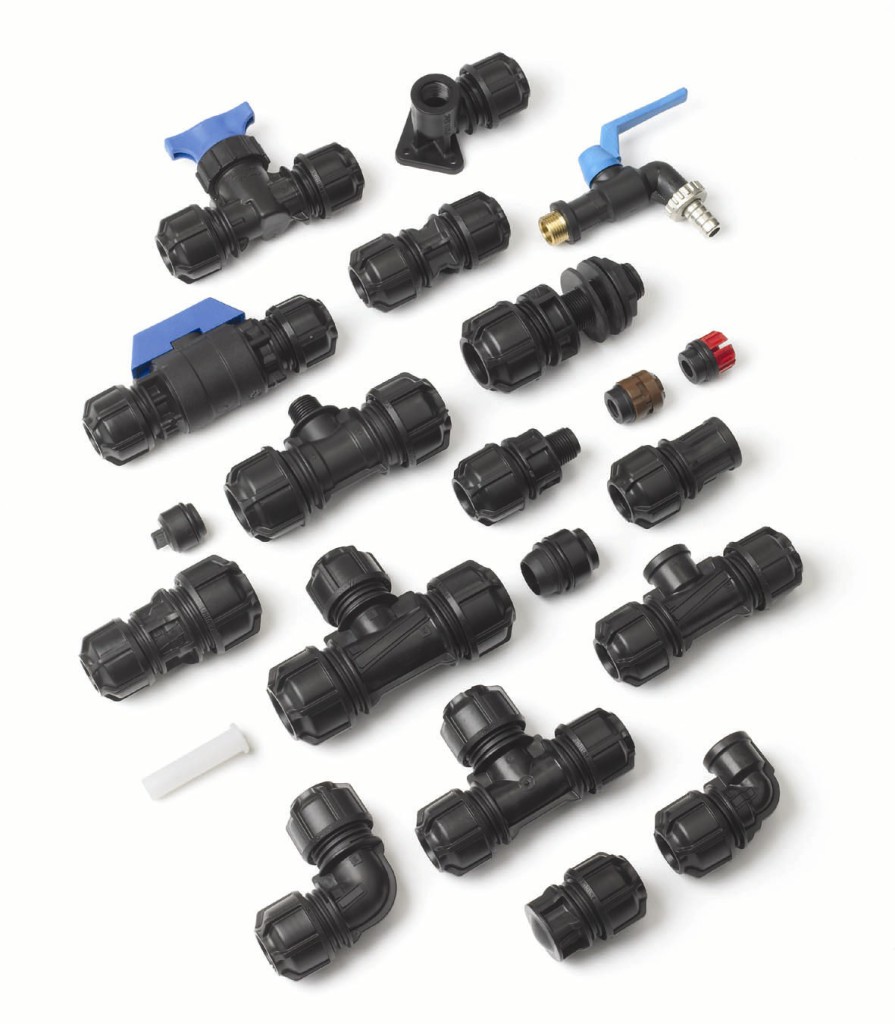
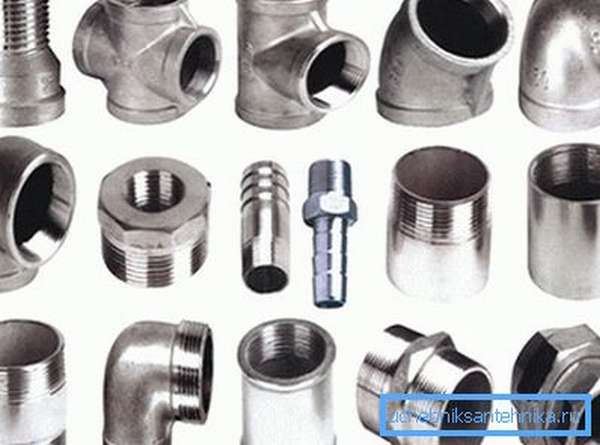
- Classification
- How to choose fittings for soldered polypropylene pipes
- Types of fittings and their features
- How to choose the best PP option
- materials
- Recommendations for use
- How to choose
- PVC tee construction
- Technical properties of fittings for heating systems
- Standards and assortment
- Hot-formed GOST 8732-78
- Cold-formed GOST 8734-75
- Steel pipes
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Standards and sizes
- Pipes in sewerage systems
- Features and benefits of polymer sewer pipes
- Section types and coatings
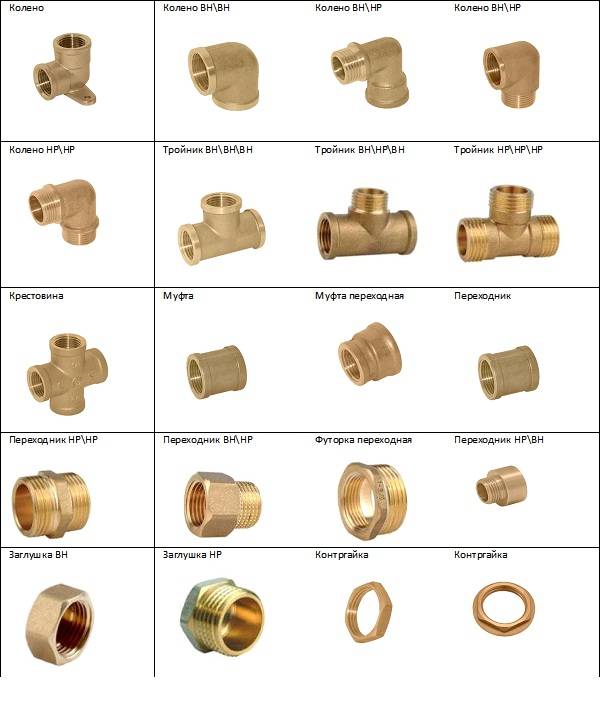
Classification
Types of fittings are determined depending on the parameter in question, so familiarize yourself with several classifications at once. Depending on the material used, there are:
- Stainless. When creating, stainless steel is used. Among the main figurations, it is worth highlighting tees, crosses, bends, transitions. The most common type is threaded.
- Bronze. Differs in big service life. They are versatile and can be used in conjunction with pipes made of steel, plastic or copper.
- Metal. In production, only ferrous metals (steel, cast iron) or non-ferrous metals (bronze, brass or copper) are used.
- Cast iron. Belongs to the threaded category.Optimal for creating sealed structures using seals.
- Chrome plating is often used to improve the performance of fasteners. They can be used with pipes of various materials.
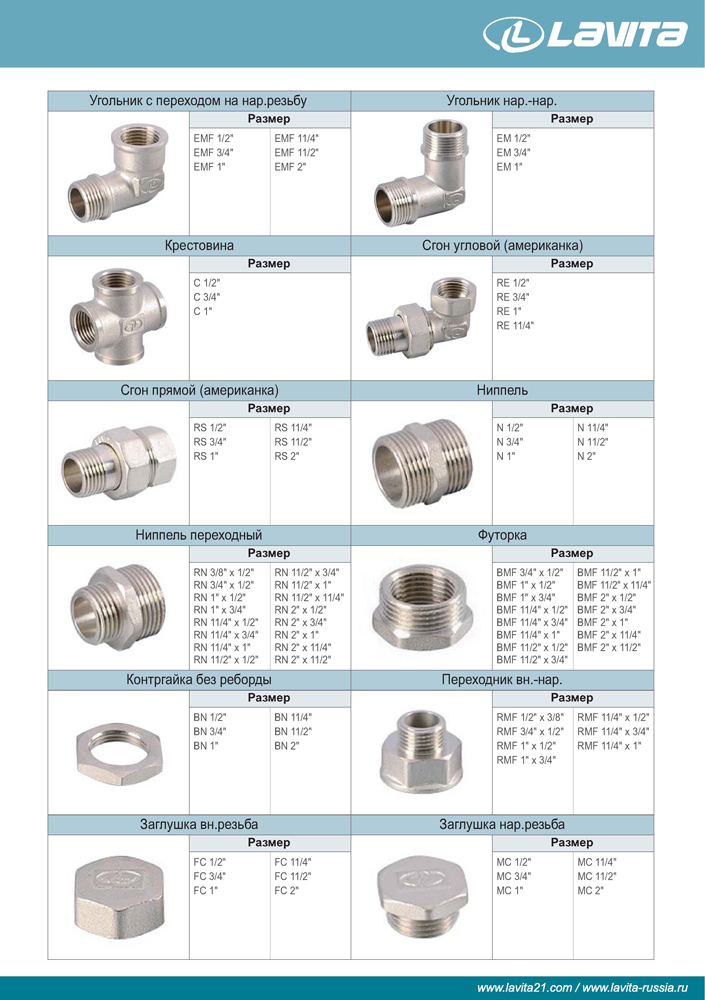
The second type of classification involves the division of fisting according to the design features:
- DKO with metric straight thread. In the subcategory, it is customary to single out straight, angular structures of 45 or 90 degrees.
- For straight sections, a straight construction is used.
- To create a sealed structure, the connecting fittings are crimped using two special rings. The design avoids leaks over time.
- Push fitting. Visually it consists of a seal in the form of a ring, a coupling and a ferrule. No additional press tools are used for creation. Relevant for the creation of heating systems or water supply.
- Baggio. Visually, the design does not imply any difficulties. There is a body, rings with seals and threaded bolts. You can also find straight or at angles of 45 and 90 degrees. Suitable for creating a control system for machines 6-25mm
- A container connection will be required to install containers of various orientations.
The third classification system is built according to the type of connection:
- collet. Belong to the category of crimp. Experts do not advise using them to connect pipes made of PVC material, since there is a high probability of causing serious mechanical damage.
- With the inclusion of a union nut, it presents a split view. Actual to carry out the dismantling of pipes without the need to additionally create rotation.
- Air is referred to as a quick-release type.Ideal for creating pneumatic systems. Used in the manufacture of plastic or metal.
- Hydraulic - the main representative of threaded or crimped connections.
- American is made from various types of materials.
- To work with polymer pipes, electric welded structures are the most relevant. Overlapping or end-to-end installation is allowed.
The last classification implies the type of pipe connection:
- Polypropylene. Relevant when creating hot or cold water supply. They can create a combined version using brass inserts.
- Pneumatics with steel, copper fittings, bronze or brass polymers. Suitable for pipes made of polypropylene.
- Polyethylene with laying of electric heating elements. As a rule, a heating wire is used. With its help, reliable welding of the connecting element and the pipe is carried out.
- With high pressure relevant for hydraulics. The system transports fluid.
How to choose fittings for soldered polypropylene pipes
For the correct selection of polypropylene fittings, the following rules must be followed. If you plan to hide the polypropylene pipe in concrete after installation, then it must be taken into account that stray currents destroy metal joints for 15–20 years. Therefore, in places of contact with concrete, it is necessary to choose fittings for soldering.
When installing the plumbing yourself, choose solder fittings. The cost of a soldering iron and fittings is small, so buy fittings with a margin and practice before installation.
Polypropylene fittings are available in the following sizes: 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 75 and 90 mm.The connection is carried out according to the bell principle - when soldering, the pipe is inserted into the fitting.
By the diameter of the pipe, you can determine where it will be installed. In buildings where there are a large number of people, polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 200 mm are used. It is better to buy such pipes in bulk, as this will save you money.
How to choose fittings for polypropylene pipes in individual construction? Polypropylene pipes and fittings with a diameter of up to 30 mm are often used here. But when choosing, it is worth remembering that each heating branch performs certain functions, and the material must be selected in accordance with them. Buy polypropylene pipes in specialized stores and be sure to consult with sellers.
For use in hot water systems, polypropylene pipes and fittings with a diameter of 20 mm are usually chosen. Pipes with a diameter of 25 mm are suitable for risers. This diameter is also used in central heating. In autonomous systems, you can choose pipes of other diameters. In the photo you can see polypropylene pipes, which are in the greatest demand. For underfloor heating, polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 16 mm are preferred.
Docking of a fitting with a polypropylene pipe is carried out only after heating and melting of the walls of the contacting parts. It is impossible to join the cold pipe and fitting due to insufficient clearance. If you still manage to connect the parts in a cold state, then this indicates their poor quality. Such parts cannot guarantee the reliability and tightness of the connection.
The material from which the fittings are made is the same as that used for other elements of the pipeline.The characteristics of such products are determined by its brand. The method of manufacturing polypropylene products divides them into:
-
Cast - products that do not have joints (solid).
-
Segment - elements created by soldering segments of polypropylene pipes. Due to the large number of seams, they are less reliable and their cost is lower.
Installation of polypropylene is carried out with a low-temperature soldering iron. A special nozzle melts the polypropylene pipe and fitting at the junction. After cooling, such a connection is strong and tight.
When soldering, the following guidelines should be followed:
-
soldering iron temperature - not higher than +260 ° С;
-
for an even connection, the movement of elements at the time of connection must be carried out along one axis.
To connect pipes with fittings, a soldering iron and nozzles are required in accordance with the diameter of the connected products.
The sequence of operations is as follows:
-
We cut off the polypropylene pipe with special scissors (pipe cutter) strictly at a right angle.
-
Using a file, remove the burrs from the cut.
-
We heat the soldering iron to a temperature of +250 ... +260 ° C, and insert the pipe and fitting onto the heated nozzles.
-
We hold in this position for some time (depending on the diameter of the fitting and pipe).
-
After that, we remove the elements from the nozzles and connect by inserting the pipe into the fitting until it stops.
-
We fix the connection for the time specified in the table. We do not allow movement along the axis of the product. Cool at room temperature and use a rag to remove the influx of plastic.
Read material on the topic: Wholesale of polypropylene pipes
Types of fittings and their features
In different sections of the pipeline, the connecting elements perform different functions, it is the task solved by the fitting that determines its design.
But in addition to the shape of the body, the shaped elements differ in the way they are threaded:
| Name | body shape | thread | functions |
| full bore coupling | straight cylinder | internal | connection of fixed elements of the same diameter |
| adapter sleeve | two different-sized cylinders connected by a straight truncated cone | internal | connection of fixed elements of different diameters |
| nipple | short, straight pipe section with a nut-shaped thickening in the middle, can be hollow or equipped with a valve | outdoor | temporary or permanent connection of two pipes or a pipe with a fitting, in the presence of a valve, is used to change the pressure in the pipeline |
| adapter nipple | nozzles on opposite sides of the nut have different diameters | outdoor | connection of pipes of different sizes or pipes with a fitting |
| adapter | a short cylinder with a small diameter branch pipe attached to it | internal in the cylinder and external on the branch pipe | the formation of a transition between pipes of different diameters with threads of different types |
| corner or bend | the body is bent at an angle of 30º | three options: internal-internal, external-external, internal-external | pipeline redirection |
| tee | coupling with an additional side branch pipe, the diameters of the pipes can be the same or different | various combinations of threads on the nozzles are possible | connection to the pipeline of a household or plumbing fixture, bringing or diverting an additional branch of the pipeline |
| cross | cruciform body with four or more nozzles | internal or external, the same on all nozzles | connection of several pipeline elements |
| nut (compression nut) | a short piece of thick-walled hexagonal pipe | internal | fixation of elements with external thread, crimping of smooth-walled pipes (mainly polymer) when connected using threaded fittings |
| lock-nut | narrow nut (1-2 thirds shorter than a crimp nut) with a small number of threads | internal | strengthening of the knot, prevention of loosening of the threaded connection |
| futorka | single socket nut | external on the branch pipe, internal on the side of the nut | connection of different-sized elements with different types of threads |
| plug for pipe | wide nut closed on one side | internal | sealing of an unused branch pipe with an external thread |
| plug in the pipe | futorka closed on the side of the nut | external on the branch pipe | sealing of an unused socket with an internal thread |
| drive | piece of pipe threaded at both ends | external, on the one hand 5-6 turns, on the other - up to 30 | connection of fixed elements that are a short distance apart, used in combination with couplings or nuts |
| union | two connected nozzles: one cylindrical or hexagon threaded, the second can be hexagonal, smooth cylindrical or cylindrical with helical or transverse threads | external or internal | an additional part used to connect smooth-walled pipes (mainly polymer) to the main pipeline using threaded fittings |
| American | collapsible coupling, consists of two threaded pipes and a union nut, can be straight or angled | on the outer branch pipes external or internal, under the union nut - external | connection of two elements of the pipeline, collapsible design simplifies installation |
How to choose the best PP option
In order not to make a mistake and choose the best fittings, it is recommended to take into account the material from which the connection is made and its diameter for:
organization of solid structures made of copper or steel - flanges. They are suitable if it is impossible to avoid welding or the components are threaded. When ordering a batch, you need to consider how flat they are, whether the ends are perpendicular. From these indicators depends on how tight the connection will be. To achieve tightness, it is better to use a special FUM tape. The locknut will help to achieve optimal fixation of the seal made of various metals (cast iron, steel or bronze).
solving plumbing problems, it is better to select connecting elements from identical material, like pipes. Usually it's PVC.
Soldering is carried out with special tools
It is important to take into account that such models are characterized by high cost.
systems with metal-plastic present, it is better to use several fasteners, on average 3-4. When ordering them, it is important to consider the weight
As a rule, the better the design, the more it weighs.
It is not recommended to save on the purchase of connecting elements, since the likelihood of serious leaks and pipe deformations depends on them. This is especially true for systems that must withstand high pressure.
The popularity of polymer models, which differ from the above categories in ease (you can install it yourself without the help of a team of professionals), the duration of operation (an average of 30-40 years without replacement), it is allowed to create water supply systems of various levels of complexity. However, it is also necessary to take into account the specifics of the planned work and the material, from which pipes are made and their diameter to ensure tightness and maximum tightness of connections.
materials
Products with threaded connections are made of brass, cast iron, bronze, stainless steel, copper. Brass and bronze threaded fittings are installed at the points of attachment and connection of pipelines made of copper. High reliability of the parts is ensured by the compression ring located on the inside of the fitting. To mount the connecting thread, you only need a wrench, which tightens the nut to the required degree. In this case, care must be taken to avoid twisting the threads, which can lead to leakage.

A threaded connection made of brass and bronze has the following negative properties:
- loosening of the connection during untimely maintenance of the element, which leads to failure of the fitting;
- limited use with increased pressure in the system.
Copper threaded fittings are good because they are resistant to any temperature stresses, easy to install and do not require much effort. Copper fittings are used to connect various types of pipelines. And also they are protected from corrosive destruction of the circulating liquid.Experts do not recommend using pipelines made of various materials for connection, as this will significantly reduce the life of the circuit. If it is necessary to combine, the combination of copper with galvanized or chrome-plated unalloyed steel should be avoided. This combination leads to oxidative processes, as a result of which threaded products and extreme sections of pipes fail.
Steel threaded devices are required for the connection of steel pipes "under the thread". It is easy to connect any shut-off and control valves to them. To increase the reliability of the thread, it is necessary to wrap a fum tape on the part.
Threaded connections made of stainless steel are designed for connecting pipelines with different diameters. They have gained popularity due to their functionality, affordable cost and high quality. Inside they have a special sealing ring, which allows the use of stainless steel devices for water and gas supply systems. The main advantage of connectors with a special seal is the possibility of repeated use even after disassembly or repair of a pipe section. Stainless steel products are common in the oil, gas, construction and petrochemical industries. And also they are used in every house in heating circuits. These elements also allow you to change the direction of the coolant in the heat pipe.
Threaded fittings made of cast iron are characterized by a long service life. The device is a piece with a threaded end. Cast iron is also used in the manufacture of other locking devices.Cast iron devices can be operated several times, they provide maximum tightness of the circuit. However, it is necessary to take care of the gasket made of waterproof material. Ferrous metal products are distinguished by their low price, ease of installation, during which no special tools are required. These are the most reliable and durable parts for metal pipelines. They have a significant drawback - this is a low resistance to corrosion.


Recommendations for use
The thread is the simplest and most convenient fitting installation option.
To do this, you will need the following tools:
- key gas and adjustable;
- klupp;
- sealing agent.
To enhance the tightness of the joint connected by a thread, in pipelines for supplying hot and cold water, linen cloth impregnated with minium or fum-tape is used.
The installation itself is carried out as follows:
- the pipe is clamped;
- in the absence of a thread, it must be cut, having previously processed the place of its location with drying oil;
- then the material selected to enhance the sealing is wound onto the thread;
- on the opposite side, the clutch is screwed up to the stop on the run-off;
- on the other hand, processing is carried out similarly to the first one and docked to the second side of the fitting, after which the coupling is screwed onto it until it stops on the run-off;
- with the help of a pipe wrench, the coupling is tightened even more;
- then it is necessary to test the tightness of the system by filling the pipeline with water;
- when a leak is detected on its side, the lock nut is tightened;
- if this action does not help, the thread is screwed unevenly and it is necessary to reinstall it again.
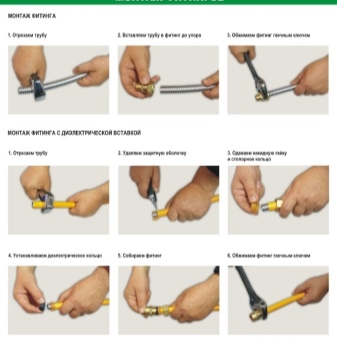
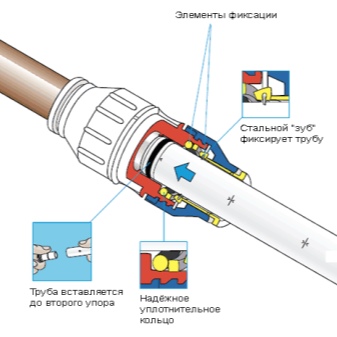
In the absence of a thread or if it is damaged or otherwise, for which a threaded connection cannot be installed, a coupling is used.
To install a compression fitting, do the following:
- the ends of the pipes to be connected are cleaned of burrs, the adjacent inner and outer surfaces of the pipe are also processed;
- the pipe is inserted into the fitting exactly in the center;
- a compression ring is put on the pipe;
- the crimp nut is installed and tightened until the connection is completely sealed;
- when tightening the nut, the force must be moderate, otherwise there is a possibility of stripping the thread or breaking it.

How to choose fittings for polypropylene pipes, see the video.
How to choose
When choosing fittings for pipeline installation, it should be remembered that detachable connecting elements can only be used when pipes are placed in an open way. For the formation of knots in walls, ceilings or floors, the use of threaded connections is unacceptable.
However, even when laying communications in plain sight or in places where they will be available, it is important to choose the right fittings that exactly match the connected pipes and nozzles of connected devices and equipment.
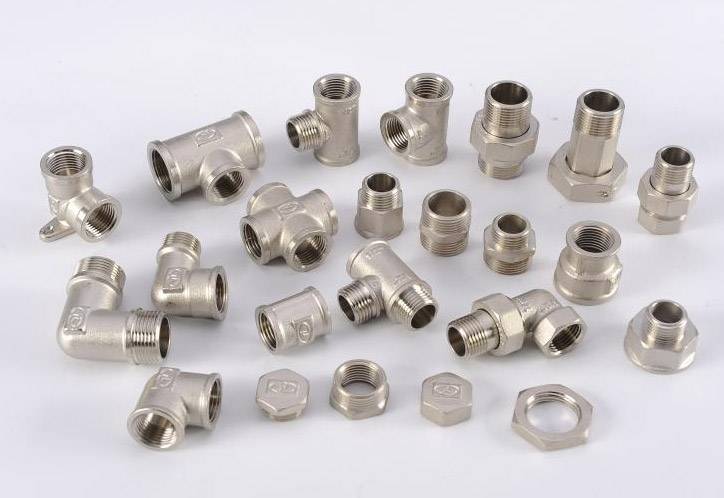

The fitting and the pipeline element connected with it must comply with:
- section diameter, throughput,
- thread pitch,
- thread direction - left or right,
- thread edge height.
All of these parameters are usually indicated either in the form of markings on pipes, household and plumbing appliances and fittings, or in the accompanying documentation.
In addition, the total length of the threaded section of the fitting must not be less than the length of the threaded socket of the device to be connected or the end of the pipe.
PVC tee construction
Externally, the tee is a part of a pipe with a side outlet, to which it is easy to attach an additional pipe and create the desired branch.

A tee can also be used for a conventional connection without connecting another line, but taking into account the fact that this may be needed in the future. For example, if it is planned to bring out another pipe after some time, then the tee can be installed in advance, and the additional outlet can still be closed with a plug. Installing a pipe branch when the time comes is a fairly simple operation: you just need to remove the plug and connect the pipe.
We recommend that you read: Features of the use of fittings made of stainless steel
Technical properties of fittings for heating systems
Modern fittings for metal heating pipes or metal-plastic structures are classified according to certain criteria.

Such elements should be selected based on a whole range of technical and operational properties, the most important of them include:
- scope, and in which system the functional element will be installed;
- material and manufacturing technology of the fitting, tools necessary for this;
- structural purpose and configuration, purpose of the fitting element.
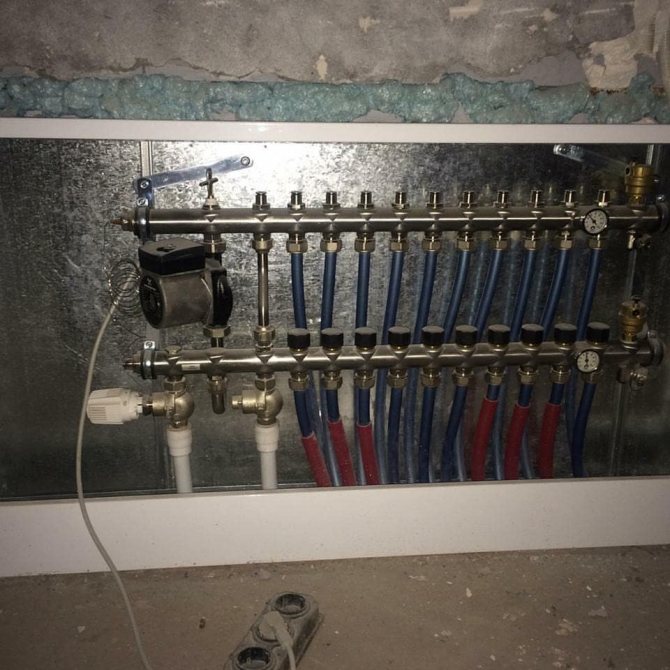

The correct choice of connection elements will ensure a long service life of the entire heating system of its individual elements, increasing the performance properties of the overall design.
- Heat accumulator for heating - a description of the system and features of its use in a private house (120 photos)
-
Pumps that increase pressure - an overview of models in 2020 recommendations for choosing parameters for a heating system (105 photos)
-
Pumps for pressure testing of heating - manual and automatic models for modern heating systems (90 photos and videos)

Standards and assortment
Seamless steel pipes are produced according to two standards depending on the production method:
- Hot-formed pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 8732-78;
- Cold-formed pipes are manufactured in accordance with GOST 8734-75.
What do the standards say about these types of pipes?
Hot-formed GOST 8732-78
The range of steel pipes of this standard includes diameters from 20 millimeters to 550. The minimum wall thickness is 2.5 millimeters; the thickest-walled pipe has a wall thickness of 75 millimeters.
Pipes can be made in random lengths from 4 to 12.5 meters or to measure lengths within the same limits. Production of pipes of multiple measured length is possible. Size range - the same 4-12.5 meters; for each cut, an allowance of 5 millimeters is made.
The curvature of an arbitrary section of the pipe must be within one and a half millimeters for pipes with a wall thickness of less than 20 millimeters; two millimeters for walls in the range of 20-30 mm and 4 millimeters for walls thicker than 30 mm.
The standard regulates the maximum deviations for the outer diameter of the pipe and the thickness of its walls. The full range table and the table of maximum deviations in the production of pipes can be found in the appendix to the article.
The most thick-walled pipes are produced according to this standard.
Cold-formed GOST 8734-75
Pipes are produced with a diameter of 5 to 250 millimeters with a wall thickness of 0.3 to 24 millimeters.
In the range table (also present in the appendices), the pipes are clearly divided into four groups according to wall thickness.
- Pipes with a ratio of outer diameter to wall thickness of more than 40 are especially thin-walled;
- Pipes, in which the ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness in the range from 12.5 to 40, is referred to as thin-walled by the standard;
- Thick-walled pipes have this ratio in the range of 6 - 12.5;
- Finally, with an outer diameter to wall thickness ratio of less than six, pipes are considered to be particularly thick-walled.
In addition, pipes with a diameter of 20 mm or less can be classified into two categories based on the absolute value of their wall thickness: pipes with walls thinner than 1.5 millimeters are thin-walled, if the walls are thinner than 0.5 mm, pipes are classified as especially thin-walled.
What else does the standard say?
- Pipes with a diameter to wall ratio of more than fifty with a diameter of more than 100 mm and pipes with an outer diameter to wall thickness ratio of less than four are delivered only after the technical documentation has been agreed with the customer;
- Slight ovality and wall variation of pipes are acceptable. The limitation is the tolerances for the diameter and thickness of the walls (they are also given in the appendix): if the difference in wall thickness and ovality do not take the pipe beyond these tolerances, then everything is in order.
- The curvature of an arbitrary pipe section per linear meter should not exceed 3 millimeters for pipes from 4 to 8 millimeters, 2 millimeters for pipes in the diameter range of 8 to 10 mm and one and a half millimeters for pipes over 10 millimeters.
- By agreement with the customer, it is possible to supply pipes without final heat treatment. But ONLY by convention: in general, annealing is mandatory.
Cold-formed thin-walled pipes have the highest strength at low weight
Steel pipes
Advantages and disadvantages
As already mentioned, the main disadvantage of black steel is its susceptibility to corrosion. Unfortunately, this material has been used in home plumbing systems for many years; the consequences are yet to be unraveled.
Galvanizing does not have this problem.
But galvanizing is another matter.
However, both those and other pipes are quite difficult to install - on or by welding. In addition, the electrical conductivity of the material should also be written down as a disadvantage: the number of electric shocks through the water supply is very high.
Standards and sizes
Water and gas pipeline, or more simply - the VGP pipe has the same assortment as prescribed by the standards. Let's turn to regulatory documents: we have GOST 3262-75.
| Conditional pass | Outside diameter | Pipe Wall Thickness | Weight of 1 m of pipes, kg |
| ordinary | enhanced | ordinary | enhanced |
The size table is relevant for both galvanized pipes and pipes without anti-corrosion coating. As we can see, the range of VGP pipes ends at a diameter of 150 mm.
However, in addition to intra-house engineering networks, there are also highways. Pipes for them are seamless steel hot-worked pipes GOST 8732-78, having dimensions of 20-550 mm with a wall thickness of 2.5-75 mm; however, the pipe range is not limited to them - there are also cold-formed pipes GOST 8734-75.
Their diameters are 5 - 250 millimeters, wall thickness - 0.3 - 24 mm. Of course, pipes of small diameter are not used for heating mains and water supply of quarters and microdistricts.
Pipes in sewerage systems
Previously, most domestic sewer systems were made of cast iron pipes connected by metal fittings. At the same time, the installation was almost always associated with the use of various types of welding (more often than others, electric welding).
In addition, as practice has shown, cast iron sewer systems, despite their apparent durability, lose their original performance over time, since they are prone to lime build-up on the inner walls.
Polymer systems have become a modern alternative to old systems, which are usually based on sewer pipes and PVC fittings.
Schematic representation of the most commonly used sewer fittings
Features and benefits of polymer sewer pipes
Among the polymer products used in the installation of sewerage systems, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, polybutylene, polypropylene or simply PP pipes and fittings for sewerage are most often used.
The reason for this was the high level of practicality of plastic pipes in comparison with any type of metal pipes and their relatively low cost.
Since PVC sewer pipes and fittings are the most popular solution due to the price / quality ratio, we will dwell on their features in more detail.
PVC sewer pipes and fittings are distinguished by the following undeniable advantages:
- Installation of sewerage systems using these components can be done manually without the use of equipment for gas or electric welding.The main method of connecting pipes in such systems is a socket, the tightness of which is ensured by a rubber sealing gasket embedded in the socket.
- Low weight parts.
Sewer pipes and fittings: dimensions of slopes, diameters and lengths provided for in various nodes of the sewer system
- The durability of pipes is due to their immunity to aggressive media, moisture, ultraviolet radiation, and temperature fluctuations. In addition, sewer pipes and PVC fittings are not prone to the formation of corrosion deposits on the inner walls and, as a result, their cross-sectional size remains unchanged throughout the entire period of operation.
- Due to the wide variety of PVC fittings, variability in the design of sewer systems is provided. Thus, it is possible to design a system of almost any complexity. Among other things, PVC sewer pipes and fittings are suitable for both internal and external installation.
- Despite the impressive list of advantages, products of this type are quite cheap.
Section types and coatings
According to the type of cross section, steel pipe elements are divided into round and profile. Round ones belong to the universal type, have the widest gradation in hole diameter and wall thickness. They are produced only in industrial conditions from steel alloys and various additives that enhance the physical characteristics of the material.

From a polished steel pipe with a round cross section, you can make a practical and beautiful canopy that will retain an attractive appearance for a long time and protect the entrance from rainfall.
The range of applications covers almost all industrial and domestic areas.Round steel pipes of different diameters are used to transport oil and gas, to equip reliable isolation of communication systems of any complexity and size, to create light buildings and various elements of external and internal decor.
Profile pipes are a progressive type of building metal with an oval, square or rectangular section. It is made from low-alloy and carbon steel, less often from stainless steel, by cold or hot deformation of a longitudinally welded round-caliber electric-welded billet.
Forming is carried out by passing the part through the rolls, which provide the required cross section.

Pipes with a profile section are used to build metal structures of various types and purposes, mount building frames, supports, complex interfloor and span ceilings. Structures withstand significant physical, vibrational and mechanical loads, serve reliably for many years and are suitable for intensive use in any atmospheric conditions.
Finished steel pipes are checked for the integrity of the weld and subjected to additional heat treatment to relieve internal mechanical stress. Then they are cut according to the required dimensions. To improve the physical properties of steel pipes, a protective coating is applied to them.
The most popular types include:
- zinc (cold or hot);
- polyethylene multilayer or extruded;
- epoxy-bituminous;
- cement-sand.
Zinc protects pipes from corrosion, polyethylene creates a dense, impermeable layer on the surface and prevents the destruction of the metal structure, bitumen-epoxy reduces the effect of stray currents, and cement-sand protects the inner surface from biological fouling.