- What should be the seams?
- Slag removal
- Rules and features of welding
- Important Welding Tips
- Features of welding in the apartment
- Types of semi-automatic welding machines, their advantages and disadvantages
- Gas torch welding technology
- Preparing for work and soldering
- Flux application
- Final stage
- Methods for galvanizing steel
- Galvanic way
- Spraying
- hot dip galvanizing
- Semiautomatic welding methods
- What electrodes to cook galvanizing.
- Welding of galvanized pipes with electrodes
- What technologies are used
- Process Nuances
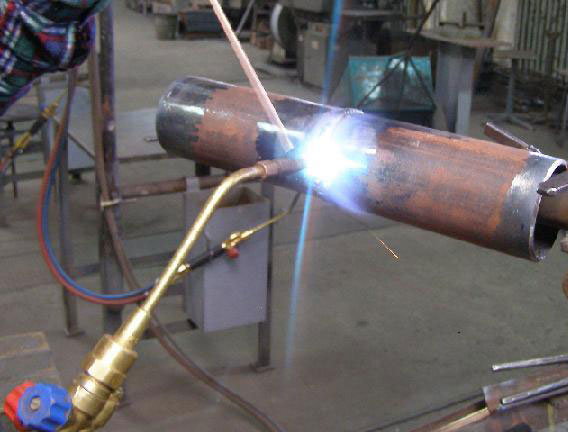
- Gas burner application
- Preparation and soldering
- Conclusion
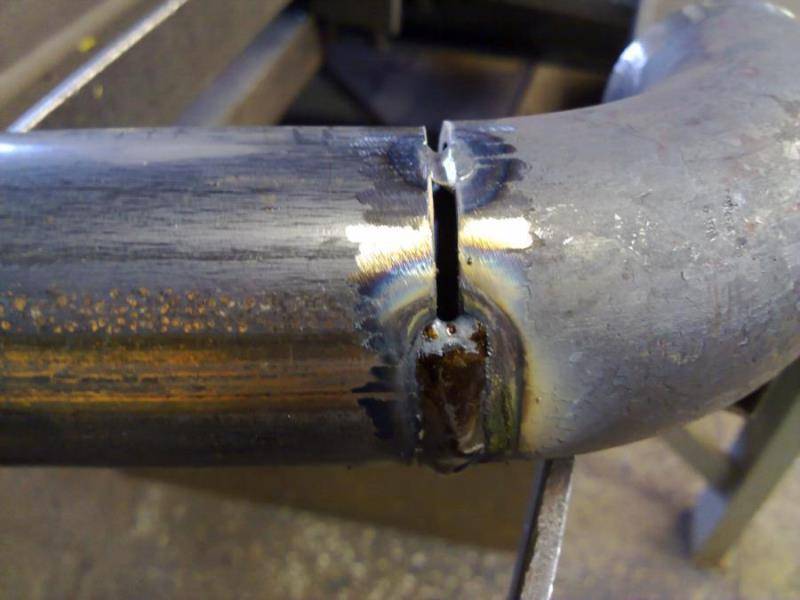
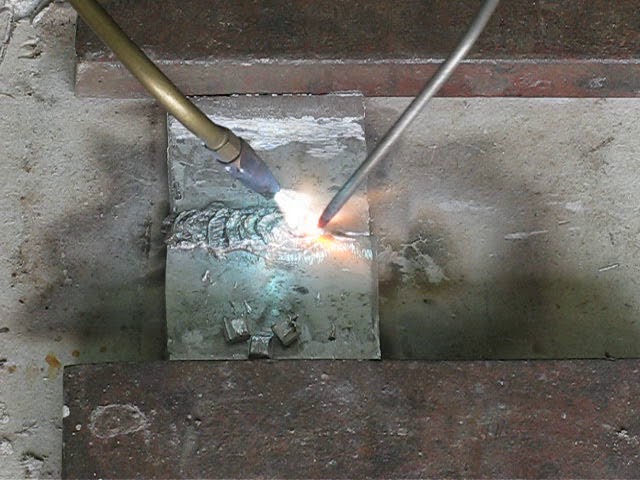
What should be the seams?
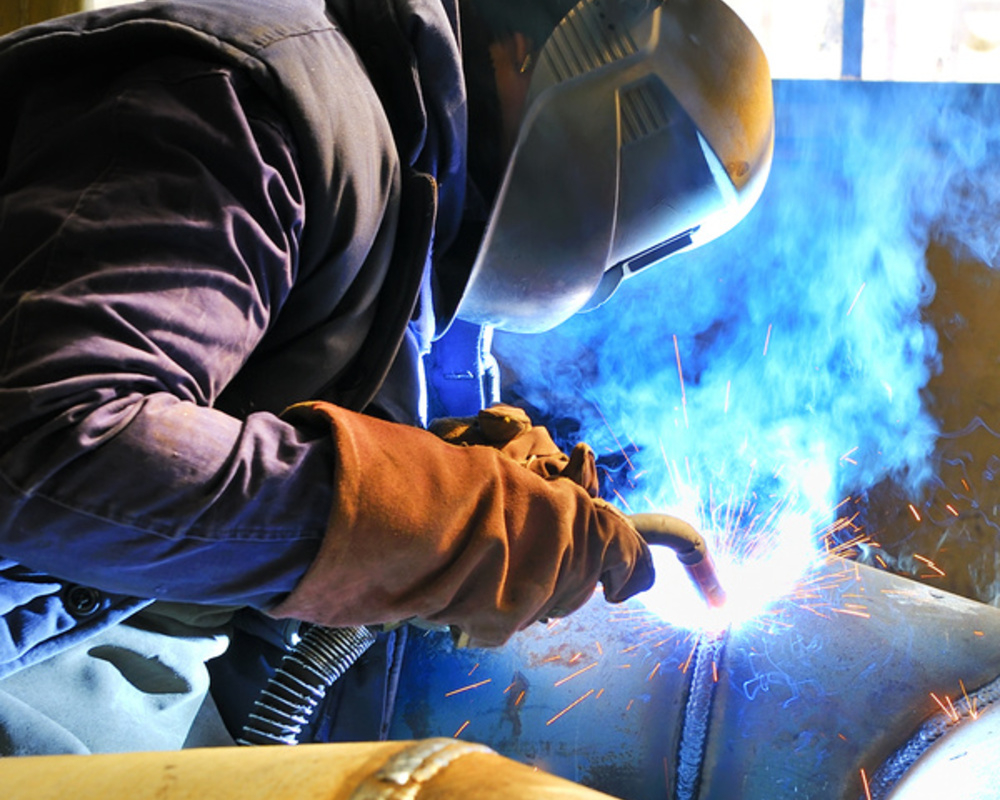
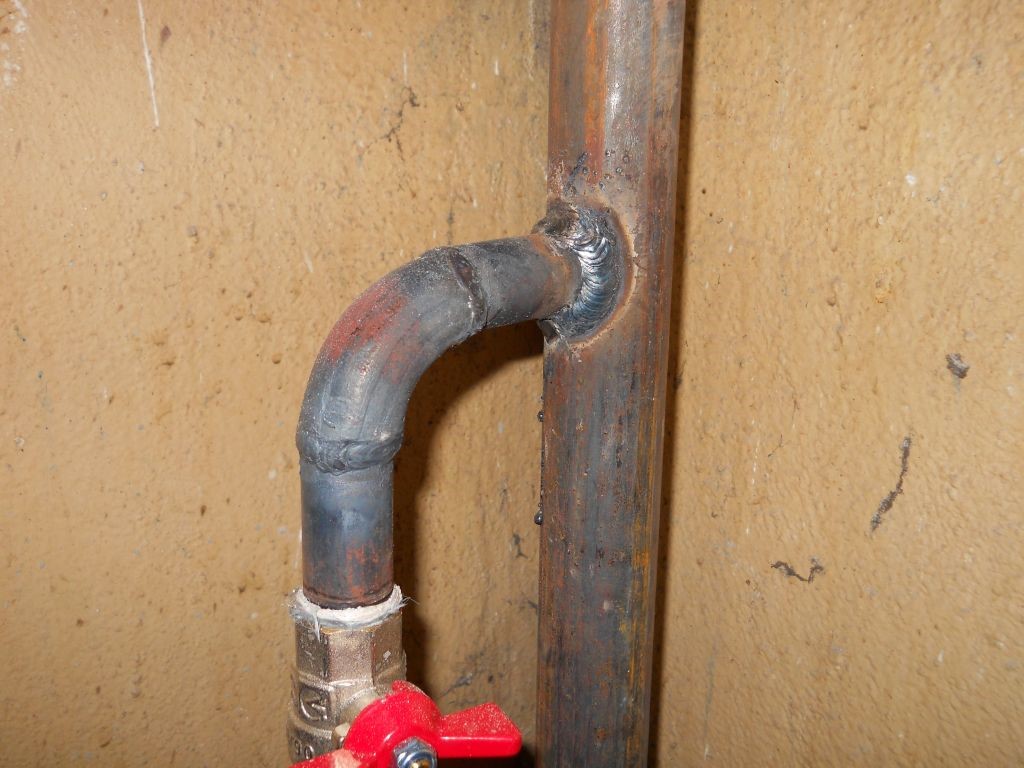
Electric welding of pipes.
Pipes are welded in compliance with the conditions and requirements, ease of use
It is important to foresee how the arc will move, in which direction to start work. You should immediately determine the direction and magnitude of the arc
If it is long, then the metal will oxidize during melting, begin to nitride, and drops will splatter on the working surface. The seam this results in no of such good quality, it becomes porous, it is completely unsuitable for plumbing.
When carrying out welding work, it must be taken into account that the movement of the arc can be carried out in three directions:
- Translational movement along the axis of the electrode.In this case, the welding arc is maintained in optimal condition, the quality of the seam is excellent. In the space between the electrode and the weld pool, exactly those conditions are observed that are necessary to ensure fast and high-quality work. During welding, the electrode must be constantly moved along its axis so that the distance remains the same and the length of the arc is constant.
- If the movement is longitudinal, then a thread-like bead will appear along the axis of the welding seam being formed. The thickness of the resulting seam will depend on the speed of the electrode. The roller has a width that is about 2-3 mm larger than the diameter of the electrode used. The bead itself is a weld, but it is narrow, not enough to create a strong connection when two pipe sections are connected. To make the seam stronger and wider, during movement it is necessary to move the electrode in such a way that it also moves horizontally, i.e. across the future seam.
- Lateral movement is also used during welding. It is required to perform reciprocating movements of an oscillatory type. The width of movements for each individual case is different, it is determined on an individual basis. Step width is influenced by various factors. This is the size, the position of the future seam, the characteristics of the materials that are being welded, the requirements that apply to the connection. Electric welding usually provides a seam width of 1.5-5 times the diameter of the electrode.
When choosing the direction of movement, it must be taken into account that the two pipes must have edges. They are completely melted, the seam must be strong and reliable so that it can withstand the planned loads.
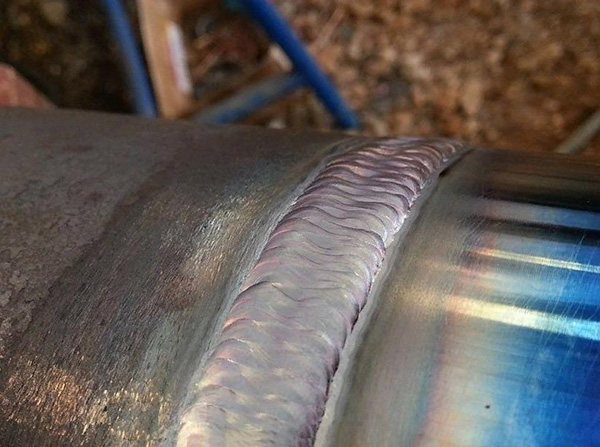
Slag removal
After the connection between the two pipes is completed, it is necessary to allow the seam to cool, then you can inspect its condition. For the most part, it needs to be cleaned from the resulting slag. It is formed during the welding process when the flux on the electrode burns out. Checking this is not so difficult, after cooling, you need to knock on the seam with a hammer. If there is slag, then it will fly off, under it a shiny and clean seam will open, remaining after electric welding. In order not to damage the connection and pipes, it is better to first practice in small areas having a length of 2-3 cm. If everything turns out cleanly and neatly, then you can start welding the metal pipeline.
Electric welding is not as difficult as it might seem, but it is important to follow all the steps and requirements correctly. You should choose only high-quality equipment and other tools
After that, the type of welding itself and the seam is selected. Do not forget about the use of protective equipment for hands, face and eyes.
Rules and features of welding
Before starting the process, you need to familiarize yourself with the following nuances of the process:
- Difficulty in choosing the temperature of exposure. Zinc can begin to melt at +400°C. If you slightly increase the temperature, the coating begins to burn through and evaporate. This prevents the formation of a strong seam. The connection is porous, covered with cracks.
- Arc instability. Only an experienced welder can choose the correct mode of operation of the device. Beginning craftsmen are advised to use coated electrodes, a gas protective environment or filler material. The latter option is used when it is necessary to form a high quality seam.
- Difficulty removing holes.Damaged areas of the sheet are pre-cleaned of dirt, traces of rust and oils. With a large diameter of the defect, metal inserts are used, which are fixed by the point method. For part thicknesses greater than 2 mm, mild steel plugs or baffles are used. Small holes are drilled to the desired size. Internal surfaces of defects should not be threaded.
Important Welding Tips
Any welding is considered a complex technological process in which a number of important requirements must be observed. Welding of galvanized steel is complicated by the fact that it is additionally necessary to work with a protective zinc coating. The main feature of this process is that galvanizing begins to melt already at a temperature of 420 degrees, and at 906 degrees it boils and evaporates.

All these processes have a negative impact on the quality of the welded joint, cracks, pores, and various defects begin to form in it. And to prevent this from happening, welding of galvanized steel must be carried out at other temperatures, and there must also be a special protected gas environment.
Galvanized steel welding wire and copper are commonly used for efficient welding. The most suitable are wires made of aluminum-bronze and copper-silicon alloy. If a filler wire is used, then the galvanization welding will be correct.
This method has a number of positive qualities:
- when carrying out the working process, there is no corrosion damage to the weld;
- there is a minimum degree of spatter;
- slight burnout of the zinc coating;
- low level of heat input;
- soldering of steel is further accompanied by simple processing;
- cathodic protection of the material is maintained.
During the welding process, zinc passes into a special weld pool, and this causes cracks, damage, pores in the joint. For this reason, before starting work, the zinc layer must be removed.
Removal is usually carried out with a gas burner, abrasive wheel, brushes. There are also chemical methods for cleaning zinc, which use alkalis. After treatment, the area is washed with water and dried well.
Features of welding in the apartment
For welding a low-pressure pipeline of small diameter, electric arc manual or semi-automatic welding is traditionally used. At the junction of sections of different diameters, adapters are needed; without them, the reliability of the gas pipeline is reduced.
Before welding gas pipes in the apartment, they check whether the gas is shut off. If dismantling of the site is required, use a cutter. When transferring the pipe, the joint is muffled by welding a nickel from metal. Main stages of work:
- the installation area is purged to remove residual natural gas;
- the cutter dismantles the replaced section;
- joint edges are cleaned, degreased;
- after welding, the line is filled;
- each joint is checked in test mode for tightness (a soap mixture is applied to the joint, if bubbles appear, there is a leak).
Work on the main wiring is carried out with the permission of the gas supply organization after the approval of the project.It is imperative to provide for a tie-in of shut-off valves - special taps that shut off the gas supply.
In apartment buildings, work is carried out under the control of the gas service; in private houses, owners can install pipes on their own, but adhering to the requirements of SNiP.
Butt connection of pipes by the forces of experienced welders. The fire safety of the building depends on the tightness of gas pipelines. Even with a small defect, leaks are possible, so the control of connections is carried out without fail.
Types of semi-automatic welding machines, their advantages and disadvantages
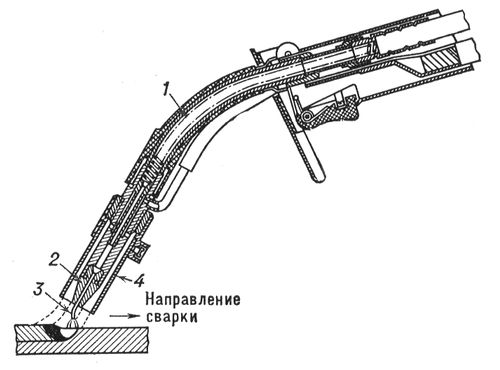
Torch for semi-automatic consumable electrode welding: 1 - mouthpiece; 2 - replaceable tip; 3 - electrode wire; 4 - nozzle.
Currently, a large number of semi-automatic welding machines are being produced. The semi-automatic welding machine performs welding of steel, aluminum and other metals. In factory workshops, parts are welded to the metal surface of machines using semi-automatic welding machines. For this, factory semi-automatic devices are equipped with a side nozzle. In semi-automatic machines, aluminum or steel wire can be used as an electrode. The welded seam of the devices is performed under the protection of a flux or in protective gases. There are designs in which the weld is protected with a flux-cored wire. Semi-automatic machines are divided into the following types:
- stationary;
- portable;
- mobile.
Advantages of cooking with the device:
- It is possible to weld metal having a small thickness, up to 0.5 mm.
- The appliance can even be used for cooking dirty or rusty surfaces.
- Welding has a low labor cost.
- It is possible to weld galvanized parts with copper alloy wire. This does not damage the zinc coating.
Disadvantages of semi-automatic welding:
- Metal may splatter during welding if shielding gas is not used.
- An open arc has intense radiation.

Semi-automatic is used for welding car parts.
The semiautomatic device is applied at cooking of details of cars. Most of all, semi-automatic welding is used when welding steel and aluminum parts.
In the process of work, a protective gas is used: carbon dioxide, argon or helium. Most often, steel is welded in argon or carbon dioxide.
The power source is direct reverse current. The semi-automatic welding machine includes a power source, a torch and a wire feeder.
The main mechanism of the semiautomatic device is the welding torch. It supplies welding wire and shielding gas to the work area. The feed mechanism is of three types:
- pulling;
- pushing;
- universal.
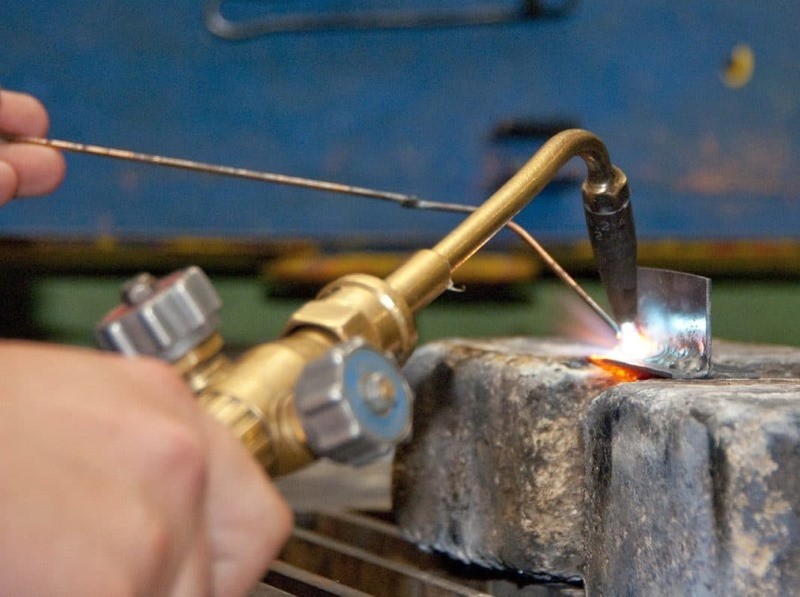
Gas torch welding technology
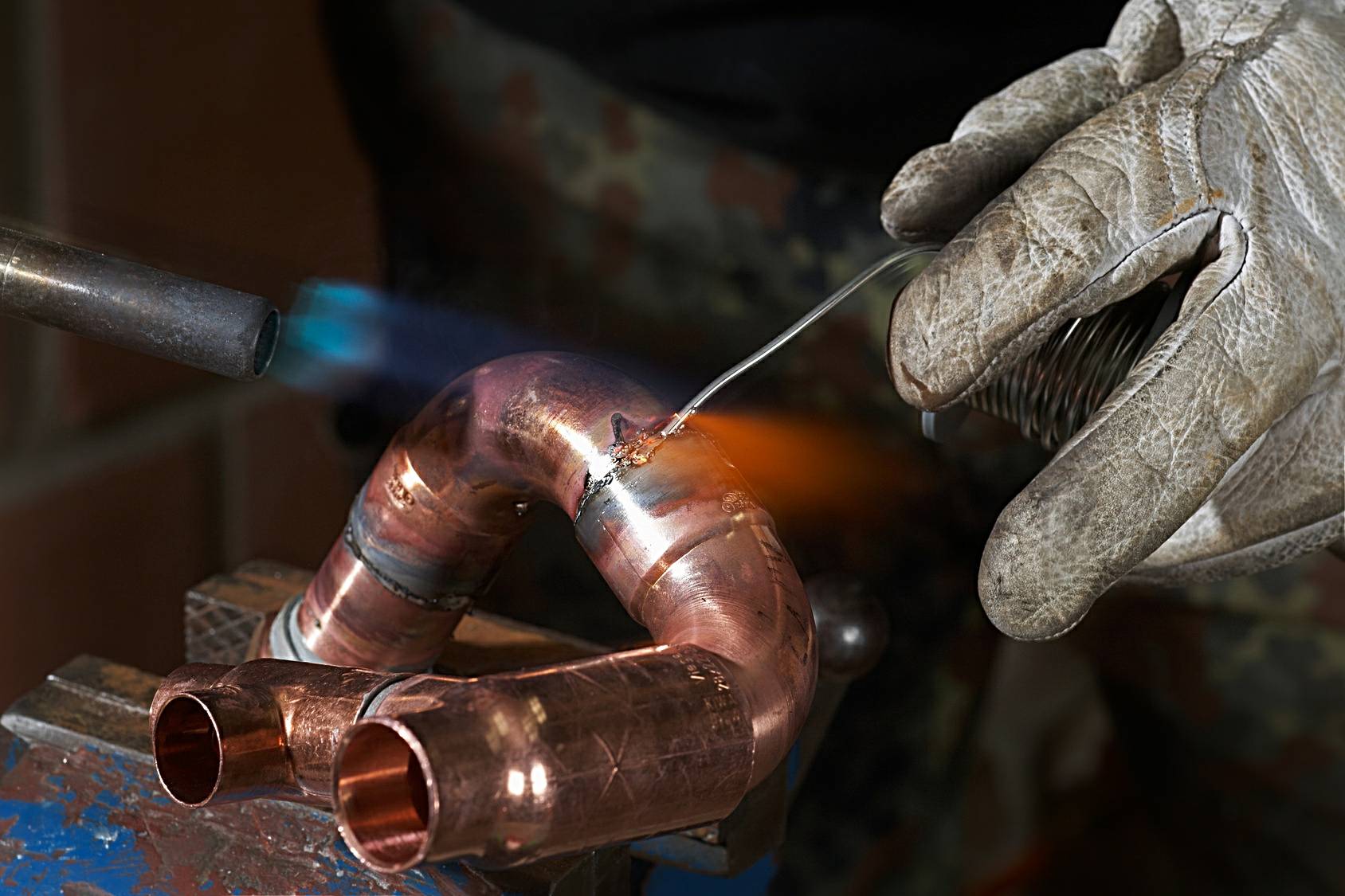
The method was invented by the Germans, also known as UTP. At present, soldering with a gas burner uses UTP-1 solder in combination with HLS-B flux. Solder is produced in the form of a rod based on copper and zinc, it is suitable for welding copper alloys, cast iron.
Preparing for work and soldering
Choose a burner 1-2 positions less than if you had to cook ordinary steel. There must be more oxygen in the acetylene flame so that the silicon, which is part of the solder, and oxygen can combine to form oxide. It is that important protective element that prevents evaporation of zinc.
Before cooking, the pieces of galvanized pipes are heated to a length of 5 cm away from the soldering area.During welding, the solder rod at an angle of 40 ° is brought into the joint gap, where it melts and the seam is filled with molten metal. It is better to use the “pull on” method, holding the bar not behind, but in front of the burner. The flame does not heat the segments themselves, but the solder.
Flux application
Preliminary places of welding are filled with gumboil brand HLS-B. The composition of the pasty consistency is applied in such a way that it captures each segment of the welded galvanized pipes for a length of at least 2 cm. The flux layer should be 2-3 times more abundant than when soldering steel pipes without a special coating.
Final stage
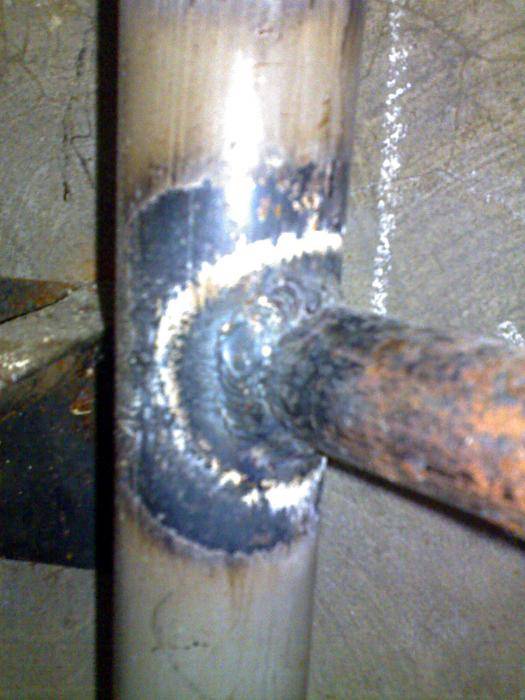
Zinc pipes with a wall thickness of not more than 4 mm are welded in one pass, thicker ones are soldered in 2-3 times. After cooling, flux will remain in the area of the seam, it is removed with water and a metal brush
When cleaning, it is important not to overdo it, as the zinc coating is easily damaged. Inside the pipe is washed with running tap water during the day
Methods for galvanizing steel
There are several ways to apply zinc to a steel surface. The most common are the following methods:
- galvanic method;
- spraying;
- hot galvanizing.
Galvanic way
The galvanic coating method consists in the process of deposition of a protective metal on the product using an electric current. This method is very common, since it can be used to obtain a good quality protective coating, easily change the thickness of the protective layer, and carefully use non-ferrous metals that are in short supply (zinc, for example). This is not the best way to increase the resistance to seizure of rubbing surfaces.But this method is simple, technologically advanced and makes it possible to carry out work with great accuracy.
Spraying
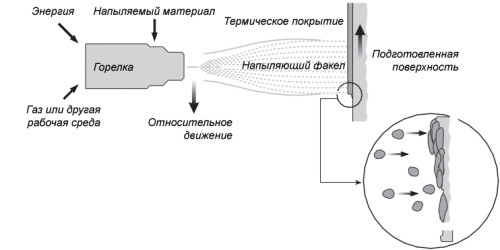
Scheme of zinc deposition.
The method consists in spraying molten metal from special electric arc or gas flame guns onto the surface to be coated. Zinc wire is placed in the spray gun, melted and sprayed onto the product. Zinc molten droplets on the surface solidify, becoming like small flakes that form a coating. To use this method of galvanizing, energy-consuming and large-sized equipment (baths, for example) is not required. Spraying can be used not only in the workshop, but also in the field directly during installation.
hot dip galvanizing
Scheme of the process of hot-dip galvanizing of steel.
Hot dip galvanizing is considered to be the largest method of applying zinc coating to steel. It is applied by short-term immersion in a bath of molten zinc (zinc temperature is about 500-520 degrees Celsius) previously pickled or mechanically cleaned, degreased ferrous metal fasteners. Before immersion in the zinc melt, the products undergo fluxing and preparatory heating. After removing the products from the melt, they are subjected to centrifugation in order to cool and remove excess zinc. This type of galvanization is very widespread. It is unique in that it creates a double anti-corrosion protection: the shell itself and the possibility of cathodic reduction of steel in case of damage to the zinc coating.
The thickness of the zinc layer applied to the steel surface can vary from 2 to 150 microns.
Semiautomatic welding methods
There are various welding methods. Butt welding is used when parts are not completely replaced. For example, they are welded end-to-end when installing a patch on the wing. With such welding, it is not necessary to remove the chamfers on the side of a thin sheet of metal. If the thickness of the metal is more than 2 mm, then the chamfers must be removed.
Before starting work, it is necessary to perform an exact fit of the parts. When fitting, there should be no gaps between the edges of the parts. If the fitting is not performed, this may lead to deformation of the parts and the metal surface to which they will be welded.
This method is used for welding body parts and the outer surface of the car. Butt welding is used in cases where high welding accuracy is required. It may be necessary to weld a new element in place of the damaged area. In this case, not the entire part is replaced, but only part of it. To do this, butt welding is carried out with a continuous seam. Then they clean up. With high-quality welding, after stripping, you will not have to putty.
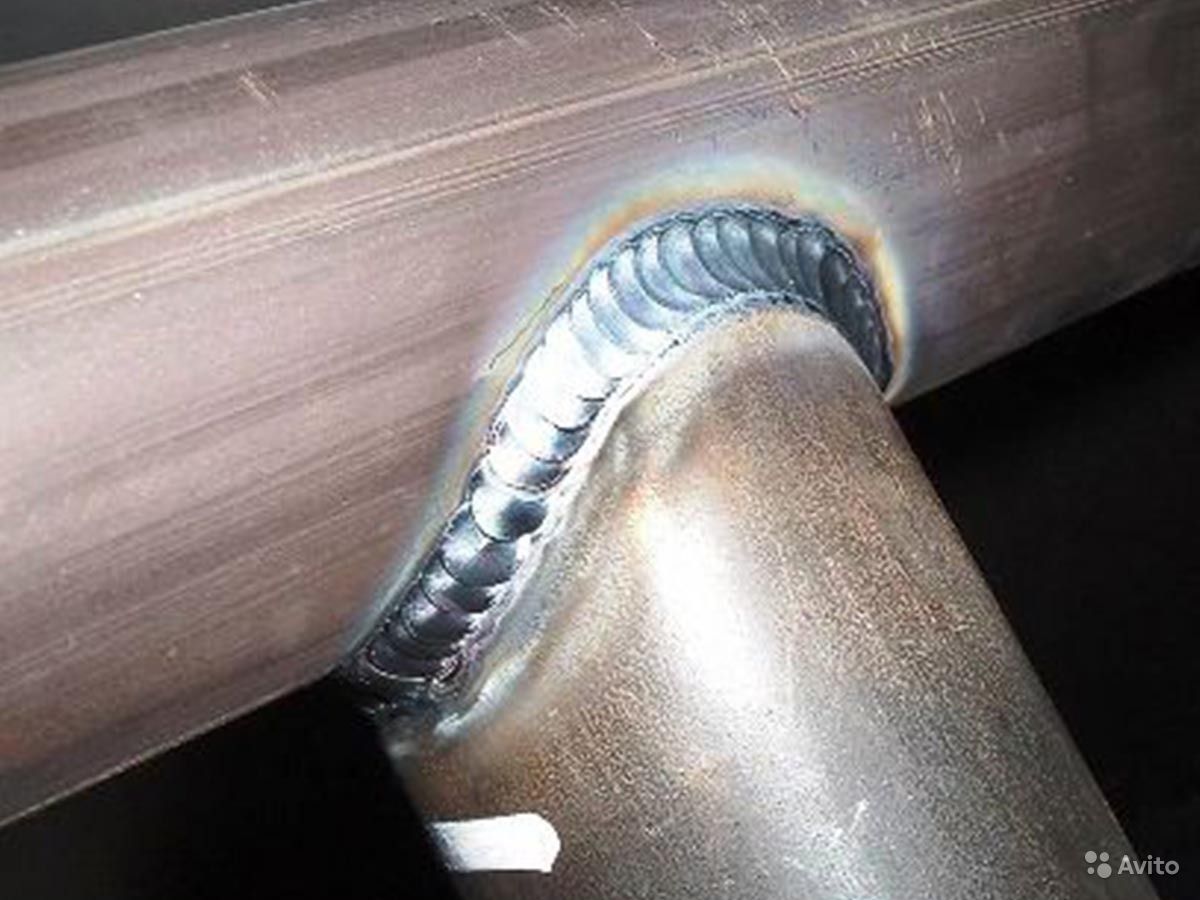
Butt welding scheme.
When welding butt, you need to do a lot of work on fitting parts. Therefore, such work should be carried out by a highly qualified welder. Butt welding of metal with a large thickness is much easier to perform. It does not require an exact fit. Welding is performed with a continuous spot seam.
Overlap welding is the most common. With such welding, one part of the metal is superimposed on another. Overlap welding is used when welding repair patches. This type of welding is used when replacing or repairing thresholds, spars, amplifiers.
Welding through a hole is a type of overlap welding. Used for car repairs.Also, using the electric rivet method, new parts can be welded, for example, wings, thresholds on the power elements of the body.
There are the following types of welds:
- point;
- solid;
- continuous intermittent.

A spot weld is a welding spot located at a certain distance from each other.
A spot weld is a welded spot that is located at a certain distance from each other. This distance varies from 1 mm to several cm.
A continuous seam consists of points that are next to each other and overlap one another. A continuous seam is used when butt welding metal having a different thickness. In the car body, such a seam is not used, since the body must be plastic in order to avoid deformations.
A continuous seam has high strength, but does not give elasticity to the joints. A continuous seam is used to create high strength welded joints, for example, when welding a water tank, which is installed in a bathhouse, or when making parts from a steel profile.
A continuous intermittent seam is an alternation of continuous sections of the seam with gaps. The distances of solid sections and gaps are selected by the welder depending on the goal. With such a seam, the power elements of the body, made of metal of great thickness, are welded.
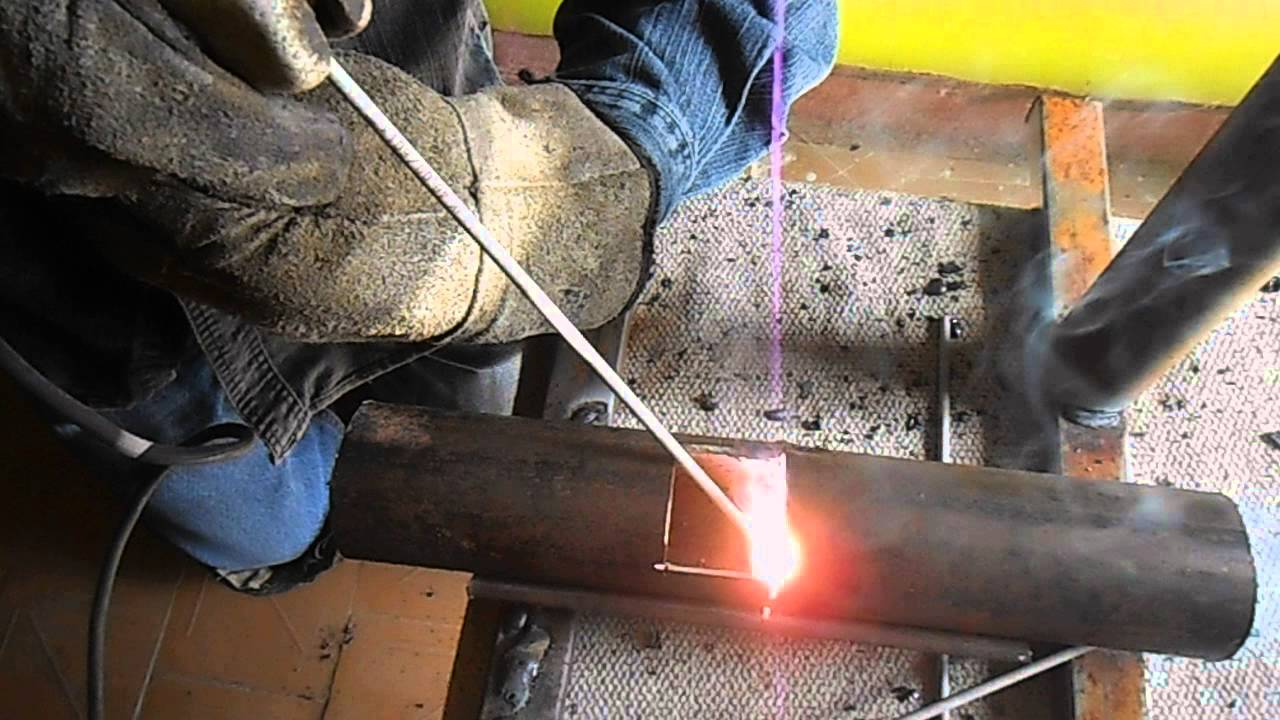
What electrodes to cook galvanizing.
Galvanizing is one of the most effective ways, protection of steel against corrosion. It is widely used in the manufacture of building structures, pipes, hydraulic structures. There are several ways to apply zinc to metal - this is a galvanic method, hot-dip galvanizing and spraying. The thickness of the sawn zinc layer varies from 3 to 150 microns.
Since the boiling point of zinc is 906 C, it tends to evaporate rapidly during welding. When evaporated, zinc releases harmful fumes, which in turn can cause an asthma attack. With intense evaporation at the time of welding, zinc enters the weld pool and because of this, pores and crystallization cracks are formed in the weld. In this regard, it is necessary to clean off the zinc layer from the place of welding. In some cases, it is not possible to remove the zinc layer, and then it is necessary to apply methods that make it possible to obtain a high-quality weld. When choosing a method of manual arc welding, the correct choice of electrode plays an important role. For welding on carbon steels, rutile-coated electrodes are best, and for welding on low-alloy steels, basic-coated electrodes should be preferred.
To prevent the occurrence of pores in welded butt and fillet welds of galvanized pipes, it is necessary to increase the current and reduce the welding speed. Zinc does not have a big effect on the quality of the seams only if the pipes are operated at a positive temperature. To connect galvanized pipes without damaging the zinc layer, use the soldering method. The resulting seam has very high characteristics, installation time and cost are significantly reduced, the seam has high tightness and corrosion resistance. To obtain seams by this method, it is necessary to use electrodes and solder coated with flux.Ordinary galvanized water pipes are perfectly welded using a conventional electrode.
Steel welding electrodes
Electrodes LEZ
Welding of galvanized pipes with electrodes

Steel pipes without a protective coating quickly corrode and fail. Therefore, a technology was developed for applying a protective zinc layer, which increases the service life of the material by almost ten times.
Galvanized pipes are used everywhere today, they are cheaper than stainless steel products and will not yield to them in terms of technical characteristics. But there is a negative point associated with the melting point of zinc and other properties of this metal.
What technologies are used
Taking into account all the above-mentioned disadvantages of welding galvanized pipes, two special technologies have been developed in which the welding process is carried out so that the galvanization does not collapse.
In the first technology, the welding zone is treated with a special material - a flux, which closes the joint and prevents the zinc from burning out, that is, from passing into a gaseous state.
It draws some of the thermal energy onto itself, and inside, under the flux, the zinc melts and becomes viscous-liquid. This metal envelops the connection of two galvanized pipes, evenly covering their ends. The protective layer is thus not broken.
The second technology uses special electrodes that can withstand high current. This method is based on the position of reducing the welding time, during which zinc does not have time to evaporate.
That is, the welding process is carried out so quickly and without reducing the quality of the connection that the protective coating does not have time to turn into a gas.
These technologies are used everywhere today when it comes to welding galvanized pipes. And not only those that are assembled into pipelines for gas or into load-bearing structures in construction.
In the water supply, under the action of running water, zinc dissolves and is partially removed to the outside. So it does not pose a danger to human health.
Process Nuances
As for the welding process itself, it is based on the thickness of the pipe wall. If this indicator does not exceed 3 mm, then the ends of the pipes are connected by an electrode without preliminary preparation, leaving a gap of 2-3 mm between them.
Of course, the cleanliness of surfaces (both external and internal) must be perfect, so they are cleaned of dirt and degreased with alcohol or a solvent.
If the thickness is more than 3 mm, then a chamfer is made at the ends of galvanized pipes with a blunting of 1.5-2 mm, depending on the wall thickness. The space between the chamfers during the welding process is filled with molten metal from the electrode rod.
The same applies to electrodes with a large diameter. Conversely, if the current is small or the diameter of the consumable is small, then lack of penetration will occur. And this is a decrease in the quality of the joint.
Much will also depend on the speed of movement of the electrode along the welding zone. Here, as in previous cases, slow movement is the likelihood of burning through the steel and galvanized layer.
High speed is still the same lack of penetration. The right welding speed comes with experience. And the more often you have to weld galvanized pipes, the better the seam is obtained.
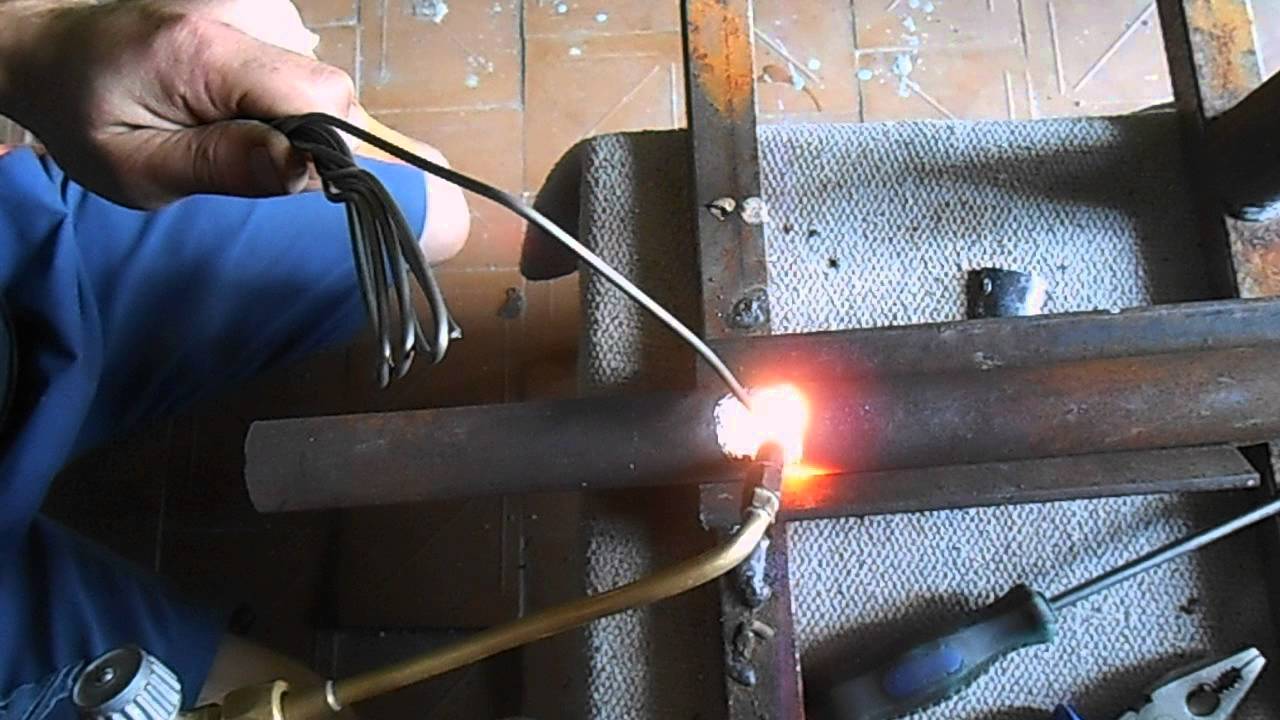
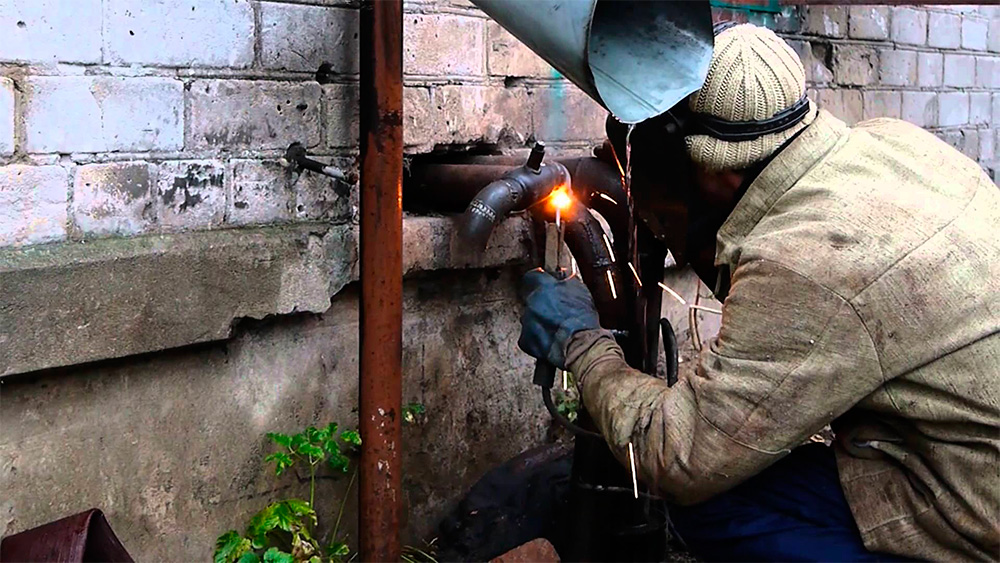
Gas burner application
You can connect two galvanized pipes using a gas burner. Increasingly, they use the technology labeled "UTP", which was once invented by the Germans.
To do this, they used HLS-B flux, which protects the zinc coating from fading. Today, rods of the UTP-1 brand are offered using this technology - this is a copper-zinc solder in the form of a rod 2 mm thick. With it, you can cook not only galvanized products, but also copper alloys, cast iron.
Preparation and soldering
Preparation for the process is identical to that used for welding galvanized pipes with electrodes. But there are certain features and norms that are established by GOSTs and SNiPs.
The heater number is selected 1-2 positions less than when welding ordinary steel pipes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, I emphasize that it is still possible to use welding in the case of galvanized pipes. The technologies make it possible to preserve the protective coating and not expose the pipeline at the welding points to the risk of rapid corrosion. It is enough to follow the rules and regulations that are enshrined in SNiP, use suitable electrodes, fluxes, solders.