- Types of ejector devices
- With remote ejector
- With built-in ejector
- Choice: built-in or external?
- Connection
- Initial launch and further operation
- Types of pumping stations and distance to the water table
- Pump stations with built-in ejector
- Pumping stations with remote ejector
- The principle of operation of the ejector
- How to start a water supply system
- What it is
- A special case
Types of ejector devices
According to their design and principle of operation, jet pumps can belong to one of the following categories.
Steam
With the help of such ejector devices, gaseous media are pumped out of confined spaces, and a rarefied state of air is also maintained. Devices operating on this principle have a wide range of applications.

Steam ejector for turbine with oil cooler
Steam jet
In such devices, the energy of a steam jet is used to suck gaseous or liquid media from a closed space. The principle of operation of this type of ejector lies in the fact that steam flying out of the nozzle of the installation at high speed entrains the transported medium that exits through the annular channel located around the nozzle.Ejector pumping stations of this type are used primarily for the rapid pumping of water from the premises of ships for various purposes.

Water heating installation with a steam jet ejector
Gas
Stations with an ejector of this type, the principle of operation of which is based on the fact that the compression of a gaseous medium, initially under low pressure, occurs due to high-pressure gases, are used in the gas industry. The described process takes place in the mixing chamber, from where the flow of the pumped medium is directed to the diffuser, where it slows down, and hence the pressure increases.
Air (gas) ejector for chemical, energy, gas and other industries
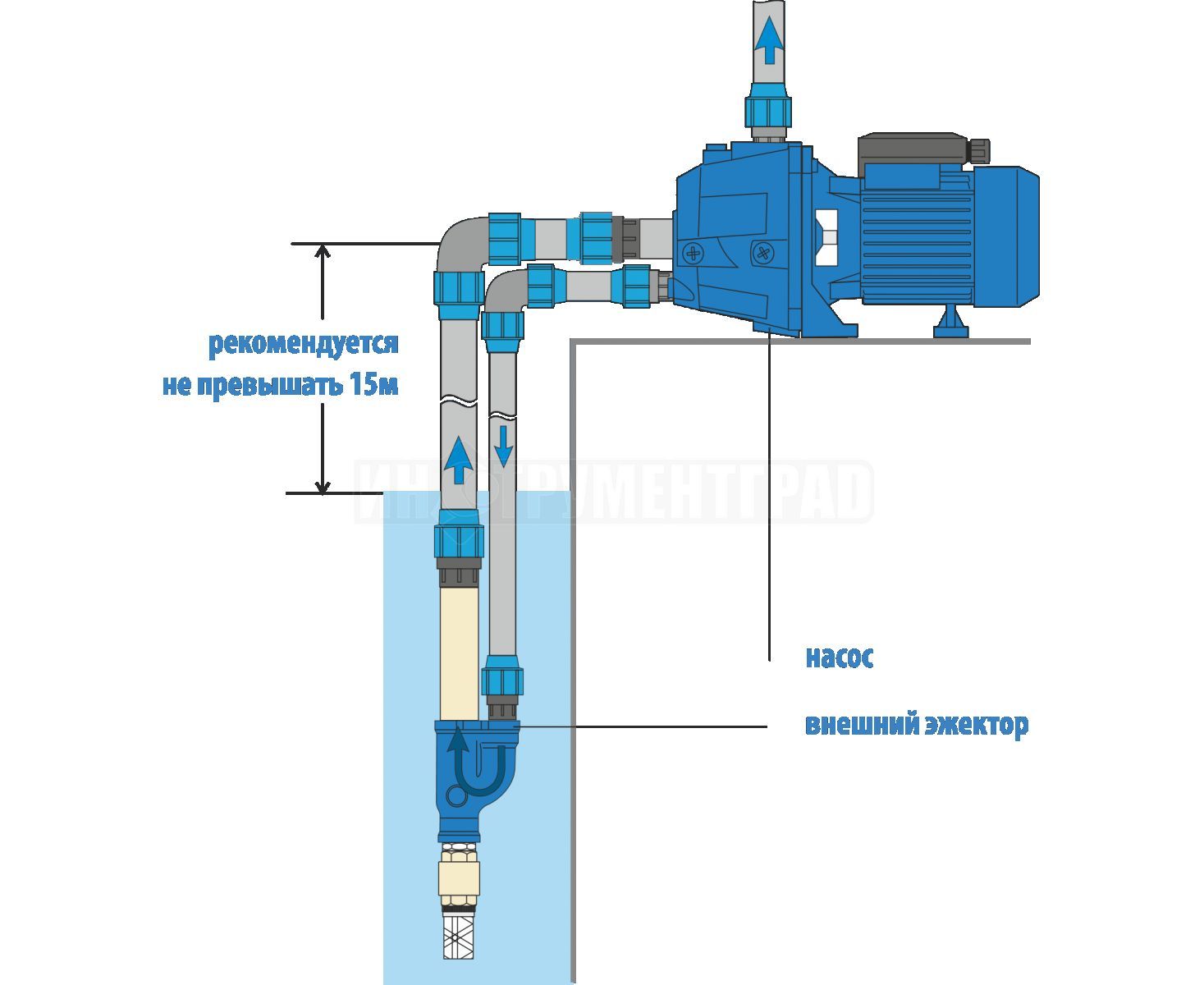
With remote ejector
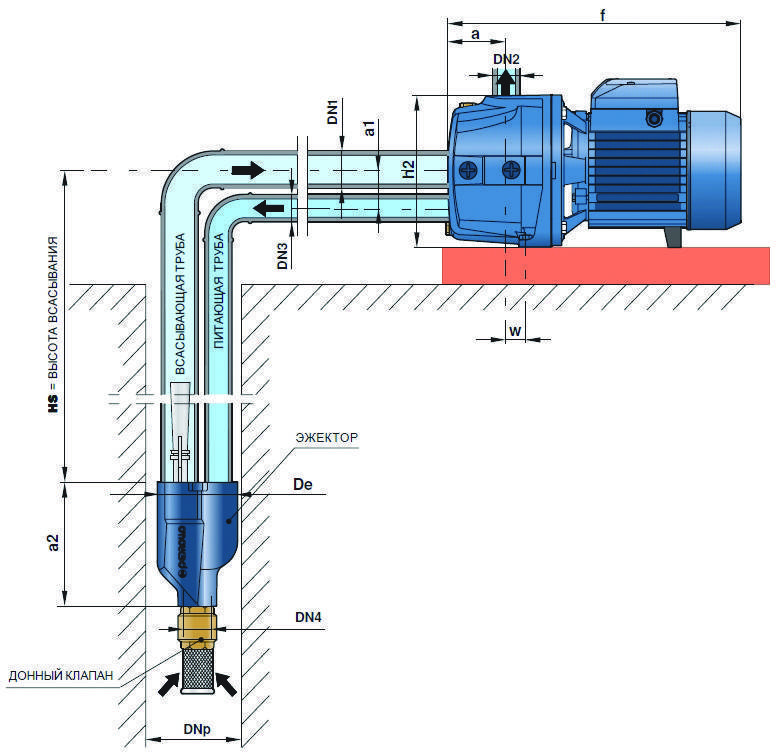
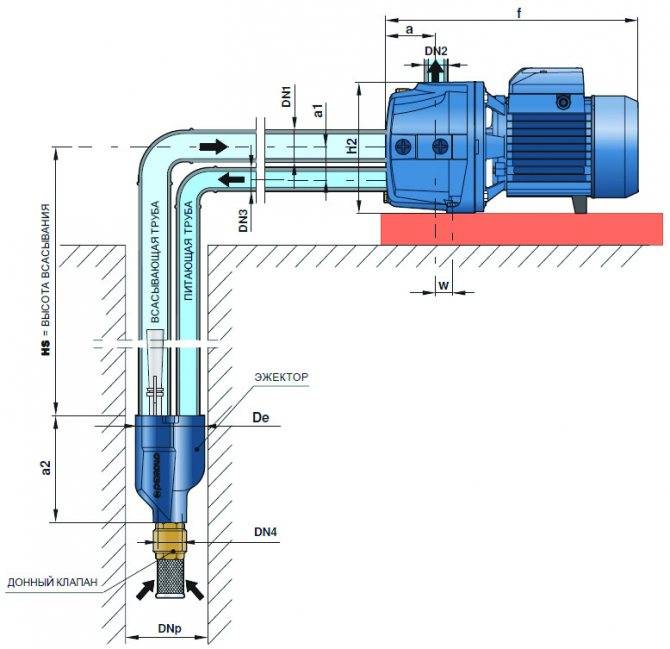
Such pumps for water intake must be lowered deep into a well or well. The remote ejector pump has two pipes. According to one of them, liquid under a certain pressure is fed into the ejector. This leads to the fact that a kind of suction jet is produced.
A pump with an external ejector is significantly inferior in its characteristics to models with an integrated ejector. It's all about the specifics of the design.

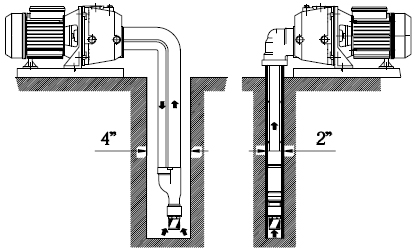
Installation diagram of two types of ejector pumps
So, a pump with an external type ejector will be “afraid” of contaminated water and air entering the structure. Its efficiency is noticeably lower, but the remote pump ejector also has its own significant advantage - it can be located inside the living quarters.
With built-in ejector
An internal centrifugal ejector pump lifts the water with artificial vacuum.
Due to the design features, an ejector pump is much more expensive than conventional devices of this type, as it is able to lift water even from great depths up to 50 meters.
High performance, however, is somewhat offset by the high level of noise emitted during operation of the device.
Therefore, ejector pumps are mounted exclusively in basements and utility rooms of residential buildings.
A modern steam jet vacuum electric pump is a good solution for organizing a water supply system at a large enterprise and when irrigating large areas with vegetation.
Choice: built-in or external?
Depending on the installation location, remote and built-in ejectors are distinguished. There is no big difference in the design features of these devices, but the location of the ejector still affects in some way both the installation of the pumping station and its operation.
So, built-in ejectors are usually placed inside the pump housing or in close proximity to it. As a result, the ejector takes up a minimum of space, and it does not have to be installed separately, it is enough to perform the usual installation of a pumping station or the pump itself.
In addition, the ejector located in the housing is reliably protected from contamination. Vacuum and reverse water intake is carried out directly in the pump housing. There is no need to install additional filters to protect the ejector from clogging with silt particles or sand.
An external ejector for a pumping station is more difficult to install than an internal model, but this option creates a much lower noise effect.
However, it should be remembered that such a model demonstrates maximum efficiency at shallow depths, up to 10 meters.Pumps with a built-in ejector are designed for such relatively shallow sources, their advantage is that they provide an excellent head of incoming water.
As a result, these characteristics are enough to use water not only for domestic needs, but also for irrigation or other business operations. Another problem is the increased noise level, since the sound effect from the water passing through the ejector is added to the vibration of the running pump.
If a decision is made to install a pump with a built-in ejector, then you will have to take care of sound insulation especially carefully. Pumps or pumping stations with a built-in ejector are recommended to be installed outside the house, for example, in a separate building or in a well caisson.
The electric motor for a pump with an ejector must be more powerful than for a similar non-ejector model.
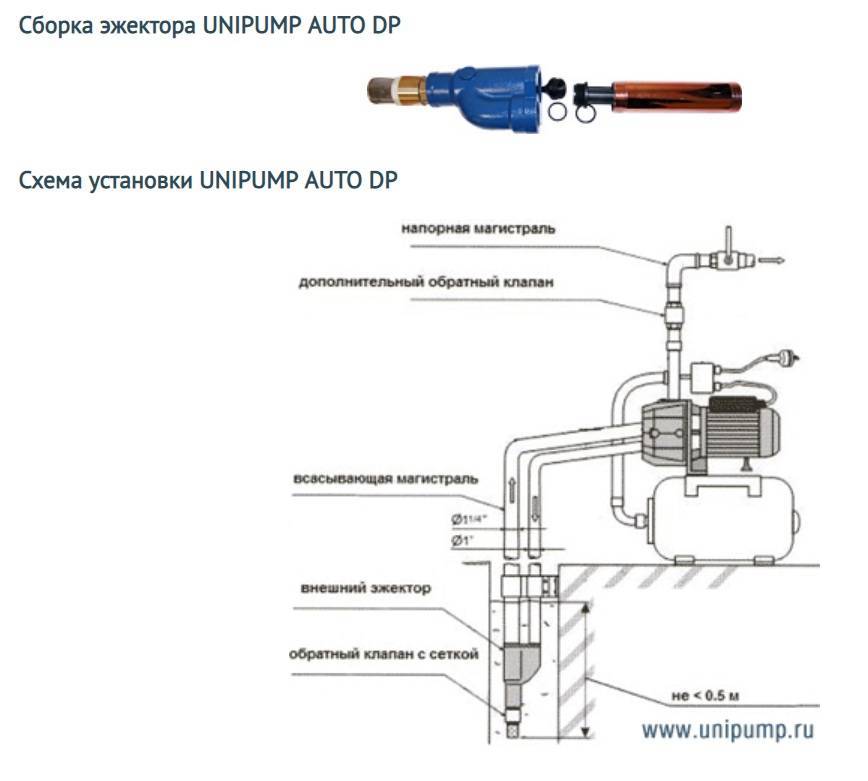
A remote or external ejector is installed at some distance from the pump, and this distance can be quite significant: 20-40 meters, some experts even consider 50 meters acceptable. Thus, a remote ejector can be placed directly in a water source, for example, in a well.
The external ejector not only increases the performance of the pump, but is designed to increase the depth of water intake from the source, which can reach 20-45 m
Of course, the noise from the operation of an ejector installed deep underground will no longer disturb the residents of the house. However, this type of device should be connected to the system using a recirculation pipe, through which water will return to the ejector.
The greater the installation depth of the device, the longer the pipe will have to be lowered into the well or well.
It is better to provide for the presence of another pipe in the well at the design stage of the device. Connecting a remote ejector also provides for the installation of a separate storage tank, from which water will be taken for recirculation.
Such a tank allows you to reduce the load on the surface pump, saving some amount of energy. It is worth noting that the efficiency of the external ejector is somewhat lower than that of the models built into the pump, however, the ability to significantly increase the depth of the intake forces one to come to terms with this drawback.
When using an external ejector, there is no need to place the pumping station directly next to the water source. It is quite possible to install it in the basement of a residential building. The distance to the source can vary within 20-40 meters, this will not affect the performance of pumping equipment.
Connection
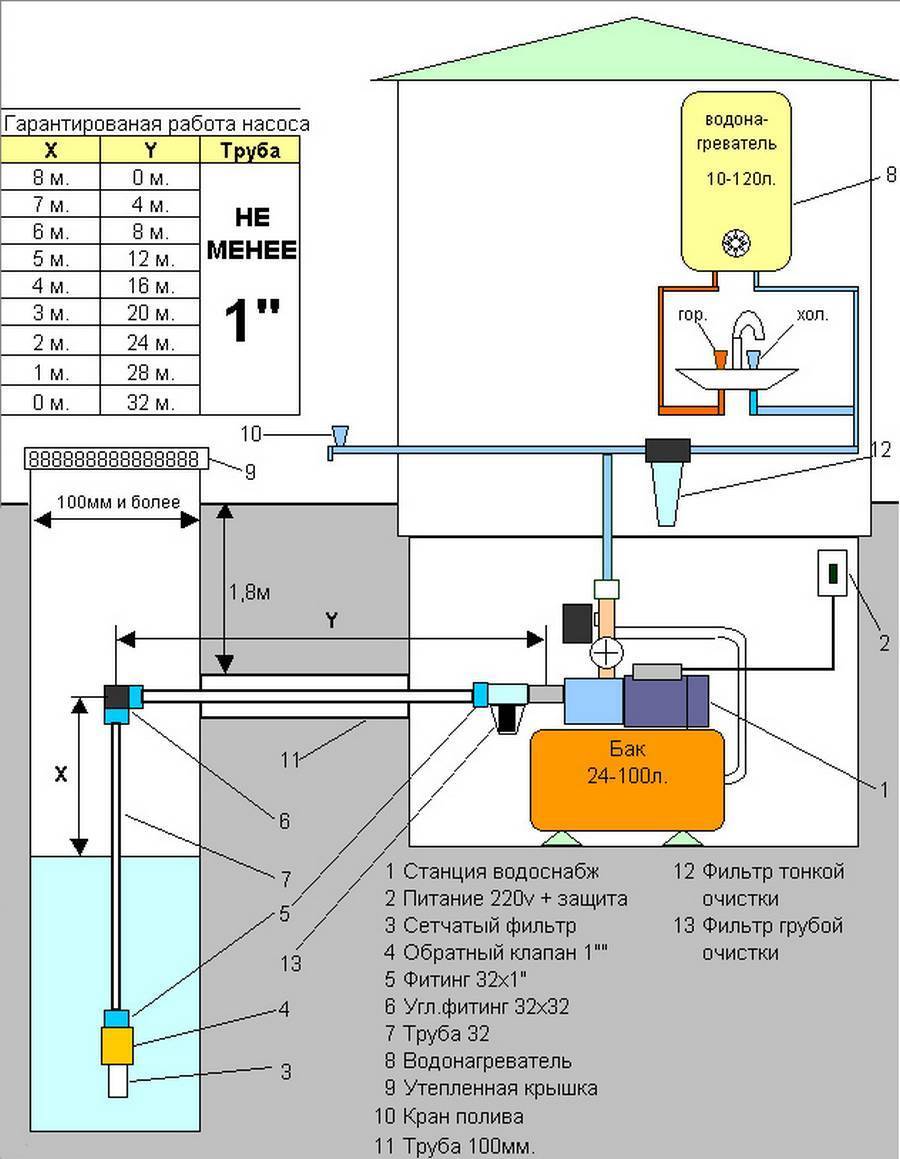
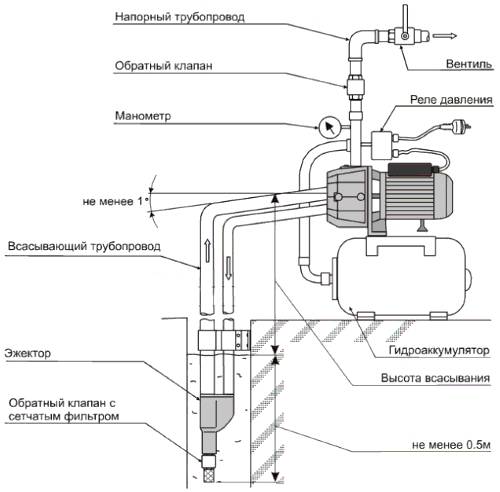
In the case of an internal ejector, if it is included in the design of the pump itself, the installation of the system is not much different from the installation of an ejectorless pump. It is enough just to connect the pipeline from the well to the suction inlet of the pump and equip the pressure line with related equipment in the form of a hydraulic accumulator and automation that will control the operation of the system.
For pumps with an internal ejector, in which it is fixed separately, as well as for systems with an external ejector, two additional steps are added:
- An additional pipe for recirculation is laid from the pressure line of the pumping station to the inlet of the ejector. The main pipe is connected from it to the suction of the pump.
- A branch pipe with a check valve and a coarse filter is connected to the suction of the ejector for drawing water from the well.
If necessary, a valve for adjustment is installed in the recirculation line. This is especially beneficial if the water level in the well is much higher than the pumping station is designed for. You can reduce the pressure in the ejector and thereby raise the pressure in the water supply system. Some models have a built-in valve for this setting. Its placement and method of adjustment is indicated in the instructions for the equipment.
Initial launch and further operation
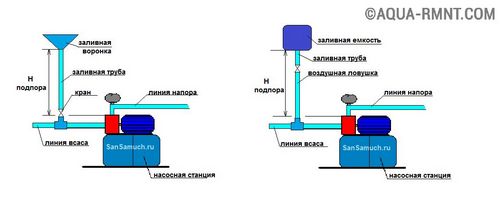
The initial start-up of the pumping station is recommended to be carried out according to the following scheme:
- Pour water into the pump through a special hole.
- Turn off the tap through which water flows from the pumping station to the water supply system.
- Turn on the pump for about 10-20 seconds and turn it off immediately.
- Open the valve and bleed some of the air from the system.
- Repeat the pump on/off cycle in combination with air bleeding until the pipes are filled with water.
- Switch on the pump again.
- Wait for the accumulator to fill and the pump to turn off automatically.
- Open any faucet.
- Wait until the water flows out of the accumulator and the pump turns on automatically.
If no water came out when starting the system with an ejector, it is possible that air is somehow leaking into the pipes, or the initial filling with water was not performed correctly. It makes sense to check the presence and condition of the check valve. If it is not there, the water will simply pour into the well, and the pipes will remain empty.
These points should also be taken into account when using a pumping station with an ejector, which is started up after a long period of storage.The check valve, the integrity of the pipes and the tightness of the connections are best checked immediately.
If an ejector is needed to improve the water pressure in the system, and not to increase the depth of water intake, you can use the homemade ejector model described above.
Types of pumping stations and distance to the water table
There are pumping stations with a built-in and remote ejector. The built-in ejector is a structural element of the pump, the remote one is a separate external unit, immersed in the well. The choice in favor of one or another option depends primarily on the distance between the pumping station and the water surface.
From a technical point of view, the ejector is a fairly simple device. Its main structural element - the nozzle - is a branch pipe with a tapered end. Passing through the place of narrowing, the water acquires a noticeable acceleration. In accordance with Bernoulli's law, an area with low pressure is created around a stream moving at an increased speed, i.e., a rarefaction effect occurs.
Under the action of this vacuum, a new portion of water from the well is sucked into the pipe. As a result, the pump spends less energy to transport liquid to the surface. The efficiency of pumping equipment is increasing, as is the depth from which water can be pumped.
Pump stations with built-in ejector
Built-in ejectors are usually placed inside the pump casing or located in close proximity to it. This reduces the overall dimensions of the installation and somewhat simplifies the installation of the pumping station.
Such models demonstrate maximum efficiency when the suction height, i.e.the vertical distance from the pump inlet to the level of the water surface in the source does not exceed 7-8 m.
Of course, one should also take into account the horizontal distance from the well to the location of the pumping station. The longer the horizontal section, the smaller the depth from which the pump is able to lift water. For example, if the pump is installed directly above the water source, it will be able to lift water from a depth of 8 m. If the same pump is removed from the water intake point by 24 m, then the depth of water rise will decrease to 2.5 m.
In addition to low efficiency at large depths of the water table, such pumps have another obvious drawback - an increased noise level. The noise from the vibration of a running pump is added to the sound of water passing through the ejector nozzle. That is why it is better to install a pump with a built-in ejector in a separate utility room, outside a residential building.
Pumping station with built-in ejector.
Pumping stations with remote ejector
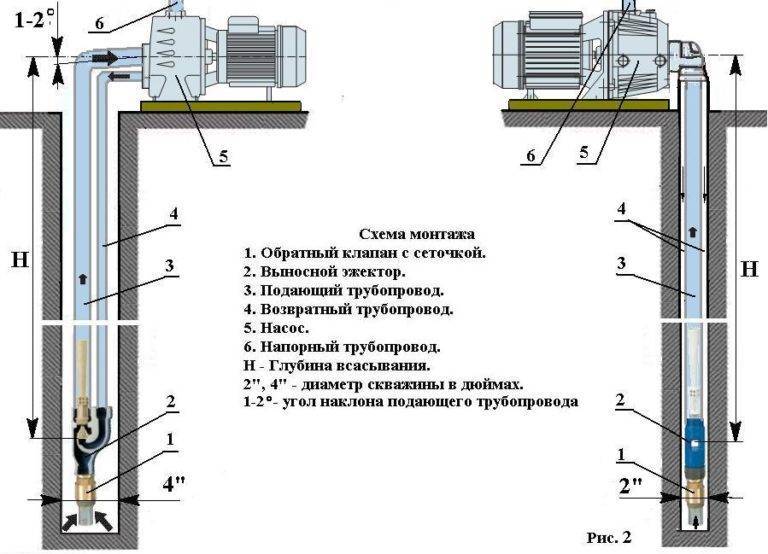
The remote ejector, which is a separate small unit, unlike the built-in one, can be located at a considerable distance from the pump - it is connected to the part of the pipeline immersed in the well.
Remote ejector.
To operate a pumping station with an external ejector, a two-pipe system is required. One of the pipes is used to lift water from the well to the surface, while the second part of the raised water returns down to the ejector.
The need to lay two pipes imposes some restrictions on the minimum allowable well diameter, it is better to foresee this at the design stage of the device.
Such a constructive solution, on the one hand, allows to significantly increase the distance from the pump to the water surface (from 7-8 m, as in pumps with built-in ejectors, to 20-40 m), but on the other hand, it leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the system to 30- 35%. However, having the opportunity to significantly increase the depth of water intake, you can easily put up with the latter.
If the distance to the water surface in your area is not too deep, then there is no need to install a pumping station directly near the source. This means that you have the opportunity to move the pump away from the well without a noticeable decrease in efficiency.
As a rule, such pumping stations are located directly in a residential building, for example, in the basement. This improves equipment life and simplifies system setup and maintenance procedures.
Another undoubted advantage of remote ejectors is a significant reduction in the noise level produced by a working pumping station. The noise of water passing through an ejector installed deep underground will no longer disturb the residents of the house.
Pumping station with a remote ejector.
The principle of operation of the ejector
The deeper the water is, the more difficult it is to raise it to the surface. In practice, if the depth of the well is more than seven meters, the surface pump can hardly cope with its tasks.
Of course, for very deep wells, it is more appropriate to purchase a high-performance submersible pump. But with the help of an ejector, it is possible to improve the performance of a surface pump to an acceptable level and at a much lower cost.
The ejector is a small but very effective device.This knot has a relatively simple design, it can even be made independently from improvised materials. The principle of operation is based on giving the flow of water an additional acceleration, which will increase the amount of water coming from the source per unit of time.
Image gallery
Photo from
Ejector - a device required to raise water with a surface pump from a depth of more than 7 m. They are used to form pressure in the suction line
Ejectors are divided into built-in and remote varieties. Remote devices are used to lift water from an average depth of 10 to 25 m.
Two pipes of different diameters are connected to the ejector device, due to the pressure difference in adjacent pipes, pressure is created
Factory-made ejectors are supplied to pumping stations and automatic pumps
Devices are used in landscaping schemes requiring pressurized water supply for sprinkler systems, fountains and similar structures.
To install the ejector, the pump unit must have two inlets
Using the schemes and dimensions of factory-made ejectors, you can make a device that is useful in pumping out with your own hands.
A check valve with a strainer is installed on the suction port of a homemade ejector, which ensures normal circulation during the pumping process
This solution is especially convenient for those who are going to install or have already installed a pumping station with a surface pump. The ejector will increase the depth of water intake up to 20-40 meters. It should also be noted that the purchase of more powerful pumping equipment will lead to a noticeable increase in electricity consumption.In this sense, the ejector will bring noticeable benefits.
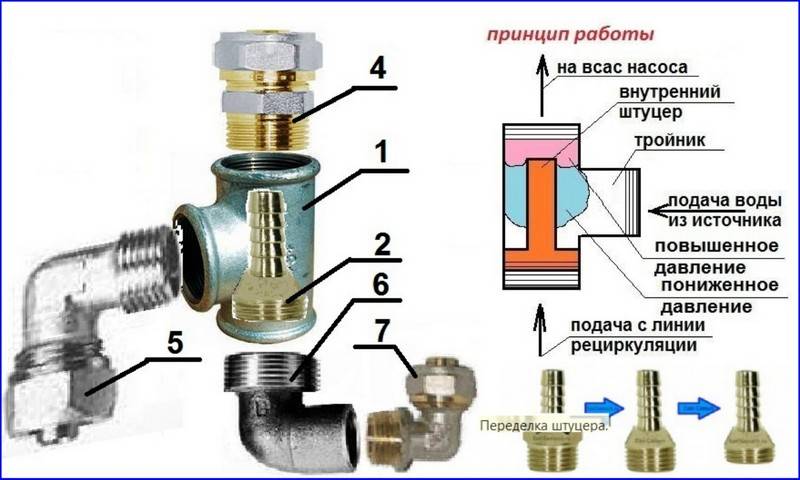
The ejector for a surface pump consists of the following elements:
- suction chamber;
- mixing unit;
- diffuser;
- narrowed nozzle.
The operation of the device is based on the Bernoulli principle. It says that if the speed of the flow increases, an area with low pressure is created around it. In this way, a dilution effect is achieved. Water enters through a nozzle, the diameter of which is smaller than the dimensions of the rest of the structure.
This diagram allows you to get an idea of the device and the principle of operation of the ejector for a pumping station. The accelerated reverse flow creates an area of low pressure and transfers kinetic energy to the main water flow
A slight constriction gives a noticeable acceleration to the flow of water. Water enters the mixer chamber, creating an area with reduced pressure inside it. Under the influence of this process, a stream of water at a higher pressure enters the mixer through the suction chamber.
Water in the ejector does not come from a well, but from a pump. Those. the ejector must be installed in such a way that part of the water raised by the pump returns to the ejector through the nozzle. The kinetic energy of this accelerated flow will be constantly transferred to the mass of water that is sucked from the source.
To create a rarefied pressure area inside the ejector, a special fitting is used, the diameter of which is smaller than the parameters of the suction pipe.
Thus, a constant acceleration of the flow will be ensured. Pumping equipment will need less energy to transport water to the surface. As a result, its efficiency will increase, as will the depth from which water can be taken.
Part of the water extracted in this way is sent back to the ejector through the recirculation pipe, and the rest enters the house's plumbing system. The presence of an ejector has another "plus". It sucks in water on its own, which additionally insures the pump against idling, i.e. from the “dry running” situation, which is dangerous for all surface pumps.
The diagram shows the device of an external ejector: 1- tee; 2 - fitting; 3 - adapter for a water pipe; 4, 5, 6 - corners
To regulate the operation of the ejector, use a conventional valve. It is installed on the recirculation pipe, through which water from the pump is directed to the ejector nozzle. Using a tap, the amount of water entering the ejector can be reduced or increased, thereby reducing or increasing the reverse flow rate.
How to start a water supply system
You should start by preparing the source of water intake. If there is already a well or a well, then it is recommended to first drain 2-3 m3 of water from it, make a control sampling and send the water for laboratory analysis (biological and chemical). For this, you can contact the Sanitary and Epidemiological Station at the place of residence or private laboratories. The results of the analysis are necessary in order to know in advance what types of filters will need to be installed on the water supply (depending on whether the water will be used for cooking).
Tap water treatment
Also, if necessary, strengthen and clean the source of water intake. Available options:
- Well.Water from such sources is most often the lowest quality (with a large amount of impurities, limestone, sand), therefore, such systems have to be supplemented with a full-fledged filter station, including coarse and fine filters, as well as a reverse osmosis system. In the presence of bacterial contamination, filters are also installed for preliminary disinfection of water, and before eating it must be boiled.
- Well. The best option is a deep-water well (over 30 meters deep). In such sources, the water in most cases is clean, ready for consumption. In such systems, only a coarse and fine filter is installed. It is highly desirable that the well pipeline be made of PVC plastic (food grade). Metal pipes are subject to corrosion, after 2-3 years plaque forms on them, and after 10 years the well is simply clogged without the possibility of cleaning it.
- Hydraulic accumulator. In fact, this is an ordinary container, into which water is poured from water carriers. Filters in such a system are installed only basic (coarse and carbon). If the tower is used as a hydraulic accumulator, then you can do without a pumping station, since the water pressure in the water supply system is provided by the cistern itself (if it is above the level of the water supply at home).
- Connection to a centralized water supply network. The simplest option, but not in all cities, the water in such systems fully complies with sanitary and epidemiological standards. The reason is simple - plumbing systems are not restored for 20 - 40 years, while their maintenance should be performed annually. Yes, and the laying of centralized water supply systems is now carried out only in large cities with a population of one million.
The installation of such a water tower eliminates the need for a pumping station. The water pressure in the pipes is provided by the force of attraction acting on the lower layers of water in the tank
As for the results of water analysis, even the most polluted (including those exceeding the permissible norm of bacteria) today can be made drinking water using filter stations. It is not cheap, so experts recommend installing a separate input to the house. That is, one pipe is for drinking, the second is for technical needs (bathroom, toilet). In this case, filters are installed only for the entry of a drinking pipe.
An analysis is a must. If there is an overestimated level of nitrates without a reverse osmosis filter, it does not make sense to install a water supply system - such water is even unsuitable for technical needs
What it is
- How is the pumping station set up?
It is a complex of equipment mounted on a common frame, including:
- Centrifugal surface pump;
- Membrane hydraulic accumulator;
- Automatic relay for turning on the pump with a pressure sensor.
Station device
The price of a pumping station depends on the power of the pump, the volume of the accumulator and varies from 5 to 15 or more thousand rubles.
The device works like this:
- When power is applied, the pump pumps water into the membrane tank. The pressure in it rises to the upper limit of the automatic relay setting and is maintained by air compression in the air compartment of the accumulator;
- As soon as the pressure in the tank of the pumping station reaches the upper value in the relay settings, the pump turns off;
- When water flows through plumbing fixtures, the pressure is provided by air compressed in the accumulator.When the pressure drops to the lower limit of the relay setting, it turns on the pump, and the cycle repeats.
Station Neoclima: the optimal mode of operation - no more than 20 inclusions per hour
A special case
In the vast majority of pumping stations, the suction of water is provided only by the vacuum created in the suction pipe. Accordingly, the theoretical maximum suction depth is limited by the height of the water column at an excess pressure of one atmosphere - 10 meters. In practice, for devices on the market, the suction depth does not exceed 8 meters.
Calculation of the height of the water column for an overpressure of one atmosphere
Meanwhile, the so-called two-pipe stations with an external ejector are capable of lifting water from a depth of 25 meters or more.
How? Isn't that against the laws of physics?
Not at all. The second pipe descending into the well or well supplies water to the ejector with excess pressure. The inertia of the flow is used to entrain the masses of water surrounding the ejector.
Device with external ejector and suction depth of 25 meters
Schemes for mounting stations with a remote ejector