- Are the vaults sealed?
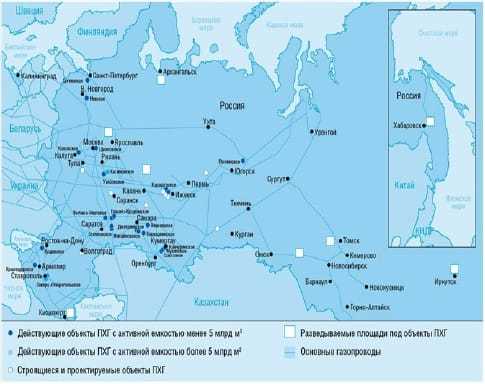
- Location and distribution
- United States
- Absorbing East
- Consuming West
- Production South
- What's next?
- Requirements for tanks and gas storage parks
- 5.2 Organization of operation
- Gas storage technologies at the exhibition
- Recall that the functions of UGS facilities are different
- Types of gas storages
- UGS classification
- UGS operation mode
- Purpose
- Objects of operation
- Fluctuations and peaks
- How are underground gas storage facilities built?
- Self-healing caves
- 9.1. General provisions
- Underground gas storage
- What you need to know about UGS?
- Shaftless tanks in rock salt
- Isothermal storage of liquefied gas
Are the vaults sealed?
Fuel leaks are frequent processes that cannot be avoided. Because there are too many reasons.
For convenience, they are divided into 3
- geological;
- technological;
- technical.
The group of geological reasons includes the heterogeneity of UGS covers, the presence of tectonic faults, as well as features of hydrodynamics and geochemistry. For example, gas can simply migrate through the reservoir, and specialists will not affect this in any way.
Technological reasons are among the most frequent, as errors occur regularly in the assessment of any facts. For example, the efficiency of hydraulic traps, gas reserves, ongoing physical and chemical processes.
Often, well drilling is used to get to the desired reservoirs. Moreover, its technology is no different from similar procedures when trying to get to gas and oil deposits.
Technical reasons are most often associated with the condition of the wells used, through which gas is injected.
This is interesting: Storm - explain the essence
Location and distribution
United States
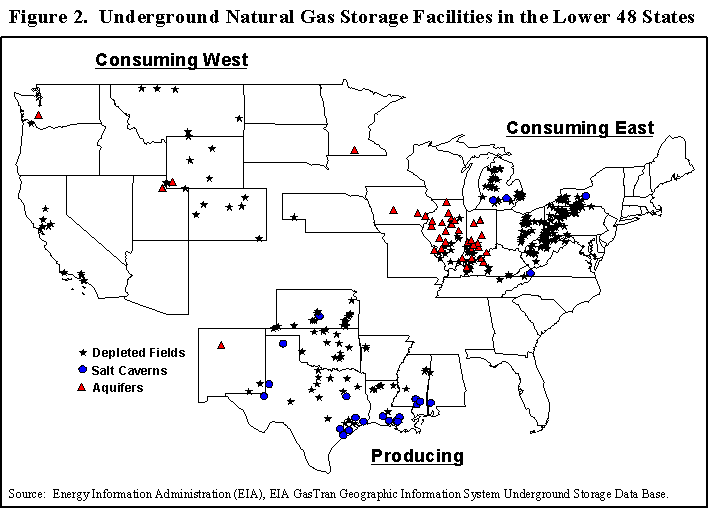
The United States is usually divided into three main regions when it comes to gas consumption and production. It is the consuming East, the consuming West and the producing South.
 Source.
Source.
Absorbing East
The consuming eastern region, especially states in the northern part, are heavily dependent on stored gas to meet peak demand during the cold winter months. It is not surprising that due to the prevailing cold winters, large population centers and developed infrastructure, this region has the highest level of working gas storage capacity among other regions and the largest number of storage sites, mainly in depleted tanks. In addition to underground storage, LNG is playing an increasingly important role in providing additional backup and/or peak supplies to LDCs on a short-term basis. Although the overall capacity of these LNG facilities is not up to the scale of underground storage, the high short-term productivity compensates for this.
Consuming West
The consuming western region has the smallest share of gas storage facilities both in terms of the number of sites and in terms of gas capacity / delivery. The storage facilities in this area are mainly used to ensure that the domestic and Alberta gas coming from Canada can flow at a fairly constant rate.In northern California, Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) has about 100 billion cubic meters of underground storage. Feet of gas at three storage facilities. PG&E uses storage to store gas when it's cheap to use in the summer, when purchased gas is expensive.
Production South
The storage facilities of the producing south are linked to market centers and play a crucial role in the efficient export, transportation and distribution of produced natural gas to consumer regions. These storage facilities allow gas that is not immediately sold to be stored for later use.
| Region | Number of sites | Working gas volume (10 9 ft 3 ) | Daily Delivery (10 6 ft 3 ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| East | 280 | 2 045 | 39 643 |
| West | 37 | 628 | 9 795 |
| South | 98 | 1,226 | 28 296 |
In Canada, the maximum amount of working gas stored was 456×10 9 cubic feet (1.29 × 10 10 m 3 ) in 2006 year. Storage in Alberta accounts for 47.5% of the total working gas. It is followed by Ontario with 39.1 percent, British Columbia with 7.6 percent, Saskatchewan with 5.1 percent and finally Quebec with 0.9 percent.
What's next?
From data on the injection of gas owned by Gazprom into European UGS facilities, the conclusion is often made that the Russian monopoly will sell this fuel at peak spot prices on the exchange market. Perhaps that is how it will be.
At the same time, it should be noted that Gazprom has been pumping fuel into European storage facilities for more than a year with a standard formulation - for the stable fulfillment of export contracts.Will this winter bring surprises? Gazprom's strategy in the European direction is changing right before our eyes. Plus, the company has acquired or expanded UGS facilities in salt caverns, which are most convenient for exchange trading operations, while earlier Gazprom relied more on traditional UGS facilities (the same Austrian Haidach is a storage facility based on a depleted field) .
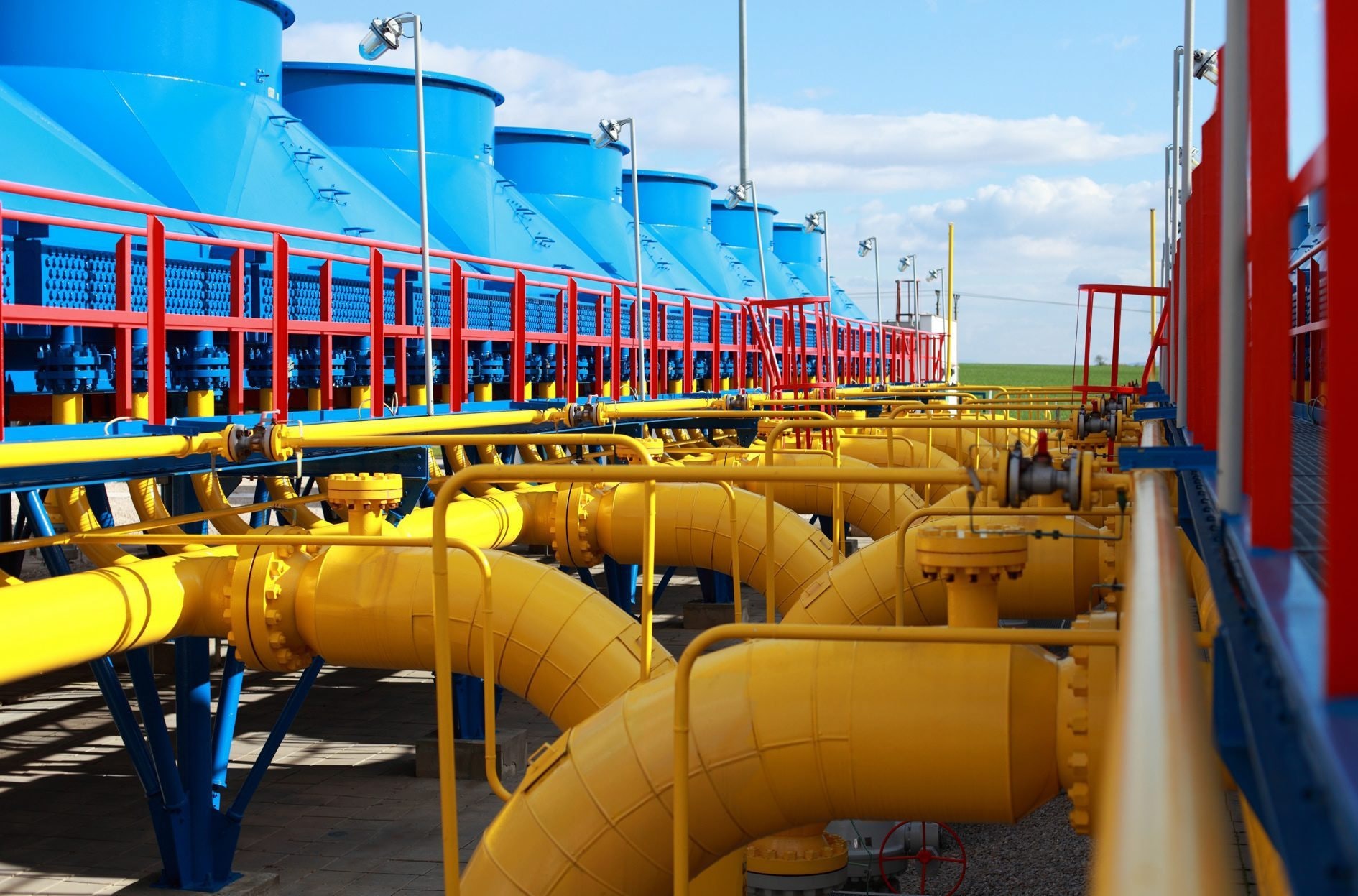
Requirements for tanks and gas storage parks
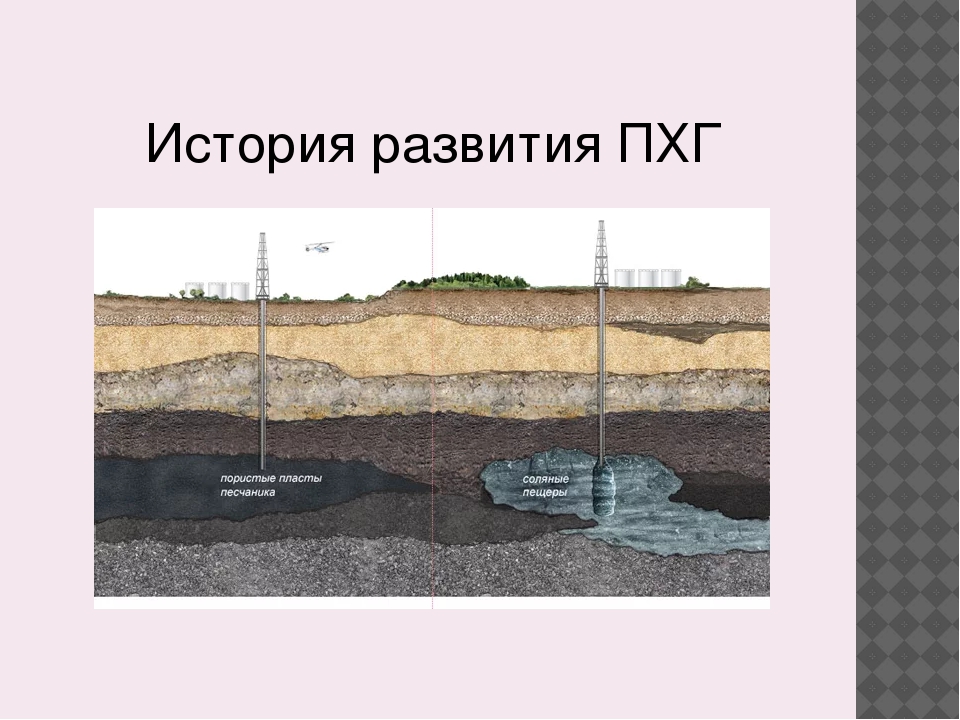
It is important to understand that gas storage requires significantly more volume than solid or liquid storage. Therefore, the most difficult task is to find sealed tanks, storage tanks for liquefied gas and other products.
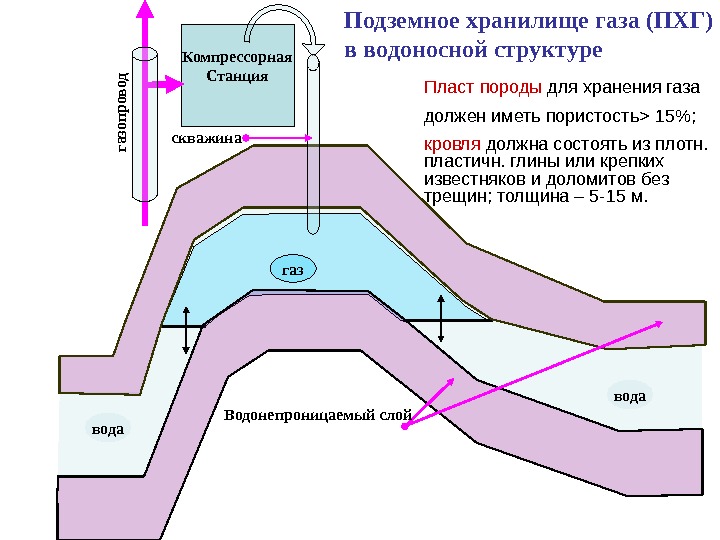
But nature in this case has served as a good helper and has already built them. Natural UGS facilities here are porous sandstone layers in the earth's crust, hermetically sealed from above by a dome made of a layer of clay. Water can be found in the pores of sandstone, just as hydrocarbons can accumulate there. In the course of work to create an underground storage facility in the aquifer, the gas that collects under the clay cover pushes the water down.
To determine whether a given reservoir is a gas and oil field, it is necessary to first check whether it contains hydrocarbons. Thus, the tightness of this structure has already been proven by the fact that hydrocarbons have accumulated in it.
At the moments of storage formation, part of the gas is closed in the reservoir in order to create the required pressure. Such a gas is called a buffer gas. The volume of buffer gas is almost half of the total gas injected into the storage. The gas that will be used in the extraction from UGS facilities is called active or working.
You should know that the largest storage facility for active gas is called the Severo-Stavropol UGSF. Its volume is 43 billion cubic meters of active gas. Such a figure is no problem enough to provide for a year the consumption of countries such as France or the Netherlands. It is known that the Severo-Stavropol UGS facility was built in a depleted gas field. And gas storage in underground storage facilities of this complex is considered to be quite effective.
Parks that are in a depleted deposit or aquifer have the distinction of being large in volume and having little flexibility. Many times faster injection and extraction of gas are carried out in storage facilities located in rock salt caves. There are now two storage facilities in Russia, which are located in rock salt deposits. Their location is the Kaliningrad and Volgograd regions. Pyrolysis and natural gas are stored here.
5.2 Organization of operation
Creation and
UGS operation is carried out in accordance
with this standard and PB 08-621-03 and
includes the following stages:
- reconnaissance structure
for the creation of underground storage facilities, including seismic
research, structural drilling,
exploratory well drilling,
field geophysical, hydrodynamic
(hydraulic exploration), geochemical, etc.
research;
— development
technological and technical projects
creation of underground storage facilities;
- drilling of the wells;
— commissioning
work on the industrial site until full withdrawal
of the whole complex for the design mode
operation;
— pilot industrial
UGS operation;
- cyclic
UGS operation;
— decoration of the mountain
recusal, obtaining appropriate
permits and licenses.
While doing
preparatory work before entering into
operation of UGS facilities created in depleted
deposits, in the process of pilot
injection of gas into an aquifer or
salt caverns all mounted on
UGS facilities, technological installations,
communications and production wells
tested for strength and
test pressure according to methods,
defined in the relevant
documents, for tightness and
performance at maximum and
the minimum values of the parameters.
Ground equipment and technological
pipelines pass basic technical
diagnosis.
On the stage
operation of UGS facilities by the technical part
work on the main production
UGS facilities are managed by the chief engineer
(technical supervisor),
geological and commercial part - the main
geologist. Technical and methodical
management of work in production
workshops and in the gas field carry out
heads of departments and departments
in accordance with job descriptions,
as well as the relevant instructions
and service manuals
equipment drawn up in relation to
to specific operating conditions
UGS.
Technical
operations for wells are repaired
on the the basis of approved in the prescribed
order of the work plan (project), agreed
with the UGS geological service and
authorized supervisory authorities and
control of the Russian Federation.
It is forbidden to hold
any work on UGS wells without
appropriate coordination and control
from the geological service.
During operation
UGS facilities are carried out once every five years
geological and technological survey
(audit) performance evaluation
ground arrangement and tightness
UGS facilities (well plumes, treatment plants,
gas estimates, CS, etc.).
According to the results
geological and technological survey
(audit) of ground facilities
are developing:
— recommendations for
technology improvement and
operation of the main elements
ground facilities, their automation;
- conclusion about
the need for reconstruction of the ground
arrangement and modernization of the facility with
to replace obsolete equipment.
Annually after
completion of the selection (download) season
by UGS operating services
conduct performance analysis
fishing equipment
technological chain "well -
main gas pipeline. results
research and proposals for elimination
"bottlenecks" to approve at the seasonal
meetings of the Gas Industry Commission
for field development and research
bowels
Gas storage technologies at the exhibition
There is great confidence that Exhibition "Neftegaz" will effectively influence the development and become a sensational event in the field of the oil refining industry. The duties of the organizer of the international exposition are assumed by the experienced Expocentre Fairgrounds. The project is considered the biggest event in the CIS zone.
During the exhibition, considerable attention will be paid to the consideration of various types of tanks and storage of liquefied hydrocarbon gases.Also, during the event, various types of storage bases, advanced equipment for the sector and modern technologies, including automation of the gas production and transportation complex, will be considered.
Also during the event, various types of storage bases, advanced equipment for the sector and modern technologies, including automation of the gas production and transportation complex, will be considered.
The Neftegaz event includes a set of diverse topics and will provide useful information on:
- groups of pumps for pumping resources;
- equipment for petrochemical needs;
- types of gas pipelines;
- welding devices;
- accessories for installation;
- natural gas storage complexes;
- complex automation devices.
It will host a variety of events that will touch on the main painful topics of the industry, showcase innovative liquefied gas storage options and advanced engineering designs.
Crude Oil Storage RequirementsUnderground Gas Storage AutomationGas Cylinder Storage Rules
Recall that the functions of UGS facilities are different
First, it is the optimization of gas transportation. After all, demand increases in winter, so it is easier to pump part of the “winter” gas into UGSFs not far from the places of consumption in the summer. Then a gas pipeline that is too powerful for the winter peak demand will not be needed. We have seen this combination every year in the case of transit through Ukrainian territory.
Secondly, balancing the current demand in the short term.Indeed, from remote regions, for example, from the same Western Siberia, it takes more than a day to deliver gas through pipelines to Europe, and therefore it is not always technically possible to quickly increase the volume of supplies.
Thirdly, this is actually a strategic role in the event of an emergency or cessation of supplies.
If we talk about the European market, here, despite the stagnation of gas demand, the role (and capacities) of storage facilities will also increase: perhaps even faster than in the whole world. The reasons for this are as follows:
- Reducing domestic gas production and, accordingly, the growth of imports.
- Decline in the role of Ukrainian UGS facilities against the backdrop of a drop in Ukrainian transit volumes and a general turbulent situation with supplies in this direction.
- The EU's policy of diversifying supplies through an increase in the share of LNG. In this case, the seasonal delivery maneuver will not be possible, and tanker deliveries are, by definition, more risky compared to the pipe.
- The virtual abandonment of the use of gas to generate electricity has led to the fact that gas in Europe has been used primarily for domestic purposes. This has become another factor in the gap between the volumes of winter and summer demand for gas. And smoothing out these differences is actually one of the tasks of UGS facilities.
Types of gas storages
A gas storage is a geological structure or artificial reservoir used to store gas. Storage operation is characterized by two main parameters — volumetric and power. The first characterizes the storage capacity - active and buffer volumes of gas; the second indicator characterizes the daily productivity during gas extraction and injection, the duration of the storage facility operation at maximum productivity.
According to the operating mode, UGS facilities are divided into basic and peak.
Basic UGS is intended for cyclic operation in the basic technological mode, which is characterized by relatively small deviations (increase or decrease in the range from 10 to 15%) of the daily productivity of UGS facilities during gas withdrawals and injections from the average monthly productivity values.
Peak UGS is intended for cyclic operation in the peak technological mode, which is characterized by significant increases (peaks) of more than 10-15% of the UGS daily productivity for several days during gas withdrawals and injections relative to average monthly productivity values.
According to their purpose, UGS facilities are divided into basic, regional and local.
Base UGS characterized by active gas volume up to several tens of billions of cubic meters and a capacity of up to several hundred million cubic meters per day, is of regional importance and affects the gas transmission system and gas production enterprises.
Regional UGS characterized by active gas volume up to several billion cubic meters and a capacity of up to several tens of millions of cubic meters per day, is of regional significance and affects consumer groups and sections of the gas transmission system (gas production enterprises, if any).
Local UGS characterized by active gas volume up to several hundred million cubic meters and productivity up to several million cubic meters per day, has a local significance and area of influence limited to individual consumers.
By type, ground and underground gas storage facilities are distinguished. Ground-based include gas holders (for storing natural gas in gaseous form) and isothermal tanks (for storing liquefied natural gas), to underground - gas storages in porous structures, in salt caverns and mine workings.
UGS classification
In order to balance the seasonal consumption of the resource, which occurs unevenly in any gas field or main gas pipeline, reserves must be stored hermetically in certain storage facilities. To do this, deposits are used, the development of which is depleted, traps in water systems in rock layers, as well as special cracks or caverns formed naturally or artificially. All UGS facilities can be divided into categories depending on their performance characteristics and operating features.
UGS operation mode
Classification according to work in a porous reservoir makes it possible to distinguish several types of underground storage facilities:
- basic ones are set up to adjust the unevenness in the gas consumption schedule for several months. The mode of operation during the selection period is stable;
- peaks are required to meet the daily unevenness of gas extraction, while the productivity varies greatly;
- the gas holder surface storage ensures the stability of the injection of a natural resource at the height of the extraction season, while the amount of the injected resource is enough for a short period of time;
- strategic ones are needed for resource reserves in exceptional cases, so their work must be safe for a long period of time.
Purpose
According to their purpose, underground storages can be divided into basic, local and district. Each type is distinguished by its volume:
basic UGS facilities contain tens of billions of cubic meters of gas, producing up to several hundred million cubic meters per 24 hours
Such a repository is of regional importance and is important for industrial enterprises and the transport system;
district UGS facilities contain up to 10 billion cubic meters of resource, generating tens of millions of
cubic meters per day. The value of such a storage facility is regional, designed for end-user groups and part of the gas transmission system;
the local UGSF is designed for hundreds of million cubic meters, the productivity reaches 10 million cubic meters per day. The value of this type is distinguished by locality, and consumers are distinguished by units.
Objects of operation
Underground gas storages can operate in the following facilities:
- aquifer;
- depleted gas storage or oil field, gas condensate well.
For each of the objects, a quantity is provided - one layer or a multi-layer system of warehouses.
Fluctuations and peaks
UGS facilities (underground gas storage facilities) contribute significantly to the reliability of gas supply to consumers. They make it possible to equalize daily fluctuations in gas consumption and meet peak demand in the winter. UGSFs are especially important in Russia with its climatic features and remoteness of resource sources from end users. The Unified Gas Supply System (UGSS), which has no analogues in the world, operates in Russia, its integral part is the UGS system.Underground storage facilities ensure guaranteed supply of natural gas to consumers regardless of the season, temperature fluctuations, or force majeure.
In winter, the operating 25 storage facilities provide up to a quarter of the daily gas resources of the UGSS of Russia, which is comparable to the total withdrawal from the Yamburgskoye, Medvezhye and Yubileinoye fields.
This is interesting: Barotrauma - sharing knowledge
How are underground gas storage facilities built?
In aquifers, underground storage requires careful site analysis, exploration and commercial injection of the resource into numerous new wells. When drawing up a project, first of all, they take into account the optimal ways of stable and uniform operation of the gas pipeline being created during peak seasons.
Only after that a decision is made on the arrangement, construction is underway and a schedule of resource consumption is drawn up by the hour for several months in advance. To equalize the uneven consumption of gas storage stocks, three methods are used:
- degree and temperature insufficiency, as well as the value of heat to provide one degree day with a lack of temperature;
- stock consumption rate for heating consumers during the heating season;
- calculation of gas consumption coefficients taking into account monthly unevenness.
Self-healing caves
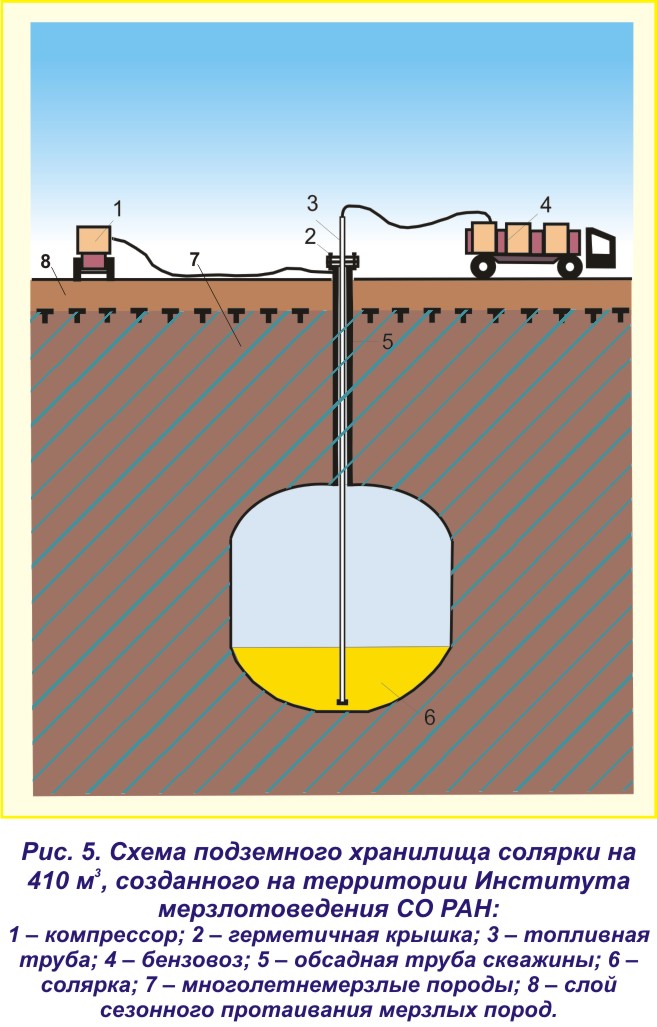
Salt caves are ideal reservoirs in terms of tightness. Building an underground salt cavern to store gas is not that difficult, although it is a long process. Wells are drilled in a suitable rock salt layer. Then water is supplied to them, a cavity of the required volume is washed out in the salt layer.The salt dome is not only impervious to gas, the salt has the ability to “heal” cracks and faults on its own.
At present, two storage facilities in rock salt deposits are being built in Russia - in the Kaliningrad and Volgograd regions.
9.1. General provisions
The main goal of GIS technical control is to provide
the optimal amount of geophysical information on the technical condition of wells in
purposes:
— effective management
the processes of creation and operation of underground storage facilities,
- timely correction
technological and design solutions by improving the reliability of construction,
operation, reconstruction and liquidation of wells;
— ensuring the protection of life and
health of citizens and prevention of pollution of ground facilities and underground
hydrogeological complexes;
- timely implementation
expert technical diagnostics of UGS wells by system geophysical
researches by obligatory and additional complexes of methods.
Underground gas storage
Definition 1
Underground gas storage is a technological process of gas storage, extraction and injection in reservoirs or reservoir workings that are built in rocks.
Definition 2
Underground gas storage is engineering buildings and structures in mine workings and reservoirs, which are designed for storage, injection and extraction of gas.
The first underground gas storage in the bowels of the earth on the territory of the Soviet Union was built in 1958 in the Samara region. Successful experience was the reason for the creation of similar structures at the Elshansky and Amanaksky fields.And the first underground storage in the aquifer on the territory of our country was built in 1955, near the city of Kaluga.
Underground gas storage facilities are usually built near main pipelines or large gas consuming centers in order to quickly cover its peak consumption. Such structures are created in order to compensate for the uneven consumption of gas and reserve gas in the event of an accident on pipelines. The main characteristics of a gas underground storage facility are its capacity (daily output) and volume (underground storage capacity). All underground gas storages are divided according to the mode of operation and purpose. An example of an underground gas storage in conjunction with a gas production station is shown in the figure.
 Figure 1. Underground gas storage in conjunction with a gas production station. Author24 - online exchange of student papers
Figure 1. Underground gas storage in conjunction with a gas production station. Author24 - online exchange of student papers
According to the operating mode of the gas storage, there can be peak or base. The basic storage is intended for cyclic operation in the technological mode, which is characterized by small deviations in daily productivity (from 10 to 15 percent). Peak underground gas storage is designed to operate in a mode that is characterized by significant increases in daily production over several days.
According to their purpose, underground storage facilities can be:
- Basic. Such storage can contain up to several billion cubic meters of natural gas. These storage facilities are of regional importance and significantly affect gas production enterprises and gas transportation systems.
- Regional gas storages can contain tens of billions of cubic meters of gas and have a capacity of several million cubic meters per day.Such repositories are of regional importance and have an impact on the activities of consumer groups.
- Local underground gas storage facilities can contain hundreds of millions of tons of minerals. Such repositories have an impact on the activities of a limited number of consumers.
What you need to know about UGS?
The most important thing to know about UGS facilities is the safety rules for underground gas storage facilities. In addition, it must be taken into account that depleted seams and deposits of rock salt are increasingly being used. Also, technologists recognized suitable mine workings of minerals - coal and other rocks.
In total, about 600 UGSFs have been equipped around the world, designed for 340 billion m3. Most of the gas reserve is located in depleted gas and condensate fields. Salt caverns are less capacious, as are rock mines.
For UGS equipment, collectors of a natural porous and permeable type are created, also using impermeable and non-porous rocks. The operation of underground gas storage facilities requires the accumulation of large resource reserves and control of gas supply to consumers in different seasons. The creation of resource reserves is necessary for the following purposes:
- satisfaction of peak values of demand during the heating season and winter period;
- cost reduction for compressor equipment in main gas pipelines;
- creation of optimal conditions for the most economical operating mode of gas pipelines of uninterrupted type;
- providing different regions with the necessary resource reserve.
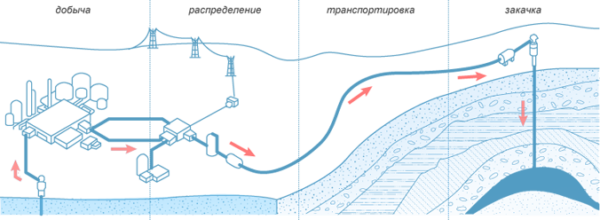
How does UGS work?
Shaftless tanks in rock salt
8.6 constructive
Shaftless gas tank solutions must provide speed
gas flow through the well is not more than 35 m/s and the rate of pressure decrease in
tank during gas sampling during operation no more than 0.5
MPa/h
8.7 Capacity
shaftless gas tanks should be determined based on
storage of active and buffer gas volumes based on technological
parameters and mining and geological conditions for the placement of reservoirs.
8.8 Coefficient
using the capacity of the tank when storing liquid
hydrocarbons should be taken no more than the following values:
a) in the presence of an external
suspension column (in fractions of the capacity of the underground reservoir above
outer column shoe):
for oil and oil products —
0,985;
for LPG - 0.95;
b) in the absence of external
suspension column (in fractions of the capacity of the underground reservoir above
shoe of the central suspension column):
for oil and oil products —
0,95;
for LPG - 0.9.
8.9 During operation
underground tanks according to the brine scheme to displace LPG, oil and
petroleum products should be used, as a rule, concentrated
brine.
8.10 Allowed
combine storage operation with a further increase in storage capacity
underground tanks.
8.11 When displaced
storage product with non-concentrated brine or water in design
solutions must take into account changes in capacity and configuration
production-capacity due to the dissolution of salt. The number of cycles
displacement should be determined depending on the change
brine concentration and maximum permissible dimensions of the tank according to
condition of stability.
Isothermal storage of liquefied gas
Isothermal storage of liquefied gas is quite possible. It is worth emphasizing that this is the most expensive gas storage method of all listed.This expensive method of storage is used precisely in the conditions of the impossibility of other options for creating a storage of another type near large consumers, but a decree on the construction of this type of storage is issued only in cases where it is not possible to create a storage of another type in the area near large consumers. For example, the possibility of creating such a storage facility in the St. Petersburg area is now being actively considered by the best specialists of Gazprom. Moreover, the Russian gas industry owns helium storage technology.
The process of storing liquefied natural gas (LNG) is carried out only in those tanks that have a low temperature and are called isothermal. In this case, difficulties arise, as a result of the low storage temperature, low heat of vaporization of LNG. The use of highly efficient thermal insulation is the best condition for long-term and high-quality storage of the resource.
It is possible to store the gas in the form of hydrates. Stabilization of the processed resource occurs under the influence of its exposure at operating pressure in accordance with a temperature of -10 ° C during the day. The hydration density is 0.9-1.1 g/cm3, i.e. this slightly exceeds the density of ice (0.917 g/cm3). A ready-made version of gas from this resource is possible only when it is heated. The storage of such gas takes place directly in gas holders.