- Requirements for the location of the radiator in a private house
- How to increase the heat transfer of a heating pipe with your own hands
- What systems need calculation?
- How to optimize the heat transfer of steel pipe?
- We make a calculation
- We calculate the return for 1 m. of the product
- It's worth remembering
- Increasing the heat transfer of the heating main
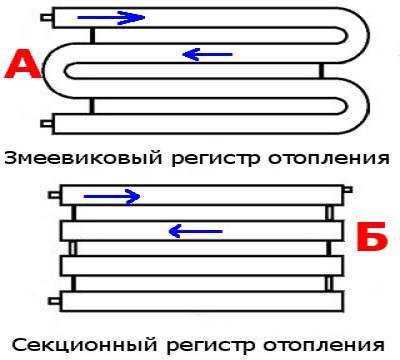
- Types of registers
- Rules for the operation of heating registers
- Types of heating registers
- Thermal registers of various designs
- Section registers
- Classification by section shape
- Types of registers according to the material of manufacture
- Homemade register from a profile pipe
- What materials are registers made of?
- How to make a homemade register from shaped, smooth steel pipes
- DIY tools and materials
- The order of work: how to weld the structure?
- Quantity calculation
Requirements for the location of the radiator in a private house
Radiators should be installed in places of greatest heat loss in the house (window openings and entrance doors).
As a rule, heating devices are installed under each window of the dwelling and in the hallway on the wall, next to the front door of the house, as a thermal curtain and a dryer for wet things.
For maximum heat transfer from the heating device, the following optimal distances from the radiator are available:
- To the floor 8-12 cm;
- to the windowsill 9-11 cm;
- to the wall 5-6 cm;
- the protrusion of the radiator beyond the window sill is 3-5 cm (so that the heat from the radiator heats the window unit).
Requirements for the construction of the wall and floor:
- The wall on which the heater will be mounted must be plastered.
- When attaching to a plasterboard wall, a reinforcing frame made of timber is preliminarily installed in it.
- Floor mounts for the radiator are installed on the finished floor.
Installation tool:
- Drill or perforator,
- Drill 10 mm,
- A hammer,
- Screwdriver for screwing screws when using angle brackets,
- Building level with spirit level or laser,
- Pencil,
- Roulette,
- Radiator wrench made of plastic,
- American key.
How to increase the heat transfer of a heating pipe with your own hands
Calculation heat dissipation pipes required when designing heating, and is needed to understand how much heat is required to warm up the premises and how long it will take. If the installation is not carried out according to standard projects, then such a calculation is necessary.
What systems need calculation?
The heat transfer coefficient is calculated for a warm floor. Increasingly, this system is made of steel pipes, but if products from this material are selected as heat carriers, then it is necessary to make a calculation. The coil is another system, during the installation of which it is necessary to take into account the heat transfer coefficient.
Steel pipe radiator
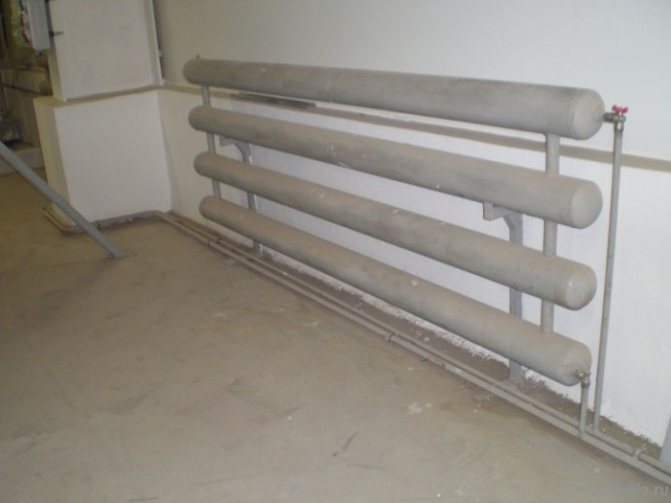
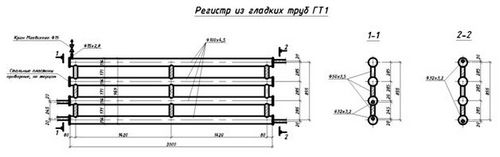
Registers - are presented in the form of thick pipes connected by jumpers. The heat output of 1 meter of this design is on average 550 watts. The diameter ranges from 32 to 219 mm. The structure is welded so that there is no mutual heating of the elements. Then the heat transfer increases.If you correctly assemble the registers, you can get a good room heating device - reliable and durable.
How to optimize the heat transfer of steel pipe?
During the design process, specialists face the question of how to reduce or increase the heat transfer of 1 m of steel pipe. To increase, you need to change the infrared radiation upwards. This is done with paint. Red color enhances heat dissipation. Better if the paint is matte.
Another approach is to install fins. It is mounted outside. This will increase the heat transfer area.
In what cases is it necessary to reduce the parameter? The need arises when optimizing a pipeline section located outside the residential area. Then experts recommend insulating the site - isolating it from the external environment. This is done by means of foam, special shells, which are made from special foamed polyethylene. Mineral wool is also often used.
We make a calculation
The formula for calculating heat transfer is as follows:
- K - coefficient of thermal conductivity of steel;
- Q is the heat transfer coefficient, W;
- F is the area of the pipe section for which the calculation is made, m 2 dT is the temperature pressure (the sum of the primary and final temperatures, taking into account room temperature), ° C.
The thermal conductivity coefficient K is selected taking into account the area of the product. Its value also depends on the number of threads laid in the premises. On average, the value of the coefficient lies in the range of 8-12.5.
dT is also called temperature difference. To calculate the parameter, you need to add the temperature that was at the outlet of the boiler with the temperature that was recorded at the inlet to the boiler. The resulting value is multiplied by 0.5 (or divided by 2).The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
If the steel pipe is insulated, then the value obtained is multiplied by the efficiency of the thermal insulation material. It reflects the percentage of heat that was given away during the passage of the coolant.
We calculate the return for 1 m. of the product
It is easy to calculate the heat transfer of 1 m of a pipe made of steel. We have a formula, it remains to substitute the values.
Q \u003d 0.047 * 10 * 60 \u003d 28 W.
- K = 0.047, heat transfer coefficient;
- F = 10 m 2. pipe area;
- dT = 60° C, temperature difference.
It's worth remembering
Do you want to make the heating system competently? Do not pick up pipes by eye. Heat transfer calculations will help optimize construction costs. In this case, you can get a good heating system that will last for many years.
Increasing the heat transfer of the heating main
Studying ways to efficiently heat rooms of various types, the owners are wondering how to increase the heat transfer of the heating pipe. The main thing in this is the ratio of the volume of the pipe to the entire area of its surface.
The obtained indicators will help to make all the calculations correctly and avoid mistakes. In addition, this issue should be raised even during construction work, since it is more difficult to resolve this issue in a finished facility.
Types of registers
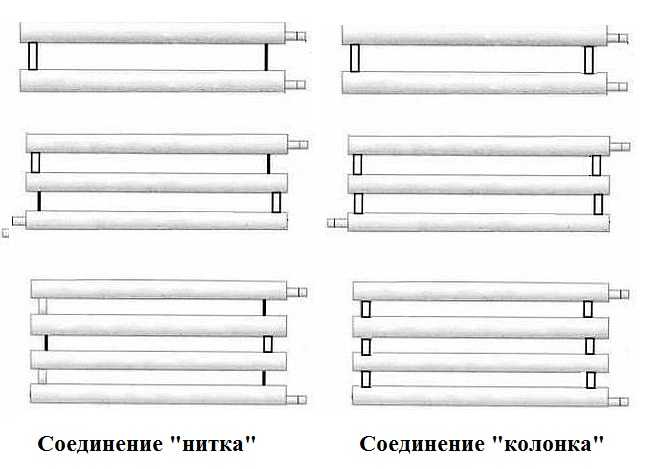
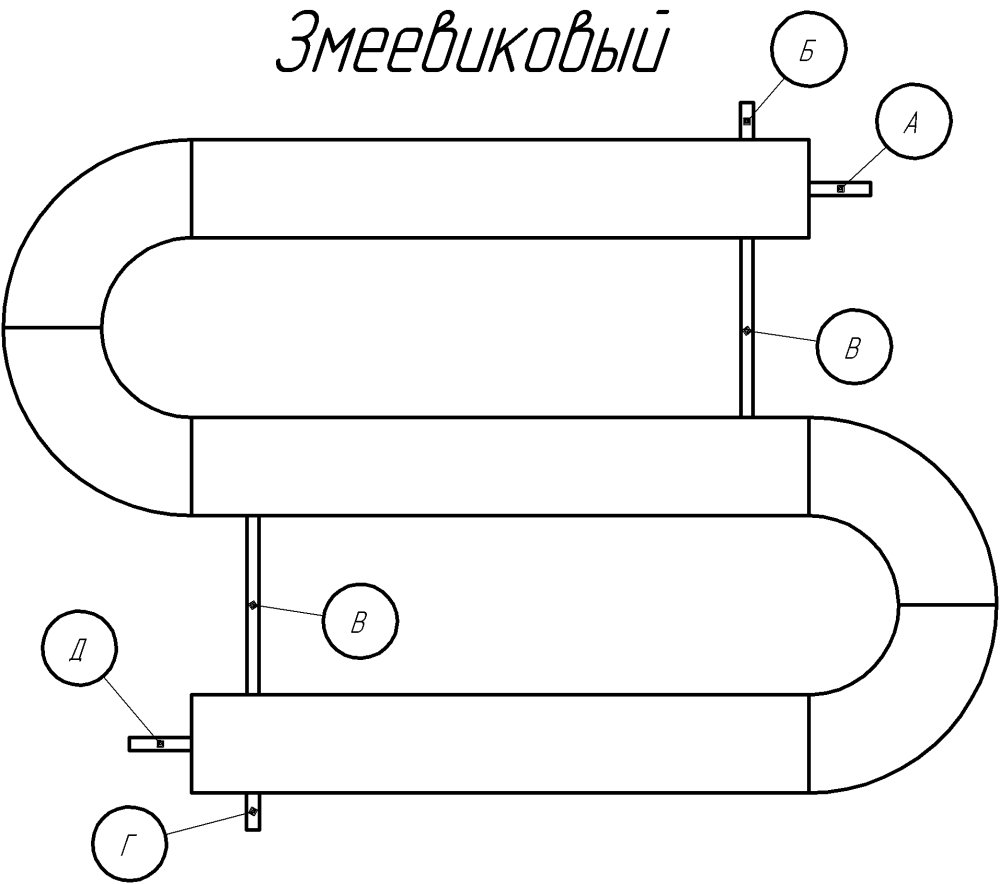
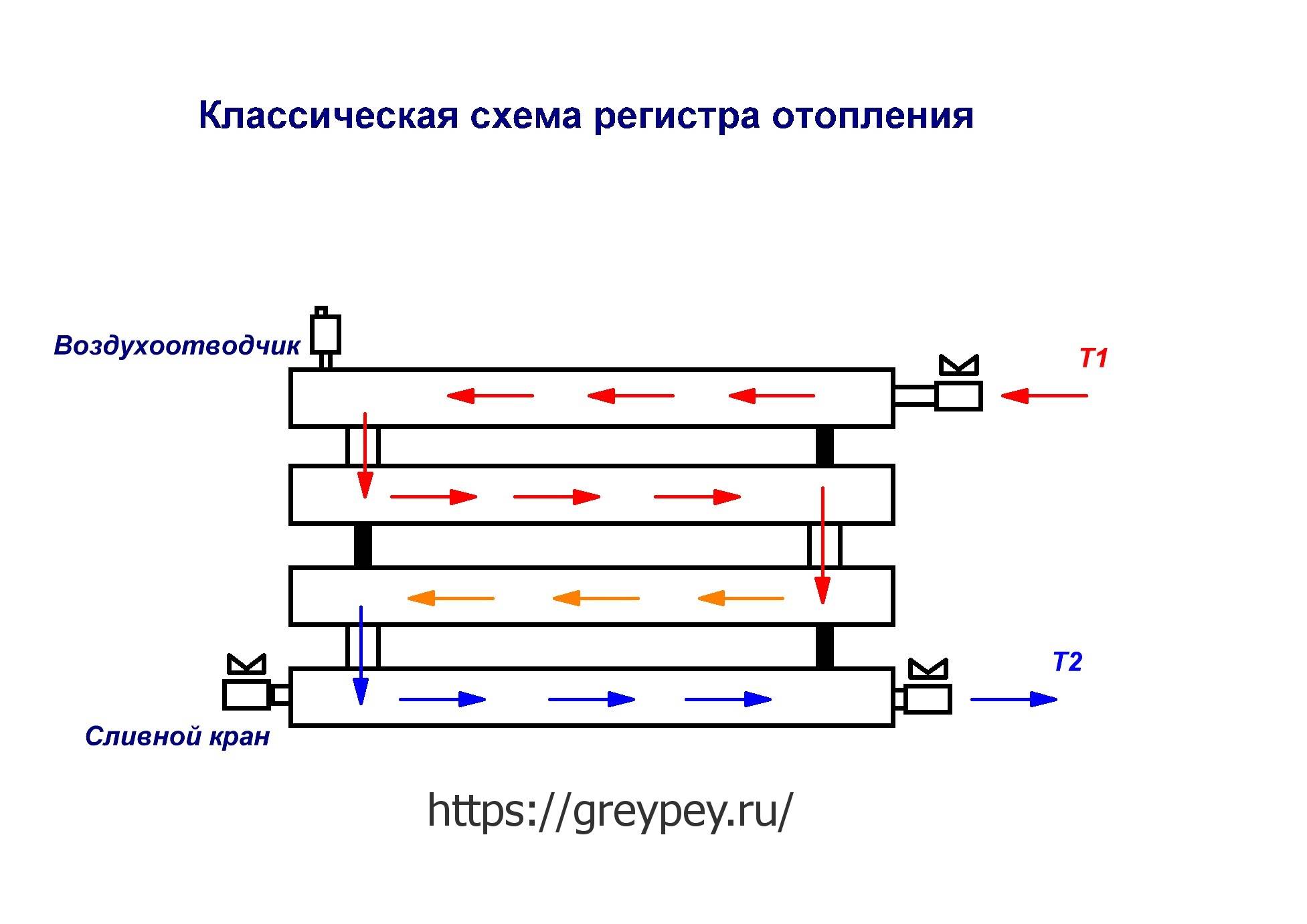
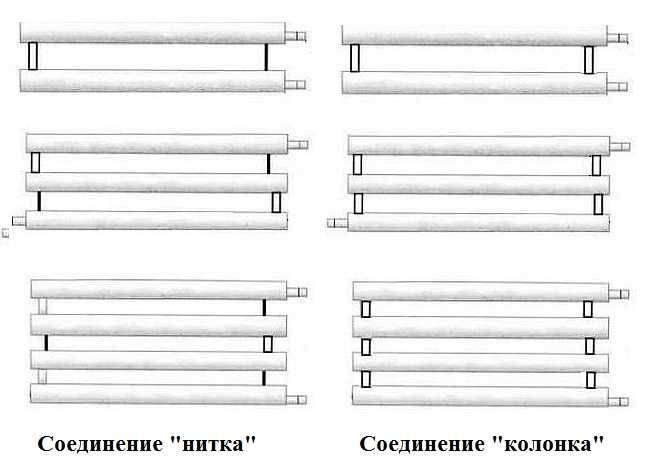
The most common type is registers made of smooth pipes, and most often steel electric-welded ones. Diameters - from 32 mm to 100 mm, sometimes up to 150 mm. They are made of two types - serpentine and register. Moreover, register ones can have two types of connections: a thread and a column. A thread is when the jumpers, through which the coolant flows from one pipe to another, are installed either on the right or on the left.It turns out that the coolant sequentially runs around all the pipes, that is, the connection is serial. When connecting the "column" type, all horizontal sections are interconnected at both ends. In this case, the movement of the coolant is parallel.
Types of smooth pipe registers
In the case of use in systems with natural circulation, it is required to observe a slight slope towards the movement of the coolant of the order of 0.5 cm per meter of pipe. Such a small slope is explained by a large diameter (low hydraulic resistance).
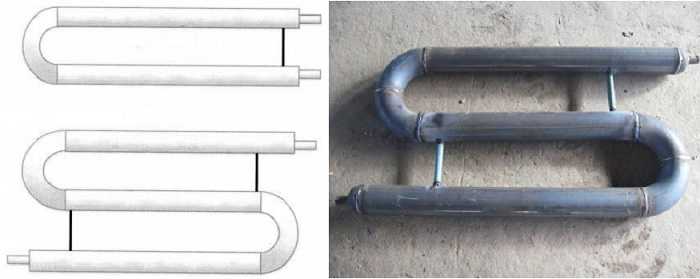
This is a serpentine heating register
These products are made not only of their round, but also of square pipes. They are practically no different, only it is more difficult to work with them, and the hydraulic resistance is slightly greater. But the advantages of this design include more compact dimensions with the same volume of coolant.

Square tube registers
There are also registers made of pipes with fins. In this case, the area of \u200b\u200bcontact of the metal with air increases, and heat transfer increases. Actually, until now, in some budget new buildings, builders install just such heating devices: the well-known “pipe with fins”. With not the best appearance, they heat the room well.
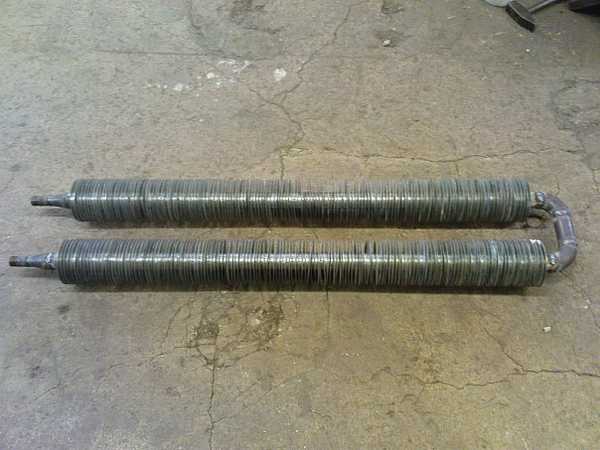

A register with plates will have a much higher heat dissipation
If you insert any register heater, you can get a combined heater. It can be separate, not connected to the system, or used as an additional heat source. If the radiator is insulated with heating only from the heating element, it is necessary to install an expansion tank at the top point (10% of the total coolant volume).When heated from a domestic boiler, an expansion tank is usually built into the structure. If it is not there (often happens in solid fuel boilers), then in this case it is also necessary to install an expansion tank. If the material for the registers is steel, then the tank needs a closed type.
Electric heating can be useful in the most severe cold, when the boiler power is not enough. Also, this option can help out in the off-season, when it makes no sense to load a long-burning solid fuel boiler and overclock the system “to the fullest”. You just need to warm up the room a little. This is not possible with solid fuel boilers. And such a fallback option will help warm up in the offseason.
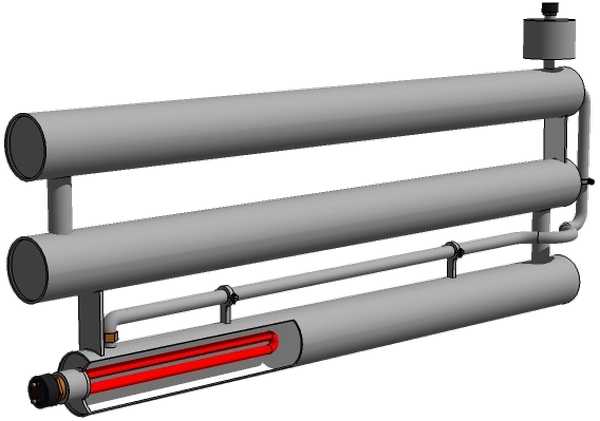
By adding a heating element to the register and putting an expansion tank, we get a combined heating system
Rules for the operation of heating registers
Register in the bathroom
To increase the service life, it is necessary to carry out a number of measures to maintain the heating registers in working condition. It is recommended to draw up a schedule of control checks, including a visual inspection and analysis of the temperature regime of the register.
In addition, you should periodically clean the internal surface of the structure from scale and rust. For this, it is best to use the hydrodynamic method, since chemical cleaning will require a large amount of a special liquid. This can be done without dismantling the structure - it is enough to install branch pipes during manufacture to provide access to the internal cavity of the register.
Each time before a new heating season, the integrity of the structure, the reliability of welded and threaded joints are checked. If necessary, gaskets are replaced and repair seams are welded.
The video shows an example of the manufacture of a register from a steel profile pipe:
Types of heating registers
There are several types of heat-transfer devices of this type, depending on their design features, the shape of the pipes and the material of manufacture.
Thermal registers of various designs
The design of the heating register can be serpentine, sectional.
They consist of several parallel pipes connected by arcuate pipes, or one pipe, curved by a snake. Depending on the characteristics of the room and the required temperature, the device is made with one or more bends.

With this design, all elements of the register participate in the heat exchange process, providing high heating efficiency while saving space. Coils are difficult to manufacture: either a welding machine is required to assemble the register from separate parts, or a pipe bender is required to bend a long pipe, which requires certain skills in working with these tools.
Section registers
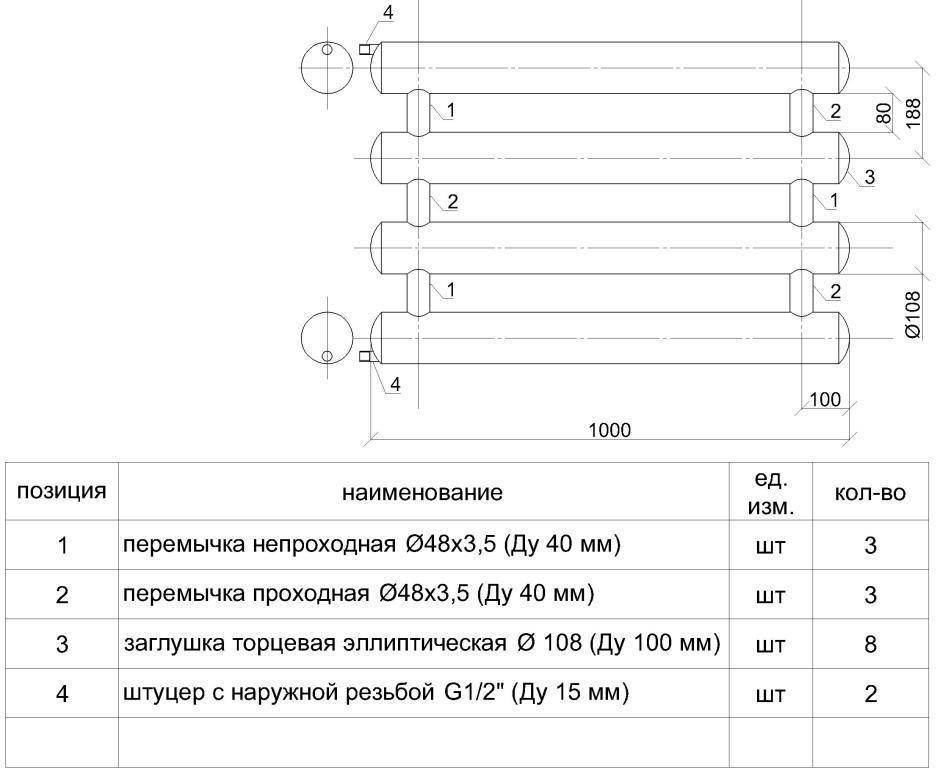
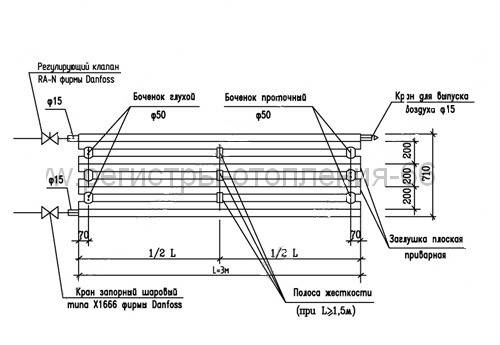
Registers made in the form of sections are much easier to manufacture, since they are several identical pipe sections connected at the edges by connecting pipes. Sections are connected in series or in parallel:
In the first case, the connecting pipes are installed either from the left or from the right edge of the sections. The capacity of the connecting pipes is the same as that of the transport pipes. From the opposite edge, instead of a connection, a support is mounted that holds the pipes in the desired position, and the ends of the pipes are closed with plugs. The energy carrier moves along the heat-releasing circuit in the same way as in the serpentine register - passing sections one by one.

Classification by section shape
The snake or sections of heaters can be made of pipes of various shapes:
| Pipe shape | pros | Minuses |
| round section | low cost of consumables, the availability of fittings and fittings for sale, high throughput, low hydraulic resistance, ease of external cleaning; | the complexity of calculating the geometry of the holes for the connection, a large volume of the finished register; |
| Rectangular or square section | ease of calculation and installation, ease of external cleaning, compactness; | high price, lower throughput than round pipes, high hydraulic resistance |
| Pipes with fins - heat transfer plates perpendicular to the sections | increased heat dissipation compactness; | unpresentable appearance, complexity of external cleaning, installation complexity, high price. |
Types of registers according to the material of manufacture
The material used for the manufacture of pipes also affects the cost, size, efficiency and aesthetics of the register:
| Material | pros | Minuses |
| Carbon steel | low cost, ease of installation, | low heat transfer susceptibility to corrosion the need for staining |
| Steel galvanized | low cost, corrosion protection | low heat transfer installation complexity due to the impossibility of using electric welding, unaesthetic appearance |
| Stainless steel | resistance to corrosion, ease of installation, staining is not required, but possible | low heat dissipation high price |
| Copper | high heat dissipation compactness, light weight, plasticity, allowing you to perform a register of any shape, corrosion resistance, aesthetics | high price, inapplicability in heating circuits made of alloys incompatible with copper (cast iron, steel, aluminium) due to possible oxidation, suitable only for pure and chemically neutral heat transfer fluids, resistance to mechanical damage |
| Aluminum | high heat dissipation light weight, | high price, the impossibility of self-manufacturing, since specialized equipment is required for welding, |
| Cast iron | high heat dissipation durability, resistance to mechanical damage, average price range chemical inertness | big weight, big sizes, installation complexity, heat up slowly and cool down slowly |
Registers from pipes of various shapes and materials can be made independently or purchased ready-made, then all that remains is to install and connect the device to the thermal circuit.
Homemade register from a profile pipe
To make a heating register from a profile pipe with your own hands, choose a product of rectangular section (60 by 80 mm), the wall thickness of which is 3 mm. A home-made heating battery (register) is assembled in several stages:
- first cut the pipe into several pieces of a certain length;
- then, on the blanks, markings are made for the holes into which the jumpers will be welded;
- four jumpers are made from an inch round pipe (25 mm);
- cut plugs from a 3 mm sheet of metal, the size of which is determined by the rectangular section of the profile;
- holes are cut out for jumpers in the places of the marking, while in the upper and lower tubes of the register there should be two holes on one side, and in the middle tube - four holes (two on both sides of the part);
- three pipes are laid out on wooden stands (beams), parallel to each other;
- jumpers are inserted into the holes in the pipes, the parts are leveled and each jumper pipe is seized by electric welding in three places;
- after the product is turned from a horizontal position to a vertical position;
- they begin to weld all stuck jumpers in two seams, adjusting the welding current to prevent the formation of places of possible leaks;
- after the profile pipes are cleaned of slag and metal debris that got inside the cavity of the product;
- previously prepared plugs are applied to the ends of the profile pipes, they are grabbed diagonally, and then they are thoroughly boiled around the entire perimeter of the rectangular section of the profile;
- grinder lightly grind the welding seams throughout the heating register;
- in the upper pipe of the homemade register, a hole is cut out for the Mayevsky tap;
- connection of the register to the heating system can be made from below, from the side, from above, or by a combination of the above options (from below and from above, diagonally, etc.):
- the exit hole is closed with a plug, the register is filled with water, after which the master looks through all the welded joints, excluding the possibility of leakage through microcracks;
- weld floor supports made of steel angles or brackets that allow you to fix the device on the wall.
Such a register has a high heat transfer due to the large amount of coolant flowing through the profile pipes.Jumpers should be placed as close as possible to the end edges of the horizontal parts. The coolant is supplied through the inlet pipe located in the upper pipe. After passing through all the elements of the device, the coolant flows out through the outlet pipe located on the bottom pipe.

The heating register of four parallel pipes connected by side riser pipes heats the living space
As you can see, it’s not difficult to make a heating register with your own hands if you have a welding machine and experience working with it. Home-made heaters can be welded exactly according to the dimensions of the heated room. Three times more funds will have to be prepared for the purchase of a ready-made heating register than for the purchase of all the necessary materials for self-welding the product. To ensure long-term operation of the device, purchase pipes made of carbon steel, low-alloy stainless steel or cast iron.
What materials are registers made of?
Depending on what material the register is made of, the efficiency of its heat transfer, appearance, dimensions, weight and cost will depend. Each material has its pros and cons, which must be considered when choosing:
- steel registers. You can choose from carbon steel, galvanized steel or stainless steel. The first has high indicators of resistance to high temperatures and endurance. Carbon material is susceptible to corrosion, so it must either be painted or coated with special products. Steel pipes are joined by welding. Heating registers made from such pipes, made independently, will be inexpensive and of high quality, and installation will not cause difficulties.Galvanized steel is corrosion resistant, cheap, unattractive and requires electric welding. Stainless steel can not be painted, it does not rust, easy to install, but more expensive. The disadvantages of any type of steel is that it has low heat transfer (45.4 W / m x 0 C);
- aluminum registers. Compared to steel, they have a higher heat transfer rate (209.3 W / m x 0 C). In addition, the material is lightweight, which makes it easy to install. The disadvantage of aluminum is its high cost. Such registers cannot be made at home, because. this requires special equipment;
- copper registers. The heat transfer index of copper is 389.6 W / m x0 C. This is the highest level of thermal conductivity compared to all materials. The advantages of copper include its low weight, ductility, which allows the manufacture of devices of various shapes, corrosion resistance and beautiful appearance. The disadvantages of the material are high price, impossibility to use with alloys incompatible with copper, instability to mechanical damage. Only pure coolant with a chemically neutral environment can flow through copper registers;
- cast iron registers. The thermal conductivity of cast iron is 62.8 W / m x0 C. They are purchased only in finished form. Due to the large weight and size, cast iron appliances are difficult to install on their own, but possible. The material heats up for a long time and also cools down for a long time. However, the disadvantages are offset by low cost, resistance to damage and durability.
 Steel heating registers
Steel heating registers
In addition to monometallic, there are also bimetallic registers. They are manufactured only in factories.They consist of a stainless core and a copper or aluminum casing with fins. The inner surface of bimetal pipes is protected from corrosion, and the outer surface with plates serves to increase heat transfer. Such devices are expensive, but effective and will last a long time.
How to make a homemade register from shaped, smooth steel pipes
The welding work underlying the manufacture of registers for a heating system requires a certain number of different tools and materials.
DIY tools and materials
In addition to the welding machine, the following devices will be required:
- for cutting: grinder, plasma cutter or gas burner (cutter);
- tape measure and pencil;
- hammer and gas key;
- building level;
Materials for welding:
- electrodes, if electric welding is used;
- wire, if gas;
- oxygen and acetylene in cylinders.
The order of work: how to weld the structure?
Depending on the chosen type of construction (sectional or serpentine), the assembly of registers will be very different. The most difficult are sectional, because they have the most joints of elements of different sizes.
Before proceeding to the assembly of the register, it is necessary to make a drawing, deal with the dimensions and quantity. They depend on the heat transfer of the pipe. For example, 1 m of a pipe with a diameter of 60 mm or a section of 60x60 mm and a thickness of 3 mm is intended for heating 1 m² of the area of the heated room, taking into account that the ceiling height does not exceed 3 m.
The first thing to do is to cut segments from the selected pipe in accordance with the estimated length of the sections. The ends must be ground and cleaned of scale and burrs.
Before assembling sectional devices, you need to put markings on them, along which jumpers will be installed. Usually it is 10-20 cm from the edges of the sectional pipes. Immediately on the upper element, a mark is made where the air vent valve (Mayevsky crane) will be installed. It is located on the opposite side and along the edge of the section, and along the outer plane.
- With a gas burner or a plasma cutter, holes are made in the pipes according to the marks, taking into account that the jumper pipe can enter them.
- The lintels of 30-50 cm are cut out of pipes of a smaller diameter.
- Segments of the same length as the pipe jumpers are cut from the metal profile. They will be installed in the form of supports for section pipes on the opposite side from the installation of the adjoining element.
- Cut out of sheet metal with a thickness of 3-4 mm plugs in the shape of the main pipe (circle or rectangle). In two of them, holes are made for the spurs, to which the supply and return circuits of the heating system will be connected through shut-off valves.
- First of all, plugs are welded to the sections.
- Drives are welded to the latter.
- Welding of jumpers with pipe sections is carried out.
- Support elements made of cut steel profiles are immediately attached by welding.
- A branch pipe is welded for the installation of a Mayevsky crane.
- All seams are cleaned with a grinder and a grinding disc.
The assembly and welding process is best carried out on a flat plane, on which two or three wooden bars are laid (they can be replaced with steel profiles: a corner or a channel). It is on the bars that the pipe sections are laid out parallel to each other, taking into account the distance between the sections.As soon as the structure is assembled with tacks, you can begin to weld all the seams by rotating the device so that welding is carried out only in a horizontal plane.
As for the installation of registers. Depending on which plane they will be attached to, it is necessary to think over the fasteners. There are several commonly used options.
If the device will be based on a floor base, then legs are installed under it. If it will be attached to the wall, then use conventional brackets with curved hooks up.
After complete assembly of the register, it must be checked for tightness of the seams. To do this, one of the drives is closed with a threaded plug, and water is poured through the second. Welds are checked. If a smudge is found, then the defective place is boiled again and cleaned. After all the operations performed, the device is stained.
Making a serpentine register is much easier. Firstly, bends are ready-made factory parts that are selected according to the diameter of the pipe section. Secondly, they are boiled among themselves in the same way as with a pipe.
First, two outlets are connected to each other. The resulting C-shaped fitting is connected in series to the ends of two pipes, combining them into a single structure. Plugs are installed in the two free ends of the register, in which holes are pre-made, and the spurs are welded.
Quantity calculation
Registers are devices in which a significant amount of coolant moves, because they are made from large diameter pipes, plus several sections are included. To heat such a large amount of water, you need a powerful heating boiler. And this is not only a considerable fuel consumption, these are the considerable dimensions of the heating equipment itself.

Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the heating system, which includes registers, exactly taking into account the heat consumed by the premises.
There are already ready-made tabular values of the ratio of the dimensions of steel pipes and their heat transfer. This simplifies the calculation of the number of devices.
Heat transfer can also be calculated using the formula: Q \u003d π d l k (Tr - To), where:
- d is the pipe diameter;
- l is its length;
- k - heat transfer equal to 11.63 W / m²;
- Tr is the temperature in the room;
- To is the coolant temperature.
It is on the basis of the calculations made that the length of the register, the number of sections in it and the number of devices themselves are selected.