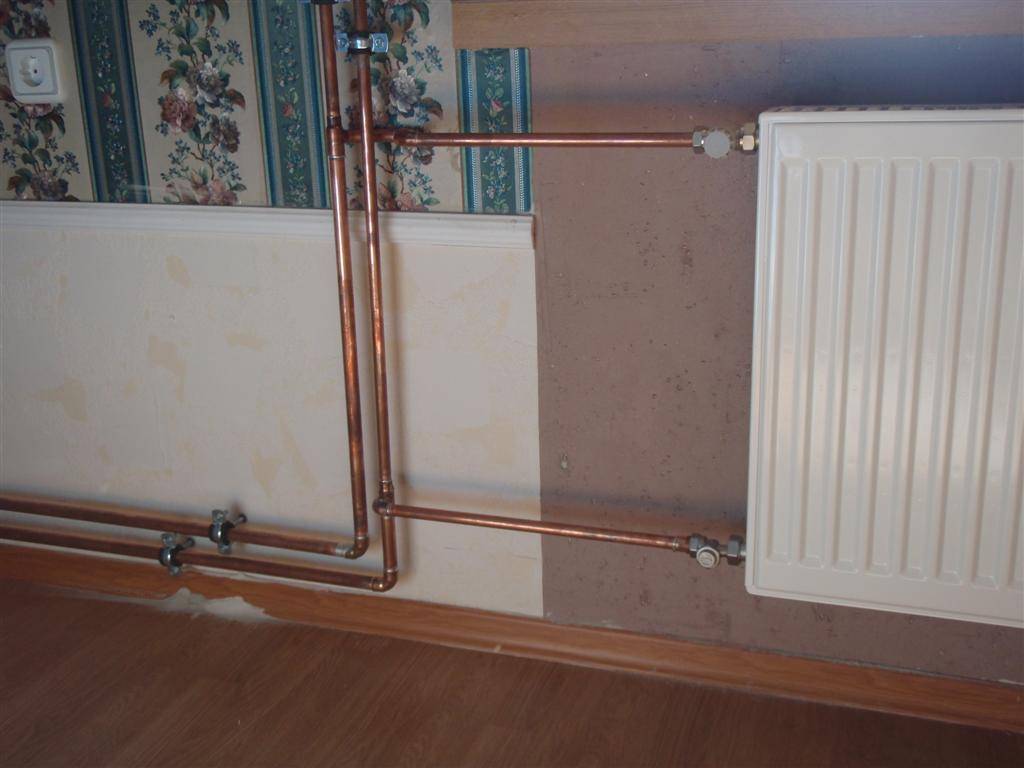
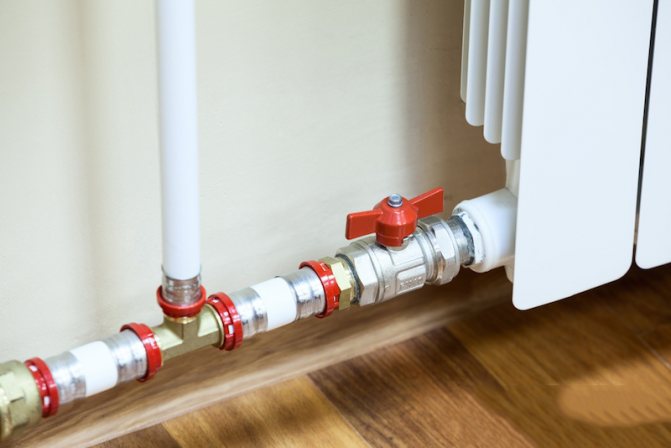
Copper
In the question of which pipes are better to choose for heating, the answer is unequivocal - copper.This is a material that gives off heat better than others, is completely non-corrosive even in the most adverse conditions, and the service life of a copper pipeline with proper installation is 100 years or more.
Features of copper heat pipe:
- The ability of the line to withstand heating up to +500°C. Of course, the liquid in the system does not reach such a temperature, but the pipes always have a margin of safety for unforeseen situations.
- The strength of the walls is sufficient to withstand hydraulic shocks of various strengths.
- A feature of copper is the absence of reaction with oxygen and many chemicals. For this reason, plaque does not form on the inner walls even after 100 years.
Like steel, copper has excellent heat dissipation, but this is an advantage only when the network is indoors. In unheated areas, it is necessary to isolate the heat pipe with a heater.
The installation of copper pipes requires the participation of specialists: the segments are connected by soldering with capillary fittings and silver-containing solder.
The main disadvantage of a copper heat pipe is the very high cost of the components.
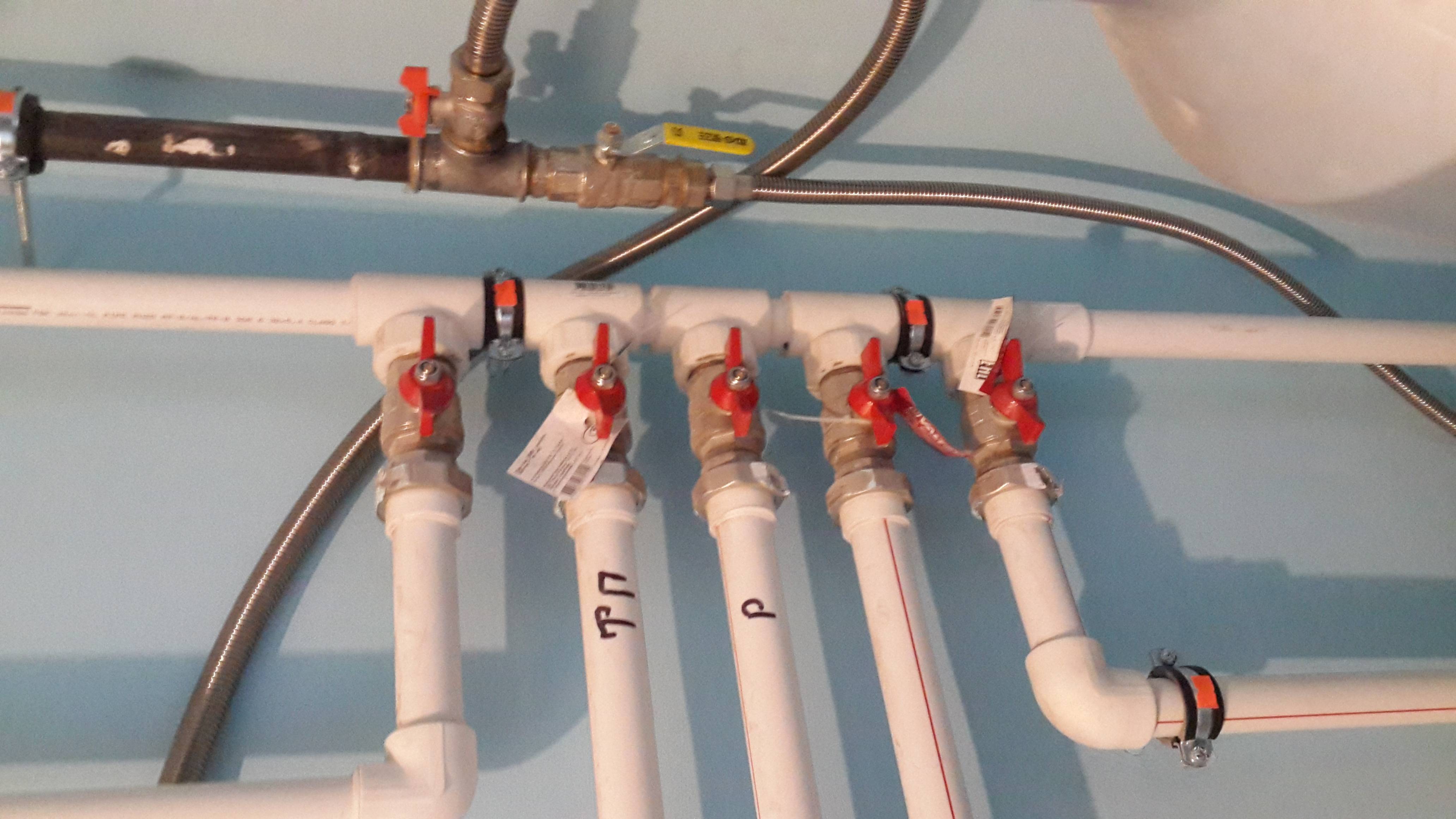
Choose the diameter for your heating
Do not count on the fact that you will immediately be able to choose the right pipe diameter for heating your home. The fact is that you can get the desired efficiency in different ways.
Now in more detail
What is the most important thing in a proper heating system? The most important thing is uniform heating and delivery of liquid to all heating elements (radiators)
In our case, this process is constantly supported by a pump, due to which, for a specific time period, the liquid moves through the system.Therefore, we can choose from only two options:
- buy large-section pipes and, as a result, a low coolant supply rate;
- or a pipe of small cross section, naturally the pressure and velocity of the fluid will increase.
Logically, of course, it is better to choose the second option for the diameter of pipes for heating a house, and for these reasons:
with external pipe laying, they will be less noticeable;
with internal laying (for example, in a wall or under a floor), the grooves in the concrete will be more accurate, and it is easier to hammer them;
the smaller the diameter of the product, the cheaper it is, of course, which is also important;
with a smaller pipe section, the total volume of the coolant also decreases, thanks to which we save fuel (electricity) and reduce the inertia of the entire system.
Yes, and working with a thin pipe is much easier and easier than with a thick one.
Difficulties in choosing a pipeline diameter

The main difficulty in selecting the diameter lies in the planning features of the highway. Taken into account:
- external indicator (copper and plastic) - the surface of the reinforcement can give off heat fluxes to the room;
- inner diameter (steel and cast iron) - allows you to calculate the throughput characteristics of a separate section;
- conditional parameters - rounded value in inches, needed for theoretical calculations.
The dependence of the size on the speed of the coolant
The choice of the diameter indicator will determine the throughput of the line, taking into account the recommended speed of 0.4-0.6 m / s. At the same time, it is taken into account that at a speed of less than 0.2 m/s, air locks are formed, and at a speed of more than 0.7 m/s, there is a risk of increasing the pressure of the coolant.

How evenly the thermal energy is distributed along the contour determines the diameter of the nozzles.The smaller it is, the faster the water moves, but the speed indicators have a limitation:
- up to 0.25 m / s - otherwise there are risks of air jams and the impossibility of their removal by vents, heat loss in the room;
- no more than 1.5 m / s - the coolant will make noise during circulation;
- 0.36-0.7 m / s - the reference value of the coolant velocity.
Coolant volume parameters
For systems with natural circulation, it is better to choose fittings with an increased diameter. This will reduce heat loss during the friction of water on the inner surface. When using this technique, it should be taken into account that with an increase in the volume of water, the energy costs for heating it increase.
Hydraulic losses
The phenomenon occurs if the pipeline is made of plastic products of different diameters. The reason is the difference in pressure at the joints and an increase in hydraulic losses.
How to make registers from round pipes with your own hands
This option is the most widespread of all the above designs for several reasons: manufacturing does not require specific skills, round pipes are commercially available, and the product layout is simple. Required materials and tools:
- round pipes of the desired diameter (40–70 mm);
- branch pipes Ø 25 mm;
- end caps;
- drain valve;
- grinder, hacksaw;
- welding machine;
- measuring tool.
Standard quad radiator
If it is planned to manufacture an autonomous "samovar", then an additional purchase of a heating element and an expansion tank will be required. The scheme of work on the manufacture and connection of the device is as follows:
- The choice of the model suitable for a particular case: horizontal or vertical heating radiators.
- Determination of dimensions, drawing up a diagram.
- Purchase of materials.
- Welding of the product (or less often assembly with a threaded connection).
- Leak test.
- Connection to the heating circuit system.
Below are recommendations for the independent production of registers from round pipes.
Any plumber or person who has the skill of assembling pipes or wiring according to a pattern or scheme will be able to mount the product.
For the manufacture of registers, drawings are not required, a simple diagram or drawing is enough to give an idea of what kind of design the output should be.
It is important not to succumb to the temptation to "weld the pipe thicker." The larger the diameter of the pipes, the more water will have to be heated, and this is an additional load on the boiler plus an unjustified increase in the heating bill. Optimum conditional pipe diameter - Ø 32 mm
The optimal conditional diameter of the pipe is Ø 32 mm.
You can increase heat transfer by increasing the distance between the pipes - add 5 cm to the value of the pipe diameter.
The most reliable connection is welding. If a thread is used, then UNITEC plumbing linen or adhesive-sealant, which is specially designed for threaded connections in plumbing systems, is used as a gasket.
Influence of pipe diameter on efficiency for a heating system in a private house
It is a mistake to rely on the “more is better” principle when choosing a pipeline section. Too large a pipe cross section leads to a decrease in pressure in it, and hence the speed of the coolant and heat flow.
Moreover, if the diameter is too large, the pump simply may not have enough capacity to move such a large volume of coolant.
Important! A larger volume of coolant in the system implies a high total heat capacity, which means that more time and energy will be spent on heating it, which also affects the efficiency not for the better.
Pipe section selection: table
The optimal pipe section should be the smallest possible for a given configuration (see table) for the following reasons:
However, do not overdo it: in addition to the fact that a small diameter creates an increased load on the connecting and shut-off valves, it is also not able to transfer enough thermal energy.
To determine the optimal pipe section, the following table is used.
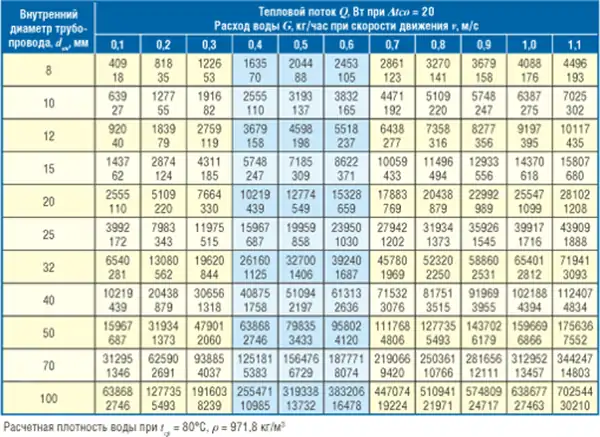
Photo 1. A table in which the values are given for a standard two-pipe heating system.
How much heat should the pipeline supply
Let us consider in more detail, using an example, how much heat is usually supplied through pipes, and we will select the optimal diameters of pipelines.
There is a house with an area of 250 square meters, which is well insulated (as required by the SNiP standard), so it loses heat in winter by 1 kW per 10 square meters. To heat the whole house, an energy supply of 25 kW (maximum power) is required. For the first floor - 15 kW. For the second floor - 10 kW.
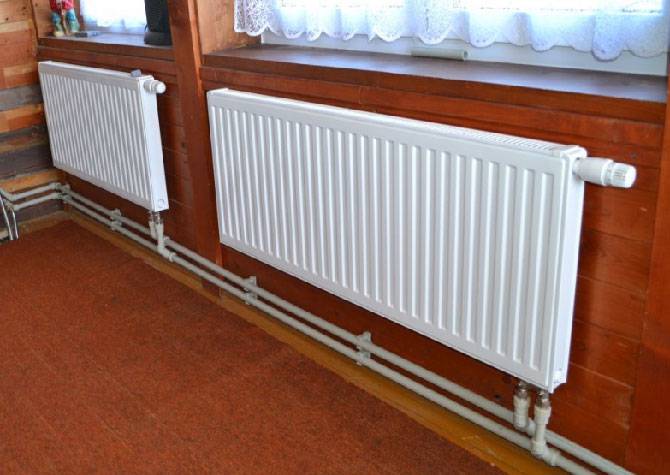
Our heating scheme is two-pipe. Hot coolant is supplied through one pipe, and the cooled coolant is discharged to the boiler through the other. Radiators are connected in parallel between the pipes.
On each floor, the pipes branch into two wings with the same heat output, for the first floor - 7.5 kW each, for the second floor - 5 kW each.
So, 25 kW comes from the boiler to the interfloor branching. Therefore, we need main pipes with an internal diameter of at least 26.6 mm so that the speed does not exceed 0.6 m / s. Fits 40mm polypropylene pipe.
From the interfloor branching - along the first floor to the branching on the wings - 15 kW is supplied. Here, according to the table, for a speed of less than 0.6 m/s, a diameter of 21.2 mm is suitable, therefore, we use a pipe with an outer diameter of 32 mm.
7.5 kW goes to the wing of the 1st floor - an inner diameter of 16.6 mm is suitable, - polypropylene with an outer diameter of 25 mm.
Accordingly, we take a 32mm pipe to the second floor before branching, a 25mm pipe to the wing, and we also connect radiators on the second floor with a 20mm pipe.
As you can see, it all comes down to a simple choice among the standard diameters of commercially available pipes. In small home systems, up to a dozen radiators, in dead-end distribution schemes, polypropylene pipes 25 mm - “on the wing”, 20 mm - “on the device” are mainly used. and 32 mm "on the line from the boiler."
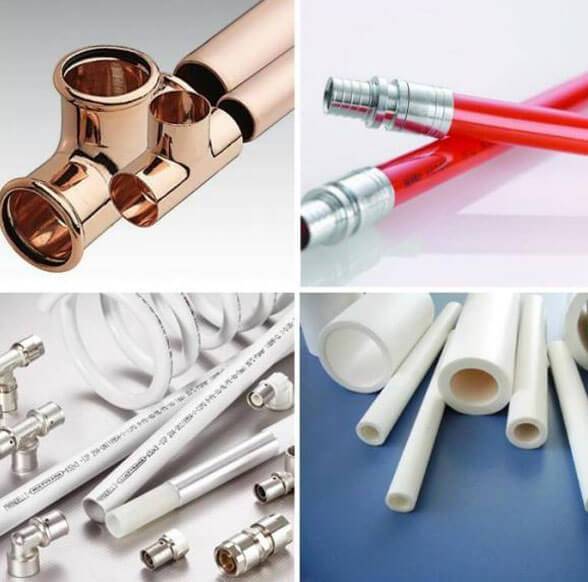
Advantages and disadvantages of pipes from different materials
So, in order not to be unfounded, we will give a few facts about pipes from various raw materials. Having studied the information, you can make the right choice in favor of one or another material for your own heating system:
Copper and brass
Pipes made of this material are aesthetic, have high thermal conductivity and a long service life. However, installation and welding require experience and a special apparatus - it is easy to damage soft metal.
In addition, their cost is high, and given the length of communications, it is fabulous. Such heating is permissible in luxurious mansions, where it will give a retro atmosphere. Copper pipes are good for drinking water, as the metal has an antibacterial effect.
Somewhat soften the cost of heating from brass - a copper alloy. These pipes are not afraid of corrosion. Withstand mechanical loads and pressure, have good thermal conductivity. Among the shortcomings, one can distinguish features when choosing - brass pipes come in several types and it is difficult to figure it out without experience.

Steel pipes
Until recently, they held the lead, however, with the development of technology, they ceased to attract attention. And it is clear why - high susceptibility to corrosion, metal destruction during welding, low tightness during installation using fittings. In addition, you will have to constantly update the appearance - paint, clean
The service life of steel heating is up to 10 years
In addition, you will have to constantly update the appearance - paint, clean. The service life of steel heating is up to 10 years.
Another thing is if stainless pipes are used for it. They are beautiful, strong and durable. They arrange not only traditional wiring, but also underfloor heating, boiler piping - where not every material can withstand high temperatures. The shiny surface perfectly gives off heat, which is why the economic component of the project, even with the high cost of pipes, is obvious.
metal-plastic
The option is quite good for laying heating - on the outside it is a layer of plastic, on the inside aluminum - it withstands high temperatures, pressure, without damage to the shells. The material is easy to install.Nevertheless, the disadvantages are significant - all fasteners occur with threaded connections, which eventually lose their tightness, cracks occur. The latter are a frequent occurrence if the pipes are not reinforced, but only glued with aluminum foil.
Polyethylene
"Sewn" from several layers of raw materials are durable and suitable for any purpose. In heating, it has been used recently, and the material has proven itself on the good side. Withstands maximum pressure, resistant to chemical reactions in the medium of the carrier. However, the maximum temperature that will not destroy the pipe body is small - 95? Such pipes cannot be installed in the piping of a boiler, furnace or other heat source.
Polypropylene
All the advantages necessary for high-quality home heating are collected in polypropylene pipes. Judge for yourself:
- The material does not lend itself to any destructive processes - corrosion, chemical influences. It does not emit harmful components into water and air - it is often used in the construction of drinking water supply.
- The shelf life of polypropylene is calculated in tens of years, unlike other, even metallic materials.
- Installation is simple and durable. After it, the pipes turn into a monolithic single structure, which is not threatened by leaks. For work, a special soldering iron is used, after a short action of which, the nozzles can withstand a burst pressure of 40 atm.
- Pipes made of polypropylene withstand temperatures up to 125 C, working pressure up to 25 atm, they are not threatened with mechanical damage.
So, we conclude from the above - polypropylene pipes become the best option for home heating.Their reliable performance, as well as budget in an era of constant crises, is a worthy way out for your own comfort.
Water heating devices
As heating elements of the premises can be:
- traditional radiators installed under window openings and near cold walls, for example, on the north side of the building;
- pipe contours of floor heating, otherwise - warm floors;
- baseboard heaters;
- floor convectors.
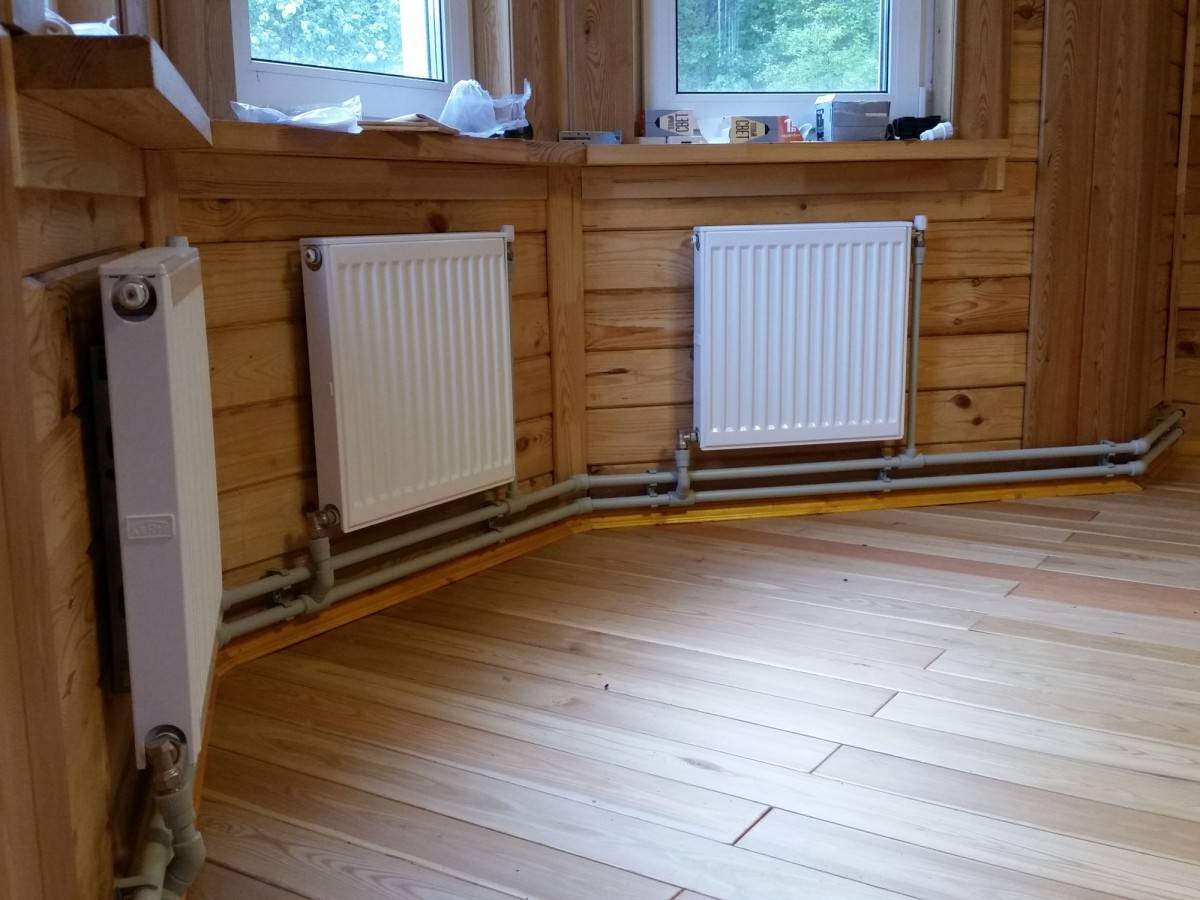
Water radiator heating is the most reliable and cheapest option among those listed. It is quite possible to install and connect the batteries yourself, the main thing is to choose the right number of power sections. Disadvantages - weak heating of the lower zone of the room and the location of the devices in plain sight, which is not always consistent with the interior design.
All commercially available radiators are divided into 4 groups according to the material of manufacture:
- Aluminum - sectional and monolithic. In fact, they are cast from silumin - an alloy of aluminum with silicon, they are the most effective in terms of heating rate.
- Bimetallic. A complete analogue of aluminum batteries, only a frame made of steel pipes is provided inside. Scope of application - multi-apartment high-rise buildings with central heating, where the heat carrier is supplied with a pressure of over 10 bar.
- Steel panel. Relatively cheap monolithic type radiators made of stamped metal sheets plus additional fins.
- Pig-iron sectional. Heavy, heat-intensive and expensive devices with an original design. Due to the decent weight, some models are equipped with legs - it is unrealistic to hang such an "accordion" on the wall.
In terms of demand, the leading positions are occupied by steel appliances - they are inexpensive, and in terms of heat transfer, thin metal is not much inferior to silumin. Following are aluminum, bimetallic and cast iron heaters. Choose which ones you like best.
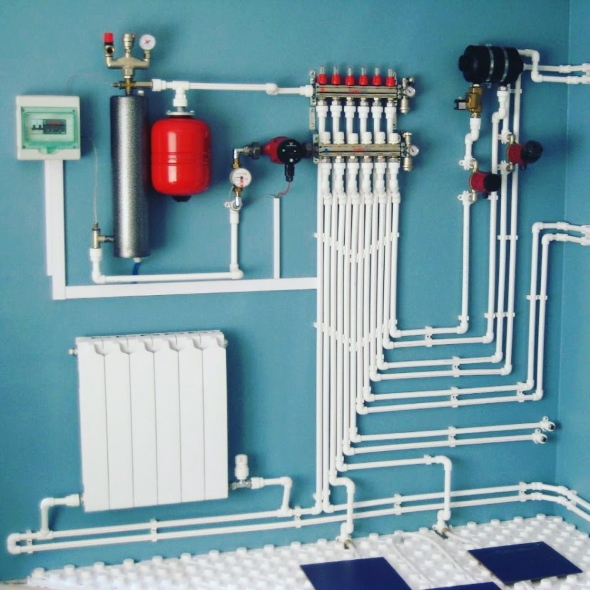
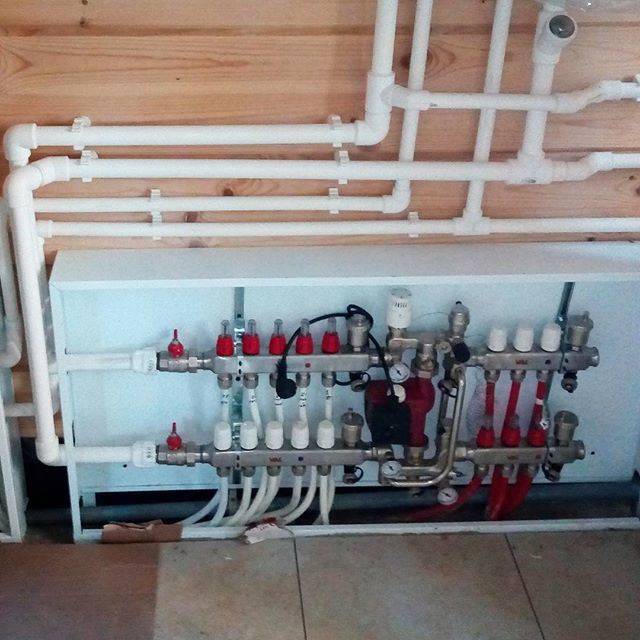
Underfloor heating construction
The floor heating system consists of the following elements:
- heating circuits made of metal-plastic or polyethylene pipes, filled with cement screed or laid between logs (in a wooden house);
- distribution manifold with flow meters and thermostatic valves to control the water flow in each loop;
- mixing unit - a circulation pump plus a valve (two- or three-way), maintaining the temperature of the coolant in the range of 35 ... 55 ° C.
The mixing unit and the collector are connected to the boiler by two lines - supply and return. Water heated to 60 ... 80 degrees is mixed in portions with a valve into the circuits as the circulating coolant cools down.
Underfloor heating is the most comfortable and economical way of heating, although installation costs are 2-3 times higher than the installation of a radiator network. The optimal heating option is shown in the photo - floor water circuits + batteries regulated by thermal heads.
Warm floors at the installation stage - laying pipes on top of the insulation, fastening the damper strip for subsequent pouring with cement-sand mortar
Skirting and floor convectors
Both types of heaters are similar in the design of the water heat exchanger - a copper coil with thin plates - fins.In the floor version, the heating part is closed with a decorative casing that looks like a plinth; gaps are left at the top and bottom for the passage of air.
The heat exchanger of the floor convector is installed in a housing located below the level of the finished floor. Some models are equipped with low-noise fans that increase the performance of the heater. The coolant is supplied through pipes laid in a hidden way under the screed.
The described devices successfully fit into the design of the room, and underfloor convectors are indispensable near transparent outer walls made entirely of glass. But ordinary homeowners are in no hurry to purchase these appliances, because:
- copper-aluminum radiators of convectors - not a cheap pleasure;
- for full heating of a cottage located in the middle lane, you will have to install heaters around the perimeter of all rooms;
- floor heat exchangers without fans are inefficient;
- the same products with fans emit a quiet monotonous hum.
Baseboard heating device (pictured left) and underfloor convector (right)
What materials can be used?
All materials can be divided into: plastic and metal.
The first are made of cross-linked polyethylene, or polypropylene, or metal-plastic.
The second is made of steel, iron or copper.
Reference. Metal and polymer pipes can be easily combined. It is necessary to choose and connect them correctly.
Copper
Differ in durability and reliability.
Advantages:

- Ease.
- Strength.
- Withstand high temperatures.
- The pipe bends when heated.
- No additional fasteners needed.
- Inexpensive parts for connection.
- High thermal conductivity.
- If the water contains a minimum of impurities, the heating main will last a century.
Minuses:
- Long to install.
- Heaviness. It won't be cheap to ship.
- Susceptibility to corrosion. Hidden in the wall, deteriorating.
- They quickly lose heat if the rooms are cold.
- The roughness of metal surfaces is an excellent environment for the appearance of oxidation.
- High cost.
metal-plastic
Made of plastic, with a thin layer of aluminum inside.
Pros:
- Inexpensive.
- Easy to clean.
- They hide in the walls.
- The plastic is smooth, and plaque rarely forms in the pipe.
- Lightweight - you can bring your own.
- They serve 20 years or more.
Photo 3. Metal-plastic pipes for the heating system. In the central part of the products is an aluminum layer.
Flaws:
- If there is a breakdown in some heating main, a separate segment cannot be removed. Remove the area between the two fittings.
- Do not bend when heated. If you need an angle, then use special parts: fittings.
- Difficult to connect.
- Additional wall mounts required.
- If you turn off the heating in winter, the pipes will crack.
Made of cross-linked polyethylene
Modern and high tech.
Advantages:
- Durable. They last half a century or more.
- Inexpensive. Both the price and delivery will not hit the budget.
- Unique property: when hot liquid enters, the pipe bends and then returns to its place.
- Easy to assemble. Additional details are simple and accessible.
- Smooth inside, do not accumulate mineral deposits.
- High density.
- Ideal for hiding in walls.
- Withstand a temperature load of 90 °C.
Photo 4. Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene for heating systems. Often used for arranging underfloor heating.
No deficiencies found.
Steel
Made of steel using two different technologies:
- sewn from a sheet;
- use special equipment.
Pros:
- Tightness.
- They are inexpensive.
Minuses:
- Due to the high electrical conductivity, they are not suitable for electric boilers.
- Subject to destruction over time.
- Heaviness. Difficult to deliver and install.
Polypropylene
Inexpensive and great for heating a private house.
Advantages:
- Long service life (from 30 years).
- Easy to mount on the wall.
- When used in a country house with seasonal residence, they will not freeze when the heat is turned off.
The disadvantages are similar to metal-plastic ones: additional fasteners, fittings, the inability to repair a separate segment.
No. 6. Polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene pipes are actually an ideal option for organizing water supply. They can be non-reinforced and reinforced. The former are suitable only for cold water supply, the latter are used in both heating and hot water supply. The pipe can be reinforced with aluminum, fiberglass or other materials. Reinforcement increases strength and reduces the thermal elongation of polypropylene. The best option is fiberglass reinforcement.
Polypropylene pipes for water supply
To date, the highest quality reinforced pipes are produced in Germany. Detailed technical characteristics and a list of facilities where such piping systems are installed can be found on the website of the representative of the German plant aquatherm GmbH
Advantages of polypropylene pipes:
- durability up to 50 years;
- the ability to withstand temperatures inside pipes up to + 90-95C and pressure up to 20 atmospheres (this applies to the reinforced version);
- relatively easy installation.Pipes are connected using a special welding machine for polypropylene. It is not difficult to work with him, it will take a little time to learn and bring the process to automatism;
- strong connections;
- such pipes will even withstand the freezing of water inside them;
- resistance to corrosion;
- sufficiently high strength;
- relatively low price
Among the minuses is the fear of high external temperatures, so this is not an option for fire hazardous premises. In addition, even when reinforced with aluminum or nylon thread, the material retains a high level of thermal deformation, therefore, it is impossible to do without the use of insulation for hidden pipe wiring, or compensators for open wiring. If we weigh all the pros and cons, then it is better to choose polypropylene pipes for water supply at home.

What pipes to put on heating. Central
The normal mode of central heating systems is as follows:
Central heating differs from autonomous circuits in that deviations from normal modes are possible in it. It's simple: the more complex any system, the more likely it is that something will go wrong during its operation.
Here are some of the most realistic scenarios I've personally encountered:
- When the circulation in a large circuit stops abruptly or, conversely, when a discharged heating system is filled with a small amount of air, a water hammer occurs in it: at the front of the water flow, the pressure briefly rises to values 4-5 times higher than the nominal ones;
- Incorrect switching of shut-off valves on the route or in the elevator unit can lead to the fact that when testing the heating main for density, the pressure in the circuit rises to 10-12 kgf / cm2;
- In some cases, the operation of a water-jet elevator with a removed nozzle and a muffled suction is practiced. Usually this configuration is going to be in extreme cold with a lot of heat complaints and is a temporary alternative to increasing the diameter of the nozzle. From a practical point of view, this means that water is supplied to the radiators directly from the supply line of the heating main.
.
Within the framework of the current temperature schedules, the supply temperature at the lower peak of winter temperatures should reach 150C. In practice, the coolant cools somewhat on the way from the CHP to the consumer, but still remains heated noticeably above the boiling point. Water does not evaporate just because it is under pressure.