- How to choose the right RCD
- How to choose an RCD
- We put an RCD in the apartment: how to choose a device for power?
- Important parameters for RCD
- Product type
- Rated current
- Residual current
- Selectivity
- Purpose
- According to the principle of operation
- Electromechanical
- Electronic
- main parameters
- RCD selection options
- Trip type
- Selectivity
- Number of poles
- Rated protection current
- Rated residual breaking current
- Rated breaking time
- Operating temperature
- General rules for selection and installation
- Types of VDT according to the principle of operation
How to choose the right RCD
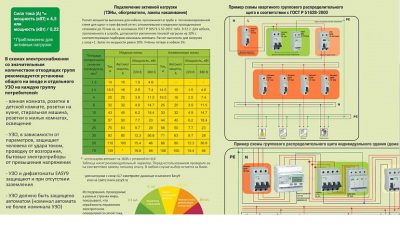
In order to choose the best option for a residual current device, you need to know its main parameters. Devices with different characteristics are used in specific conditions, which must be considered when choosing. The nature of leakage currents allows us to divide them into different types. This division depends on a smooth or sudden increase in current. RCDs with such characteristics are most widely used as the most suitable for the widest operating conditions.
Tripping technology allows you to divide the RCD into electromechanical and electronic. In the first case, high-precision mechanisms are triggered as a result of leakage currents.These are the most reliable and expensive devices that can work under any conditions. Electronic devices are cheaper, however, for the normal operation of electronics, the use of external power is required. Their effectiveness is significantly reduced when voltage drops occur. The operating speed of RCDs allows their use in multilevel protection systems. This allows you to disable all emergency sections individually.
There are other parameters that require knowledge of electrical engineering. Therefore, when choosing an RCD, it is best to seek help from qualified specialists. However, if the exact characteristics of the electrical network are known in advance, you can independently choose the most suitable protective device. Among them, the most important are the following:
- Voltage. The RCD can be designed for a single-phase network with a voltage of 220 V or a three-phase network for 380 V. The first option is usually used in apartments, and the second in private houses, summer cottages and cottages. If there are sections with one phase in the three-phase wiring, then protective devices designed for 220 volts are used for them.
- Number of poles. In single-phase networks, two-pole RCDs are used, designed for one phase and zero, and in three-phase networks, four-pole devices are used, to which three phases and zero are connected.
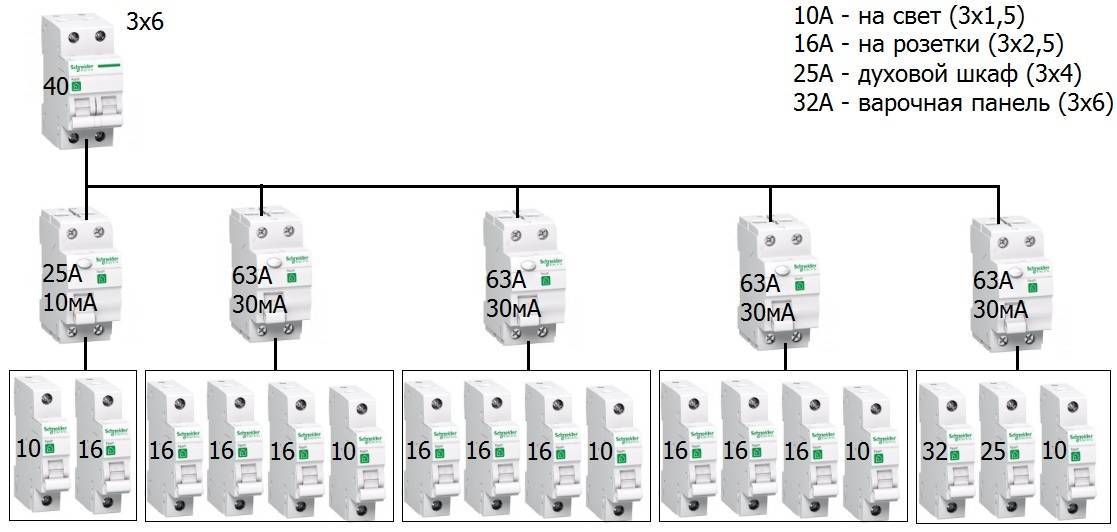
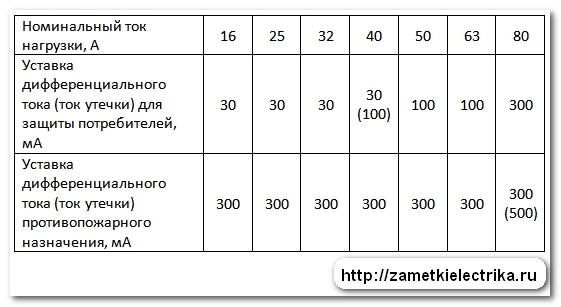
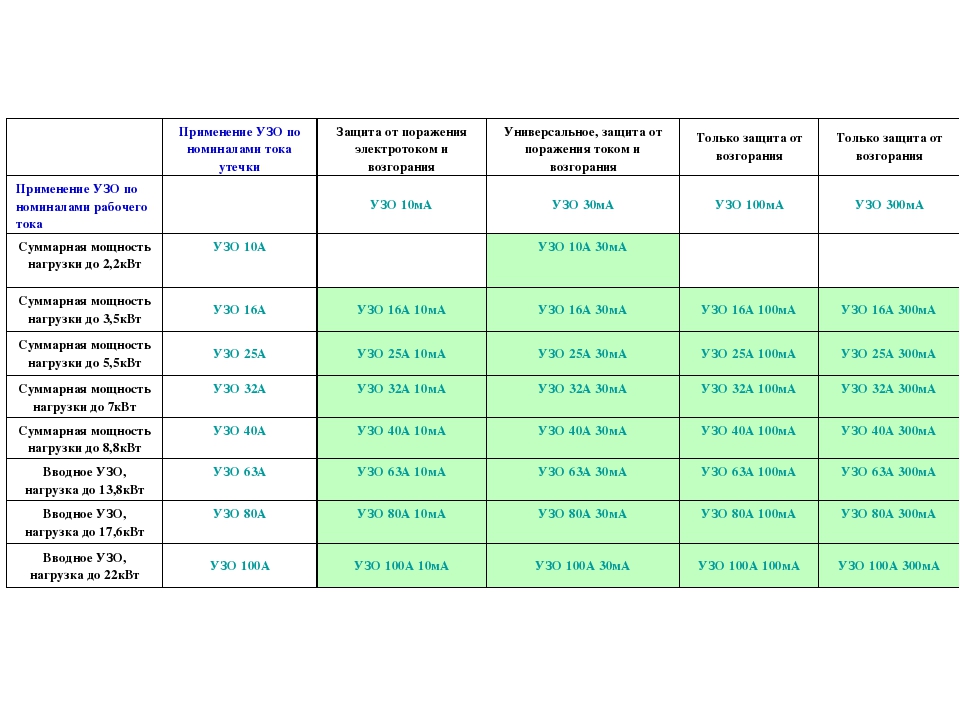
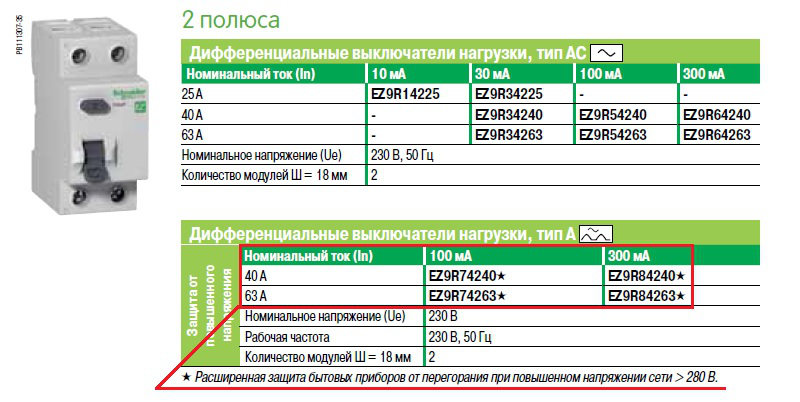
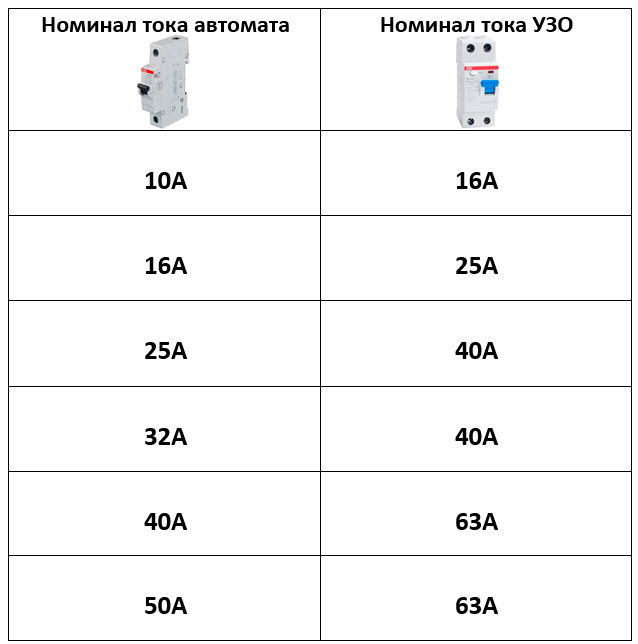
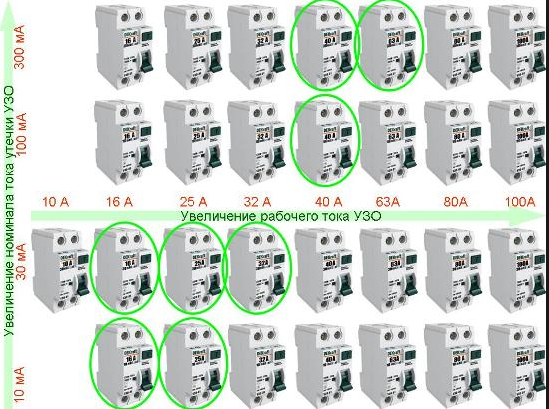
- Rated current. It is also the throughput current of the RCD, depending on the number and power of the connected electrical appliances and equipment. Therefore, this indicator for a general (introductory) protective device must be calculated for all installed consumers. For linear RCDs, the total power is calculated based on the number of devices on a particular line.RCD ratings set by manufacturers are 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80, 100 A.
- RCD leakage current. The value at which it turns off. It also comes in 10, 30, 100, 300, and 500mA ratings. For ordinary apartments, a 30 mA device is best suited. With a lower current rating, the device will constantly respond even to slight fluctuations in the network and turn off the power.
- Type of leakage current. The symbols AC, A, B, S and G are marked on the body of the device. For example, AC reacts only to alternating leakage current, and B reacts to direct and alternating currents. The rest of the marking also corresponds to certain parameters, including the time delay for turning off the device.
How to choose an RCD
Taking into account the above characteristics, knowing the value of your introductory circuit breaker, for a country house or apartment, you can select an RCD, operating only with these data, without delving into the complexity of electrical calculations. A suitable value for the protective device would be 25A, type A, a requirement often found on many household electrical appliances.
The In value of the RCD must also be higher by one value. According to the requirement of PUE 7. Also, the above paragraph of PUE requires that the rated differential trip current of the device exceed three times the total leakage current.
Suppose you want to calculate the RCD to ensure reliable fire safety of a large wooden three-story house used as a guest yard in a ski resort.

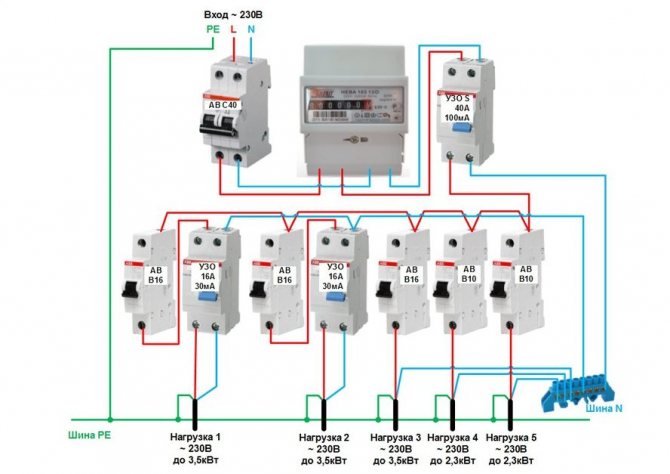
We assume that the calculations for individual user groups have already been made, it is required to calculate the total input protection device type S.You can find out the current consumption for each device from the passport of the electrical appliance, using a calculator to make calculations.
Using a ruler, tape measure, measure the length of the entire cable under voltage, regardless of the load connected to it. We assume that the length of the wires in the amount of m.
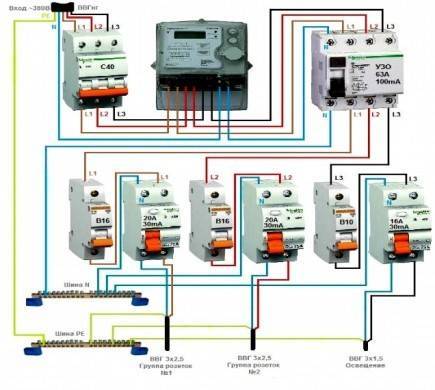
RCD residual current device - a switching device or a set of elements that, when the differential current reaches a predetermined value under certain operating conditions, should cause the contacts to open. There are a large number of different RCDs differing in their technical characteristics, purpose, functionality. In this article, we will look at the basic rules that should be followed when choosing an RCD. In the absence of data on the leakage currents of electrical receivers, it should be taken at the rate of 0.3 mA per 1A of the load current, and the network leakage current at the rate of 10 μA per 1 meter of the length of a different conductor.

k. How to choose an RCD Like any other device, RCDs, or as they are also called differential current switches, have different technical characteristics.
We put an RCD in the apartment: how to choose a device for power?
After that, you need to determine the value of the rated current of the RCD. To do this, you need to take the maximum current consumption and select the appropriate protective device. Thus, a disconnect device suitable for protecting a given electric stove should be rated at 25A 30mA or 32A 30mA. The differential machine for RCD protection must have the appropriate parameters - 25A for the first and A for the second case.
It should be said that the RCD and the machine must be selected correctly in order to their operating parameters allowed to turn off the power supply at the right time. In situations where an automat-RCD is installed to protect the wiring from fire, devices with a very high leakage current rating are taken - from mA or mA. Such a backlog prevents constant false shutdowns, but has a certain feature.
It turns out that fire protection is done correctly, but contradicts the requirements for protecting a person from electric shock.
To date, certain standards have been adopted on how to choose the right residual current device for an apartment or a private house. To begin with, it must be said that today for both cases it is recommended to install only AC type residual current devices that support the operation of electrical appliances with pulsating direct current.
Important parameters for RCD
If the RCD is chosen incorrectly during use, some problems may arise: too frequent operation, or vice versa, in the event of a dangerous situation, a blackout of the electrical network will not occur.
In the end, the device may simply not work and not perform its protective functions. To avoid such situations, you need to study the main characteristics that are inherent in these devices.
So, when choosing an RCD, the following must be considered:
- the number of poles - two-pole and four-pole;
- at what current does the power supply system turn off;
- what is the maximum current the device can withstand;
- design feature of the protective device - electronic or electromechanical;
- in which network can an RCD be used - 220V or 380V.
It is also recommended to pay attention to: the magnitude of the load current; indicator of the conditional current at which a short circuit occurs; operating principle
Product type
Each type of product has its own purpose:
- AC - used in single-phase and three-phase electrical circuits to protect household appliances, with the exception of appliances with pulsating current;
- A - this type provides protection for electrical appliances with pulsating current, for example, a washing machine;
- B - used for industrial and industrial purposes, the use of the device at home will be inappropriate;
- S - this type is installed to protect all electrical wiring completely, the rated leakage current is 100 mA;
- G - connects to each device separately for the purpose of monitoring and preventing fire, while having a shorter turn-off time.
Rated current
How to choose an RCD depending on the current? Rated current is the main indicator when choosing. It shows what current the RCD is intended for. In order to correctly determine this parameter, it is necessary to understand why the equipment will be installed.
 Three-pole machine
Three-pole machine
If its purpose is to protect electrical household appliances, such as a washing machine or electric titanium, then the value of such a rated current may correspond to an indicator not exceeding 16A. In order to protect the entire electrical wiring of the home, it is necessary to install a device with a current value of 32A.
In addition, when choosing, it is required to calculate the load of all electrical appliances located in the apartment, based on this, select the required value of the rated current.It will not be difficult to do this, since this indicator is indicated on each electrical equipment.
Residual current
The protection of the consumer from electric shock is able to provide installations from 6 - 100 mA
In this case, it is necessary to pay attention to the fact that a person can be struck by a current leakage of more than 30 mA. For this reason, in children's rooms and in showers, it is recommended to choose a 10 mA model, and for the protection of lighting fixtures and sockets, 30 mA
In addition, each household appliance has its own leakage current, which is specified in the device data sheet. Therefore, in order to exclude false positives, it is necessary to take into account the total current of natural leakages, which should not exceed the nominal value of the RCD by more than 30%.
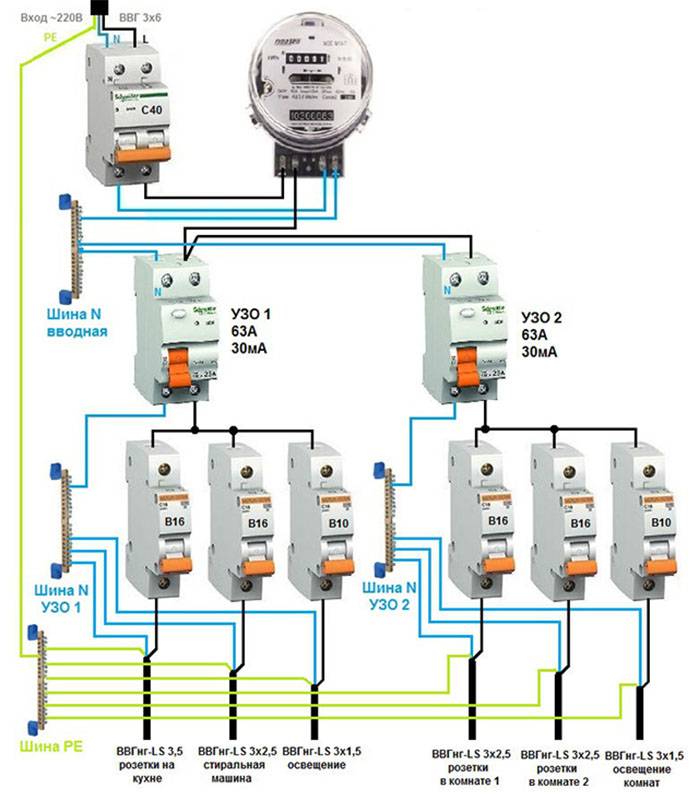
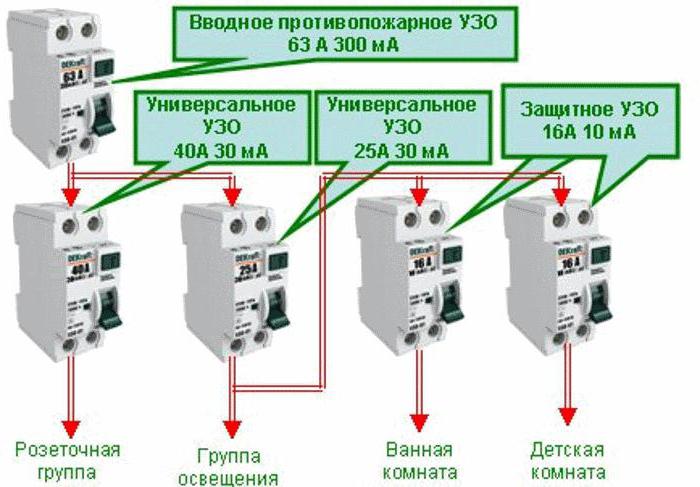
Selectivity
The meaning of this word is that in the event of a current leakage, the device that is closest to the damaged area will work. This is the case if the given electric circuit is serial. This property simplifies troubleshooting, troubleshooting, and also promotes the operation of undamaged sections of the circuit.
 The machine is connected
The machine is connected
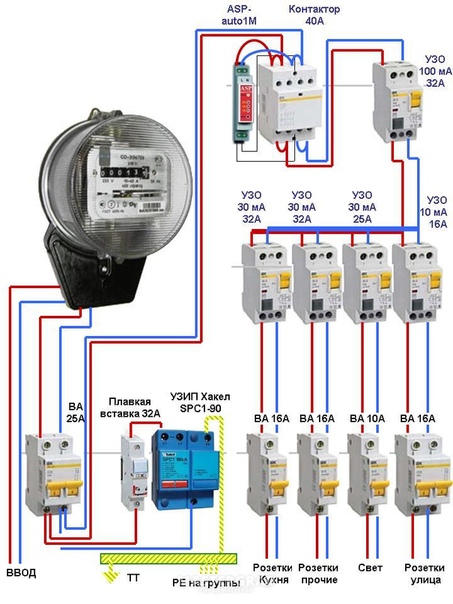
The first requirement is implemented by placing a protective device closer to the power source, the operating time of which should be three times longer than the RCD located near the consumed electrical appliance.
The second condition refers to the rated current. So, an RCD located near the power source should have a differentiated current, also three times higher than the current of the protective device, near which the electrical appliance is located.
Purpose
The RCD compares the input and output currents of the circuit being served. When a difference is detected, indicating that the electron flow has gone to foreign objects, the device opens the contacts.
Current leakage occurs in one of the following cases:

- the user received an electric shock;
- a phase short circuit occurred on the grounded case of the device: an accident that also threatens the user with electrical injury;
- there is contact between live parts and grounded metal objects, such as a building structure, which is fraught with a fire.
Thus, in the event of an unauthorized loss of current, it is extremely important to quickly de-energize the circuit.
It must be understood that the RCD does not protect the circuit from overloads and short circuit currents. This function is performed by circuit breakers. There are two-in-one devices that incorporate an RCD and a circuit breaker. In everyday life they are called difavtomatami.
According to the principle of operation
Comparison of currents is carried out in the same way. It is connected to the phase and neutral by the coil and, if the currents are equal, the magnetic fields created by the coils cancel each other out. If the currents are different, there will be a residual magnetic field and it will induce an EMF in the third coil.
Electromechanical
 The EMF induced in the third coil causes the electromagnetic relay opening contacts. This is the most reliable option and therefore the most preferred.
The EMF induced in the third coil causes the electromagnetic relay opening contacts. This is the most reliable option and therefore the most preferred.
Its disadvantages:
- high price;
- large dimensions.
They prompted Chinese and other Asian manufacturers to develop an alternative - electronic RCD.
Electronic
In electronic RCDs, the EMF in the 3rd coil is amplified by the electronic circuit before it enters the relay. This approach made it possible to reduce the size of the elements and reduce the cost of the device.But there was also a significant drawback: the amplification circuit needs power, and if it disappears due to a zero break, the device becomes inoperable.
 In this case, all current-carrying parts remain energized, so that the possibility of electric shock exists.
In this case, all current-carrying parts remain energized, so that the possibility of electric shock exists.
The latest models of electronic RCDs are supplemented with an emergency electromagnetic relay that de-energizes the circuit in the absence of power to the amplifier circuit
But experts advise using such RCDs with caution.
There are cases when electronic RCDs as part of difavtomatov refused to work after the circuit breaker tripped for a short circuit.
In some models of electronic RCDs with a shutdown function, in the absence of power to the amplifier, the following are provided:
- time delay: the device does not turn off during short-term power failures;
- automatic restart: after the restoration of the integrity of the neutral wire, the device turns on automatically.
There are three ways:
- according to the diagram shown on the box. On the electromechanical, a differential transformer is drawn, there is no supply voltage. The electronic symbol shows the amplifier board with power connected to it. This method is suitable for a radio amateur who understands electrical circuits;
- the connection of one of the differential transformer coils to the battery is carried out with two wires, the RCD is first turned on. The electromechanical apparatus will work during the experiment, the electronic one will not;
- the effect of a permanent magnet on the device. Before that, it is also included. The electromechanical option will turn off, the electronic one will not.The reliability of this method is not 100%: if the magnet is weak or incorrectly located, then the electromechanical device will not work either.
Externally, electromechanical and electronic devices do not differ, and therefore a potential buyer should be able to recognize them.
main parameters
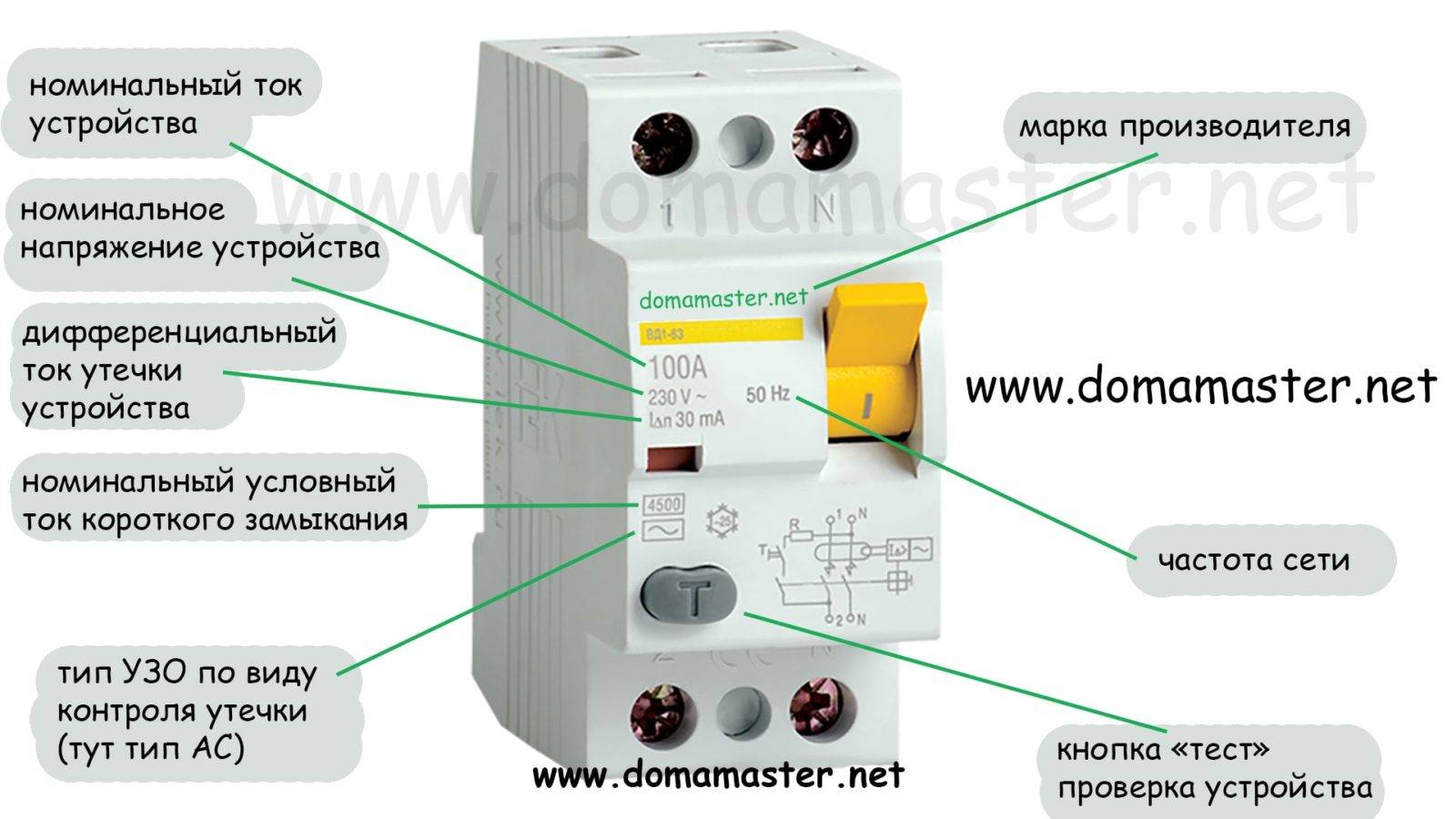
After the trademark on the case, the main ratings and operating characteristics of the RCD are indicated.
Model name and series
Please note that here you will not always see the letters RCD, some manufacturers designate this device as a VDT (residual current switch).
The value of the rated voltage and frequency. In the Russian power system, the operating frequency is 50 Hz
As for the voltage, for a single-phase network in an apartment it is 220-230 V. For a private house, a three-phase network is sometimes needed and the operating voltage will be 380 V.
Characteristics of the RCD on the video:
- The rated operating current is the maximum value that the RCD can switch.
- Rated residual breaking current. This is the value at which the device operates.
- Also, the temperature limits for the operation of the RCD are indicated here (minimum - 25 degrees, maximum + 40).

- Another current value is the rated conditional short-circuit current. This is the maximum short circuit current that the device can withstand and not turn off, but provided that a suitable machine is installed in series with it.
- Rated operating time. This is the time interval from the moment when a current leakage suddenly occurred and until it must be extinguished by all poles of the RCD. The maximum allowable value is 0.03 s.
- Be sure to draw an RCD diagram on the case.
RCD selection options
Trip type
RCDs installed in apartments have two types of tripping: A and AC.
AC type devices respond to an alternating sinusoidal leakage current that appears suddenly or gradually increases.
Type A devices respond to alternating sinusoidal and direct pulsating leakage currents that occur suddenly or gradually increase (recommended for installation on lines serving household electrical appliances where rectifiers and switching power supplies are installed: computers, televisions and other equipment equipped with electronics).
Selectivity
A selective RCD (S - with a longer exposure, G - with a shorter exposure) is installed at the input in front of other devices serving different groups in an apartment or cottage.
It fixes the leak, but it only works after a certain period of time (delay 0.2-0.5 seconds). Thanks to this, groups where there was no leakage are not de-energized.
Number of poles
Depending on the voltage in the network, the number of poles in the device used depends: for a 220 V network - two-pole, for a 380 V network - four-pole.
Rated protection current
The parameter determines how much current the device can pass during continuous operation. The indicator must be equal to or one step higher than that of the circuit breaker protecting the same section of the circuit.
Rated residual breaking current
This indicator determines the leakage current at which the circuit breaker will trip. An RCD with an indicator of 30mA is considered universal, it will provide protection against electric shock and fire, and can be used in lines with a sufficiently large load without false positives.
Switches with an indicator of less than 30mA are not always able to provide fire safety; under significant loads, they often work erroneously.
Rated breaking time
An indicator that determines the time interval between the moment a leak occurs and the moment the circuit breaker operates. Standards define the maximum allowable response time to 0.3 seconds, high-quality devices are triggered in 0.02-0.03 seconds.
Operating temperature
Most of the switches are designed for operation in the temperature range from -5 °C to + 40 °C, if necessary, you can purchase a device that can respond to frost down to -25 °C.
General rules for selection and installation
In addition to the RCD selection criteria, there are general useful recommendations when buying and installing this equipment.
They will help you not to make a mistake and immediately purchase a model suitable for a particular apartment or house.
Ignoring wiring rules and the absence of an RCD in the power supply circuit can lead to a fire throughout the house
The selection tips are as follows:
It is recommended to take RCDs, which, when triggered, turn off not only the phase, but also “zero”.
Within the circuit controlled by the apparatus, there should be no grounded electrical appliances.
The device must operate with short-term voltage drops of 50% of the nominal voltage, which can occur in the first moments of a short circuit.
RCD terminals must be made of a slightly oxidizable material and equipped with a reliable wire fixing system.
The advantage when buying should be given to devices with the function of protection against short circuit and overload.
RCDs of the second level can not be installed on safe groups of equipment, for example, on ceiling lights.
It is recommended to install devices with a threshold differential current of 10 mA for showers and jacuzzis.
Attention should be paid to the possibility of connecting aluminum wires to the device. Some devices do not work correctly with them .. You can install the right RCD yourself
This process is not much different from installing a socket or switch.
You can install the right RCD yourself. This process is not much different from installing a socket or switch.
It is important to carefully consider the wiring diagram and do as indicated on it.
Types of VDT according to the principle of operation
According to the principle of operation, RCDs are divided into electronic and electromechanical. Electronic RCDs are much cheaper than electromechanical RCDs. This is due to its lower reliability and low cost of production. The electronic RCD is “powered” by the network, and the operation of the electronic RCD depends on the parameters and quality of this very electrical network.
I will give such an example, we have burnt out zero in the floor shield, accordingly, the power of the electronic RCD will be lost and it will not work. And if at this time a phase short circuit occurs on the body of the device, and a person touches it, then the electronic RCD will not work, because. it simply simply does not work, there is no power to the electronics due to a zero break. Or if, in a simple way, electronics is electronics, and Chinese electronics is doubly “electronics”, which can fail at any moment. Therefore, an electromechanical RCD, which does not depend on the state of the network, is much more reliable than an electronic RCD.
The principle of operation is based on the comparison of the incoming and outgoing current of the RCD of a conventional differential current transformer, and if the current is not equal to or greater than the setting (rated RCD breaking current in mA), as already mentioned above, then the RCD is turned off.
According to these schemes, it is possible to determine whether an electronic RCD or an electromechanical one, the schemes are applied to the RCD housings.
Well-known manufacturers such as ABB, Schneider Electric, Hager or Legrand do not produce electronic RCDs, only electromechanical RCDs. I put electromechanical RCDs in my electrical panels.
To compare the electronic and electromechanical RCDs, I offer a photo with their “insides”. I would post an electronic RCD, of some well-known brand, not Chinese, but, as I wrote above, ABB, Schneider Electric, Legrand and other serious manufacturers do not produce electronic RCDs.