- Selection of conductor cross-section by power and length
- Section calculation by formulas
- Section and laying method
- pivot table
- We measure the cross section of wires depending on the diameter
- About Measuring Instruments, Process Description
- Three main ways to determine the diameter of the wire
- Dependence of current, power and cross-section of conductors
- Power
- electric current
- Load
- Wire diameter measurement
- Micrometer
- Caliper
- Ruler
- Section according to GOST or TU
- General information about cable and wire
- Conductor materials
- Calculation of the cross-section of the wire of the electrical wiring according to the power of the connected electrical appliances
- Selection of the wire section for connecting electrical appliances to a three-phase 380 V network
- How to calculate the cable cross-section by power?
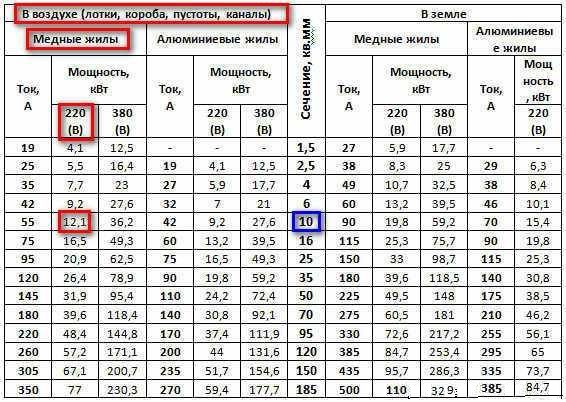
- Table of copper cable cross-section by current according to PUE-7
- Table of the section of the aluminum cable for current according to PUE-7
- Cable selection according to the PUE and GOST tables
- Why is it necessary to specify the cable cross-sections
- Ways to find out the real diameter of the wire
- What formulas should be used
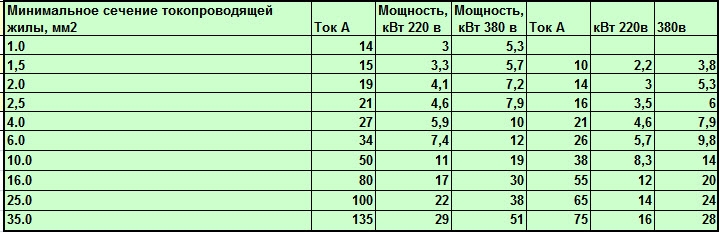
- Determine the cross section of the wire using the table
- How to calculate the cross section of a stranded wire
Selection of conductor cross-section by power and length
The length of the conductor determines the voltage that is supplied to the end point. A situation may arise when at the point of consumption the voltage is insufficient for the operation of electrical appliances.
In household electrical communications, these losses are neglected and a cable is taken ten to fifteen centimeters longer than necessary. This surplus is spent on switching. When connected to a switchboard, the margin is increased, taking into account the need to connect circuit breakers.
Cable laid in a closed way
When laying long lines, the inevitable voltage drop should be taken into account. Everyone has their own resistance, which is influenced by three main factors:
- Length measured in meters. With an increase in this indicator, losses increase.
- Cross section measured in square millimeters. If this parameter is increased, then the voltage drop decreases.
- The resistance of the conductor material, the value of which is taken from the reference data. They show the reference resistance of a wire with a cross section of one millimeter and a length of one meter.
The product of resistance and current represents the voltage drop numerically. This value should not exceed five percent. If it exceeds this indicator, then it is necessary to take a conductor with a large cross section.
More about how to calculate the cable cross section in the video:
Section calculation by formulas
The selection algorithm is as follows:
The conductor area is calculated along the length and maximum power according to the formula:
Source infopedia.su
Where:
P is power;
U - voltage;
cosf - coefficient.
For household electrical networks, the value of the coefficient is equal to one. For industrial communications, it is calculated as the ratio of active power to apparent power.
- In the PUE table there is a current cross section.
- The wiring resistance is calculated:
Where:
ρ is the resistance;
l is the length;
S is the cross-sectional area.
At the same time, do not forget that the current moves in both directions and in fact the resistance is equal to:
The voltage drop corresponds to the relationship:
In percentage terms, the voltage drop is as follows:
If the result exceeds five percent, then the nearest cross section with a large value is searched in the directory.
Such calculations are rarely performed by generic consumers of electricity. To do this, there are specialized specialists and a lot of reference material. Moreover, there are many online calculators on the Internet, with the help of which all calculations can be done in a couple of clicks.
Visually calculate the cable cross section using the formulas in the video:
Section and laying method
Another factor that affects the choice of conductor cross-section is the method of laying lines. There are two of them:
- open;
- closed.
In the first method, the wiring is placed in a special box or corrugated pipe and is located on the wall surface. The second option involves immuring the cable inside the finish or the main body of the walls.
Here, the thermal conductivity of the environment plays a major role. In the ground, heat is removed from the cable better than in air. Therefore, with a closed method, wires with a smaller cross section are taken than with an open one. The table below shows how the laying method affects the cross section of the conductor.
Laying method and conductor cross section
pivot table
There are tables that allow you to determine the required cross section using several parameters at once - current, power, conductor material, and so on. They are more convenient to use and one of them is placed below. It indicates the cross section of the wire for current and power, and also takes into account the laying method.
Wire cross section for current and power - table for copper and aluminum conductors
Perhaps the article came out somewhat boring and saturated with technical terms. However, the information contained in it should not be neglected. Since the reliability and safety of the functioning of the home electrical network depends on how correctly the wiring was chosen.
We measure the cross section of wires depending on the diameter
The cross section of a cable or other types of conductors is determined in several ways. The main thing is to take care of preliminary measurements. To do this, it is recommended to remove the top layer of insulation.
About Measuring Instruments, Process Description
Caliper, micrometer - the main tools to help with measurements. Most often, preference is given to devices of the mechanical group. But it is permissible to choose electronic analogues. Their main difference is digital special screens.
 Electronic caliper
Electronic caliper
The caliper is one of the tools available in every household. Therefore, it is often chosen when measuring the diameter of wires and cables. This also applies when the network continues to work - for example, inside an outlet or a switchboard device.
The following formula helps determine the cross section based on the diameter:
S = (3.14/4)*D2.
D is the letter indicating the diameter of the wire.
If there is more than one core in the structure, then measurements are carried out for each of the constituent elements separately. The results are then added together.
Further, everything can be calculated using the following formula:
Stot= S1+ S2+…
Stot is an indication of the total cross-sectional area.
S1, S2 and so on are the cross sections defined for each of the cores.
It is recommended to measure the parameter at least three times in order for the results to be accurate. Turning the conductor in different directions occurs every time. The result is an average value that is as close to reality as possible.
A regular ruler can be used if a caliper or micrometer is not at hand. The following manipulations are expected:
- Complete cleaning of the insulation layer at the core.
- Winding the turns around the pencil, as close as possible to each other. The minimum number of such components is 15-17 pieces.
- The winding is measured, along the length as a whole.
- The total value is divided by the number of turns.
The accuracy of the measurement is questionable if the turns do not fit evenly on the pencil, with gaps of a certain size left. To make the accuracy higher, it is recommended to measure the product from different sides. It is difficult to wind thick strands on ordinary pencils. Better yet, use calipers.
The cross-sectional area of the wire is calculated using the formula described earlier. This is done after completing the main measurements. You can rely on special tables.
A micrometer is advised to use in the case of the presence of ultra-thin veins in the composition. Otherwise, there is a high probability of mechanical damage.
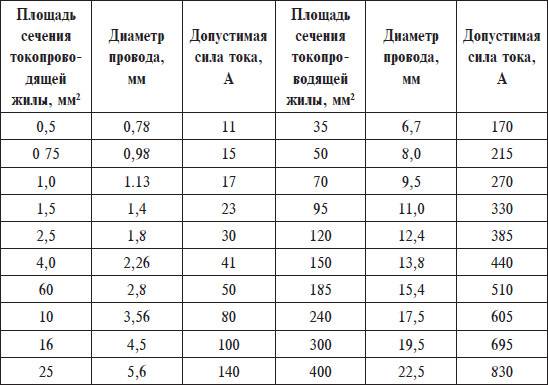
 Correspondence table for wire diameters and their cross-sectional area
Correspondence table for wire diameters and their cross-sectional area
Three main ways to determine the diameter of the wire
There are several ways, but each of them is based on determining the diameter of the core, followed by calculations of the final results.
Method one. With the help of appliances. Today, there are a number of devices that help measure the diameter of a wire or wire strand. This is a micrometer and caliper, which are both mechanical and electronic (see below).
This option is primarily suitable for professional electricians who are constantly involved in the installation of electrical wiring. The most accurate results can be obtained with a caliper. This technique has the advantage that it is possible to measure the diameter of a wire even on a section of a working line, for example, in a socket.
After you have measured the diameter of the wire, you need to make calculations using the following formula:
It must be remembered that the number "Pi" is 3.14, respectively, if we divide the number "Pi" by 4, we can simplify the formula and reduce the calculation to multiplying 0.785 by the diameter squared.
Method two. We use a line. If you decide not to spend money on the device, which is logical in this situation, then you can use a simple proven method to measure the cross section of a wire or wire ?. You will need a simple pencil, ruler and wire. Strip the core from the insulation, wind it tightly onto a pencil, and then measure the total length of the winding with a ruler (as shown in the figure).
Then divide the length of the wound wire by the number of strands. The resulting value will be the diameter of the wire section.
However, the following must be taken into account:
- the more cores you wind on a pencil, the more accurate the result will be, the number of turns should be at least 15;
- press the turns tightly against each other so that there is no free space between them, this will significantly reduce the error;
- take measurements several times (change the measurement side, the direction of the ruler, etc.). A few results obtained will help you again avoid a large error.
Pay attention to the disadvantages of this method of measurement:
- You can only measure the cross section of thin wires, since you can hardly wind a thick wire around a pencil.
- To begin with, you will need to purchase a small piece of the product before making the main purchase.
The formula discussed above applies to all measurements.
Method three. We use a table. In order not to carry out calculations according to the formula, you can use a special table that indicates the diameter of the wire? (in millimeters) and the cross section of the conductor (in square millimeters). Ready-made tables will give you more accurate results and save you a lot of time, which you do not have to spend on calculations.
| Conductor diameter, mm | Conductor cross section, mm² |
| 0.8 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 0.75 |
| 1.1 | 1 |
| 1.2 | 1.2 |
| 1.4 | 1.5 |
| 1.6 | 2 |
| 1.8 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 2.3 | 4 |
| 2.5 | 5 |
| 2.8 | 6 |
| 3.2 | 8 |
| 3.6 | 10 |
| 4.5 | 16 |
Dependence of current, power and cross-section of conductors
When choosing a cable, you must be guided by several criteria:
- the strength of the electric current that the cable will pass;
- power consumed by energy sources;
- current load on the cable.
Power
The most important parameter in electrical installation work (in particular, cable laying) is the throughput. The maximum power of the electricity transmitted through it depends on the cross section of the conductor.
Therefore, it is extremely important to know the total power of the energy consumption sources that will be connected to the wire.
Typically, manufacturers of household appliances, appliances and other electrical products indicate on the label and in the documentation attached to them the maximum and average power consumption. For example, a laundry machine may consume electricity in the range of tens of W/h in a rinse cycle to 2.7 kW/h when water is heated.
The average power of all electrical appliances and lighting devices in an apartment rarely exceeds 7500 W for a single-phase network. Accordingly, the cross-sections of cables in the wiring must be selected for this value.
On a note. It is recommended to round the cross section in the direction of increasing power due to a possible increase in electricity consumption in the future. Usually, the next largest cross-sectional area is taken from the calculated value.
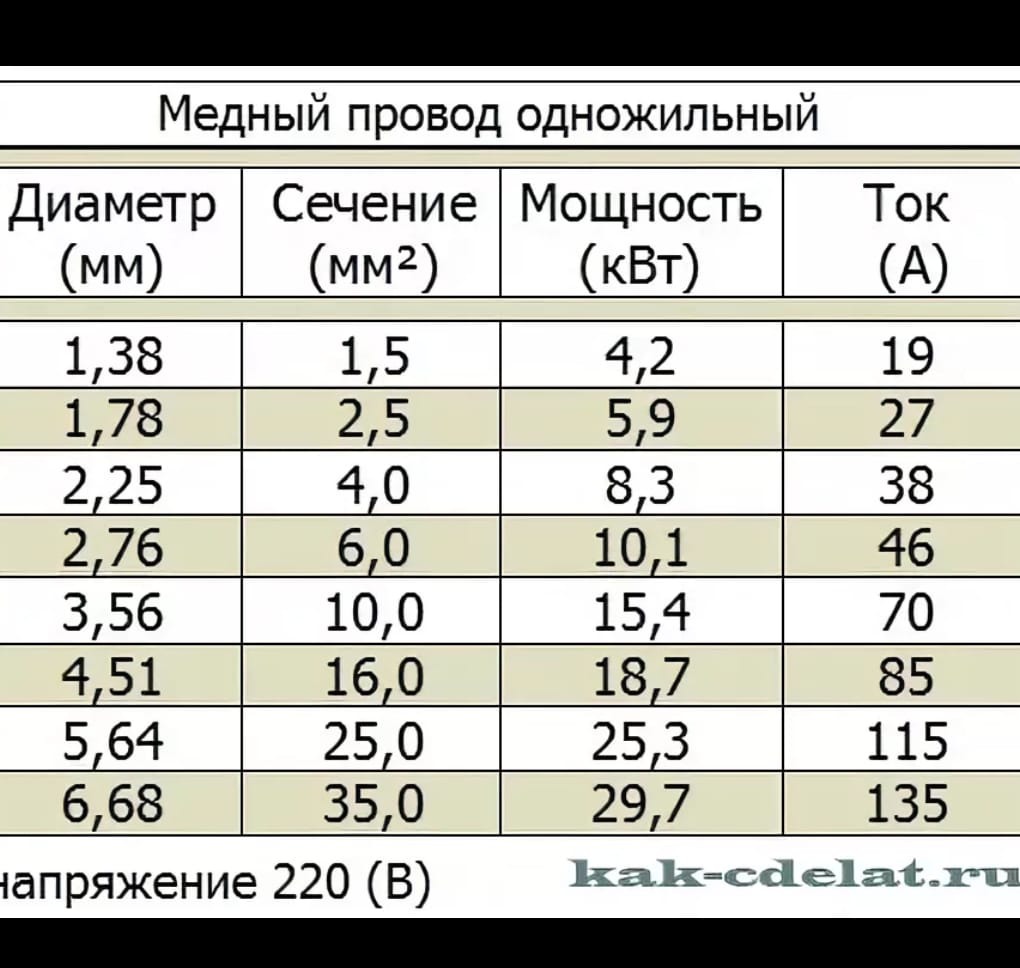
So, for a total power value of 7.5 kW must use copper cable with a core cross section of 4 mm2, which is able to pass about 8.3 kW. The cross section of the conductor with an aluminum core in this case must be at least 6 mm2, passing a current power of 7.9 kW.
Marking labels of electrical appliances and household appliances, which indicate their rated power
electric current
Often, the power of electrical equipment and equipment may not be known to the owner due to the absence of this characteristic in the documentation or completely lost documents and labels. There is only one way out in such a situation - to calculate according to the formula yourself.
P = U*I, where:
- P - power, measured in watts (W);
- I - electric current strength, measured in amperes (A);
- U is the applied electrical voltage, measured in volts (V).
When the strength of the electric current is unknown, then it can be measured with instrumentation: an ammeter, multimeter, current clamps.
Current measurement with current clamps
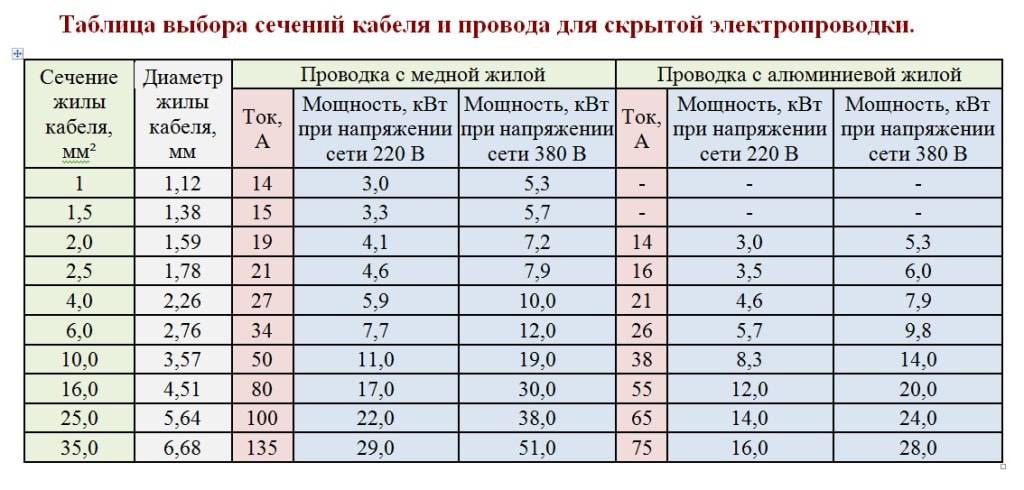
After determining the power consumption and the strength of the electric current, you can find out the required cable cross-section using the table below.
Load
The calculation of the cross section of cable products according to the current load must be made to further protect them from overheating.When too much electric current passes through the conductors for their cross section, destruction and melting of the insulating layer can occur.
The maximum permissible continuous current load is the quantitative value of the electric current that can pass the cable for a long time without overheating. To determine this indicator, it is initially necessary to sum up the capacities of all energy consumers. After that, calculate the load according to the formulas:
- I = P∑*Ki/U (single-phase network),
- I = P∑*Ki/(√3*U) (three-phase network), where:
- P∑ is the total power of energy consumers;
- Ki is a coefficient equal to 0.75;
- U is the voltage in the network.
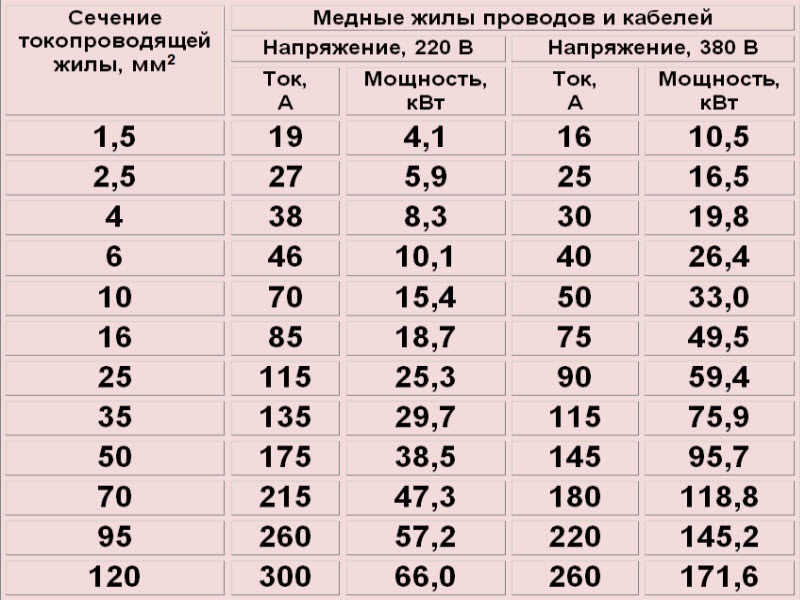
| Cross section of cable and wire products | Electrical voltage 220 V | Electrical voltage 380 V | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength current, A | power, kWt | Strength current, A | power, kWt | |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 6 | 50 | 11 | 40 | 26,4 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33 |
| 16 | 90 | 19,8 | 75 | 49,5 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,3 | 90 | 59,4 |
| 35 | 140 | 30,8 | 115 | 75,9 |
| 50 | 175 | 38,5 | 145 | 95,7 |
| 70 | 215 | 47,3 | 180 | 118,8 |
| 95 | 260 | 57,2 | 220 | 145,2 |
| 120 | 300 | 66 | 260 | 171,6 |
Determining a cable product in cross section is a particularly important process in which miscalculations are unacceptable. It is required to take into account all factors, parameters and rules, trusting only your own calculations. The measurements taken must match the tables described above - in the absence of specific values \u200b\u200bin them, they can be found in the tables of many electrical engineering reference books.
Wire diameter measurement
According to the standard, the wire diameter must correspond to the declared parameters, which are described in the marking. But the actual size may differ from the declared one by 10-15 percent. This is especially true for cables that are manufactured by small firms, but large manufacturers can also have problems. Before buying an electrical wire for transmitting high currents, it is recommended to measure the diameter of the conductor. To do this, various methods can be used, differing in error.Before performing the measurement, it is required to clean the cable cores from insulation.
Measurements can be made directly in the store if the seller allows you to remove the insulation from a small section of the wire. Otherwise, you will have to purchase a small piece of cable and measure on it.
Micrometer
Maximum accuracy can be obtained using micrometers, which have a mechanical and electronic circuit. The tool shaft has a scale with a division value of 0.5 mm, and on the circle of the drum there are 50 marks with a division value of 0.01 mm. The characteristics are the same for all models of micrometers.
When working with a mechanical device, follow the sequence of actions:
- By rotating the drum, the gap between the screw and the heel is set close to the measured size.
- Bring the screw with a ratchet closer to the surface of the part to be measured. The eyeliner is performed by hand rotation without effort until the ratchet is activated.
- Calculate the transverse diameter of the part according to the readings on the scales placed on the stem and drum. The product diameter is equal to the sum of the value on the rod and the drum.
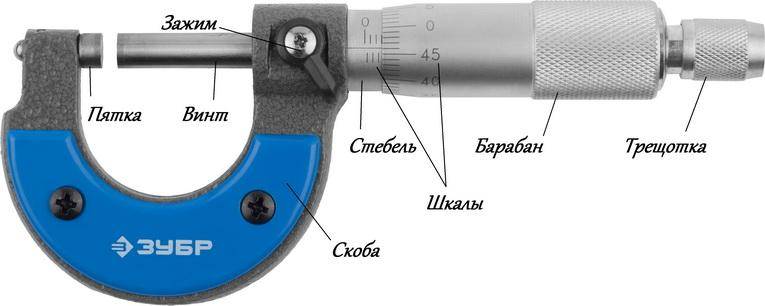
Measuring with a mechanical micrometer
Working with an electronic micrometer does not require rotation of the nodes, it displays the diameter value on the LCD screen. It is recommended to check the settings before using the instrument, as electronic devices measure in millimeters and inches.
Caliper
The device has a reduced accuracy compared to a micrometer, which is quite enough to measure the conductor. Calipers are equipped with a flat scale (vernier), a circular dial or digital indication on a liquid crystal display.
To measure the transverse diameter, you must:
- Clamp the measured conductor between the jaws of the caliper.
- Calculate the value on the scale or view it on the display.
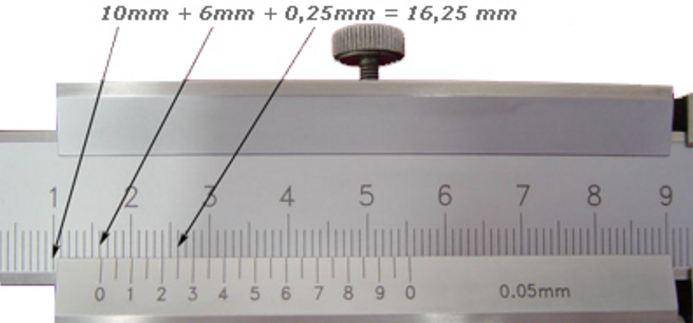
An example of calculating the size on a vernier
Ruler
Measuring with a ruler gives a rough result. To perform the measurement, it is recommended to use tool rulers, which have greater accuracy. The use of wooden and plastic school products will give a very approximate diameter.
To measure with a ruler, you need:
- Strip a piece of wire with a length of up to 100 mm from insulation.
- Wrap the resulting segment tightly around a cylindrical object. The turns must be complete, that is, the beginning and end of the wire in the winding are directed in the same direction.
- Measure the length of the resulting winding and divide by the number of turns.
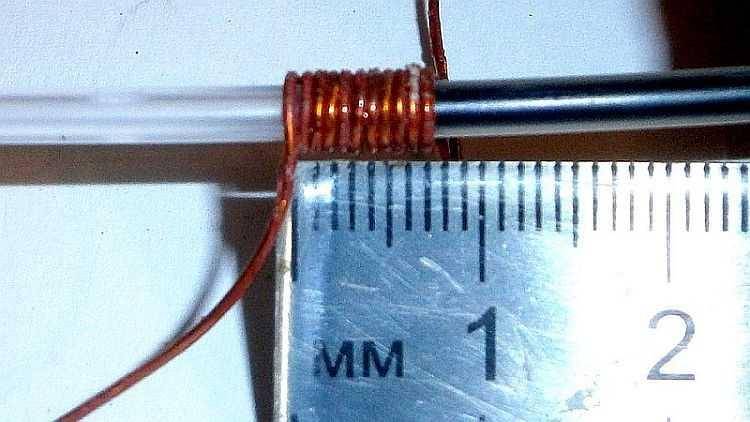
Measuring the diameter with a ruler by the number of turns
In the example above, there are 11 turns of wire that are about 7.5mm long. By dividing the length by the number of turns, you can determine the approximate value of the diameter, which in this case is 0.68 mm.
On the websites of stores selling electrical wires, there are online calculators that allow you to calculate the cross section by the number of turns and the length of the resulting spiral.
Section according to GOST or TU
A wide range of electrical goods contributes to the rapid solution of problems that are associated with electrical work. The quality of these products plays a very important role and all products must comply with the requirements of GOST.
Often, manufacturers, wanting to save money, find loopholes to deviate from the requirements of GOSTs and develop technical production specifications (TU) themselves, taking into account the allowed errors.
As a result, the market is oversaturated with low-quality and cheap goods that need to be double-checked before buying.
If the cables of a suitable value available at retail outlets do not meet the declared characteristics, the only thing that can be done is to purchase a wire with a margin in cross-section. Power reserve will never adversely affect the quality of electrical wiring
It would also be useful to pay attention to products from manufacturers who value their name - although it costs more, it is a guarantee of quality, and wiring is not replaced so often to save on it.
General information about cable and wire
When working with conductors, it is necessary to understand their designation. There are wires and cables that differ from each other in their internal structure and technical characteristics. However, many people often confuse these concepts.
A wire is a conductor that has in its construction one wire or a group of wires woven together and a thin common insulating layer. A cable is a core or a group of cores that have both their own insulation and a common insulating layer (sheath).
Each type of conductor will have its own methods for determining sections, which are almost similar.
Conductor materials
The amount of energy that a conductor transmits depends on a number of factors, the main of which is the material of the conductors. The following non-ferrous metals can act as the material for wire and cable cores:
- Aluminum. Cheap and light conductors, which is their advantage. They have such negative qualities as low electrical conductivity, susceptibility to mechanical damage, high transient electrical resistance of oxidized surfaces;
- Copper.The most popular conductors, which, in comparison with other options, have a high cost. However, they are characterized by low electrical and transient resistance at the contacts, sufficiently high elasticity and strength, ease in soldering and welding;
- Aluminum copper. Cable products with aluminum conductors coated with copper. They are characterized by a slightly lower electrical conductivity than their copper counterparts. They are also characterized by lightness, average resistance at relative cheapness.
 Different types of cables according to the core material
Different types of cables according to the core material
Important! Some methods for determining the cross section of cables and wires will depend precisely on the material of their core component, which directly affects the throughput power and current strength (method for determining the cross section of conductors by power and current)
Calculation of the cross-section of the wire of the electrical wiring according to the power of the connected electrical appliances
To select the cross section of the cable wires with laying electrical wiring in the apartment or at home, you need to analyze the fleet of existing electrical appliances in terms of their simultaneous use. The table provides a list of popular household electrical appliances with an indication of the current consumption depending on the power.
You can find out the power consumption of your models yourself from the labels on the products themselves or passports, often the parameters are indicated on the packaging. If the strength of the current consumed by the electrical appliance is not known, then it can be measured using an ammeter.
Typically, the power consumption of electrical appliances is indicated on the case in watts (W or VA) or kilowatts (kW or kVA). 1 kW=1000 W.
Table of power consumption / current strength of household electrical appliances
| electrical appliance | Power consumption, W | Current strength, A |
|---|---|---|
| Washing machine | 2000 – 2500 | 9,0 – 11,4 |
| Jacuzzi | 2000 – 2500 | 9,0 – 11,4 |
| Electric floor heating | 800 – 1400 | 3,6 – 6,4 |
| Stationary electric stove | 4500 – 8500 | 20,5 – 38,6 |
| microwave | 900 – 1300 | 4,1 – 5,9 |
| Dishwasher | 2000 – 2500 | 9,0 – 11,4 |
| Freezers, refrigerators | 140 – 300 | 0,6 – 1,4 |
| Meat grinder with electric drive | 1100 – 1200 | 5,0 – 5,5 |
| Electric kettle | 1850 – 2000 | 8,4 – 9,0 |
| Electric coffee maker | 630 – 1200 | 3,0 – 5,5 |
| Juicer | 240 – 360 | 1,1 – 1,6 |
| Toaster | 640 – 1100 | 2,9 – 5,0 |
| Mixer | 250 – 400 | 1,1 – 1,8 |
| hair dryer | 400 – 1600 | 1,8 – 7,3 |
| Iron | 900 –1700 | 4,1 – 7,7 |
| A vacuum cleaner | 680 – 1400 | 3,1 – 6,4 |
| Fan | 250 – 400 | 1,0 – 1,8 |
| Television | 125 – 180 | 0,6 – 0,8 |
| radio equipment | 70 – 100 | 0,3 – 0,5 |
| Lighting devices | 20 – 100 | 0,1 – 0,4 |
The current is also consumed by a refrigerator, lighting devices, a radiotelephone, chargers, and a TV in standby condition. But in total, this power is no more than 100 W and can be ignored in calculations.
If you turn on all the electrical appliances in the house at the same time, then you will need to select a wire section that can pass a current of 160 A. You will need a wire as thick as a finger! But such a case is unlikely. It is hard to imagine that someone is able to grind meat, iron, vacuum and dry hair at the same time.
Calculation example. You got up in the morning, turned on the electric kettle, microwave, toaster and coffee maker. The current consumption will be respectively:
7 A + 8 A + 3 A + 4 A = 22 A
Taking into account the included lighting, refrigerator and in addition, for example, a TV, the current consumption can reach 25 A.
Selection of the wire section for connecting electrical appliances to a three-phase 380 V network
During the operation of electrical appliances, for example, an electric motor connected to a three-phase network, the consumed current no longer flows through two wires, but through three, and, therefore, the amount of current flowing in each individual wire is somewhat less. This allows you to use a smaller wire to connect electrical appliances to a three-phase network.
To connect electrical appliances to a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 V, for example, an electric motor, the wire cross-section for each phase is taken 1.75 times less than for connecting to a single-phase network of 220 V
Attention, when choosing the wire section for connecting the electric motor by power, it should be taken into account that the nameplate of the electric motor indicates the maximum mechanical power that the motor can create on the shaft, and not the consumed electric power
For example, you need to connect an electric motor that consumes power from a network of 2.0 kW. The total current consumption by an electric motor of such power in three phases is 5.2 A. According to the table, it turns out that a wire with a cross section of 1.0 mm2 is needed, taking into account the above 1.0 / 1.75 = 0.5 mm2. Therefore, to connect a 2.0 kW electric motor to a 380 V three-phase network, you will need a three-core copper cable with a cross section of each core of 0.5 mm2.
It is much easier to choose a section wires for connecting a three-phase motor, based on the magnitude of the current of its consumption, which is always indicated on the nameplate. For example, the current consumption of a motor with a power of 0.25 kW for each phase at a supply voltage of 220 V (the motor windings are connected according to the "triangle" scheme) is 1.2 A, and at a voltage of 380 V (the motor windings are connected according to the "star" scheme) in total 0.7 A.
Taking the current strength indicated on the nameplate, according to the table for selecting the wire section for apartment wiring, we select a wire with a cross section of 0.35 mm2 when connecting the motor windings according to the "triangle" scheme or 0.15 mm2 when connecting according to the "star" scheme.
How to calculate the cable cross-section by power?
First step. The total power of all electrical appliances that can be connected to the network is calculated:
Psum = (P1 +P2 + .. +Pn) × KWith
- P1, P2 .. - power of electrical appliances, W;
- KWith – demand factor (probability of simultaneous operation of all devices), by default equals 1.
Second step. Then the rated current in the circuit is determined:
I=Psum / (U × cos ϕ)
- Psum - total power of electrical appliances;
- U - voltage in the network;
- cos ϕ – power factor (characterizes power losses), default is 0.92.
Third step. At the last stage, tables are used, according to the PUE (Electrical Installation Rules).
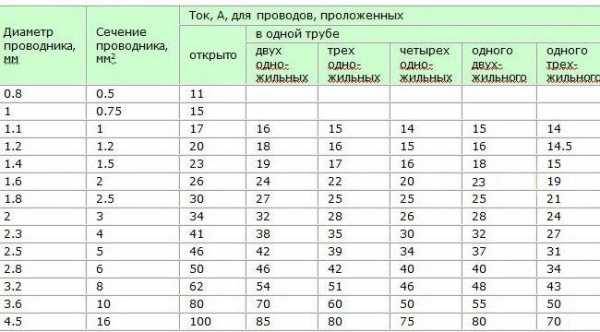
Table of copper cable cross-section by current according to PUE-7
| Conductor cross section, mm2 | Current, A, for wires laid | |||||
| open | in one pipe | |||||
| two single-core | three single-core | four single-core | one two-core | one three-core | ||
| 0.5 | 11 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0.75 | 15 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 1 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 14 |
| 1.2 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 15 | 16 | 14.5 |
| 1.5 | 23 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 18 | 15 |
| 2 | 26 | 24 | 22 | 20 | 23 | 19 |
| 2.5 | 30 | 27 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 21 |
| 3 | 34 | 32 | 28 | 26 | 28 | 24 |
| 4 | 41 | 38 | 35 | 30 | 32 | 27 |
| 5 | 46 | 42 | 39 | 34 | 37 | 31 |
| 6 | 50 | 46 | 42 | 40 | 40 | 34 |
| 8 | 62 | 54 | 51 | 46 | 48 | 43 |
| 10 | 80 | 70 | 60 | 50 | 55 | 50 |
| 16 | 100 | 85 | 80 | 75 | 80 | 70 |
| 25 | 140 | 115 | 100 | 90 | 100 | 85 |
| 35 | 170 | 135 | 125 | 115 | 125 | 100 |
| 50 | 215 | 185 | 170 | 150 | 160 | 135 |
| 70 | 270 | 225 | 210 | 185 | 195 | 175 |
| 95 | 330 | 275 | 255 | 225 | 245 | 215 |
| 120 | 385 | 315 | 290 | 260 | 295 | 250 |
| 150 | 440 | 360 | 330 | — | — | — |
| 185 | 510 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 240 | 605 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 300 | 695 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 400 | 830 | — | — | — | — | — |
Table of the section of the aluminum cable for current according to PUE-7
| Conductor cross section, mm2 | Current, A, for wires laid | |||||
| open | in one pipe | |||||
| two single-core | three single-core | four single-core | one two-core | one three-core | ||
| 2 | 21 | 19 | 18 | 15 | 17 | 14 |
| 2.5 | 24 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 16 |
| 3 | 27 | 24 | 22 | 21 | 22 | 18 |
| 4 | 32 | 28 | 28 | 23 | 25 | 21 |
| 5 | 36 | 32 | 30 | 27 | 28 | 24 |
| 6 | 39 | 36 | 32 | 30 | 31 | 26 |
| 8 | 46 | 43 | 40 | 37 | 38 | 32 |
| 10 | 60 | 50 | 47 | 39 | 42 | 38 |
| 16 | 75 | 60 | 60 | 55 | 60 | 55 |
| 25 | 105 | 85 | 80 | 70 | 75 | 65 |
| 35 | 130 | 100 | 95 | 85 | 95 | 75 |
| 50 | 165 | 140 | 130 | 120 | 125 | 105 |
| 70 | 210 | 175 | 165 | 140 | 150 | 135 |
| 95 | 255 | 215 | 200 | 175 | 190 | 165 |
| 120 | 295 | 245 | 220 | 200 | 230 | 190 |
| 150 | 340 | 275 | 255 | — | — | — |
| 185 | 390 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 240 | 465 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 300 | 535 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 400 | 645 | — | — | — | — | — |
In the rules for the installation of electrical installations of the 7th edition, there are no tables for the cable cross-section by power, there are only data for the current strength. Therefore, when calculating sections according to load tables on the Internet, you risk getting incorrect results.
Cable selection according to the PUE and GOST tables
When buying a wire, it is recommended to look at the GOST standard or the conditions of the technical specifications according to which the product is made. GOST requirements are higher than similar parameters of technical conditions, so products made according to the standard should be preferred.
Tables from the rules for electrical installations (PUE) represent the dependence of the strength of the current transmitted through the conductor on core cross-section and laying method in the main pipe. The permissible current decreases as the individual cores increase or the use of a multi-core cable in insulation. The phenomenon is associated with a separate paragraph in the PUE, which specifies the parameters of the maximum allowable heating of the wires. The main pipe is understood as a box, including plastic or when laying the wiring in a bundle on a cable tray.
Loading …
The parameters in the tables are indicated taking into account the operating temperature of the conductor 65 ° C and only phase wires (zero tires are not taken into account). If a standard three-core cable is laid in the room pipe for supplying single-phase current, then its parameters are taken into account according to the data column for one two-core wire. The following information is for cables made from different materials. Please note that tables are used to select wires. In the case of determining the type of cables, other data are used, which are also available in the PUE.
The second way to select a cable is the tables of the GOST 16442-80 standard, which exist in two versions - for copper and. In this information, the choice is made depending on the type of laying and the number of cores in the cables.
Why is it necessary to specify the cable cross-sections

On most wires and cables, the manufacturer is required to apply a marking indicating their type, the number of conductive cores and their cross section. If the wire is marked as 3x2.5, this means that the cross section of the wire in diameter is 2.5 mm². The actual values may differ from those indicated by about 30%, because some types of posting (in particular, PUNP) are made according to outdated standards, which allow an error of a specified percentage and basically it appears downward.As a result, if you use a cable with a smaller section than the calculated one, then for the wire the effect will be about the same if a thin polyethylene hose is connected to a fire hydrant. This can lead to dangerous consequences: overheating of the electrical wiring, melting of the insulation, changes in the properties of the metal. Therefore, before making a purchase, it is imperative to check that the cross-sectional area of the conductor does not differ from that declared by the manufacturer.
Ways to find out the real diameter of the wire
The easiest and most accurate method to measure the diameter of a wire strand is to use special tools such as a caliper or a micrometer (electronic or mechanical). In order for the measurement to be accurate, the measured wire must be cleaned of insulation so that the tool does not cling to it. You also need to inspect the tip of the wire so that it is without kinks - sometimes they appear if the core is bitten with blunt wire cutters. When the diameter is measured, you can begin to calculate the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe wire core.
A micrometer will give a more reliable reading than a caliper.
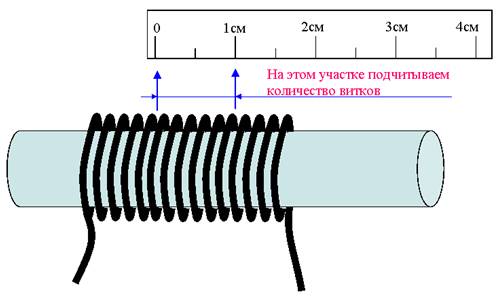
In the case when there is no accurate measuring tool at hand, there is another way to find out the cross section - you will need a screwdriver (pencil or any tube) and a measuring ruler for it. You will also have to buy at least one meter of wire (50 cm is enough, if only such an amount is sold) and remove the insulation from it. Next, the wire is wound tightly, without gaps, on the tip of a screwdriver and the length of the wound section is measured with a ruler. The resulting winding width is divided by the number of turns and the result will be the required wire diameter, along which you can already search for the cross section.
How to take measurements is shown in detail in this video:
What formulas should be used
What is a wire cross section is known from the basics of geometry or drawing - this is the intersection of a three-dimensional figure with an imaginary plane. According to their points of contact, a flat figure is formed, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich is calculated by suitable formulas. The core of the wire is most often cylindrical in shape and gives a circle in cross section, respectively, the cross section of the conductor can be calculated by the formula:
S = ϖ R²
R is the radius of the circle, equal to half the diameter;
ϖ = 3.14
There are wires with flat conductors, but there are few of them and it is much easier to find the cross-sectional area on them - just multiply the sides.
To get a more accurate result, you need to keep in mind:
- The more turns (there must be at least 15) to screw onto a screwdriver, the more accurate the result will be;
- The distances between the turns should not be, due to the gap, the error will be higher;
- It is necessary to take several measurements, each time changing its beginning. The more of them, the higher the accuracy of calculations.
The disadvantage of this method is that it is possible to use conductors of small thickness for measurements, it will be difficult to wind a thick cable.
Determine the cross section of the wire using the table
The use of formulas does not give a guaranteed result, and, as luck would have it, they are forgotten at the right time. Therefore, it is better to determine the cross section according to the table, which summarizes the results of the calculations. If it was possible to measure the diameter of the core, then the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe wire can be viewed in the corresponding column of the table:
If you need to find the total diameter of a multi-wire cable core, you will have to separately calculate the diameter of each wire, and add the resulting values. Then everything is done in the same way as with a single-wire core - the result is found according to the formula or table.
When measuring the cross section of the wire, its core is carefully cleaned of insulation, since it is possible that its thickness will be greater than the standard. If for some reason there is doubt about the accuracy of the calculations, then it is better to choose cables or wires with a power reserve.
To approximately find out the cross section of the wire that will be purchased, you need to add up the power of the electrical equipment that will be connected to it. Power consumption must be indicated in the device passport. Based on the known power, the total current that will flow through the conductor is calculated, and based on it, the section is already selected.
How to calculate the cross section of a stranded wire
Stranded wire, or as it is also called stranded or flexible, is a single-core wire twisted together. To calculate the cross section of a stranded wire, you must first calculate the cross section of one wire, and then multiply the result by their number.
Consider an example. There is a stranded flexible wire, in which there are 15 cores with a diameter of 0.5 mm. The cross section of one core is 0.5 mm × 0.5 mm × 0.785 = 0.19625 mm2, after rounding we get 0.2 mm2. Since we have 15 wires in the wire, to determine the cross section of the cable, we need to multiply these numbers. 0.2 mm2×15=3 mm2. It remains to determine from the table that such a stranded wire can withstand a current of 20 A.
It is possible to estimate the load capacity of a stranded wire without measuring the diameter of an individual conductor by measuring the total diameter of all stranded wires. But since the wires are round, there are air gaps between them. To exclude the area of the gaps, the result of the wire section obtained by the formula should be multiplied by a factor of 0.91.When measuring the diameter, make sure that the stranded wire is not flattened.
Let's look at an example. As a result of measurements, the stranded wire has a diameter of 2.0 mm. Let's calculate its cross section: 2.0 mm × 2.0 mm × 0.785 × 0.91 = 2.9 mm2. According to the table (see below), we determine that this stranded wire will withstand a current of up to 20 A.