- Advantages and disadvantages of induction boilers
- The device and principle of operation of the boiler
- Options for choosing electric boilers
- We reveal the main myth of induction heating
- Principle of operation
- Varieties of induction heaters for the heating system
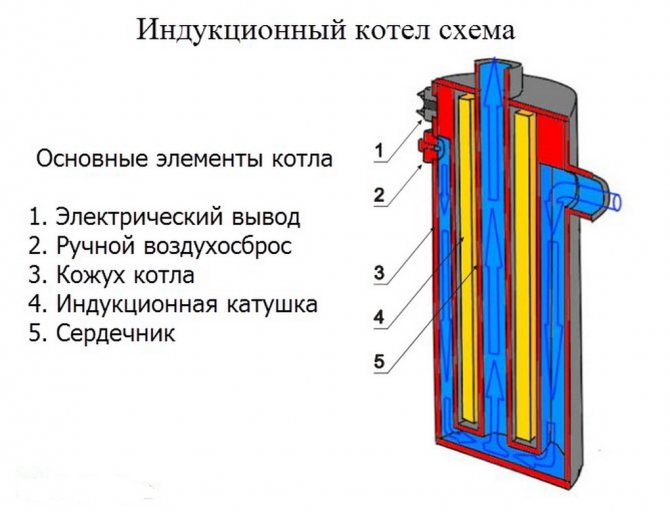
- The main elements and arrangement of boilers
- Reducing the efficiency of the electric boiler
- How to choose a heating device
- How does an induction heater work?
- The mechanism of action of heat supply from an induction hob
- How an induction heating boiler works
Advantages and disadvantages of induction boilers
Electric heating is the simplest alternative to conventional heating with gas boilers. A properly installed system will delight consumers with warmth, and induction heating equipment will allow you to count on the absence of problems. Let's look at the main advantages of induction units:
- Compactness - these boilers are really very small, in their appearance they resemble a large diameter pipe with smaller diameter pipes (the heating system is connected to the pipes). Although some industrial designs cannot be called compact;
- Efficiency close to 100% - almost all electricity is converted into heat. Nevertheless, there are still small losses, since there is nothing ideal in the world;
- Long service life - manufacturers claim that it is at least 20-25 years. And this is true, because there are no traditional heating elements here;
- Ability to work with any type of coolant;
- Scale does not form in induction boilers - this is how they compare favorably with heating elements, on which a small amount of lime deposits are still formed;
- Increased reliability - the induction coil has a decent turn-to-turn distance, and the turns are separated from the core by reliable insulation. Therefore, there is nothing to break here. Only the power system, which includes electronic components, can fail;
- The possibility of self-assembly - there is nothing complicated about it. Yes, and there are no settings here.
There are also certain disadvantages:

Properly and efficiently mounted induction boiler is not only a nice looking picture, but also a guarantee of long and reliable operation of the entire system.
- High cost - in a home heating system, an induction boiler will become the most expensive unit. But the cost is worth it;
- High electricity consumption - provides high costs for the operation of heating;
- A more complex design - there is a power circuit here, which is absent in heating elements and electrode assemblies.
The main drawback is the high prices for equipment, although there is nothing complicated about it.
In addition, if you use an induction boiler with a power of more than 7 kW, then you will need a three-phase power supply - this is true not only for induction, but also for any other electric heating units.
The device and principle of operation of the boiler
When an electric current is passed through a conductive material, heat is released in the latter, the power of which is directly proportional to the current strength and its voltage (the Joule-Lenz law). There are two ways to cause current to flow in a conductor. The first is to connect it directly to a source of electricity. We will call this method contact.
The second - contactless - was discovered by Michael Faraday at the beginning of the 19th century. The scientist found that when the parameters of the magnetic field crossing the conductor change, an electromotive force (EMF) appears in the latter. This phenomenon is called electromagnetic induction. Where there is an EMF, there will be an electric current, and hence heating, and in this case, non-contact. Such currents are called induced or eddy or Foucault currents.
Induction heating boiler - principle of operation
Electromagnetic induction can be caused in different ways. The conductor can be moved or rotated in a constant magnetic field, as is done in modern electric generators. And you can change the parameters of the magnetic field itself (the intensity and direction of the lines of force), while leaving the conductor motionless.
Such manipulations with the magnetic field became possible thanks to another discovery. As Hans-Christian Oersted found out in 1820, a wire wound in the form of a coil, when connected to a current source, turns into an electromagnet. By changing the parameters of the current (strength and direction), we will achieve a change in the parameters of the magnetic field generated by this device. In this case, an electric current will occur in the conductor located in this field, accompanied by heating.
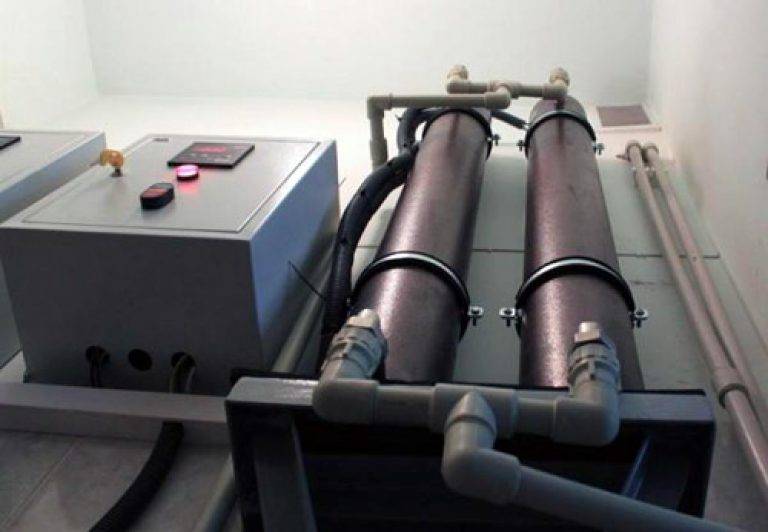
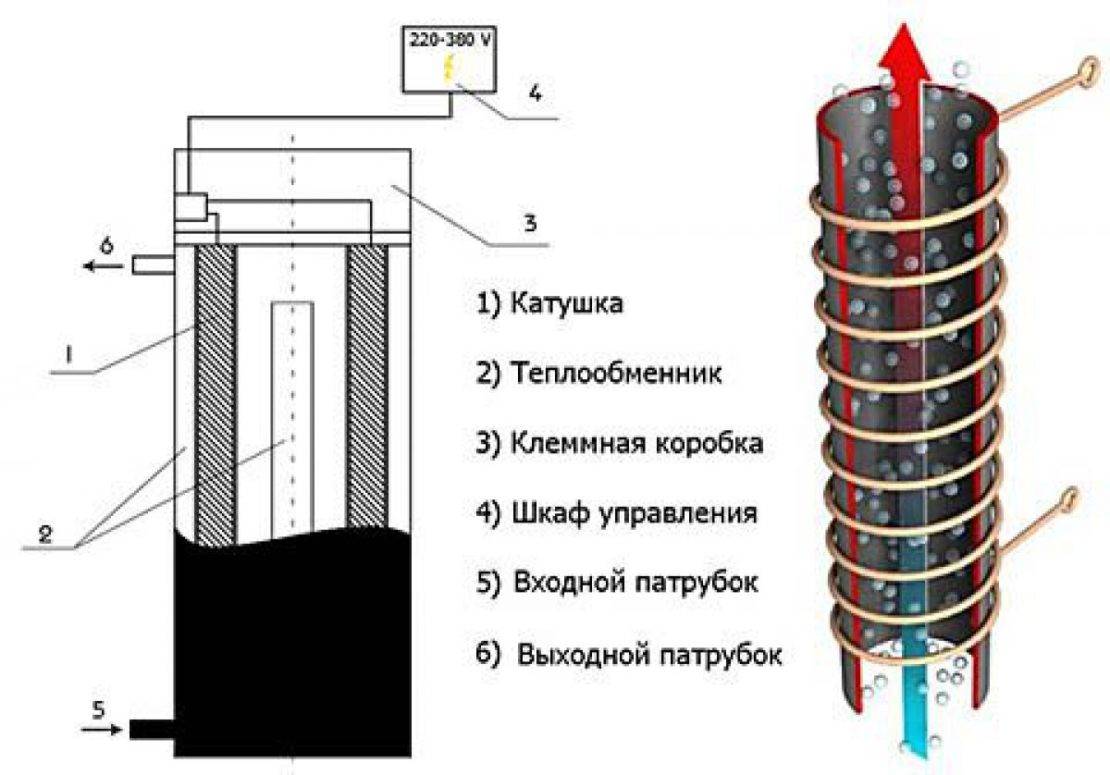
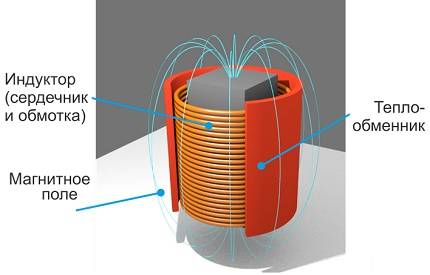
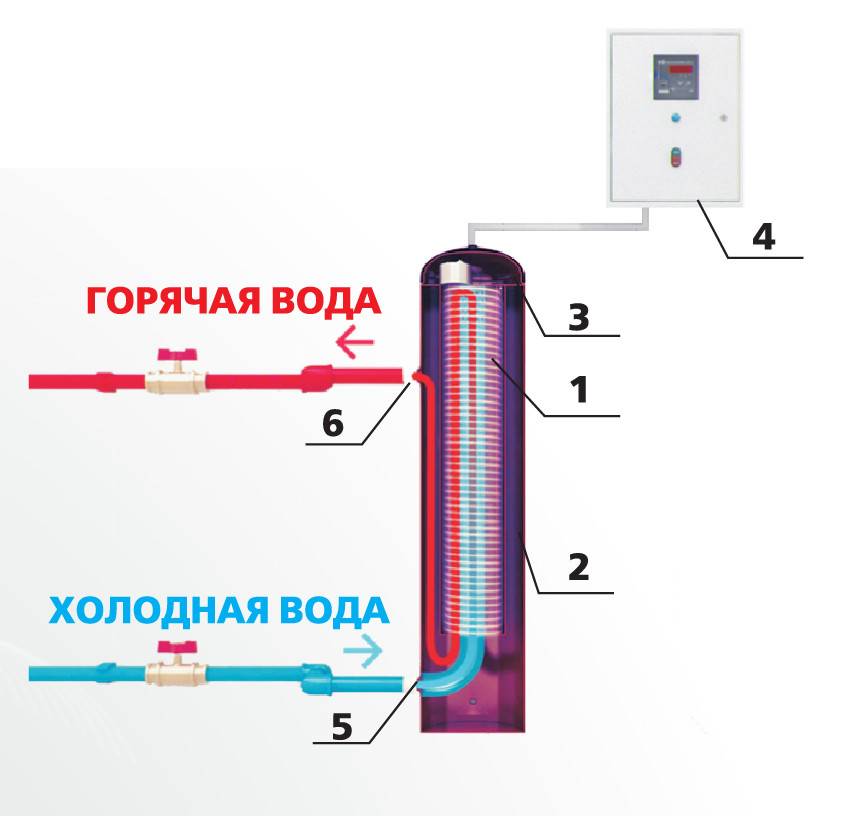
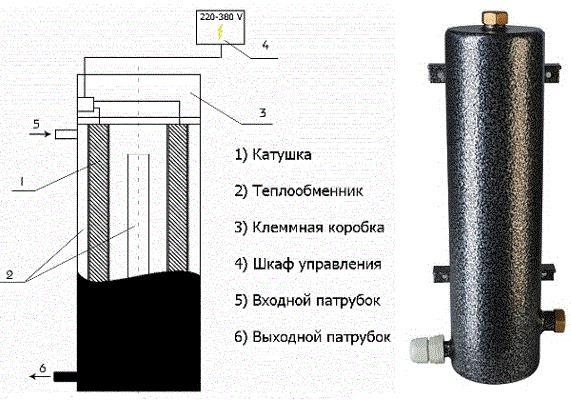
Having become acquainted with this simple theoretical material, the reader must have already imagined in general terms the device of an induction heating boiler. Indeed, it has a rather simple design: inside the shielded and heat-insulated housing there is a pipe made of a special alloy (steel can also be used, but the characteristics will be slightly worse), installed in a sleeve made of dielectric material; a copper bus is wound on the sleeve in the form of a coil, which is connected to the mains.
Boiler induction after installation
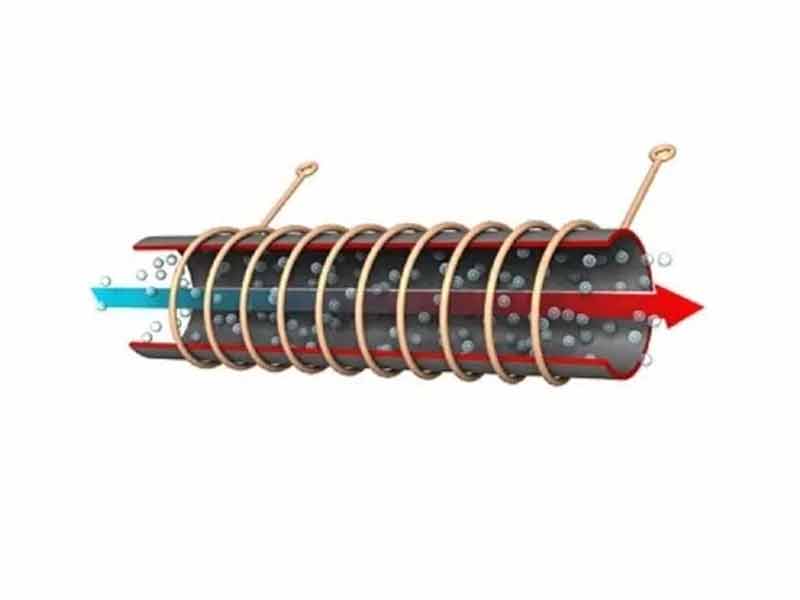
Through two pipes, the pipe cuts into the heating system, as a result of which the coolant will flow through it. An alternating current flowing through the coil will create an alternating magnetic field, which in turn will induce eddy currents in the pipe. Eddy currents will cause heating of the pipe walls and partially of the coolant throughout the entire volume enclosed inside the coil. For faster heating, several parallel tubes of smaller diameter can be installed instead of one pipe.
Readers aware of the cost of induction boilers have, of course, suspected that there was more to their design. After all, a heat generator, consisting only of a pipe and a piece of wire, cannot cost 2.5 - 4 times more than a heating element analogue. In order for the heating to be intense enough, it is necessary to pass through the coil not an ordinary current from the city network with a frequency of 50 Hz, but a high-frequency one, so the induction boiler is equipped with a rectifier and an inverter.
The rectifier turns the alternating current into direct current, then it is fed to the inverter - an electronic module consisting of a pair of key transistors and a control circuit.At the output of the inverter, the current becomes alternating again, only with a much higher frequency. Such a converter is not available in all models of induction boilers, some of them still operate at a frequency of 50 Hz. However, the use of high-frequency alternating current can significantly reduce the size of the device.
Principle of electromagnetic induction
In various descriptions, the authors point to the similarity of an induction boiler with a transformer. This is quite true: a coil of wire plays the role of a primary winding, and a pipe with a coolant plays the role of a short-circuited secondary winding and at the same time a magnetic circuit.
Why then the transformer is not heated? The fact is that the magnetic circuit of the transformer is not made of a single element, but of a multitude of plates isolated from each other. But even this measure is not able to completely prevent heating. So, for example, in the magnetic circuit of a transformer with a voltage of 110 kV in the idle mode, no less than 11 kW of heat is released.
Options for choosing electric boilers
At the first stage, it is necessary to solve the question of how to choose the right electric boiler for heating. Currently, manufacturers offer a number of models that differ not only in design features, but also in functionality. Therefore, the consumer needs to know the basic parameters of choice.
Before choosing an electric boiler for heating a house, you should correctly calculate its power. The work of any heat supply system is aimed at compensating the heat losses of the building. Therefore, it is first necessary to calculate this most important parameter. To do this, you can use specialized programs.
After that, the question arises - to purchase a factory model or to make a home-made electric boiler for heating. To solve it, experts recommend analyzing the following factors:
- The intensity of the device. If you plan to constantly operate the equipment, it is best to purchase a reliable factory-made electric boiler for water heating. When organizing heating of a utility room (garage) or a country cottage with a small area, you can make a home-made boiler;
- Hot water supply. To provide hot water, it is necessary to install a double-circuit electric boiler for heating the house. It is problematic to make it yourself, since the design will not have the proper degree of reliability. Installation and calculation of the parameters of the second circuit at home is almost impossible;
- Dimensions. They directly depend on the configuration of the equipment and its power. The heat supply of a small house can be done using electrode or induction models. Since it is difficult to make an electric boiler for heating a house of this type, schemes with heating elements are chosen;
- Mains voltage. Depends on the power of the equipment. Almost all do-it-yourself electric boilers for heating have a power of no more than 9 kW. This makes it possible to connect to a 220 V network.
But for the consumer, the determining parameter is still the cost of an electric boiler for heating batteries. That is why recently there have been many options for the independent manufacture of this type of heating equipment. However, to compare do-it-yourself electric boilers for heating, you should find out the design and operation features of factory models.
We reveal the main myth of induction heating
Recently, they have already stopped saying that the efficiency of induction heating is 2-3 times higher than the efficiency of a heating boiler. But supporters of the induction boiler claim that the heating element boiler quickly loses its properties and goes out of service, because scale grows on it!
They say that during the year the capacity of the heating element boiler is reduced by 15-20%. Is it really?
Yes, non-heating deposits are indeed present, but you should never confuse the heating system and the water supply system. For example, scale does form in the water supply, just as scale forms in the kettle we see in the kitchen every morning. This never interferes with our work, we know, and there is no doubt that water boils in a kettle in any case.
On the contrary, in the heating system known to us, impurities rarely enter the water. The deposit layer is very thin and does not constitute any significant barrier to heat transfer.
If the energy has left the network somewhere, it does not completely disappear anywhere. It turns into absolute heat and heats up the coolant, which, in turn, heats up exactly with the same efficiency as it was heated before and how it will always be heated. If it were not so, then the ten would have been torn apart by excess energy.
As soon as scale appears, heat exchange takes place at a higher temperature. There can be no question of any decrease in efficiency, no matter what the temperature in the heating element is.
Principle of operation
The principle of electromagnetic induction was identified in 1831 by the English physicist Michael Faraday. At the beginning of the twentieth century, his postulate was introduced into production in the form of a heating element for melting metals.It turns out that induction boilers have become known for a very long time, and they were used, but only at the production level.
The principle of operation of electromagnetic induction is based on the formation of an electromagnetic field that heats any ferromagnetic material (to which a magnet sticks) if placed in the center of this field. Creating an electromagnetic field is easy. This requires a coil, preferably made of copper wire, which is energized. It is inside the coil that a magnetic field is formed.
A pipe made of a dielectric (which does not transmit electric current) is installed inside, a coil is wound around it, and a steel rod is installed inside.
If, for example, a steel rod is installed in it, then it will certainly heat up to high temperatures. It is on this principle that the design of the induction heating boiler is built.
And a coolant (water or antifreeze) flows through the inner cavity of the pipe, washing the rod. The rod heated by an electromagnetic field transfers heat to the coolant.
There is one subtle point in the principle of operation of induction boilers that loops on the Joule Lenz law. If you increase the resistance of the rod, you can increase its heating. And the increase is carried out in two ways:
- increase the length and reduce the cross section;
- make it from a metal with high resistivity, for example, from nichrome.
Reference! These methods are used either singly or in combination. It is in this way that the power of the boiler is controlled.
Varieties of induction heaters for the heating system
There are two types of devices on the market.The first unit works with eddy currents to warm up the coolant, supplying a mains voltage of 220 V (50 hertz) to the primary winding, the second one with the same currents, but transmitting voltage through an inverter. In the second case, the unit is responsible for converting the standard mains voltage into currents of increased frequency up to 20 kilohertz.
An inverter is a device that increases the efficiency of an induction boiler without increasing the size and weight of the equipment. Thanks to the inverter, the equipment operates in an economical mode. There is only one minus - the use of copper winding, due to which inverter heaters are more expensive than standard models with heating elements.
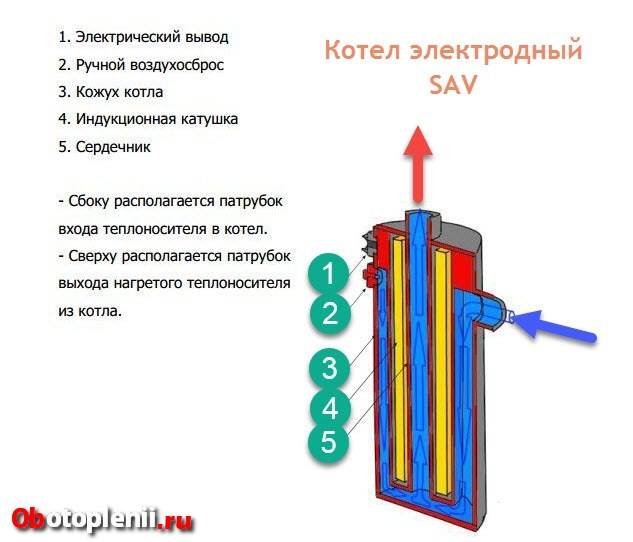
Devices are classified according to the type of materials - vortex devices are equipped with a heat exchanger made of ferromagnetic alloys, SAV boilers have closed-type tubular steel heat exchangers.
Induction heating is formed using one of the types of heaters:
- VIN. Vortex inverter boilers that convert the frequency of the power grid. Compact and non-massive devices are conveniently mounted on limited areas. The devices include a heat exchanger made of a ferromagnetic alloy, the secondary winding and the magnetic circuit are represented by a heat exchanger and a housing. The unit is supplemented with an automatic control unit, supply and circulation pump.
- SAV. These are boilers without inverters, they operate on a current of 220 V (50 hertz), which is fed to the inductor. The secondary winding looks like a tubular steel heat exchanger, heated by Foucault currents. The boiler is equipped with a pump to circulate the coolant. On sale there are units for operation from a voltage network of 220 V, 380 V.
The main elements and arrangement of boilers

If the scheme of the induction cooker is familiar, then the design of the boiler will also not cause difficulties.
Main details:
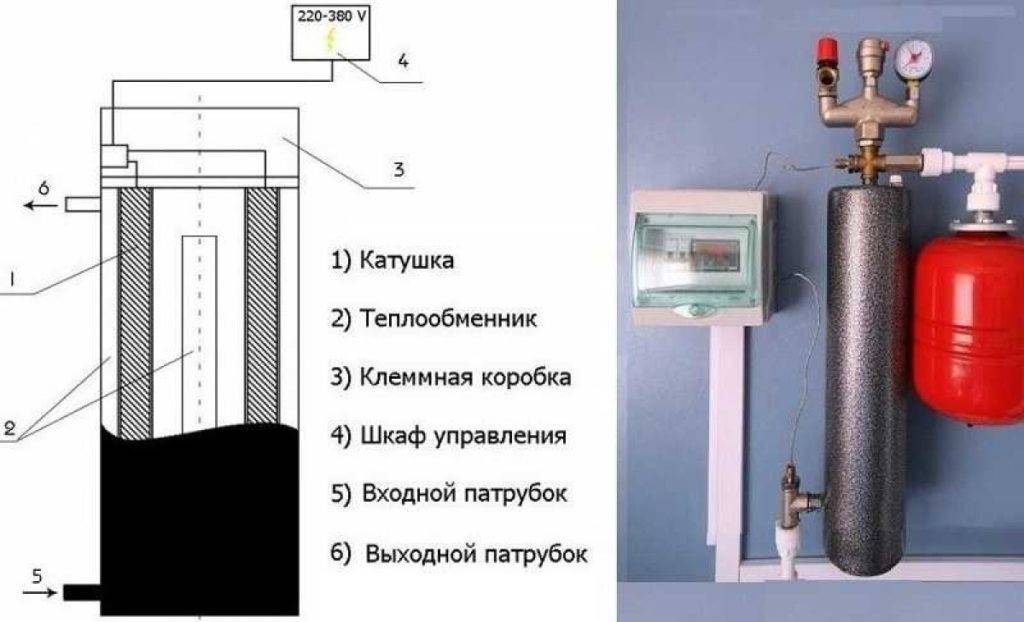
- Heater. This is the core of the coil, which can be in the form of one or more pipes. If this is one pipe, then its dimensions are quite large, a grid of pipes of a smaller section is connected in parallel.
- Inductor. A type of transformer with multiple windings. The first is the addition of the core, due to which an electromagnetic field is formed that drives eddy currents. Secondary winding - the body of the unit, which receives currents and transfers heat to the coolant
- inverter. There is VIN in boilers, it is needed to convert direct current to high-frequency.
- Branch pipes. Elements for connecting the heating network. One branch pipe is designed to supply the coolant for heating, the second - to transport heated water to the heating system.
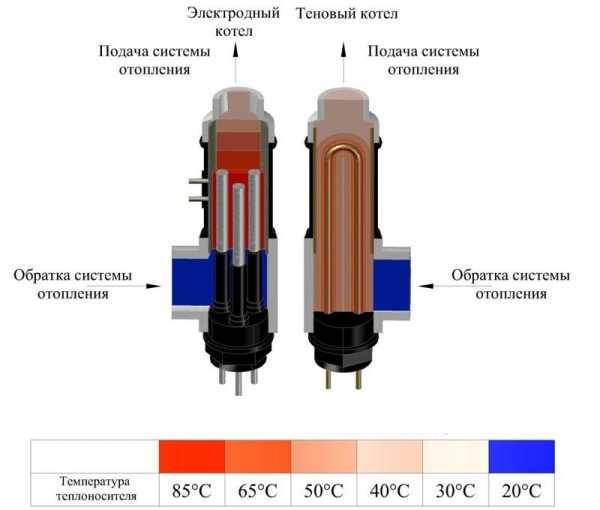
Reducing the efficiency of the electric boiler
Another argument when comparing is that the induction boiler does not lose its original power during the period of operation. But in the heating element due to the formation of scale, this happens in the order of things.

Even sometimes calculations are given, according to which, within just one year, the power of the heating element decreases by 15-20%. This means that its efficiency also decreases.
Let's take a closer look at this.
Almost any electric boiler efficiency exceeds 98%. And even boilers operating on ultra-high frequency currents from 25 kHz and above, what can change for you? Add an extra one and a half percent, but at the same time jump in price by 100%?!
As for the deposits on the heating element, they are really present.


And what happens where there is no constant supply of impurities? A small layer of deposits may settle on the heating element, however:
this layer is not thick enough
it does not interfere with the transfer of heat in any way
And accordingly, the boiler does not lose its original efficiency in any way.
That is, in fact, both on a clean heating element and on a dirty one, the same amount of energy is transferred, only at different temperatures.

How to choose a heating device
When choosing an inverter boiler for heating, it is worth considering many factors.
First of all, you need to pay attention to its power. Throughout the life of the boiler, this parameter remains unchanged. It is taken into account that 60 W is needed to heat 1 m2
Making the calculation is very easy. It is necessary to add the area of \u200b\u200ball rooms and multiply by the specified number. If the house is not insulated, then it is better to choose more powerful models, as there will be significant heat losses.
It is taken into account that 60 watts are needed to heat 1 m2. Making the calculation is very easy. It is necessary to add the area of \u200b\u200ball rooms and multiply by the specified number. If the house is not insulated, then it is better to choose more powerful models, as there will be significant heat losses.
An important factor is the features of the operation of the house. If it is used only for temporary residence, then there is no need to constantly maintain the temperature in the premises at a given level. In such cases, you can completely get by with a unit with a power of not more than 6 kW.
When choosing, pay attention to the configuration of the boiler. Convenient is the presence of an electronic program unit with a diode thermostat. With it, you can set the unit to work for several days and even a week in advance
In addition, in the presence of such a unit, it is possible to control the system from a distance. This makes it possible to pre-heat the house before arrival.
With it, you can set the unit to work for several days and even a week in advance. In addition, in the presence of such a unit, it is possible to control the system from a distance. This makes it possible to preheat the house before arrival.
An important parameter is the thickness of the walls of the core. The resistance of the element to corrosion will depend on this. Thus, the thicker the walls, the higher the protection. These are the main parameters that should be considered when choosing a device and constructing a heating system. If the price is not acceptable, then you can use analogues or build a boiler yourself. To do this, you just need to have certain knowledge and skills.
How does an induction heater work?
Very simple. We apply operating voltage to the coil. An electromagnetic field is created in the coil. We read carefully - here is the essence of his work:
The electromagnetic field induces Foucault currents or eddy currents in the heating pipe and the metal pipe begins to heat up.
If anyone does not know, the magnetic circuit of the transformer is specially recruited from many thin plates of electrical steel, isolated from each other.
This is done precisely in order to avoid energy losses from heating by eddy currents.
The fact is that the more massive the conductor, the more it will heat up from the Foucault currents, in turn, the force of the eddy currents can be increased by the rate of change in the magnetic flux.
Do you know that a power transformer voltage 110 kV on idling, even without load, a thermal power of about 11 kilowatts is released?
This is mainly due to the effect of eddy currents, which heat the magnetic circuit, on which the primary and secondary windings are dressed.
At the same time, the magnetic circuit is laminated, and if it were solid, then the heat losses would increase many times over!
And the transformer would simply burn out from overheating.
The induction electric boiler works on the same principle and the steel pipe with water passing inside the coil heats up very much, BUT! - due to the circulation of water, the heat has time to be removed from the pipe to the heating system and overheating does not occur.
But can it be more economical compared to electric boilers on heating elements? For what?
Here, let's first think without parsing and comparing these two types of boilers:
Have a house
It doesn't matter what and it doesn't matter where. Though under water, even on Everest. This house has a heat loss of 6 kilowatts
This house has a heat loss of 6 kilowatts.
Through walls, through windows, through the ceiling, etc. - heat is lost and in order to maintain a constant temperature, these heat losses must be compensated and for this, of course, 6 kilowatts of heat is also needed.
And it doesn’t matter where and how this heat is taken, this thermal energy is 6 kilowatts - even burn a fire, even gas, even gasoline, the most important thing is that these necessary kilowatts of heat are released!
Now the most important thing:
to heat such a house, you will need both an induction heater and an electric boiler on heating elements - all the same, the power is also at least 6 kW.
In other words, the boiler simply converts electrical energy into thermal energy.
And how he does it is absolutely not important, because for us the most important thing is that it would be warm in the house.Energy is simply transformed from one form to another, from electrical to thermal. And if the boiler allocated heat for 6 kW, then it took at least the same amount of electricity from the network, and given that the efficiency of the boilers is not 100%, then even a little more energy is consumed from the network
And if the boiler allocated heat for 6 kW, then it took at least the same amount of electricity from the network, and given that the efficiency of the boilers is not 100%, then even a little more energy is consumed from the network
Energy is simply transformed from one form to another, from electrical to thermal. And if the boiler allocated heat for 6 kW, then it took at least the same amount of electricity from the network, and given that the efficiency of the boilers is not 100%, then even more energy is consumed from the network.
Then maybe the efficiency of the induction boiler is higher? According to the manufacturers, this value reaches 98%.
The same is true for an electric boiler with heating elements. Their efficiency reaches 99%.
Well, think for yourself - where else can the energy in the heating element go, except how to stand out in heat?
All energy consumed from the heating element network is converted into thermal energy. I took 5 kW - allocated 5 kW of heat.
I took 100 kW - allocated 100 kW of heat. Well, maybe a little less if you take into account the energy loss in the transient resistance at the heating element clamps, but again, this energy loss is released in the form of heat (the clamp is heated) and in the supply cables.
But what about the clamps, that the cable cross-section is the same in terms of parameters for both the vortex induction electric boiler and the heating element.
The mechanism of action of heat supply from an induction hob
The design of the boiler is based on electric inductors, they include 2 short-circuited windings. The internal winding modifies the incoming electrical energy into eddy currents.In the middle of the unit, an electric field appears, which then enters the second turn.

The secondary component acts as the heating element of the heat supply unit and the boiler body.
It transfers the energy that has appeared to the heat carrier of the system for heating. In the role of heat carriers that are intended for such boilers, they use specialized oil, filtered water or non-freezing liquid.
The internal winding of the heater is affected by electrical energy, which contributes to the appearance of voltage and the formation of eddy currents. The received energy is transferred to the secondary winding, after which the core is heated. When the heating of the entire surface of the heat carrier has occurred, it will transfer the heat flow to the heating devices.
How an induction heating boiler works
Recall the physics of the school curriculum. If a ferromagnetic conductor is placed in an alternating electromagnetic field, then the energy of the electromagnetic field will irreversibly transform into the thermal energy of this conductor. The physics of the process is described by two Maxwell laws and the Lenz-Joule law, which are not of interest to us here.
That is, if an alternating current is passed through the coil (inductor), then the electrical energy of the inductor will transfer contactlessly into the thermal energy of the conductor placed in the field of the coil. After that, the conductor can be used as a heating element of the heating system.
In this principle, the word "contactless" is important. That is, in this system there are no losses due to the resistance of contact groups and wires.
That is why induction electric boilers are considered the most economical (very high efficiency).