- How to choose the power of a gas boiler
- Calculation of a single-circuit heating boiler
- How to calculate the power of a double-circuit boiler
- Calculation of the power of an indirect heating boiler and a single-circuit boiler
- What power reserve should a gas boiler have
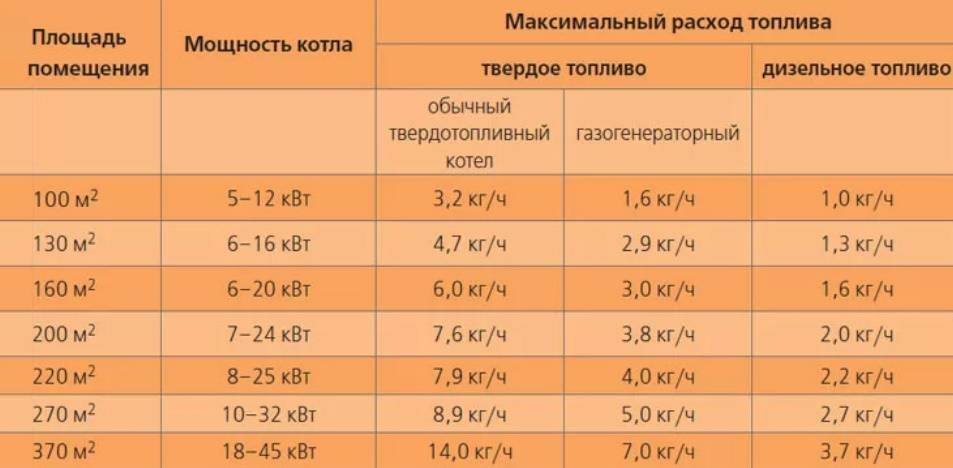
- Calculation of gas demand based on boiler power
- The concept of dissipation factor
- What is room heat loss
- 3 Correcting the calculations - additional points
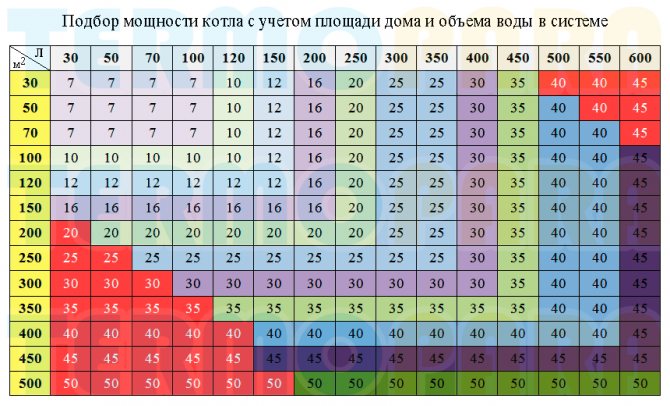
- Calculation of the power of a gas boiler depending on the area
- Calculation of a single-circuit heating boiler
- How to calculate the power of a double-circuit boiler
- Calculation of the power of an indirect heating boiler
- A banal question - why know the required power of the boiler
- Prices for popular heating boilers
- Why you should not select a boiler with too much power reserve
- When excessive heat output is still appropriate
- Eventually
How to choose the power of a gas boiler
Most consultants who sell heating equipment independently calculate the required performance using the formula 1 kW = 10 m². Additional calculations are carried out according to the amount of coolant in the heating system.
Calculation of a single-circuit heating boiler
- For 60 m² - a unit of 6 kW + 20% = 7.5 kilowatts can satisfy the need for heat
. If there is no model with a suitable performance size, preference is given to heating equipment with a large power value. - In a similar way, calculations are made for 100 m² - the required power of boiler equipment, 12 kW.
- For heating 150 m², you need a gas boiler with a power of 15 kW + 20% (3 kilowatts) = 18 kW
. Accordingly, for 200 m², a 22 kW boiler is required.
How to calculate the power of a double-circuit boiler
10 m² = 1 kW + 20% (power reserve) + 20% (for water heating)
The power of a double-circuit gas boiler for heating and hot water heating for 250 m² will be 25 kW + 40% (10 kilowatts) = 35 kW
. Calculations are suitable for two-circuit equipment. To calculate the performance of a single-circuit unit connected to an indirect heating boiler, a different formula is used.
Calculation of the power of an indirect heating boiler and a single-circuit boiler
- Determine what volume of the boiler will be sufficient to meet the needs of the residents of the house.
- In the technical documentation for the storage tank, the required performance of the boiler equipment is indicated in order to maintain the heating of hot water, without taking into account the necessary heat for heating. A 200 liter boiler will require an average of about 30 kW.
- The performance of the boiler equipment required for heating the house is calculated.
The resulting numbers are added up. The amount equal to 20% is subtracted from the result. This must be done for the reason that the heating will not simultaneously work for heating and DHW. The calculation of the thermal power of a single-circuit heating boiler, taking into account an external water heater for hot water supply, is done taking into account this feature.
What power reserve should a gas boiler have
- For single-circuit models, the margin is about 20%.
- For two-circuit units, 20% + 20%.
- Boilers with connection to an indirect heating boiler - in the storage tank configuration, the required additional performance margin is indicated.
Calculation of gas demand based on boiler power
In practice, this means that 1 m³ of gas is equal to 10 kW of thermal energy, assuming 100% heat transfer. Accordingly, with an efficiency of 92%, fuel costs will be 1.12 m³, and at 108% no more than 0.92 m³.
The method for calculating the volume of consumed gas takes into account the performance of the unit. So, a 10 kW heating device, within an hour, will burn 1.12 m³ of fuel, a 40 kW unit, 4.48 m³. This dependence of gas consumption on the power of boiler equipment is taken into account in complex heat engineering calculations.
The ratio is also built into the online heating costs. Manufacturers often indicate the average gas consumption for each model produced.
In order to fully calculate the approximate material costs of heating, it will be necessary to calculate the electricity consumption in volatile heating boilers. At the moment, boiler equipment operating on main gas is the most economical way of heating.
For heated buildings of a large area, calculations are carried out only after an audit of the heat loss of the building. In other cases, when calculating, they use special formulas or online services.
Gas boiler - universal heat exchanger, providing circulation of hot water for household purposes and space heating.
The device looks like like a small refrigerator.
When installing a heating boiler, it is necessary to correctly calculate its power.
The concept of dissipation factor
The dissipation coefficient is one of the important indicators of heat exchange between the living space and the environment. Depending on how well the house is insulated. there are such indicators that are used in the most accurate calculation formula:
- 3.0 - 4.0 is the dissipation factor for structures in which there is no thermal insulation at all. Most often in such cases we are talking about makeshift houses made of corrugated iron or wood.
- A coefficient from 2.9 to 2.0 is typical for buildings with a low level of thermal insulation. This refers to houses with thin walls (for example, one brick) without insulation, with ordinary wooden frames and a simple roof.
- The average level of thermal insulation and a coefficient from 1.9 to 1.0 are assigned to houses with double plastic windows, insulation of external walls or double masonry, as well as with an insulated roof or attic.
- The lowest dispersion coefficient from 0.6 to 0.9 is typical for houses built using modern materials and technologies. In such houses, the walls, roof and floor are insulated, good windows are installed and the ventilation system is well thought out.
Table for calculating the cost of heating in a private house
The formula in which the value of the dissipation coefficient is used is one of the most accurate and allows you to calculate the heat loss of a particular building. It looks like this:
In the formula, Qt is the level of heat loss, V is the volume of the room (the product of length, width and height), Pt is the temperature difference (to calculate, you need to subtract the minimum air temperature that can be in this latitude from the desired temperature in the room), k is the scattering coefficient.
Let's substitute the numbers into our formula and try to find out the heat loss of a house with a volume of 300 m³ (10 m * 10 m * 3 m) with an average level of thermal insulation at a desired air temperature of + 20 ° C and a minimum winter temperature of - 20 ° C.
Having this figure, we can find out what power the boiler needs for such a house. To do this, the obtained value of heat loss should be multiplied by a safety factor, which is usually from 1.15 to 1.2 (the same 15-20%). We get that:
Rounding the resulting number down, we find the desired number. To heat a house with the conditions we set, a boiler of 38 kW is required.
Such a formula will allow you to very accurately determine the power of the gas boiler required for a particular house. Also, to date, a wide variety of calculators and programs have been developed that allow you to take into account the data of each individual building.
Do-it-yourself heating of a private house - tips for choosing the type of system and type of boiler Requirements for installing a gas boiler: what is necessary and useful to know about the connection procedure? How to correctly and without errors calculate heating radiators for a house The water supply system of a private house from a well: recommendations for creating
What is room heat loss
Any room has a certain heat loss. Heat comes out of walls, windows, floors, doors, ceilings, so the task of a gas boiler is to compensate for the amount of outgoing heat and provide a certain temperature in the room. This requires a certain thermal power.

It has been experimentally established that the greatest amount of heat escapes through the walls (up to 70%). Up to 30% of thermal energy can escape through the roof and windows, and up to 40% through the ventilation system.The lowest heat loss at the door (up to 6%) and the floor (up to 15%)
The following factors affect the heat loss of the house.
The location of the house. Each city has its own climatic features. When calculating heat losses, it is necessary to take into account the critical negative temperature characteristic of the region, as well as the average temperature and duration of the heating season (for accurate calculations using the program).
The location of the walls relative to the cardinal points. It is known that the wind rose is located on the north side, so the heat loss of the wall located in this area will be the largest. In winter, a cold wind blows with great force from the western, northern and eastern sides, so the heat loss of these walls will be higher.
The area of the heated room. The amount of outgoing heat depends on the size of the room, the area of \u200b\u200bwalls, ceilings, windows, doors.
Heat engineering of building structures. Any material has its own coefficient of thermal resistance and heat transfer coefficient - the ability to pass a certain amount of heat through itself. To find out, you need to use tabular data, as well as apply certain formulas. Information on the composition of walls, ceilings, floors, their thickness can be found in the technical plan of housing.
Window and door openings. Size, modification of the door and double-glazed windows. The larger the area of window and door openings, the higher the heat loss.
It is important to take into account the characteristics of the installed doors and double-glazed windows when calculating.
Accounting for ventilation. Ventilation always exists in the house, regardless of the presence of an artificial hood
The room is ventilated through open windows, air movement is created when the entrance doors are closed and opened, people walk from room to room, which contributes to the escape of warm air from the room, its circulation.
Knowing the above parameters, you can not only calculate the heat loss of the house and determine the power of the boiler, but also identify places that need additional insulation.
3 Correcting the calculations - additional points
In practice, housing with average indicators is not so common, so additional parameters are taken into account when calculating the system. One determining factor - the climatic zone, the region where the boiler will be used, has already been discussed. We give the values of the coefficient Woud for all areas:
- the middle band serves as a standard, the specific power is 1–1.1;
- Moscow and Moscow region - we multiply the result by 1.2–1.5;
- for the southern regions - from 0.7 to 0.9;
- for the northern regions, it rises to 1.5–2.0.
In each zone, we observe a certain scatter of values. We act simply - the further south the area in the climatic zone, the lower the coefficient; the further north, the higher.
Here is an example of adjustment by region. Suppose that the house for which the calculations were made earlier is located in Siberia with frosts up to 35 °. We take Woud equal to 1.8. Then we multiply the resulting number 12 by 1.8, we get 21.6. We round off towards a larger value, it turns out 22 kilowatts. The difference with the initial result is almost twice, and after all, only one amendment was taken into account. So the calculations need to be corrected.
In addition to the climatic conditions of the regions, other corrections are taken into account for accurate calculations: the height of the ceiling and the heat loss of the building.The average ceiling height is 2.6 m. If the height is significantly different, we calculate the coefficient value - we divide the actual height by the average. Suppose the ceiling height in the building from the example considered earlier is 3.2 m. We consider: 3.2 / 2.6 \u003d 1.23, round it up, it turns out 1.3. It turns out that to heat a house in Siberia with an area of 120 m2 with ceilings of 3.2 m, a boiler of 22 kW × 1.3 = 28.6 is required, i.e. 29 kilowatts.
It is also very important for correct calculations to take into account the heat loss of the building. Heat is lost in any home, regardless of its design and type of fuel. Through poorly insulated walls, 35% of warm air can escape, through windows - 10% or more
An uninsulated floor will take 15%, and a roof - all 25%. Even one of these factors, if present, should be taken into account. Use a special value by which the received power is multiplied. It has the following stats:
Through poorly insulated walls, 35% of warm air can escape, through windows - 10% or more. An uninsulated floor will take 15%, and a roof - all 25%. Even one of these factors, if present, should be taken into account. Use a special value by which the received power is multiplied. It has the following stats:
- for a brick, wooden or foam block house, which is more than 15 years old, with good insulation, K = 1;
- for other houses with non-insulated walls K=1.5;
- if the house, in addition to non-insulated walls, does not have an insulated roof K = 1.8;
- for a modern insulated house K=0.6.
Let's return to our example for calculations - a house in Siberia, for which, according to our calculations, a heating device with a capacity of 29 kilowatts is needed.Suppose that this is a modern house with insulation, then K = 0.6. We calculate: 29 × 0.6 \u003d 17.4. We add 15-20% to have a reserve in case of extreme frosts.
So, we calculated the required power of the heat generator using the following algorithm:
- 1. We find out the total area of the heated room and divide by 10. The number of specific power is ignored, we need average initial data.
- 2. We take into account the climatic zone where the house is located. We multiply the previously obtained result by the coefficient index of the region.
- 3. If the ceiling height differs from 2.6 m, take this into account as well. We find out the coefficient number by dividing the actual height by the standard one. The power of the boiler, obtained taking into account the climatic zone, is multiplied by this number.
- 4. We make a correction for heat loss. We multiply the previous result by the coefficient of heat loss.
Placement of boilers for heating in the house
Above, it was only about boilers that are used exclusively for heating. If the appliance is used to heat water, the rated power should be increased by 25%
Please note that the reserve for heating is calculated after adjusting for climatic conditions. The result obtained after all calculations is quite accurate, it can be used to select any boiler: gas, liquid fuel, solid fuel, electric
Calculation of the power of a gas boiler depending on the area
In most cases, an approximate calculation of the thermal power of the boiler unit is used for heating areas, for example, for a private house:
- 10 kW per 100 sq.m;
- 15 kW per 150 sq.m;
- 20 kW per 200 sq.m.
Such calculations may be suitable for a not very large building with an insulated attic floor, low ceilings, good thermal insulation, double-glazed windows, but no more.
 According to the old calculations, it is better not to do it. Source
According to the old calculations, it is better not to do it. Source
Unfortunately, only a few buildings meet these conditions. In order to carry out the most detailed calculation of the boiler power indicator, it is necessary to take into account a full package of interrelated quantities, including:
- atmospheric conditions in the area;
- the size of the residential building;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity of the wall;
- the actual thermal insulation of the building;
- gas boiler power control system;
- the amount of heat required for DHW.
Calculation of a single-circuit heating boiler
Calculation of the power of a single-circuit boiler unit of wall or floor modification of the boiler using the ratio: 10 kW per 100 m2, must be increased by 15-20%.
For example, it is necessary to heat a building with an area of 80 m2.
Calculation of the power of a gas heating boiler:
10*80/100*1.2 = 9.60 kW.
In the case when the required type of device does not exist in the distribution network, a modification with a larger kW size is purchased. A similar method will go for single-circuit heating sources, without a load on hot water supply, and can be used as the basis for calculating gas consumption for a season. Sometimes, instead of living space, the calculation is performed taking into account the volume of the residential building of the apartment and the degree of insulation.
For individual premises built according to a standard project, with a ceiling height of 3 m, the calculation formula is quite simple.
 Another way to calculate the OK boiler
Another way to calculate the OK boiler
In this option, the built-up area (P) and the specific power factor of the boiler unit (UMC) are taken into account, depending on the climatic location of the facility.
It varies in kW:
- 0.7 to 0.9 southern territories of the Russian Federation;
- 1.0 to 1.2 central regions of the Russian Federation;
- 1.2 to 1.5 Moscow region;
- 1.5 to 2.0 northern regions of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, the formula for the calculation looks like this:
Mo=P*UMK/10
For example, the required power of a heating source for a building of 80 m2, located in the northern region:
Mo \u003d 80 * 2/10 \u003d 16 kW
If the owner will install a double-circuit boiler unit for heating and hot water, professionals advise adding another 20% of the power for water heating to the result.
How to calculate the power of a double-circuit boiler
The calculation of the heat output of a double-circuit boiler unit is carried out on the basis of the following proportion:
10 m2 = 1,000 W + 20% (heat loss) + 20% (DHW heating).
If the building has an area of 200 m2, then the required size will be: 20.0 kW + 40.0% = 28.0 kW
This is an estimated calculation, it is better to clarify it according to the rate of water use of hot water supply per person. Such data are given in SNIP:
- bathroom - 8.0-9.0 l / min;
- shower installation - 9 l / min;
- toilet bowl - 4.0 l / min;
- mixer in the sink - 4 l / min.
The technical documentation for the water heater indicates what heating output of the boiler is required to guarantee high-quality water heating.
For a 200 l heat exchanger, a heater with a load of approximately 30.0 kW will suffice. After that, the performance sufficient for heating is calculated, and at the end the results are summarized.
Calculation of the power of an indirect heating boiler
In order to balance the required power of a single-circuit gas-fired unit with an indirect heating boiler, it is necessary to establish how much heat exchanger is required to provide hot water to the residents of the house. Using the data on the norms of hot water consumption, it is easy to establish that the consumption per day for a family of 4 will be 500 liters.
The performance of an indirect heating water heater directly depends on the area of \u200b\u200bthe internal heat exchanger, the larger the coil, the more heat energy it transfers to water per hour. You can detail such information by examining the characteristics of the passport for the equipment.
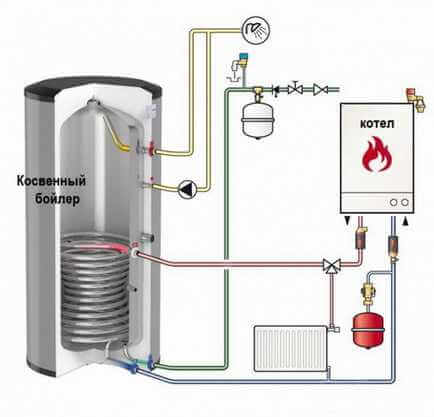 Source
Source
There are optimal ratios of these values for the average power range of indirect heating boilers and the time to obtain the desired temperature:
- 100 l, Mo - 24 kW, 14 min;
- 120 l, Mo - 24 kW, 17 min;
- 200 l, Mo - 24 kW, 28 min.
When choosing a water heater, it is recommended that it heats the water in about half an hour. Based on these requirements, the 3rd option of the BKN is preferable.
A banal question - why know the required power of the boiler
Despite the fact that the question does seem rhetorical, it still seems necessary to give a couple of explanations. The fact is that some owners of houses or apartments still manage to make mistakes, falling into one or another extreme. That is, purchasing equipment of either obviously insufficient thermal performance, in the hope of saving money, or greatly overestimated, so that, in their opinion, it is guaranteed, with a large margin, to provide themselves with heat in any situation.
Both are completely wrong, and negatively affect both the provision of comfortable living conditions and the durability of the equipment itself.
Well, with the lack of calorific value, everything is more or less clear. With the onset of winter cold weather, the boiler will operate at its full capacity, and it is not a fact that there will be a comfortable microclimate in the rooms. This means that you will have to “catch up with heat” with the help of electric heaters, which will entail considerable extra costs. And the boiler itself, functioning at the limit of its capabilities, is unlikely to last long. In any case, after a year or two, homeowners clearly realize the need to replace the unit with a more powerful one. One way or another, the cost of a mistake is quite impressive.

Whichever heating boiler is chosen, its thermal output must meet a certain “harmony” - completely cover the needs of a house or apartment from thermal energy and have a reasonable operating margin
Well, why not buy a boiler with a large margin, what can prevent it? Yes, of course, high-quality space heating will be provided. But now we list the "cons" of this approach:
- Firstly, a boiler of greater power can cost much more by itself, and it is difficult to call such a purchase rational.
- Secondly, with increasing power, the dimensions and weight of the unit almost always increase.
These are unnecessary installation difficulties, “stolen” space, which is especially important if the boiler is planned to be placed, for example, in the kitchen or in another room in the living area of the house
- Thirdly, you may encounter uneconomical operation of the heating system - part of the spent energy resources will be spent, in fact, in vain.
- Fourthly, excess power is regular long shutdowns of the boiler, which, in addition, are accompanied by cooling of the chimney and, accordingly, abundant formation of condensate.
- Fifth, if powerful equipment is never properly loaded, it does not benefit him. Such a statement may seem paradoxical, but it is true - wear becomes higher, the duration of trouble-free operation is significantly reduced.
Prices for popular heating boilers
An excess of boiler power will be appropriate only if it is planned to connect a water heating system for household needs to it - an indirect heating boiler. Well, or when it is planned to expand the heating system in the future. For example, in the plans of the owners - the construction of a residential extension to the house.
Why you should not select a boiler with too much power reserve
With a lack of heat output, everything is very clear: the heating system simply will not provide the desired temperature level even during continuous operation. However, as we already mentioned, an overabundance of power can also become a serious problem, the consequences of which are:
- lower efficiency and increased fuel consumption, especially on one- and two-stage burners that are not able to smoothly modulate performance;
- frequent clocking (on / off) of the boiler, which disrupts normal operation and reduces the life of the burner;
- simply a higher cost of the boiler, given that the performance for which the increased payment was made will not be used;
- often larger and heavier.
When excessive heat output is still appropriate
The only reason to choose a version of the boiler that is much larger than necessary, as we have already mentioned, is to use it in conjunction with a buffer tank. A buffer tank (also a heat accumulator) is a storage tank of a certain volume filled with a coolant, the purpose of which is to accumulate excess heat power and further distribute it more rationally in order to heat a house or provide hot water supply (DHW).
For example, a heat accumulator is an excellent solution if the performance of the DHW circuit is not enough or when the solid fuel boiler is cyclic, when the fuel burns out it gives off maximum heat, and after burning out the system cools down quickly. Also, the heat accumulator is often used in conjunction with an electric boiler, which heats the tank during the period of the reduced nightly electricity tariff, and during the day the accumulated heat is distributed throughout the system, maintaining the desired temperature for a long time without the participation of the boiler.
InstructionsBoilers
Eventually
As you can see, the calculation of the heating capacity comes down to calculating the total value of the four above elements.
Not everyone can determine the required capacity of the working fluid in the system with mathematical accuracy. Therefore, not wanting to perform the calculation, some users act as follows. To begin with, the system is filled by about 90%, after which the performance is checked. Then bleed the accumulated air and continue filling.
During the operation of the heating system, a natural decrease in the level of the coolant occurs as a result of convection processes.In this case, there is a loss of power and productivity of the boiler. This implies the need for a reserve tank with a working fluid, from where it will be possible to monitor the loss of coolant and, if necessary, replenish it.