- Specific thermal power of battery sections
- Which radiators to choose for a wooden house
- Lamellar convectors
- Installation rules
- Don't overdo it!
- calculation of heating batteries by the number of sections
- Factors affecting the calculation
- Orientation of rooms to the cardinal points
- Influence of external walls
- The dependence of radiators on thermal insulation
- Climate zones
- Room height
- The role of the ceiling and floor
- frame quality
- Windows size
- Battery closed
- Connection method
- How to calculate the optimal number and volumes of heat exchangers
- Video description
- Conclusion
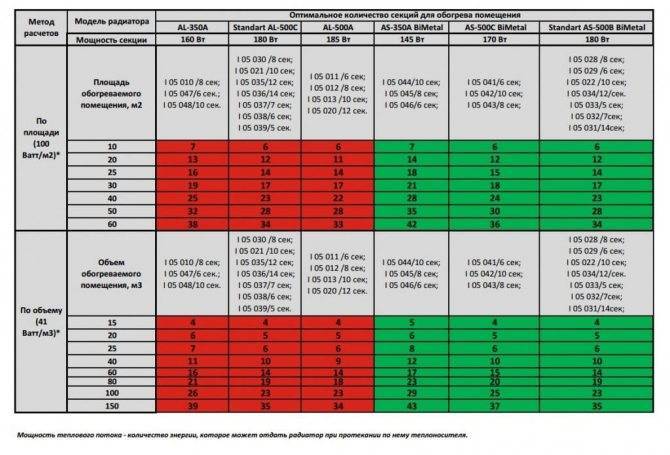
- How to calculate the number of heating radiator sections
- Calculation based on room area
- Calculation of the number of sections in radiators, based on the volume of the room
- Popular electric heating batteries and their functionality
- Calculation by room volume
- Amendments
- Conclusions regarding the choice of a radiator for an apartment
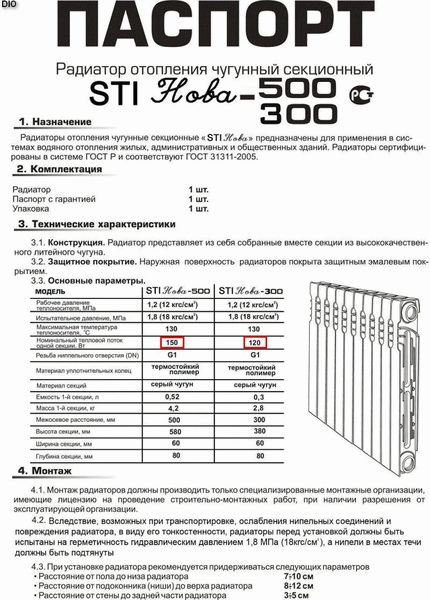
Specific thermal power of battery sections
Even before performing a general calculation of the required heat transfer of heating devices, it is necessary to decide which collapsible batteries from what material will be installed in the premises.
The choice should be based on the characteristics of the heating system (internal pressure, heating medium temperature). At the same time, do not forget about the greatly varying cost of purchased products.
How to correctly calculate the required number of different batteries for heating, and will be discussed further.
With a coolant of 70 °C, standard 500 mm sections of radiators made of dissimilar materials have an unequal specific heat output "q".
- Cast iron - q = 160 watts (specific power of one cast iron section). Radiators made of this metal are suitable for any heating system.
- Steel - q = 85 watts. Steel tubular radiators can work in the most severe operating conditions. Their sections are beautiful in their metallic sheen, but have the least heat dissipation.
- Aluminum - q = 200 watts. Lightweight, aesthetic aluminum radiators should be installed only in autonomous heating systems in which the pressure is less than 7 atmospheres. But in terms of heat transfer, their sections have no equal.
- Bimetal - q \u003d 180 watts. The insides of bimetallic radiators are made of steel, and the heat-removing surface is made of aluminum. These batteries will withstand all sorts of pressures and temperatures. The specific thermal power of bimetal sections is also on top.
The given values of q are rather conditional and are used for preliminary calculation. More accurate figures are contained in the passports of purchased heaters.
Which radiators to choose for a wooden house
Heating a wooden house (we are talking primarily about log cabins), indeed, has its own characteristics, since the thermal conductivity of the tree is low and depends on its species. In addition, it is necessary to ensure maximum fire safety. But in general, the issue of providing heat, as well as safety, rests primarily on the correct installation of the heating system, the choice of the boiler and the number of radiators.There are no restrictions on the type of radiators here: steel, cast iron, bimetallic, aluminum - all of them can be used in a wooden frame.

All types of radiators are suitable for a wooden house
Lamellar convectors
There are different types of convectors. the most popular of them are accordions. Structurally, they consist of many plates mounted on pipes through which the coolant circulates. Some models have a protective casing so that a person cannot get to the heating elements and get burned. There are models with a heating element that run on electricity.
- Strength (leaks or breaks are rare);
- High heat dissipation;
- Possibility of regulation of heat transfer by automatic equipment;
- Ease of installation;
- Automatic setting of operating modes for efficient use of the heating device (for electric models);
- Reducing the peak load in the power grid due to automatic regulation (for electric models);
- Possibility of installation on the floor, ceiling.
- Uneven heating of the air in the room;
- Difficulty removing dust
- Electric models raise dust, allergy sufferers may have problems.
Installation rules
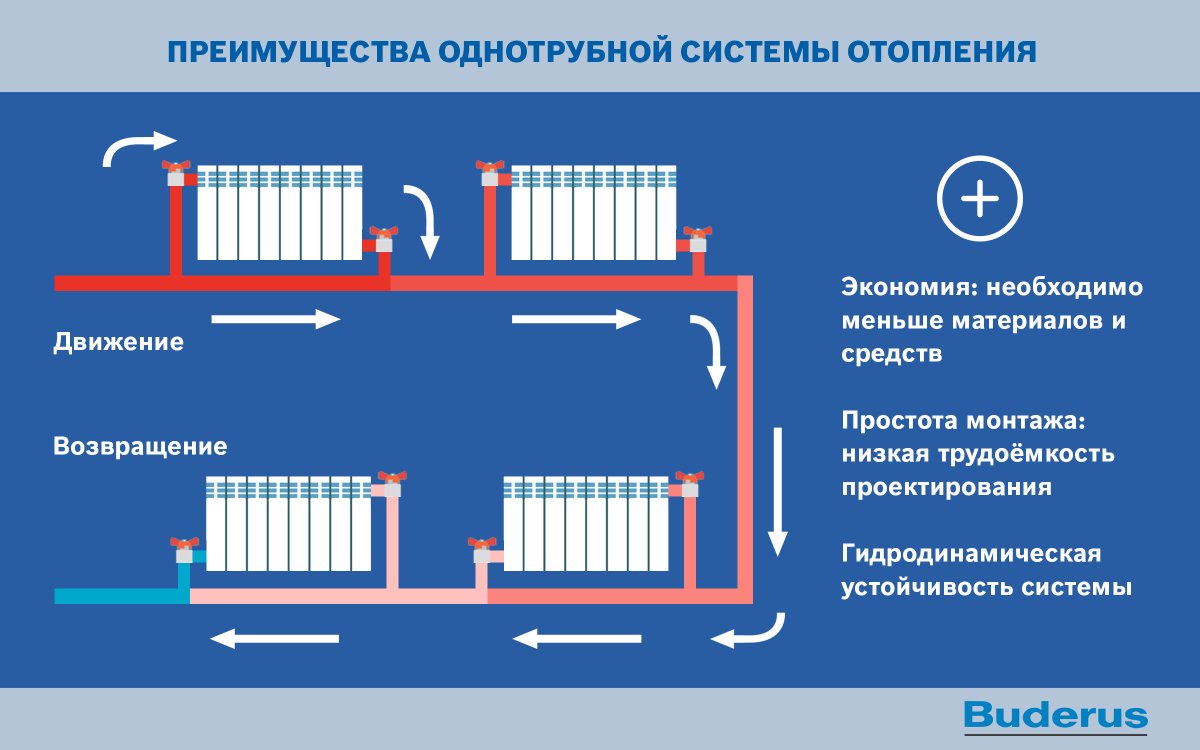
Radiator-type heating in your own home is a guarantee of comfort and coziness in autumn and winter. It is good when such a mechanism has already been connected to a centralized heating mechanism. If something like this is not there, then it becomes necessary to use autonomous heating. If we are talking about how to install the heating system with our own hands correctly, then it should be said that the most important element will be the choice of options for connecting radiators in a house of our own construction.
The first thing to deal with is piping.This can be called an important point, because the residents of their own houses at the stage of their construction are rarely able to clearly and correctly calculate the costs that will be made to form the heating system, therefore, they have to make savings on various kinds of materials. Typically, the pipe connection method can be either one- or two-pipe. The first option is economical, in which a pipe is laid from the heating boiler along the floor, which goes through all the walls and rooms and which returns to the boiler. Radiators should be installed on top of it, and the connection will be made using pipes from below. At the same time, hot water flows into the pipes, completely filling the batteries. Then the water descends and through another pipe enters the pipe. In fact, there is a serial connection of radiators due to the bottom connection. But there is a minus, because at the end of such a connection in all subsequent radiators, the temperature of the heat carrier will be lower.
There are two ways to solve this moment:
- connect a special circulation pump to the entire mechanism, which allows you to distribute hot water evenly over all heating appliances;
- connect additional batteries in the last rooms, which will increase the heat transfer area to the maximum.
When everything became clear with this issue, you should stop your attention on the scheme for connecting heating batteries. The most common will be lateral
To make it, pipes should be led out to the side of the wall and connected to two battery pipes - top and bottom. From above, a pipe is usually connected that supplies the coolant, and from below - the output. A diagonal type connection will also be effective.To perform it, you must first connect a pipe supplying a coolant to the nozzle at the top, and a return pipe to the lower one, located on the other side. It turns out that the coolant will be transported diagonally inside the radiator. The effectiveness of such a mechanism will depend on how the liquid is distributed in the radiator. It is rare that several battery sections can be cold. This happens only in cases where the ability to pass or the pressure is rather weak.
Note that the connection of the radiator from below can be not only in single-pipe, but also in two-pipe versions. But such a system is considered extremely inefficient. In this case, it will still be necessary to install a circulation pump, which will significantly increase the cost of creating a heating mechanism and create electricity costs that are needed to operate the pump. If you say what you don’t need to do, then this is not to replace the water supply with a return line. Typically, the presence of this problem shows debugging.
Do-it-yourself installation of heating radiators in your own home is associated with a number of points that do not allow us to say that this is an easy process. Its complexity also lies in the fact that in each individual case it is necessary to select batteries for a particular building, and also to know exactly how pipes pass in a private house that has already been built. Also, an equally important fact will be understanding the needs for heating and making all the necessary calculations.
In addition, we should not forget that there are various connection schemes and what may be inefficient in one house, in another will be a great solution.
If you decide to install heating radiators yourself, then you should carefully study the theoretical points, and if possible, at least consult with a specialist who will tell you what you should pay special attention to during the installation of radiators and the heating system as a whole.
How to choose the right heating radiator, see the following video.
Don't overdo it!
14-15 sections for one radiator is the maximum. Installing radiators of 20 or more sections is inefficient. In this case, you should divide the number of sections in half and install 2 radiators of 10 sections. For example, put 1 radiator near the window, and the other near the entrance to the room or on the opposite wall.
Same with steel radiators. If the room is large enough and the radiator comes out too big, it's better to put two smaller ones, but the same total power.
If there are 2 or more windows in a room of the same volume, then a good solution would be to install a radiator under each of the windows. In the case of sectional radiators, everything is quite simple.
14/2=7 sections under each window for a room of the same volume
Radiators are usually sold in 10 sections, it is better to take an even number, for example 8. A stock of 1 section will not be superfluous in case of severe frosts. The power from this will not change much, however, the inertia of heating the radiators will decrease. This can be useful if cold air enters the room frequently. For example, if it is an office space that customers often visit. In such cases, radiators will heat the air a little faster.
calculation of heating batteries by the number of sections
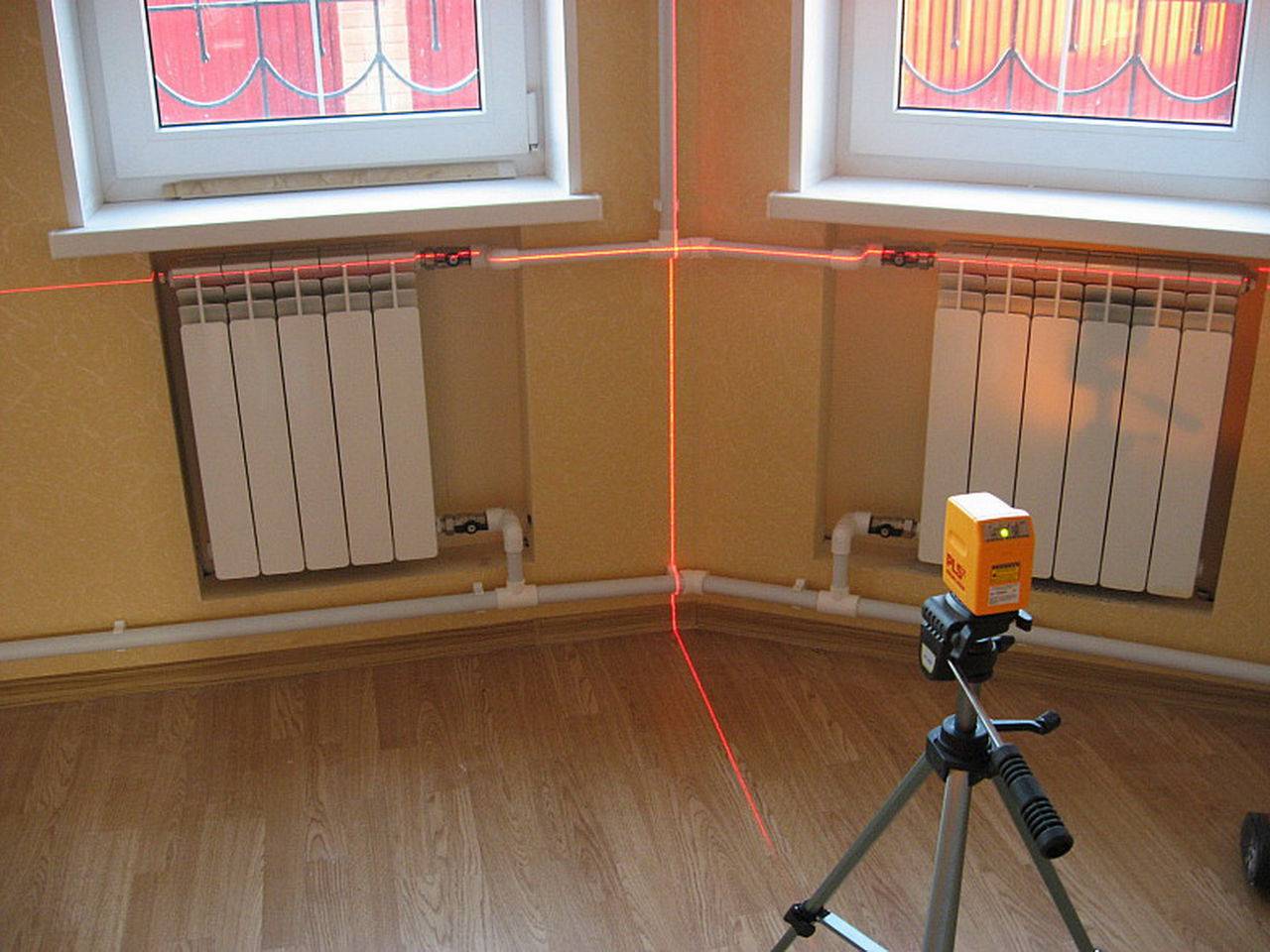
After the "arrangement" of the radiators on the diagram, you need to indicate the number of sections of each radiator.
How to find out how many sections of radiators should be?
Very simple: you need to divide the heat demand (heat loss) of the room by the power of one section.
Explanation. In past materials, I talked about the insulation of my house: walls, floors, ceilings, windows. As a result, heat losses have decreased. However, I will calculate the radiators as if the house was not insulated. Well, in fact, it’s easier to “put out” the boiler or adjust the radiator with a thermal head or a room thermostat than to hang additional sections later. This is me so that you are not surprised that I take in the calculations the values of heat loss before insulation.
So, in my example of a house, the heat demand of the hall is ~ 2040 W. The power of one section, for example, a bimetallic radiator, is on average 120 watts. Then the hall needs 2040: 120 = 17 sections. But since radiators are sold with an even number of sections, we round up: 18.
There are three windows in the room, and 18 is easily divisible by 3. So everything is simple: I put six sections under each window.
Radiators made of different materials and different manufacturers have different power. So, bimetallic radiators are produced with a power of one section from 100 to 180 W; cast iron 120-160 W; I found aluminum ones with a power of 180 W, 204 W and a few more different values ...
Conclusion: you need to inquire in advance about the type and power of radiators sold in stores in your city, and then count the sections.
And that is not all! In the store, the seller can tell you, for example, for a bimetallic radiator, the power of one section is 150 watts. But this characteristic is not enough, you should definitely ask in the radiator passport for such a characteristic as DT.
DT is the difference between the temperature of the coolant in the supply and return pipes.Usually, the passport indicates DT 90/70 - inlet temperature 90 degrees, outlet 70 degrees.
In reality, such temperatures are rare, the boiler, as a rule, does not work in the maximum mode. Often the boiler even has a limit of 80 degrees, so you cannot achieve such heat transfer, as indicated in the radiator passport. It is more realistic to focus on DT 70/55. Naturally, the power of the radiator will be 20 percent less in this mode, i.e. the same 120 watts. From these considerations, the number of sections of radiators for the premises of the house is taken.
Another condition to take into account.
The outside air temperature in the calculation program is taken as an average. But winters are different, sometimes the temperature drops even lower. In this case, the calculated power of the radiators may also not be enough. Why during the period of lower temperatures in the house will not be comfortable. For these reasons, it is also necessary to provide for a power reserve of radiators.
Let's take a look at the bathroom. Humidity in the bathroom is always high
With increased humidity, the temperature begins to drop sharply. In addition, after taking a bath or shower, +20 degrees will not feel comfortable at all, so it is better to focus on +25.
Based on all of the above, I took (for example calculation) the following number of radiator sections (bimetallic, based on 120 W per section):
— hall — 18 sections;
- living room - 10 sections;
- entrance hall - 6 sections;
– kitchen – 6 sections;
- bathroom - 4 sections;
- bedroom 2 - 10 sections;
- bedroom 1 - 6 sections.
But again, that's not all. Let's put our eyes on the plan and realize what we see:
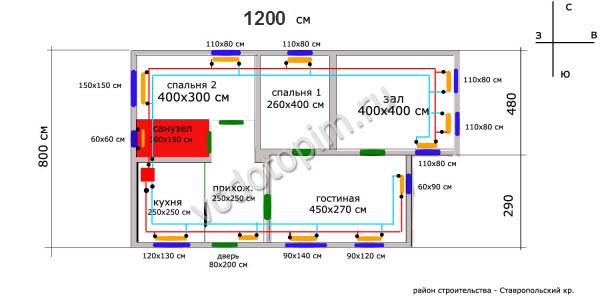
Let's pay special attention to the living room.There are three windows in the living room and preferably the same number of radiators; but 10 by 3 is divisible, so you need to either put it with a different number of sections, for example, 4 under the south windows and two under the east
Or increase the total number to 12 and install the same radiators under all windows, 4 sections each. I choose the second option, because two sections of almost three meters of the eastern wall are somehow modest.
And after all these considerations, I noted the number of sections of each radiator on the plan (in green numbers):
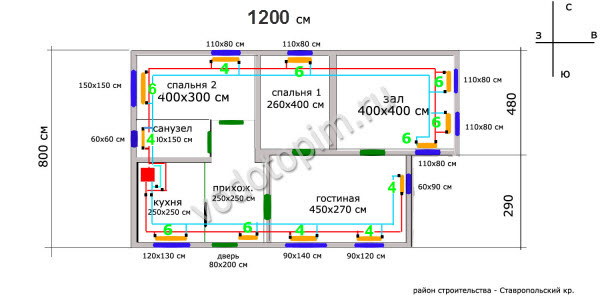
Important! I repeat once again: radiators are sold with an even number of sections - DO NOT unwind and separate them; if according to your calculations, for example, you need 5 sections, then buy and put 6, etc.
Factors affecting the calculation
The following factors influence the calculation of the power of heating radiators.
Orientation of rooms to the cardinal points
It is generally accepted that if the windows of the room face south or west, then it has sufficient sunlight, so in these two cases the coefficient "b" will be equal to 1.0.
An addition of 10% to it is required if the windows of the room are oriented to the east or north, since the sun here practically does not have time to heat the room.
Reference! For the northern regions, this indicator is taken in the amount of 1.15.
If the room faces the windward side, then the coefficient for the calculation increases to b = 1.20, with a parallel arrangement relative to wind flows - 1.10.
Influence of external walls
Their number is directly determined by the indicator "a". So, if the room has one external wall, then it is taken equal to 1.0, two - 1.2. The addition of each subsequent wall leads to an increase in the heat transfer coefficient by 10%.
The dependence of radiators on thermal insulation
To reduce the cost of heating an apartment or house will allow competent wall insulation. The value of the coefficient "d" contributes to an increase or decrease in the heat output of heating batteries.

Depending on the degree of insulation of the external wall, the indicator is as follows:
- Standard, d=1.0. They are of normal or small thickness and are either plastered on the outside or have a small layer of thermal insulation.
- With a special method of insulation d=0.85.
- With insufficient resistance to cold -1.27.
With space allowing, it is allowed to fix the thermal insulation layer to the outer wall from the inside.
Climate zones
This factor is determined by low temperatures for different regions. So c=1.0 in weather down to -20 °C.
For areas with a cold climate, the indicator will be as follows:
- c=1.1 at temperatures up to -25 °C.
- c=1.3: up to -35 °C.
- c=1.5: below 35 °C.
Its own gradation of indicators for warm regions:
- c=0.7: temperature down to -10 °C.
- c=0.9: light frost down to -15 °C.
Room height

The higher the level of overlap in the building, the more heat this room needs.
Depending on the indicator of the distance from the ceiling to the floor, a correction factor is determined:
- e=1.0 at a height of up to 2.7 m.
- e=1.05 from 2.7 m to 3 m.
- e=1.1 from 3 m to 3.5 m.
- e=1.15 from 3.5 m to 4 m.
- e=1.2 over 4 m.
The role of the ceiling and floor
The preservation of heat in the room is also facilitated by its contact with the ceiling:
- Coefficient f=1.0 if there is an attic without insulation and heating.
- f=0.9 for an attic without heating, but with a heat-insulating layer.
- f=0.8 if the room above is heated.
The floor without insulation determines the indicator f=1.4, with insulation f=1.2.
frame quality
To calculate the power of heating devices, it is important to take into account this factor. For a window frame with a single-chamber double-glazed window h=1.0, respectively for two- and three-chamber - h=0.85. For an old wooden frame, it is customary to take h = 1.27 into account
For an old wooden frame, it is customary to take h = 1.27 into account.
Windows size

The indicator is determined by the ratio of the area of window openings to square meters of the room. Usually it is from 0.2 to 0.3. So the coefficient i= 1.0.
With the result obtained from 0.1 to 0.2 i=0.9 to 0.1 i=0.8.
If the window size is higher than the standard (ratio from 0.3 to 0.4), then i=1.1, and from 0.4 to 0.5 i=1.2.
If the windows are panoramic, then it is advisable to increase i by 10% with each increase in the ratio by 0.1.
For a room in which a balcony door is regularly used in winter, automatically increases i by another 30%.
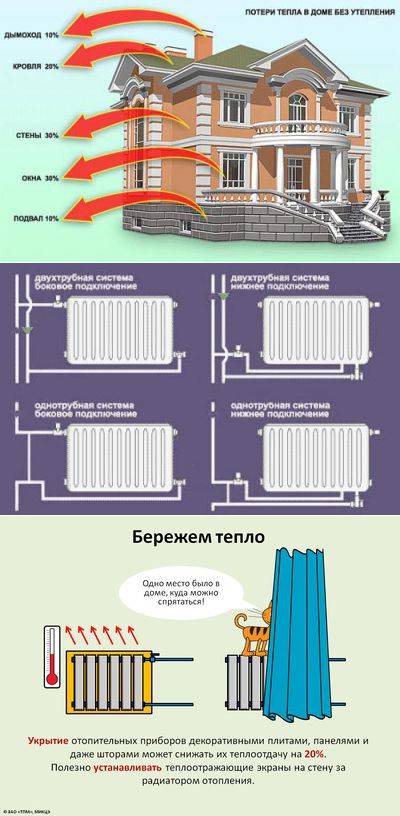
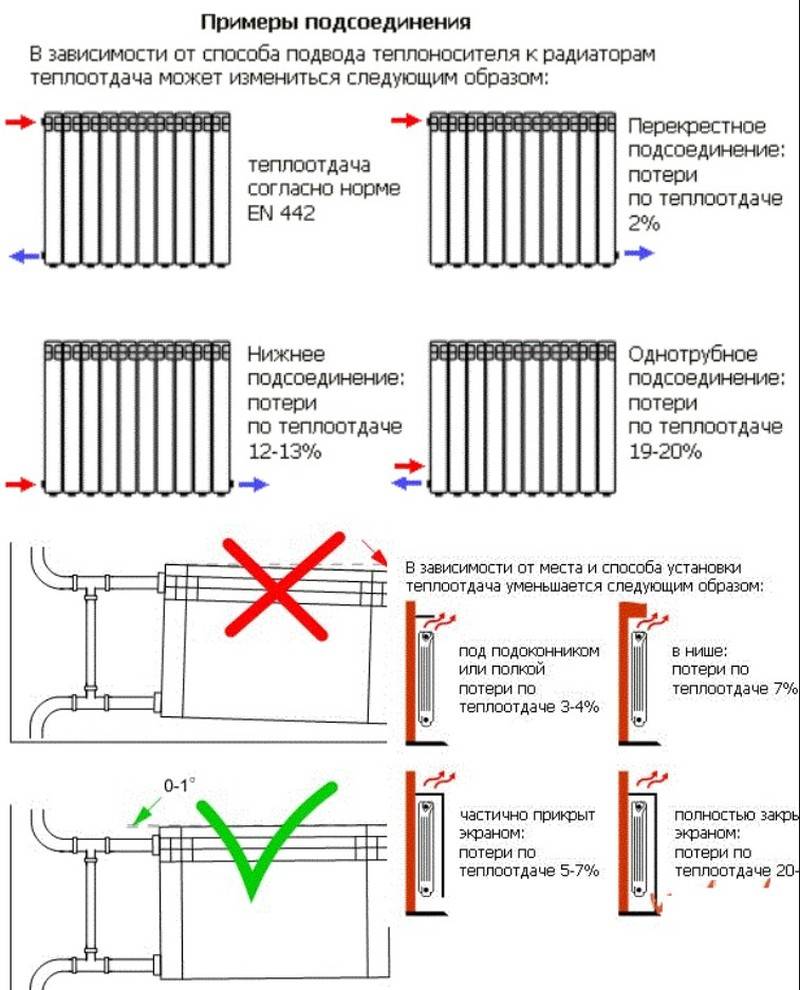
Battery closed
Minimal heating radiator enclosure contributes to faster heating of the room.
In the standard case, when the heating battery is located under the windowsill, the coefficient j=1.0.
In other cases:
- Fully open heating device, j=0.9.
- The heating source is covered with a horizontal wall ledge, j=1.07.
- The heating battery is closed by a casing, j=1.12.
- Completely closed heating radiator, j=1.2.
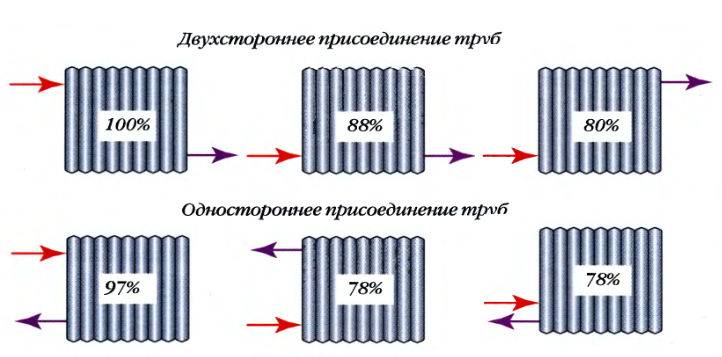
Connection method

There are several ways to connect heating radiators, and each of them is determined by the indicator k:
- The method of connecting radiators "diagonally". Is standard, and k=1.0.
- Side connection. The method is popular because of the small length of the eyeliner, k=1.03.
- The use of plastic pipes according to the "bottom on both sides" method, k=1.13.
- The solution "from below, on the one hand" is ready, there is a connection to 1 point of the supply pipe and return, k = 1.28.
Important! Sometimes additional correction factors are used to improve the accuracy of the results.
How to calculate the optimal number and volumes of heat exchangers
When calculating the number of required radiators, one should take into account what material they are made of. The market now offers three types of metal radiators:
- Cast iron,
- Aluminum,
- bimetallic alloy,
All of them have their own characteristics. Cast iron and aluminum have the same heat transfer rate, but aluminum cools quickly, and cast iron heats up slowly, but retains heat for a long time. Bimetallic radiators heat up quickly, but cool down much slower than aluminum ones.
When calculating the number of radiators, other nuances should also be taken into account:
- thermal insulation of the floor and walls helps to save up to 35% of heat,
- the corner room is cooler than the others and needs more radiators,
- the use of double-glazed windows on windows saves 15% of heat energy,
- up to 25% of heat energy “leaves” through the roof.
The number of heating radiators and sections in them depends on many factors.
In accordance with the norms of SNiP, heating 1 m³ requires 100 W of heat. Therefore, 50 m³ will require 5000 watts. On average, one section of a bimetallic radiator emits 150 W at a coolant temperature of 50 ° C, and a device for 8 sections emits 150 * 8 = 1200 W. Using a simple calculator, we calculate: 5000: 1200 = 4.16. That is, approximately 4-5 radiators are needed to heat this area.
However, in a private house, the temperature is regulated independently and it is usually believed that one battery emits 1500-1800 W of heat.We recalculate the average value and get 5000: 1650 = 3.03. That is, three radiators should be enough. Of course, this is a general principle, and more accurate calculations are made based on the expected temperature of the coolant and the heat dissipation of the radiators to be installed.
You can use the approximate formula for calculating radiator sections:
N*= S/P *100
The symbol (*) shows that the fractional part is rounded according to general mathematical rules, N is the number of sections, S is the area of the room in m2, and P is the heat output of 1 section in W.
Video description
An example of how to calculate heating in a private house using an online calculator in this video:
Conclusion
Installation and calculation of the heating system in a private house is the main component of the conditions for comfortable living in it. Therefore, the calculation of heating in a private house should be approached with great care, taking into account many related nuances and factors.
The calculator will help if you need to quickly and averagely compare various construction technologies with each other. In other cases, it is better to contact a specialist who will correctly carry out the calculations, correctly process the results and take into account all the errors.
Not a single program can cope with this task, because it contains only general formulas, and the heating calculators for a private house and tables offered on the Internet serve only to facilitate calculations and cannot guarantee accuracy. For accurate, correct calculations, it is worth entrusting this work to specialists who can take into account all the wishes, capabilities and technical indicators of the selected materials and devices.
How to calculate the number of heating radiator sections
In order for heat transfer and heating efficiency to be at the proper level, when calculating the size of radiators, it is necessary to take into account the standards for their installation, and by no means rely on the size of the window openings under which they are installed.
Heat transfer is not affected by its size, but by the power of each individual section, which are assembled into one radiator. Therefore, the best option would be to place several small batteries, distributing them around the room, rather than one large one. This can be explained by the fact that heat will enter the room from different points and evenly warm it up.
Each separate room has its own area and volume, and the calculation of the number of sections installed in it will depend on these parameters.
Calculation based on room area
To correctly calculate this amount for a certain room, you need to know some rules:
You can find out the required power for heating a room by multiplying by 100 W the size of its area (in square meters), while:
- The radiator power is increased by 20% if two walls of the room face the street and there is one window in it - this can be an end room.
- You will have to increase the power by 30% if the room has the same characteristics as in the previous case, but it has two windows.
- If the window or windows of the room face the northeast or north, which means that there is a minimum amount of sunlight in it, the power must be increased by another 10%.
- The radiator installed in a niche under the window has a reduced heat transfer, in this case it will be necessary to increase the power by another 5%.
Niche will reduce the energy efficiency of the radiator by 5%
If the radiator is covered with a screen for aesthetic purposes, then the heat transfer is reduced by 15%, and it also needs to be replenished by increasing the power by this amount.
Screens on radiators are beautiful, but they will take up to 15% of the power
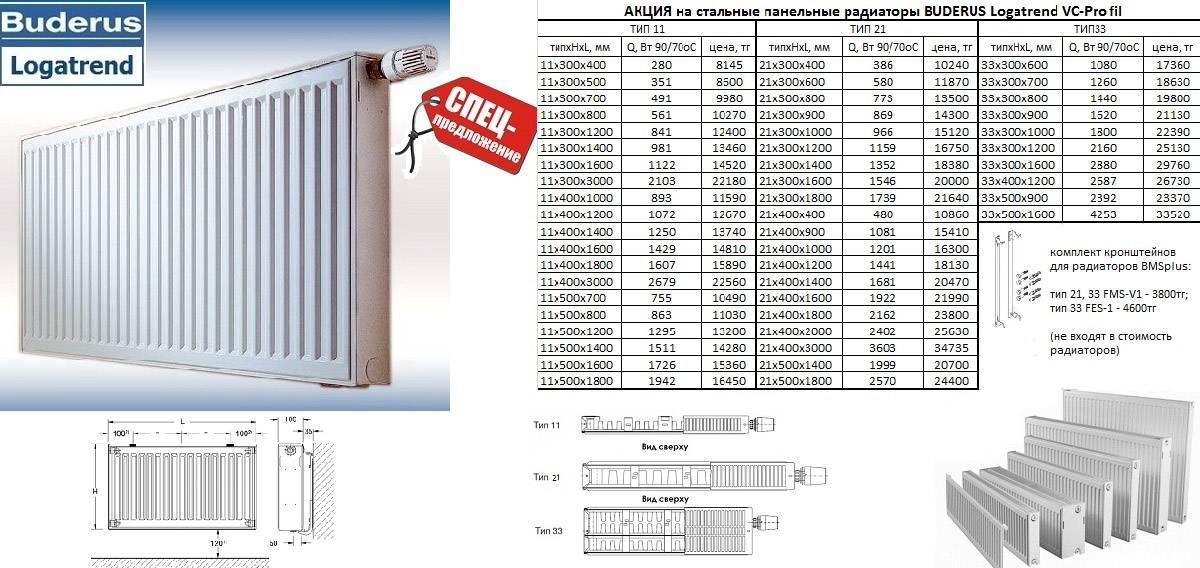
The specific power of the radiator section must be indicated in the passport, which the manufacturer attaches to the product.
Knowing these requirements, it is possible to calculate the required number of sections by dividing the resulting total value of the required thermal power, taking into account all the specified compensating corrections, by the specific heat transfer of one section of the battery.
The result of the calculations is rounded up to an integer, but only up. Let's say there are eight sections. And here, returning to the above, it should be noted that for better heating and heat distribution, the radiator can be divided into two parts, four sections each, which are installed in different places in the room.
Each room is calculated separately
It should be noted that such calculations are suitable for determining the number of sections for rooms equipped with central heating, the coolant in which has a temperature of no more than 70 degrees.
This calculation is considered quite accurate, but you can calculate in another way.
Calculation of the number of sections in radiators, based on the volume of the room
The standard is the ratio of thermal power of 41 W per 1 cubic meter. meter of the volume of the room, provided that it contains one door, window and external wall.
To make the result visible, for example, you can calculate the required number of batteries for a room of 16 square meters. m and a ceiling, 2.5 meters high:
16 × 2.5 = 40 cubic meters
Next, you need to find the value of thermal power, this is done as follows
41 × 40=1640 W.
Knowing the heat transfer of one section (it is indicated in the passport), you can easily determine the number of batteries. For example, heat output is 170 W, and the following calculation is made:
1640 / 170 = 9,6.
After rounding, the number 10 is obtained - this will be the required number of sections of heating elements per room.
There are also some features:
- If the room is connected to the adjacent room by an opening that does not have a door, then it is necessary to calculate the total area of the two rooms, only then the exact number of batteries for heating efficiency will be revealed.
- If the coolant has a temperature below 70 degrees, the number of sections in the battery will have to be proportionally increased.
- With double-glazed windows installed in the room, heat losses are significantly reduced, therefore the number of sections in each radiator can be less.
- If old cast-iron batteries were installed in the premises, which coped well with creating the necessary microclimate, but there are plans to change them to some modern ones, then it will be very simple to calculate how many of them will be needed. One cast-iron section has a constant heat output of 150 watts. Therefore, the number of installed cast iron sections must be multiplied by 150, and the resulting number is divided by the heat transfer indicated on the sections of new batteries.
Popular electric heating batteries and their functionality
Throughout its development, man has sought to improve the heating of the home. Primitive fires were replaced by stoves and fireplaces that heated the house locally or centrally, and later heat was supplied through specially designed systems.
Today, private houses are heated with water or steam heating batteries, which are heated by gas.But this type of heating is acceptable for areas where connection to the central highway is possible. What should consumers who are unable to connect to gas do? Electric radiators for space heating are a worthy replacement for water radiators heated by gas or solid fuel.
Calculation by room volume
The calculation of the required power of heaters based on the volume of the room gives more accurate results, since the height of the room's ceilings is also taken into account. This calculation method is used for rooms with high ceilings, non-standard configurations and open living spaces, such as halls with a second light. This calculation method is used for rooms with high ceilings, non-standard configurations and open living spaces, such as halls with a second light.
This calculation method is used for rooms with high ceilings, non-standard configurations and open living spaces, such as halls with a second light.
The general principle of calculations is similar to the previous one.
According to the requirements of SNIP, for normal heating of 1 cubic meter of a dwelling, 41 W of the thermal power of the device is required.
Thus, the volume of the room is calculated (length * width * height), the result is multiplied by 41. All values are taken in meters, the result is in W. Divide by 1000 to convert to kW.
Example: 5 m (length) * 4.5 m (width) * 2.75 m (ceiling height), the volume of the room is 61.9 cubic meters. The resulting volume is multiplied by the norm: 61.9 * 41 \u003d 2538 W or 2.5 kW.
The number of sections is calculated, as above, by dividing by the power of one section of the radiator, indicated in the manufacturer's model passport. Those.if the power of one section is 170 W, then 2538 / 170 is 14.9, after rounding, 15 sections.
Amendments

Cast iron batteries - a classic in a new way
If the calculation is made for apartments in a modern multi-storey building with high-quality insulation and installed double-glazed windows, then the value of the power rate per 1 cubic meter is 34 watts.
In the radiator passport, the manufacturer may indicate the maximum and minimum values \u200b\u200bof the thermal power per section, the difference is related to the temperature of the coolant circulating in the heating system. To make correct calculations, either the average or the minimum value is taken.
Conclusions regarding the choice of a radiator for an apartment
In conclusion, we can conclude which heating radiator is better to choose for an apartment. As practice shows, aluminum and steel models are not able to withstand the tests that accompany operation in the conditions of domestic heating systems. Such batteries are not able to withstand pressure and temperature changes. There are only cast-iron and bimetallic devices to choose from.
What to buy - you can decide by evaluating the budget, as well as the characteristics of the models. However, there are a few tips you can use. If you still do not know which heating radiator is best for an apartment, then you should evaluate how old the house you live in is. If we are talking about "Khrushchev", then it is best to use cast iron products. For residents of high-rise buildings, where the pressure is higher, it is recommended to purchase bimetallic radiators. If earlier cast iron batteries were installed in the apartment, then the choice can be stopped on any of the two options.However, those who are going to replace a battery made of another metal should purchase bimetallic models.