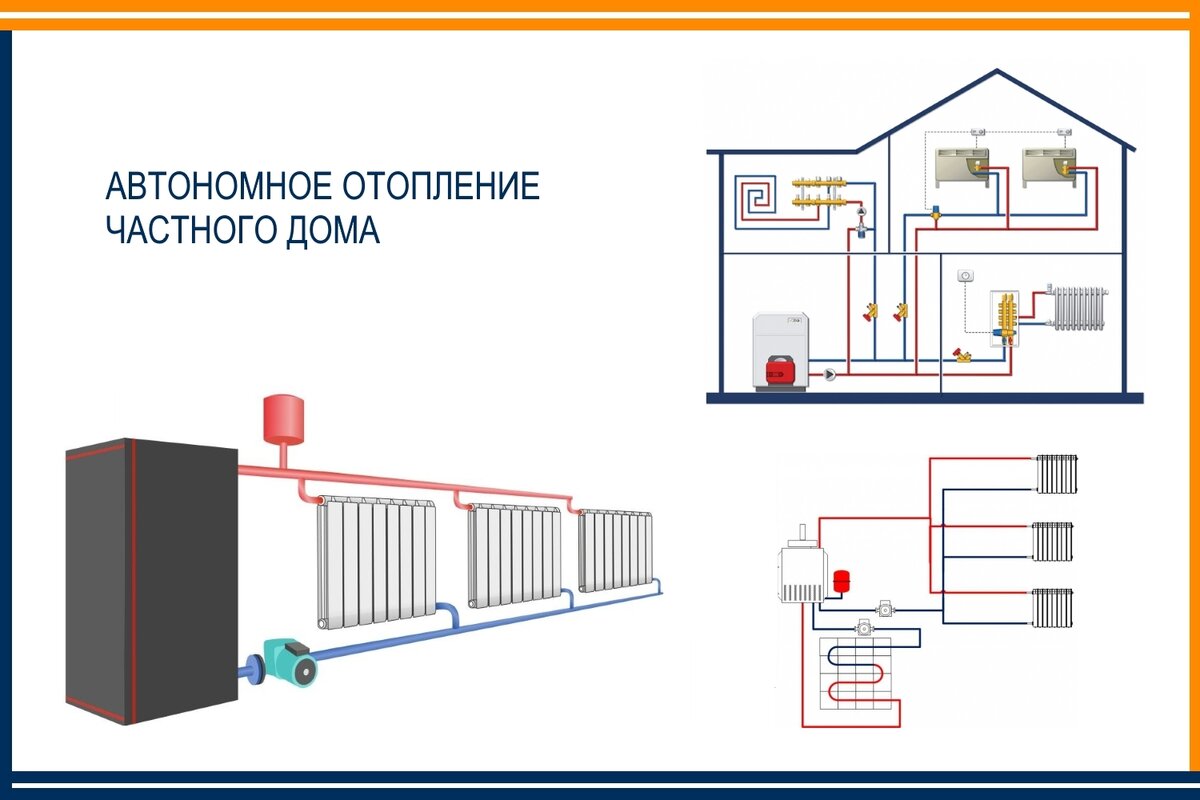
- Power connection
- Where to put the pump - for supply or return
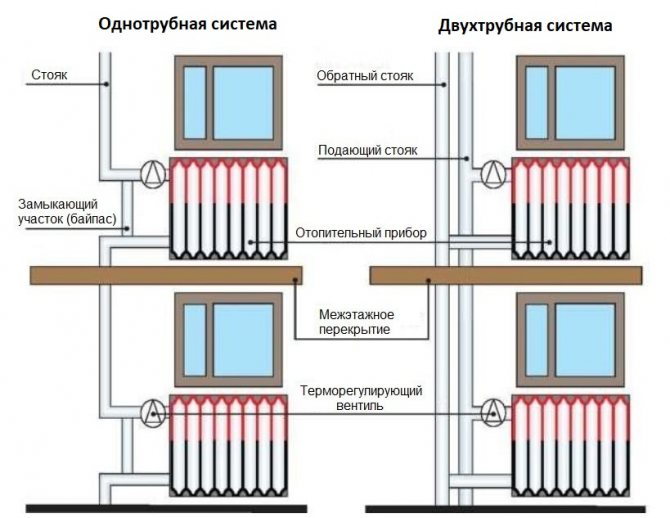
- One-pipe and two-pipe systems
- What is a circulation pump and why is it needed
- 2 Types of pumps and their features
- Price factor
- Video description
- Benefits of a separate pumping unit
- Conclusion
- Device device diagram
- Sequence of work and preparation for installation
- How to choose a water pump for home heating
- performance and pressure
- Rotor type
- Power consumption
- Control type
- Heat carrier temperature
- Other characteristics
- Where to put
- forced circulation
- natural circulation
- Mounting Features
Power connection
Circulation pumps operate from a 220 V network. The connection is standard, a separate power line with a circuit breaker is desirable. Three wires are required for connection - phase, zero and ground.
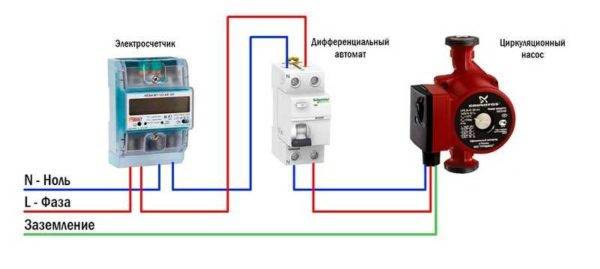
Electrical connection diagram of the circulation pump
The connection to the network itself can be organized using a three-pin socket and plug. This connection method is used if the pump comes with a connected power cable. It can also be connected via a terminal block or directly with a cable to the terminals.
The terminals are located under a plastic cover. We remove it by unscrewing a few bolts, we find three connectors.They are usually signed (pictograms are applied N - neutral wire, L - phase, and "earth" has an international designation), it is difficult to make a mistake.

Where to connect the power cable
Since the entire system depends on the performance of the circulation pump, it makes sense to make a backup power supply - put a stabilizer with connected batteries. With such a power supply system, everything will work for several days, since the pump itself and the boiler automation “pull” electricity to a maximum of 250-300 watts. But when organizing, you need to calculate everything and select the capacity of the batteries. The disadvantage of such a system is the need to ensure that the batteries are not discharged.

How to connect a circulator to electricity through a stabilizer
Hello. My situation is that a 25 x 60 pump stands right after the 6 kW electric boiler, then the line from the 40 mm pipe goes to the bathhouse (there are three steel radiators) and returns to the boiler; after the pump, the branch goes up, then 4 m, down, rings the house of 50 sq. m. through the kitchen, then through the bedroom, where it doubles, then the hall, where it triples and flows into the boiler return; in the bath branch 40 mm up, leaves the bath, enters the 2nd floor of the house 40 sq. m. (there are two cast-iron radiators) and returns to the bath in the return line; the heat did not go to the second floor; the idea to install a second pump in the bath for supply after a branch; the total length of the pipeline is 125 m. How correct is the solution?
The idea is correct - the route is too long for one pump.
Where to put the pump - for supply or return
Despite the abundance of information on the Internet, it is rather difficult for the user to understand how to properly install the pump for heating in order to ensure the forced circulation of water in the system of their own home. The reason is the inconsistency of this information, which causes constant disputes on thematic forums. Most of the so-called specialists claim that the unit is placed only on the return pipeline, citing the following conclusions:
- the temperature of the coolant at the supply is much higher than at the return, so the pump will not last long;
- the density of hot water in the supply line is less, so it is more difficult to pump;
- the static pressure in the return pipe is higher, which makes the pump easier to operate.
Interesting fact. Sometimes a person accidentally gets into a boiler room that provides central heating for apartments, and sees the units there, embedded in the return line. After that, he considers such a decision to be the only correct one, although he does not know that in other boiler rooms centrifugal pumps can also be installed on the supply pipe.
We answer the following statements point by point:
- Domestic circulation pumps are designed for a maximum coolant temperature of 110 °C. In a home heating network, it rarely rises above 70 degrees, and the boiler will not heat water more than 90 ° C.
- The density of water at 50 degrees is 988 kg / m³, and at 70 ° C - 977.8 kg / m³. For a unit that develops a pressure of 4-6 m of water column and is capable of pumping about a ton of coolant in 1 hour, the difference in the density of the transported medium of 10 kg / m³ (the volume of a ten-liter canister) is simply negligible.
- In practice, the difference between the static pressures of the coolant in the supply and return lines is just as insignificant.
Hence a simple conclusion: circulation pumps for heating can be inserted into both the return and supply pipelines of the heating system of a private house. This factor will not affect the performance of the unit or the heating efficiency of the building.
Boiler room made by our expert Vladimir Sukhorukov. There is convenient access to all equipment, including pumps.
The exception is cheap direct combustion solid fuel boilers that are not equipped with automation. When overheated, the coolant boils in them, since burning firewood cannot be extinguished at once. If the circulation pump is installed on the supply, then the resulting steam mixed with water enters the housing with the impeller. The further process looks like this:
- The impeller of the pumping device is not designed to move gases. Therefore, the performance of the apparatus is sharply reduced, and the flow rate of the coolant drops.
- Less cooling water enters the boiler tank, which causes overheating and even more steam.
- An increase in the amount of steam and its entry into the impeller leads to a complete stop of the movement of the coolant in the system. An emergency situation arises and as a result of an increase in pressure, a safety valve is activated, ejecting steam directly into the boiler room.
- If measures are not taken to extinguish the firewood, then the valve cannot cope with the release of pressure and an explosion occurs with the destruction of the boiler shell.
For reference. In cheap heat generators made of thin metal, the safety valve threshold is 2 bar. In higher quality TT boilers, this threshold is provided at 3 bar.
Practice shows that no more than 5 minutes pass from the beginning of the overheating process to the valve actuation. If you install a circulation pump on the return pipe, then steam will not get into it and the time interval before the accident will increase to 20 minutes. That is, mounting the unit on the return line will not prevent the explosion, but will delay it, which will give more time to fix the problem. Hence the recommendation: it is better to install pumps for wood-fired and coal-fired boilers on the return pipeline.
For well-automated pellet heaters, the installation location does not matter. You will learn more information on the topic from the video of our expert:
One-pipe and two-pipe systems
Specialists distinguish between two heating schemes with forced circulation of the heating agent - one-pipe and two-pipe. The choice of one or another option depends not only on the location of the circuits, but also on the length of the pipelines, as well as the type and quantity of equipment for shutdown, regulation and control.
 A single-pipe heating system is characterized by the sequential inclusion of heating radiators in the circuit. The coolant returns through a separate pipeline to the boiler only after it has been rotated in turn through all the devices of the system. The disadvantage of this method is that radiators that are closer to the thermal block become warmer than those that are further away, and this reduces the thermal efficiency and life of the equipment. The introduction of a circulation pump into the circuit and temperature equalization is achieved at all points in the system.
A single-pipe heating system is characterized by the sequential inclusion of heating radiators in the circuit. The coolant returns through a separate pipeline to the boiler only after it has been rotated in turn through all the devices of the system. The disadvantage of this method is that radiators that are closer to the thermal block become warmer than those that are further away, and this reduces the thermal efficiency and life of the equipment. The introduction of a circulation pump into the circuit and temperature equalization is achieved at all points in the system.
A two-pipe layout has advantages over a single-pipe layout, since all heaters are connected in parallel to the supply and return lines, which contributes to an even distribution of temperature throughout all rooms. Forced circulation of the refrigerant leads to an increase in the efficiency of the system and the possibility of regulating its thermal power.
What is a circulation pump and why is it needed
A circulation pump is a device that changes the speed of movement of a liquid medium without changing the pressure. In heating systems, it is placed for more efficient heating. In systems with forced circulation, it is an indispensable element, in gravitational systems it can be set if it is necessary to increase the thermal power. Installing a circulation pump with several speeds makes it possible to change the amount of heat transferred depending on the temperature outside, thus maintaining a stable temperature in the room.
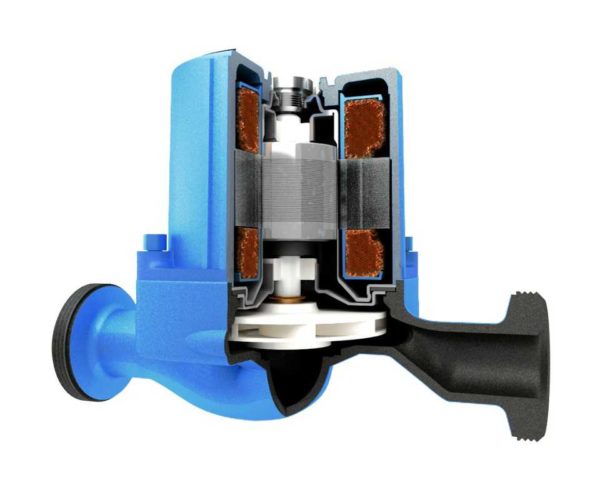

Sectional view of a wet rotor circulation pump
There are two types of such units - with a dry and wet rotor. Devices with a dry rotor have a high efficiency (about 80%), but they are very noisy and require regular maintenance. Wet rotor units operate almost silently, with normal coolant quality, they can pump water without failures for more than 10 years. They have a lower efficiency (about 50%), but their characteristics are more than enough to heat any private house.
2 Types of pumps and their features
Various circulation units can be mounted in the heating system of a private house. They are divided into two large groups. The circulation pump can be "dry" or "wet".When installing devices of the first type with your own hands, it should be borne in mind that their motor is separated from the working part by sealing rings. They are made from stainless steel. During the start of the installation, the process of movement of these rings begins, which leads to the sealing of the connection with a water (very thin) film. The latter is located between the seals.

Circulation pumping unit
High-quality sealing in this case is ensured due to the fact that the pressure in the external atmosphere and in the heating system itself is characterized by different indicators. A “dry” pump makes quite loud sounds during operation. In this regard, its installation is always carried out in a specially soundproofed separate room of a private house. The efficiency of such a circulation unit is at the level of 80%.
There are three types of "dry" devices for connection to the heating system: horizontal, vertical, block. The electric motor in the units of the first type is placed horizontally. The discharge pipe is attached to them on the body of the apparatus, and the suction pipe is mounted on the shaft (on its front side). In vertical installations, the nozzles are on the same axis. And the engine in this case is located vertically. In block circulating units, heated water exits radially, and enters the system in an axial direction.
Caring for a "dry" unit is objectively difficult. Its elements must be regularly lubricated with a special compound. If this is not done, the end seals will quickly fail, causing the pump to stop. In addition, in a private house, “dry” devices should be placed in rooms where there is no dust.Its turbulence during equipment operation often causes pump depressurization.
In "wet" units, the coolant itself performs the function of lubrication. The impeller and rotor of such installations are immersed in water. "Wet" devices are much less noisy, they are easier to mount with your own hands. And their maintenance is simpler compared to "dry" pumps.
The body of the "wet" installation, as a rule, is made of brass or bronze. Between the stator and the rotor there must be a special separator made of stainless steel. It is called a glass. It is necessary to give the required tightness to the engine (more precisely, its elements under electrical voltage). It is the “wet” units that are most often mounted in a private house in the heating system.
They do a good job of heating relatively small areas. For large objects, such devices are not suitable, since their performance usually does not exceed 50%. The low efficiency of "wet" installations is due to the impossibility of high-quality sealing of the glass placed between the stator and the rotor.
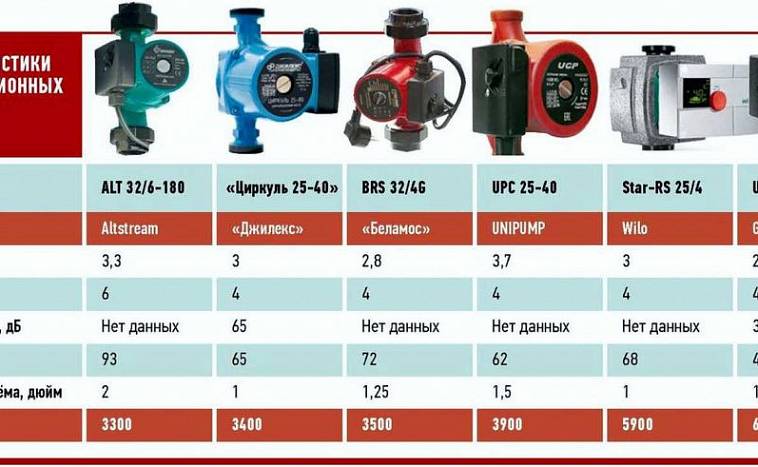
Price factor
When choosing a circulation pump, the cost of the device itself and its efficiency during operation are important. As a rule, the operation of the pump is justified by saving on fuel consumption, and the cost of the model itself is determined by its performance. In Moscow, the range of prices for pumps is very large. Conventionally, they can be divided into 3 categories:
For 3.5-7 thousand rubles, you can buy basic functions, with a minimum period of work and most often one-time use;

Comparison of characteristics of economy segment pumps
- Devices for 7.5-20 thousand are “workhorses” that accurately provide the declared characteristics, with a service life not less than that specified by the manufacturer and with several degrees of protection and an optimal margin of safety;
- VIP systems with full automation, a set of additional functions, a high margin of safety and the ability to provide heat to a large volume will already cost from 20 to 45 thousand rubles.
Video description
And some more thoughts about circulation pumps in the following video:
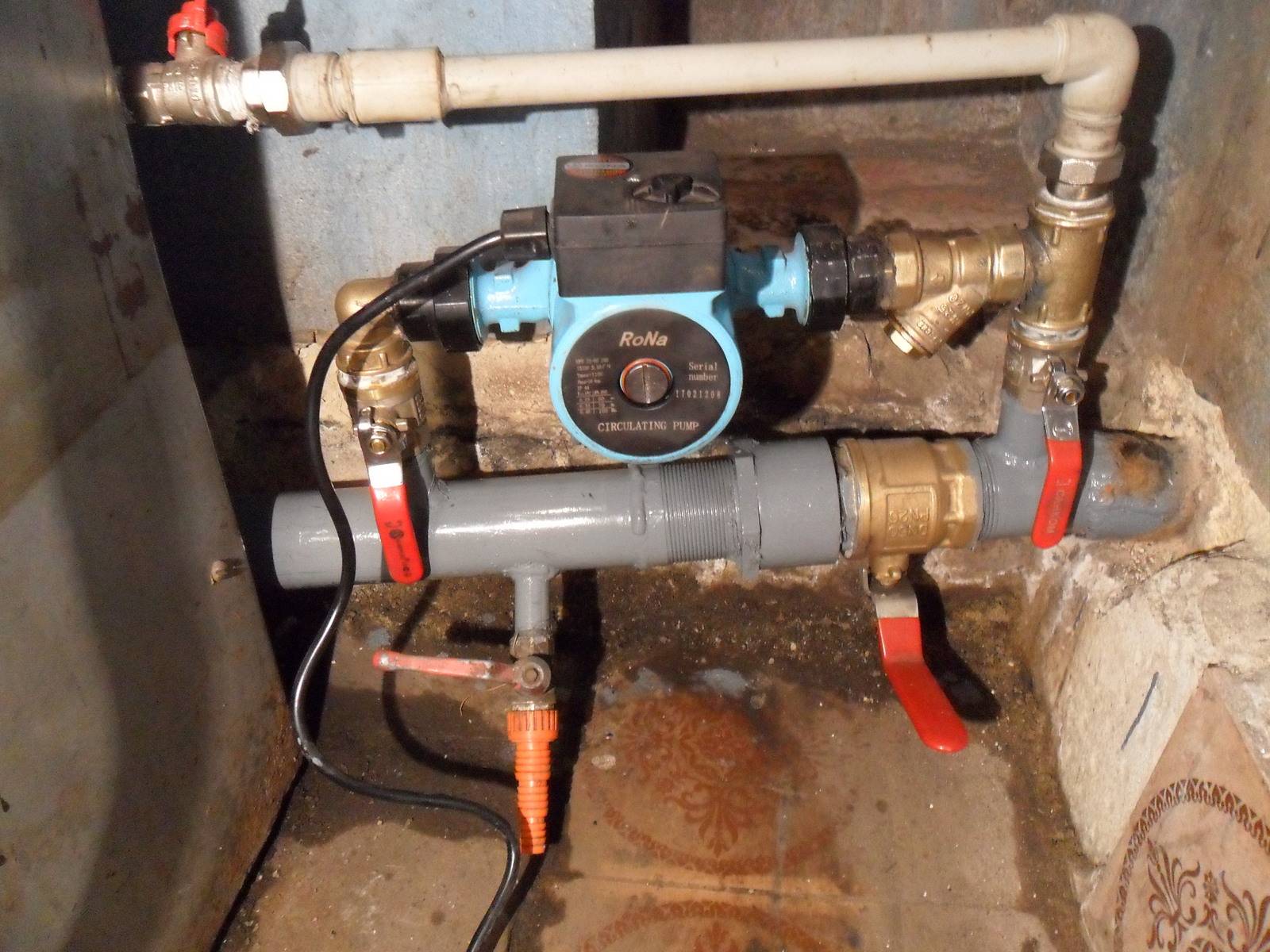
Benefits of a separate pumping unit
The use of pumping equipment is justified in terms of fuel economy and increase in boiler efficiency, so many companies build pumping units into boilers. But a separate installation of the unit has its advantages: quick replacement without removing the boiler, the ability to control the process in case of emergency situations (for example, using a bypass). In addition, the pump can be installed in a system not provided for by the project at the initial stage.
Conclusion
Despite the apparent simplicity of the choice, the pump parameters must be technically justified, for which mathematical calculations are carried out taking into account the laws of heat engineering, the characteristics of the individual system, so the exact choice should be made by a specialist who takes into account all factors based not only on theoretical knowledge, but also on practical experience.
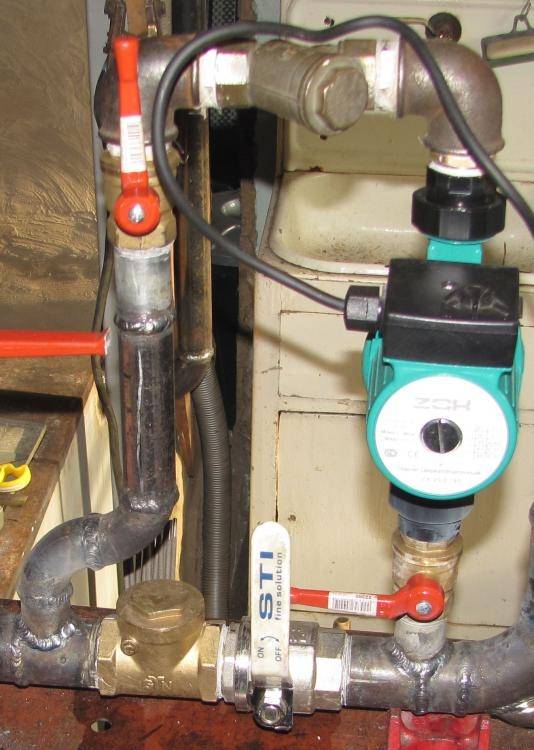
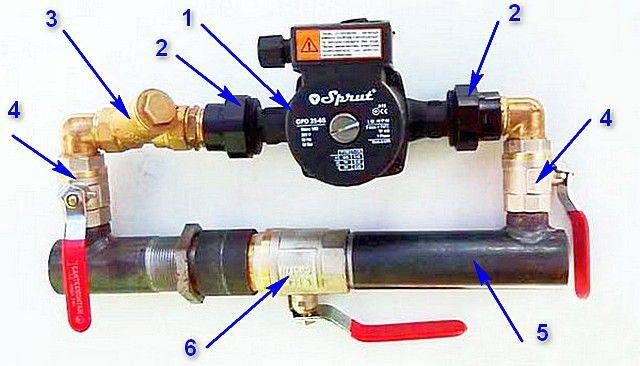
Device device diagram
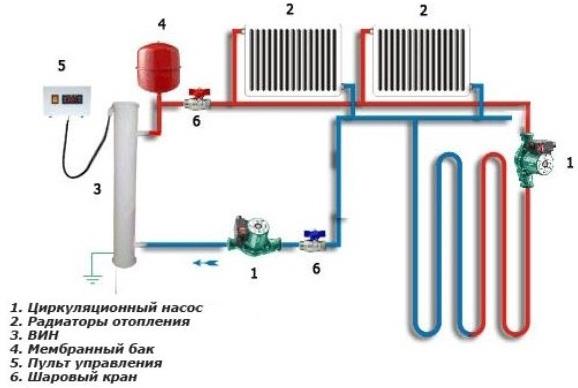
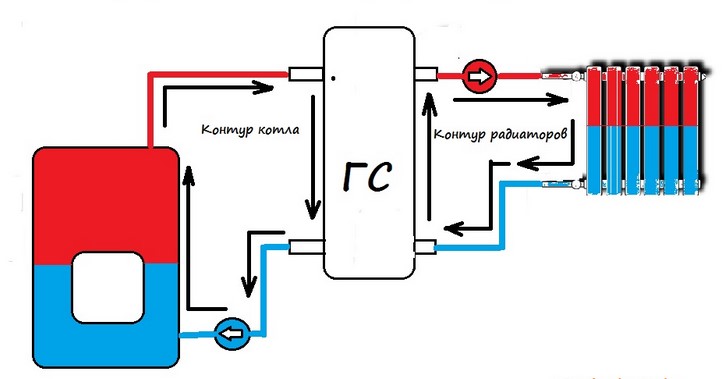
Heating with two circulation pumps
The process of carrying out installation actions for installing the pump is regulated by the instructions below:
– Ball-type valves are being installed on both sides of the proposed location of the pumping equipment, in order, if necessary, to carry out an emergency shutdown of water access until possible system malfunctions are eliminated;
- It is mandatory to install a valve with a filtering value in front of the flow of water entering the pump cavity in order to clean it from mechanical entries that can disable the equipment;
– Performing the installation of a manual type clan used as needed to remove the accumulation of steam;
- Take into account all the markings on the body of the equipment being installed in order to perform the correct operation of the system and mechanism in general;
- The installation of a submersible pump is carried out in a horizontal position in order to avoid situations of failure of the main working elements of the internal mechanical systems;
- To exercise control over the correct location of the terminals, which should be located in the upper part of the equipment above the surface of the water;
- In order to minimize the occurrence of leaks, use a special sealant or sealing elements to tightly connect the parts of the threaded plan.
- Connection to the battery with electric current having a well-made grounding in order to avoid electric shock when touching the heating system, which is not allowed according to the rules for operating equipment of this type.
Sequence of work and preparation for installation

Installation by a master
To carry out a competent installation process, the following rules should be followed:
- Drain the system before starting work on installing the pump in the system. In the case of a system that has been in operation for a long time, clean it by repeatedly filling and draining clean water in order to eliminate possible contaminating components;
- Considering the scheduled course of work in the previous section, carry out a phased installation of all the component parts of a single system;
- Filling the system with water in order to check the quality of the equipment;
- Starting the system by opening the screw located in the central part of the cover of the main pump body. After the appearance of liquid droplets on the surface of the hole, it shows the complete filling of the system with water and the exclusion of all possible air entries from it.
To assist novice users of the system of this plan, it is necessary to supplement the information with a recommendation to carry out the verification process in the above way before taking steps to start the system in working condition.
Performing these steps will help to avoid air inclusions in parts of the system.
In the event of a lack of time to carry out such actions, it is recommended to purchase and install more expensive equipment operating in automatic mode without the need to perform the actions of the above plan.
How to choose a water pump for home heating
The pump for heating in a private house is selected according to several main parameters:
- performance and pressure;
- rotor type;
- Power consumption;
- Control type;
- Heat carrier temperature.
Let's see how water pumps are chosen for heating a private house.
performance and pressure
Correctly made calculations will help you choose the unit that best meets your needs, which means it will help save the family budget.
The performance of an electric water pump is its ability to move a certain amount of water per minute. The following formula is used for calculation - G=W/(∆t*C). Here C is the thermal capacity of the coolant, expressed in W * h / (kg * ° C), ∆t is the temperature difference in the return and supply pipes, W is the required heat output for your home.
The recommended temperature difference when using radiators is 20 degrees. Since water is usually used as a heat carrier, its heat capacity is 1.16 W * h / (kg * ° C). Thermal power is calculated for each household individually and is expressed in kilowatts. Substitute these values into the formula and get the results.
The head is calculated according to the pressure loss in the system and is expressed in meters. Losses are calculated as follows - losses in pipes (150 Pa / m), as well as in other elements (boiler, water purification filters, radiators) are considered. All this is added and multiplied by a factor of 1.3 (provides a small margin of 30% for losses in fittings, bends, etc.). There are 9807 Pa in one meter, therefore, we divide the value obtained by summing up by 9807 and we get the necessary pressure.
Rotor type
Domestic heating uses wet rotor water pumps. They are characterized by a simple design, minimal noise and maintenance-free operation. They are also characterized by small dimensions. Lubrication and cooling in them is carried out using a coolant.
As for dry-type water pumps, they are not used in home heating. They are bulky, noisy, require cooling and periodic lubrication. They also need periodic replacement of seals. But their throughput is large - for this reason they are used in heating systems of multi-storey buildings and large industrial, administrative and utility buildings.
Power consumption
The most modern water pumps with energy efficiency class "A" have the lowest power consumption. Their disadvantage is the high cost, but it is better to invest once in order to get reasonable energy savings. In addition, expensive electric pumps have a lower noise level and a long service life.
Control type
Through a special application, you can get information about the operation of the device wherever you are.
Typically, the adjustment of rotation speed, performance and pressure is performed by a three-position switch. More advanced pumps are endowed with electronic control systems. They control the parameters of heating systems and save energy. The most advanced models are controlled wirelessly, directly from your smartphone.
Heat carrier temperature
Water pumps for heating a private house differ in their operating temperature range. Some models can withstand heating up to + 130-140 degrees, this is exactly what should be preferred - they will cope with any thermal loads.
As practice shows, operation at the maximum temperature is possible only for the shortest time, so having a solid supply will be a plus.
Other characteristics
When choosing a water pump for heating, it is necessary to pay attention to the maximum operating pressure for the selected model, the installation length (130 or 180 mm), the type of connection (flanged or coupling), the presence of an automatic air vent. Also pay attention to the brand - in no case do not buy cheap models from little-known developers. The water pump is not the part to save on
The water pump is not the part to save on.
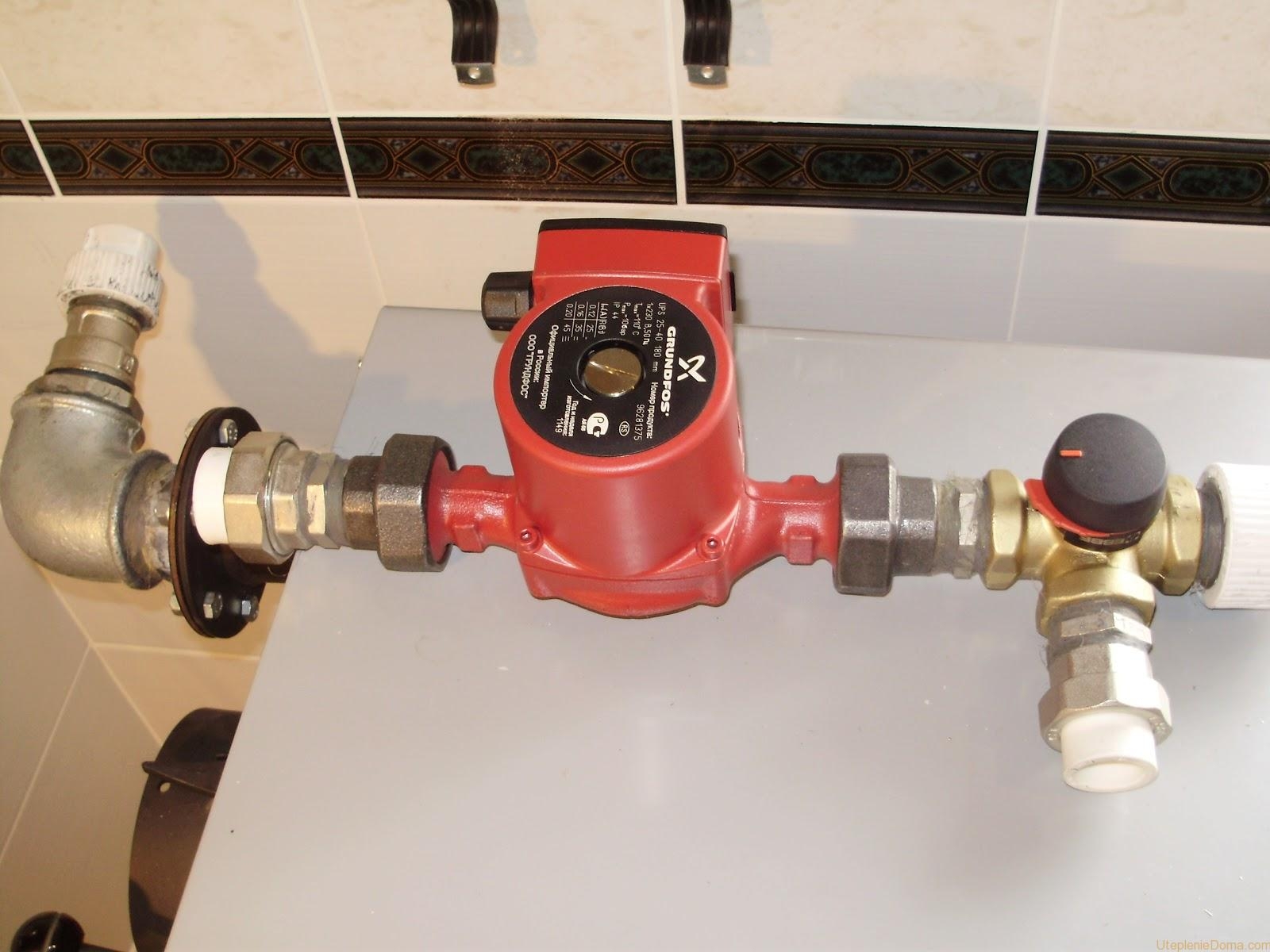
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but it does not matter on the supply or return pipeline. Modern units are made from materials that normally tolerate temperatures up to 100-115 ° C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, therefore considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you are so calmer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system, it does not matter whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in the sense of tying, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point at the installation site.If there are two separate branches in the heating system - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floors - it makes sense to put a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule is preserved on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal regime in each of the parts of the house independently of the other, as well as save on heating in two-story houses. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of the coolant is set much less, and this allows you to burn less fuel, and without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - with forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump, with natural circulation they work, but in this mode they have a lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is slammed into it. This gives high efficiency and reliability of heating. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems has differences.
All heating systems with underfloor heating are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
forced circulation
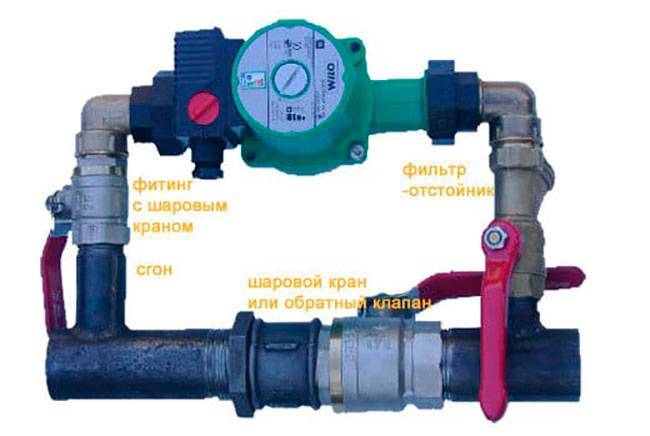
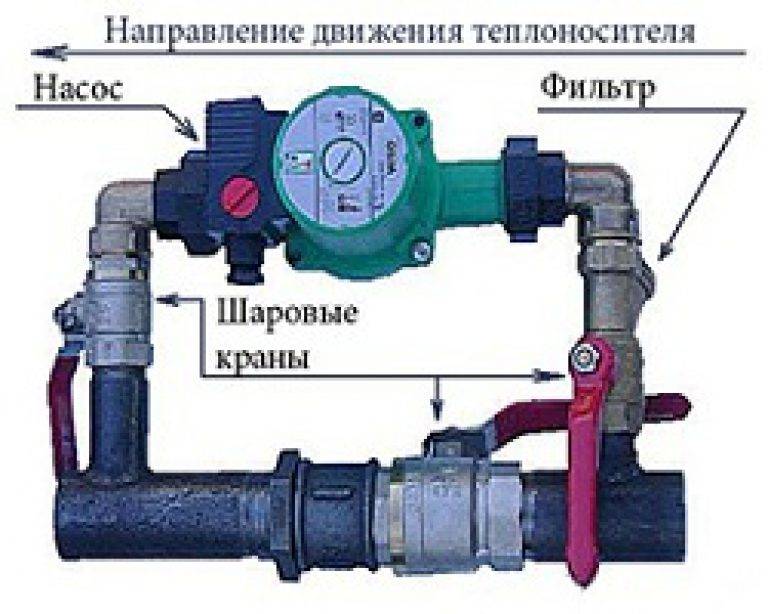
Since a forced circulation heating system is inoperative without a pump, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They are able to jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a strainer must be placed in front of the unit.
Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also desirable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps, remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not running. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed all the time while pumping is in operation. In this mode, the system works as a forced one.
Scheme of installation of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When electricity fails or the unit fails, the faucet on the jumper is opened, the faucet leading to the pump is closed, the system works like a gravitational one.
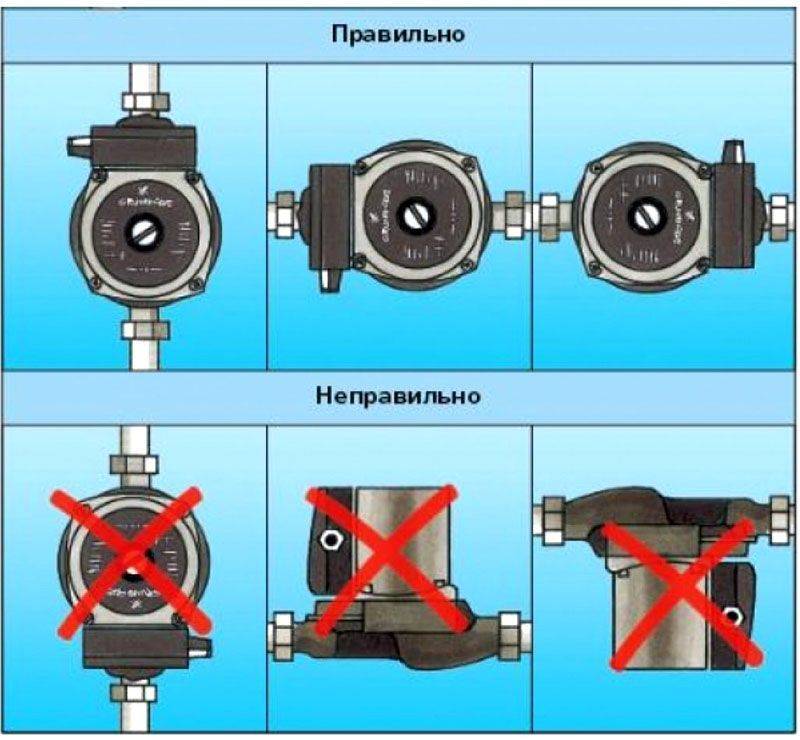
Mounting Features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require alteration: it is required to turn the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of the flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating in which direction the coolant should flow.So turn the unit around so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, only when choosing a model, see that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (created pressure) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.