MATERIALS AND REQUIREMENTS FOR THEM
2.1. The following materials are used for wall cladding:
– ceramic tiles and fittings for interior wall cladding;
- polymer (polystyrene) colored tiles for interior wall cladding;
- adhesives and adhesive mastics for fixing tiles to wall surfaces;
- compositions for the treatment of seams.
Approved by the General Plan Development Department of Moscow
October 30, 1996
Entry into force
"1" January 1997
2.2. Ceramic tiles and shaped parts are made from clay with or without additives by pressing, followed by glaze and firing in kilns. They have square, rectangular and shaped forms with a smooth and embossed front surface covered with one-color (white or colored) or multi-color glaze, as well as glaze with a marble pattern.
The type, shape and dimensions of tiles and fittings must comply with the technical requirements of GOST 6141-91.
Basically, square and rectangular tiles with a side length of 200 ´ 200 are used for wall cladding; 150 ´ 150; 200 ´ 300; 200 ´ 150; 200 ´ 100; 150 ´ 100; 150 ´ 75 mm, with a thickness of 5.6 mm.
It is allowed to manufacture tiles and fittings of other sizes and shapes upon agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
2.3. Polymer tiles (polystyrene) are made by injection molding from molten polystyrene and copolymer under pressure. They have dimensions: square - 100 ´ 100 ´ 1.25 and 150 ´ 150 ´ 1.35 mm; rectangular - 300 ´ 100 ´ 1.35 mm; frieze - 100 ´ (20; 50) ´ 1.25 (1.35) mm.
The type, shape and dimensions of the tiles must comply with the technical requirements of GOST 9589-72 or the manufacturer's specifications.
Polymer tiles are used in residential, public and industrial buildings for lining bathrooms and toilets, shower rooms, sanitary cabins, cafes, canteens, laboratories and other premises with increased requirements for sanitary and hygienic maintenance, as well as in industrial premises with a wet operating mode.
Polymer tiles are resistant to acids, alkalis, and do not conduct electricity well.
These tiles should not be used near sources of open fire, for example, near gas stoves and water heaters, when the air temperature or base for lining is above 70 ° C, in children's institutions, evacuation corridors and stairwells, on bases made of combustible structures.
Tiles are made in various colors, plain and marble-like.
2.4. The color, shade, pattern and relief of the front surface of facing tiles and fittings must correspond to the standard samples.
2.5. Tiles must be of the correct shape, not have bulges, potholes and cracks.The surface of the tiles should not have spots, efflorescence and other defects.
The glazed surface should not have underfilling, leakage, bubbles, "hairy" cracks.
Deviations and external indicators of tiles must comply with the requirements of GOST 6141-91 table. 4 and 5.
2.6. Physical and mechanical properties of facing ceramic and polystyrene tiles must comply with the requirements specified in Table. one .
Physical and mechanical properties of facing tiles
SNiP plaster. Code of Practice (SP)
In SP 71.13330.2017, the requirements for plastering work are specified in Chapter 7 "Finishing Works". This document applies to both internal and external works, including the plastering of the plinth and facade. It defines the requirements for the technology of work, the presence and control of errors in the performance of plastering.
Below are the main excerpts from this document regarding plastering work.
7.1.1 Finishing work in the premises should be carried out at an ambient temperature and surfaces to be finished from 5°С to 30°С, relative air humidity not more than 60%, unless otherwise specified by the material manufacturer. This temperature and humidity regime in the room must be maintained around the clock throughout the entire period of finishing work and at least 2 days before the start and 12 days after the end of the work.
7.1.8 Before applying each subsequent layer, it is necessary to dedust the treated surface and, if necessary, treat the base with a primer to reduce or equalize its absorbency.
7.2.6 Plaster mortar based on cement or lime-cement binder may be applied both in one layer and in layers according to the material manufacturer's instructions.When installing a multi-layer plaster coating, each layer must be applied after the previous one has set. Depending on the type of work, plaster mortar, type of base, unevenness of the wall and layer thickness, if it is provided for by the project, a plaster mesh is selected, if necessary, and fixed to the wall.
7.2.7 When performing internal plaster work with gypsum-based solutions, it is allowed to carry out work without the use of a plaster mesh. Plaster solutions based on gypsum are applied in one layer, unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer of the material.
7.2.13 The quality of plastering work is evaluated according to the requirements:
| simple plaster | Improved plaster | High quality plaster | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical deviation | Not more than 3 mm per 1 m, but not more than 10 mm for the entire height of the room | Not more than 2 mm per 1 m, but not more than 10 mm for the entire height of the room | Not more than 0.5 mm per 1 m, but not more than 5 mm for the entire height of the room |
| Horizontal deviation | No more than 3 mm per 1 m | No more than 3 mm per 1 m | Not more than 1 mm per 1 m |
| Smooth surface irregularities | No more than 4 pcs. per 1 m, but not more than 10 mm for the entire element | No more than 2 pieces, depth (height) up to 3 mm | No more than 2 pieces, depth (height) up to 1 mm |
| Deviation of window and door slopes, pilasters, pillars, etc. from vertical and horizontal | Not more than 4 mm per 1 m, but not more than 10 mm for the entire element | On area 4 no more than 4 mm per 1 m, but no more than 10 mm for the entire element | On area 4 no more than 2 mm per 1 m, but no more than 5 mm for the entire element |
| Deviation of the radius of curved surfaces from the design value | Not more than 10 mm for the entire element | Not more than 7 mm for the entire element | Not more than 4 mm for the entire element |
| Deviation of the slope width from the design | Not more than 5 mm | no more than 3 mm | no more than 2 mm |
The requirements of SP 71.13330.2017 regarding the quality of plastering works correspond to the German standard for plastering DIN V 18550 "Plaster and plaster systems". This European Standard contains a set of recommendations for the preparation and evaluation of surface quality depending on various types of finish coatings from the lowest Q1 to the highest Q4.
In addition to the current Code of Practice, there is a draft National Standard of the Russian Federation GOST R 57984-2017 / EN 13914-1: 2005 “Plaster for exterior and interior work. Rules for selection, preparation and application. Part 1. Plasters for outdoor work, but at the moment this document has not entered into force.
GOSTs
- Interstate standard. fittings
- Interstate standard. concretes
- Interstate standard. Concrete blocks
- Interstate standard. Ventilation blocks.
- Interstate standard. Rock blocks.
- Interstate standard. Wall blocks.
- Interstate standard. Water.
- Interstate standard. Water supply.
- State standard. Gas supply
- State standard. soils
- State standard. Doors and windows
- State standard. Design and estimate documentation
- Interstate standard. Unified system of design documentation. ESKD.
- Interstate standard. Wood and lumber.
- State standard. Buildings and constructions.
- State standard. Asbestos-cement products.
- Interstate standard. Products and details wooden.
- State standard. Reinforced concrete products and structures
- State standard. Sanitary products.
- Interstate standard. Tests
- Interstate standard. Cables
- Interstate standard. Stones and bricks
- State standard. Building structures
- State standard. Boilers
- State standard. Cranes
- Interstate standard. Paints and varnishes
- Interstate standard. Fasteners
- State standard. roofs
- State standard. Stairs, railings
- Interstate standard. elevators
- Interstate standard. Oils
- State standard. Decoration Materials
- Interstate standard. Construction Materials
- Interstate standard. Thermal insulation materials
- Interstate standard. construction machines
- Interstate standard. Metal and metal products
- Interstate standard. Metrology and measurements
- Interstate standard. heating equipment
- Interstate standard. Pumps
- Interstate standard. Waste management
- Interstate standard. Windows, window blocks
- Interstate standard. Lighting
- State standard. environmental protection
- State standard. Slabs concrete, reinforced concrete
- State standard. wood boards
- State standard. Handling equipment
- State standard. Fire safety
- State standard. Floors, floor coverings
- Interstate standard. rental
- State standard. Gaskets sealing
- State standard. Profiles
- State standard. Construction solutions
- Interstate standard. Thread
- State standard. piles
- Interstate standard. Welding
- State standard. Quality systems certification
- State standard. Reinforcing meshes
- State standard. Bank protective means
- State standard. Means of protection for workers
- State standard. Scaffolding
- State standard. Precision systems in construction
- Interstate standard. Steel
- State standard. Glass
- Interstate standard. Double-glazed windows
- Interstate standard. Reinforced concrete racks
- State standard. steps
- Interstate standard. Water meters
- State standard. Pipelines
- State standard. Pipes
- State standard. Ultrasound
- State standard. Domestic services
- State standard. Farms
- State standard. Forms for the manufacture of reinforced concrete products
- State standard. cements
- Interstate standard. Mounting seams
- State standard. Noises
- State standard. Sand, gravel, crushed stone
- Interstate standard. Electric Energy
- State standard. electrical equipment
- Interstate standard. electrical installations
- Interstate standard. Energy and electrification
- State standard. Product quality indicators system
- State standard. Occupational safety standards system
Improved plaster
This type of plaster is used for finishing surfaces in residential buildings, children's institutions, in special utility rooms and other rooms that require special treatment of walls and ceilings. Improved plaster is applied to the walls in three layers. The first is spraying, which, depending on the base, has a different layer thickness. So, spraying on concrete and brick walls is applied with a height of 5 mm.
The second layer - the soil can have several layers.At the same time, the height of the cement coating is 5 mm, and the lime mixture coating is 7 mm. The third is a coating, the layer thickness of which is 2 mm. The treated surface with this plaster is checked by the rule, and the covering is smoothed out.
With improved plaster, according to building codes, tighter requirements for various tolerances are noted. So, for 1 meter of vertical area, only 2 mm is allowed, and along the entire height - 10 mm and no more. For 4 sq.m. only two uneven waves are allowed, the depth of which is allowed no more than 3 mm. On the horizontal plane, the tolerance is 2 mm.
Document text
Construction
norms and rules SNiP 3.04.01-87
"Insulating
and finishing coatings
(approved
Decree of the Gosstroy of the USSR of December 4
1987 N 280)
Instead
sections of SNiP III-20-74*; SNiP III-21-73*; SNiP
III-B.14-72; GOST 22753-77; GOST 22844-77; GOST 23305-78
Term
entry into force - July 1, 1988
emulsion-bitumen
compositions
mixtures,
bitumen perlite and bitumen expanded clay
tough
and semi-rigid fiber products
and device
coverslips
shells of thermal insulation made of rigid
materials
elements
designs
technological
equipment from corrosion
(anti-corrosion
work)
interiors
buildings
1.
General provisions
1.1.
Current building codes
apply to production and
acceptance of work on the installation of insulation,
finishing, protective coatings and floors
buildings and structures, except
works subject to special conditions
operation of buildings and structures.
1.2.
Insulating, finishing, protective
floor coverings and structures
be carried out in accordance with the project
(finishing coatings in the absence of
project requirements - according to the standard).
Replacement of those provided by the project
materials, products and compositions are allowed
only in agreement with the design
organization and customer.
1.3.
Works on the production of thermal insulation
work can only start after
execution of an act (permit) signed
customer, representatives of the assembly
organization and organization that performs
thermal insulation work.
1.4.
The device of each insulation element
(roof), floor, protective and finishing
coatings should be done after
performance checks
corresponding underlying element
with drawing up certificate of examination
hidden works.
1.5.
With appropriate justification
agreement with the customer and design
organization is allowed to appoint
ways of doing work and
organizational and technological solutions,
and establish the methods, scope and
types of quality control registration
works other than those
these rules.
2.
Insulating coatings and roofs
emulsion-bitumen
compositions
mixtures,
bitumen perlite and bitumen expanded clay
tough
and semi-rigid fiber products
and device
coverslips
shells of thermal insulation made of rigid
materials
elements
designs
General
requirements
2.1.
Insulation and roofing works
allowed to perform from 60 to minus
30°C ambient (production
works using hot mastics -
at ambient temperature
not lower than minus 20°C, with the use of compounds
water based without antifreeze
additives not lower than 5°С).
2.2.
In bases under roofing and insulation in
according to the project
do the following work:
close up
seams between prefabricated slabs;
arrange
temperature shrinkage seams;
mount
embedded elements;
plaster
vertical surfaces
stone structures to the height of the junction
rolled or emulsion-mastic
roofing carpet and insulation.
2.3.
Insulating compositions and materials must
be applied uniformly and uniformly
layers or one layer without gaps and
influxes. Each layer is necessary
arrange on a hardened surface
previous with leveling applied
compositions, with the exception of paints.
In preparation and preparation
insulating compositions must be observed
Table 1 requirements.
Table
1
Download the file to continue reading...
Elastic floor coverings
| Index | Name | Description | Link to download |
| GOST 17241-71 | Polymeric materials and products for flooring. Classification | Types and characteristics of polymer products used for flooring. | |
| GOST 7251-77 | Polyvinylchloride linoleum on woven and non-woven backing. Specifications | PVC linoleum: material requirements, types, laying rules. | |
| GOST 18108-80 | Polyvinyl chloride linoleum on a heat and sound insulating subbase. Specifications | Roll polymer linoleum, description and installation. | |
| GOST 26604-85 | Antiseptic non-woven fabrics (subbase) made of fibers of all types for heat and sound insulating linoleum. Specifications | Characteristics of the base used when laying linoleum. | |
| GOST 27023-86 | Welded carpets from polyvinylchloride linoleum on a heat and sound insulating underlay. Specifications | Floor coverings made of synthetic linoleum obtained by welding. | |
| GOST 24064-80 | Adhesive rubber mastics.Specifications | Description of adhesive compositions that are used for laying elastic flooring. | |
| CH 2.2.4/2.1.8.566 | Sanitary standards. Industrial vibration, vibration in the premises of residential and public buildings. | Vibration performance requirements for residential floor coverings. |
Code of norms and rules for finishing work
Finishing work allows you to create the interior you dreamed about
The code of norms and rules, and abbreviated as SNiP, is a document that defines the rules for conducting the processes of construction and repair of buildings and structures. Each type of work has its own SNiP. Each type of construction and repair work must be carried out according to its own rules and canons.
According to SNiP, all finishing work is divided into two categories:
- Rough finish;
- Fine.
Violation of certain norms, as a rule, leads to poor-quality work and entails rework or unscheduled repairs, which will be carried out within a few months after the facility is put into operation.
Rough finishing of premises
SNiP precisely breaks down the entire finishing process into stages. The rough finish includes several, if I may say so, the dirtiest stages. The most important stage of rough work is the plastering of the walls. The quality of the entire finishing process depends on it.
In the process of plastering surfaces, various solutions can be used. Basically, they include sand, but the fastening component can be different: cement, gypsum, lime. Sometimes clay is added to the plaster solution. The composition of the solution depends on the premises in which it will be used, and what loads it will be subjected to.
High-quality rough finish is the necessary basis for high-quality repairs
The next most important step in finishing the premises is leveling the surfaces. All surfaces of the room can be divided into three groups: wall, ceiling and floor
The requirements for plaster and putty solutions for each of these surfaces are different.
It should be borne in mind that each finishing material requires a certain preparation of the base surface.
When carrying out a rough finish, special attention is paid to the surface difference. If this indicator does not exceed five millimeters, then putty is used for leveling, and for large differences, a plaster mortar is used
floor leveling method depends on the material of its base. The concrete floor is leveled with special cement-based mortars. To align the wooden use sheets of chipboard or fiberboard.
SNiP for finishing rooms with plasterboard sheets appeared quite recently, and, as the documentation shows, the standards are quite strict
Here it is important not only to carry out the work accurately and correctly, but also to choose the right size of drywall, especially its thickness. There are two ways to fix it:
- adhesive;
- using guide metal profiles.
The second is considered the main one, but during its implementation one must be prepared for the fact that the size of the room will be reduced.
Normative base
Interior and exterior decoration of residential premises is regulated by a whole list of various documents, the key of which are Building Norms and Rules - the so-called SNiPs. These sets of rules contain the most important information regarding the arrangement of certain finishing elements.
That is why it is very important to study them before starting work.
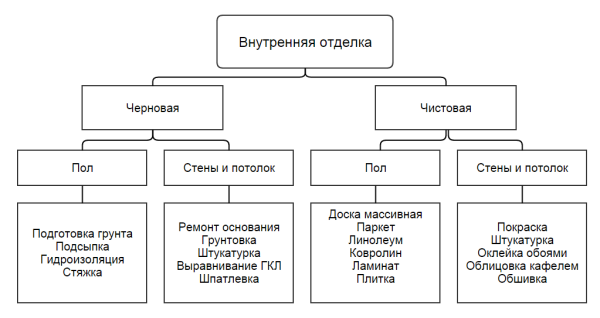
The regulations describe a variety of technologies. Some of them are shown in this diagram.
The key documents that need to be taken into account in the design and production of finishing works, we will describe in the table below:
Index
Name
Summary
SNiP 3.04.01-87
Insulating and finishing coatings
Basic SNiP for the interior decoration of residential premises, which includes requirements for the production of plastering, puttying, surface decoration, as well as for the arrangement of floors and floor coverings.
The requirements of this SNiP do not apply to cooling units that are operated under special conditions (extreme temperatures, unusual humidity conditions, etc.).
SNiP 2.03.13-88
floors
A standard that is used in the design and arrangement of floor coverings. Regulates the choice of floor construction depending on the type of building and planned loads, and also describes the technologies used in the finishing of floors.
SNiP 3.05.01-85
Internal sanitary systems
A set of rules that relate to the arrangement of sanitary systems for residential and industrial buildings. Formally, these processes do not apply to finishing work.
But when repairing or reconstructing apartments, houses and cottages, they must be taken into account.
Naturally, this is only a small part of all the documents that are used in the design of interior decoration of houses and apartments. For almost every operation, there is a separate GOST, SNiP or instruction that will help you understand the nuances of the work.
Rough finishing: what the process includes
The rule of interior decoration

What does rough and finish work according to SNiP include?
SNiP interior decoration provides for the implementation of the following rules and regulations:
All work indoors must be carried out only at a certain temperature. It must be at least +10 degrees. This also takes into account air humidity inside the room, which should be no more than 60%.
Also, work is carried out in accordance with the temperature regime:
- At +10 - when using paint or other means of paint and varnish production, mastic or putty, when pasting the surface, when using polystyrene, and so on.
- At +15 - when using polymer concrete and other similar materials, sealants, synthetic finishes, polymer metal coatings, and so on.
Works are carried out in such a way and in such a sequence as indicated in the project for the production of works.
- Initially, the atmospheric protection of the rooms from the effects of weather and climatic phenomena is done. High-quality insulation must be carried out: heat, sound, waterproofing.
- All screeds are preliminarily carried out on the floor surface with a certain procedure for performing the insulation of the building. All seams and joints of the laying of building materials are well sealed and special tools are used for this.
- Window and door openings are also subject to preparation. Their surface is processed and isolated. Such work is necessary to ensure that the glazing of these structures is of high quality, and the door is mounted correctly.
- All systems of lighting, heating, water supply and other communications that are necessary for a normal life in the house have been installed.
Quality control
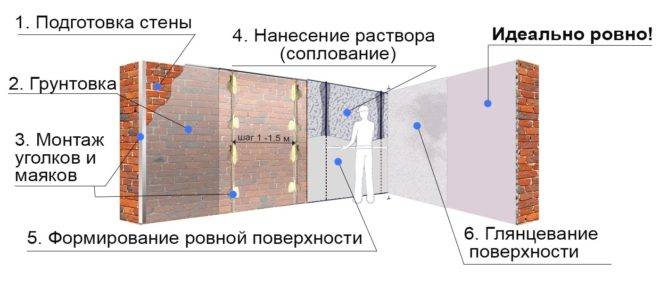
Not only the plastering technique is subject to requirements in accordance with regulatory documents. This also applies to the mixtures themselves.If you need an improved type of plaster, then according to GOST, the requirements are as follows:
- The solution used for spraying and priming must penetrate a mesh with a mesh diameter of 0.3 cm.
- For the covering layer, the mixture must pass through the mesh, the cells of which are 0.15 cm.
- Sand that is used for mixtures can have grains no larger than 0.25 cm in size, if it concerns a primer composition, and 0.125 cm, if it is used for final finishing work.
In addition, regulatory documents regulate various technical indicators. This applies to the strength of the composition, the ability to retain moisture, the tendency to delamination and mobility, and so on. The solution must have a document indicating the time when it was prepared, its volume, the brand of materials used, the presence of binders and the tendency to mobility.
Be sure to check the quality of the solution at the first stage. It is necessary to make sure that the air temperature meets the requirements, the walls are moistened and cleared of debris. Next, you need to control that the walls and ceilings are even. As a result, it remains only to check the adhesion of the substance.