- Instrument check
- RCD test method: step-by-step diagnostics
- What is an UZO?
- When do you need to check?
- Checking the operation of the RCD with a control lamp
- The nuances of the control assembly
- Calculation of the resistance of the control
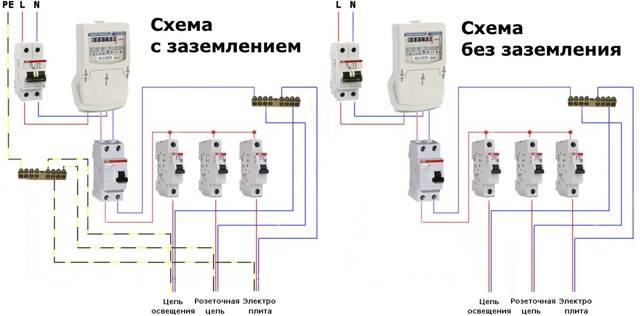
- RCD test in a grounded network
- RCD test in a single-phase network without grounding
- Laboratory testing and on-site testing of circuit breakers
- Regulatory reference
- Checking the RCD for performance
- Testing with the TEST button
- Battery test method
- How to test an RCD with an incandescent bulb
- Tester test method
- When to check
- Washing machine example
- Methods for Performing Verification
- Control by "Test" button
- control light
- Socket test
- How to check the differential machine
- Types of difavtomat checks
- Checking with the "TEST" button
- Battery test
- Checking the leakage current with a resistor
- Testing permanent magnet protection
Instrument check
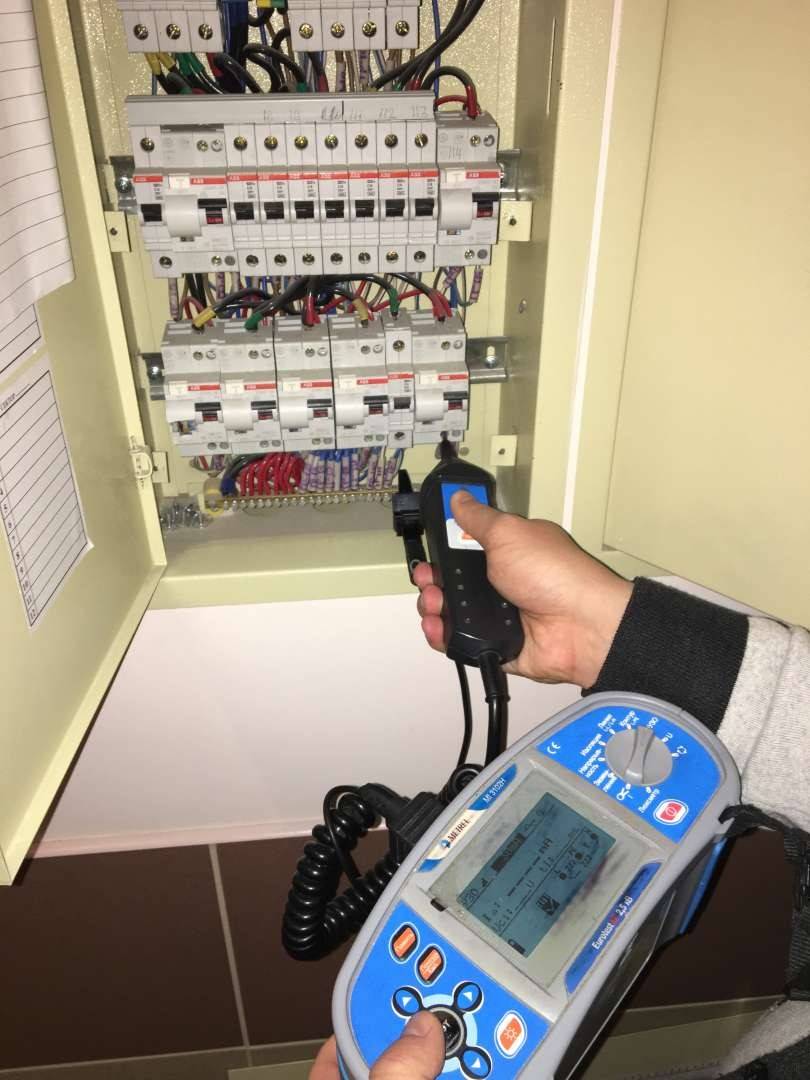
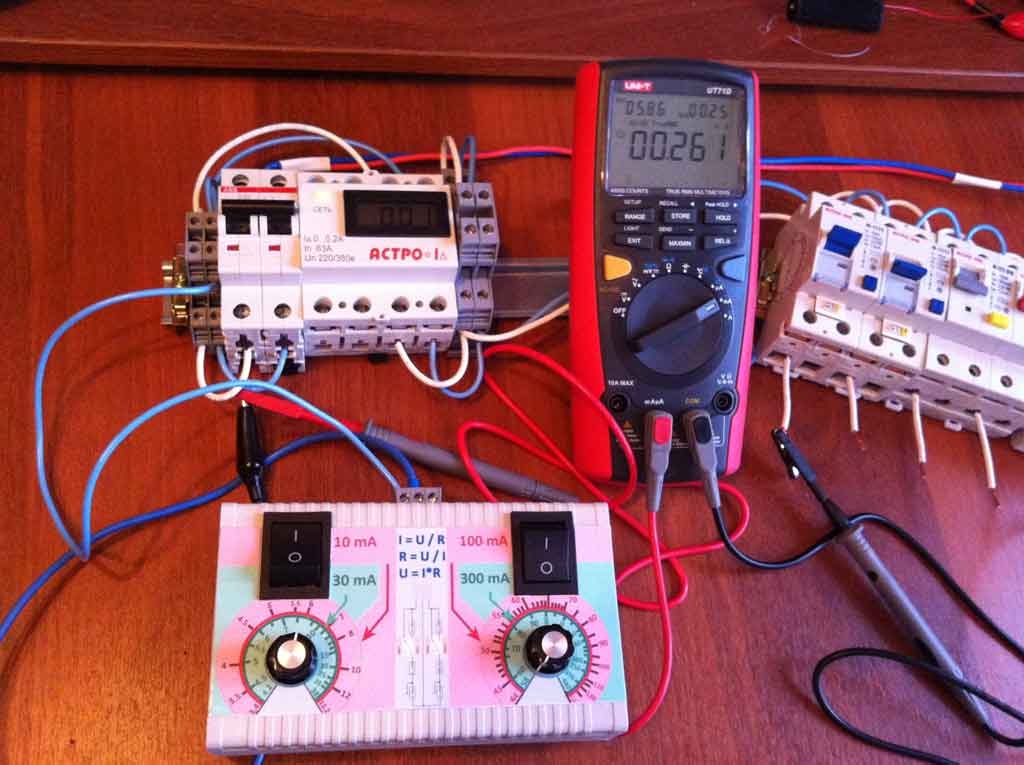
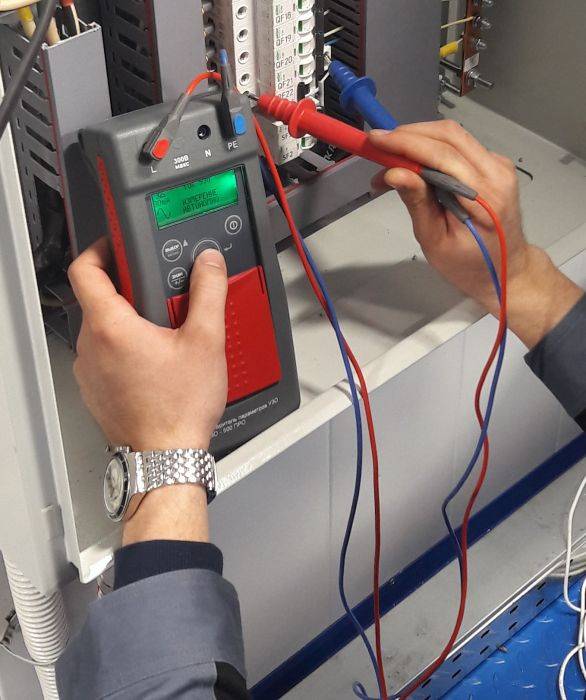 In factories and laboratories where periodic testing of all devices is mandatory, a special RCD tester is used.
In factories and laboratories where periodic testing of all devices is mandatory, a special RCD tester is used.
An example of such a device is the parameter meter PZO-500, PZO-500 Pro, MRP-200 and other professional devices. They allow, without additional circuits, to check the parameters of RCDs of various types, with different limits for differential current.
Professional meters are used where regular, for example, monthly checks of all available VDTs are practiced, and there are high requirements for accuracy and reliability. Such devices are quite expensive, so for domestic purposes their use is irrational.
RCD test method: step-by-step diagnostics
If the safety device is defective, unpleasant consequences can be expected. A timely check will help to identify the fact of a malfunction of the RCD. The method is also suitable for testing a differential automaton (difavtomat).
When the current difference reaches a life-threatening value (usually 30 mA), the RCD turns off the voltage
The RCD is able to provide protection against touching objects that may be in front of voltage, for example, if the wire insulation has been broken.
The RCD must be checked immediately after its installation, as well as once a month. According to the rules, the check must be carried out in accordance with the rules that are prescribed in the technical recommendations for the device. A full scan includes a number of steps.
- Check control lever.
- Run a button tester.
- Measure the setting current.
- Check the tripping time of the RCD.
Checks should be carried out at regular intervals. Simple checks with light bulbs can be done once a month. In modern devices, a DVR or radar detector can be built in, which will allow you to find out about the current leakage much faster. You can independently check the operation of Ouzo with a multimeter. A simple tester can be purchased at the store. To check, you can make a circuit using a battery and a light bulb
It is very important to take responsibility for the frequency of checks or their quality, since the failure of the device can lead to sad consequences.
What is an UZO?
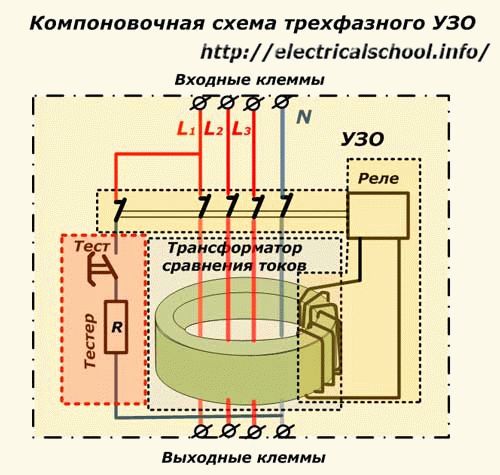
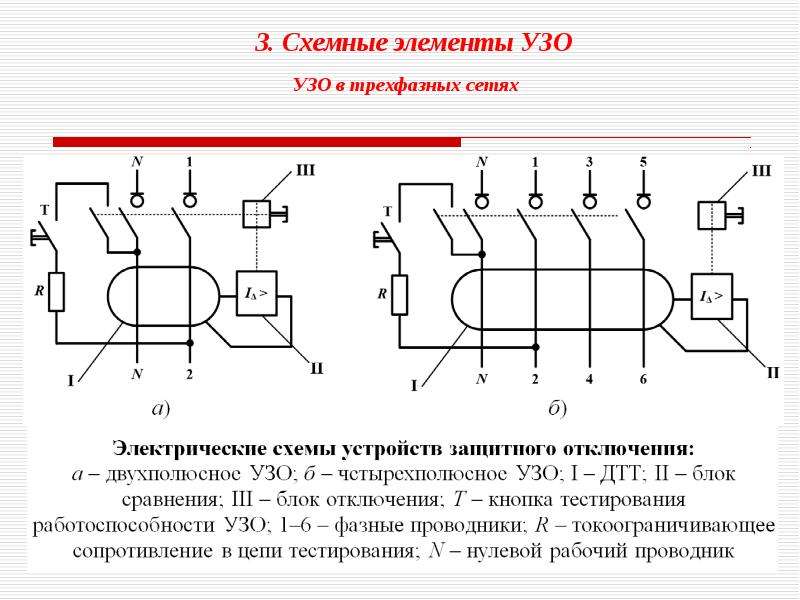
The correct name of the RCD is an automatic circuit breaker controlled by differential current. This switching device is used to automatically interrupt the circuit during the excess of the set figures of the unbalance current that occurs under certain conditions. The operation of the internal mechanism of the device is based on the following rules: neutral and phase conductors are connected to the terminals, after which they are compared in current. In the normal state of the entire system, there is no difference between the indicators of the current strength of the phase and the data of the neutral conductor. Its appearance indicates a leak. After analyzing the abnormal state, the device turns off.
The functions that the residual current device performs are not typical of conventional switches. The latter react only to overload or short circuit.
In simpler terms, the RCD trips and breaks the network when the current begins to flow outside the electrical wiring or devices connected to the mains.
In those circuits in which leaks are possible and the possibility of electric shock to people is very likely, RCDs are most often installed. In a house or apartment, these are places where vapors accumulate, thereby causing increased humidity. This is the kitchen and bathroom. In addition, it is these rooms that are the most saturated with various kinds of electrical appliances.
The minimum current, the flow of which is felt by the human body, is 5 mA. At a value of 10 mA, the muscles spontaneously contract and a person cannot independently let go of a dangerous electrical appliance. Exposure to 100 mA is fatal
One of the usual electrical assistants can shock a person in the case when it is not possible to ground it or this was not taken into account in the design. When the insulation of the leading wires is broken in one of the devices, the current will flow to the body of the unit.
In the absence of grounding, when touching such a surface, a person will receive an electric shock. To prevent this from happening, the installation of a protective shutdown device is required.
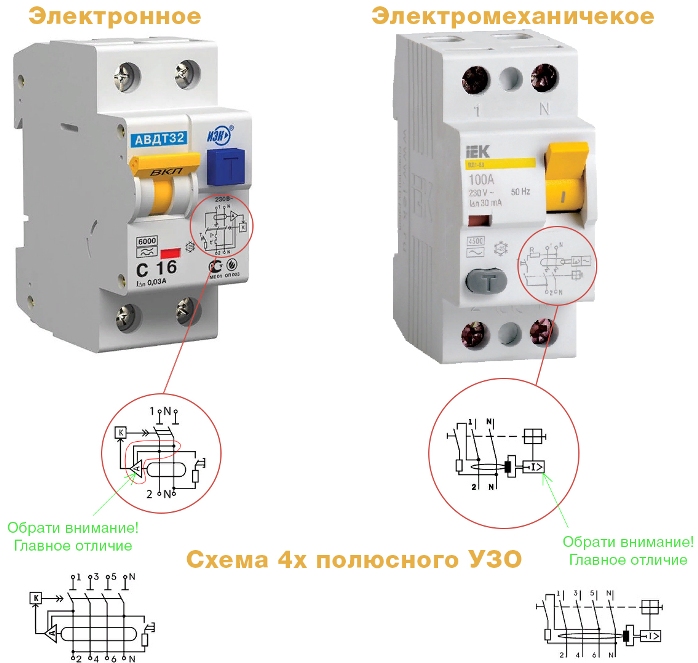
RCD designs may differ in the mode of action. Manufacturers produce devices that have an auxiliary power source for the normal operation of the electronic circuit and devices that do without it.
Electromechanical protective devices operate directly from the leakage current, using the potential of a pre-charged mechanical spring. The operation of RCDs on electronic components is completely dependent on the presence of voltage in the network. To turn it off, it needs additional power. In this regard, the latter device is considered less reliable.
When do you need to check?
The state of the current operability is checked after the connection of the RCD is completed. In addition, the test must also be carried out during operation of the protective device.
 At home, it is necessary to periodically check the RCD, even for no apparent reason
At home, it is necessary to periodically check the RCD, even for no apparent reason
It should be said that a complete diagnosis of the device at home is impossible. To do this, you need to turn to the help of specialists who have the necessary knowledge and special tools to carry out such a procedure.
The regulatory documentation says that a complete check of the device with only improvised means is insufficient, therefore the RCD must be subjected to a complete diagnosis. Only then can you gain complete confidence in the reliability of such devices.
For full confidence in the reliability and non-failure operation of the device, the check should be carried out every month.
Checking the operation of the RCD with a control lamp
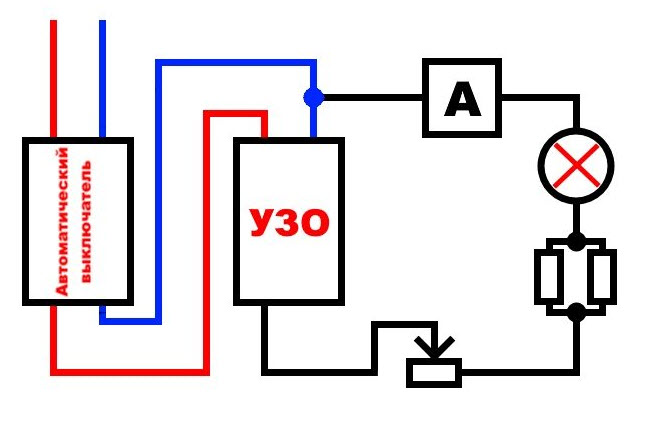
In this case, current leakage is directly created from the circuit, which is protected by the RCD. For the correct verification, it must be understood here whether there is a ground in the circuit or a residual current device is connected without it.
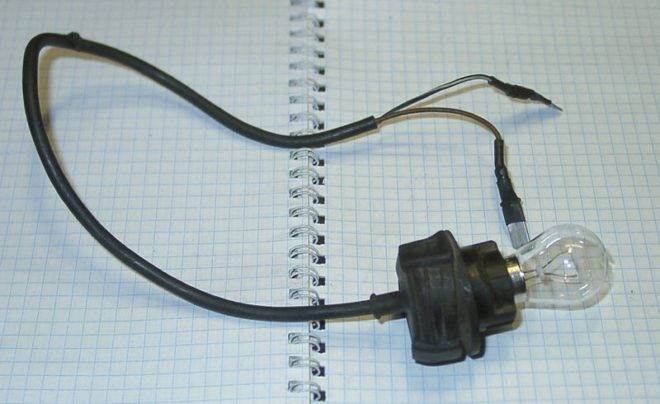

To assemble the control you will need the light bulb itself, a cartridge for it and two wires. In fact, a carrying lamp is assembled, but instead of a plug, bare wires remain that can be used to touch the contacts being tested.
The nuances of the control assembly
When assembling the control, two important nuances must be taken into account:
Firstly, the lamp must be powerful enough to create the necessary leakage current. If the standard is checked RCD set to 30 mA, then there are no problems here - even a 10-watt light bulb will take a current of at least 45 mA from the network (calculated by the formula I \u003d P / U \u003d 10/220 \u003d 0.045).
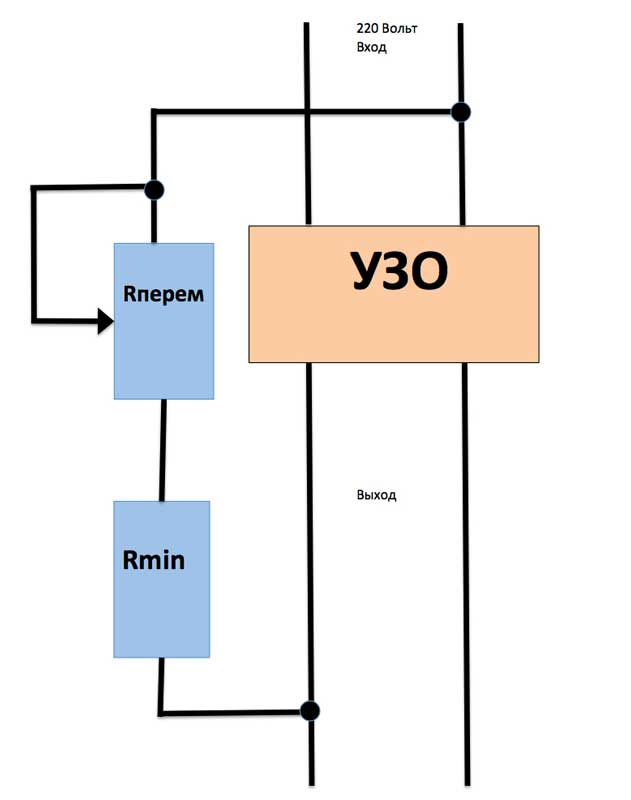
Calculation of the resistance of the control
Ohm's law will help to calculate the required resistance - R \u003d U / I. If you take a 100 watt light bulb to test a residual current device with a setting of 30 mA, then the calculation procedure is as follows:
- The voltage in the network is measured (for calculations, a nominal value of 220 Volts is taken, but in practice, plus or minus 10 volts can play a role).
- The total circuit resistance at a voltage of 220 volts and a current of 30 mA will be 220 / 0.03≈7333 ohms.
- With a power of 100 watts, a light bulb (on a 220 volt network) will have a current of 450 mA, which means its resistance is 220 / 0.45≈488 ohms.
- To get a leakage current of exactly 30 mA, a resistor with a resistance of 7333-488≈6845 ohms must be connected in series to the light bulb.
If you take bulbs of a different power, then the resistors will need others. It is also necessary to take into account the power for which the resistance is designed - if the light bulb is 100 watts, then the resistor must be appropriate - either 1 with a power of 100 watts, or 2 of 50 (but in the second version, the resistors are connected in parallel and their total resistance is calculated by the formula Rtot = (R1*R2)/(R1+R2)).
For a guarantee, after assembling the control, you can connect it to the network through an ammeter and make sure that the current of the required strength passes through the circuit with the light bulb and resistor.
RCD test in a grounded network
If the wiring is laid in accordance with all the rules - using grounding, then here you can check each outlet separately. To do this, the voltage indicator is to which terminal of the socket the phase is connected, and one of the control probes is inserted into it. The second probe must touch the ground contact and the residual current device should work, since the current from the phase went to ground and did not return through zero.
In this case, additional checks are required and if the earth test is a separate issue, then the RCD test can be performed directly in the following way.
RCD test in a single-phase network without grounding
To a properly connected residual current device, wires from the switchboard come to the upper terminals, and to the protected devices they depart from the lower ones.
In order for the device to decide that a leak has occurred, it is necessary to touch the lower terminal with one control probe, from which the phase leaves the RCD, and with the other probe touch the upper zero terminal (to which zero comes from the switchboard). In this case, by analogy with checking with a battery, the current will flow through only one winding and the RCD should decide that there is a leak and open the contacts. If this does not happen, then the device is faulty.
Laboratory testing and on-site testing of circuit breakers
In the laboratory, you can accurately test the circuit breaker for three main characteristics:
- Rated operating current;
- The current at which the protection is triggered;
- Time of protective operation in case of overload (setting of thermal release) and short circuit (setting of electromagnetic release).
For obvious reasons, laboratory testing of a circuit breaker is done in exceptional cases and is certainly not suitable for testing a circuit breaker at purchase.
There is a simpler technology for checking machines, this is a test load of a circuit breaker. It is done, or rather, should be done, before installing the circuit breaker in the electrical panel. For local loading of circuit breakers, special loading devices are produced.
If you do the electrician with your own hands, then for a restful sleep, you can rent a loading device and check by loading all the automatic protection devices of your apartment or house (cottage) electrical panel.
But again, this type of check of the circuit breaker is not suitable for checking the machine at the time of purchase. What to do?
By the way, do not be paranoid and think that most circuit breakers are potentially faulty.The same applies to "smart" advice on the Internet, that the machines of such a company are "ga-no", but these are just class. All this is nonsense. Defective machines can be of any company.
IEK machines were installed in my house 10 years ago for free, there was such a program, during this time they worked 20-30 times, and I see no reason to change them.
Regulatory reference
GOST R 50345-2010: Circuit breakers for overcurrent protection for domestic and similar purposes. (Download directly in DOC format)
Checking the RCD for performance
To feel safe, you should regularly, at least once a month, check the protective device. You can do this yourself at home. All known verification methods are quite simple and affordable.
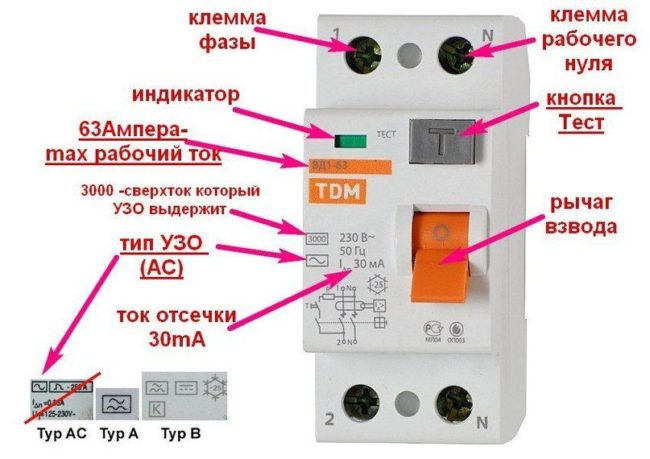
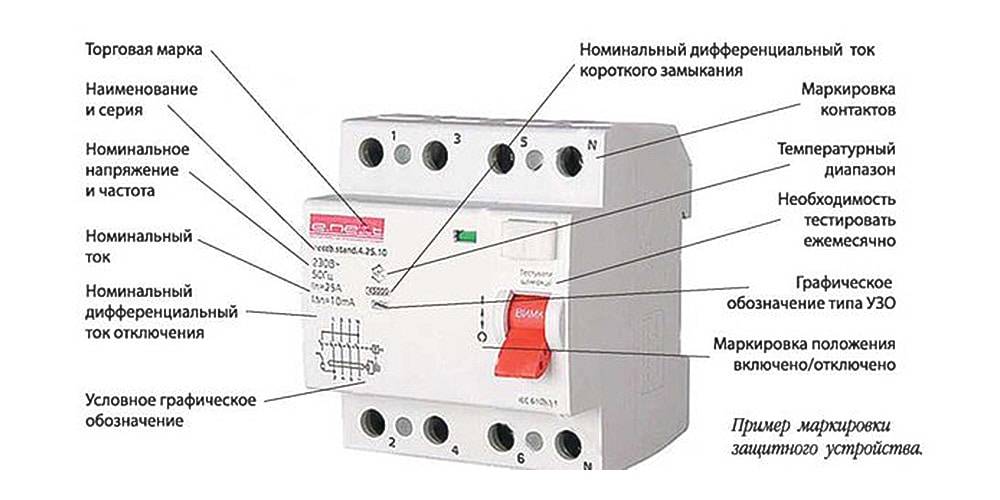
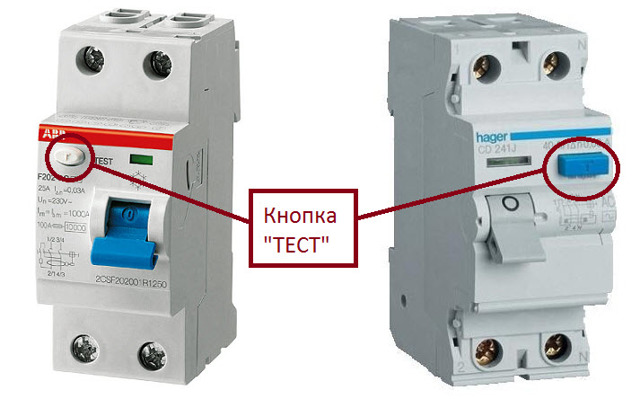
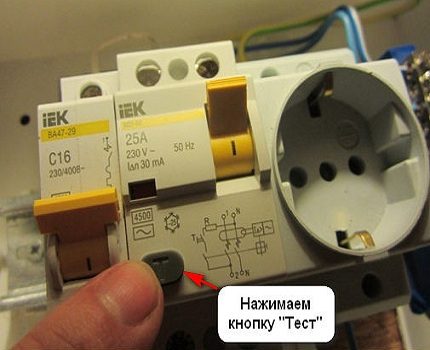
Testing with the TEST button
The test button is located on the front panel of the device and is marked with the letter "T". When pressed, a leak is simulated and protective mechanisms are triggered. As a result, the device cuts off the power.
However, under certain conditions, the RCD may not work:
- Incorrect device connection. A thorough study of the instructions and reconnecting the device in accordance with all the rules will help correct the situation.
- The TEST button itself is faulty, that is, the device is working normally, but no leakage is simulated. In this case, even with the correct installation, the RCD will not respond to testing.
- Malfunctions in automation.
You can only validate the last two versions using alternative verification methods.
To make sure that the test mechanism is working reliably, you should repeat pressing the button 5-6 times. In this case, after each disconnection of the network, you must not forget to return the control key to its original position (“On” state).
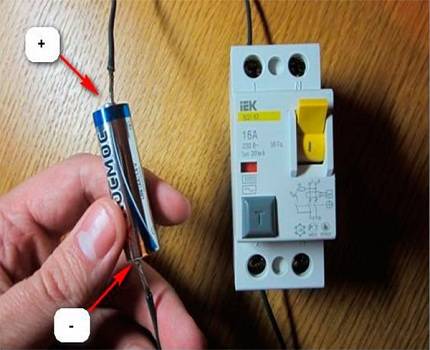
Battery test method
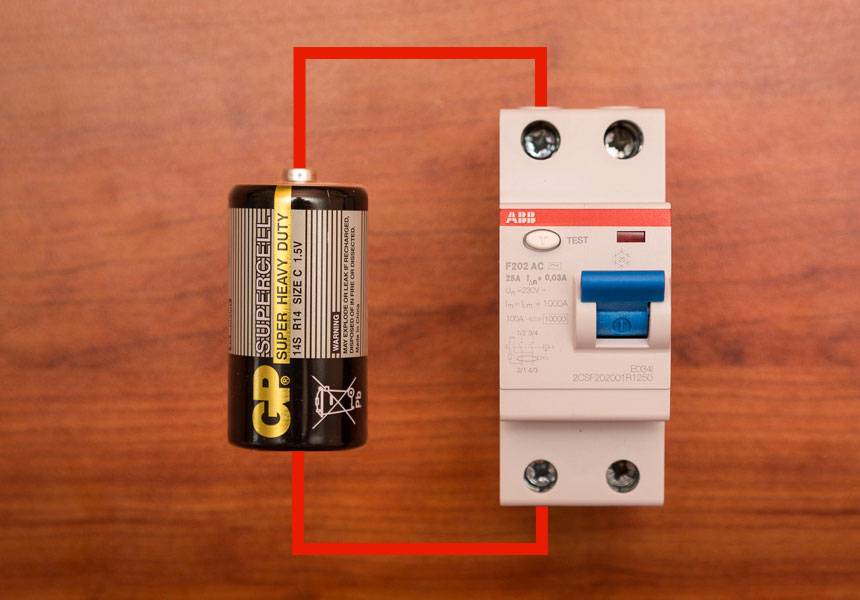
The second simple way, how you can check the RCD yourself at home for operability, is to use a finger-type battery familiar to everyone.
This test can only be carried out with a protection device rated from 10 to 30 mA. If the device is designed for 100-300 mA, the RCD will not trip.
Using this technique, do the following:
- Wires are connected to each pole of a 1.5 - 9 Volt battery.
- One wire is connected to the input of the phase, the other to its output.
As a result of these manipulations, a working RCD will turn off. The same should happen if a battery is connected to the zero input and output.
Before arranging such an audit, it is necessary to study the characteristics of the device. If the device is marked A, it can be checked with a battery with any polarity. When checking the AC protective device, the instrument will only respond in one case. Therefore, if no operation occurred during the test, the polarity of the contacts should be reversed.
How to test an RCD with an incandescent bulb
Another sure way to check the functionality of a protective device is with a light bulb.
For its implementation you will need:
- piece of electrical wire;
- incandescent lamp;
- cartridge;
- resistor;
- screwdrivers;
- insulating tape.
In addition to the listed items, a tool can be useful with which you can easily remove the insulation.
Incandescent lamps and resistors planned for testing must necessarily have suitable characteristics, because the RCD reacts to certain numbers.Most often, a protective device that is purchased for installation in a house or apartment is designed to respond with a leakage of 30 mA.
The required resistance is calculated by the formula: R \u003d U / I, where U is the voltage in the network, and I is the differential current for which the RCD is designed (in this case it is 30 mA). The result is: 230 / 0.03 = 7700 ohms.
A 10W incandescent lamp has a resistance of approximately 5350 ohms. To get the desired figure, it remains to add another 2350 ohms. It is with this value that a resistor is needed in this circuit.
After selecting the required elements, they assemble the circuit and, performing the following manipulations, check the performance of the RCD:
- One end of the wire is inserted into the socket phase.
- The second end is applied to the ground terminal in the same outlet.
During normal operation of the protective device, it is knocked out.
If there is no grounding in the house, the verification method changes slightly. On the input shield, namely in the place where the automation is located, insert the wire into the zero input terminal (marked N and located on top). Its other end is inserted into the phase output terminal (indicated by L and located at the bottom). If everything is fine with the RCD, it will work.
Tester test method
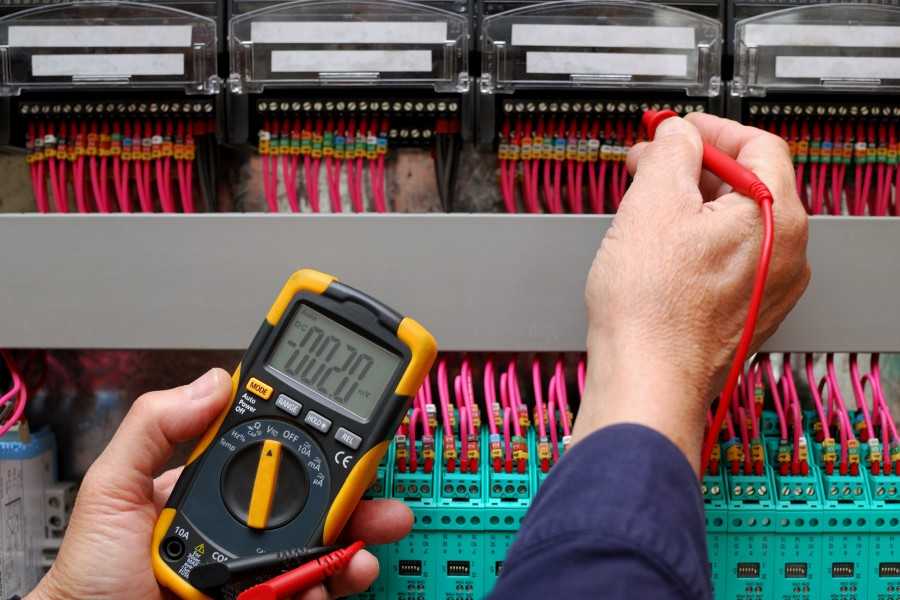
The method of checking the health of the protection device using special ammeter or multimeter devices is also used at home.
For its implementation you will need:
- light bulb (10 W);
- rheostat;
- resistor (2 kOhm);
- wires.
Instead of a rheostat, you can use a dimmer to check. It is endowed with a similar principle of operation.
The circuit is assembled in the following sequence: ammeter - light bulb - resistor - rheostat. The ammeter probe is connected to the zero input in the protective device, and the wire is connected from the rheostat to the phase output.
Next, slowly turn the rheostat regulator in the direction of increasing current leakage. When the protection device trips, the ammeter will record the leakage current.
When to check
First of all, it is recommended to check the RCD upon purchase in order to avoid purchasing a defective device. The pre-test procedure is as follows:
- check the device for external integrity (case damage is unacceptable);
- check the conformity of the marking on the housing with the specified requirements (for domestic use, only RCDs of type A or AC are used);
- check the travel and fixation of the lever switch, it must be firmly fixed in each of the two positions - on / off.
If you have an AA battery and a piece of electrical wire or a magnet with you, then you can use them to pre-check the RCD - the methods are described below. But it should be remembered that tests with a battery or a magnet are only valid for electromechanical VDTs.
Cheaper electronic devices need to be connected to a power source, so testing such RCDs is possible only after purchase - on a special stand or after direct installation into the mains.
In fact, for household electrical systems, it is enough to do a check once every six months. In production, the cycle of verification work is standardized, checks are carried out according to the schedule, the data is entered into the RCD test report and the check log.
Washing machine example
For example, let's analyze the cases of turning off the washing machine due to the operation of the difavtomat. The first step is to rule out a load fault.
To do this, instead of a typewriter, we will connect an iron or a refrigerator to the same outlet.If the machine does not respond, then you should look for the cause of the malfunction in the washing machine.
Check if the phase wire is shorting to the case. It is possible that the brushes of the electric motor are worn out, and current flows through the graphite dust to the housing.
Measure the insulation resistance of the motor windings. If it falls below 7-10 kOhm, then the leakage currents are such that they can cause the difavtomat to trip. There is no need to go further than this, repairing a washing machine is not an easy task, it is better to call a specialist.
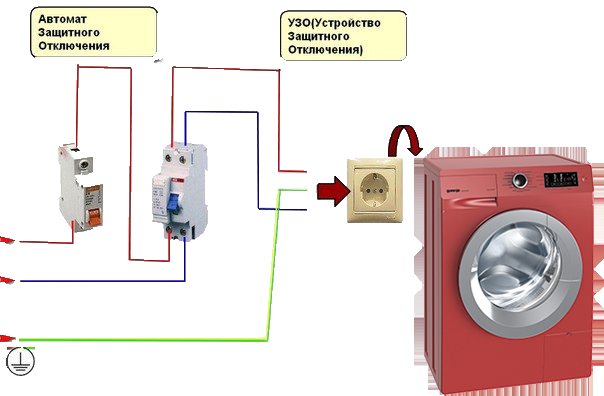
But the reason for turning off the difavtomat may not only be in the load. Putting the washing machine in place after the repair, the situation may repeat itself again.
The fact is that the difavtomat, like the RCD, reacts to the total leakage current in the line: in the wires from the protection device to the load and in the machine itself. Therefore, the total leakage current with the control load and the washing machine may turn out to be such that in the first case the difavtomat will not work, and in the second it will turn off.
Methods for Performing Verification
There are a lot of effective methods for monitoring the ability of RCDs to work correctly. They can also be used at home. Let's take a look at some of them as an example.
Control by "Test" button
This option is widely used due to high security. Testing in this way involves pressing the test button located on the instrument panel. Such actions do not require appropriate qualifications, and are used by the average consumer. The button has an inscription in the form of a large letter "T". It can simulate cases associated with current leakage, in other words, the passage of current around the device.
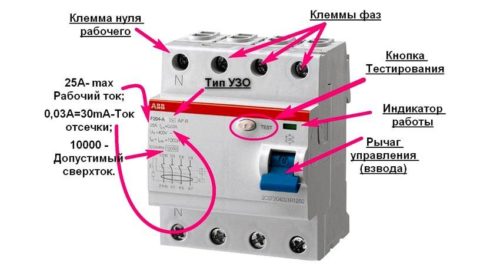
 RCD IEK for 25 A. The "Test" button here is gray and large in size
RCD IEK for 25 A. The "Test" button here is gray and large in size
Inside the RCD there is a resistor with a resistance value equal to the nominal leakage current. Its selection is carried out depending on the assumption that the passage of an electric current is not higher than the value that the differential current has, for the value of which the device itself is designed.
With the correct operation of the device and the appropriate connection, it should work and turn off the electricity. The presence of built-in functionality simulates a real current leakage and its reaction should be to instantly turn off.
control light
Using a similar method, it is possible to make sure that the device is reliable and works correctly. The RCD is triggered only in the presence of current leakage. Using improvised devices in the form of an ordinary light bulb and additional resistances, an imitation of a real electric current leakage is created.
To perform a check in this way, you need to prepare the following tools:
- wiring;
- incandescent bulb 10-15 W;
- a cartridge in which an electric lamp is placed;
- resistance in a certain amount;
- tools for the installation of electrical devices.
First you need to calculate the amount of current passing through the light bulb. For these purposes, there is a simple expression I=P/U. The P value reflects the power, and U characterizes the voltage in the mains. When carrying out simple arithmetic calculations, it becomes clear that for a 25-watt light bulb, the value associated with loading the differential leakage current will be 114 mA.
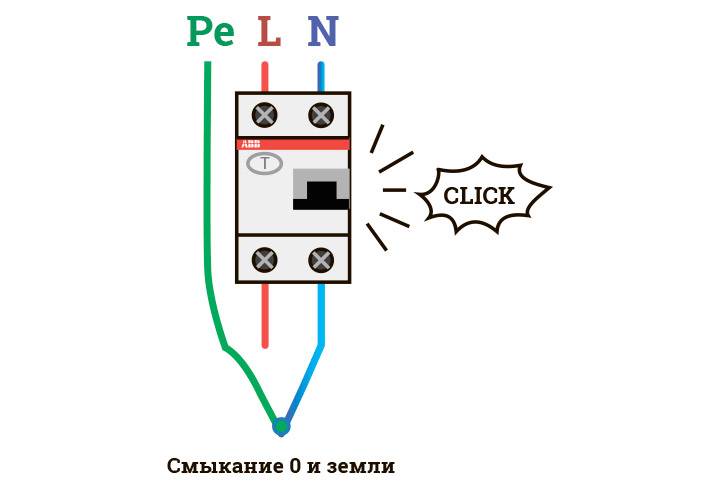
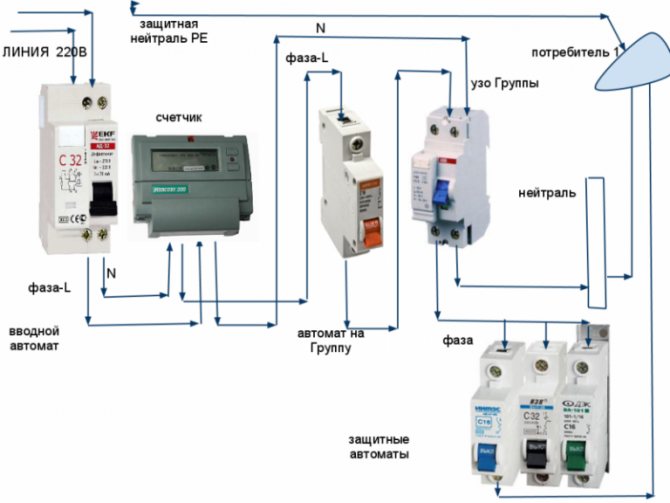
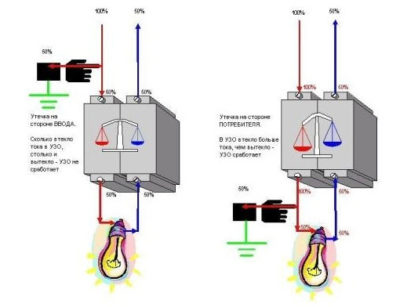
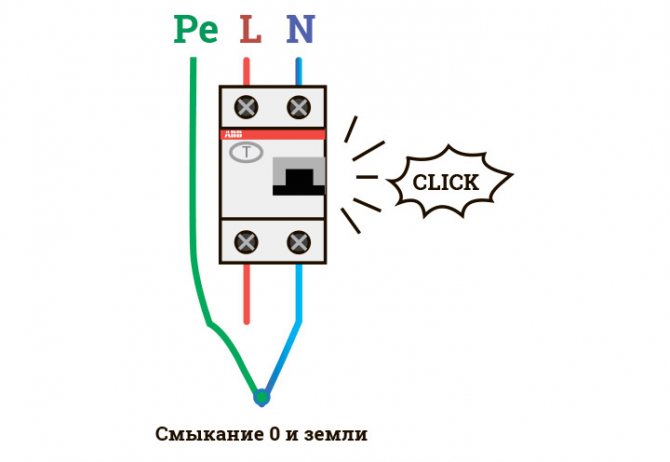
 Connection diagram of the protective device. The working conductor must not be connected to the protective conductor.
Connection diagram of the protective device. The working conductor must not be connected to the protective conductor.
This method of definition is inherently approximate. It should be noted that the calculated operating current load on the RCD is 30mA, and 114mA is loaded.
When using a 10 W light bulb, the resistance value will correspond to a value of 5350 ohms. The current strength will be 43mA. It's too big current strength for RCD designed for 30mA. For a normal test, it will have to be reduced, this can be done by adding additional resistance.
According to the passport characteristics, the operation of the device will occur with a current leakage of 30 mA. The operation will also occur at a lower value, which will be 15 - 25 mA.
As a visual aid, you can make such a device where a current of 30 mA flows through a 230 V circuit. If we use the well-known formula R \u003d U / I, then the resistance in the network will be 7700 Ohms (7.7 kOhm). It is known that the lamp itself has a certain resistance. It equals 5.35 kOhm. Not enough 2.35 kOhm.
 Checking the RCD using a test lamp and adding additional resistances
Checking the RCD using a test lamp and adding additional resistances
Socket test
Checking the RCD through such an outlet is simple and convenient.
The wire at one end is superimposed on the phase, and the other is placed on "zero". The device trips and the power is turned off.
In the absence of zero, it is impossible to test each outlet. But the state of the device can be monitored where the RCD is installed, in other words, in the electrical panel itself. One end of the wire is connected to zero, and the other to phase.
How to check the differential machine
Unfortunately, checking at difavtomatov, at home, such important characteristics as response time, overload characteristics, short circuit current will not work. Since to check these parameters it is necessary to have special instruments and equipment.
The difference between a difavtomat and an RCD
For the home, it is enough to check the differential machine for operation and compliance with the protection leakage current, at which the machine turns off and provides protection against electric shock. The differential machine differs from the RCD device only in the presence of a circuit breaker. That is, this is the same RCD plus an automatic machine in one case. Therefore, all checks for the suitability of a difavtomat are similar to testing an RCD.
Types of difavtomat checks
There are several ways to test protective devices for operability, these are:
- Checking with the "TEST" button located on the instrument case.
- A conventional battery from 1.5 V to 9 V.
- A resistor that simulates a violation of the insulation resistance of electrical wiring and household appliances.
- A simple permanent magnet.
- A special electronic device for checking the parameters of the differential machine and RCD used in industry.
Before purchasing a security device, you need to know what tasks it will perform. For firefighting purposes, difavtomat and RCD are selected with a leakage current of 300 mA. If protection against electric shock is required, a device with a leakage current of 30 mA is used. In damp and humid bathrooms or baths, protection with a leakage current of 10 mA is required.
Checking with the "TEST" button
This button is located on the front side of the differential machine. Before checking the performance of the device, it is connected to the network.When you press the "TEST" button, the protection turns off the network. The "TEST" button imitates the leakage current, as in case of violation of the integrity of the wire insulation.
Check button test
By pressing this button, the neutral wire of the input terminal and the phase wire at the output of the device are short-circuited through a resistor rated for a current of 30 mA (or other leakage current indicated on the machine). The protection device turns off and provides a protective function. This check can be done without load. The differential machine can be electromechanical or electric, the main thing is to connect it to the network correctly.
Battery test
Such devices are tested with a 1.5 V - 9 V battery with a leakage current rating of 10 - 30 mA. A device with a lower sensitivity of 100 - 300mA from a battery will not work. A protection device with characteristic A will operate from a battery connected to the terminals with either polarity.
And for devices with AC characteristic, the battery is connected with one polarity, if the device does not work, you need to change the polarity of the battery (minus to the output of the device, and plus to the input). Only electromechanical RCDs are tested in this way.
Checking the leakage current with a resistor
The leakage current of the differential machine is checked with a resistor connected at one end to the input of the neutral wire, and at the other to the output of the phase terminal. For RCDs with a leakage current of 10 mA, 30 mA, 100 mA and 300 mA, the resistor is calculated by the formula: R = U/I and 300mA - 733 ohms.
When checking for the trip current, one end is connected to the output terminal of the phase, and the other to the input terminal of the neutral wire. The RCD must be connected to the mains (no load required).With this connection of the resistor, protection should work. Sometimes the differential machine does not work. This is due to some variation in the value of the resistors.
Visually, the leakage current is checked by connecting a variable resistor (for a leakage current of 30 mA) 10 kΩ in series with a multimeter with an alternating current scale of 100 mA. It is desirable to take a multi-turn resistor, for a smooth change in resistance.
Connect a resistor with a multimeter, supply the network to the differential machine and smoothly rotate the resistor knob from the maximum, detect the current at which the protective device turns off. Next, measure the resistance of the variable resistor, it should be approximately for a leakage current of 30 mA - 7.3 kΩ. This measurement method is suitable for electromagnetic and electronic devices.
Testing permanent magnet protection
Only the electromechanical protection device can be checked with a magnet, the electronic device will not work.
This is due to the fact that when the magnet is brought to one of the sides of the RCD, a constant electromagnetic field acts on the differential transformer and causes a potential imbalance at the output of the machine, the protection is turned off. The electronic type of devices does not have such a differential transformer.