- Causes of condensation
- Which way to choose: underground or above ground?
- Recommendations for the selection of condensate traps
- Criterion # 1 - the shape of the condensate collector
- Criterion # 2 - pressure in the gas pipeline
- Criterion #3 - other hardware parameters
- Construction stages
- Useful information
- How to do without gas condensate collectors?
- Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
- Why do you need a condensate collector on a gas pipeline?
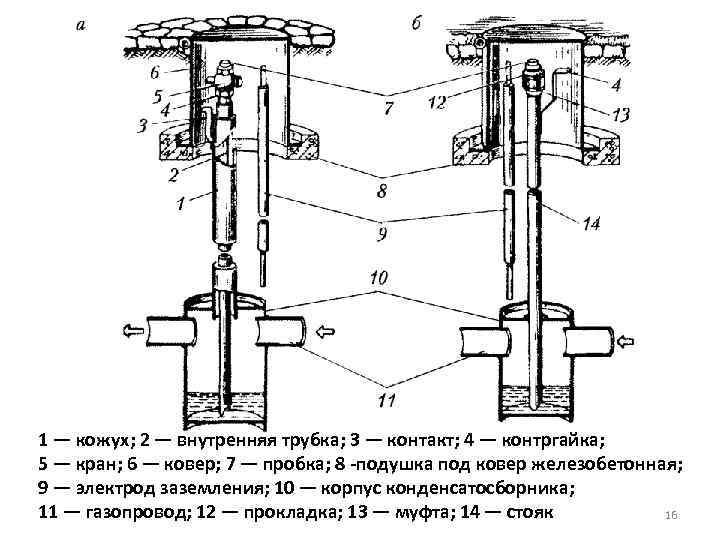
- Gas condensate collectors on a gas pipeline: structure and purpose of a condensate collector + nuances of installation and maintenance
- Gas condensate collector Du 100 (1.6 MPa) From the Manufacturer
- Principle of operation
- Device and overall dimensions
- Instrumentation and control devices in gas pipeline systems
- A condensate trap for a chimney: is it necessary?
- Should a condensate trap be installed or not?
- Why does condensation appear
Causes of condensation
Stove builders call the process of condensate formation in the chimney - furnace crying, and regardless of how the chimney is assembled according to smoke or condensate. Now we need to understand why she starts crying. There are several reasons for this:
1. Use when burning, fuel with high humidity.The homeowner should know that perfectly dry firewood does not exist, in addition, some boilers provide forced humidification of the incoming fuel. Even when using purified gas or dried fuel, condensate cannot be dispensed with. Regardless of the type of flue system, condensate will always form on its walls;
2. Insufficiently high level of heating of the exhaust gases. When the temperature drops below 100 degrees, condensation occurs;
3. Draft weakened due to insufficient speed of movement of exhaust gases inside the chimney system. If the thrust meets all the requirements, then the chances of education condensate on the pipe of a gas boiler practically non-existent. If the draft is insufficient, then the formation of condensate is guaranteed;
3. The difference between the outdoor temperature and the one in the pipe. That is, if it is cool enough outside, moisture will be deposited on the outer surface.
Which way to choose: underground or above ground?
The choice of laying method depends on the specific case, namely: on the characteristics of the soil, climatic conditions, built-up area, etc. Therefore, it is impossible to give an unambiguous answer to this question.
Consider the main tips for choosing the method of laying gas pipelines:
- if the soil at the site has a high corrosion coefficient, then it is recommended to carry out the gas pipeline by the above-ground method.
- if there is a high-voltage power line near the site where the installation work will take place, the pipes are laid underground.
- if the gas pipeline is supposed to be laid on the territory of neighboring sections, then it should be done in an open way (aerial).
- in addition, if the gas pipeline is to be laid through the auto canvas, it is advisable to choose a combined pipe installation option. The combined option includes: underground laying under the roadbed and aboveground along the territory of the site. Thus, an optimal solution to the problem is obtained.
In most cases, an underground method of laying pipes is used to protect the pipeline from the effects of various negative factors.
Depending on which of the methods of installation of gas pipeline communications will be carried out, pipes from various materials are used. There are two types of gas pipes according to the material of manufacture:
- steel;
- polyethylene (PE);
Steel pipes are versatile - they can be used for any laying (aboveground and underground), but modern polyethylene products are used for underground installation of gas pipelines. This is due to the fact that polyethylene has poor resistance to ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of ultraviolet rays, polyethylene loses its properties and is destroyed
However, it has a number of useful advantages that are worth paying attention to.
Recommendations for the selection of condensate traps
Depending on the parameters of your gas pipeline, there is a huge range of gas pipeline condensate collectors on the market. Some manufacturers are ready to produce a unit of any modification according to your personal order, exactly meeting all the requirements, if a suitable model is not in the presented product line.
Gas systems are diverse in form, pressure, operating conditions, filling, operating conditions - there are many options for combining these parameters. And therefore, there are no less options for condensate collectors for gas pipelines.
An incorrectly selected unit will not cope with the tasks assigned to it or will be unreasonably large and expensive, so we advise you to entrust the final choice to specialists. And in order to orient a little in this diversity, let's look at their main differences and the principles of choosing according to these parameters.
Criterion # 1 - the shape of the condensate collector
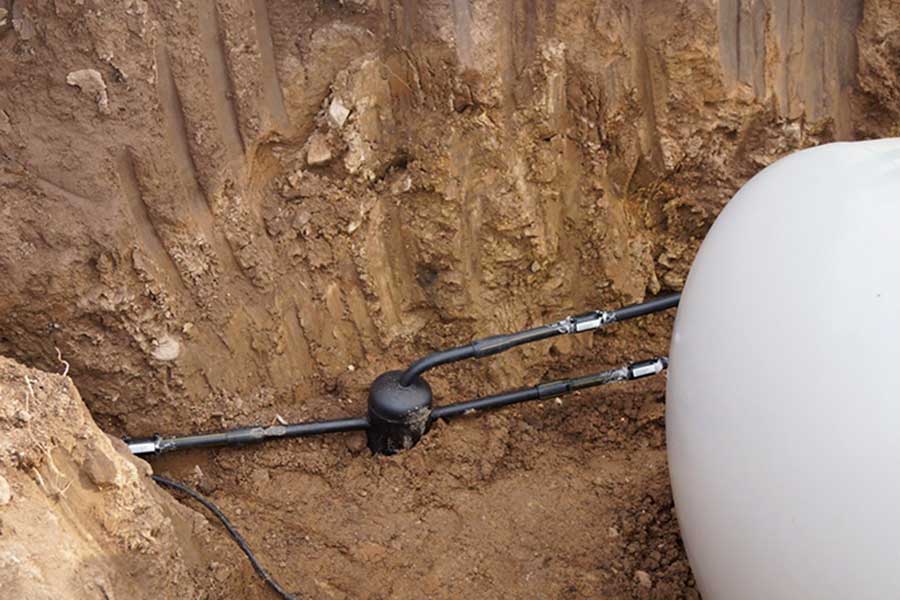
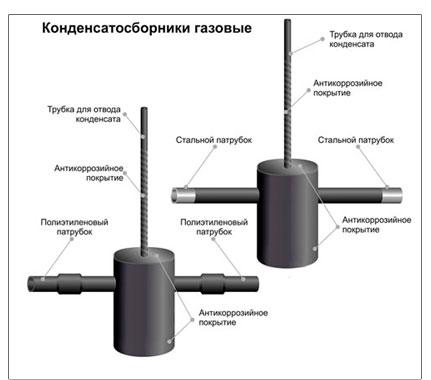
The condensate collection tank itself can be located horizontally, like a tube or a small tank, or vertically, resembling a pot. It is possible to determine how the selected condensate trap should be located not only by the shape, but also by the location of the connection pipes: they are always directed horizontally.
Vertical condensate collectors are most often used on gas tanks, they are connected to a tank and to a vertical pipe supplying gas to the house, while the condensate collection pot is located vertically, parallel to the pipe.
Horizontal models are usually hung or mounted on supports under a horizontal pipe, parallel to it. They are often high pressure and large volumes.
Criterion # 2 - pressure in the gas pipeline
It is important to purchase a condensate collector designed for the same pressure as the entire gas pipeline. There are 3 options: for low, medium and high pressure
They differ not only in the size and diameter of the pipes for connection, but also in the internal structure, installation and maintenance method.Therefore, a pressure mismatch can make installation and operation not only inefficient, but dangerous.
Criterion #3 - other hardware parameters
In addition to the mentioned shape and pressure, they differ in the following parameters:
- Volume - from a couple of hundred milliliters to several cubic meters, depending on the tendency of the gas pipeline to form condensate, the composition of the gas mixture, climatic conditions, the volume of transported gas and the installation location of the condensate collector.
- The material from which the condensate receiver is made is usually stainless steel. Without additional processing, it can withstand the aggressive environment of moisture and liquid butane for a long time. However, often condensate collectors, especially large volumes, are also made of ordinary steel. For additional protection, it is treated not only outside, like the entire gas pipeline, but also inside - for example, with an epoxy composition.
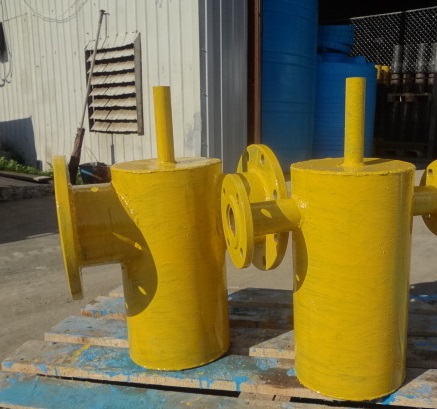
- At the place of installation, condensate collectors are underground and aboveground. On the second, the marking "Gas", "Flammable" is required.
- External waterproofing should be the same as on the gas pipeline. Most often these are polyethylene adhesive tapes, but there may also be bituminous mastic or a bitumen-polymer coating. For above-ground equipment, protection with waterproof paint, always yellow, is sufficient.
- Branch pipes for connecting to a gas pipeline differ in diameter, and can also be designed for a weld or a permanent connection of steel with plastic.
- Optional equipment. In addition to the inlet and outlet pipes, there must be a pipe for draining or pumping out the collected condensate. There may also be connectors for a pressure gauge, liquid level sensor, tank full alarm, for pressure equalization.
Private consumers, as a rule, purchase a condensate collector for private gas tanks, when arranging an autonomous gas supply to the estate.
For such purposes, small devices are usually used with a vertical, glass-like container and a long tube for pumping condensate. They are often installed underground, directly at the inlet of the gas tank, and usually do not have additional equipment.
High pressure condensate collectors are installed on main gas pipelines, at gas distribution points and in front of large industrial consumers. They have a large volume and the shape of a tank, almost always equipped with additional sensors and signaling devices.
Construction stages
 Before the start of construction work, a detailed drawing of the well is developed with the location of all gas equipment, as well as a binding scheme to the terrain, which takes into account a safe approach to the hatch and all standards for the remoteness of various objects. The construction itself is carried out in the following order:
Before the start of construction work, a detailed drawing of the well is developed with the location of all gas equipment, as well as a binding scheme to the terrain, which takes into account a safe approach to the hatch and all standards for the remoteness of various objects. The construction itself is carried out in the following order:
- Digging a well to the desired depth.
- Backfilling of a cushion of crushed stone and sand with careful tamping. The thickness of the layer is 10-20 cm, depending on the size of the structure and the composition of the soil.
- Installation of reinforcement from steel bars with a diameter of 8-12 mm in the form of a grid.
- Pouring concrete. The thickness of the bottom is 15-20 cm. Formwork is installed to make the pit.
- Building walls. With a monolithic structure, a wooden formwork is erected, steel reinforcement is installed, after which concrete is poured.Reinforced concrete rings alternately fall down and are installed strictly vertically, while the seam is sealed with cement mortar. To enter pipes, channels are formed at the desired height.
- Wall waterproofing. It is performed in the gap between the walls of the well and the ground. For its manufacture, bitumen and roofing material are used. If necessary, thermal insulation made of mineral wool is laid.
- Input termination. The pipes are sealed with sleeves filled with bitumen.
- Cover installation. For this, a reinforced concrete slab with a hole for the hatch is used.
- Installation of equipment and installation of the hatch.
- Quality control of construction and control tests.
Useful information
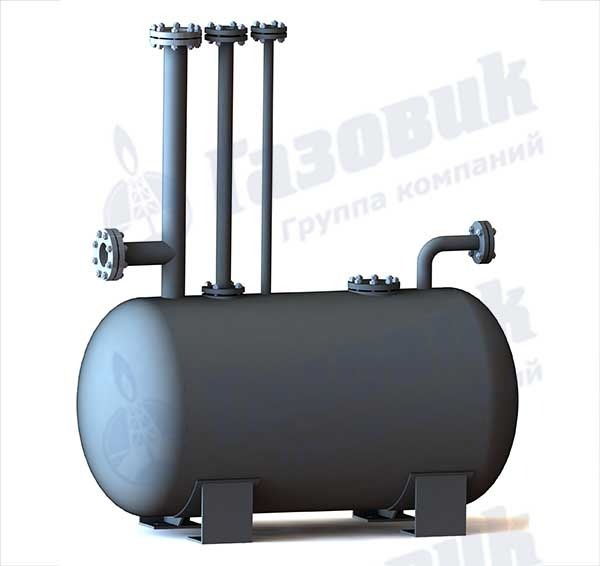
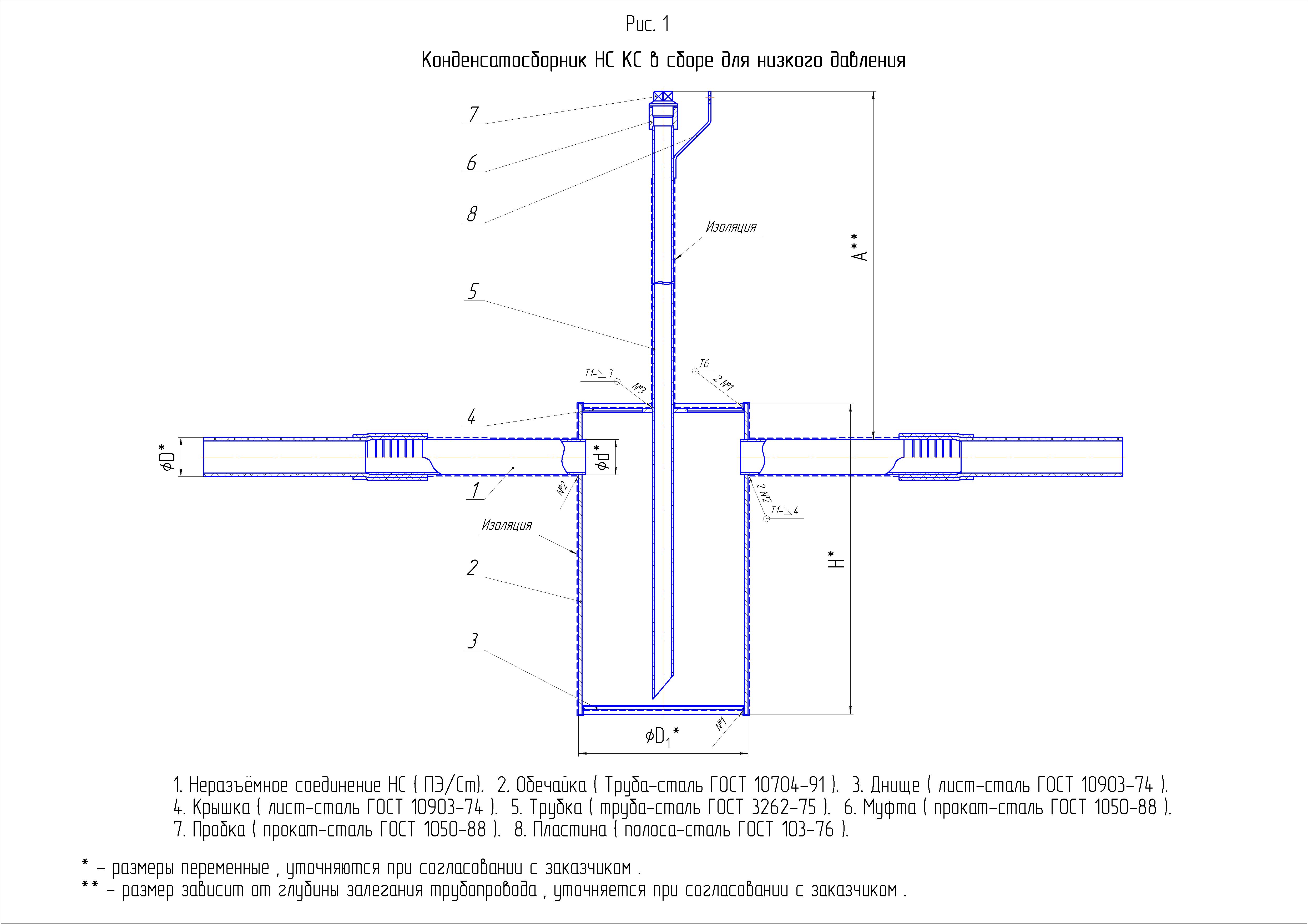
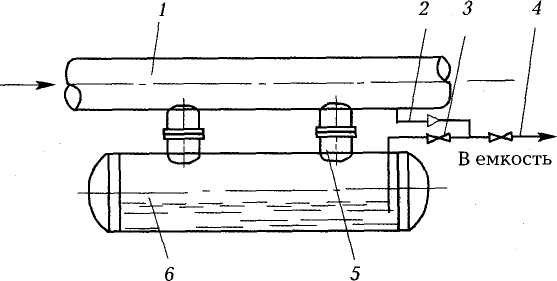
The condensate collection tank or condensate collector is a horizontal cylindrical vessel with elliptical bottoms, fittings for receiving and discharging condensate, as well as fittings for shut-off control and measuring valves. The condensate collection tank is designed for collection, storage and subsequent removal from the gas pipeline of condensate and water that got into the gas pipeline during flushing.
Scope of containers for collecting condensate:
The condensate collection tank is used at AGDS gas distribution stations, hydraulic fracturing points and compressor stations. Also, condensate collectors are used to collect condensate and other sediment on main gas pipelines and as part of other gas pipeline communications. Condensate collection tanks are installed at low sections of the gas pipeline to prevent the formation of hydraulic plugs and at the head of the gas pipeline system, where the bulk of the condensate settles.
Condensate trap
Connection table
| A1, A2 | B1 | IN 1 | G1 | D1 | E1 | G1 | L1 | P1 |
| Entrance condensate | Condensate outlet | For purge | For pressure sensor | For level sensor | For maximum level switch | For pressure equalization | Manhole hatch | For draining water |
Main parameters of condensate collectors
| Volume, m³ | Pressure design, MPa | Diameter, D mm | Length, L mm | Weight, kg |
| 7,5 | ||||
| 1,5 | ||||
| 2,5 | ||||
| 3,5 | ||||
| 4,5 | ||||
| 4,0 | ||||
| 4,0 |
Condensate collectors are selected based on the degree of humidity of the gas and the pressure in the gas pipeline.
Types of condensate trap
There are three types of condensate collectors depending on the pressure of the transported gas:
-
low pressure condensate collectors
-
medium pressure condensate collectors
-
high pressure condensate collectors
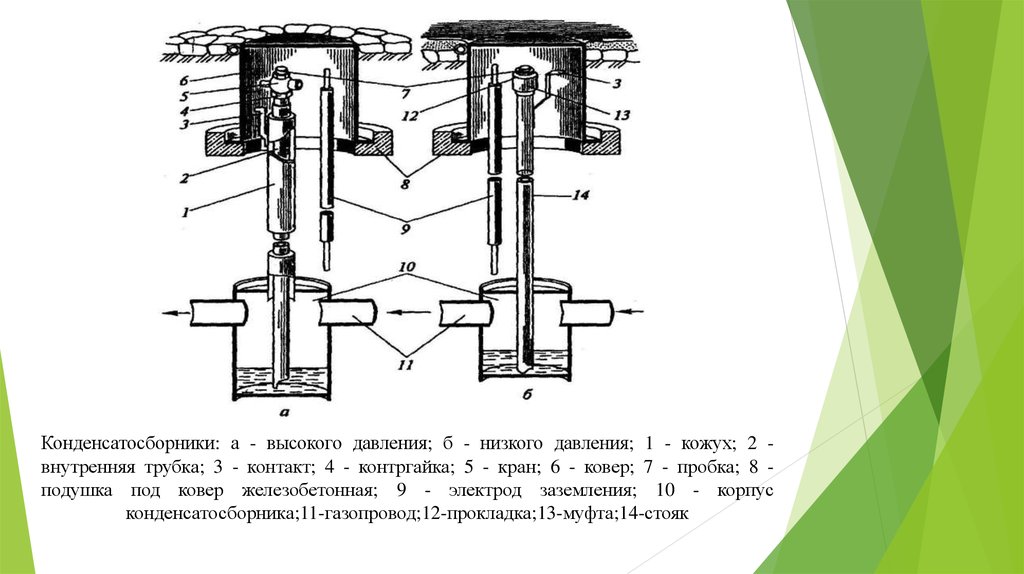
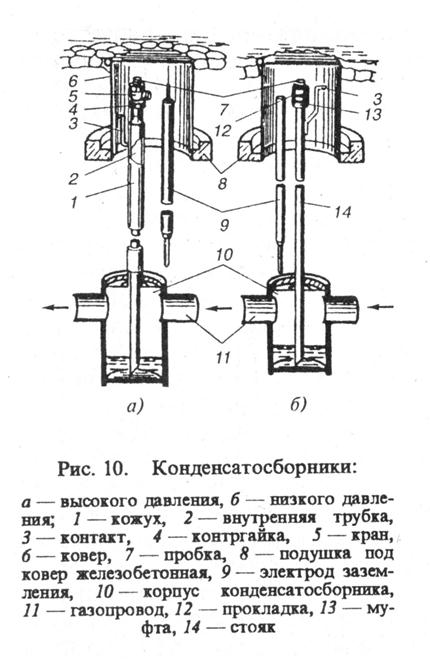
Medium and high pressure condensate collectors, as a rule, are equipped with a drainage (purge) tube connected by a tank, at the end of which a shut-off valve is installed - a tap, valve or valve. Condensate is removed from medium and high pressure condensate collectors under gas pressure. Low-pressure condensate collectors with a drain pipe led under a gas carpet are usually equipped with a plug or a coupling at the end. In this equipment, condensate is removed from the steam traps using pumps through a special riser pipe. Condensate traps for gas pipelines are produced with and without special insulation made of polyene, with weld-on fittings made of steel or with permanent steel-polyethylene joints.
The principle of operation of condensate collectors
The condensate trap consists of a collector, which is installed under the gas pipeline, condensate drains, a purge pipe with shut-off valves and an automatic liquid removal device.The condensate collector is filled with water, the operation of the condenser pumps and their interlocks is checked, the condensate is recirculated with the heating steam condensate level regulator turned on, and then steam is supplied to the heater. The condensate collector at the compressor intake is equipped with a device that automatically stops the compressor when the level of condensate and water rises above the permissible norm. Pumps supplying propane to the plant must have double mechanical shaft seals. The oil pumps used to lubricate the propane pumps have an electrical interlock that guarantees automatic activation of the standby ones. The condensate collector at the compressor outlet is designed to capture condensate falling out of the gas in the outlet gas pipeline, mainly during compressor shutdowns and in the process of replenishing gas tanks in the process of pumping oil out of them. Condensate tanks are covered with anti-corrosion insulation, which must correspond to the insulation of the pipeline in this section, and subjected to a preliminary hydraulic pressure test equal to one and a half working pressure in the gas pipeline.
How to do without gas condensate collectors?
A condensate collector installed on a gas pipeline is a guarantee of safety and equipment safety.
But there are also alternative options. As a rule, they are aimed at preventing the formation of condensate. Among such means are evaporators that return vaporous butane to the gas tank, thermal insulation and heating of the pipeline, laying it deeper than the freezing point, and using pipes of a larger diameter.
Heating the gas pipeline will prevent the formation of the most dangerous part of the condensate - the liquid phase of butane, but its arrangement and operation are not cheap
However, their use is not always possible and efficient, moreover, it is usually more expensive to install a condensate trap.
Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas

Gas inputs to buildings from the yard line or street network are laid into stairwells or basements. In residential buildings, inputs are arranged separately for each section. When laying pipes through the laying of the foundation, measures are taken to protect them from destruction during the settlement of the building. The pipe located in the wall is wrapped with a pitched rope and placed in a case - a pipe of a larger diameter.
Gas inlets to houses are preferably made basement. The entry of gas pipelines into basements and semi-basements and the laying of gas pipelines along them (if there are no special technical corridors) is prohibited. It is not allowed to install plugs on the basement and intra-house gas pipelines.
Gas input can be made not only in the stairwell, but also in the non-residential basement of the building.
Gas inlets of gas tanks are passed through special chambers, in which shutoff valves, gas tanks, valves for manual discharge and PC for gas discharge into the atmosphere when gas tanks are overfilled, as well as control units for the heating system and valves of non-combustible gas pipelines for purging gas tanks and gas inlets are placed.
Buried steel gas inlets laid under buildings must be enclosed in a gas-tight cartridge. The latter should be included in an accessible and commonly used part of the building.Where the cartridge ends, the annulus between the cartridge and the inlet pipe must be hermetically sealed to prevent gas leakage.
Low-pressure gas inlets of short length (up to 25 m) are allowed to be put into operation without testing them for density under air pressure. In this case, the density of the gas pipeline (inlet) is checked in an unfilled trench under the working pressure of the gas by coating the joints with soapy emulsion or another equivalent method.
| Scheme of the yard gas pipeline. /, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 - gas risers. |
A gas inlet is a gas pipeline running from the distribution (street) network to the riser of the intra-house gas network.
| Scheme of the yard gas pipeline. 1, 2, h, 4, 5, c, 7 8 - gas risers. |
A gas inlet is a gas pipeline waiting from the distribution (street) network to the riser of the intra-house gas network.
| Scheme of the yard gas pipeline. |
A gas inlet is a gas pipeline running from the distribution (street) network to the riser of the intra-house gas network.
The gas inlets and risers are blown through sequentially, starting from the most distant inlet and riser.
Since there are gas inlets to the building on each of the two stairwells, and the gas pipeline wiring in the left half of the building completely coincides with the wiring in its right half, the gas pipeline scheme can only be drawn up for half of the building.
Pages: 1 2 3 4 5
Why do you need a condensate collector on a gas pipeline?
Both methane and liquefied propane-butane mixture need additional purification. This is due to the conditions of storage and use, the imperfection of gas distribution systems.
Impurities in gases are different:
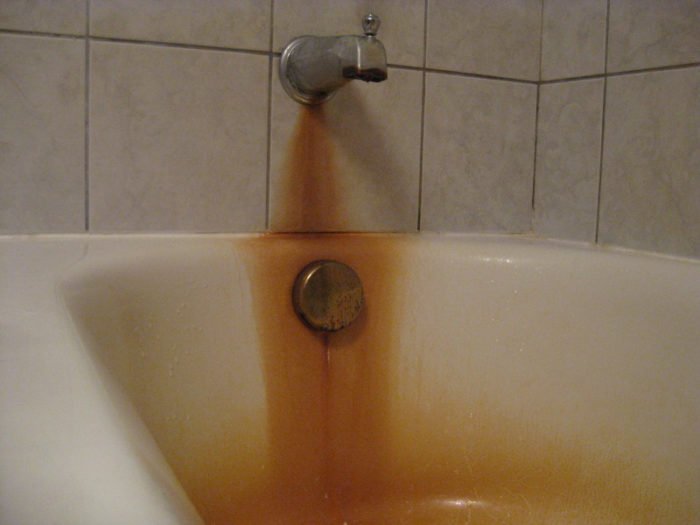
- Water can get into the gas pipeline during its construction, testing and purging, as well as through the smallest holes or cracks. It promotes corrosion of steel and destroys the chimney.
- Butane (liquid) can be recondensed from a propane-butane mixture. It does not evaporate and does not rise through the gas pipeline at low temperatures, in the cold. Liquid butane in a gas burner forms a torch, and in a boiler provokes a stop or explosion.
- Small solids can enter the gas from the tanks and piping of the system, especially if they are not new and the inside has begun to corrode. Because of them, the nozzles are clogged.
Each of these types of impurities is dangerous in its own way. Water, liquid butane in a gas burner forms a torch, and in a boiler provokes an explosion; solid particles clog the nozzles.
The condensate collector is engaged in filtration, accumulation and removal of foreign inclusions.
The condensate collector collects everything heavy, including liquid butane, preventing dangerous situations that it can provoke.
Gas condensate collectors on a gas pipeline: structure and purpose of a condensate collector + nuances of installation and maintenance
Are you planning to gasify your home? Perhaps you are equipping an autonomous gas supply system with a gas tank? In this case, you need to know about gas condensate collectors.
They will help to avoid many problems in the use of gas and extend the life of the equipment that consumes gas, as well as the gas pipeline itself and chimneys. A properly selected and installed condensate trap significantly improves the quality of the gas and ensures the safety of the operation of the entire system.
In this article, we will tell you what functions condensate collectors perform on a gas pipeline, what settles in them, what they are and how they differ, what is the principle of operation of this valve, how to install and maintain them.
Gas condensate collector Du 100 (1.6 MPa) From the Manufacturer

A gas condensate trap is a special device designed to collect and remove condensate present in the transported medium in the pipeline. Designed for installation on steel and polyethylene pipelines.
Gas condensate collectors are used to collect and remove water vapor and heavy hydrocarbons from the transported gas.
Gas, which contains moisture, gives certain difficulties to the operation of pipeline valves installed on the gas pipeline.
note
Excessive presence of condensate in the composition of the transported medium hinders the operation of compressor equipment and causes unstable operation of gas control stations and installations.
Depending on the gas pressure in the line, condensate collectors can be of low, medium and high pressure. Condensate traps are also different. for above and below ground installation. Underground condensate collectors additionally have 2 types of waterproofing and an elongated condensate drain pipe.
By default, condensate traps are manufactured with steel spigots with a welded connection type. On request, it is possible to manufacture with polyethylene pipes or flanges.
Principle of operation
The natural gas transported through the pipeline, entering the condensate collector, enters the zone of rarefaction, due to which the moisture suspended in natural gas tends to form droplets.
Further, passing through the housing, natural gas passes through a system of internal partitions, as a result of which moisture remains on the partitions and flows down, remaining inside the housing, when natural gas continues to be transported further along the main.
The moisture accumulated in the condensate collector is removed through the condensate drain pipe, which can be equipped with a ball valve, gate valve or just flanges.
Device and overall dimensions
D = 100 mm, D1 = 32 mm; L = 1300 mm; H = 2460 mm; H1 = 570 mm; H2 = 760 mm; B = 380 mm.
We deliver equipment throughout Russia: Murmansk, Apatity, Belomorsk, Petrozavodsk, St. Petersburg, Veliky Novgorod, Pskov, Velikiye Luki, Tver, Yaroslavl, Moscow, Smolensk, Kaluga, Tula, Ryazan, Bryansk, Oryol, Lipetsk, Kursk, Voronezh , Belgorod, Vladimir, Kaliningrad, Arkhangelsk, Kotlas, Kostroma, Kirov, Ivanovo, Yoshkar-Ola, Nizhny Novgorod, Arzamas, Cheboksary, Kazan, Saransk, Ulyanovsk, Syzran, Penza, Tambov, Saratov, Balakovo, Kamyshin, Rostov-on- Don, Volgograd, Novorossiysk, Krasnodar, Tikhoretsk, Armavir, Maikop, Stavropol, Cherkessk, Elista, Nalchik, Vladikavkaz, Pyatigorsk, Prokhladny, Astrakhan, Naryan-Mar, Ukhta, Syktyvkar, Perm, Izhevsk, Ufa, Samara, Orenburg, Orsk, Magnitogorsk, Vorkuta, Inta, Salekhard, Priobye, Serov, Khanty-Mansiysk, Yekaterinburg, Tyumen, Tobolsk, Chelyabinsk, Kurgan, Ishim, Novy Port, Nov.Urengoy, Petrozavodsk, Tobolsk, Noyabrsk, Surgut, Nizhnevartovsk, Tara, Omsk, Dixon, Dudinka, Norilsk, Igarka, Turukhansk, Narym, Bely Yar, Tomsk, Kemerovo, Novosibirsk, Novokuznetsk, Barnaul, Gorno-Altaisk, Krasnoyarsk, Kansk, Abakan , Kyzyl, Khatanga, Tura, Suntar, Lensk, Ust-Ilimsk, Bratsk, Ust-Ordynsky, Irkutsk, Ulan-Ude, Aginsky, Chita, Severobaikalsk, Yakutsk, Neryugri, Tynda, Blagoveshchensk, Vladivostok, Birobidzhan, Khabarovsk, Ussuriysk, Nakhodka , Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Nikolaevsk-on-Amur, Okhotsk, Magadan, Palana, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Anadyr and others.
Instrumentation and control devices in gas pipeline systems
In addition to all of the above, numerous instrumentation and control devices (instruments and automation) are used in gas pipeline systems.
 In addition to gas fittings, instrumentation is installed on gas pipelines. This allows you to constantly monitor the condition of the equipment and the progress of the technological process. As well as promptly identify pre-emergency and emergency situations
In addition to gas fittings, instrumentation is installed on gas pipelines. This allows you to constantly monitor the condition of the equipment and the progress of the technological process. As well as promptly identify pre-emergency and emergency situations
The most popular devices used in gas systems are:
- gas alarms;
- equipment for emergency shutdown of incoming gas;
- equipment for measuring the volume of the passed gas;
- electronic regulators of the passed volume of gas;
- autonomous power supplies;
- gas valves for automating various processes and optimizing the operation of pipelines;
- gas regulators for regulating the volume of the medium passing through a section of the pipeline.
Such devices are high-tech equipment operated in a variety of conditions.
A condensate trap for a chimney: is it necessary?

The main purpose of the chimney is to remove combustion products to the outside.The performance of the heating equipment and the safety of its use depend on the operation of the system. Nowadays, for the construction of chimneys, people use various materials, but most often they prefer stainless pipes. When designing and building a system, people often make the same mistakes. For example, many people decide to save money on installing a condensate trap, because they believe that it is not necessary. The desire to save money or the lack of necessary knowledge often leads to sad consequences.

Should a condensate trap be installed or not?
The condensate collector has a simple design. It is a tee, one end of which is adapted to drain liquid to the outside. For these purposes, a mount is usually provided to which the hose is connected. Also there are condensate collectors with a special capacity. Such devices need to be serviced periodically - drain the accumulated liquid.
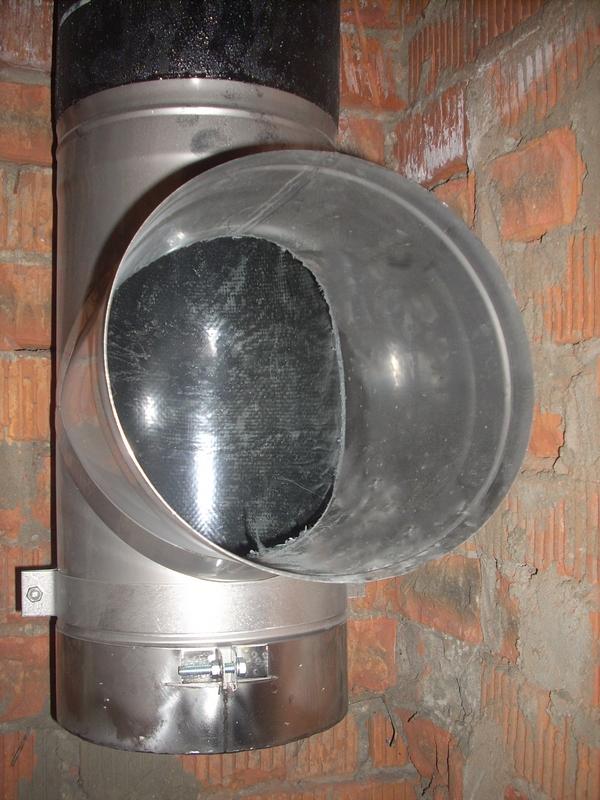

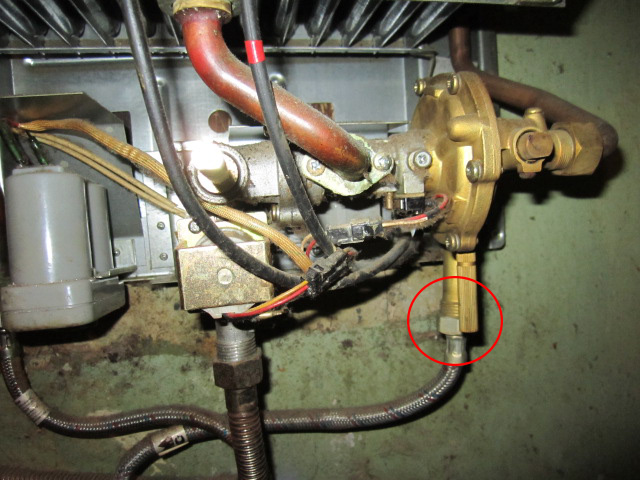
Despite the simplicity of design, the condensate trap performs several important functions. Provides access to the system for maintenance, removes the moisture formed inside the system, thereby preventing its rapid destruction. According to regulatory documents, the installation of a condensate collector is mandatory when using gas heating equipment.
It is worth noting that the connection of gas boilers to the chimney must be carried out by specialists. Mistakes made when designing a chimney can have unpleasant and even dangerous consequences.
It is important to follow a number of rules regarding the location of the pipe, the number of turns and other nuances.If you want autonomous heating in your home to work efficiently and safely, do not try to save on the services of specialists or components.
For any questions, you can consult with the staff of our company.
Why does condensation appear
Condensation in the chimney pipe can form for the following reasons:
- The flue pipe is clogged. The accumulation of blockages leads to a decrease in traction, due to which the heated gas does not pass through the pipe as quickly as it should. As a result, it interacts with air, which leads to condensation.
- Temperature difference at gas outlet. In winter and autumn, a rather low temperature is set inside the chimney. When heated gases rush into it, a wet deposit is formed.
- Significant moisture content of the fuel. For heating a private house, it is recommended to use well-dried firewood or other types of fuel. Otherwise, when exposed to fire, the evaporation of internal moisture begins, followed by its settling inside the chimney.
- External influences. This mainly happens due to precipitation, if they have the opportunity to get inside the chimney.