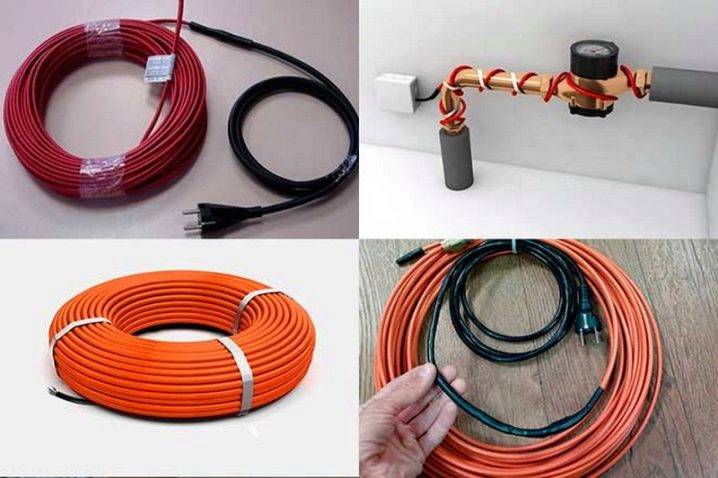
- Types of heating cable
- Resistive heating cables
- Self-regulating heating cables
- The principle of operation of the heating cable
- Resistive heating cable
- Self-regulating heating cable
- Thermal relay
- Design differences of self-regulating systems
- The nuances of roof heating
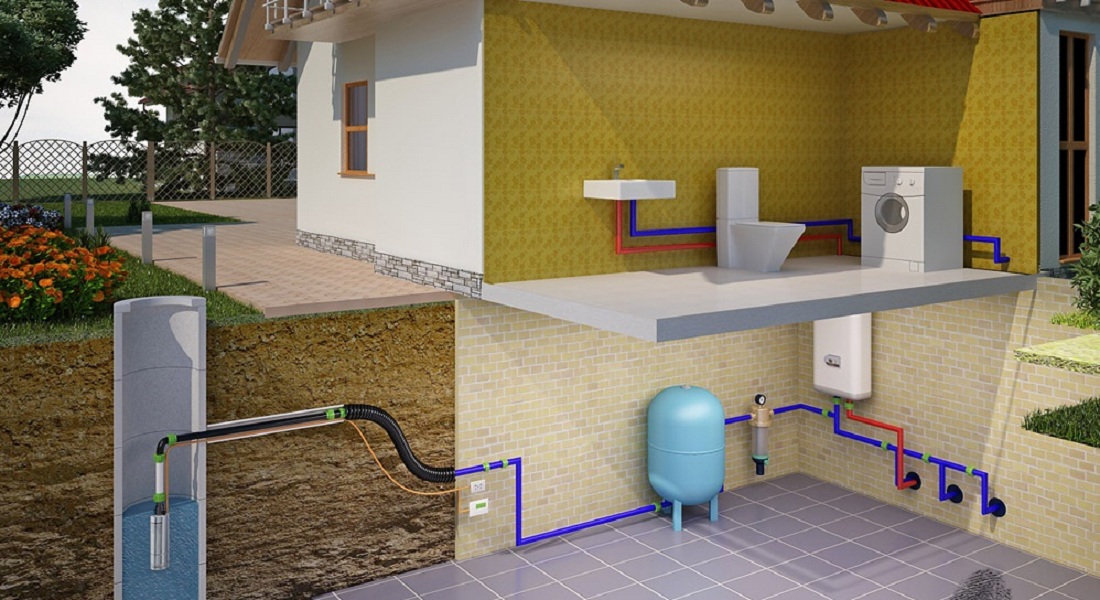
- Internal heating systems for sewer pipes
- Laying the heating cable inside the sewer pipes
- Cables used for indoor laying in an apartment
- Laying a self-regulating thermal conduit
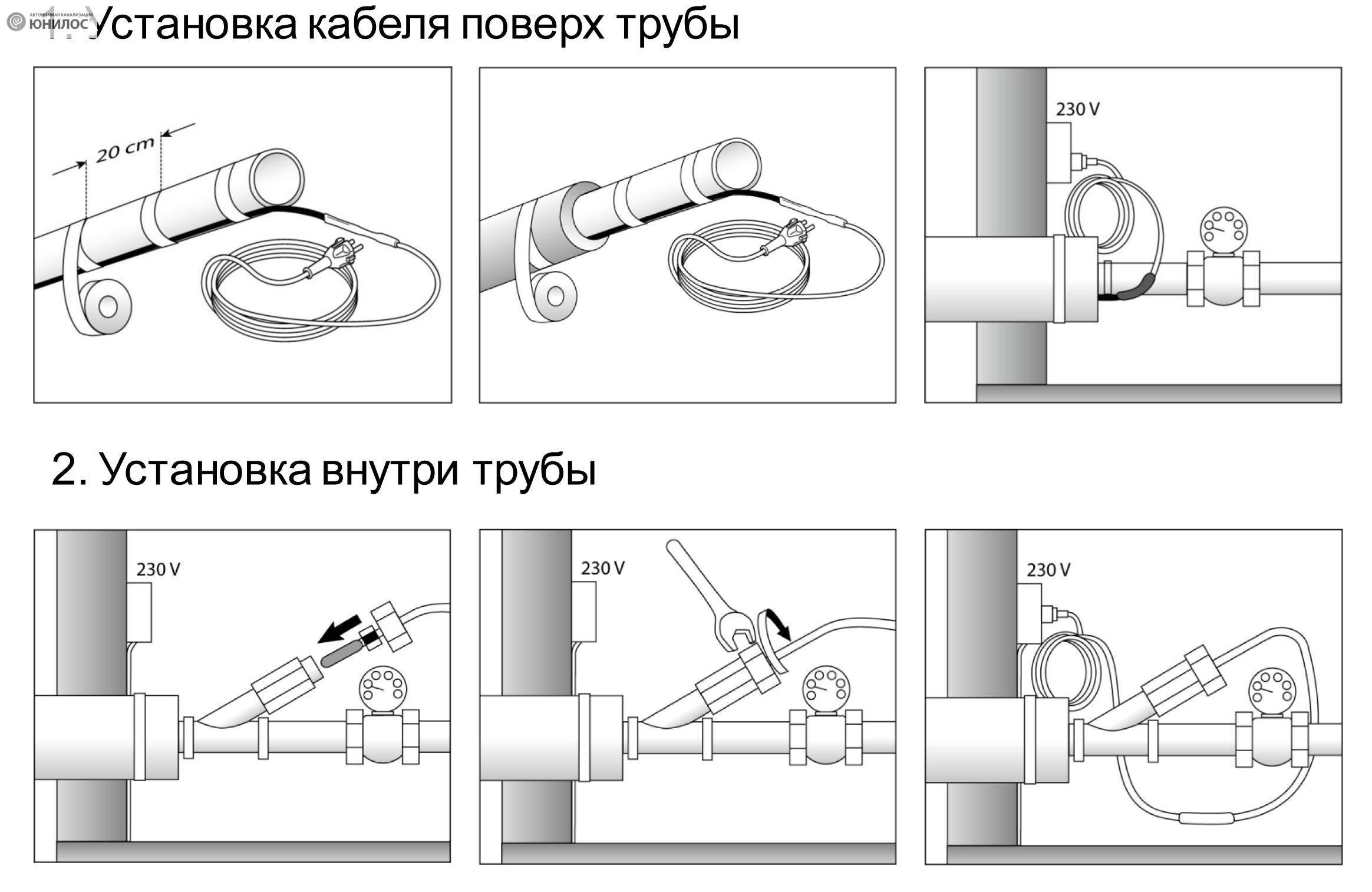
- External fastening
- Direct laying
- Spiral laying
- Internal reinforcement
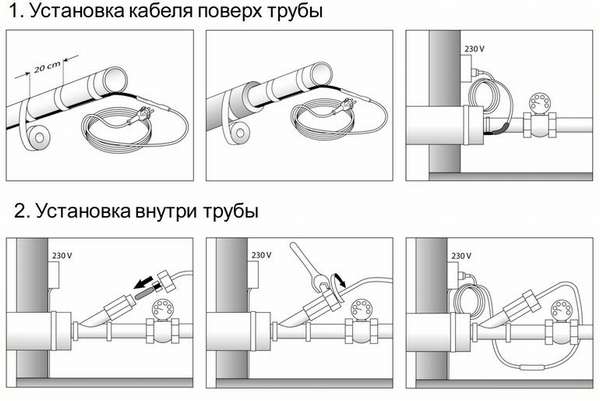
- Mounting
- Ways of laying the heating element
- Internal heater installation
- External installation of pipe heating
- Set or cut?
- Video: coupling the heating cable inside the pipe
- Types of pipeline heating
- Resistive option for heating
- Semiconductor self-adjusting
- How to choose the right cable?
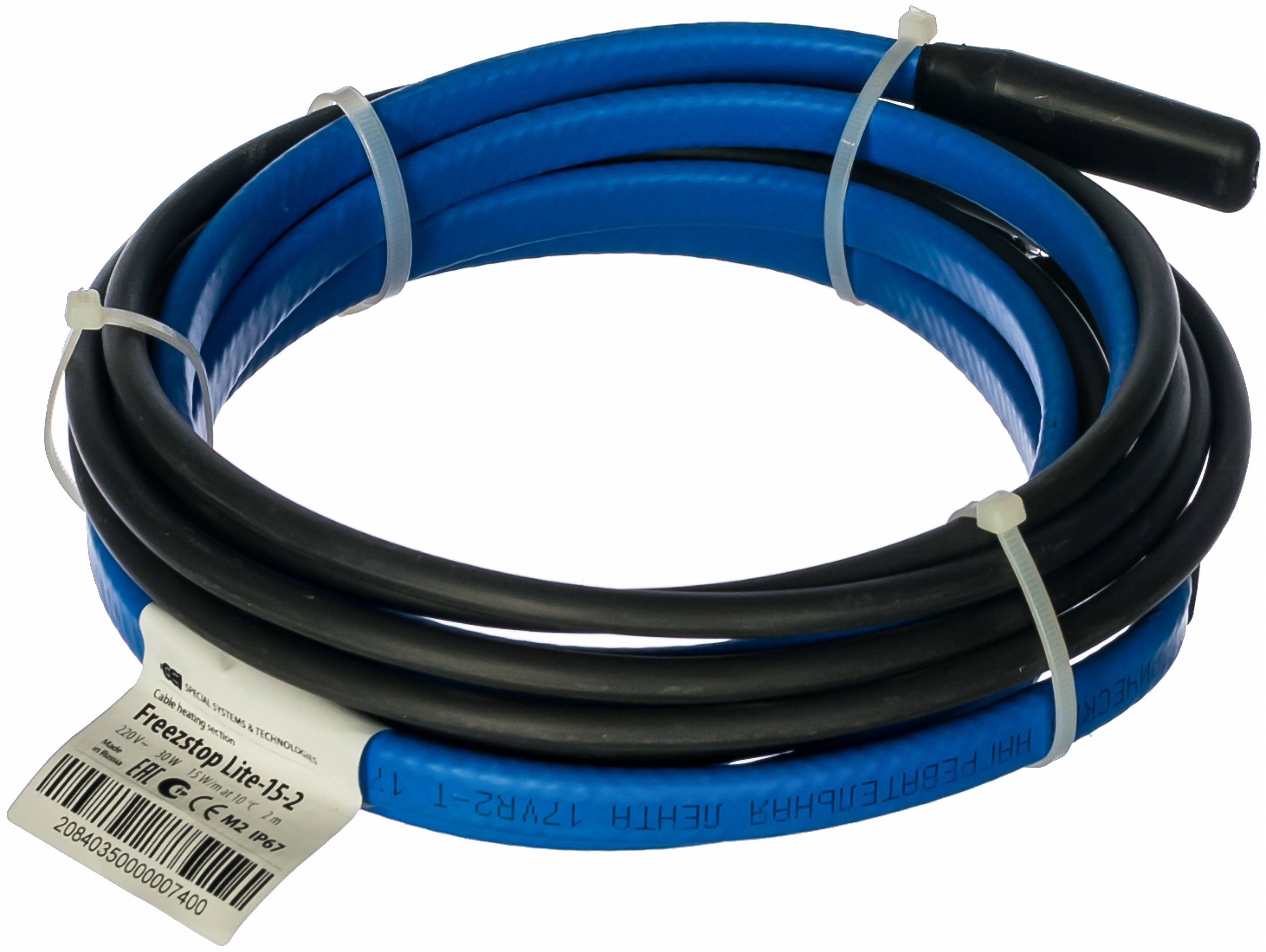
Types of heating cable
TSA Self-Regulating Low Temperature Heating Cable
To learn more
Self-Regulating Low Temperature Heating Cable TSL
To learn more
Self-regulating medium temperature heating cable TSS
To learn more
Resistive heating cable 50HT(FA).
To learn more
Resistive heating cable TS-RD
To learn more
Resistive heating cable TS-RS
To learn more
Heating cable RTS
To learn more
Heating cable LTS
To learn more
The whole variety of cable products presented on the Russian market can be divided into two large groups: resistive and self-regulating models. Let's consider each option in more detail.
Resistive heating cables
A classic of the genre, which is gradually losing ground under the onslaught of more modern solutions. One of the undoubted advantages of resistive products is their affordable cost. Regardless of which subspecies we are talking about, the list of main characteristics is preserved: models are offered for sale with unchanged power and length parameters. It is forbidden to cut the product into several segments, since the resistance in this case will decrease, and the temperature of the cores will increase (and become more than acceptable) - all this will naturally lead to overheating and breaking the circuit. Therefore, when creating a project, you must initially clearly calculate the required wire length.
In addition to low cost, resistive models can also boast such advantages as a simple device, easy installation, stability of characteristics throughout the entire service life, and a high level of reliability.
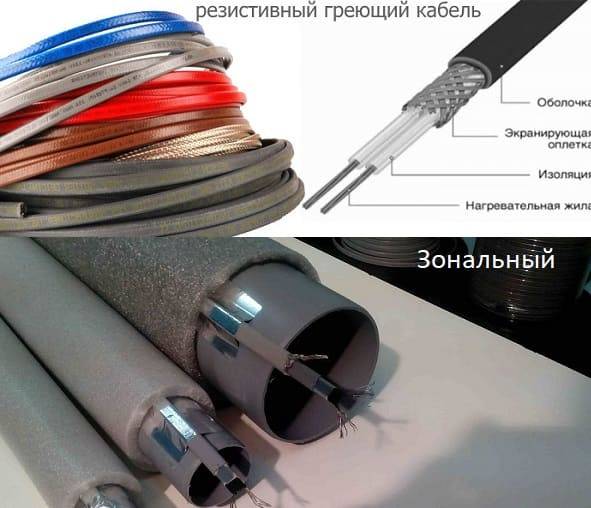
There are several types of resistive cables:
- Single core. The simplest design with a heat-resistant outer shell, under which a shielding copper braid is “hidden”. Under the braid is an insulation that protects the heating conductor. Single-core products are used only to create closed circuits. Their installation is quite simple and does not require the involvement of specialists.
- Two-core. They are an analogue of the previous version with the only difference that we are talking about two cores as the main structural elements. If you do not need a closed circuit, while the main criterion is the availability of a cable system in financial terms, this is a great option. One end of the product is connected to the power supply, the other is closed with a sealed sleeve.
- Zonal. Standard structure, improved by the presence of heating coils between the cores. The spirals are at the same distance with equal power - this eliminates the main drawback of resistive wires: thanks to the spirals, the product can be divided into segments (with a certain step).
Important!
If a spiral conductor burns out on some section of the zonal cable, a cold zone will appear here, but the system itself will function.
Self-regulating heating cables
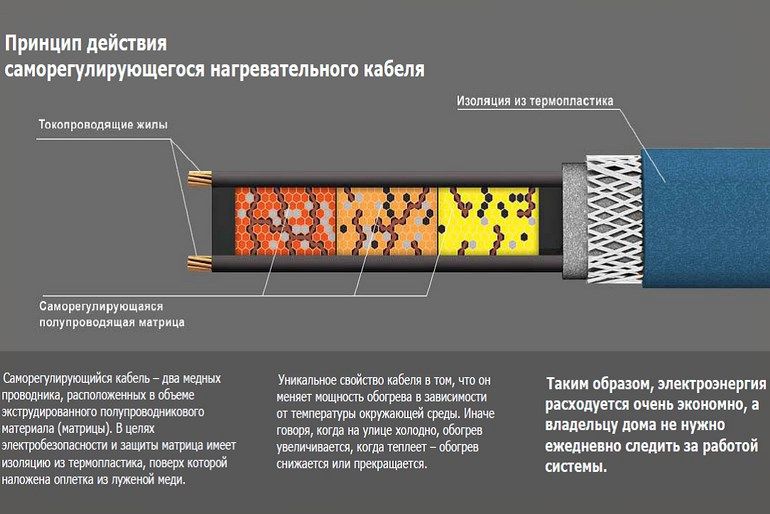
The question of which manufacturer is better is most likely to be raised unlawfully. A feature of this option is the presence of a self-regulating matrix in the cable structure, which is made of a semiconductor elastic material and is located between the current-carrying cores. The level of resistance of the matrix is determined by the ambient temperature, which determines the amount of power consumed and the heating efficiency. The wire emits heat only where it is necessary: if some section lies in ice, and the second is in heat, then the first one will heat up more.
If we talk about the advantages of self-regulating cables, we can distinguish:
- economy of electricity. The cable will not take more power than it needs;
- relative ease of installation. When laying products, parts of the wire can be crossed - this will not affect the operation of the system;
- the ability to cut the product of any length without compromising its performance parameters, power;
- flexibility and elasticity. Models can be used to heat structures of any shape, pipes of any diameter.
The principle of operation of the heating cable
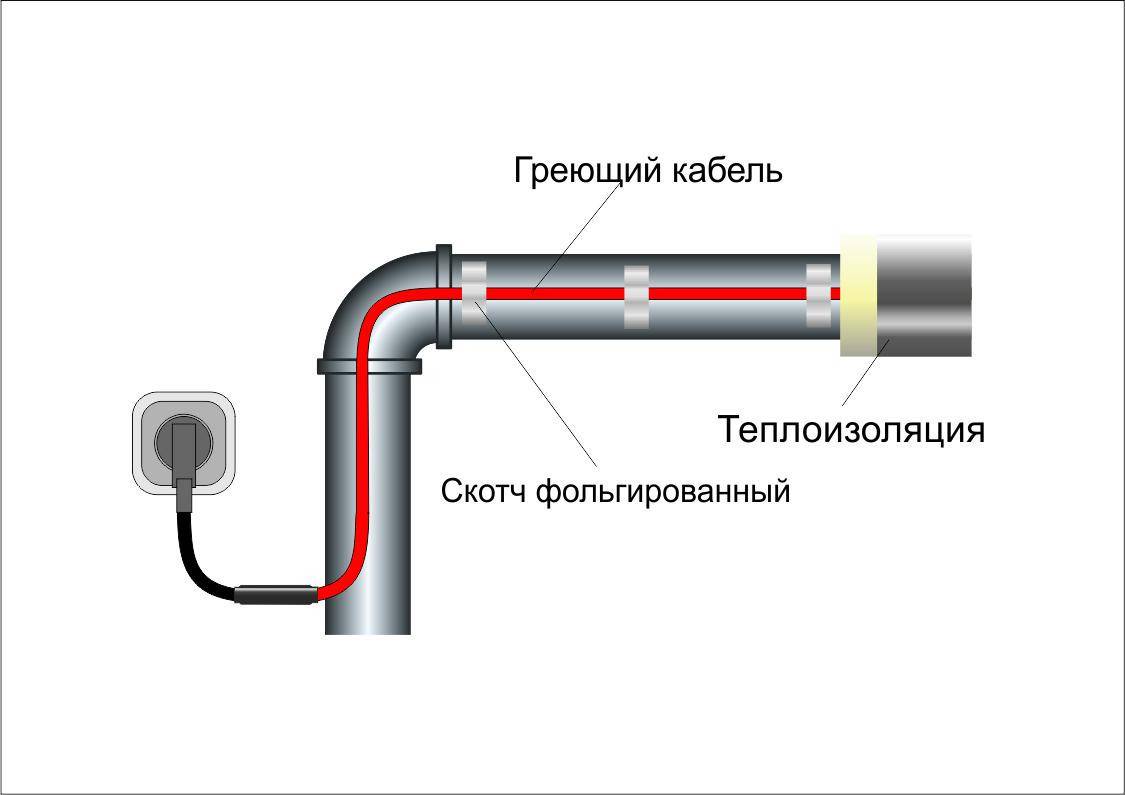
Such cables are represented by a core wire, the heating of which provides electric current at the moment it enters it. Further, heat begins to spread in all directions, as a result of which the ice turns into water. From the outside, the cable is protected by seamless insulation. An electrical cable is connected to the heating wire, for fixing which laser soldering is used. Moreover, the end of the latter has a plug. For operation, the plug must be connected to a household electrical outlet.
Based on such a parameter as the heating control option, then all heating wires can be classified into two types:
- resistive;
- self-regulating.
Moreover, each of them can be used to heat water. At the same time, they have their own characteristics.
Resistive heating cable
It is distinguished by the presence of resistance, the value of which remains unchanged all the time. When such a cable is connected, heat generation occurs without interruption in a strictly specified temperature range, which usually ranges from 5 to 13 degrees Celsius. Its use allows at any time to effectively protect pipes from ice, which never remains in a solid state in winter.
Self-regulating heating cable
For such a cable, a more complex principle of operation is characteristic.It is distinguished by the presence of dynamic resistance, the value of which can increase or decrease depending on the temperature of the water. Thus, heat begins to be released in a greater or lesser amount. It is due to the presence of a self-regulating mechanism of operation that such a cable eliminates its overheating, as well as burnout.
Thermal relay
In order for the cable to successfully cope with its task, it is usually used with additional devices. This is a thermal relay with a temperature sensor, the main purpose of which is to automatically turn on in the event of a decrease in temperature. Its other function is to disconnect the cable, which occurs at the moment when the temperature rises to the upper permissible value.
To ensure the stability of the operation of such a device, it is important to choose the right place for installing the temperature sensor. An unacceptable place for this element is the area next to the heating cable
It is recommended to select an area on the opposite side of the pipe to place the sensor. It must be borne in mind that the use of this heating in combination with a thermal relay can lead to a decrease in the operating life of the first. A contributing factor to this is an increase in resource consumption due to the frequent switching on and off of the heating.
Design differences of self-regulating systems
Samregs (abbreviated) should not be confused with resistive counterparts - the first modifications of heating cables.
In short, the disadvantages of the resistive type, due to which it is used less and less, are as follows:
- a certain length, the impossibility of increasing or shortening;
- constant resistance along the entire length, which makes it impossible to adjust the temperature in certain areas;
- connection from both ends, causing difficulties during installation;
- risk of overheating at intersections;
- lack of repair as such, you have to change the entire system as a whole.
A positive feature of the resistive type is its low cost, so it is used where small protected areas need to be heated.
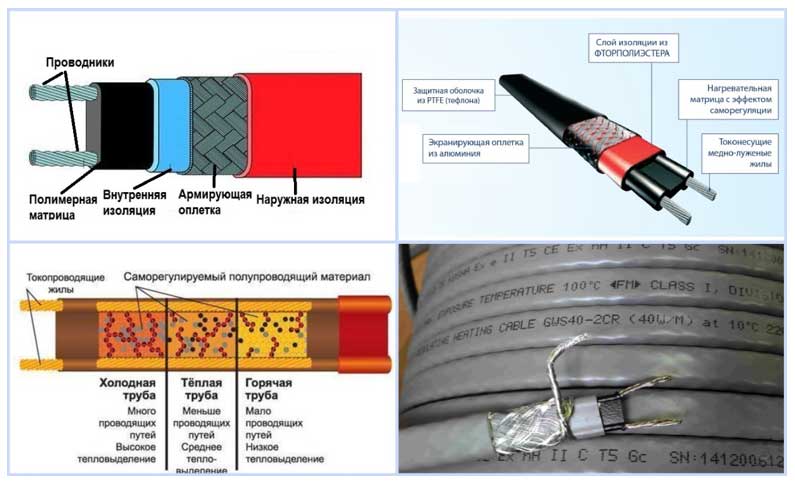
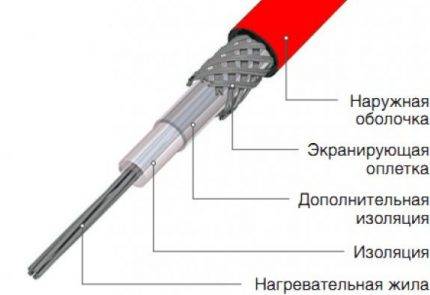 The scheme of a resistive single-core cable contains four main elements: a copper core that combines the functions of heating and heat transfer, internal and external protection, reinforcing braid
The scheme of a resistive single-core cable contains four main elements: a copper core that combines the functions of heating and heat transfer, internal and external protection, reinforcing braid
There are fundamental differences in the design of a self-regulating heating cable:
- Two strands of high resistance copper. The greater the resistance, the greater the ability to adjust the temperature.
- semiconductor matrix. This is a significant element of the cable, which makes it self-regulating. The matrix is sensitive to the ambient temperature. As the temperature drops, the resistance of the material rises and it starts to generate more heat.
- Internal insulation. High-quality material is characterized by a uniform structure and maximum thermal conductivity.
- Shielding braid. Most often it is a copper mesh or an aluminum screen. To protect the cable, the power must be connected via an RCD.
- External insulation. Its function is to protect all cable elements. The service life of the product depends on the characteristics of the external insulation.
The ability of the samreg to change its own resistance (hence, the power) from temperature fluctuations frees you from buying additional equipment - various kinds of thermostats with sensors.
Samreg scheme. The main distinguishing element is a semiconductor matrix located between two copper conductors. It is she who regulates the level of heat dissipation
The cable can be cut, and the length of the finished product can be shortened or extended if necessary.

If two cable branches accidentally cross, overheating or failure of the system will not occur. At any time, you can cut off or replace a fragment without damage to the entire heating structure.
But the main advantage of samreg is its “selectivity”. The matrix independently determines the cold areas and brings their temperature to the optimum value.
In sufficiently heated areas, it simply maintains the desired parameters (usually + 3-5 ºС). This is very convenient when it is necessary to protect a cable from freezing, which has various heating conditions throughout (for example, it passes through a heated room and through cold ground).
At the end of the cold season, there is no need to heat pipes, soil or roofs, so the cable is disconnected from the power supply. When there is a possibility of severe night frosts, you can use a thermostat that automatically turns on the system.
The nuances of roof heating
To create favorable conditions for the constant thawing of snow and ice on the roof and the drainage system, the heating cable is mounted in the following places:
- on the edge of the roof (preferably around the perimeter);
- in gutters under slopes;
- in drainpipes;
- in valleys.
In open places, the cable is fixed with clamps and brackets, in pipes it is hung on a cable or chain.
Variant of the anti-ice system device:
The final stage is carried out indoors. We install an electric control cabinet and connect the heating system. Then we turn on the thermostat and check how the system works.
Internal heating systems for sewer pipes
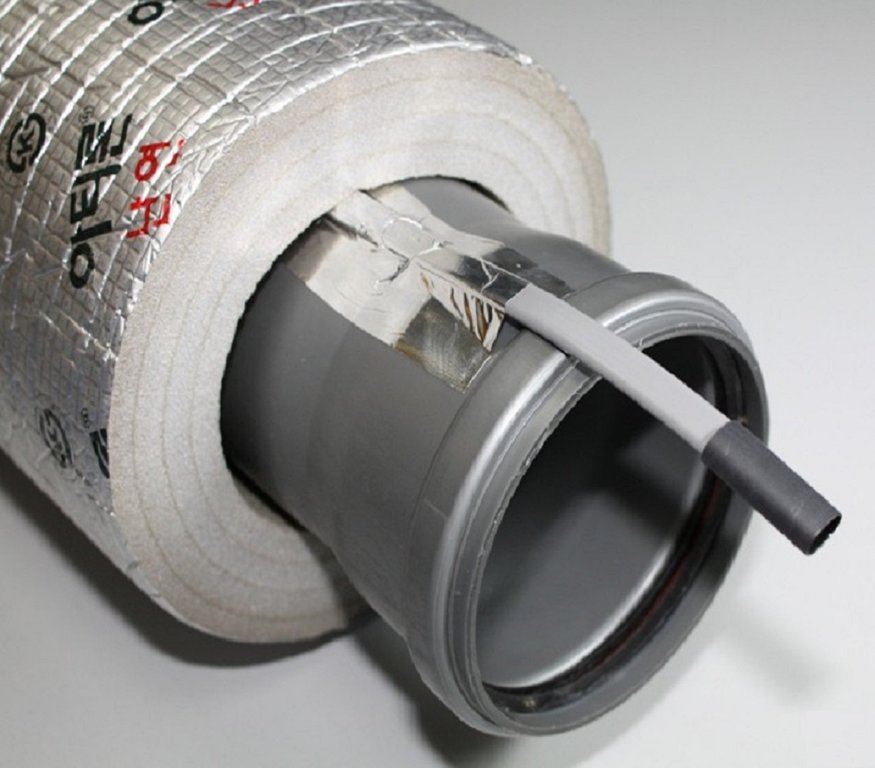
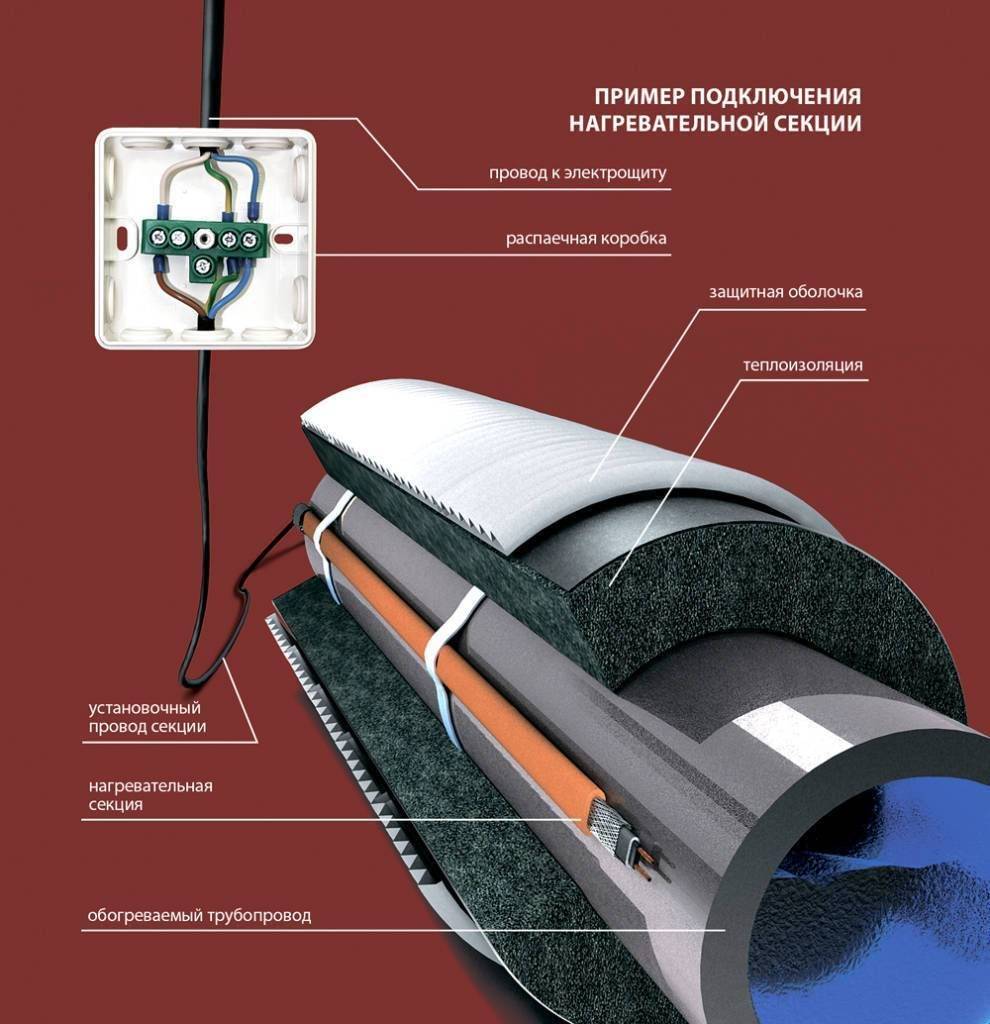
The use of internal heating systems occurs in small sections of the sewer pipeline, most often on street pumps. Internal systems are similar in principle to external systems, however, when entering the heating cable into the pipe, a tee must be installed beforehand. Through it, the heating cable will be inserted into the pipe.
Laying the heating cable inside the sewer pipes

Entering the heating cable into the sewerage system
There are cases when laying an electric heating cable is required to be carried out inside a sewer pipe. Then the cable is placed into the pipe through a special sleeve - a nipple. However, this comes with disadvantages:
- due to the introduction of the tee into the sewer pipeline, its reliability is reduced;
- the inner diameter of the pipe is reduced;
- increases the likelihood of blockages;
- if the pipeline is mounted with numerous transitions, bends, and also has a significant length, the installation of the heating cable inside the pipe is very complicated and time consuming.
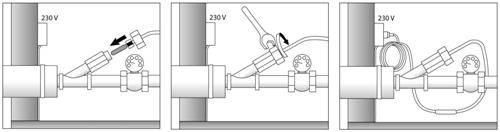
Installing the cable inside the pipe
In conclusion, I would like to say that high-quality heating of sewer pipes is an important condition for the efficient operation of sewerage in the cold season.And although heating systems consume a certain amount of electricity, they can be economical, even in the face of constantly rising electricity prices.
After all, the system can be supplemented with switches or controllers and thermostats that will monitor changes in temperature in the pipes and regulate energy consumption.
- How to replace a sewer riser with your own hands
- Where and how is the valve for domestic sewage used
- Installation, repair and ventilation of the sewer riser on their own
- Corrugated pipe for underfloor heating: selection and installation
- Autonomous sewerage
- Household pumps
- Gutter system
- Cesspool
- Drainage
- sewer well
- Sewer pipes
- Equipment
- Sewer connection
- The buildings
- cleaning
- Plumbing
- septic tank
- Choosing and installing a hanging bidet with your own hands
- How to choose an electronic bidet
- Choosing and installing a compact bidet
- How to choose a bidet manufacturer
- How to choose, install and connect a floor bidet
- How to install and adjust toilet cistern fittings
- How to connect a dishwasher with your own hands
- How to connect a washing machine with your own hands
- Cleaning sewer pipes: household recipes and equipment
- Heating system made of polyethylene pipes: how to create your own hands
Cables used for indoor laying in an apartment
The most popular and widespread type of electrical cable in the Russian Federation is VVG (vinyl-vinyl-naked). It is applied, both at open, and the closed types of laying. It has a copper core and two electrically insulating PVC layers.
There is a modification with increased protection against combustion - VVGng (non-combustible variety).The shell is made of low flammability polyvinyl chloride composition. The sheath material of this type of cable contains an additional additive that hinders the process of combustion propagation. It is recommended to use it with group laying, laying in trays and hidden wiring.

Cable brand VVGng
Another type of cable is VVGng-ls. It is a refinement of the previous modification, but unlike it, when burning, it emits a low amount of gas and smoke. Thus, providing additional safety to a person in the event of a cable fire. It is recommended to use it in places where there is a high probability of overloads, short circuits and fires. In apartments with electric stoves and ovens that consume a lot of power, it is most rational and safest to connect to the circuit from this type of cable.
Cable brand VVGngLS
The service life of all modifications of the VVG cable is at least 30 years.
NYM is an imported analogue of the VVG-ng-cable, manufactured according to German quality standards (DIN 57250). Like his "colleague" of domestic production, it is quite fireproof. In this case, a higher safety class is achieved due to the use of an additional (third) insulating layer.
NYM brand cable
PuVV - a wire with a copper core, having PVC insulation and used for hidden wiring (in strobes, concrete voids, under a thick layer of plaster). Widely used in powering sockets and switches, and especially in the installation of lighting networks. There is a multi-wire flexible version PBVVG, used in complex areas subject to numerous bends and breaks.The service life of such a cable is at least 20 years under nominal (recommended) operating conditions.
PuV or its flexible analogue PuGV is a single-core copper wire in PVC insulation, often used during electrical work in an apartment to create a ground network.
PVA is a flexible connecting wire made of copper with PVC insulation. It is widely used for powering stationary electrical appliances used for domestic purposes, as well as electric tools. The term of use of such cable products according to GOST is up to 6 years, but, as practice shows, it can reach more than 10.
PVS brand cable
PUNP - a universal flat wire, is the most "dangerous" and short-lived in comparison with other types of cable products on the market. According to the specifications, according to which it is produced, the deviation in the cross section can reach up to 30%, which negatively affects the quality. Fortunately for most people, the production of this electrical cable has been discontinued at the current time.
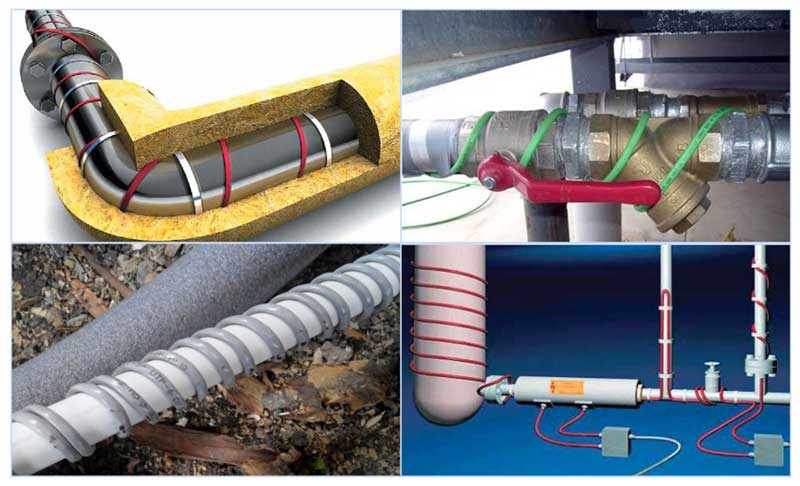
Laying a self-regulating thermal conduit
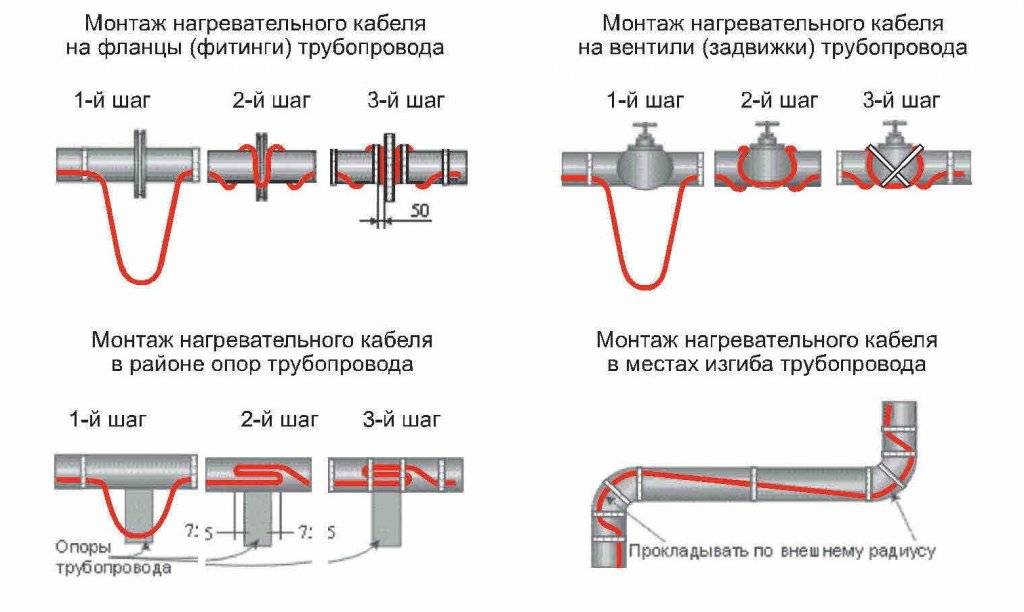
The heating wire for pipes can be laid in two ways: external and internal fastening. For each type of installation, there are certain standards. Therefore, in order to avoid mistakes, it is worth more carefully familiarizing yourself with all the styling techniques.
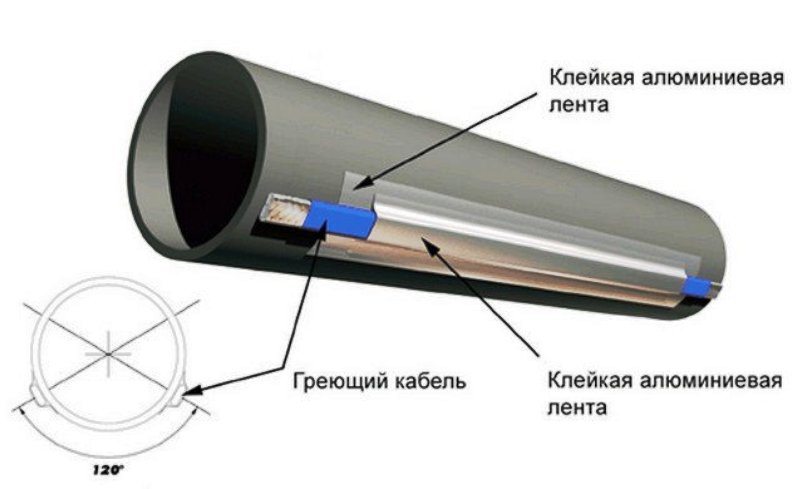
External fastening
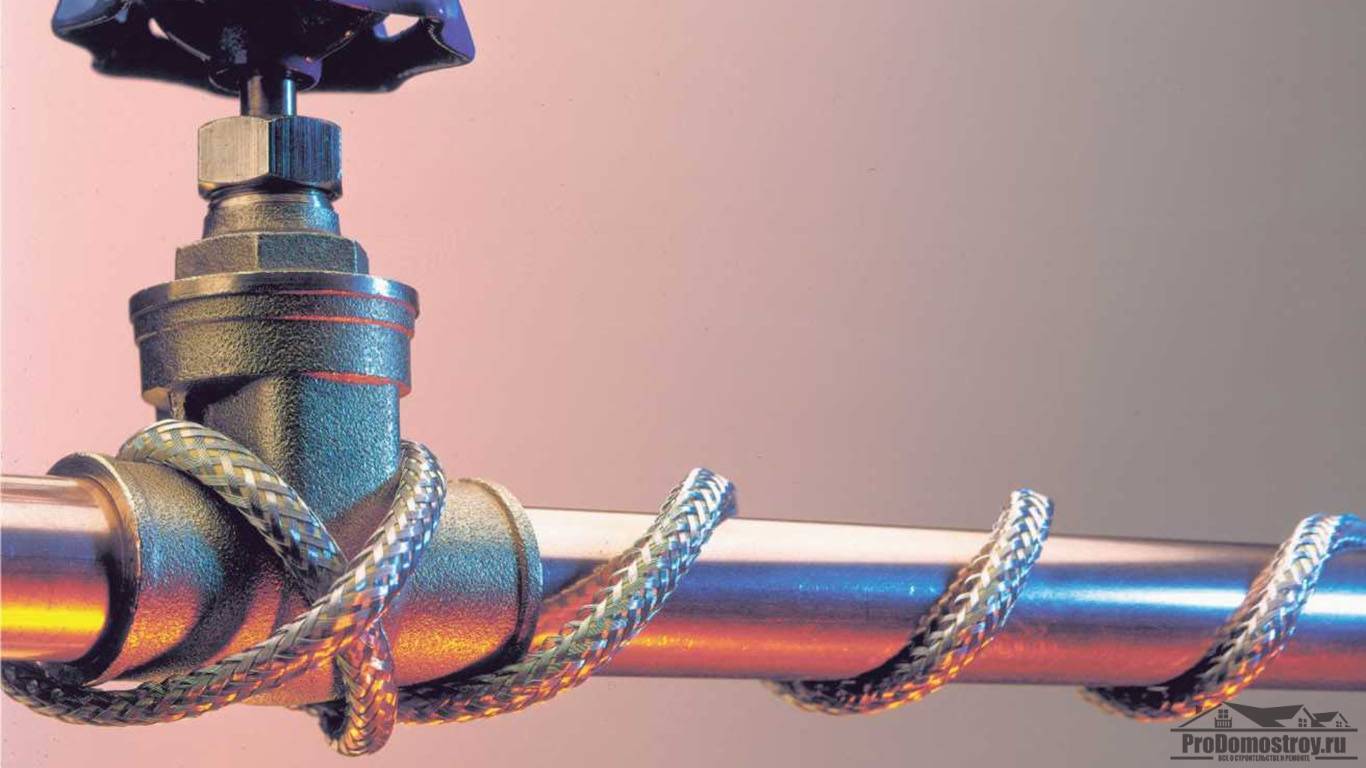
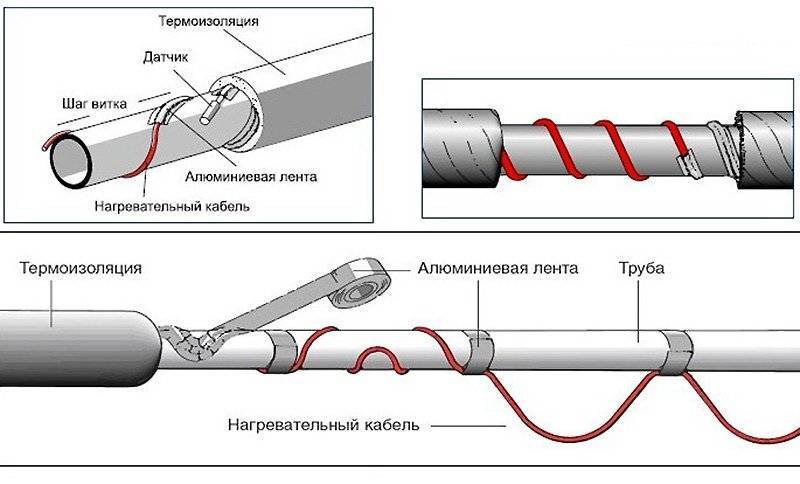
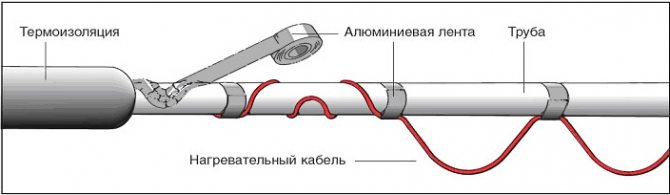
Laying the heating cable on the outer surface of the pipeline can be carried out in two ways: straight and spiral laying.
Direct laying
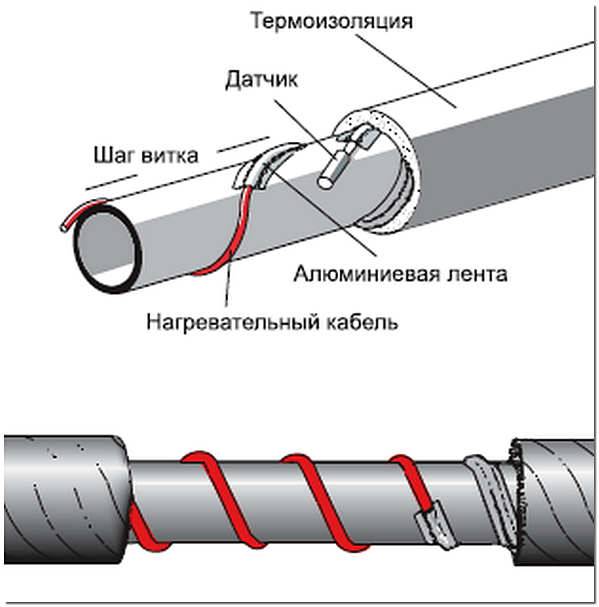
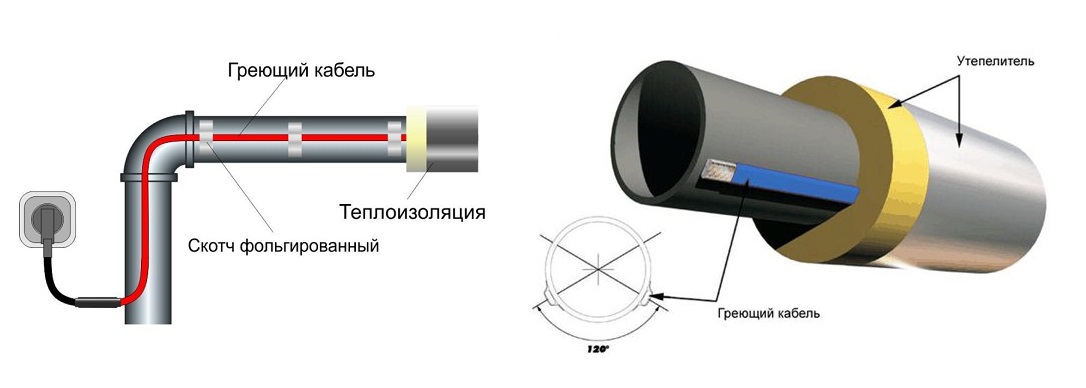
With this method, the cable must be fixed as tightly as possible over the entire surface of the pipe.Therefore, in order for the metal pipeline to have a flat surface, the pipes are first cleaned with sandpaper, and then all contaminants are removed from them, such as: dust, rust, welding residues, etc. Then, a heating cable is laid on a clean surface along the entire length, following so that the threads are located at the bottom. After laying, at least after 25 - 30 cm, it is fixed using clamps, or with metallized construction tape.
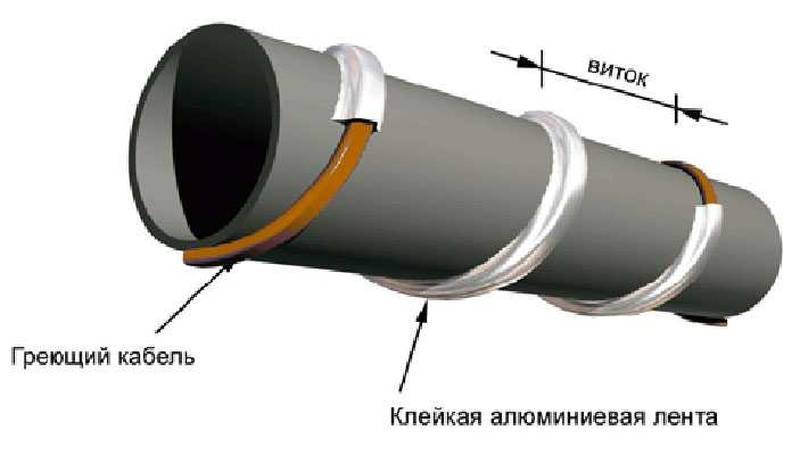
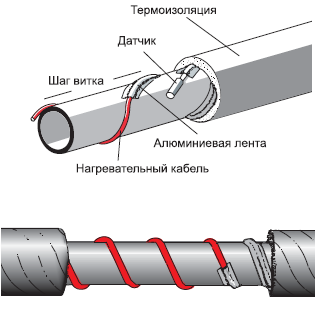
Spiral laying
With this method, the laying of the heating cable must be carried out with extreme care, since the wire will need to be wound spirally. Fastening occurs in this way: gradually taking the wire out of the sleeve, it is wound up from the bottom up pipe, making sure that there are no fractures and bends at an acute angle.
The length of the cable consumption, in these cases, will directly depend on the laying methods. In the first method, the flow rate will be the length of the pipe. In the second method, the expense will be much higher, since all communication is wrapped around from all sides.
Internal reinforcement
Before laying the heating cable for plumbing inside pipe, you need to check if it meets the following characteristics:
- The wire sheath must be made of a purely ecological material, without the content of any harmful substances for health.
- The heating cable inside the pipe must be equipped with high protection against electrical permeability.
- Mandatory presence of an end coupling.
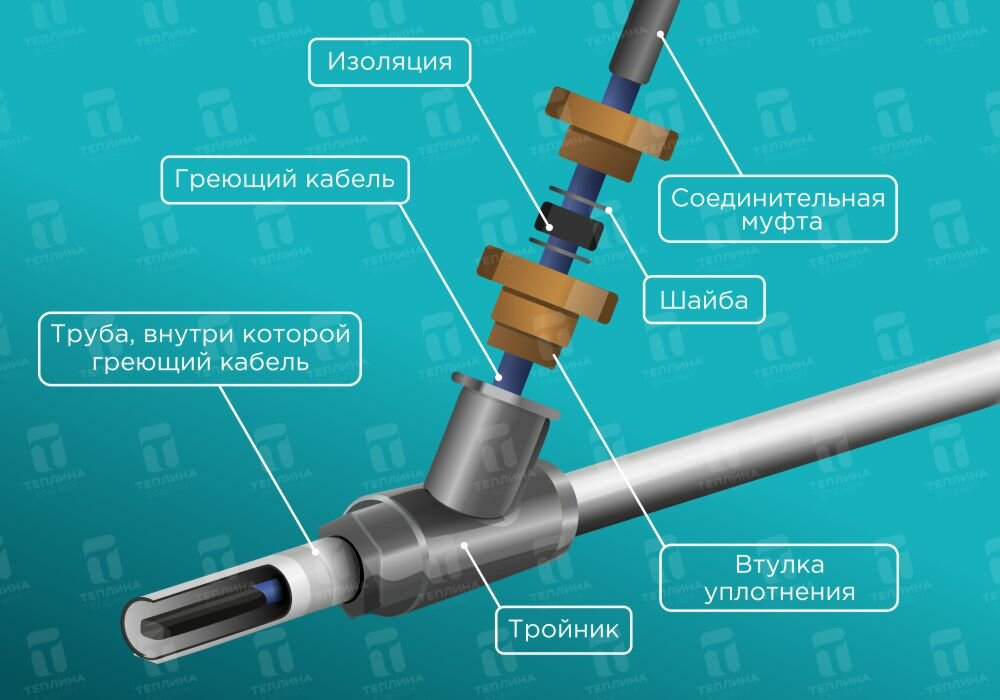
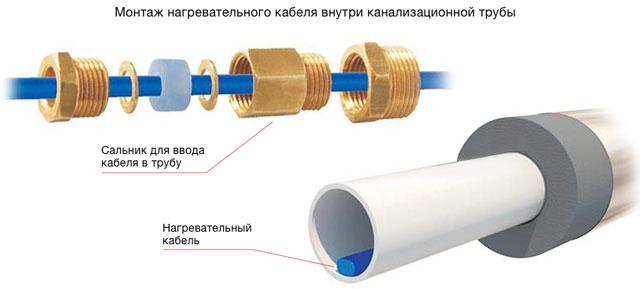
In particular, I use this installation when there is no free access to pipes, or when their diameter is about 5 centimeters. The laying itself takes place in this way: the thermal conductor is inserted through the tee into the pipe with the help of a gland.
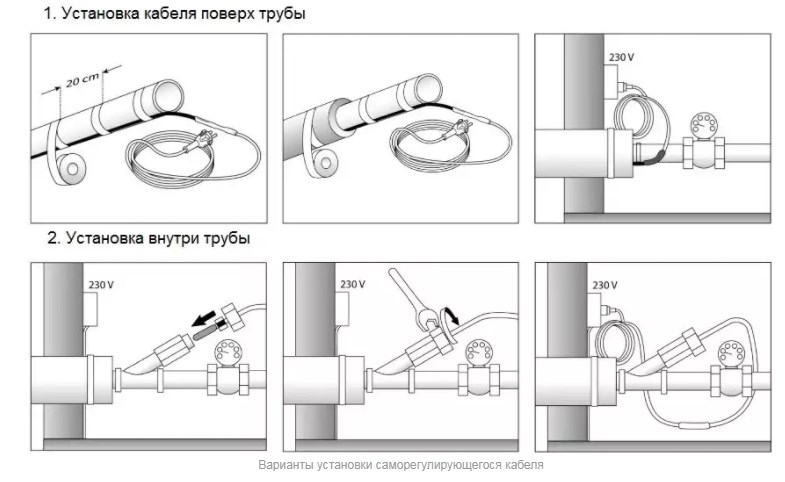
With this method, the elements of the equipment do not need to be fixed. But when laying, the following requirements must be strictly observed:
- When inserting the wire into the pipe, it is necessary to isolate the sharp edges and threads of the fitting.
- It is not allowed to use the product with deformation of the outer shell.
- Correspondence of cable length and pipeline section.
- It is forbidden to enter the wire through the shut-off valves.
Installing a heating cable inside a pipe has more freeze protection qualities. This method is often used if the water carrier is located at a great depth in the soil, or has been operating for a long time.
According to the recommendations of experienced specialists, in order to increase safety, before inserting the cable into the pipeline, it is necessary to attach a protective device against short circuit to it.
Mounting
Ways of laying the heating element
The heating cable for heating pipes can be installed in several ways, depending on the installation requirements and the diameter of the water supply.
There are three of these methods:
- laying inside the pipe;
- installing it outside with the location along the pipe in a straight line with fixing with adhesive tape;
- external mounting around the pipe in a spiral.
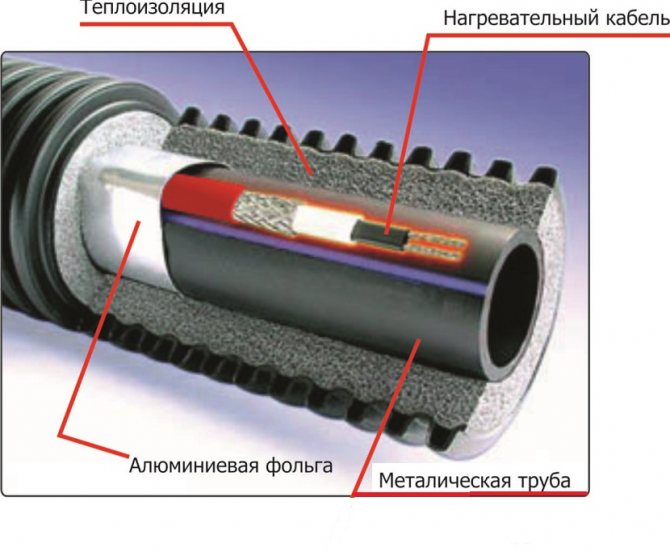
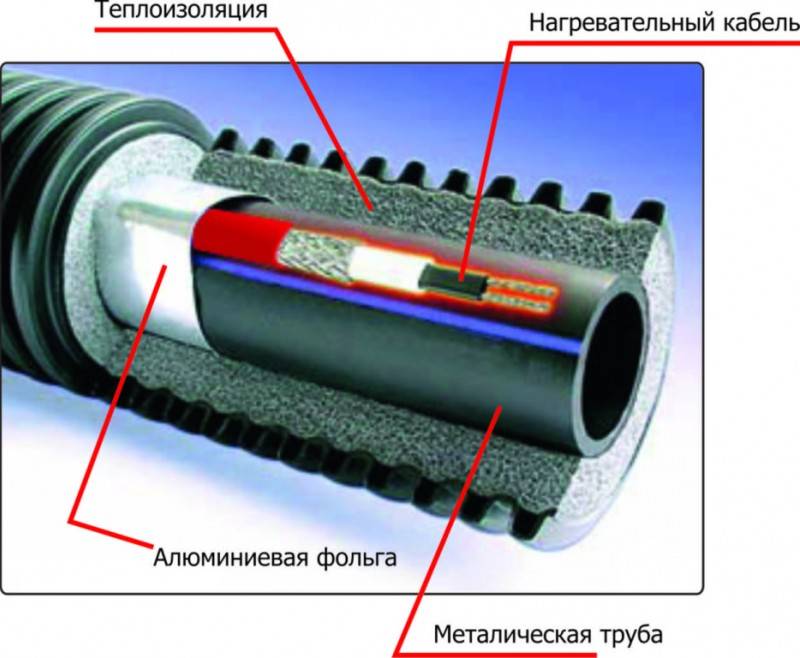
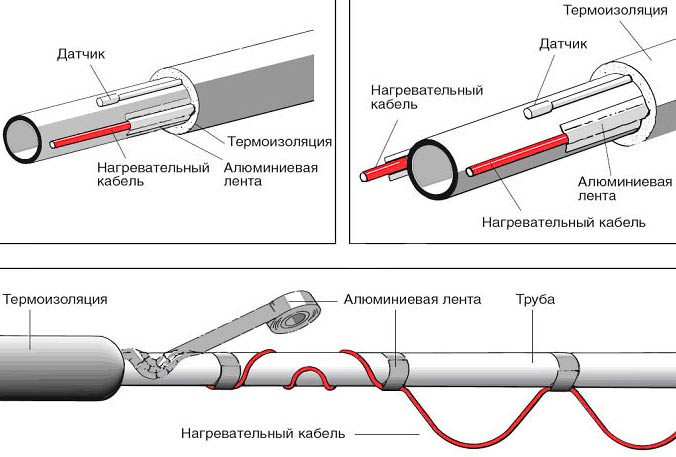
When laying a heater inside a pipe, it must meet several requirements. Its insulation must not be toxic and must not release harmful substances when heated. The level of electrical protection must be at least IP 68. Its end must end in a tight coupling.
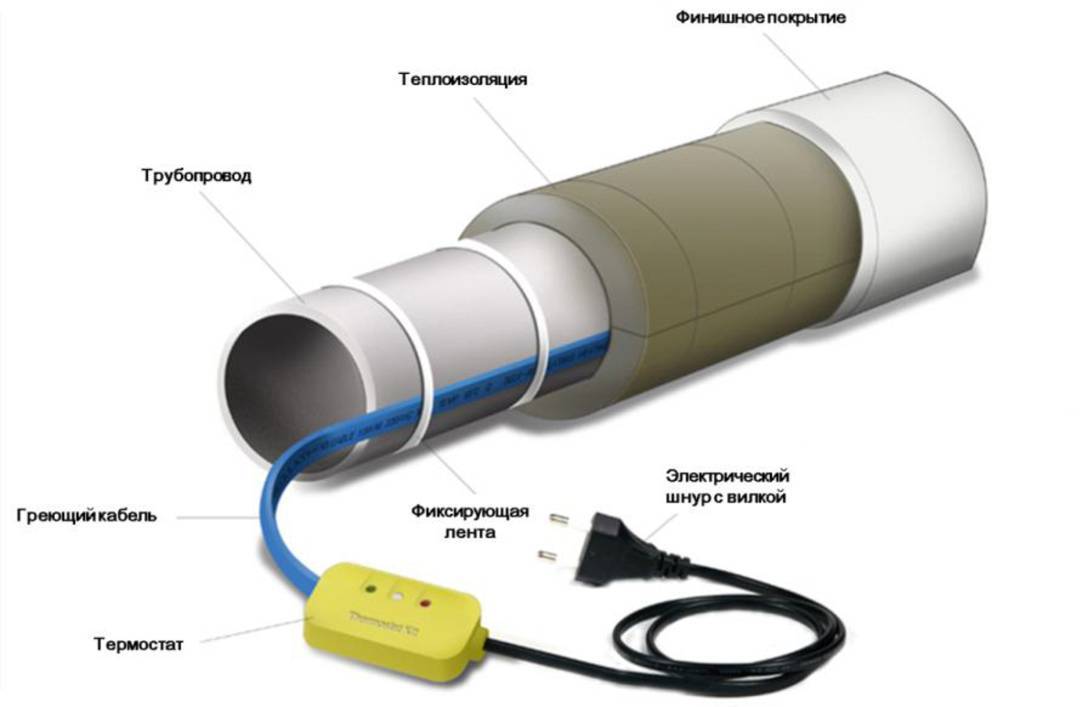
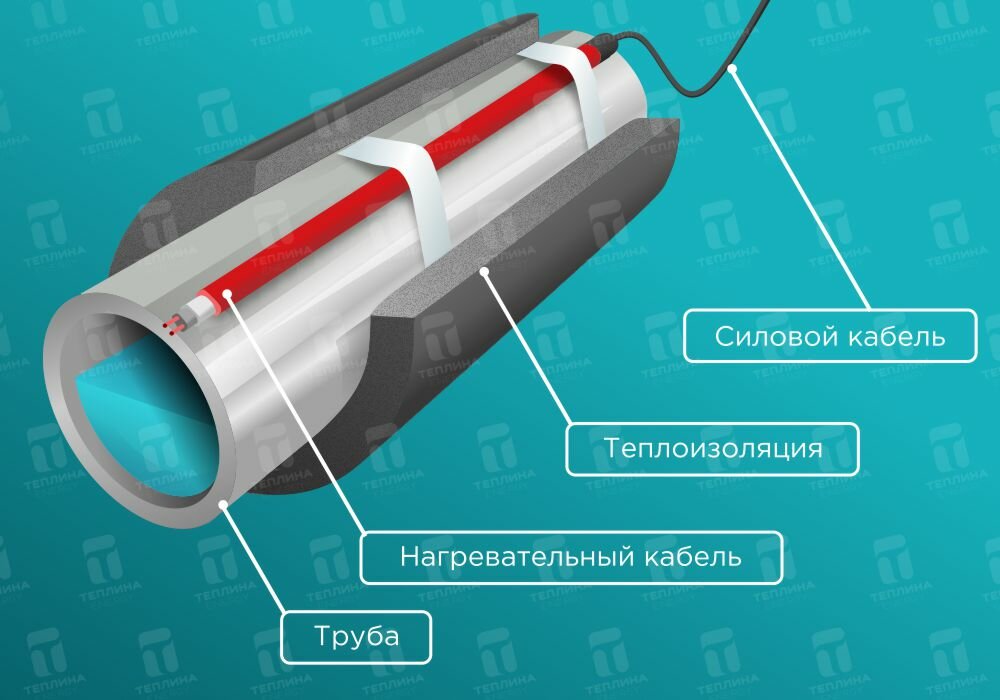
When laying outside the pipe, it must fit snugly against it, secured with adhesive tape, and polyurethane thermal insulation must be put on top of the pipe.
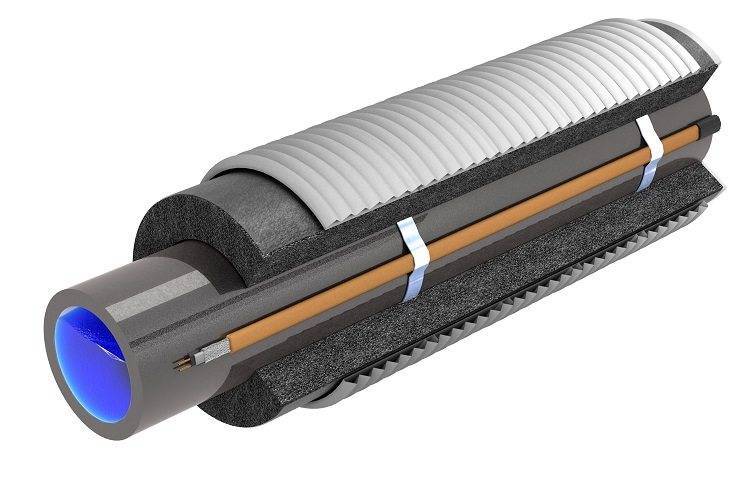
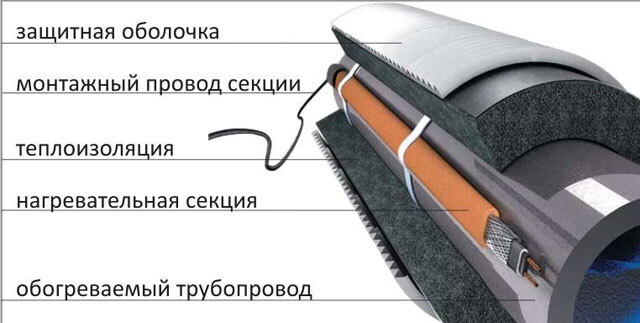
Scheme of the device of the resistive heating cable for pipes
Internal heater installation
The first method is the most difficult from a technical point of view. For this purpose, special types of heating cable with food-grade fluoroplastic outer insulation are used, which do not contain harmful substances and have an electrical protection level of at least IP 68.
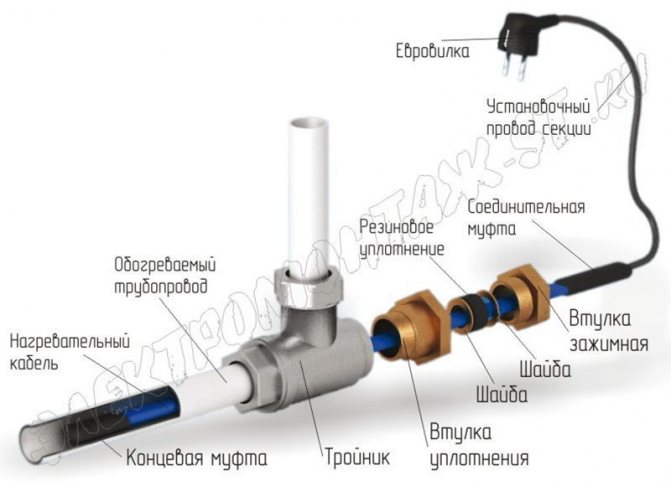
In this case, its end must be carefully sealed with a special sleeve. For this installation method, a special kit is produced, which consists of a 90 or 120 degree tee, an oil seal, as well as a standard kit for connecting to the electrical network with an end sleeve.
It is worth saying that in order to connect the heater and to install it inside the pipe, you must have basic knowledge of plumbing and electrical installation. And the sequence can be described as follows. In the presence of all components: an oil seal, a tee, as well as the necessary set of tools, we begin with the installation of a tee on the water supply system, which must be protected from freezing in winter.
The tee is installed on the pipe using a threaded connection with a seal with FUM tape or tow with paint. In the second outlet of the tee intended for the stuffing box, we insert the heating cable prepared for installation for plumbing with a washer put on it, a polyurethane stuffing box and a threaded stuffing box.
After installing it in the water supply, the gland is installed. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the connecting sleeve between the heating and electric cables is outside the pipeline by about 5-10 cm from the stuffing box. It is better to purchase a kit for internal installation from cable suppliers, since all gland gaskets are made for its cross section. This will allow in the future during operation to protect yourself from water leaks from the stuffing box.
For internal pipes, special types of heating cable are used with food-grade fluoroplastic outer insulation, which does not contain harmful substances, has an electrical protection level of at least IP 68
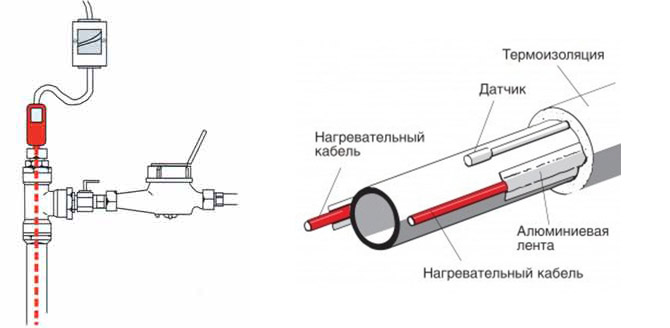
External installation of pipe heating
Heating of external pipes with a cable
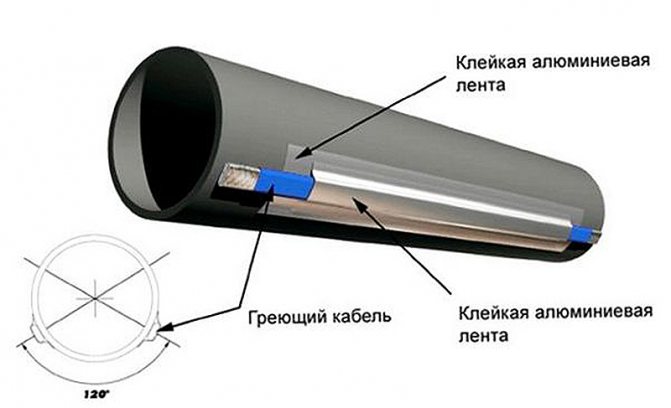
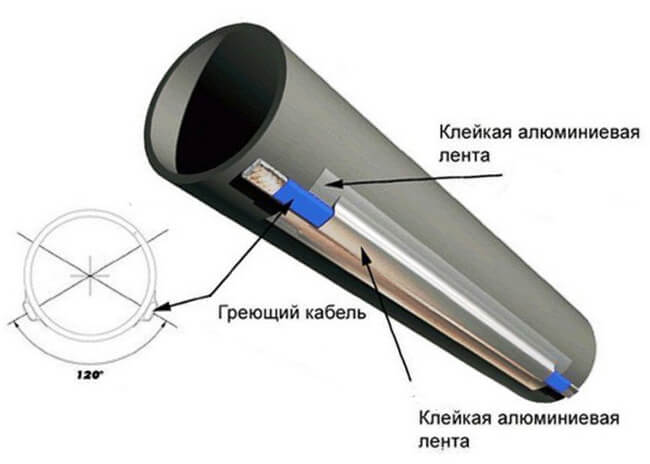
Installation of heating outside the water supply is much easier. It is laid along the pipe, fixed along the entire length with aluminum tape every 30 cm. If possible, it is attached to the bottom of the pipe so that the heating is optimal - from the bottom up.
The considered method refers to water pipes of small diameter, with large diameters it is selected more powerful and the laying is performed in a spiral around the pipe. Shut-off valves such as valves, taps, filters are wrapped with a cable in any form.
If it is self-adjusting, then the shape of the winding around the valves is not important for it, even a crosshair is allowed. Regardless of the type of installation - inside or outside, along the pipe or in a spiral - all water pipes must be insulated. There is a very convenient polyurethane shell for different diameters.
Since the protection of sewers from freezing is just as important as the protection of water pipes, sewer outlets are heated in the same way. The only difference is that the sewer pipes have a diameter of 150 mm or more and the heating system is mounted on them outside in a spiral.
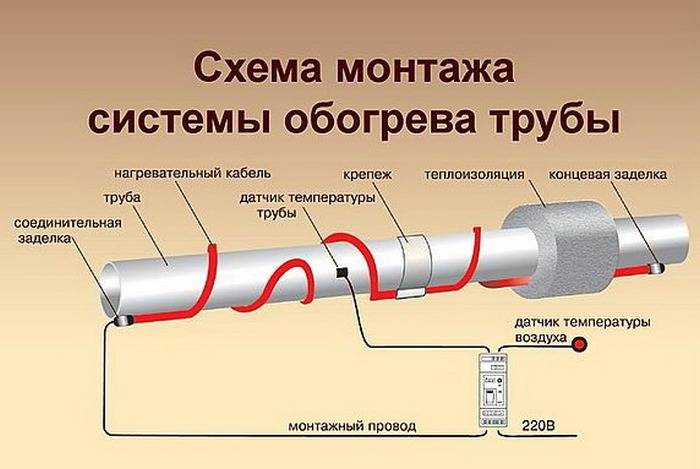
Pipe cable heating: system components
Set or cut?
There are two options for buying a cable: cut and in sets. There is practically no difference in the final cost.
Cut cables are more suitable for those who like to do everything themselves. You need to buy accessories for the cutting cable, then muff it.After that, it is necessary to prepare the conductor cable for connection to the heating cable and carry out a number of manipulations with the coupling. For work, you will need pliers, crimp, hair dryer, construction tape.
Video: coupling the heating cable inside the pipe
Ready-made kits do not require any manipulations, except for direct installation.
Types of pipeline heating
Heating wires are classified according to the heat dissipation scheme into self-regulating and resistive systems. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Resistive option for heating
The principle of operation of such a cable is to heat an insulated metal core, and it is important to monitor the temperature in order to prevent combustion of the heating element. According to the type of construction, such a cable can be with one or two cores. The first option is rarely used, as it requires the circuit to be closed. When heating pipes, such a system is sometimes impossible at all.
When heating pipes, such a system is sometimes not possible at all.
Resistive cable device
A two-core wire is more practical - one end of the cable is connected to the network, a contact sleeve is installed on the other, which ensures closure. One conductor can serve as a heat source, then the second one serves only for the necessary conductivity. Sometimes both conductors are used, increasing the power of the heating itself.
The conductors are protected by multilayer insulation, which has a grounding in the form of a loop (screen). To protect against mechanical damage, the outer contour is made of a PVC sheath.
Cross section of two types of resistive cable
Such a system has its positive and negative sides. The first ones include:
- High power and heat transfer, which is necessary for a pipeline with an impressive diameter or with a considerable number of style details (tees, flanges, etc.)
- Simplicity of design at an affordable cost. Such a cable for heating a water pipe with a minimum power costs 150 rubles per meter.
The disadvantages of the system include the following:
- For correct operation, it is necessary to purchase additional elements (temperature sensor, control unit for automatic control).
- The cable is sold with a certain footage, and the end contact sleeve is mounted in production conditions. Do-it-yourself cutting is prohibited.
For more economical operation, use the second option.
Semiconductor self-adjusting
This self-regulating heating cable system for plumbing is completely different in principle from the first option. Two conductors (metal) are separated by a special semiconductor matrix, which acts as a heating source. This ensures high current conductivity at low temperatures. At the same time, when the temperature rises, the consumption of electricity decreases markedly.
Installation option
Such features allow you to achieve the highest temperatures in more vulnerable areas. Such a cable system for heating water pipes has its advantages:
- Energy savings increase, as the system reduces power when the ambient temperature rises.
- You can buy the required length, cut places are provided in increments of 20 or 50 cm.
There is also a negative side - the high cost of the cable itself.Even for simple varieties, the price is about 300 rubles per meter, and the most “advanced” models are estimated at over 1000 rubles.
Sectional variant with self-regulating heating wire
Any system can be installed inside or outside the pipe. Each technology has its own characteristics that should be considered during installation. So, for an external structure, it is better to choose models with a flattened section, since a large surface of the cable will be in contact with the pipe, which will increase heat transfer. The power limit is wide, you can pick up from 10 to 60 watts per linear meter.
How to choose the right cable?
When choosing a suitable hot cable, it is necessary to determine not only its type, but also the right power.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account such parameters as:
- the purpose of the structure (for sewerage and water supply, calculations are performed differently);
- the material from which the sewerage is made;
- pipeline diameter;
- features of the area to be heated;
- characteristics of the heat-insulating material used.
Based on this information, heat losses are calculated for each meter of the structure, the type of cable, its power are selected, and then the appropriate length of the kit is determined. Calculations can be performed using a special formula, according to calculation tables or using an online calculator.
The calculation formula looks like this:
Qtr - heat loss of the pipe (W); - coefficient of thermal conductivity of the heater; Ltr is the length of the heated pipe (m); tin is the temperature of the contents of the pipe (C), tout is the minimum ambient temperature (C); D is the outer diameter of communications, taking into account the insulation (m); d - outer diameter of communications (m); 1.3 - safety factor
When heat losses are calculated, the length of the system should be calculated. To do this, the resulting value must be divided by the specific power of the cable of the heating device. The result should be increased, taking into account the heating of additional elements. The power of the cable for sewerage starts from 17 W / m and can exceed 30 W / m.
If we are talking about sewer pipelines made of polyethylene and PVC, then 17 W / m is the maximum power. If you use a more productive cable, then there is a high probability of overheating and damage to the pipe. Information about the characteristics of the product can be found in its technical data sheet.
Using the table, choosing the right option is a little easier. To do this, you first need to find out the diameter of the pipe and the thickness of the thermal insulation, as well as the expected difference between the temperature of the air and the contents of the pipeline. The latter indicator can be found using reference data depending on the region.
At the intersection of the corresponding row and column, you can find the value of heat loss per meter of pipe. Then the total length of the cable should be calculated. To do this, the size of the specific heat loss obtained from the table must be multiplied by the length of the pipeline and by a factor of 1.3.
The table allows you to find the size of the specific heat loss of a pipe of a specific diameter, taking into account the thickness of the heat-insulating material and the operating conditions of the pipeline (+)
The result obtained should be divided by the specific power of the cable. Then you need to take into account the influence of additional elements, if any. On specialized sites you can find convenient online calculators. In the appropriate fields, you need to enter the necessary data, for example, pipe diameter, insulation thickness, ambient and working fluid temperature, region, etc.
Such programs usually offer the user additional options, for example, they help to calculate the required diameter of the sewer, the dimensions of the thermal insulation layer, the type of insulation, etc.
Optionally, you can choose the type of laying, find out the appropriate step when installing the heating cable in a spiral, get a list and the number of components that will be needed for laying the system.
When choosing a self-regulating cable, it is important to correctly consider the diameter of the structure on which it will be installed. For example, for pipes with a diameter of 110 mm, it is recommended to take the Lavita GWS30-2 brand or a similar version from another manufacturer
For a 50 mm pipe, the Lavita GWS24-2 cable is suitable, for structures with a diameter of 32 mm - Lavita GWS16-2, etc.
Complex calculations will not be needed for sewers that are not used often, for example, in a summer cottage or in a house that is used only occasionally. In such a situation, they simply take a cable with a power of 17 W / m with a length corresponding to the dimensions of the pipe. A cable of this power can be used both outside and inside the pipe, while installing a gland is not necessary.
When choosing a suitable option for a heating cable, its performance should be correlated with the calculated data on the likely heat loss of the sewer pipe
For laying a heating cable inside a pipe, a cable with special protection against aggressive effects, for example, DVU-13, is selected. In some cases, for installation inside, the brand Lavita RGS 30-2CR is used. This is not entirely correct, but a valid solution.
This cable is designed for heating roofs or storm drains, so it is not protected against corrosive substances.It can only be considered as a temporary option, since with prolonged use in inappropriate conditions, the Lavita RGS 30-2CR cable will inevitably break.