- Device and principle of operation
- Adjustment and repair
- Disadvantages of gas heating on cylinders
- How does a cylinder reducer work:
- 1 Direct reducer
- Membrane
- 2 Reverse gear
- How a gas reducer works
- Direct drive gearbox
- Reverse gear
- A few words about the device of the HBO gearbox
- The design and principle of operation of the gas reducer.
- Purpose of the balloon propane reducer BPO 5-2
- The device and principle of operation of the propane reducer BPO 5-2
- Technical characteristics of propane reducer BPO 5-2
- Complete set of gas propane reducer BPO 5-2
- Safety measures when working with propane reducer BPO 5-2
- Rules for the operation of propane reducer BPO 5-2
- Classification of gas regulators
- Principle of operation
- Mounting Features
- Types of working gas
- Housing color and regulator type
- Scheme of devices of direct and reverse action
- Why is a gas reducer used?
- Typical malfunctions and their repair
- Classification of gas reducers
- Balloon and network
- Propane, oxygen and acetylene
- The principle of operation of the device
- What is the required volume and pressure
- Design and types
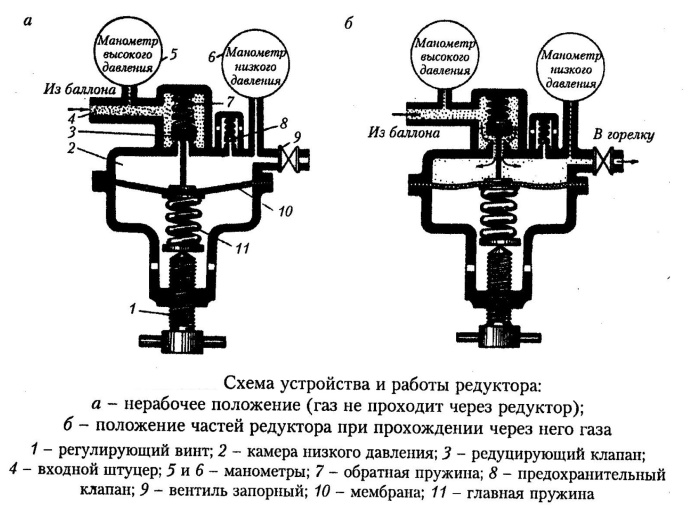
Device and principle of operation

An autonomous regulator coordinates the pressure without involving an additional energy source.Devices are divided according to their purpose, the way the valve works, the nature of the action, the method of adjustment.
Standard construction elements:
- case made of metal or PVC;
- connecting branch pipe with a nut;
- working fitting;
- filter unit;
- double chamber with central membrane;
- saddle valve on the axis;
- manometer.
Gate valves are single and double-seat, diaphragm, pinch valves, taps and butterfly valves are used in the design. In urban highways, membranes of the first two types are installed. They are sealed with rigid gaskets made of metal, rubber, fluoroplast.
Adjustment and repair
You can do it yourself with the help of available tools and a repair kit, but only if you know exactly what you are doing. Insufficiently qualified adjustment and assembly can lead to disastrous consequences. The main signs of abnormal operation of the product are as follows:
- deviation of the output pressure from the permissible limits;
- gas leak.
The pressure deviation is usually caused by a breakage or displacement of the spring, or the escape of the compensating gas that performs its function due to depressurization of a part of the housing. But if the spring malfunction is still to be eliminated with the help of a repair kit, then the gas version belongs to the category of non-repairable ones (the device is completely changed).
A gas leak can be caused by a broken diaphragm, a leak in the housing, or a malfunctioning float valve. If the latter begins to leak gas, this can also manifest itself in the consumer product (eg gas water heater).Since the pressure at the outlet of the reducer is approximately equal to the inlet, then in the absence of flow (the consuming device is temporarily turned off), leakage will be inevitable.
Such a malfunction is difficult to diagnose for the reason that turning on the consuming device normalizes the situation. It can be determined only by measuring the gas pressure at the outlet of the reducer in the absence of consumption (as a rule, it should not exceed the nominal value by more than 20%).
But it is worth noting that the gearboxes are collapsible and non-collapsible (sealed) design. The latter are subject to replacement only in their entirety.

So, having stocked up with an appropriate repair kit, the product must first be disassembled. Visually inspecting the spring and membrane removed from the housing, it should be established which of them caused the malfunction. A broken spring must be replaced with a new one from the repair kit.
If the spring has not broken, but simply tightened up, having lost elasticity from time to time, you can not change it, but simply pick up and put a gasket of the required thickness from the body side without closing the existing hole with it.
If the membrane breaks, it should be replaced using a similar one from the repair kit, but, as a rule, it is not easy to make a tight connection with the washers surrounding it. Therefore, if you are unsure of your skill, think about the advisability of purchasing a new gearbox.
This is a tube with a small hole, from the end of which a rocker is pressed through a rubber gasket. There are several typical problems regarding valve operation:
- the normal course of the rocker is disturbed;
- worn or damaged rubber gasket;
- the end of the tube is deformed.
Valve adjustment is a simple process.The mobility of the rocker arm can be restored by turning or replacing its hinges. The damaged gasket should be cut off and glued in place of the same size from the repair kit. The roughness and evenness of the end of the tube, which ensures a snug fit of the gasket, is achieved by grinding it.
If the failure of the reducer is a gas leak due to leaks in the places where the membrane fits on the housing, then the broken integrity can be restored using silicone sealant. When making adjustments or repairs, and for any other reason not initially related to depressurization, it will not be superfluous to also apply sealant in these places, which will prevent a similar problem in the future.

Upon completion of repair work, it is necessary to immediately check the tightness of the product using a soap solution. If there are no bubbles that indicate leaks, the gearbox should be re-tested after one day, then after a few more days. Subsequently, periodic monitoring (eg monthly) is recommended.
Like any other gas-related equipment, a reducer will serve you well if you choose the right model and take simple steps to ensure safe operation. Periodic maintenance and timely detection of faults will save you from trouble.
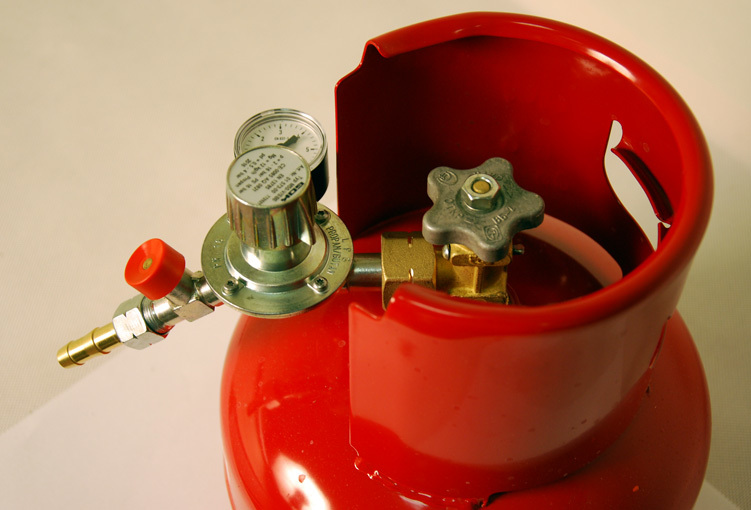
Disadvantages of gas heating on cylinders
Like any other heating method, this one also has its drawbacks:
- if the cylinder is outside, in case of severe frost, the system may turn off - the condensate will freeze and prevent the gas from escaping;
- do not place cylinders in unventilated areas;
- since the gas is heavier than air, if it leaks, it can go down (into the basement, underground), and if there is a strong concentration, serious consequences will occur.
Thus, heating with gas cylinders, if certain conditions are not met, can be very dangerous. Therefore, they should be stored only in ventilated rooms, under which there is no basement. It is even advisable to place them in a separate extension on the site. The room must be warm so that the system does not turn off in frost. If it is cool in the annex, then you will have to make an insulated metal or plastic box for the cylinders. For insulation, the walls are sheathed with foam plastic 5 centimeters thick. Ventilation holes must be made in the lid of the box.

How does a cylinder reducer work:
1 Direct reducer
The usual simple gas pressure reducing apparatus consists of two chambers with an area of high and low pressure separated by a rubber membrane. In addition, the “reducer” is equipped with an inlet and outlet fitting. Modern devices are designed so that the bellows liner is screwed directly into the gearbox. Increasingly, you can find a gas reducer with a third fitting designed for mounting the monomer.
After gas is supplied through the hose and then through the fitting, it enters the chamber. The generated gas pressure tends to open the valve. On the reverse side, a locking spring presses on the valve, returning it back to a special seat, commonly called a “saddle”. Returning to its place, the valve prevents the uncontrolled flow of high-pressure gas from the cylinder.
Membrane
The second operating force inside the reducer is a rubber membrane that separates the device into a high and low pressure area. The membrane acts as an “assistant” to high pressure and, in turn, tends to lift the valve from the seat, opening the passage. Thus, the membrane is between two opposing forces. One surface is pressed by a pressure spring (do not confuse with a valve return spring), which wants to open the valve, on the other hand, the gas that has already passed into the low pressure zone presses on it.
The pressure spring has a manual adjustment of the pressing force on the valve. We advise you to buy a gas reducer with a seat for a pressure gauge, so it will be easier for you to adjust the spring pressure to the desired output pressure.
As the gas exits the reducer to the source of consumption, the pressure in the chamber of the working space decreases, allowing the pressure spring to straighten. She then begins to push the valve out of the seat, again allowing the device to be filled with gas. Accordingly, the pressure creeps up, pressing on the membrane, reducing the size of the pressure spring. The valve moves back into the seat narrowing the gap, reducing the gas filling of the reducer. The process is then repeated until the pressure equalizes to the set value.
It should be recognized that direct-type gas cylinder reducers, due to their complex design, are not in high demand, reverse-type reducers are much more widespread, by the way, they are considered devices with a high degree of safety.
2 Reverse gear
The operation of the device consists in the opposite action described above. Liquefied blue fuel is fed into a chamber where high pressure is created. Bottled gas builds up and prevents the valve from opening. To ensure the flow of gas into the household appliance, it is required to turn the regulator in the direction of the right-hand thread.
On the reverse side of the regulator knob is a long screw, which, by twisting, presses on the pressure spring. By contracting, it begins to bend the elastic membrane to the upper position. Thus, the transfer disk, through the rod, exerts pressure on the return spring. The valve begins to move, begins to open slightly, increasing the gap. Blue fuel rushes into the slot and fills the working chamber at low pressure.
In the working chamber, in the gas hose and in the cylinder, the pressure begins to increase. Under the action of pressure, the membrane is straightened, and a constantly compressing spring assists it in this. As a result of mechanical interactions, the transfer disc is lowered, weakening the return spring, which tends to return the valve to its seat. By closing the gap, naturally, the flow of gas from the cylinder into the working chamber is limited. Further, with a decrease in pressure in the bellows liner, the reverse process starts.
In a word, as a result of checks and balances, the swing can be balanced and the gas reducer automatically maintains a balanced pressure, without sudden jumps and drops.
How a gas reducer works
Direct drive gearbox

The diaphragm responsible for pressure regulation, under the action of a spring, begins to displace the valve from the seat surface.The pressure is reduced due to a small passage and reaches a safe, serviceable.
Further, the straightened spring allows the valve to open access to the flow of a new volume of gas from the cylinder, and the regulation process is repeated. On non-adjustable gearboxes, the spring force is set at the factory, acting as a pressure regulator.
Reverse gear
Here the principle is somewhat different. Incoming gas from the source presses the valve against the seat, preventing it from escaping. The design contains a screw, with the help of which the spring compression force is adjusted.
By compressing the spring with a screw (regulator), the safety diaphragm is bent, passing a certain amount of gas. The support disc actuates the return spring, after which the valve rises, freeing the way for the fuel.
The working chamber has the same pressure as in the cylinder. The membrane under the action of the spring returns to its original state, and the support disk moves downward, while pressing on the return spring. As a result, the valve is pressed against the body seat.
It is worth saying that many note the great popularity of reverse action gearboxes. They are safer to use.
A few words about the device of the HBO gearbox
The concept of the essence of the gearbox systems that are equipped with gas equipment lies through the consideration of its general concept. Everyone knows that the gas represented by propane or methane is in a HBO cylinder under high pressure and in a liquefied state. In the standard form, the supply of such fuel to the internal combustion engine chambers is not possible, because for its operation it is necessary to prepare a fuel-air mixture. It is the preparation of the latter that a typical HBO gearbox is engaged in.
Note that not all generations of gas equipment are equipped with gearbox systems. So, for example, the last two generations of HBO under numbers 5 and 6 do not have this equipment, because they provide for liquefied gas supply. However, on gas equipment of 1-4 generations, the gearbox is an integral part of the system. In many ways, the correct functioning of gas installations depends on the stable operation and adjustment of the gear equipment, which should not be forgotten.
Structurally, HBO gas reducers of any generation are evaporator units that convert liquefied propane or methane into vaporized gas, which is already sent to the intake tract for mixing with air, and then to the engine combustion chambers. The device of the node involves a system of several sequentially located chambers, separated by valves. The principles of operation of the HBO 2-4 reducer and the partial first generation are as follows:
- Gas in liquefied format is supplied to the inlet tract of the gearbox, called the unloader valve;
- The latter produces the dosage and competent distribution of fuel, which is carried out either mechanically (on vacuum gearboxes) or electronically (on gearboxes with solenoid valves and their control unit);
- After that, the gas is evaporated, and it enters directly into the engine through its manifold, where it mixes with air.
In any mode of engine operation, it does not require liquefied gas, but a fuel-air mixture, which is prepared in the above order by means of evaporation. For the implementation of the latter, special evaporation elements and their chambers are used.Depending on how many chambers the gas passes through until complete evaporation, single-stage, two-stage and three-stage HBO reducers are distinguished. Regardless of the method of organization of evaporation, the pressure in the chambers invariably changes in its process, as a rule, to a lower side. To date, the most popular are gear systems with two evaporation chambers, which are used on HBO from Lovato, HBO on methane and the equipment of the company "Tomasseto".
The gear device, in general, is exactly the same on the equipment of the second generation, and on the equipment of the fourth. At the same time, it makes no difference whether propane HBO is used on a car or methane. That is, the "carburetor" of any gas equipment is a completely identical unit in all its formations, naturally, involving the use of this unit.
The design and principle of operation of the gas reducer.
Any propane reducer includes the following components:
- valve;
- working chamber;
- locking spring;
- pressure spring;
- membrane.
The throughput of this device depends on the degree of opening of the valve, which is affected on the one hand by the membrane and the pressure spring, and on the other by the gas and the locking spring. The higher the pressure of propane in the cylinder and the lower the flow of gas-using equipment, the closer the valve is located to the seat. Conversely, as the pressure in the chamber decreases and the flow increases, the valve opens more. The operating parameters of a household propane reducer are determined by the stiffness of the springs and the elasticity of the membrane.Some models are additionally equipped with a valve whose shaft is connected to a pressure spring, which allows you to manually adjust the gas supply in a certain range.
The principle of operation of the device:
Modern propane reducers are sometimes additionally equipped with a safety mechanism that is triggered if the propane-butane inlet pressure is exceeded. In order to increase the level of safety, such gearboxes are usually installed on gas tanks and group cylinder installations used to gasify one or more houses. You can learn more about how autonomous heating is implemented in private households in the article: Autonomous heating with propane butane.
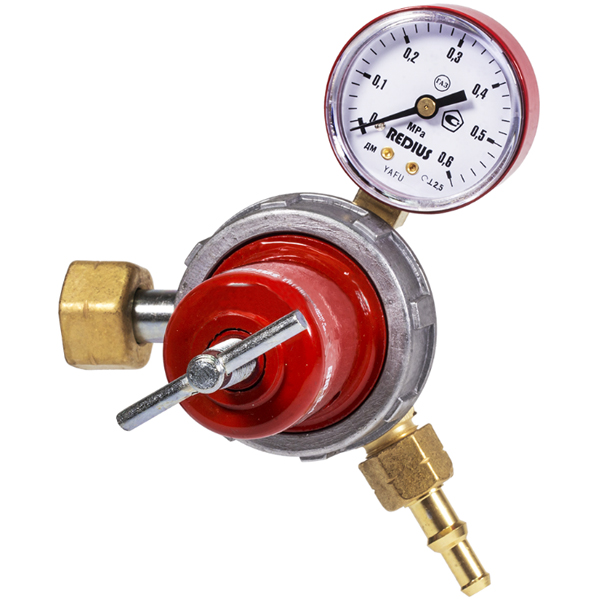
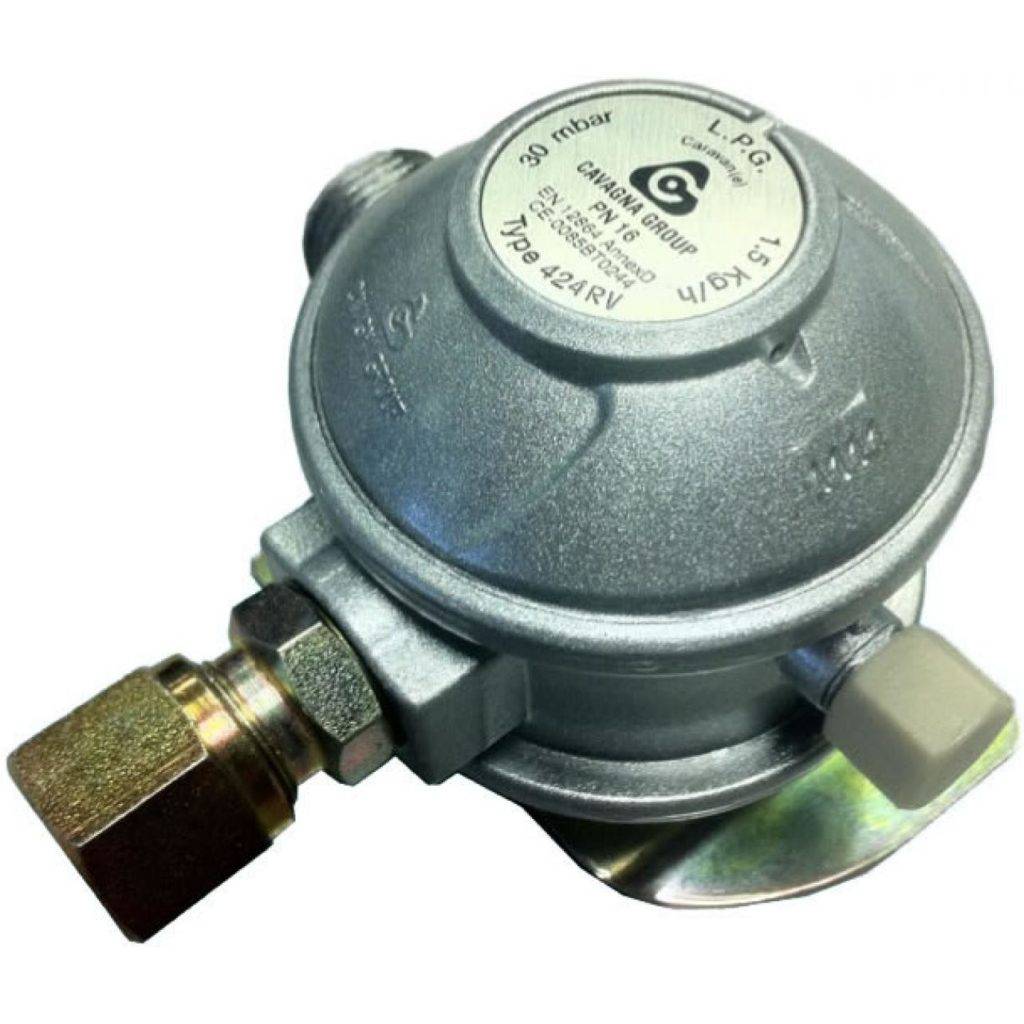
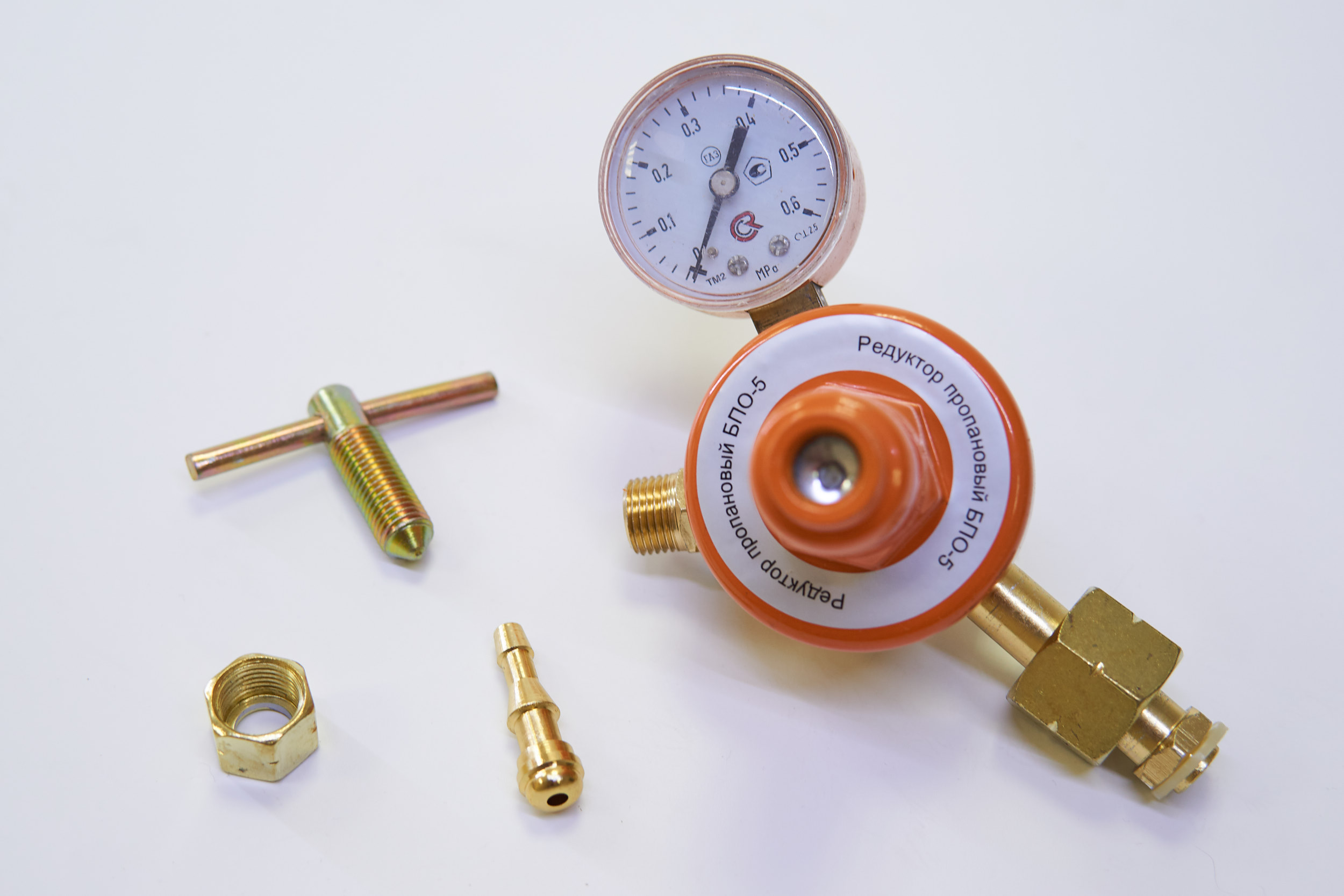
Purpose of the balloon propane reducer BPO 5-2
The propane reducer BPO 5-2 is used to reduce and stabilize the pressure of household gas supplied from standard cylinders to such consumers as welding torches and cutters, heaters and a large number of other types of consumers.
The device and principle of operation of the propane reducer BPO 5-2
This propane reducer is built according to a single-chamber scheme, at the inlet it has a branch pipe with a threaded union nut for connecting to a cylinder. The case is cast from aluminum alloy, the case cover is made from polyamide.
A feature of the propane reducer is its small size and weight, which makes BPO 5-2 convenient to transport and store.
Technical characteristics of propane reducer BPO 5-2
The propane reducer is produced by the country's oldest manufacturer of gas equipment - the Neva plant:
Gearbox Specifications
- Weight 0.34 kg.
- Length × width × height 135 × 105 × 96mm.
- Operating temperature -15+45˚С.
- Maximum inlet pressure 25 kg/cm3.
- Working pressure 3 kg/cm3.
- Maximum gas consumption, 5 m3/hour.
- Connection method W 21.8-14 threads per 1″ LH.
- Working connection М16х1,5 LH.
Complete set of gas propane reducer BPO 5-2
Package Included:
- Propane reducer assembly.
- Technical certificate.
- Nipple for sleeve 6.3 or 9 mm.
- Package.
Safety measures when working with propane reducer BPO 5-2
Propane is a source of increased danger. In order to consciously follow safety requirements, one must understand exactly what threats the gas itself and the devices using it carry:
Safety measures when working with propane reducer BPO 5-2
- First of all, propane is flammable. Improper handling of it can cause a serious threat to life and health of people, as well as material values.
- You can't breathe propane. In a propane atmosphere, a person dies. When inhaled in small amounts, it leads to poisoning, causing headache and vomiting.
- Propane is explosive under certain conditions, when a certain concentration of propane in the air is reached, a volumetric explosion occurs. An explosion also occurs with a sharp increase in temperature in the cylinder.
- With the rapid release of propane from the cylinder into the atmosphere, a strong drop in temperature occurs, which can lead to severe and deep frostbite.

Rules for working with a propane tank
To avoid these unpleasant consequences, when working with propane, the following rules must be observed:
- Do not use propane near open flames or high heat.
- Do not bring other flammable substances into the work area.
- Do not use chemically incompatible materials such as nitrates and perchlorates near propane.
- Do not use gas equipment and fittings that have visible mechanical damage and signs of gas leakage.
Rules for the operation of propane reducer BPO 5-2
The operating rules contain, first of all, the requirements for strict observance of the safety measures listed above.
Each time before starting operation, it is necessary to inspect the propane reducer, connecting fittings, supply hoses for mechanical damage and visible and audible signs of leakage. If such signs are found, it is unacceptable to start operation, the damaged equipment must be repaired or replaced.

Rules for the operation of a propane reducer
If the pressure gauge needle does not move or, on the contrary, jumps at a constant gas flow, it is faulty and must be replaced.
It is also necessary to carefully monitor the timing of the scheduled verification of the propane reducer pressure gauge for compliance with passport technical requirements. Such an inspection should be carried out by a special certified organization at least once every five years.
In addition, it is necessary to follow the procedure for connecting the propane reducer to the cylinder and to the consumer devices. Check the condition of the filter at least once a month and clean it if necessary.
Classification of gas regulators
Before using a pressure reducer, you should familiarize yourself with its varieties and the main parameters by which these devices are classified.
Principle of operation

In direct-type gearboxes, the gas passing through the fitting acts on the valve with the help of a spring, pressing it to the seat, thereby blocking the entry of high-pressure gas into the chamber. After the valve is squeezed out from the seat by the membrane, the pressure gradually decreases to the operating level of the gas appliance.
The principle of operation of the reverse type device is based on compressing the valve and blocking further gas supply. With the help of a special adjustable screw, the pressure spring is compressed, while the membrane is bent, and the transfer disc acts on the return spring. The service valve is lifted and the flow of gas to the equipment is resumed.
When the pressure of the system (cylinder, reducer, working equipment) increases in the reducer, the membrane is straightened with the help of a spring. The transfer disc, going down, acts on the return spring and moves the valve to the seat.
It should be noted that domestic reverse-acting gas cylinder reducers are safer.
Mounting Features

Ramp gas regulators are needed to reduce and stabilize the pressure level of gas supplied by a single source. Devices tend to lower the working pressure of the gas supplied from the central line or a number of sources. They are used for large volumes of welding work. Network stabilizers hold the low pressure value of the gas supplied from the distribution manifold.
Types of working gas

Devices working with acetylene are fixed with a clamp and a stop screw, while for others they use a union nut with a thread identical to the thread of the fitting at the valve.
Housing color and regulator type
Propane regulators are painted red, acetylene regulators are white, oxygen regulators are blue, and carbon dioxide regulators are black. The body color corresponds to the type of working gas medium.
Pressure stabilization devices are available for both flammable and non-flammable media. The difference between them lies in the direction of the thread on the cylinder: in the first it is left-handed, in the second it is right-handed.
Scheme of devices of direct and reverse action
Direct type devices have the following scheme of operation: propane entering the high pressure zone presses the valve from its seat. Propane enters the working chamber, filling it and increasing the pressure in it. It acts on the membrane, squeezing the main spring. The membrane goes down, pulls the stem and closes the valve at the moment the operating pressure is reached. In the process of using propane, the pressure in the working chamber drops, high-pressure propane reopens the valve and gas again enters the working area.
Diagram of a direct-acting gearbox
In reverse type devices, the main spring opens the valve, overcoming the force of the high pressure gas. After the working area is filled and the pressure reaches the set value, the stem goes down, closing the valve. In the process of using propane, the pressure in the working area decreases and the spring opens the valve again.
Reverse gear diagram
Reverse action devices are considered more reliable and safer. They have gained popularity in domestic and professional applications.
Why is a gas reducer used?
In any vessel, the gas is under high pressure. This simplifies its transportation and operation.However, to the consumer, whether it be a stove, boiler, welding or gas-flame equipment, it must be supplied under low pressure. For such a transformation, there is a special mechanical device - a gas reducer.
The figure shows a diagram of the internal device
Take, for example, a propane-butane mixture. In order to store it in a liquid state, a pressure of about 16 bar is created. At the same time, the consumer, in most cases, needs only a few tens of millibars. In addition, the outlet pressure must be maintained at a certain level during the emptying of the tank. It is for such purposes that a gearbox is needed. Any balloon installation is equipped with a similar device, without which its safe operation is impossible, regardless of whether it is used for industrial or domestic purposes. You can learn more about the operation of gas-cylinder equipment in the article: operation of cylinder installations in an autonomous gas supply system.
Typical malfunctions and their repair
The deviation of the working pressure from the set one can be caused by the following reasons:
- Spring breakage or displacement.
- Housing depressurization.
A gas leak is caused by:
- Membrane damage.
- Housing depressurization.
- Valve failure.
Some gearboxes are collapsible. They are, in principle, available for self-repair. Non-separable gas reducers, of course, in the event of a malfunction, must be replaced as a whole.
So, for example, a home foreman who has basic locksmithing skills is quite capable of replacing a spring or a membrane in an unregulated Frog gas reducer. A case with broken tightness cannot be repaired. In this case, the entire device will have to be replaced.
After replacing the damaged parts with new ones from the repair kit and assembling the gas reducer, it is necessary to check its tightness using a soapy solution.
Classification of gas reducers
 Reducer for gas tank
Reducer for gas tank
Devices that regulate the pressure of the supplied gas are required not only in autonomous gas supply. Reducers are installed on numerous factory installations, in boiler rooms. Devices are distinguished by design and type of gas with which they can work, as well as by purpose.
Balloon and network
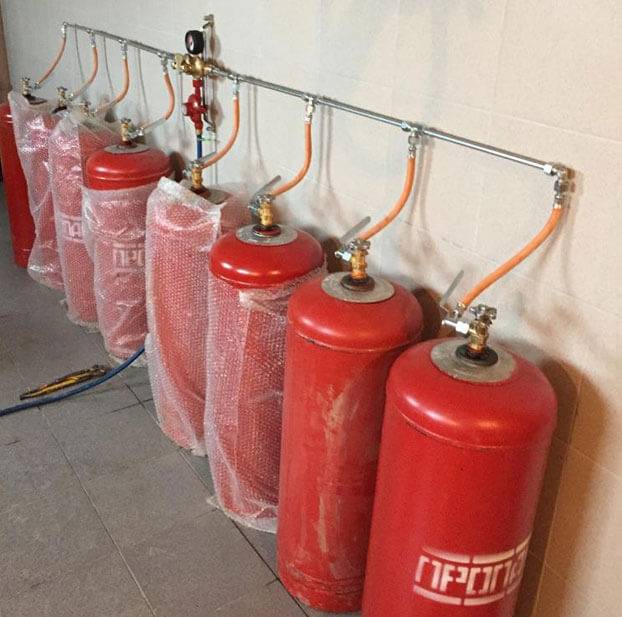
To service a gas tank, a dispensing station or a cylinder, different gearboxes are required. According to the place of installation, they distinguish:
- Network - serve working or welding posts, powered by a central gas pipeline. The same devices are mounted in an adapter between the gas pipeline and equipment or safety devices. The network reducer is equipped with only 1 pressure gauge measuring the output gas.
- Balloon - regulate the pressure when supplying propane-butane or other mixture from a cylinder or from a gas tank to gas appliances. They have a different design. Usually quite compact.
- Ramps - mounted on bypass ramps when it is required to supply gas from the main gas pipeline to consumption points.
The device is selected taking into account the power, control range, control accuracy of other parameters.
Propane, oxygen and acetylene
 Types of reducers - gas, oxygen, acetylene
Types of reducers - gas, oxygen, acetylene
If in everyday life the consumer encounters only methane or a propane-butane mixture, then in production one has to work with a variety of liquefied mixtures.According to the composition of the environment, there are:
- Oxygen - used in the welding of metals. Reducers are painted blue and are mounted directly on the cylinders. Manufactured from oxidation resistant metal alloys and thoroughly degreased.
- Propane - used both in everyday life and in production. Dyed in red. Gaskets and seals are made from materials resistant to n-pentane.
- Acetylene - used in welding. Painted white. They are made of metals with the exception of copper, zinc, silver. Seals are made of materials resistant to acetone, DMF, solvents.
- Cryogenic - designed to work with gas mixtures at temperatures below -120 C. They are made of metals that are resistant to cold, like brass, stainless steel.
The principle of operation of the device
 The reducer lowers the gas pressure when leaving the cylinder
The reducer lowers the gas pressure when leaving the cylinder
Distinguish between direct and reverse action devices. The principle of operation of the gas reducer is determined by the design.
In the direct-acting version, the gas from the tank presses on the valve through the fitting, the gas mixture penetrates into the high pressure chamber. Now propane presses from the inside - it presses the valve with a spring and blocks the access of the next portion of gas. The working membrane slowly returns the valve, the gas pressure decreases to the working one - the value with which the stove operates.
When the pressure decreases, the spring relaxes and releases the valve. The latter opens under the pressure of the gas coming from the tank, and the whole cycle is repeated.
These types of regulators are divided into 2 types:
- Single-stage - with 1 chamber, where the pressure is reduced. Minus - the gas indicator at the outlet depends on the value at the inlet.
- Two-stage - includes 2 chambers.The gas sequentially passes through the high and working pressure chamber and only then is fed to the stove. This design allows you to set any value at the output, regardless of the pressure in the cylinder and more accurately adjust the performance. Pressure surges are excluded.
Regulators can be equipped with an additional energy supply through the installation of pneumatic and hydraulic sensors or electronic automatic devices.
The principle of operation of a reverse-acting gas pressure reducer is different. When gas enters, the valve is compressed, blocking the access of the next portion of the mixture. The adjusting screw causes the base spring to compress. In this case, the membrane between the chambers is bent, and the transfer disk presses on the return spring. The valve rises and passes gas from the cylinder.
In the working chamber of the reducer, the pressure increases along with the indicator in the cylinder or pipe through which the mixture is supplied from the gas tank. The main spring straightens the membrane, the transfer disc moves down and presses on the return spring. The latter again squeezes the permeable valve and shuts off the flow.
What is the required volume and pressure
Now let's talk about the pressure of the gas reducer, as well as its volume. The throughput of the reducer should help ensure the operation of all devices connected to the system at the maximum gas consumption mode. A certain problem lies in determining the necessary parameters in different units of measurement. There are two units of pressure in gas appliances - pascals and bars. For a reducer, the inlet pressure is determined in megapascals or bar, and the outlet in pascals / millibars. The conversion of pressure values between two units can be performed using the following formula:
1 br=105 Ra
The volume of gas that is passed through the reducer and consumed by gas devices can be presented in two quantities at once - in kilograms and cubic meters. The output and input pressure indicators of a large number of Russian devices are indicated precisely in Pascals, and on foreign devices the pressure is calculated in bars.
The indicators can be correlated using data on the density of the main gas cylinders (kg / m3) at a temperature of +19 degrees and normal atmospheric pressure:
- Carbonic acid - 1.85.
- Propane - 1.88.
- Oxygen - 1.34.
- Nitrogen - 1.17.
- Helium - 0.17
- Argon - 1.67.
- Hydrogen - 0.08.
- Butane - 2.41.
- Acetylene - 1.1.
Q=1.88*0.65+2.41*0.35=2.06 kg/m3
So, if the maximum gas consumption on a four-burner stove is 0.85 m3 / h, then the gearbox should also provide the same volume. In terms of kg, this value will be equal to 2.06*0.85=1.75 kg/h. Based on GOST 20448-90, a large range of percentage gases is allowed in a propane-butane mixture, which will create uncertainty during the calculation of its density. To the calculated value, the maximum throughput of the gearbox can be increased by 25%.
This is related to the following:
- The parameters of the gas mixture may differ depending on the region, supplier and even the season!
- The gas density to be used for all calculations will depend on the temperature.
- There is a possibility of loss of elasticity of the spring, which is responsible for adjusting the volume of the low pressure chamber in the gas cylinder reducer, which may reduce its maximum throughput.
Still sometimes, complete with new equipment, it is proposed to use a proven gearbox in terms of parameters with pressure regulation in case you use a propane tank. This option is optimal from the standpoint of fire safety and system performance.
Design and types
Propane (CH 3) 2 CH 2 - natural gas with a high calorific value: at 25 ° C, its calorific value exceeds 120 kcal / kg
At the same time, it should be used with special precautions, since propane is odorless, but even at its concentration in air of only 2.1% it is explosive
It is especially important that being lighter than air (the density of propane is only 0.5 g / cm 3), propane rises, and therefore, even at relatively low concentrations, is a danger to human well-being
A propane reducer must perform two functions - to provide a strictly defined pressure level when any device is connected to it, and to guarantee the stability of such pressure values during further operation.
Most often, gas welding machines, gas heaters, heat guns and other types of heating equipment are used as such devices. This gas is also used for the propane cylinder of a car running on liquefied fuel.
There are two types of propane reducers - one- and two-chamber. The latter are used less frequently, since they are more complex in their design, and their distinctive ability - to consistently reduce the gas pressure in two chambers - is used in practice only with increased requirements for the permissible level of pressure drops. Common models of gearboxes are BPO 5-3, BPO5-4, SPO-6, etc.The second digit in the symbol indicates the nominal pressure, MPa, at which the safety device operates.

Structurally, a single-chamber propane reducer of the BPO-5 type (Balloon Propane Single-chamber) consists of the following components and parts:
- Corps.
- pusher.
- Valve seat.
- Reducing spring.
- membranes.
- Reducing valve.
- Connecting nipple.
- Inlet fitting.
- setting spring.
- mesh filter.
- pressure gauge.
- Adjusting screw.
The main technical characteristics of propane reducers are:
- Maximum throughput in terms of gas volume per unit of time, kg / h (marked with a number located immediately after the letter abbreviation; for example, a propane reducer of the BPO-5 type is designed to pass no more than 5 kg of propane per hour);
- Maximum inlet gas pressure, MPa. Depending on the size of the device, it can be in the range from 0.3 to 2.5 MPa;
- Maximum output pressure; in most designs, it is 0.3 MPa, and adapted to the same indicator for a gas-consuming unit.
All manufactured propane reducers must fully comply with the requirements of GOST 13861.