- RCD without earth
- How to connect an RCD without grounding
- RCD connection diagrams in a single-phase network
- Without grounding
- Grounded
- Features of devices for disconnecting the load
- Circuit breakers - improved "plugs"
- Prices for protective automation
- RCD - automatic protection devices
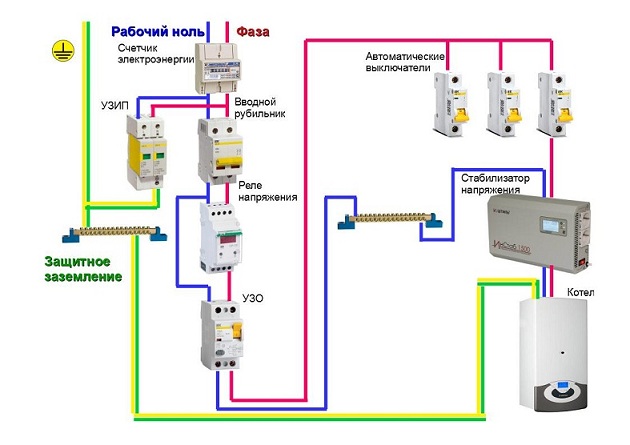
- Connection
- Errors during the installation of the RCD
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
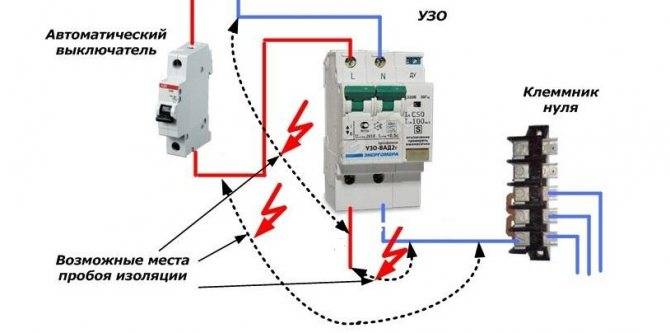
RCD without earth
RCD connection method without protective earth
Cited at the beginning of paragraph 7.1.80 exists in the PUE not in splendid isolation. It is supplemented with points explaining how, after all (well, there are no ground loops in our houses, no!) “Push” the RCD into the TN-C system. Their essence is as follows:
- It is unacceptable to install a common RCD or difavtomat on an apartment with TN-C wiring.
- Potentially dangerous consumers must be protected by separate RCDs.
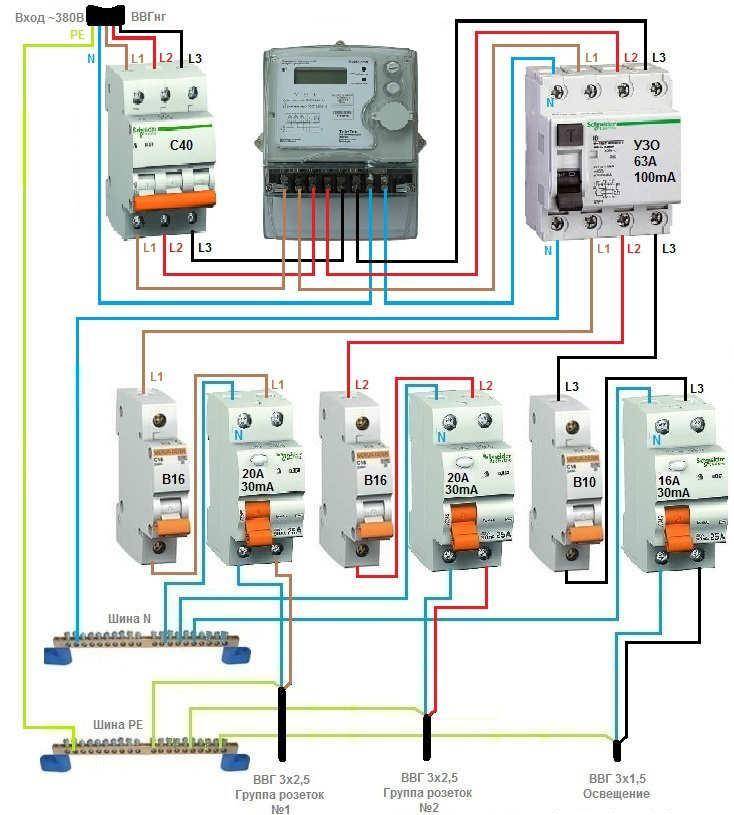
- The protective conductors of sockets or socket groups intended for connecting such consumers must be brought to the INPUT zero terminal of the RCD in the shortest way, see the diagram on the right.
- RCD cascade connection is allowed, provided that the upper ones (closest to the RCD input) are less sensitive than the terminal ones.
A smart person, but unfamiliar with the intricacies of electrodynamics (which, by the way, many certified security electricians also sin) may object: “Wait a minute, what's the problem? We put a common RCD, start all PE at its input zero - and you're done, the protective conductor is not switched, grounded without ground! Yes, not so.
The segment PE with the corresponding segment of zero and the equivalent resistance of the consumer R form a loop that encloses the magnetic circuit of the differential transformer, see the principle of operation of the UZO-D. That is, a PARASITE winding appears on the magnetic circuit, loaded on R. Although R is small (48.4 Ohm / kW), on a sinusoid of 50 Hz, the influence of a parasitic winding can be neglected: the radiation wavelength is 6000 km.
The electromagnetic field of the installation and the cord to it are also excluded from consideration. The first is concentrated inside the device, otherwise it will not pass certification and will not go on sale. In the cord, the wires pass close to each other, and their field is concentrated between them, regardless of frequency, this is the so-called. T-wave.
But in the event of a breakdown on the body of the electrical installation or in the presence of pickups in the network, a short powerful current pulse jumps through the parasitic loop. Depending on specific factors (which can only be accurately calculated by a specialist with scientific experience and on a powerful computer), two options are possible:
- “Anti-differential” effect: a surge of current in the parasitic winding compensates for the imbalance of currents in phase and zero, and the RCD will, as they say, peacefully sniff its nose into the pillow when a crooked firebrand has already hung on the wires. The case is extremely rare, but extremely dangerous.
- A “super-differential” effect is also possible: pickup increases the imbalance of currents, and the RCD operates without leakage, prompting the owner to painful thoughts: why does the RCD knock out every now and then if everything is in order in the apartment?
The magnitude of both effects strongly depends on the size of the parasitic loop; here its openness, "antenna" affects. With a PE length of up to half a meter, the effects are negligible, but even with its length of 2 m, the probability of RCD failure increases to 0.01% According to the numbers, this is small, but according to statistics, 1 chance out of 10,000. When it comes to human life, this is unacceptable a lot of. And if in apartment without grounding a web of "protective" conductors has been laid, then why be surprised if the RCD "knocks out" when the mobile phone is charged.
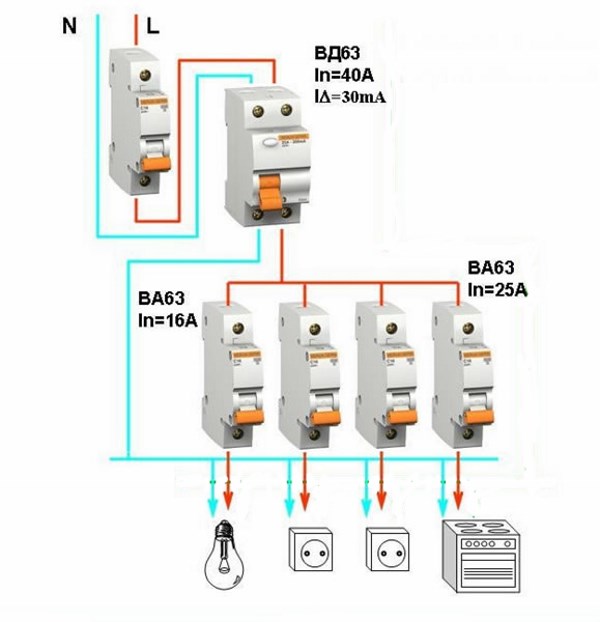
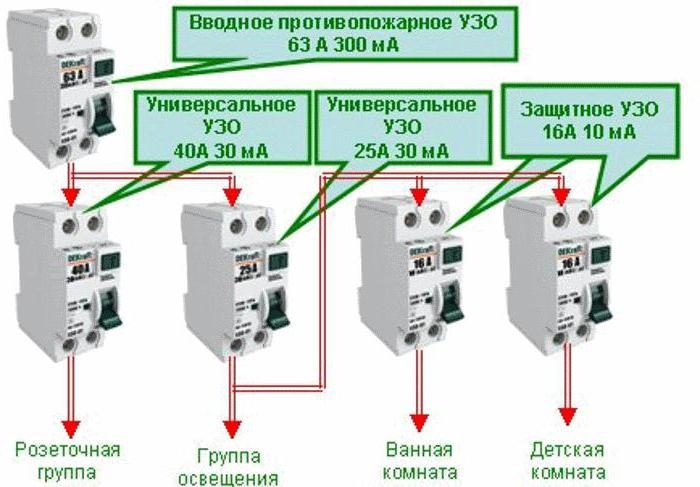
In an apartment with an increased fire hazard, it is permissible, with the obligatory presence of individual consumer RCDs connected according to the recommended circuit, to install a common FIRE RCD for 100 mA of unbalance and with a rated current one step higher than that of protective ones, regardless of the cutoff current of the machine. In the example described above, for Khrushchev, you need to connect an RCD and an automatic machine, but not a difautomatic! When the machine is knocked out, the RCD must remain in operation, otherwise the likelihood of an accident increases sharply. Therefore, the RCD at face value must be taken two steps higher than the machine (63 A for the analyzed example), and by unbalance - one step higher than the final 30 mA (100 mA). Once again: in difautomats, the RCD rating is made a step higher than the cut-off current, so they are not suitable for wiring without ground.
How to connect an RCD without grounding
Important advice: it is not recommended to use an RCD with electronic control, because if the power to the electronic circuit is interrupted, the device ceases to perform its function.
Let's move on to the most important question of our article: what is the connection diagram for an RCD without grounding?
Tip: RCDs should only be used in conjunction with circuit breakers. This is necessary because the RCD provides protection for the electrical circuit only when leakage currents occur. This device is absolutely not designed for protection against short-circuit currents and overload. Therefore, the RCD protects against electric shock, and the circuit breaker protects against overcurrents that can lead to fire, damage to wiring and electrical equipment. The only exceptions are differential protection circuit breakers, which in their design combine both an RCD and a circuit breaker.
As for the connection of the RCD itself, it can be done in two ways.
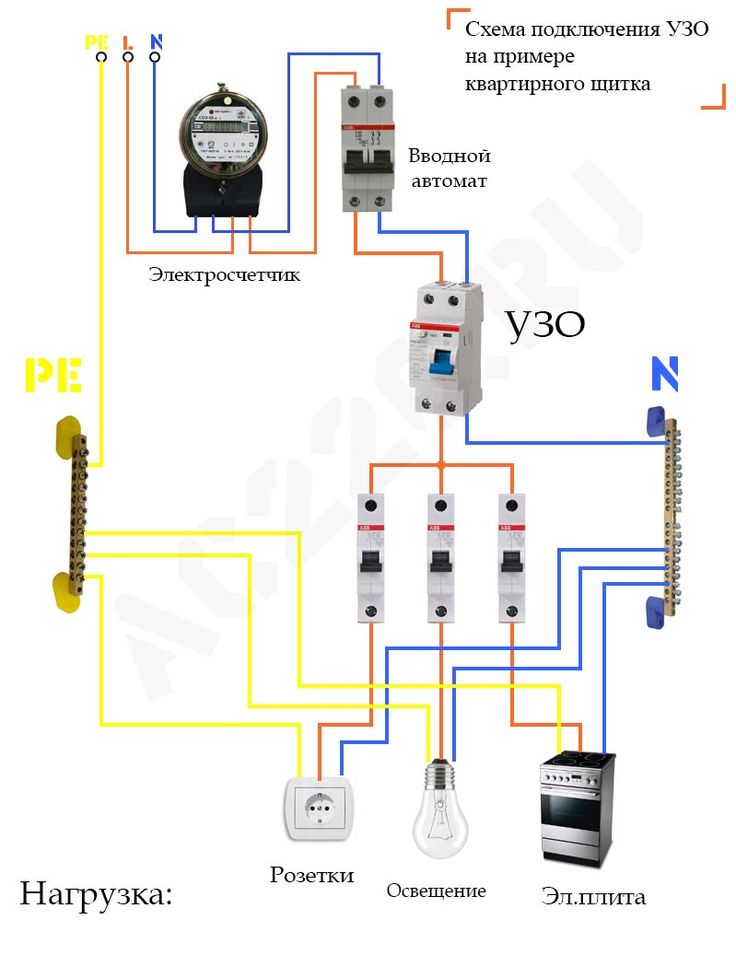
The first scheme for connecting a single-phase RCD is to install a single high-power protection device on all electrical equipment of a house or apartment. This method has the advantage of being the simplest. After the electricity metering device, the phase conductor goes to the incoming terminals of the RCD, then from the outgoing terminals the conductor goes to the circuit breakers. From the machines, the wire goes to power electrical equipment: sockets and lighting.
Such a scheme does not take up much space in the switchboard. The disadvantage of this method of installing an RCD is that when triggered, all electrical equipment of the house or apartment is turned off. It is also difficult to quickly determine the reason for the outage.
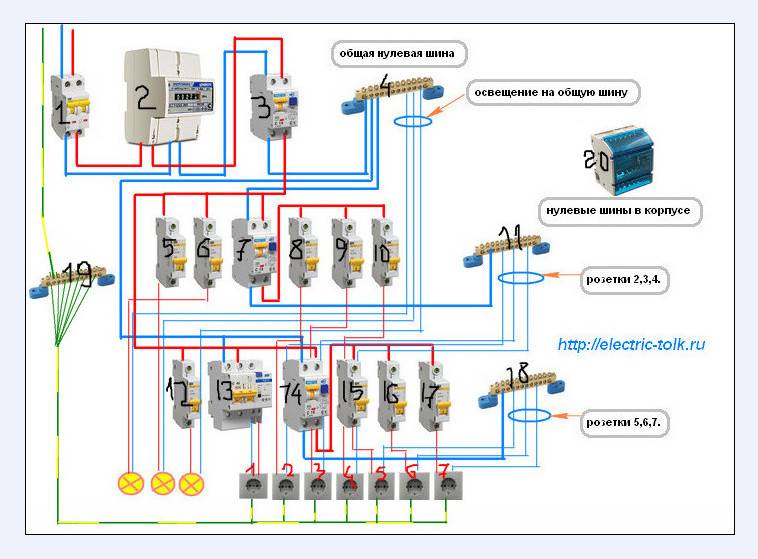
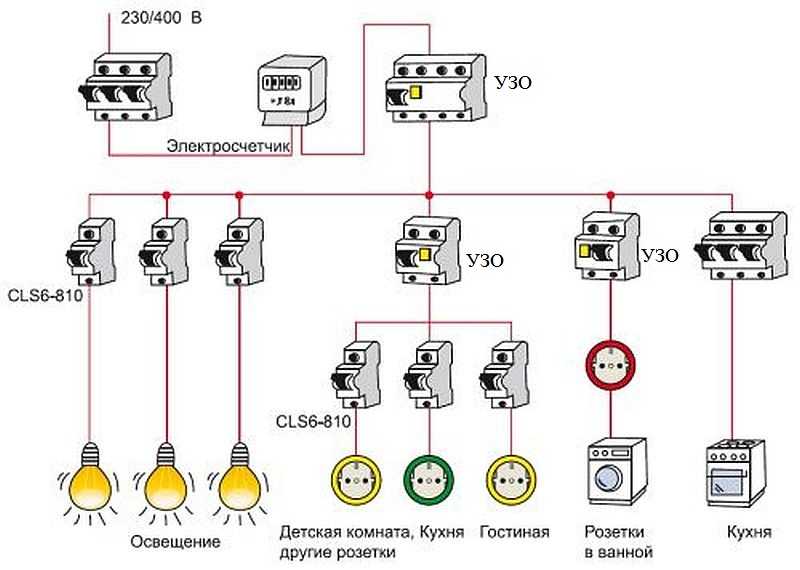
The second way to connect an RCD without grounding is the installation of a separate apparatus for each hazardous area. In this case, the protection device will cost more and take up more space in the switchboard.On the other hand, if one section of the circuit is disconnected, the others will remain connected to electricity, and you will not have to face the situation when the whole house is de-energized. In this case, the connection diagram of a single-phase RCD is as follows: from the meter, the phase wire is connected to each circuit breaker, and from it to each RCD.
When connecting the RCD to the network, the following rule should be followed: you cannot combine neutral conductors into a node after the RCD. This will lead to false positives. In addition, after installing the protective circuit, you should check whether the RCD connection diagram without grounding is correctly assembled. This can be done as follows: connect the electrical equipment to the outlet, which is located in the RCD circuit. If, after turning on the device, the RCD does not turn off, the circuit is connected correctly. You also need to check the RCD for operation as a result of the occurrence of a leakage current by pressing the "TEST" button on the RCD itself.
RCD connection diagrams in a single-phase network
Most household consumers are powered by a single-phase scheme, where one phase and neutral conductor is used for their power supply.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the network, single-phase power supply can be carried out according to the scheme:
- with solidly grounded neutral (TT), in which the fourth wire acts as a return line and is additionally grounded;
- with a combined neutral and protective conductor (TN-C);
- with a separated zero and protective earth (TN-S or TN-C-S, when connecting devices in the room, you will not find differences between these systems).
It should be noted that in the TN-C system, according to the requirements of clause 1.7.80 of the PUE, the use of differential automata is not allowed, except for the protection of individual devices with the obligatory alignment of zero and earth from the device to the RCD. In any situation, when connecting an RCD, the features of the supply network should be taken into account.
Without grounding
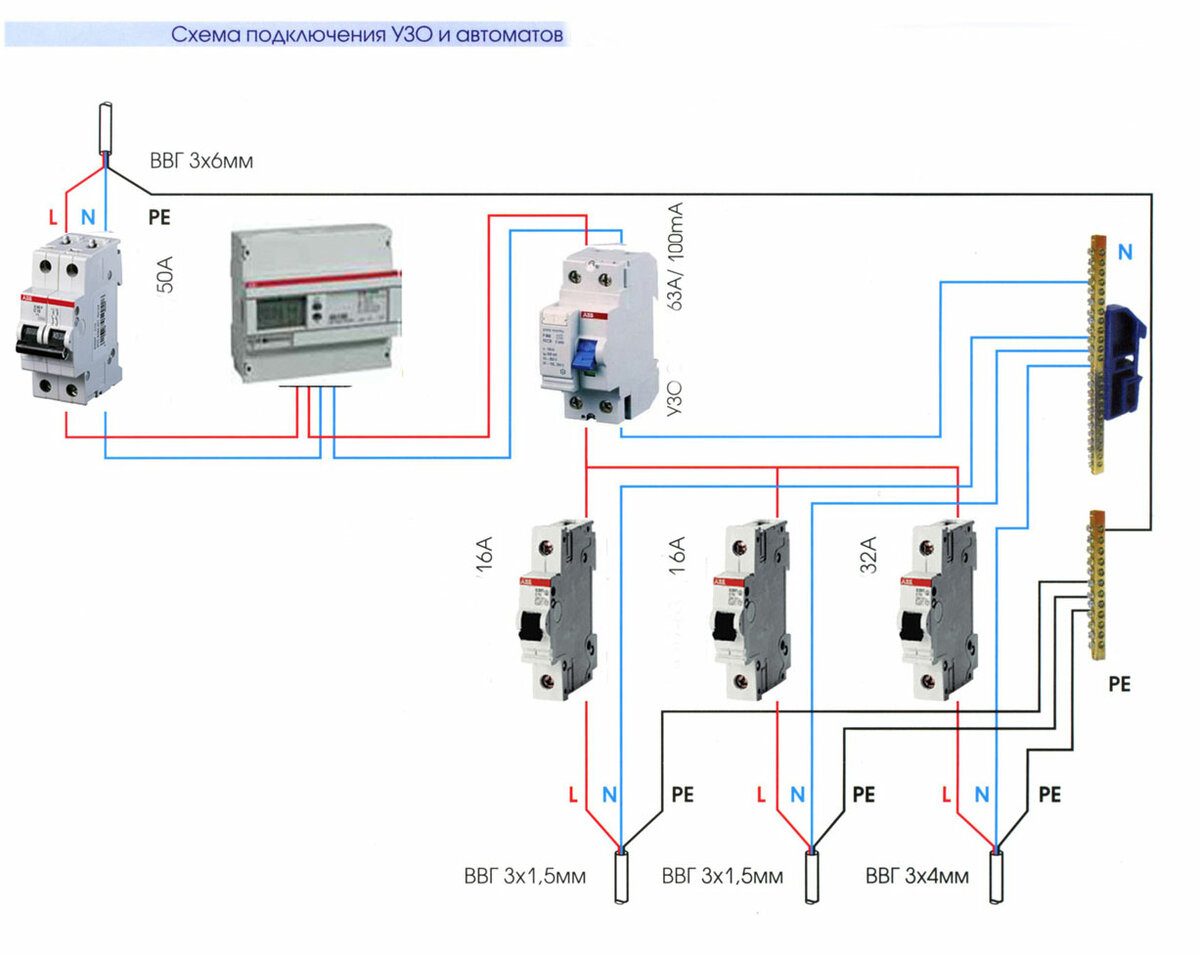
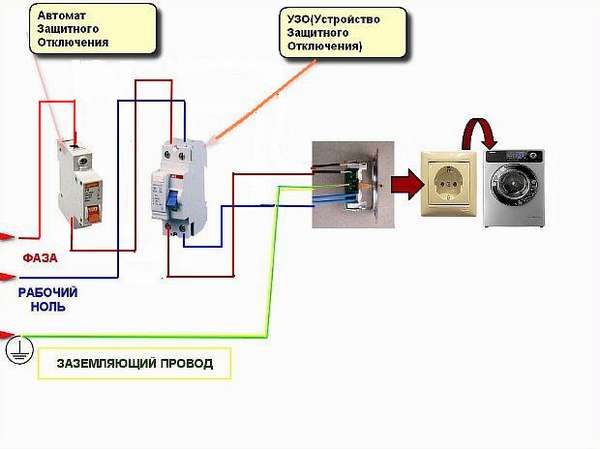
Since not all consumers can boast of having a third wire in their wiring, residents of such premises have to make do with what they have. The simplest RCD connection scheme is to install a protective element after the introductory machine and electric meter. After the RCD, it is important to connect circuit breakers for various loads with the corresponding tripping current. Note that the principle of operation of the RCD does not provide for the shutdown of current overloads and short circuits, so they must be installed together with circuit breakers.
 Rice. 1: RCD connection single-phase two-wire system
Rice. 1: RCD connection single-phase two-wire system
This option is relevant for apartments with a small number of connected devices. Since in the event of a short circuit in any of them, turning off will not bring tangible inconvenience, and finding damage will not take much time.
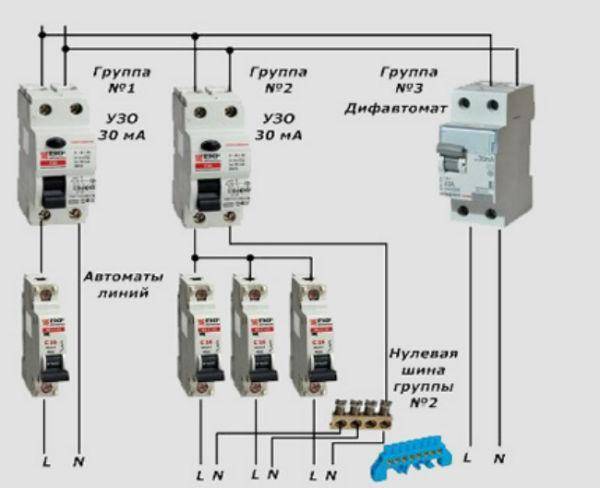
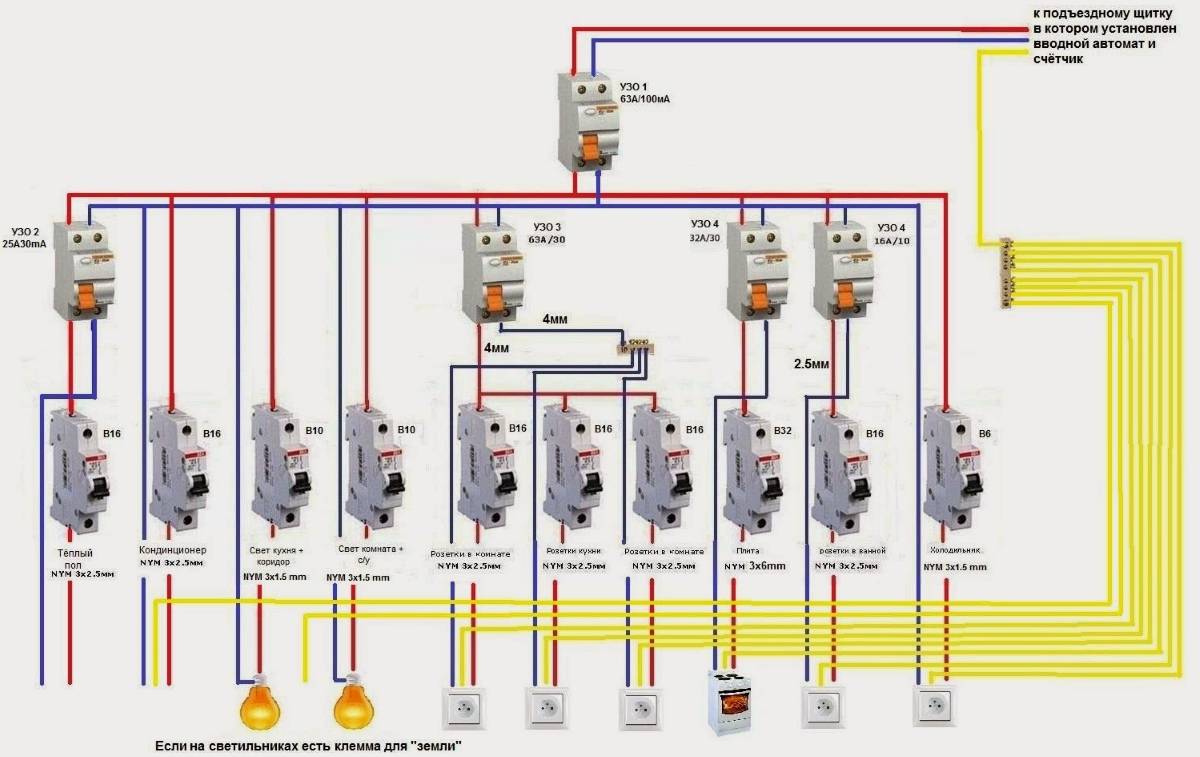
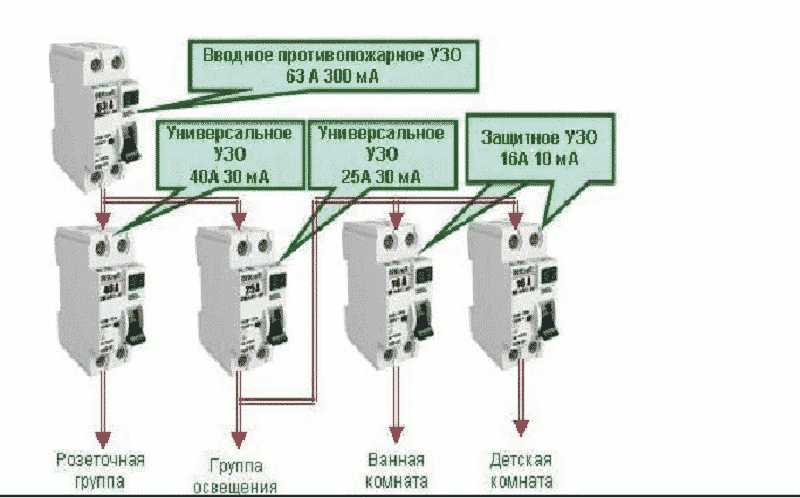
But, in cases where a sufficiently branched power supply circuit is used, several RCDs with different operating currents can be used in it.
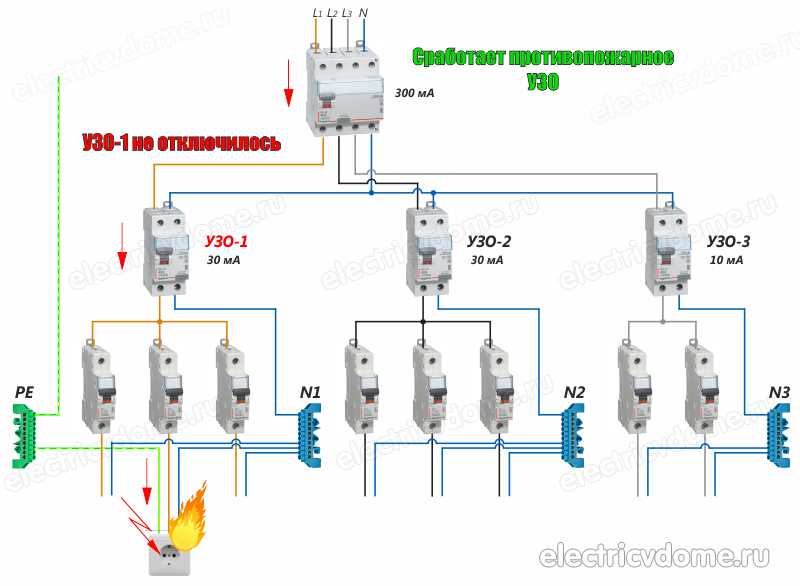
 Rice. 2: RCD connection in a branched single-phase two-wire system
Rice. 2: RCD connection in a branched single-phase two-wire system
In this connection option, several protective elements are installed, which are selected according to the rated current and the operating current.As a general protection, an introductory fire RCD of 300 mA is connected here, followed by a zero and phase cable to the next 30 mA device, one for sockets, and the second for lighting, a pair of 10 mA units is installed for the bathroom and nursery. The lower the trip rating is used, the more sensitive the protection will be - such RCDs will operate at a much lower leakage current, which is especially true for two-wire circuits. However, it is also not worth installing sensitive automation on all elements, since it has a high percentage of false positives.
Grounded
In the presence of a grounding conductor in a single-phase system, the use of an RCD is more appropriate. In such a scheme, connecting the protective wire to the instrument case creates a path for current to leak if the insulation of the wires is broken. Therefore, the protection operation will occur immediately upon damage, and not in the event of a human electric shock.
 Rice. 3: Connecting an RCD in a single-phase three-wire system
Rice. 3: Connecting an RCD in a single-phase three-wire system
Look at the figure, the connection in a three-wire system is made similarly to a two-wire one, since only a neutral and phase conductor is required for the operation of the device. Grounding is connected only to protected objects through a separate ground bus. Zero can also be connected to a common zero bus, from zero contacts it is wired to the corresponding devices connected to the network.
As in a two-wire single-phase circuit, with a large number of consumers (air conditioner, washing machine, computer, refrigerator and other benefits of civilization), an extremely unpleasant option is the freezing of all of the above electronic circuits with data loss or disruption of their performance. Therefore, for individual devices or entire groups, you can install several RCDs. Of course, their connection will result in additional costs, but it will make finding damage a more convenient procedure.
Features of devices for disconnecting the load
If the electrical system is divided into circuits, then a separate circuit breaker is installed for each line in the chain, and a protection device is mounted at the output. However, there are many connection options. Therefore, first you need to understand the differences between RCDs and other automation.
Circuit breakers - improved "plugs"
Years earlier, when there were no modern network protection devices, with an increase in the load on the common line, “plugs” were triggered - the simplest devices for emergency power outages.
Over time, they were significantly improved, which made it possible to obtain machines that work in the following situations - with a short circuit and excessive load on the line. In a common electrical panel, from one to several circuit breakers can be located. The exact number will differ depending on the number of lines that are available in a particular apartment.
It is worth noting that the more separately running electrical lines, the easier it is to carry out repairs. Indeed, in order to make the installation of one device, it is not necessary to turn off the entire electrical network.
Instead of obsolete "traffic jams" use circuit breakers
Installation of automation is a mandatory stage in the assembly of an electrical panel for home use. After all, the switches instantly respond to network overload when a short circuit occurs. However, they do not protect the system from leakage current.
Prices for protective automation
Protective automation
RCD - automatic protection devices
RCD is a device that is responsible for controlling the current strength and preventing its loss. In appearance, the protective device has no fundamental differences from the circuit breaker, but functions differently.
RCD in electrical panel
It is worth noting that this is a multi-phase device that operates at a voltage of 230/400 V and currents up to 32 A. However, the device operates at lower values.
Sometimes devices with the designation 10 mA are used to bring a line into a room with a high level of humidity. There are two main types of RCDs. In order to choose the appropriate option, you need to consider them in more detail.
Table number 1. Types of RCDs.
| View | Description |
|---|---|
| Electromechanical | Here, the main functioning device is a magnetic circuit with windings. His job is to compare the level of current that goes into the network, and then returns. |
| Electronic | This device allows you to compare current values, but only here the board is responsible for this process. However, it only functions when voltage is present. |
It should be noted that the electromechanical device is more popular. After all, if the consumer accidentally touches the phase conductor in the presence of a de-energized board, he will receive an electric shock. While the electromechanical RCD will remain operational.
It turns out that the RCD only protects the system from current leakage, but it is considered useless with increased voltage on the line. It is for this reason that it is mounted only in combination with a circuit breaker. Only two of these devices will provide full protection of the electrical network.
Connection
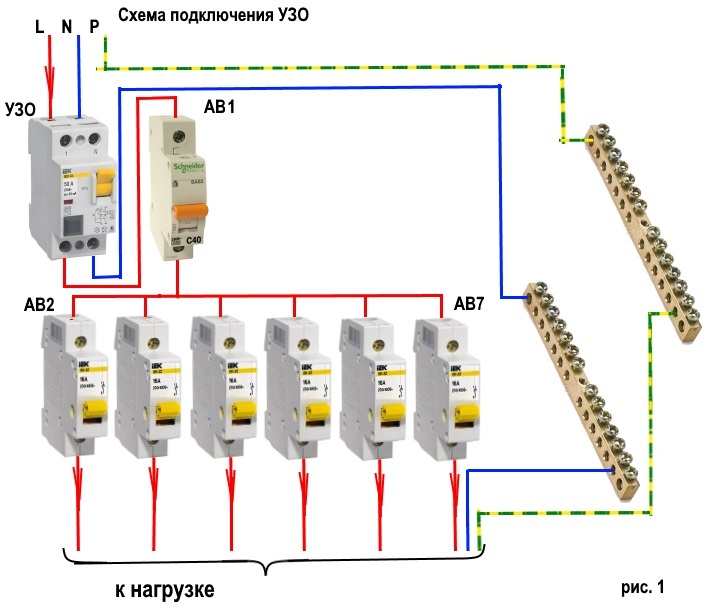
How to connect RCD? The installation of the RCD is carried out together with the machines. Such a switch is placed in the shield in front of the protective element, playing the role of a protector from very high current signals (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5 RCD connection diagram with circuit breaker
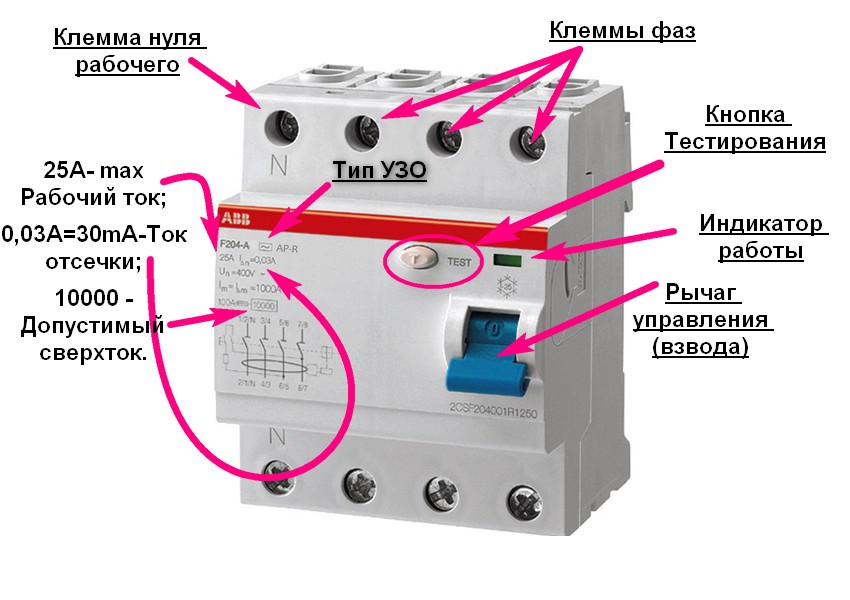
RCD in the shield must be connected to work with currents: 10 mA; 30 mA; 100 mA; 300 mA.
On the body of the installed protective device, the operating voltage, current and its circuit are indicated.
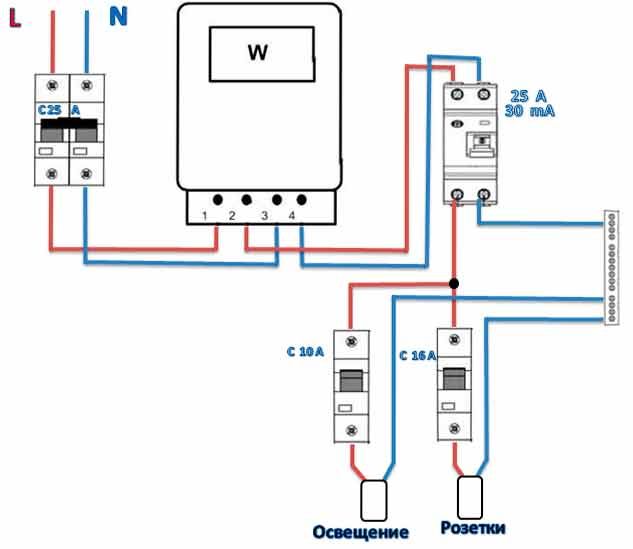
An example of connecting a device for 25A, a voltage of 400V (Fig. 6) and the connection procedure:
Rice. 6 Example of RCD working elements without grounding
- The input voltage value is applied to: connector "1"; connector "2".
- The voltage is removed from: connector "2"; connector "4".
Rice. 7 Image of working elements of protective equipment without grounding
On the outer part of the case, the value of the operating voltage values, the rated current and the leakage current value are displayed. Schematic diagram of the device and the "TEST" button (Fig. 7).
The "TEST" button must be put in the pressed position to check the functionality of the device.
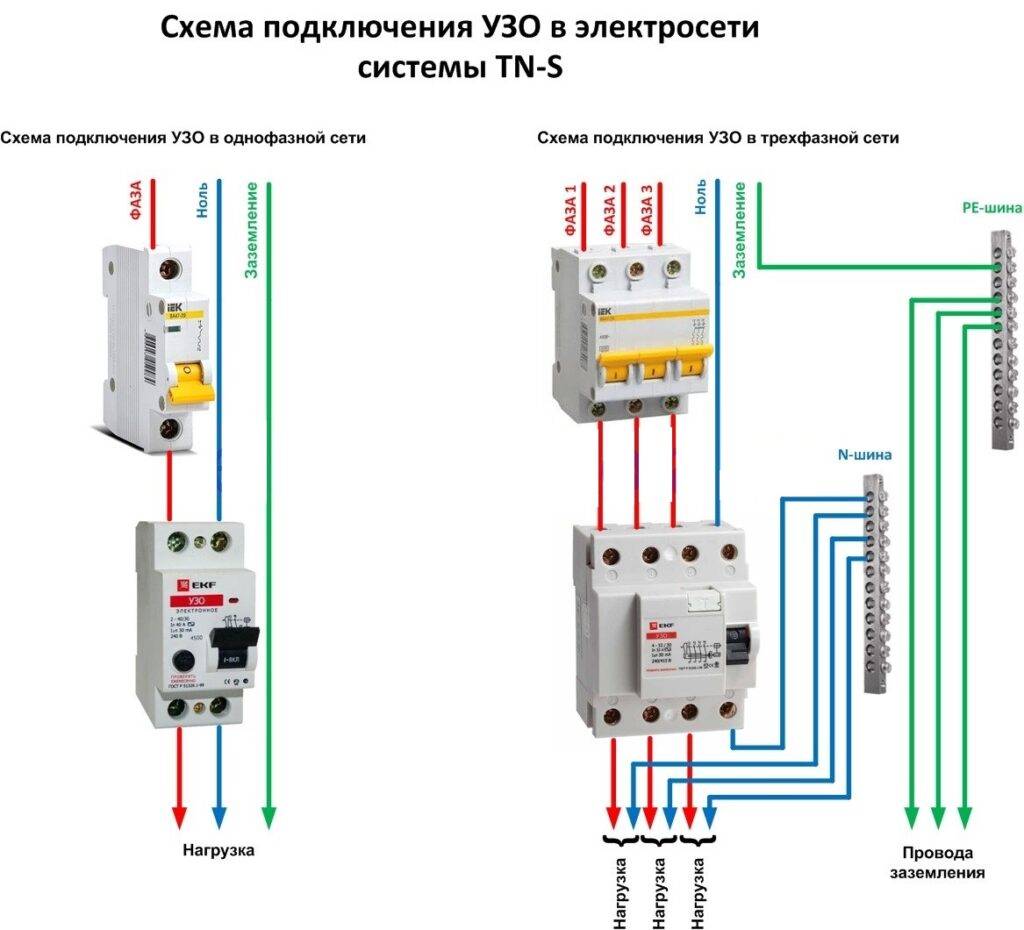
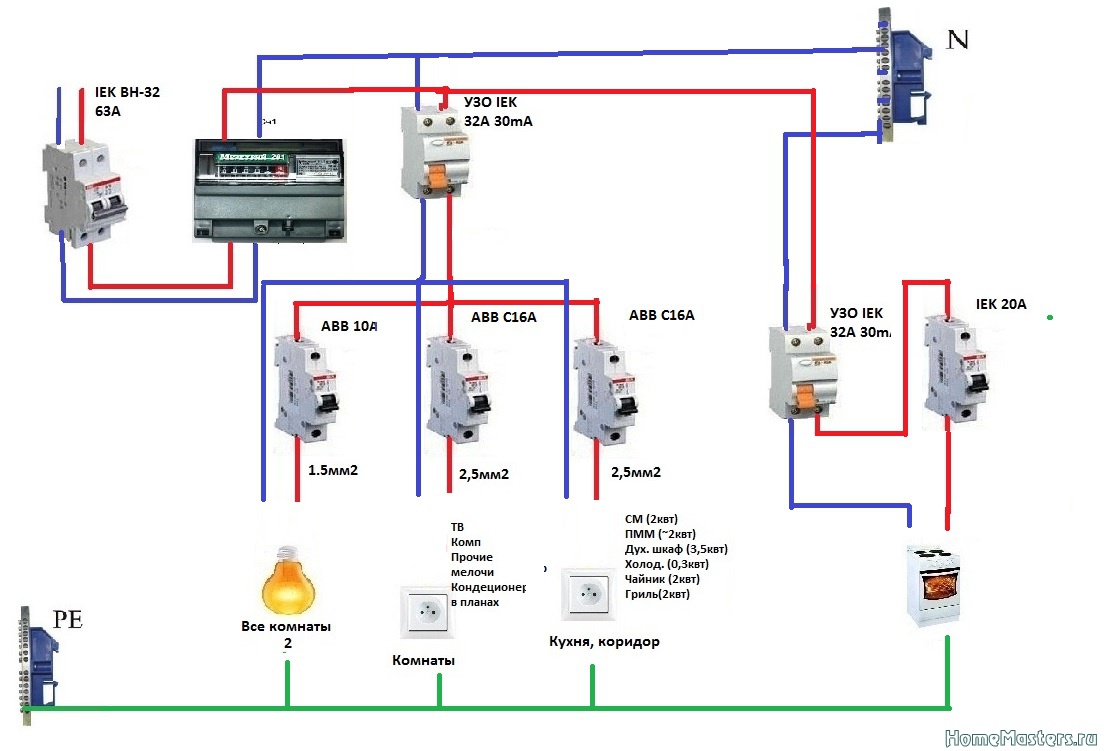
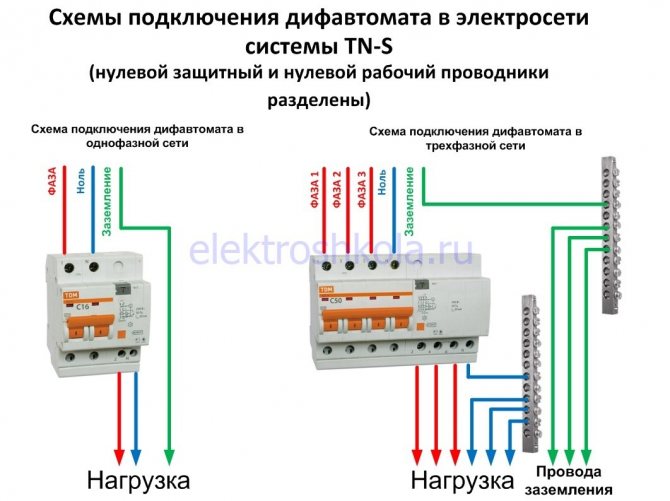
The connection of a three-phase RCD is carried out according to the "phase-zero" scheme. For the correct operation of the protective device, it is necessary to connect an RCD with grounding. Thus, an electric network "phase-zero-grounding" must be installed in the structure.
The grounding device being installed acts as a protective conductive element that diverts the supplied current into the ground. Zero and phase flows through the protective element and the switch, which monitor the leakage of electric currents. The correct operation of the RCD, as the main element, is based on its own “zero” and “phase”, thanks to which the supply currents will be controlled. If this device is used by several users, then the phase must be multiplied.
"Zero" requires the use of a separate protective element bus. If the electrical circuit uses 2 protection devices, then zero tires will turn out 3:
- total N;
- auxiliary - N1 and N2.
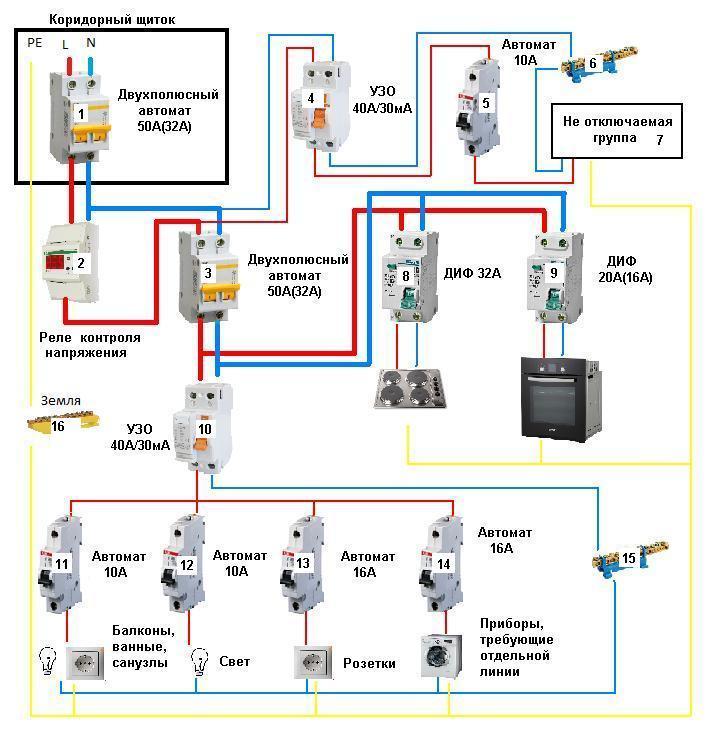
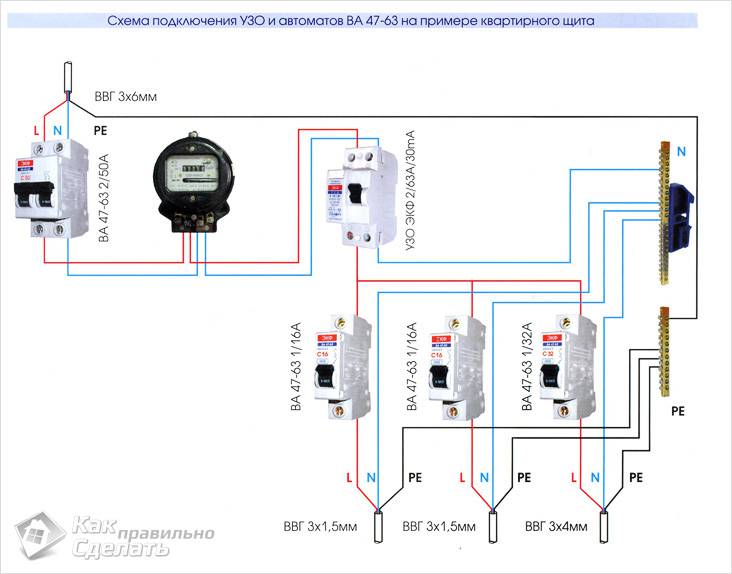
How to connect RCD correctly? RCD installation method. Schematic diagram (Fig. 8).
Rice. 8 Working diagram for connecting an RCD with grounding
The connection of the RCD in the apartment is carried out according to the plan shown in Figure 8, the essence of which is as follows.
Elements of phase (L) and zero (N) fall on the device "QF1". Next, the phase is distributed among the three switches "SF1", "SF2", "SF3". Each of them transfers the phase in the house to its user.
Zero (N) enters the protective device, and at the output the signal (N1) moves to the N1 bus, thanks to this, users receive a zero working conductor. Through the ground bus, PE conductors are connected, distributed among all consumers.
Why is it important not to make mistakes when installing a residual current device? All factors considered must be properly considered so that installation errors do not lead to dire consequences.
Errors during the installation of the RCD
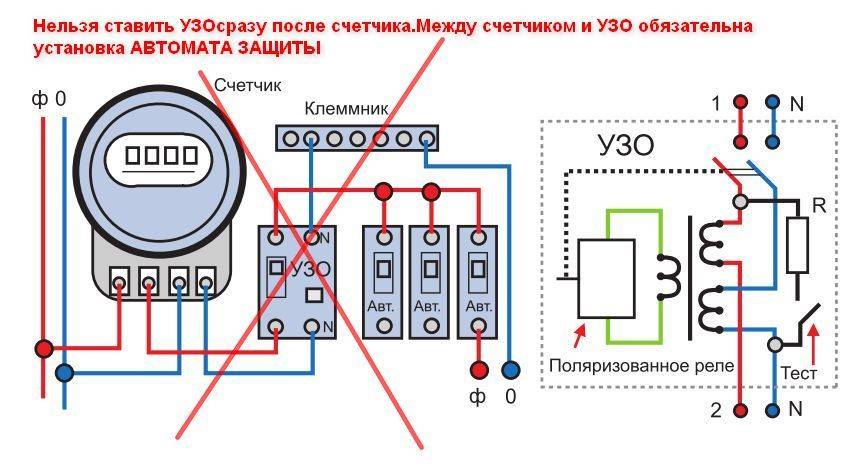
An example of an incorrect RCD connection
To ensure the stable and safe operation of the power grid, the following errors must be avoided:
RCD input terminals are connected to the network after a special machine. Direct connection is strictly prohibited.
It is necessary to connect correctly and not confuse zero and phase contacts
To facilitate this task, there are special designations on the case of the devices.
In the absence of a grounding conductor, it is strictly forbidden to replace it with a wire thrown over a water pipe or radiator.
When buying devices, pay attention to their main performance characteristics, current values. If the line is rated at 50 A, the instrument must have a minimum of 63 A.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
This video concludes an article about devices used as protective systems for electrical networks, equipment and users of apartments and private houses. Review material with all the subtleties of use, which will certainly come in handy for practice.
Connecting an RCD without grounding in modern-style apartments is not only not recommended, but also prohibited. If there is a need to install equipment in the electrical panel, be sure to contact the master serving the house. All work regarding the filling of the general apartment shield must be carried out by a qualified specialist.
Tell us about how you connected a residual current device to interrupt the power supply in the event of a dangerous situation. It is possible that your advice will be very useful to site visitors. Please leave comments in the block below, post photos, ask questions.