- Cable types
- resistive
- self-regulating
- Types of heating cable for plumbing
- resistive
- Self-regulating
- The nuances of installation work
- Video description
- Briefly about the main
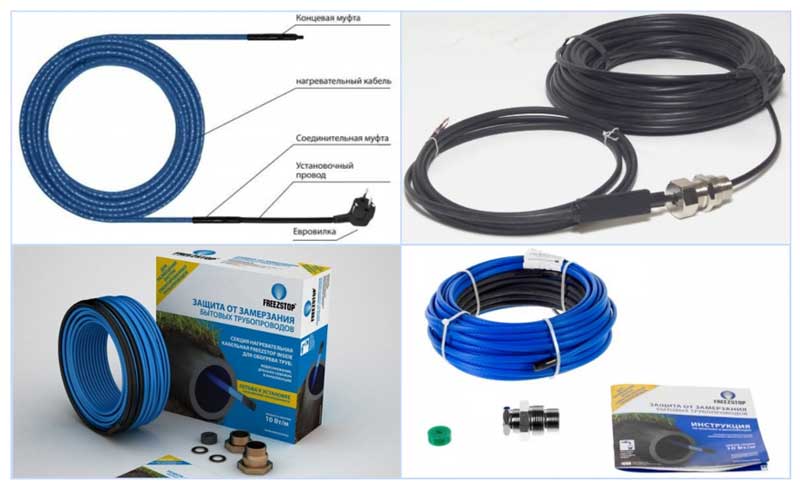
- Types of heating wire
- Table: types of heating cable with characteristics
- Means for heating the drain and roof overhang
- Which heating cable to choose
- The composition of the heating system of the drain and roof
- Types of heating cable
- Type #1 - resistive
- Type #2 - self-adjusting
- Design and scope
- Conclusion
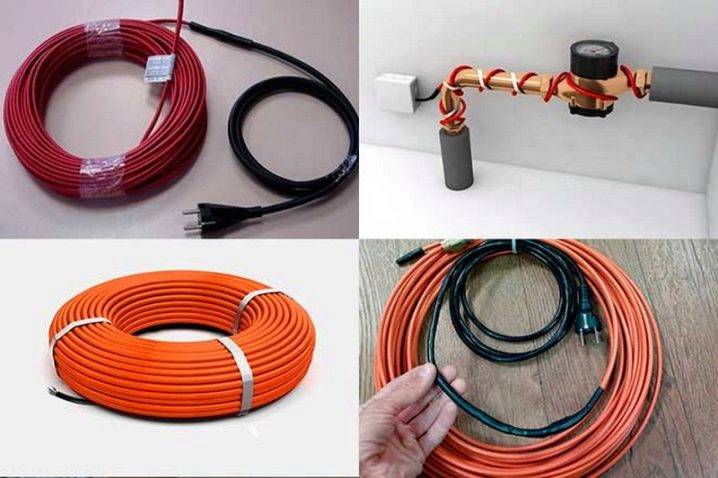
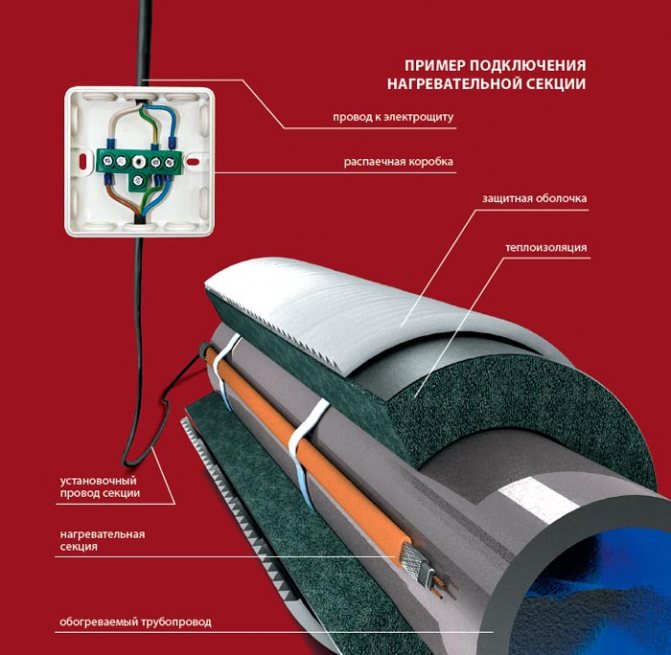
Cable types
Before installation, it is important to study what heating wires are and how to install them. There are two types of cables: resistive and self-regulating
There are two types of cables: resistive and self-regulating.
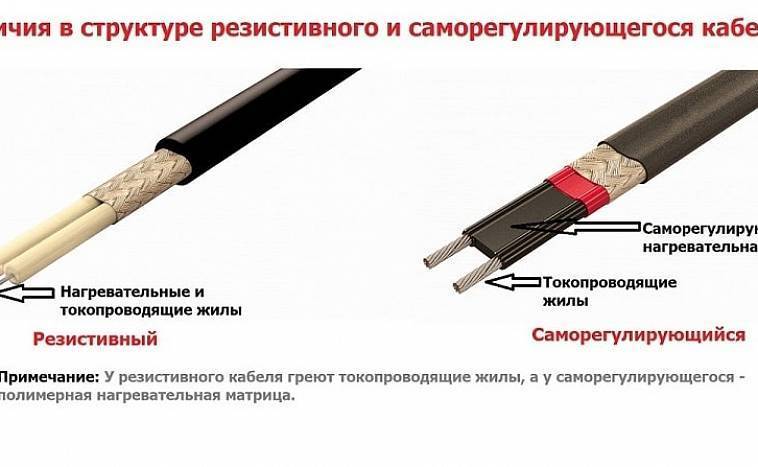
The difference between them is that when an electric current passes through the cable, the resistive one heats up evenly along the entire length, and the feature of the self-regulating one is the change in electrical resistance depending on temperature. This means that the higher the temperature of the self-regulating cable section, the lower the current strength will be on it. That is, different parts of such a cable can each be heated to the desired temperature.
In addition, many cables are produced immediately with a temperature sensor and auto control, which significantly saves energy during operation.
Self-regulating cable is more difficult to manufacture and more expensive. Therefore, if there are no special operating conditions, then more often they purchase a resistive heating cable.
resistive
A resistive-type heating cable for a water supply system has a budget cost.
Cable differences
It is divided into several varieties, depending on the design features. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages:
| cable type | pros | Minuses |
| single core | The design is simple. It has a heating metal core, a copper shielding braid and internal insulation. From the outside there is protection in the form of an insulator. Maximum heat up to +65°С. | It is inconvenient for heating pipelines: both opposite ends, which are far from each other, must be connected to the current source. |
| Two-core | It has two cores, each of which is isolated separately. An additional third core is bare, but all three are covered by a foil shield. External insulation has a heat-resistant effect. Maximum heat up to +65°C. | Despite the more modern design, it is not much different from a single-core element. The operating and heating characteristics are identical. |
| Zonal | There are independent heating sections. Two cores are isolated separately, and a heating coil is located on top. The connection is made by means of contact windows with current-carrying conductors. This allows you to create heat in parallel. | No cons were found, if you do not take into account the price tag of the product. |
Resistive wires of various types
Most buyers prefer to lay the wire "the old fashioned way" and purchase a wire with one or two cores.
Due to the fact that a cable with only two cores can be used for heating pipes, a single-core version of the resistive wire is not used. If the owner of the house unknowingly installed it, this threatens to close the contacts. The fact is that one core must be looped, which is problematic when working with a heating cable.
If you install the heating cable on the pipe yourself, then experts advise choosing a zonal option for outdoor installation. Despite the peculiarity of the design, its installation will not cause serious difficulties.
Wire design
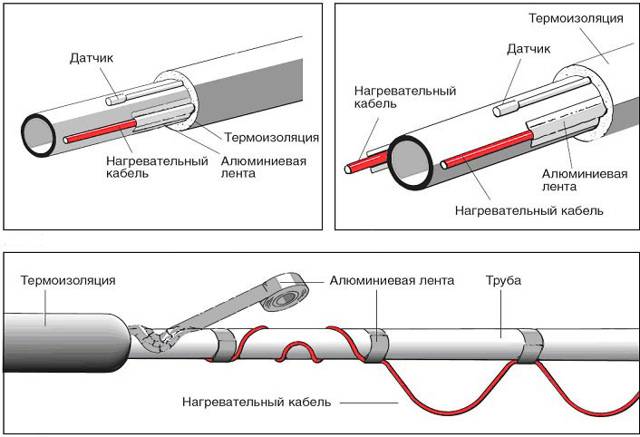
Another important nuance in single-core and twin-core structures: already cut and insulated products can be found on sale, which eliminates the possibility of adjusting the cable to the optimal length. If the insulation layer is broken, then the wire will be useless, and if damage occurs after installation, it will be necessary to replace the system throughout the area. This disadvantage applies to all types of resistive products. Installation work of such wires is not convenient. It is also not possible to use them for laying inside the pipeline - the tip of the temperature sensor interferes.
self-regulating
Self-regulating heating cable for water supply with self-adjustment has a more modern design, which affects the duration of operation and ease of installation.
The design provides:
- 2 copper conductors in a thermoplastic matrix;
- 2 layers of internal insulating material;
- copper braid;
- external insulating element.
It is important that this wire works fine without a thermostat. Self-regulating cables have a polymer matrix
When turned on, carbon is activated, and during an increase in temperature, the distance between its graphite components increases.
Self-regulating cable
Types of heating cable for plumbing
The heating cable is divided into 2 types, each of which is used in different areas. It can be self-regulating or resistive. The self-regulating model is used on long water pipes. Short pipes with a cross section of not more than 40 mm in diameter are heated with resistive models.
resistive

The cable works according to the following connection scheme: the current passes through the inner cores of the wire and heats it, releasing a large amount of heat. A high heat dissipation rate is obtained due to the high resistance and maximum current strength. You can purchase a wire that generates heat along its entire length in the same proportions. These models have constant resistance. What you need to know when connecting the wire:
- Single core. To heat a roof drain or equip a warm floor, a heating circuit of the “closed” type is used. For this, wires with one core are used. Connecting a solid wire is like a loop. The wire is wrapped around the pipe, and its ends are connected to electricity. To insulate the water supply, an external type of connection is used and the wire is laid on both sides of it.
- Two-wire. If it is necessary to make internal laying, then use a two-wire wire. It consists of two cores: heating and supplying energy. The wire is laid along the water supply, connecting one end to electricity.With the help of tees and seals, two-core wires can be laid inside the pipe.
This is an inexpensive, reliable wire that has a long service life (15 years). Its disadvantages: standard length, power is always the same and cannot be adjusted. Because of one burned-out section, you will have to change the entire cable. If 2 cables are close to each other or intersect, they will burn out. By installing a thermostat with sensors, the system will turn itself off and on. The energy will turn off if the temperature reaches +7°C. If it drops to +2°C, the heating will automatically turn on.
Self-regulating
Multifunctional self-regulating cable is used for sewer lines, plumbing systems and heating of roof structures. Its functionality - the amount of heat supplied and the power level are regulated independently. The heating of the wire occurs on its own after the temperature reaches the set point. If we compare it with a resistive analog, the insulating layers of the wires are the same, but the heating matrices are different. Principle of operation:
- Depending on the resistance of the self-regulating cable, the conductor is able to change the current strength up or down.
- As the resistance increases, the current begins to decrease, thereby minimizing the power.
- As the wire cools, the resistance decreases. The current strength increases, starting the heating process.
If you automate the system with a thermostat, then, depending on the temperature conditions on the street, it will independently control the process of switching on and off.
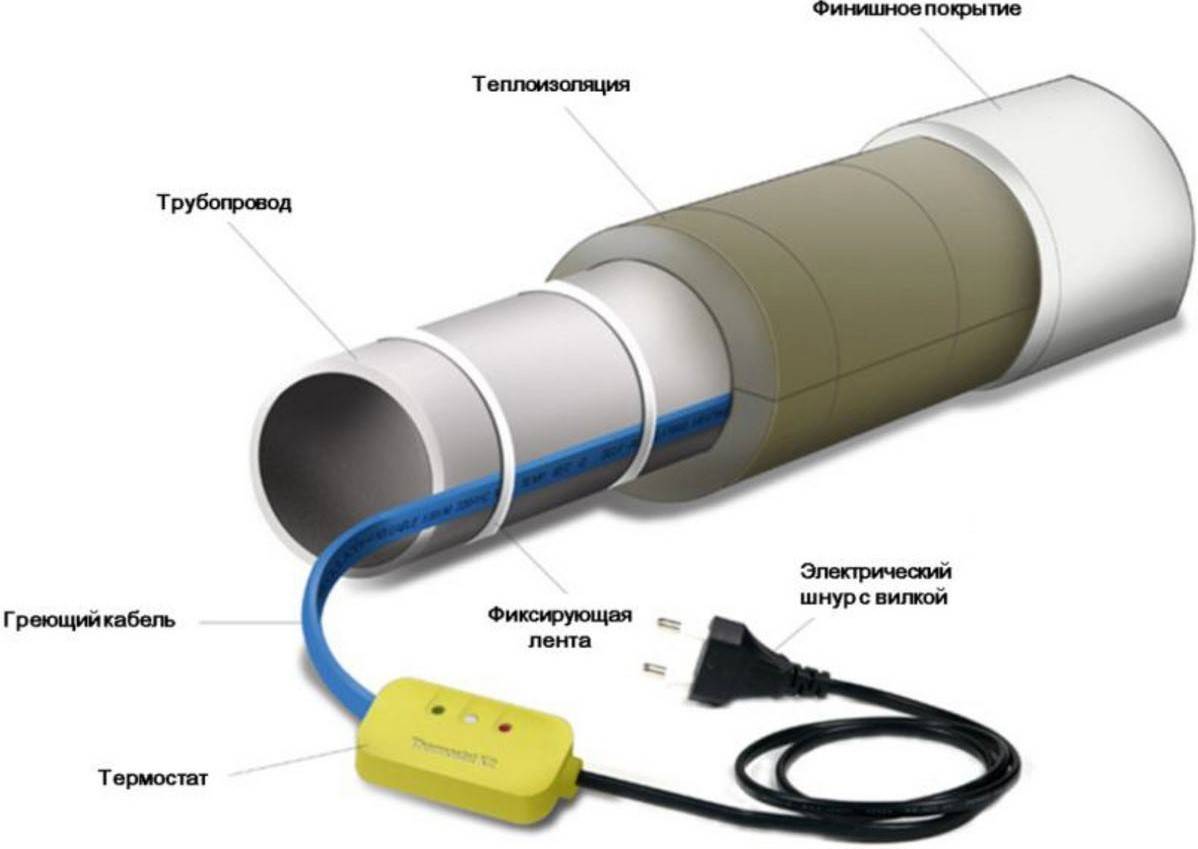
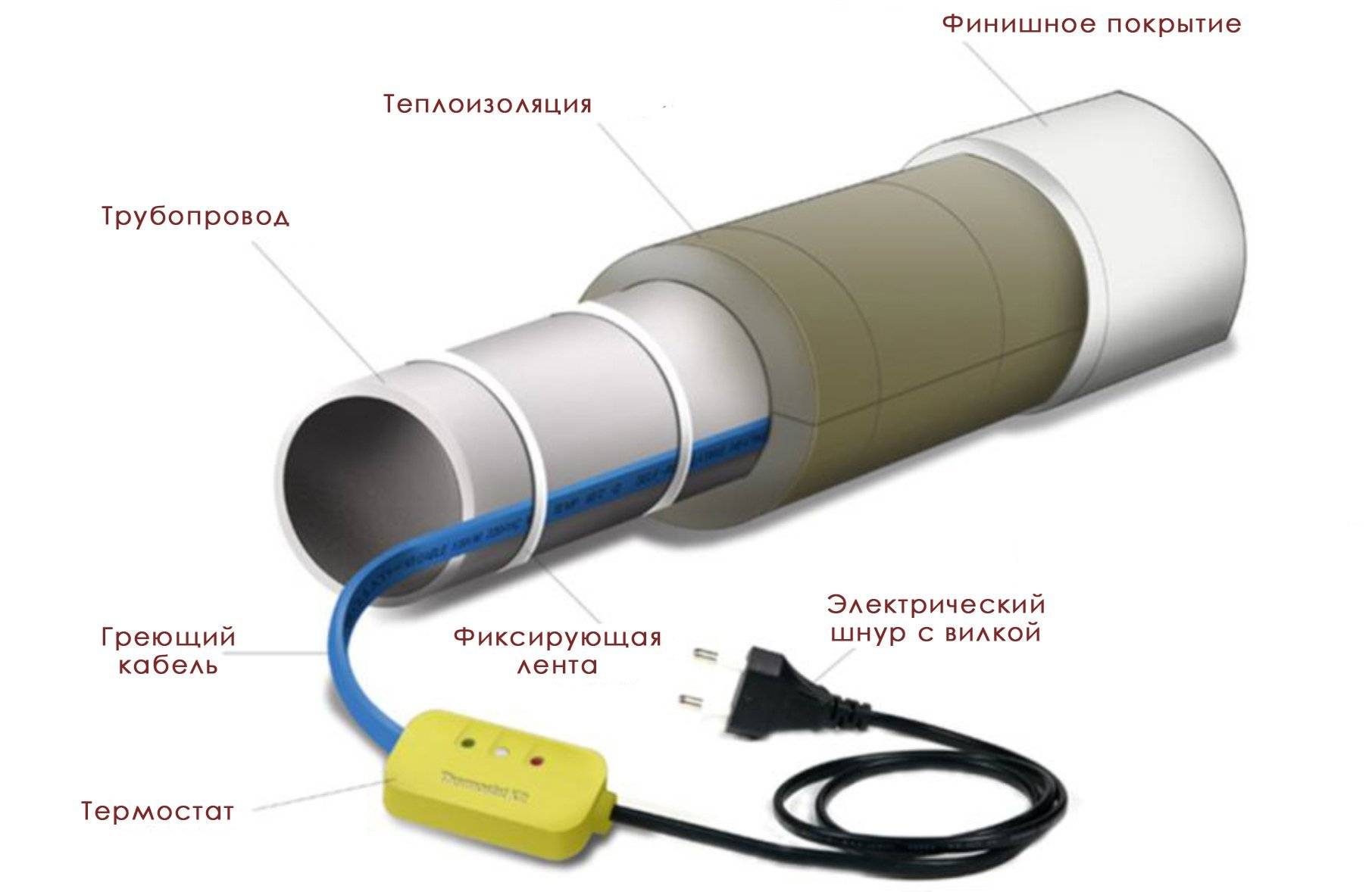
The nuances of installation work
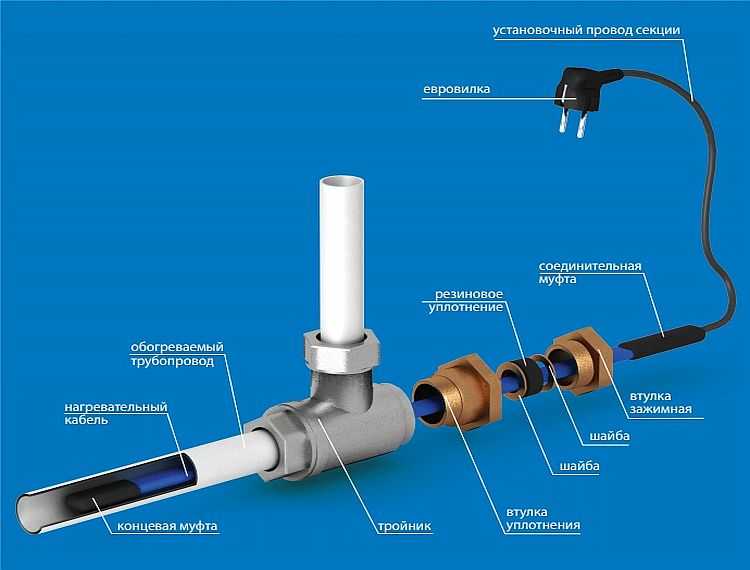
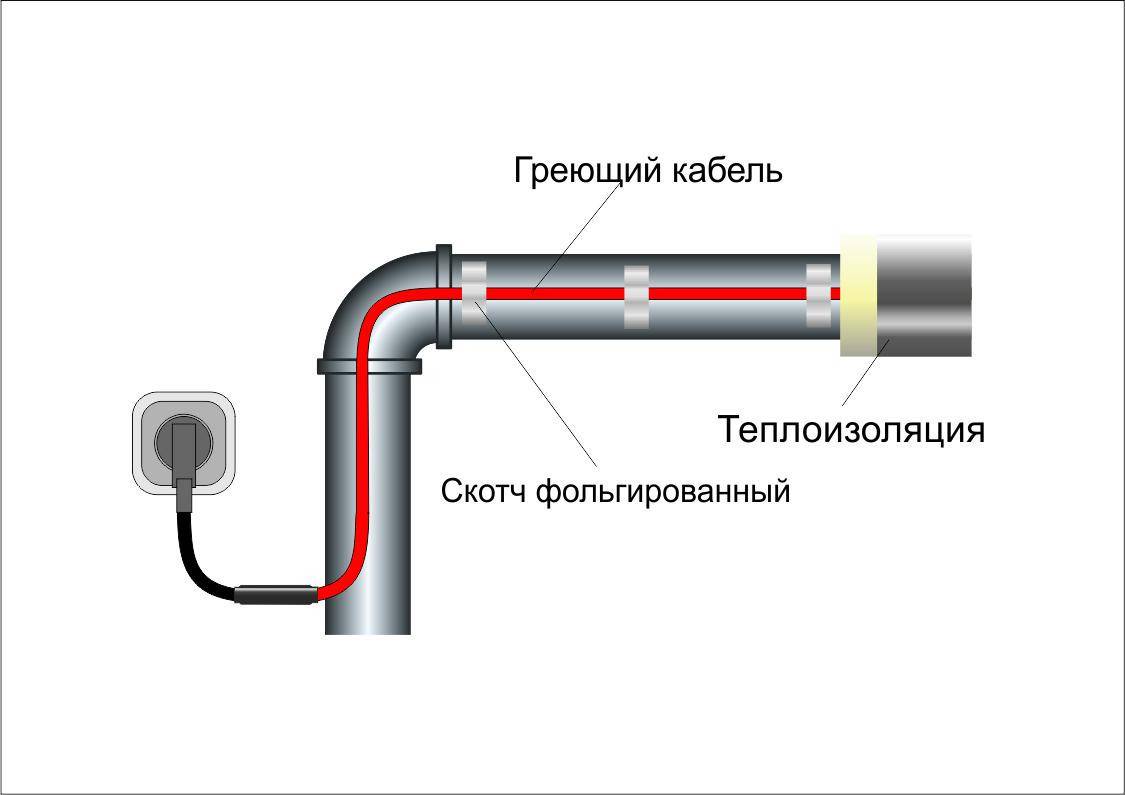
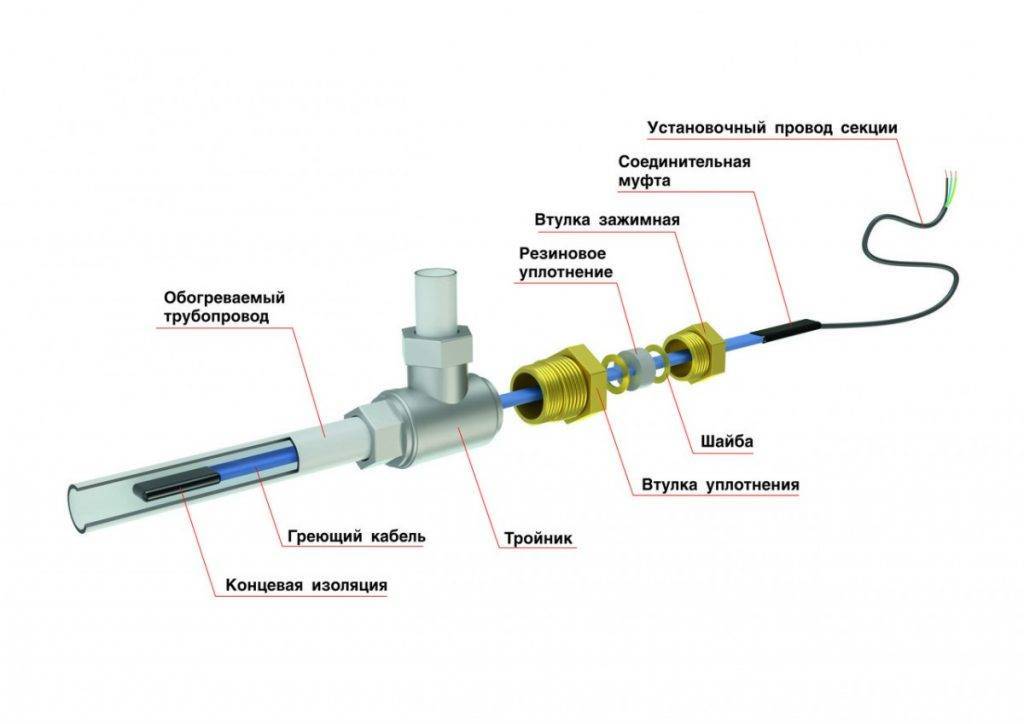
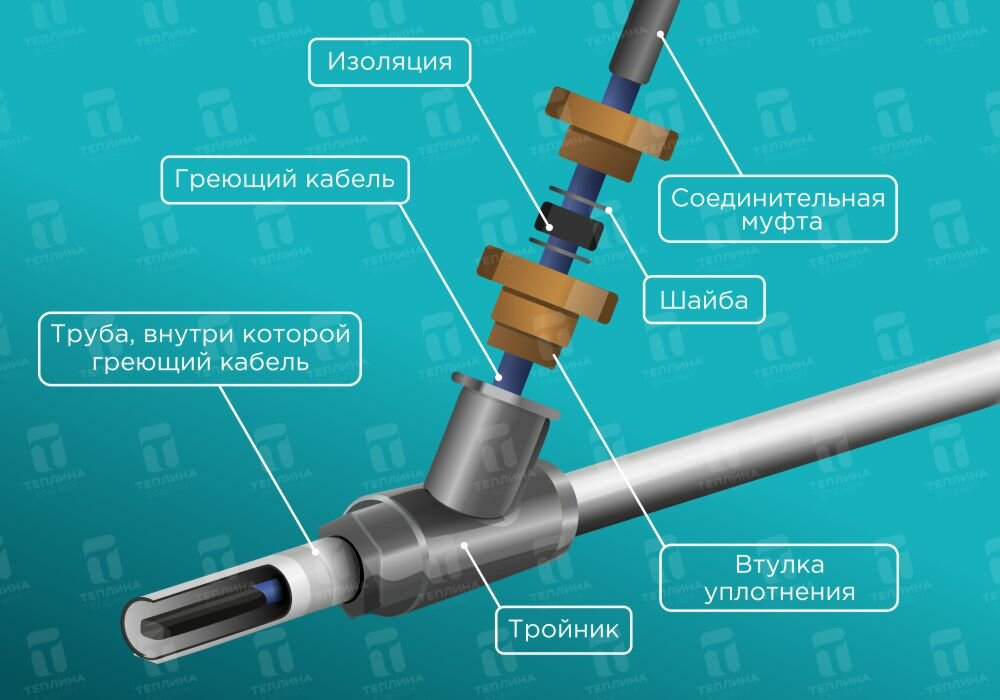
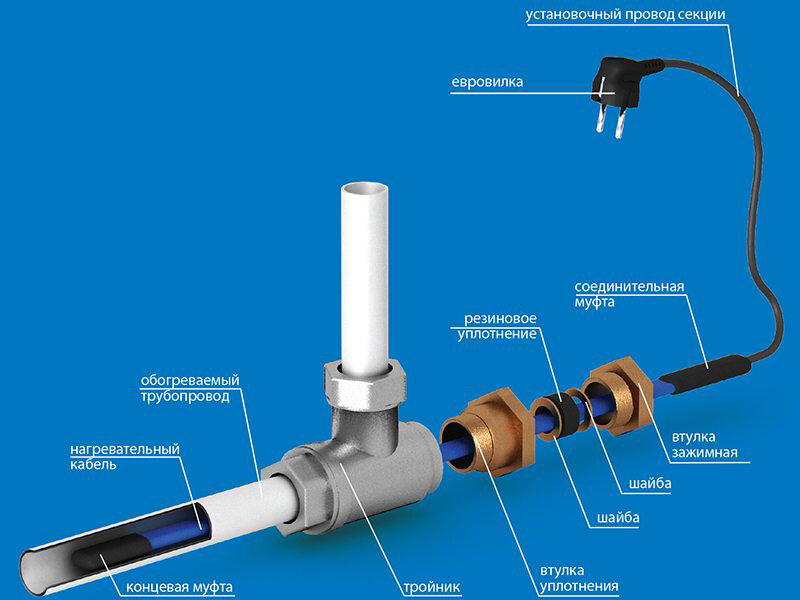
When the wire is securely fastened inside or out, it is important to take care to insulate the end of the conductor. Experts recommend using heat shrink tubing
This product will perfectly protect the cores from moisture, which will reduce the risk of short circuits and repair work. We must not forget that it is required to connect the heating part with the "cold" one.

Wire connection
Tips and advice from experienced craftsmen:
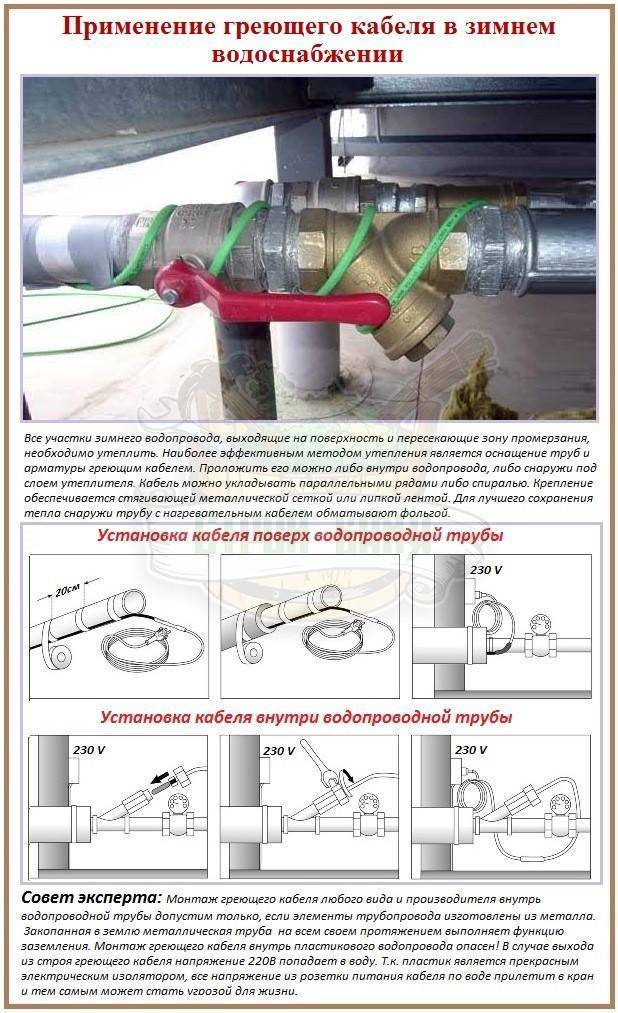
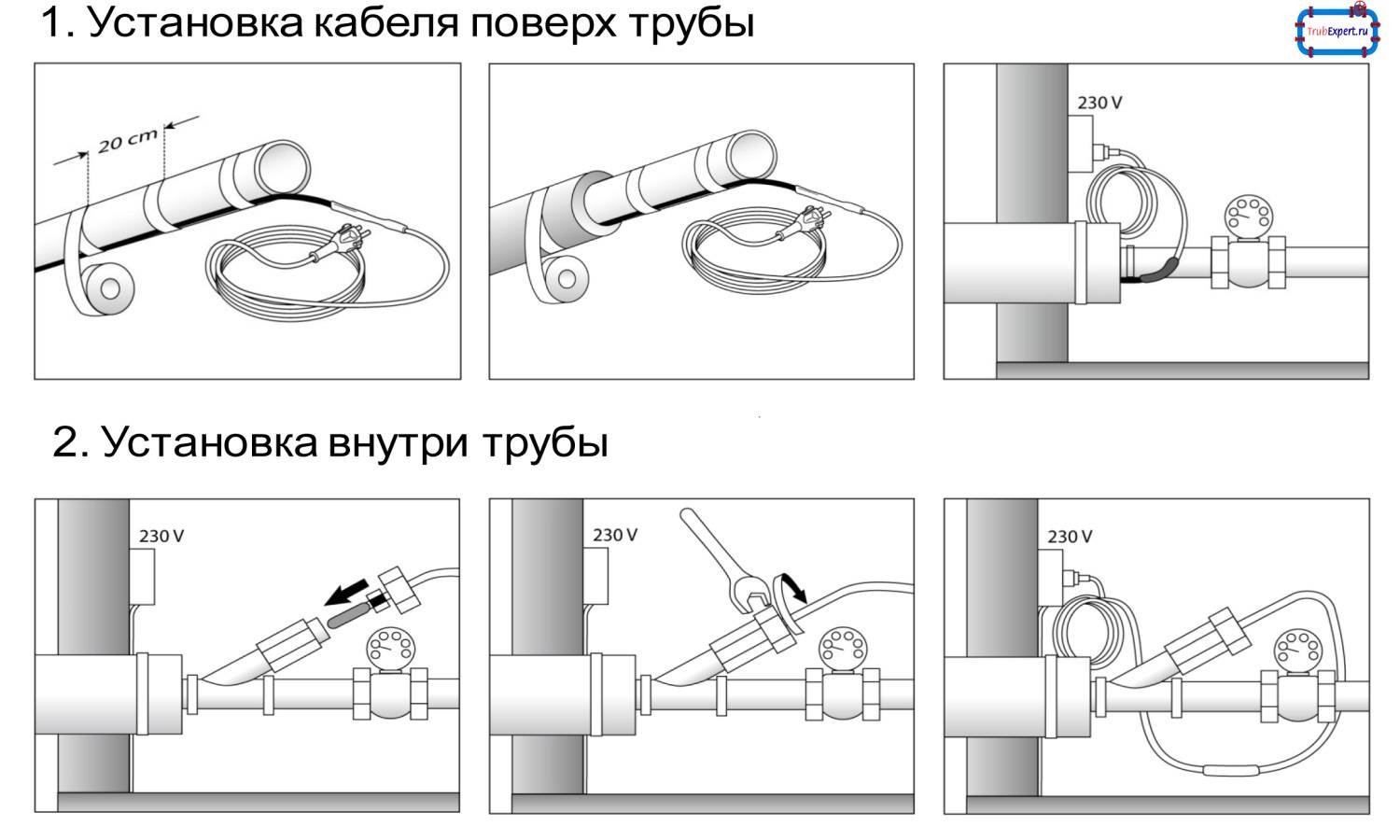
- If you use two methods of laying the wire inside and outside the pipe at once, you can increase the rate of water heating by several times, but this will require additional installation costs.
- Heating water pipes with a self-regulating heating cable will allow you to ignore warm sections and direct current to cold places. It is allowed to cut, so there will be no problems in installation even in hard-to-reach places. The length of the cable does not affect heat dissipation.
- Resistive wire is half the price, but its service life is much lower. If a conventional two-core cable was installed, but it is worth preparing for the fact that after 5-6 years it will have to be replaced.
- The braid on the wire serves to ground it. You can skip this stage of work, but it is better to familiarize yourself with the methods of grounding.
Video description
How to make a water pipe grounding is shown in the video:
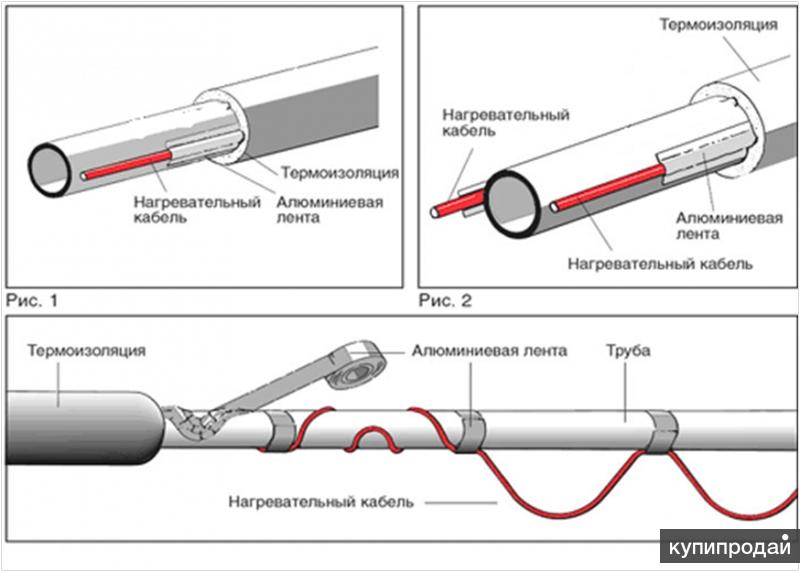
Most often, a linear cable laying method is chosen for self-assembly.
The level of heat transfer directly depends on which pipes are installed in the room
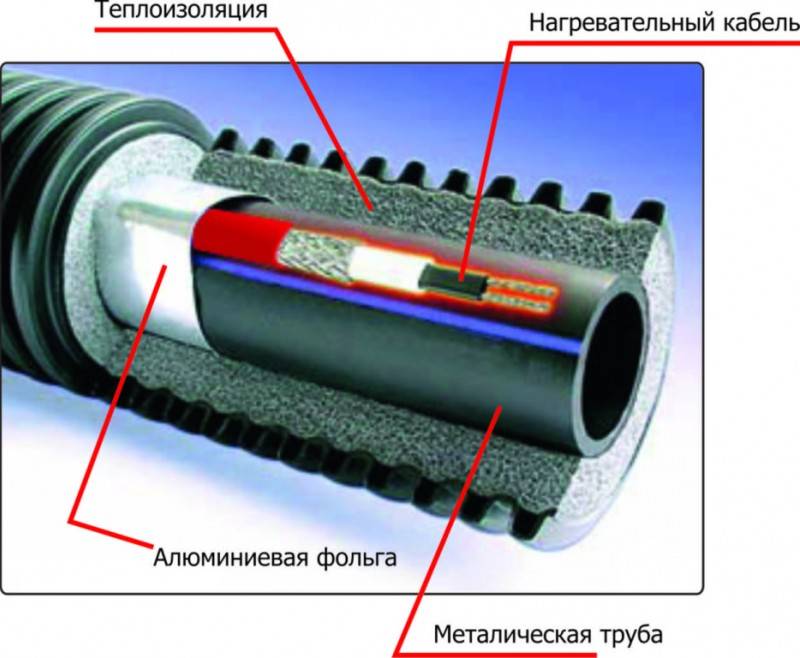
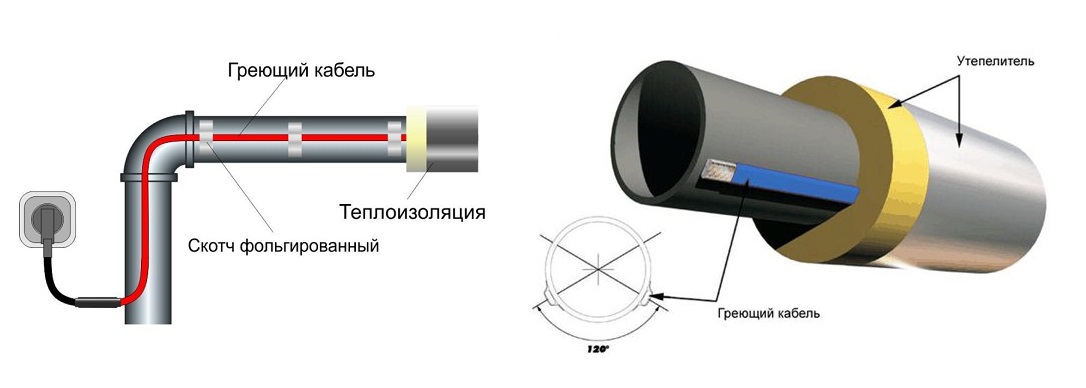
For plastic pipes, this indicator will not be high, which means that when installing a heating cable for plumbing, it will be necessary to wrap the pipes with aluminum foil.
Before attaching the cable to the outside of the metal pipe, it is important to make sure that there is no rust.If it is, cleaning and treatment with a special antiseptic is required.
If this is neglected, then in the future there is a risk of damage to the insulation.
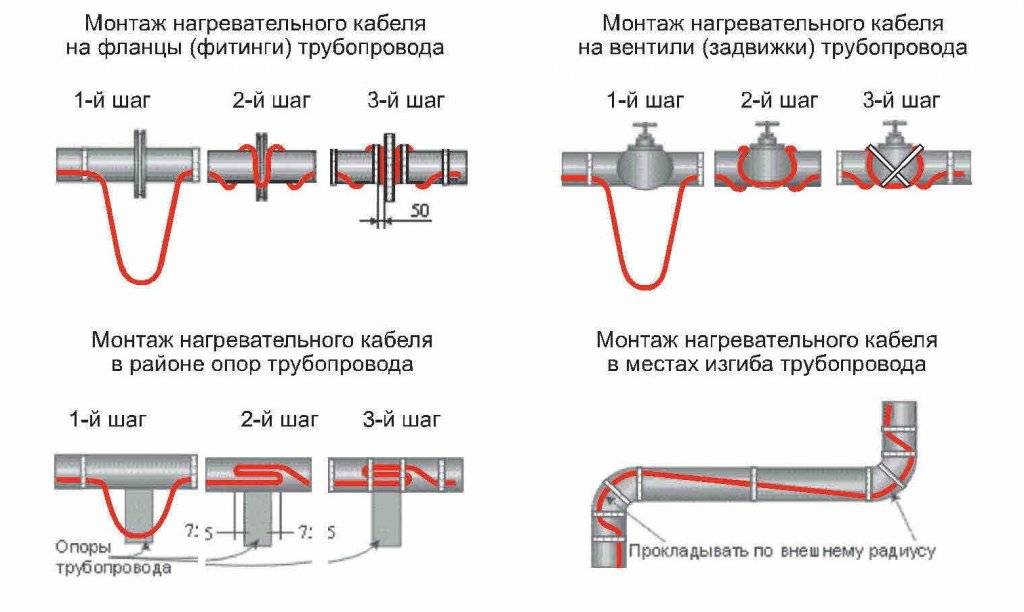
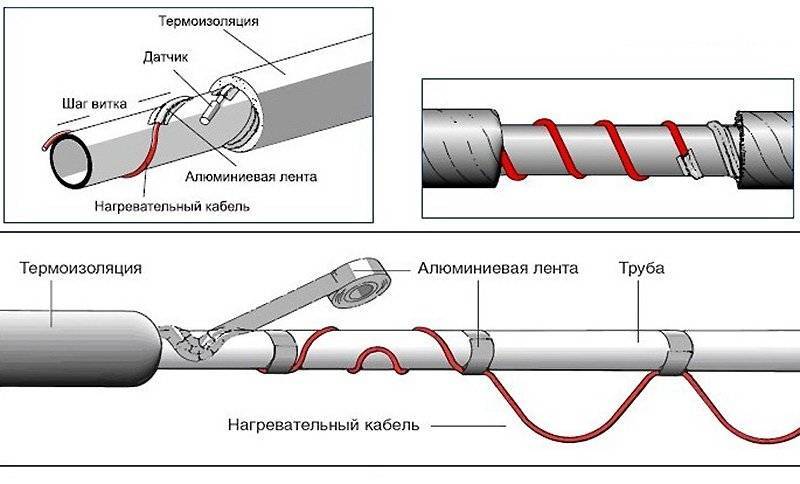
If fastening is carried out from the outside, then the distance between the insulating bundles should not be more than 30 cm. If you take a wider step, then after a while the fasteners will disperse.
In practice, some craftsmen stretch two wires at once to increase the heating rate. It is important that there is a small distance between the cables.
For fastening to plastic, it is better to use special clamps.
Fastening with clamps and thermal insulation in the section
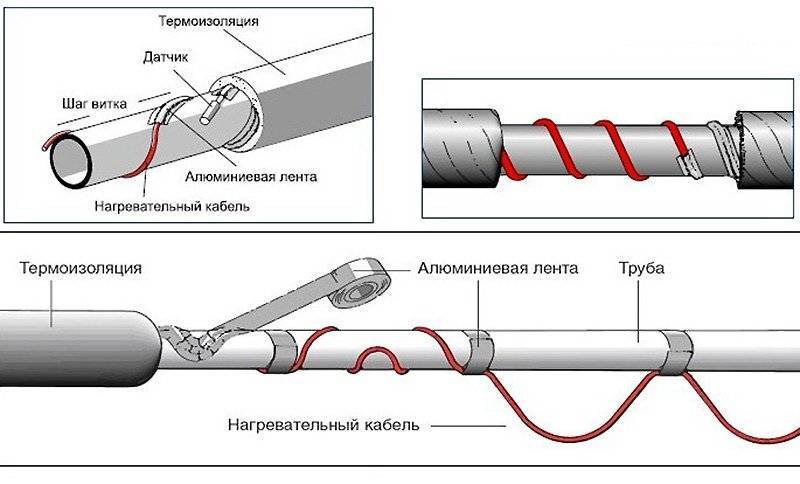
- If it is decided to twist the wire in a spiral, then initially the pipe is wrapped with metallized tape.
- To fix the insulation, it is better to use special ties. They can be purchased at any hardware store.
- It is necessary to completely isolate the temperature sensor from the electrical cable in order to eliminate the risk of short circuit and fire. This requires not only maintaining the distance between these devices, but also making the insulating gasket a special material.
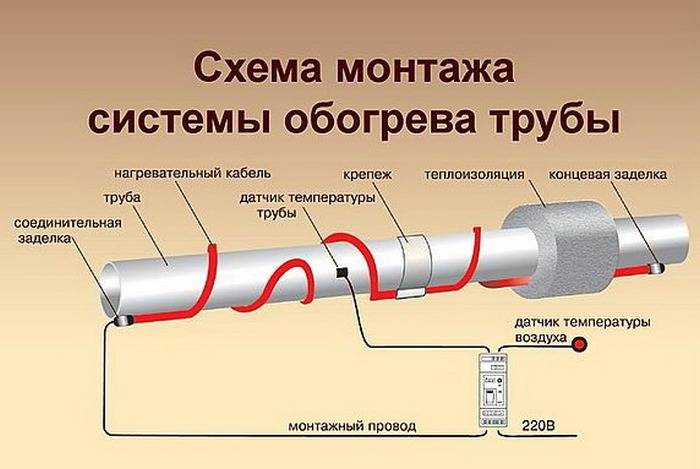
- Heating pipelines with a heating cable using a thermostat will provide constant temperature support. This device is best mounted next to the electrical panel or directly in it. It will not be superfluous to install an RCD.

wire with thermostat
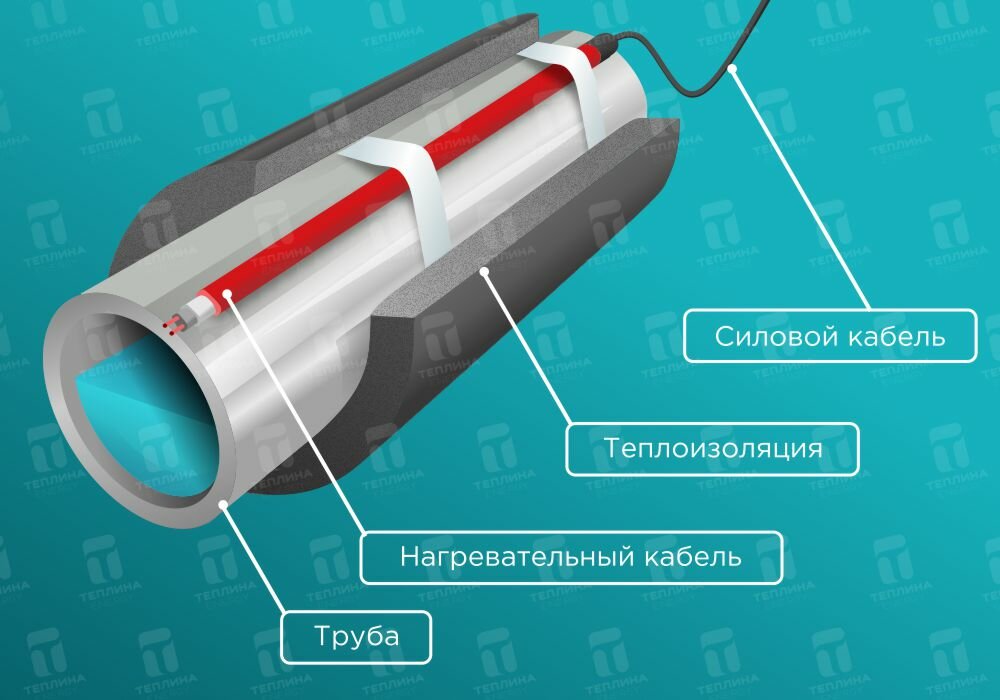
Be sure to perform thorough insulation of pipelines. Foam shells, mineral wool, foamed heat insulators are used. This will prevent heat dissipation.
Briefly about the main
First of all, it is important to choose the right cable for heating pipelines.
There are self-regulating and resistive types of cable that are used for plumbing
When choosing a cable, pay attention to the number of cores, type of section, heat resistance, length, presence of braid and other characteristics.
For plumbing, a two-core or zone wire is usually used.
Of the ways to install the wire, it is better to give preference to the outer one. Fasten the cable inside the pipe only if it is not possible to mount it from the outside. In general, internal and external installation technologies practically do not differ from each other, but the second method minimizes the risk of blockages, and also increases the life of the wiring.
Source
Types of heating wire
Manufacturers offer two types of heating cable:
- resistive; Resistive cable with one and two cores is also called serial
- self-adjusting. Self-regulating cable is considered more economical
The power of any type of flexible conductors is calculated in watts per 1 running meter. Resistive and self-regulating cables have several technical characteristics that are guided by when choosing a material for a heating system device.
- Maximum chain length. This parameter determines the maximum length of a line, including a branched one. Directly depends on the thickness and resistivity of the wire, the number of cores. If the permissible chain length is exceeded, there is a high risk of failure of the entire heating system.
- Maximum operating temperature. Indicates the ability of the cable to maintain operating temperature for an extended period of time.
- Maximum temperature without load. This characteristic determines the operating conditions of the cable in the disconnected state.
Regardless of the type of conductors, there are three lines of them.
Table: types of heating cable with characteristics
| Characteristic | Maximum operating temperature (C°) | For what purpose is it intended | Marks and brands |
| low temperature | 65 |
| Nelson CLT, CLTR, LT Raychem Frostop, ETL, BTV, GM-2-X, EM2-XR Nexans DeFrost Pipe CCT KSTM, VR, NTR. |
| medium temperature | 120 | Installation of a heating system for pipelines and tanks that are not subjected to steaming. | Nelson QLT, Raychem QTVR. |
| high temperature | 12–240 | Installation of a heating system for pipelines and tanks that are subjected to steaming. | Raychem XTV, KTV, VPL Nelson HLT CCT BTX, VTS, VC. |
Resistive and self-regulating cables differ in the principle of operation and connection methods. Each of these conductors has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Means for heating the drain and roof overhang
To prevent the formation of frost, various systems for heating gutters and roofs are currently used, but almost every one of them is based on the use of a special heating cable and automation equipment.
Let us consider in more detail what types of heating cable and control equipment exist, which of them will be preferable for selection.
Which heating cable to choose
There are two main types of heating cables for roofs and gutters:
Resistive cable. In practice, it is a conventional cable consisting of a metal core and insulation.The resistive cable has a constant resistance, a constant heating temperature during operation and a constant power. The heating of the cable comes from a closed circuit connected to electricity.
Design (diagram) of a resistive heating cable
Self-regulating cable for heating gutters and roof overhangs is more technologically advanced. It consists of a heating self-regulating element (matrix) that reacts to the ambient temperature (drainpipe) and changes its resistance and, accordingly, the degree of heating, as well as an insulating sheath, braid and outer sheath.
Each of the types of heating cables is able to provide equally effective heating of the roof and gutters. However, each of them has its own advantages. So, the main advantage of a resistive cable is its much lower price compared to a self-regulating cable. At the same time, the second type is more efficient in terms of electricity consumption and unpretentious to the laying conditions.
When the outdoor temperature rises, the number of current-carrying paths in the cable matrix decreases, due to which the power and the amount of electricity consumed decrease. The temperature of the self-regulating cable is also reduced. All this avoids the need for a temperature sensor that automatically regulates the operation of the cable.
Advice from a professional: The most effective in terms of cost and quality is considered to be a combined system of heating cables. Usually inexpensive resistance cables are used in the roof part of the system, while the heating of gutters and gutters is provided by self-regulating cables.
Design (diagram) of Devi self-regulating heating cable
As for the calculation of energy consumption and the choice of power of heating cables, here the norm for products of a resistive type is a cable with a power in the range of 18-22 W per linear meter, for self-regulating - 15-30 W per meter. However, it should be noted that in the case of a drainage system made of polymeric materials, the cable power should not exceed 17 W per linear meter, otherwise there is a risk of damage to the drain due to excessively high heating temperatures.
The composition of the heating system of the drain and roof
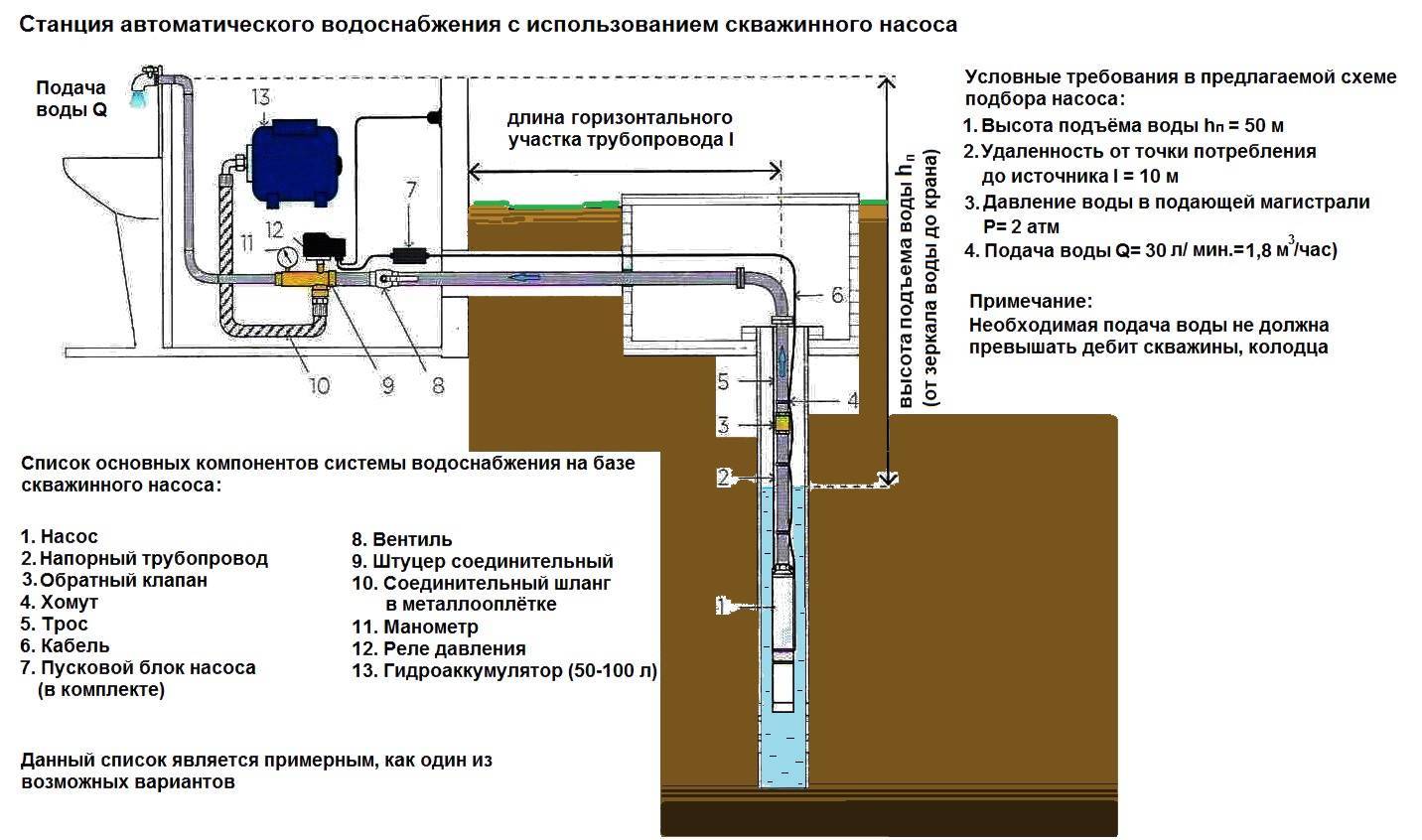
In addition to the actual heating cables, heating systems also consist of the following main components:
- fasteners.
- Control panel, usually consisting of:
- input three-phase circuit breaker;
- residual current devices, usually 30mA sensitivity;
- four-pole contactor;
- single-pole circuit breakers for each phase;
- thermostat control circuit breaker;
- signal lamp.
Distribution network components:
- power cables used to power heating cables;
- signal cables connecting thermostat sensors with the control unit;
- mounting boxes;
- couplings ensuring the tightness of connections and terminations of all types of cables.
Heating cable connection diagram
thermostat. Adjustment of the cable heating system can be carried out using two types of devices:
- Actually, the thermostat. This device is designed to turn on the heating system in a given temperature range. Usually the operating range is set within -8..+3 degrees.
- Weather stations.In addition to a certain temperature range, the weather station is able to monitor the presence of precipitation and their melting on the roof. The station includes not only a temperature sensor, but also a humidity sensor, and some weather stations are equipped with both a precipitation sensor and a melting (humidity) sensor.
When using a conventional temperature controller in the cable system, the user will need to independently turn on the system in the presence of precipitation and turn it off in their absence. The weather station, on the other hand, allows you to fully automate the process of the system and even program the time delays for its shutdown. On the other hand, the cost of conventional thermostats is much more profitable.
Types of heating cable
All heating systems are divided into 2 large categories: resistive and self-regulating. Each type has its own area of application. Suppose resistive ones are good for heating short sections of pipes of small cross section - up to 40 mm, and for long sections of the water supply system it is better to use a self-regulating (in other words - self-regulating, "samreg") cable.
Type #1 - resistive
The principle of operation of the cable is simple: a current passes through one or two cores located in an insulating winding, heating it. Maximum current and high resistance add up to a high heat dissipation coefficient. On sale there are pieces of resistive cable of a certain length, having a constant resistance. In the process of functioning, they give off the same amount of heat along the entire length.
Single-core cable, as the name suggests, has one core, double insulation and external protection. The only core acts as a heating element
When installing the system, it must be remembered that a single-core cable is connected at both ends, as in the following diagram:
Schematically, the connection of a single-core type resembles a loop: first it is connected to an energy source, then it is pulled (wound) along the entire length of the pipe and comes back
Closed heating circuits are more often used to heat a roof drainage system or for a “warm floor” device, but an option applicable to plumbing also exists.
A feature of the installation of a single-core cable on a water pipe is its laying on both sides. In this case, only the external connection type is used.
For internal installation, one core is not suitable, since laying the “loop” will take up a lot of internal space, moreover, accidental crossing of wires is fraught with overheating.
A two-core cable is distinguished by the separation of the functions of the cores: one is responsible for heating, the second for supplying energy.
The connection scheme is also different. There is no need for a “loop-like” installation: as a result, the cable is connected at one end to the power source, the other is pulled along the pipe
Two-core resistive cables are used for plumbing systems as actively as samregs. They can be mounted inside pipes using tees and seals.
The main advantage of a resistive cable is its low cost. Many note reliability, long service life (up to 10-15 years), ease of installation. But there are also disadvantages:
- high probability of overheating at the intersection or proximity of two cables;
- fixed length - can neither be increased nor shortened;
- the impossibility of replacing the burned-out area - you will have to change it completely;
- the impossibility of adjusting the power - it is always the same along the entire length.
In order not to spend money on a permanent cable connection (which is impractical), a thermostat with sensors is installed. As soon as the temperature drops to + 2-3 ºС, it automatically starts heating, when the temperature rises to + 6-7 ºС, the energy is turned off.
Type #2 - self-adjusting
This type of cable is versatile and can be used for various applications: heating of roofing elements and water supply systems, sewer lines and liquid containers. Its feature is independent adjustment of power and intensity of heat supply. As soon as the temperature drops below the set point (assume + 3 ºС), the cable begins to heat up without outside participation.
Scheme of a self-regulating cable. The main difference from the resistive counterpart is the conductive heating matrix, which is responsible for adjusting the heating temperature. Insulating layers do not differ
The principle of operation of the samreg is based on the property of the conductor to reduce / increase the current strength depending on the resistance. As the resistance increases, the current decreases, which leads to a decrease in power. What happens to the cable when it cools down? The resistance drops - the current strength increases - the heating process begins.
The advantage of self-regulating models is the "zoning" of work. The cable itself distributes its “labor force”: it carefully warms up the cooling sections and maintains the optimum temperature where strong heating is not needed.
The self-regulating cable works all the time, and this is welcome in the cold season.However, during a thaw or in the spring, when frosts stop, it is irrational to keep it on.
To fully automate the process of turning the cable on / off, you can equip the system with a thermostat that is "tied" to the outside temperature.
Design and scope
Depending on the type and technical characteristics, heating cables are used to heat drains, water and sewer pipes, tanks. The main purpose is to protect the liquid from freezing by increasing the temperature.
Heating systems are relevant for outdoor communications, that is, for use in the ground or outdoors.

The basis of functioning is the ability of the cable to convert electricity into heat. The wire itself cannot transmit energy, as power counterparts do. He only receives it, and then gives off heat to the pipe (tray, gutter, tank, etc.)
Heating systems have one useful ability - zonal application. This means that you can take a set of elements and assemble a mini-system from it for heating a single area, without connecting to the entire network.
This results in material and energy savings. In practice, you can find miniature "heaters" of 15-20 cm each, and 200-meter windings.
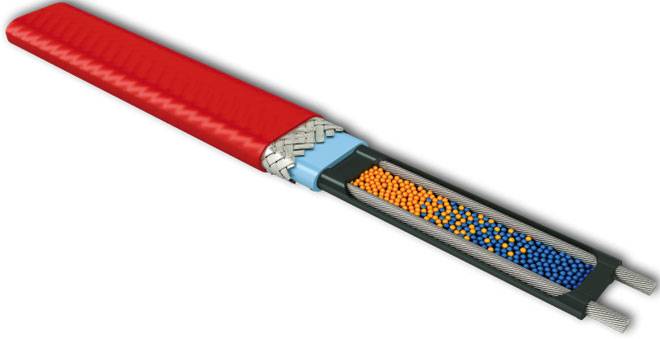
The main components of the heating cable are the following elements:
- Inner core - one or more. Alloys with a high electrical resistance are used for its manufacture. The higher it is, the greater the value of specific heat release.
- Polymer protective shell. Together with plastic insulation, an aluminum screen or copper wire mesh is used.
- Durable PVC outer sheath covering all internal elements.
Offers of various manufacturers may differ in nuances - the alloy of the core or the method of protection device.
Shielded types are considered more reliable, equipped with foil protection and having 2-3 cores instead of one. Single-core products - a budget option, which is good just for assembling systems for small sections of water supply (+)
To improve the performance, the copper braid is nickel-plated, and the thickness of the outer layer is increased. In addition, the PVC material must be moisture resistant and resistant to ultraviolet radiation.
Conclusion
What kind of heating cable to take for water supply and sewerage? If you need to heat a small section of the pipe, for example, at the entrance to the house, then you can save money by buying a resistive cable with a temperature controller - the “idle” electricity consumption will be minimal.
For large sections of the pipeline, drain or roof, as well as in conditions of frequent temperature changes or different levels of the pipe in the ground, it is better to take a self-regulating heating cable. You will spend more in the purchase, but during operation you will quickly pay for it due to energy savings and better heat transfer.
A couple more tips for home masters:
- The washing machine jumps during the spin cycle: how to fix it?
- 7 Home Electrician Safety Rules Everyone Should Follow