- What are amps
- Translation rules
- Single phase electrical circuit
- Three-phase electrical circuit
- Basic rules for converting amperes to kilowatts in three-phase networks
- Examples of converting amperes to kilowatts
- Example No. 1 - converting A to kW in a single-phase 220V network
- Example No. 2 - reverse translation in a single-phase network
- Example No. 3 - converting amperes to kW in a three-phase network
- Example No. 4 - reverse translation in a three-phase network
- Methods for selecting a difavtomat
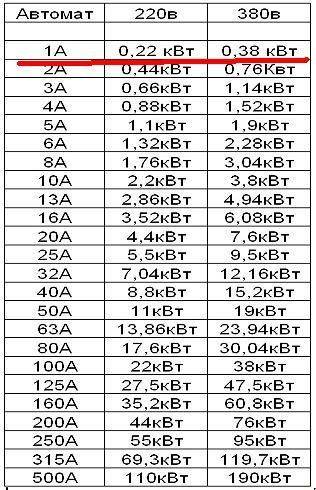
- Tabular Method
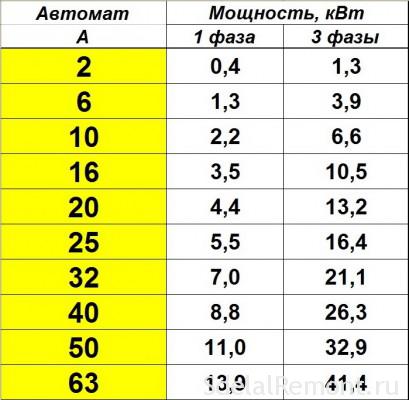
- Graphic method
- How many watts are in a kilowatt?
- We carry out calculations
- Calculator for calculating the current strength from a known value of power consumption
- Calculator for calculating power consumption by measured value of current strength
- Preliminary calculations
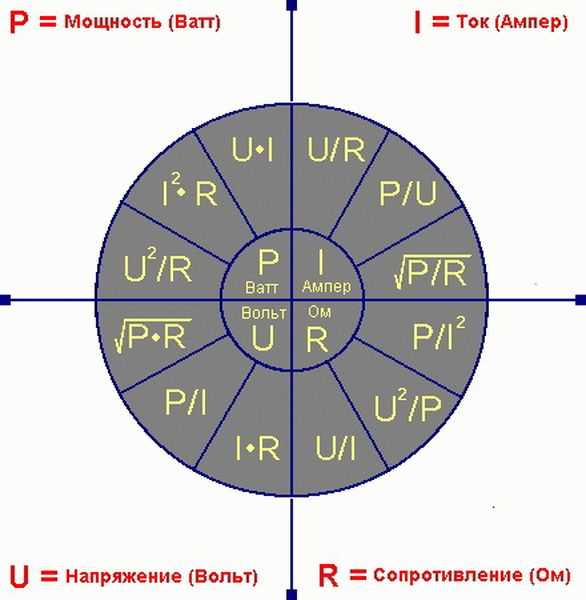
- The relationship of basic electrical quantities
- Single and three-phase connection
- Typical household voltage
- 380 volt networks
- Star connection
- Delta connection
- Automaton calculation parameters
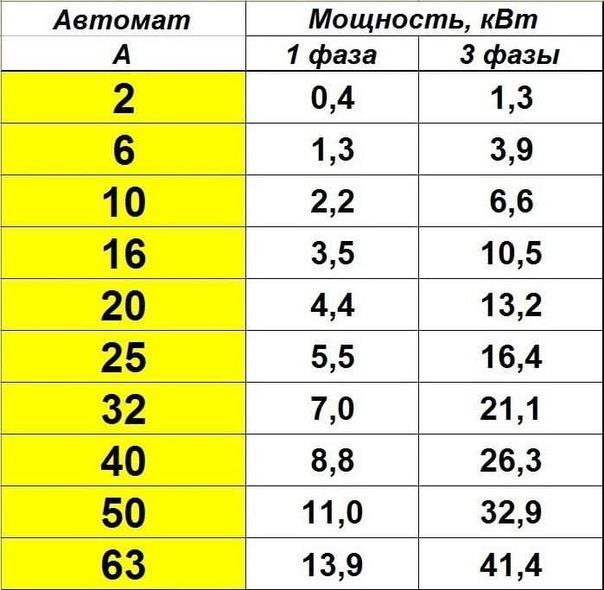
- How to convert amperes to kilowatts - table
What are amps
You should brush up on the definition of current strength, which is expressed in amperes. From the course of physics it is known that the strength of the current is determined by the amount of charge transferred through the volume in a certain period of time. It is not clear and not always clear.
It is easier to accept that the current is the amount of heating of the elements of the electrical circuit.The greater the current, the more heat will be released.
A large number of household and industrial appliances and devices use the heating property of the current:
- Heating devices (electric stoves, kettles, irons).
- Incandescent lamps (glow of an overheated filament).
 The simplest electric boiler
The simplest electric boiler
Fuses used for short circuit protection also use the heating property of the current. In fuses, this is a burnout of a thin calibrated wire, in automatic switches, it is a bending of a bimetallic plate.
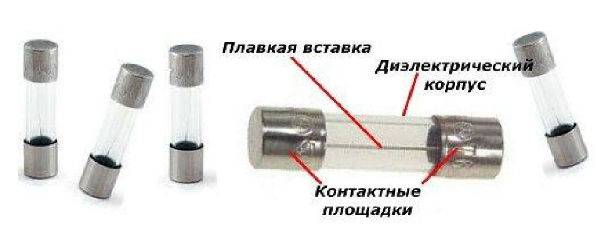 Fuse device
Fuse device
Translation rules
Often studying the instructions attached to some devices, you can see the designation of power in volt-amperes. Experts know the difference between watts (W) and volt-amperes (VA), but in practice these quantities mean the same thing, so nothing needs to be converted here. But kW / h and kilowatts are different concepts and should not be confused in any case.
To demonstrate how to express electrical power in terms of current, you need to use the following tools:
tester;
clamp meters;
electrical reference book;
calculator.
When converting amperes to kW, the following algorithm is used:
- Take a voltage tester and measure the voltage in the electrical circuit.
- Using current measuring keys, measure the current strength.
- Recalculate using the formula for DC or AC voltage.
As a result, power is obtained in watts. To convert them to kilowatts, divide the result by 1000.
Single phase electrical circuit
Most household appliances are designed for a single-phase circuit (220 V).The load here is measured in kilowatts, and the AB marking contains amperes.
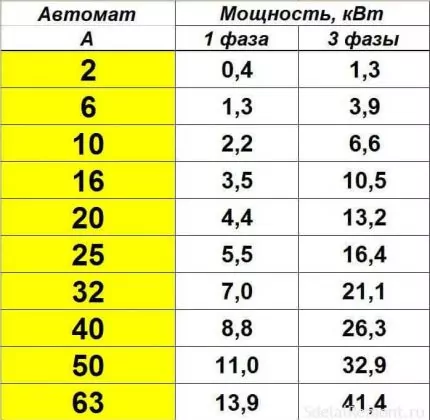
In order not to engage in calculations, when choosing a machine, you can use the ampere-watt table. There are already ready-made parameters obtained by performing a translation in compliance with all the rules
The key to the translation in this case is Ohm's law, which states that P, i.e. power, equal to I (current) times U (voltage). We talked in more detail about the calculation of power, current and voltage, as well as the relationship between these quantities, in this article.
It follows from this:
kW = (1A x 1 V) / 1 0ᶾ
But what does it look like in practice? To understand, consider a specific example.
Suppose an automatic fuse on an old-type meter is rated at 16 A. In order to determine the power of devices that can be safely connected to the network at the same time, it is necessary to convert amperes to kilowatts using the above formula.
We get:
220 x 16 x 1 = 3520 W = 3.5 kW
The same conversion formula applies for both direct and alternating current, but it is valid only for active consumers, such as incandescent lamp heaters. With a capacitive load, a phase shift necessarily occurs between current and voltage.
This is the power factor or cos φ
Whereas in the presence of only an active load, this parameter is taken as a unit, then with a reactive load it must be taken into account
If the load is mixed, the parameter value fluctuates in the range of 0.85. The smaller the reactive power component, the smaller the losses and the higher the power factor. For this reason, the last parameter is sought to be increased. Manufacturers usually indicate the value of the power factor on the label.
Three-phase electrical circuit
In the case of alternating current in a three-phase network, the value of the electric current of one phase is taken, then multiplied by the voltage of the same phase. What you get is multiplied by cosine phi.
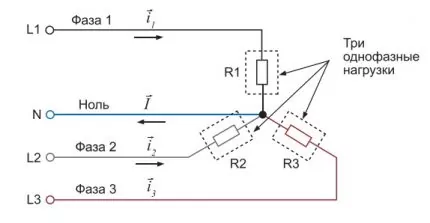
The connection of consumers can be made in one of two options - a star and a triangle. In the first case, these are 4 wires, of which 3 are phase, and one is zero. In the second, three wires are used
After calculating the voltage in all phases, the data obtained are added up. The amount received as a result of these actions is the power of the electrical installation connected to the three-phase network.
The main formulas are as follows:
Watt = √3 Amp x Volt or P = √3 x U x I
Amp \u003d √3 x Volt or I \u003d P / √3 x U
You should have an idea about the difference between phase and linear voltage, as well as between linear and phase currents. In any case, the conversion of amperes to kilowatts is carried out according to the same formula. An exception is the delta connection when calculating loads connected individually.
On the cases or packaging of the latest models of electrical appliances, both the current and power are indicated. With these data, we can consider the question of how to quickly convert amperes to kilowatts resolved.
Specialists use a confidential rule for alternating current circuits: the current strength is divided by two, if you need to roughly calculate the power in the process of selecting ballasts. They also act when calculating the diameter of conductors for such circuits.
Basic rules for converting amperes to kilowatts in three-phase networks
In this case, the basic formulas will be:
- To begin with, to calculate Watt, you need to know that Watt \u003d √3 * Ampere * Volt. This results in the following formula: P = √3*U*I.
- For the correct calculation of Ampere, you need to lean towards the following calculations:
Amp \u003d Wat / (√3 * Volt), we get I \u003d P / √3 * U
You can consider an example with a kettle, it consists in this: there is a certain current, it passes through the wiring, then when the kettle starts its work with a power of two kilowatts, and also has a variable electric power of 220 volts. For this case, you need to use the following formula:
I \u003d P / U \u003d 2000/220 \u003d 9 Amps.
If we consider this answer, we can say about it that this is a small tension. When selecting the cord to be used, it is necessary to correctly and intelligently select its section. For example, an aluminum cord can withstand much lower loads, but a copper wire with the same cross section can withstand a load twice as powerful.
Therefore, in order to correctly calculate and convert amperes to kilowatts, it is necessary to adhere to the above induced formulas. You should also be extremely careful when working with electrical appliances so as not to harm your health and not spoil this unit, which will be used in the future.
From the school physics course, we all know that the strength of the electric current is measured in amperes, and the mechanical, thermal and electrical power is measured in watts. These physical quantities are interconnected by certain formulas, but since they are different indicators, it is impossible to simply take and translate them into each other. To do this, one unit must be expressed in terms of others.
Electric current power (MET) is the amount of work done in one second. The amount of electricity that passes through the cross section of the cable in one second is called the strength of the electric current.MET in this case is a directly proportional dependence of the potential difference, in other words, voltage, and current strength in the electrical circuit.
Now let's figure out how the strength of the electric current and power are related in various electrical circuits.
We need the following set of tools:
- calculator
- electrotechnical reference book
- clamp meter
- multimeter or similar device.
The algorithm for converting A to kW in practice is as follows:
1. We measure with a voltage tester in an electrical circuit.
2. We measure the current strength with the help of current-measuring keys.
3. With a constant voltage in the circuit, the current value is multiplied by the network voltage parameters. As a result, we get the power in watts. To convert it to kilowatts, divide the product by 1000.
4. With an alternating voltage of a single-phase power supply, the current value is multiplied by the mains voltage and by the power factor (cosine of the angle phi). As a result, we will get the active consumed MET in watts. Similarly, we translate the value into kW.
5. The cosine of the angle between the active and full MET in the power triangle is equal to the ratio of the first to the second. The angle phi is the phase shift between current and voltage. It occurs as a result of inductance. With a purely resistive load, for example, in incandescent lamps or electric heaters, the cosine phi is equal to one. With a mixed load, its values vary within 0.85. The power factor always strives to increase, since the smaller the reactive component of the MET, the lower the losses.
6. With an alternating voltage in a three-phase network, the parameters of the electric current of one phase are multiplied by the voltage of this phase. The calculated product is then multiplied by the power factor.Similarly, the MET of other phases is calculated. Then all values are summed up. With a symmetrical load, the total active MET of the phases is equal to three times the product of the cosine of the angle phi by the phase electric current and the phase voltage.
Note that on most modern electrical appliances, the current strength and the consumed MET are already indicated. You can find these parameters on the packaging, case or in the instructions. Knowing the initial data, converting amperes to kilowatts or amperes to kilowatts is a matter of a few seconds.
For electrical circuits with alternating current, there is an unspoken rule: in order to get an approximate power value when calculating the cross-sections of conductors and when choosing starting and control equipment, you need to divide the current strength by two.
Examples of converting amperes to kilowatts
Converting amperes to kilowatts is a fairly simple mathematical operation.
 It happens that on the label of an electrical appliance there is a power value in kW. In this case, you will have to convert kilowatts to amperes. In this case, I \u003d P: U \u003d 1000: 220 \u003d 4.54 A. The opposite is also true - P \u003d I x U \u003d 1 x 220 \u003d 220 W \u003d 0.22 kW
It happens that on the label of an electrical appliance there is a power value in kW. In this case, you will have to convert kilowatts to amperes. In this case, I \u003d P: U \u003d 1000: 220 \u003d 4.54 A. The opposite is also true - P \u003d I x U \u003d 1 x 220 \u003d 220 W \u003d 0.22 kW
There are also many online programs where you just need to enter known parameters and press the appropriate button.
Example No. 1 - converting A to kW in a single-phase 220V network
We are faced with the task of determining the maximum power allowed for a single-pole circuit breaker with a rated current of 25 A.
Let's apply the formula:
P = U x I
Substituting the values that are known, we get: P \u003d 220 V x 25 A \u003d 5,500 W \u003d 5.5 kW.
This means that consumers can be connected to this machine, the total power of which does not exceed 5.5 kW.
Using the same scheme, you can solve the issue of selecting the wire section for an electric kettle that consumes 2 kW.
In this case, I \u003d P: U \u003d 2000: 220 \u003d 9 A.
This is a very small value. You need to seriously approach the choice of wire cross-section and material. If you give preference to aluminum, it will withstand only light loads, copper with the same diameter will be twice as powerful.
We discussed in more detail about choosing the right wire cross-section for a home wiring device, as well as the rules for calculating the cable cross-section by power and by diameter, in the following articles:
- Wire cross section for home wiring: how to calculate correctly
- Calculation of the cable cross-section by power and current: how to correctly calculate the wiring
- How to determine the wire cross-section by diameter and vice versa: ready-made tables and calculation formulas
Example No. 2 - reverse translation in a single-phase network
Let's complicate the task - we will demonstrate the process of converting kilowatts to amperes. We have a certain number of consumers.
Among them:
- four incandescent lamps, each 100 W;
- one heater with a power of 3 kW;
- one PC with a power of 0.5 kW.
The determination of the total power is preceded by bringing the values of all consumers to one indicator, more precisely, kilowatts should be converted to watts.
 Sockets, AB contain amperes in their marking. For an uninitiated person, it is difficult to understand whether the load in fact corresponds to the calculated one, and without this it is impossible to choose the right fuse
Sockets, AB contain amperes in their marking. For an uninitiated person, it is difficult to understand whether the load in fact corresponds to the calculated one, and without this it is impossible to choose the right fuse
The heater power is 3 kW x 1000 = 3000 watts. Computer power - 0.5 kW x 1000 = 500 watts. Lamps - 100 W x 4 pcs. = 400 W.
Then the total power is: 400 W + 3000 W + 500 W = 3900 W or 3.9 kW.
This power corresponds to the current I \u003d P: U \u003d 3900W: 220V \u003d 17.7 A.
It follows from this that an automatic machine should be purchased, designed for a rated current of not less than 17.7 A.
The most appropriate load with a power of 2.9 kW is a standard single-phase 20 A automatic machine.
Example No. 3 - converting amperes to kW in a three-phase network
The algorithm for converting amperes to kilowatts and vice versa in a three-phase network differs from a single-phase network only by the formula. Suppose you need to calculate what is the maximum power that an AB can withstand, the rated current of which is 40 A.
Substitute the known data into the formula and get:
P \u003d √3 x 380 V x 40 A \u003d 26,296 W \u003d 26.3 kW
A three-phase battery for 40 A is guaranteed to withstand a load of 26.3 kW.
Example No. 4 - reverse translation in a three-phase network
If the power of the consumer connected to the three-phase network is known, it is easy to calculate the current of the machine. Let's say there is a three-phase consumer with a capacity of 13.2 kW.
In watts, this would be: 13.2 kt x 1000 = 13,200 watts
Further, current strength: I \u003d 13200W: (√3 x 380) \u003d 20.0 A
It turns out that this electrical consumer needs an automatic machine with a nominal value of 20 A.
For single-phase devices, there is the following rule: one kilowatt corresponds to 4.54 A. One ampere is 0.22 kW or 220 V. This statement is a direct result of the formulas for a voltage of 220 V.
Methods for selecting a difavtomat
For example, consider a kitchen where a large amount of equipment is connected. First, you need to set the total power rating for a room with a refrigerator (500 W), a microwave oven (1000 W), a kettle (1500 W) and a hood (100 W). The total power indicator is 3.1 kW. Based on it, various methods for choosing a 3-phase machine are used.
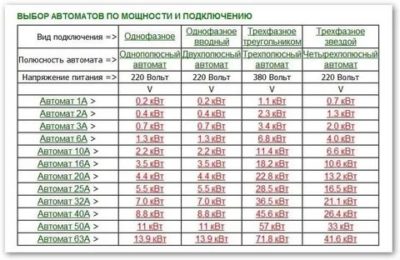
Tabular Method
Based on the table of devices, a single-phase or three-phase device is selected according to the connection power.But the value in the calculations may not match the tabular data. For a 3.1 kW network section, you will need a 16 A model - the closest value is 3.5 kW.
Graphic method
The selection technology does not differ from the tabular one - you will need to find a graph on the Internet. In the figure, as standard, horizontally there are switches with their current load, vertically - the power consumption in one section of the circuit.
To establish the power of the device, you will need to draw a line horizontally to the point with the rated current. The total network load of 3.1 kW corresponds to a 16 A switch.
How many watts are in a kilowatt?
The watt is the globally accepted unit of power, introduced into the International System of Units (SI) in 1960.
The name comes from the name of the Scotch-Irish mechanical inventor James Watt (Watt), who created the universal steam engine. Before the invention of the steam engine, there were no generally accepted units for measuring power. Therefore, to show the performance of his invention, James Watt, as a unit of measurement, began to use horsepower. He determined this value experimentally, observing the work of draft horses at the mill.
Horsepower, as a unit of power, is still used in the automotive industry today. Most European countries and Russia use "metric" horsepower. It is designated: h.p. - in Russia, PS - in Germany, ch - in France, pk - in Holland. 1 HP = 735.49875 W = 0.73549875 kW. In the US, there are two types of horsepower: "boiler" = 9809.5 watts and "electric" = 746 watts.We hope this answer will allow you to determine how many watts are in a kilowatt. If you are interested, then read about grounding.
We carry out calculations
As already mentioned, to begin with, the initial values \u200b\u200bmust be brought to a single presented. The best option is to “pure” values, that is, volts, amperes, watts.
Calculation for DC
Here - no difficulties. The formula has been shown above.
When calculating power by current strength:
P=U×I
If the current strength is calculated from a known power,
I=P/U
Calculation for single-phase alternating current
Here may be a feature. The fact is that some types of loads in operation consume not only ordinary, active power, but also the so-called reactive power. Simply put, it is spent on ensuring the operating conditions of the device - the creation of electromagnetic fields, induction, the charge of powerful capacitors. Interestingly, this component does not particularly affect the overall consumption of electricity, since, figuratively speaking, it is “dumped” back into the network. But to determine the ratings of protective automation, cable cross-section - it is desirable to take it into account.
For this, a special power factor is used, otherwise called the cosine φ (cos φ). It is usually indicated in the technical characteristics of devices and devices with a pronounced reactive power component.

The value of the power factor (cos φ) on the nameplate of the asynchronous motor.
Formulas with this coefficient take the following form:
P = U × I × cos φ
and
I = P / (U × cos φ)
For devices in which reactive power is not used (incandescent lamps, heaters, electric stoves, television and office equipment, etc.), this coefficient is equal to one, and does not affect the calculation results.But if for products, for example, with electric drives or inductors, this indicator is indicated in the passport data, it would be correct to take it into account. The difference in current strength can be quite significant.
Calculation for three-phase alternating current
We will not delve into the theory and varieties of three-phase load connection schemes. Let's just give a slightly modified formulas used for calculations in such conditions:
P = √3 × U × I × cos φ
and
I = P / (√3 × U × cos φ)
To make it easier for our reader to make the necessary calculations, two calculators are placed below.
For both, the common reference value is voltage. And then, depending on the direction of calculation, either the measured value of the current or the known value of the power of the device is indicated.
The default power factor is set to one. That is, for direct current and for devices that use only active power, it is left as is, by default.
Other questions on the calculation, probably, should not arise.
Calculator for calculating the current strength from a known value of power consumption
Go to calculations
Specify the requested values and click "CALCULATE CURRENT"
Supply voltage
Power consumption
The calculation is carried out:
- for a direct current circuit or for an alternating single-phase current
- for a three-phase alternating current circuit
Power factor (cos φ)
Calculator for calculating power consumption by measured value of current strength
Go to calculations
Specify the requested values and click "CALCULATE POWER CONSUMPTION"
Supply voltage
Current strength
The calculation is carried out:
- for a direct current circuit or for an alternating single-phase current
- for a three-phase alternating current circuit
Power factor (cos φ)
The obtained values can be used for further selection of the necessary protective or stabilizing equipment, for forecasting energy consumption, for analyzing the correct organization of your home electrical network.
And an example of how the parameters for a dedicated line are calculated, followed by the selection of a circuit breaker, is well shown in the video clip brought to your attention:
Preliminary calculations
The first step is to check which of the sockets are controlled by the same machine to which the new equipment is connected. It is possible that part of the apartment's lighting is powered by the same automatic shutdown device. And sometimes there is a completely incomprehensible installation of electrical wiring in an apartment, in which all the power supply is powered through a single machine.
After the number of consumers to be switched on is determined, their consumption must be added to obtain a total indicator, i.e. find out how many watts appliances can consume, provided they are turned on at the same time. Of course, it is unlikely that they will all work together, but this cannot be ruled out.
Stress formula
With such calculations, one nuance must be taken into account - on some devices, the power consumption is indicated not by a static indicator, but by a range. In this case, the upper power limit is taken, which will provide a small margin. This is much better than taking the minimum values, because in this case the automatic shutdown device will operate at full load, which is completely unacceptable.
Having made the required calculations, you can proceed to the calculations.
The relationship of basic electrical quantities
Power and current can be related through voltage (U) or circuit resistance (R).However, in practice, it is difficult to apply the formula P = I2 * R, since it is difficult to accurately calculate the resistance in a real section.
Single and three-phase connection
Most residential electrical wiring is single-phase.
In this case, the recalculation of the apparent power (S) and the strength of the alternating current (I) using a known voltage occurs according to the following formulas, which follow from the classical Ohm's law:
S=U*I
I=S/U
Now the practice of bringing a three-phase network to residential, domestic and small industrial facilities has become widespread. This is justified from the standpoint of minimizing the cost of cables and transformers, which is borne by the company supplying electricity.
 When summing up a three-phase network, an introductory three-pole machine is installed (top left), a three-phase meter (top right) and for each selected circuit - ordinary single-pole devices (bottom left)
When summing up a three-phase network, an introductory three-pole machine is installed (top left), a three-phase meter (top right) and for each selected circuit - ordinary single-pole devices (bottom left)
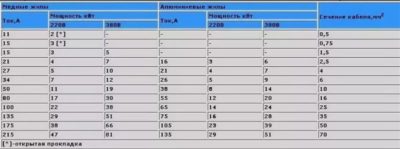
The cross section of the wires and the rated power when using three-phase consumers are also determined by the current strength, which is calculated as follows:
Il = S / (1.73 * Ul)
Here the index “l” means the linear nature of the quantities.
When planning and subsequent wiring indoors, it is better to separate three-phase consumers into separate circuits. Devices operating from standard 220 V try to scatter them more or less evenly over the phases, so that there is no significant power imbalance.
Sometimes they allow mixed connection of devices operating from both one and three phases. This situation is not the simplest, so it is better to consider it with a specific example.
Let the circuit include a three-phase induction furnace with an active power of 7.0 kW and a power factor of 0.9.Phase “A” is connected to a microwave oven 0.8 kW with a factor of “2” of the starting current, and to phase “B” - an electric kettle 2.2 kW. It is necessary to calculate the parameters of the electrical network for this section.
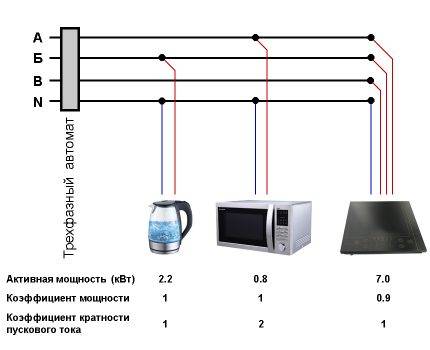 Scheme of connecting devices to the network. With this configuration, a three-phase circuit breaker is always installed. It is forbidden to use several single-phase circuit breakers for protection
Scheme of connecting devices to the network. With this configuration, a three-phase circuit breaker is always installed. It is forbidden to use several single-phase circuit breakers for protection
Let's determine the total power of all devices:
Si = Pi / cos(f) = 7000 / 0.9 = 7800 V*A;
Sm = Pm * 2 = 800 * 2 = 1600 V * A;
SWith = Pc = 2200 V * A.
Let's determine the current strength of each device:
Ii = Si / (1.73 * Ul) = 7800 / (1.73 * 380) = 11.9 A;
Im = Sm /uf = 1600 / 220 = 7.2 A;
Ic = Sc /uf = 2200 / 220 = 10 A.
Let's determine the current strength by phases:
IA \u003d Ii + Im = 11.9 + 7.2 = 19.1 A;
IB = Ii + Ic = 11.9 + 10 = 21.9 A;
IC = Ii = 11.9 A.
The maximum current with all electrical appliances on flows through phase “B” and will be equal to 21.9 A. A sufficient combination to ensure the smooth operation of all devices in this circuit is a cross section of copper conductors of 4.0 mm2 and a circuit breaker for 20 or 25 A.
Typical household voltage
Since power and current are related through voltage, it is necessary to accurately determine this value. Prior to the introduction from October 2015 of GOST 29322-2014, the value for an ordinary network was 220 V, and for a three-phase network - 380 V.
According to the new document, these indicators are brought into line with European requirements - 230 / 400 V, but most household power supply systems still operate according to the old parameters.
 You can get the real voltage value using a voltmeter. If the numbers are much less than the reference, then you need to connect the input stabilizer
You can get the real voltage value using a voltmeter. If the numbers are much less than the reference, then you need to connect the input stabilizer
A deviation of 5% of the actual value from the reference value is permissible for any period, and 10% - for no more than one hour. When the voltage drops, some consumers, such as an electric kettle, incandescent lamp or microwave oven, lose power.
But if the device is equipped with an integrated stabilizer (for example, a gas boiler) or has a separate switching power supply, then the power consumption will remain constant.
In this case, given that I = S / U, the voltage drop will cause the current to increase. Therefore, it is not recommended to select the cross section of the cable cores “back to back” to the maximum calculated values, but it is desirable to have a margin of 15-20%.
380 volt networks
The conversion of current values to power for a three-phase network does not differ from the above, only it is necessary to take into account the fact that the current consumed by the load is distributed over three phases of the network. The conversion of amperes to kilowatts is carried out taking into account the power factor.
In a three-phase network, you need to understand the difference between phase and line voltages, as well as line and phase currents. There are also 2 options for connecting consumers:
- Star. 4 wires are used - 3 phase and 1 neutral (zero). The use of two wires, phase and zero, is an example of a single-phase 220 volt network.
- Triangle. 3 wires are used.
The formulas for how to convert amperes to kilowatts for both types of connection are the same. The difference is only in the case of a delta connection for the calculation of separately connected loads.
Star connection
If we take a phase conductor and zero, then there will be a phase voltage between them. Linear voltage is called between the phase wires, and it is greater than the phase:
Ul = 1.73•Uf
The current flowing in each of the loads is the same as in the network conductors, so the phase and line currents are equal. Under the condition of load uniformity, there is no current in the neutral conductor.
The conversion of amperes to kilowatts for a star connection is made according to the formula:
P=1.73•Ul•Il•cosø
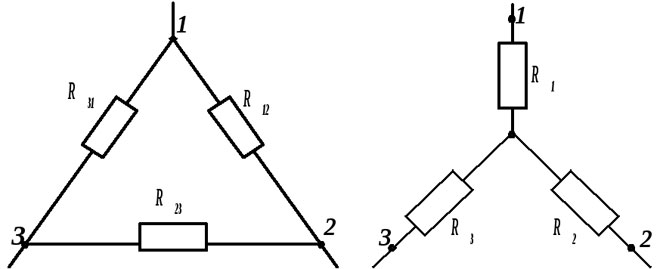
Delta connection
With this type of connection, the voltage between the phase wires is equal to the voltage on each of the three loads, and the currents in the wires (phase currents) are related to the linear (flowing in each load) expression:
Il \u003d 1.73•If
The translation formula is the same as above for the “star”:
P=1.73•Ul•Il•cosø
Such a conversion of values is used when choosing circuit breakers installed in the phase conductors of the supply network. This is true when using three-phase consumers - electric motors, transformers.
If separate loads connected by a delta are used, then the protection is placed in the load circuit in the formula for calculation using the value of the phase current:
P=3•Ul•If•cosø
The reverse conversion of watts to amperes is carried out according to inverse formulas, taking into account the connection conditions (connection type).
It will help to avoid the calculation of a pre-compiled conversion table, which shows the values for the active load and the most common value cosø=0.8.
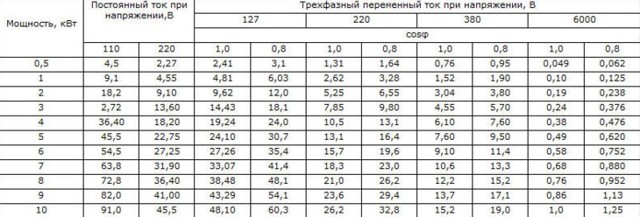
Table 1. Converting kilowatts to amperes for 220 and 380 volts with cosø correction.
| power, kWt | Three-phase alternating current, A | |||
| 220 V | 380 V | |||
| coso | ||||
| 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | |
| 0,5 | 1.31 | 1.64 | 0.76 | 0.95 |
| 1 | 2.62 | 3.28 | 1.52 | 1.90 |
| 2 | 5.25 | 6.55 | 3.,4 | 3.80 |
| 3 | 7.85 | 9.80 | 4.55 | 5.70 |
| 4 | 10.5 | 13.1 | 6.10 | 7.60 |
| 5 | 13.1 | 16.4 | 7.60 | 9.50 |
| 6 | 15.7 | 19.6 | 9.10 | 11.4 |
| 7 | 18.3 | 23.0 | 10.6 | 13.3 |
| 8 | 21.0 | 26.2 | 12.2 | 15.2 |
| 9 | 23.6 | 29.4 | 13.7 | 17.1 |
| 10 | 26.2 | 32.8 | 15.2 | 19.0 |
Read more:
How to convert amps to watts and vice versa?
What is active and reactive power of alternating electric current?
What is a voltage divider and how to calculate it?
What is phase and line voltage?
How to translate kilowatts to horsepower?
Automaton calculation parameters
Each circuit breaker primarily protects the wiring connected after it. The main calculations of these devices are carried out according to the rated load current. Power calculations are carried out when the entire length of the wire is designed for the load, in accordance with the rated current.
The final choice of rated current for the machine depends on the wire section. Only then can the load be calculated. The maximum current allowed for a wire with a certain cross section must be greater than the rated current indicated on the machine. Thus, when choosing a protective device, the minimum wire cross-section present in the electrical network is used.
When consumers have a question about which machine should be installed for 15 kW, the table also takes into account a three-phase electrical network. There is a method for such calculations. In these cases, the rated power of a three-phase machine is determined as the sum of the powers of all electrical appliances planned to be connected through a circuit breaker.
For example, if the load of each of the three phases is 5 kW, then the value of the operating current is determined by multiplying the sum of the powers of all phases by a factor of 1.52. Thus, it turns out 5x3x1.52 \u003d 22.8 amperes. The rated current of the machine must exceed the operating current. In this regard, a protective device with a rating of 25 A will be most suitable. The most common ratings of machines are 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 80 and 100 amperes.At the same time, the compliance of the cable cores with the declared loads is specified.
This technique can be used only in cases where the load is the same for all three phases. If one of the phases consumes more power than all the others, then the rating of the circuit breaker is calculated from the power of this particular phase. In this case, only the maximum power value is used, multiplied by a factor of 4.55. These calculations allow you to choose the machine not only according to the table, but also according to the most accurate data obtained.
How to convert amperes to kilowatts - table
Very often, knowing one value, it is necessary to determine another. This may be necessary for the selection of protective and switching equipment. For example, if you want to choose a circuit breaker or fuse with a known total power of all consumers.
Consumers can be incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps, irons, a washing machine, a boiler, a personal computer and other household appliances.
In another case, if there is a protective device with a known rated current, it is possible to determine the total power of all consumers that are allowed to “load” the circuit breaker or fuse.
You should be aware that the rated power consumption is usually indicated on electrical consumers, and the rated current is indicated on the protective device (automatic or fuse).
To convert amperes to kilowatts and vice versa, it is necessary to know the value of the third quantity, without which calculations are impossible. This is the value of the supply or rated voltage.If the standard voltage in the electrical (household) network is 220V, then the rated voltage is usually indicated on the consumers themselves and on the protective devices.
It should also be noted that in addition to the usual single-phase 220V network, a three-phase 380V electrical network is often used (usually in production). This must also be taken into account when calculating power and current strength.