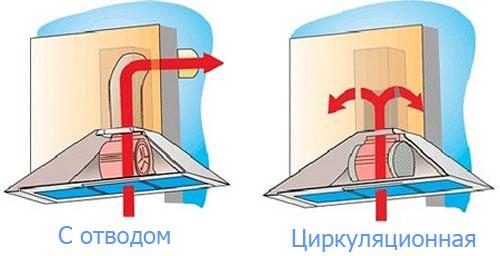
- The concept of room ventilation
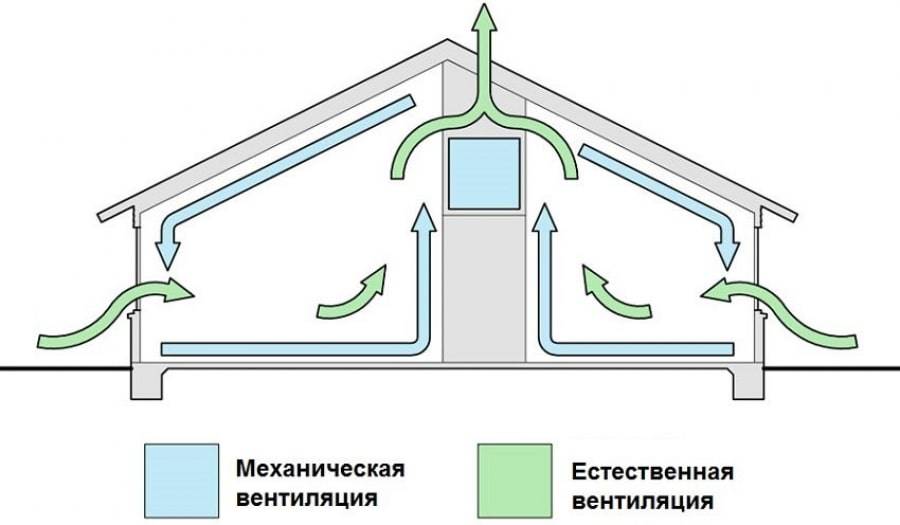
- The main types of natural ventilation
- Other Solutions
- Kinds
- Natural supply ventilation
- Natural exhaust ventilation
- Forced
- Supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery
- Do-it-yourself ventilation in a private house: some features
- Do-it-yourself ventilation
- Forced ventilation
- Choosing the optimal ventilation system
- Units for local exhaust system
- Advantages and disadvantages of natural and forced ventilation systems
- Ventilation schemes for a private house and apartment
The concept of room ventilation
 Efficient ventilation - comfortable indoor climate
Efficient ventilation - comfortable indoor climate
The main system, the principle of which underlies all others, is natural ventilation. Before considering it, you need to understand what ventilation is. This is the process of air exchange, in which air saturated with oxygen enters the room, and the spent air is removed from it. Thanks to this circulation, it is possible to maintain a certain microclimate in the premises that meets sanitary standards. Building codes and regulations 2.08.01-89 "Residential buildings" provide for the equipment of residential buildings with ventilation with certain air parameters and air exchange rates.The system is designed to maintain a favorable microclimate, neutralizing harmful gases and excessive humidity.
But it is quite obvious that certain conditions must be created for the implementation of ventilation. The reasons for the movement of air masses are:
- The difference in temperature and atmospheric pressure in the room and outside.
- mechanical drive.
- gravitational forces.
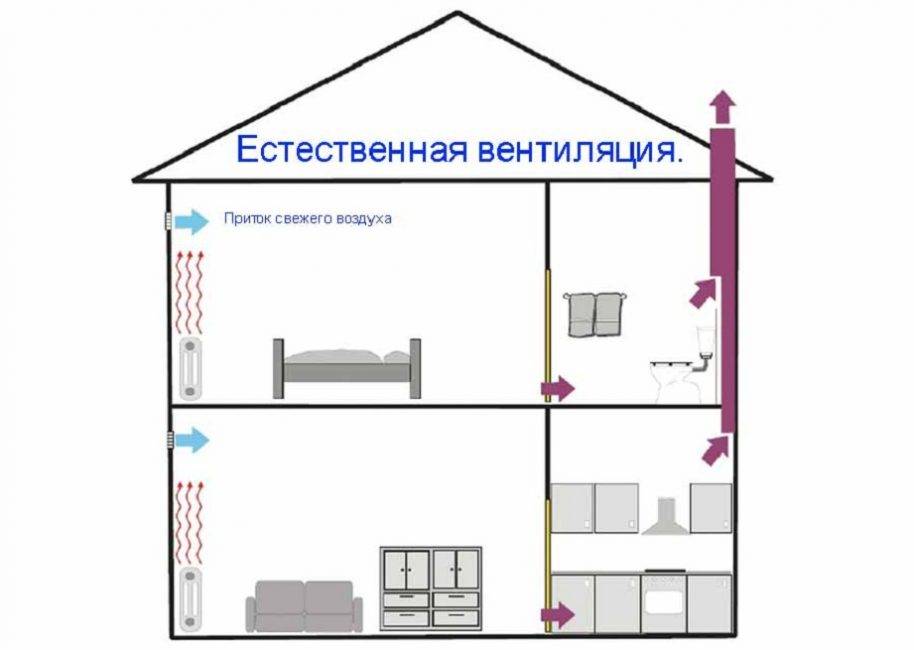
The main types of natural ventilation
Passive ventilation (it is also natural) works according to a simple scheme for the movement of air masses, from the supply to the exhaust duct. That is, this process is ventilation. Despite the uniformity of functioning, such systems may have some differences:
- according to the method of air exchange;
- by functionality;
- by the volume of air that the system serves;
- by design features.
Air exchange is carried out by natural forces or with the help of additional devices. The speed of the air drawn outside the house depends on whether fans are used in the ventilation ducts. But, it is worth knowing that such supply and exhaust ventilation is no longer natural. The use of a fan classifies it as an artificial type.
Natural ventilation is determined by three types of systems: supply, exhaust and supply and exhaust (separation by functionality). These or those systems are suitable, both for small rooms, and for the whole houses. In addition, natural ventilation is also used to service multi-storey buildings.
In addition, experts distinguish types of natural ventilation that differ in their design features. There are only two such types - organized natural ventilation and unorganized ventilation.In the first, natural ventilation is carried out using specially constructed channels and openings. In the second case, the ventilation of the house is carried out by the movement of air flows through open windows and doors.
Other Solutions
The market does not stand still, and new solutions are being offered today. For example, there are recuperator systems that immediately, through one hole in the wall, remove the exhaust air and supply fresh air. This is an ideal solution if ventilation is taken care of after renovation or if it is necessary to solve the problem only in some rooms. The main thing is that these rooms have at least one wall facing the street.
There is a device that removes exhaust air through one hole, takes fresh air. It also heats up/cools it down.
The disadvantage of this method of organizing ventilation in a house or apartment is one - the price of such equipment. The cost of one such device is more than $400.
Kinds
All types of ventilation are divided into several types, depending on its purpose, the complexity of the arrangement and the principle of operation. But the principle of operation of any of them will be based on the laws of physics on the movement of air masses. Cold air goes down and warm air goes up.
Natural supply ventilation
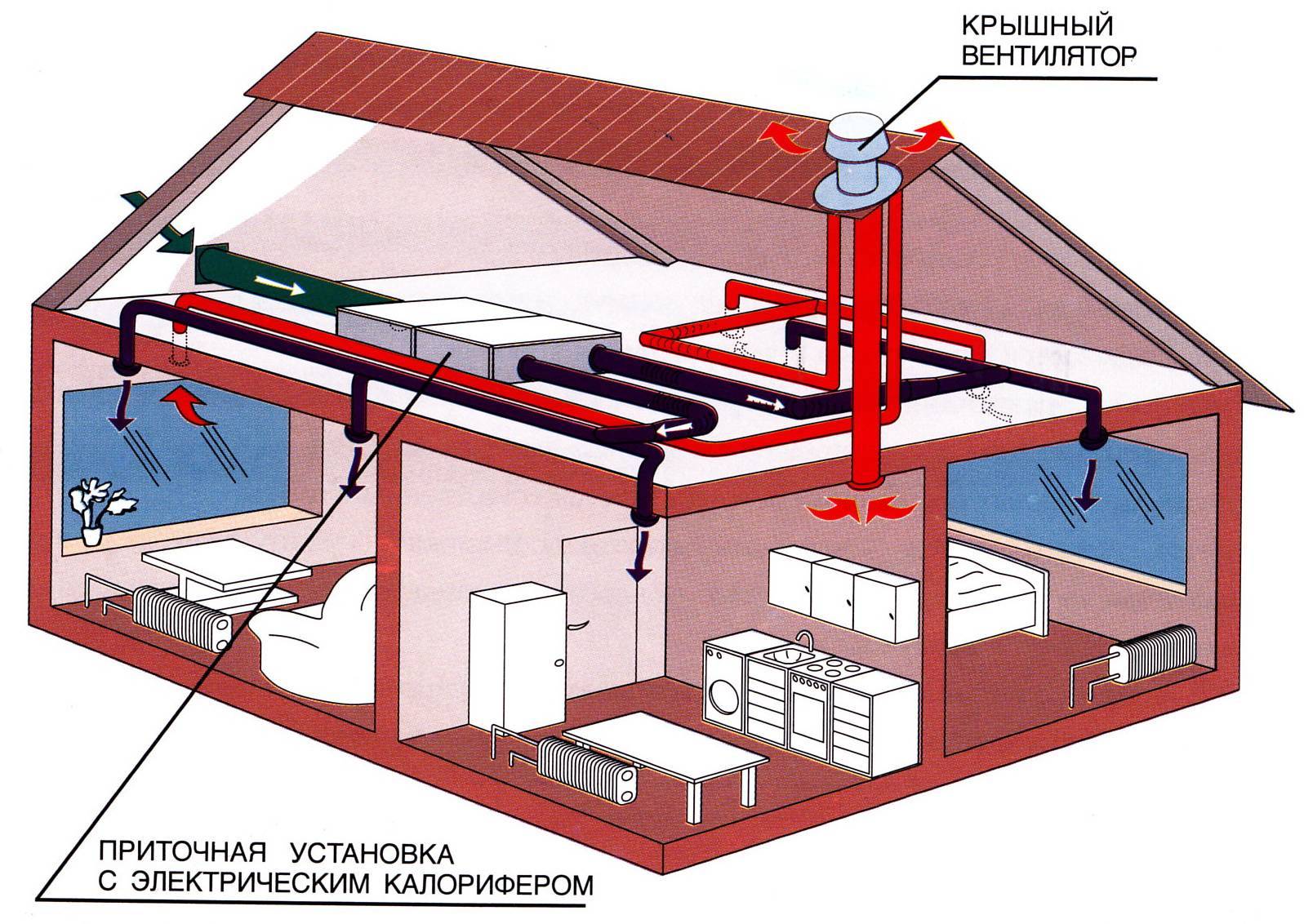
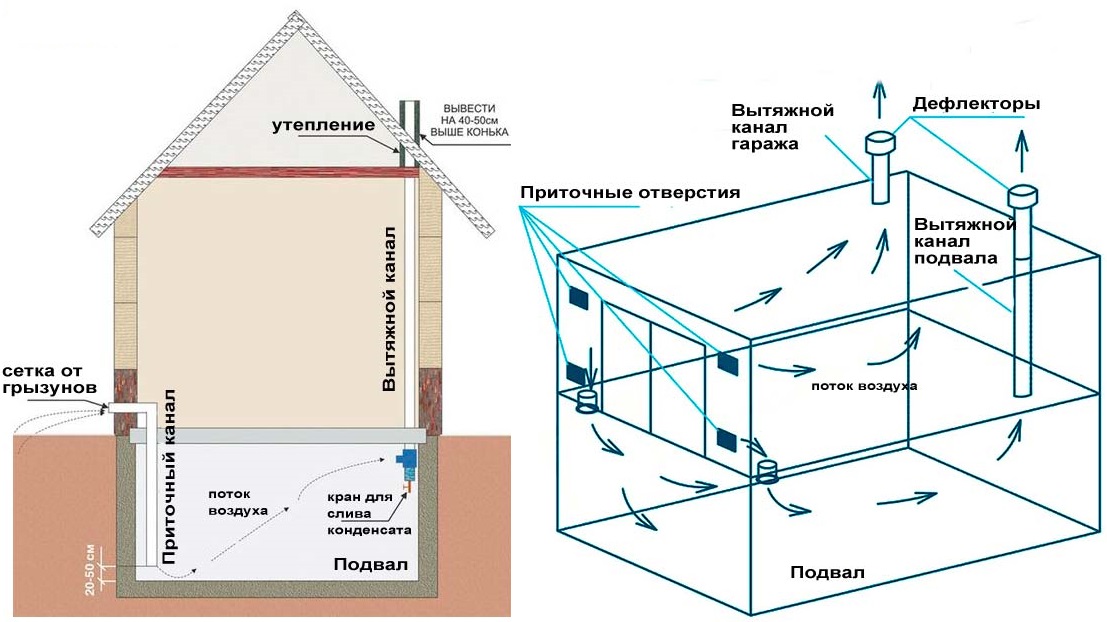
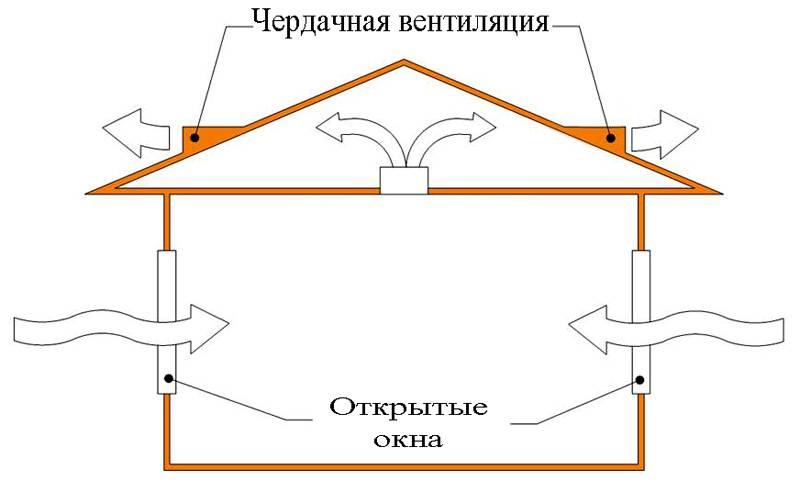
The simplest, airflow system in the foundation or basement. It is equipped at the stage of building a house and is a small hole in the upper part of the basement.
If the basement is below ground level, then the hood is equipped with plastic or asbestos-cement pipes with a diameter of 10-15 cm. They are brought out above the surface to a height of 30 cm and covered with bars from debris and rodents.This method is natural and depends on fluctuations in street temperature, wind strength, and humidity.
When calculating its throughput, 1/400 of the total basement area - so we get the total area of \u200b\u200ball the products.
Openings should be located on the leeward side, the least exposed to precipitation. Houses with a complex foundation shape and located in low-lying places can have up to one hole for every 3-4 meters. We close the vents with gratings from the outside.
This inexpensive option good for garage ventilation and non-residential basements or as an additional means to the main ventilation system.
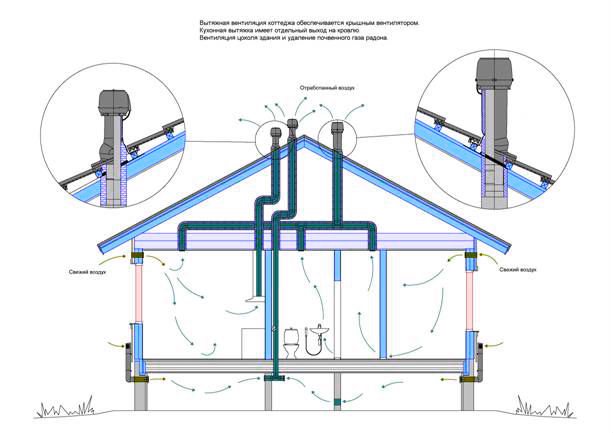
Natural exhaust ventilation
Supply and exhaust type. For proper operation, you will need to install two pipes for ventilation, and the supply and exhaust ventilation device looks like this.
- The first pipe is located under the very ceiling of the basement and is designed to drain warm air. We place the exhaust pipe as high as possible, preferably at the level of the roof ridge. This is necessary to ensure good traction. The part of the pipe that is in the open air must be insulated to prevent freezing in the winter and covered with a visor from precipitation.
- The second pipe for the influx of fresh air is located at a height of 30-40 centimeters from the floor level, and we place its entrance on the street a meter above the ground and cover it with a grate. Convection will occur due to the temperature difference between the outdoor and basement air. Such a system will work most efficiently when the supply channels are separated on different sides of the basement.
The disadvantage of all natural exhaust ventilation systems is one - it is dependent on weather conditions and prevailing winds. It will not work if the temperature in the basement and on the street is equal.
Forced
It is used if natural supply ventilation cannot cope or there is no physical possibility to use it. Usually used in the following cases:
- The basement area is from 40 m2 or has several rooms isolated from each other;
- High humidity of the room, when the condensate in the exhaust duct freezes in winter and impairs the permeability of air masses;
- The architecture of the house does not provide for high ventilation pipes;
- The basement is equipped with a sauna, cafe, gym, workshop or other source of unpleasant odors.
The device of forced supply and exhaust ventilation has a system of channels and fans that distill air.
The main condition is to make the air constantly circulate, which is ensured by the synchronous operation of the exhaust and supply fans. Their number is calculated depending on the volume of the cellar or basement and the capacity of the air ducts.
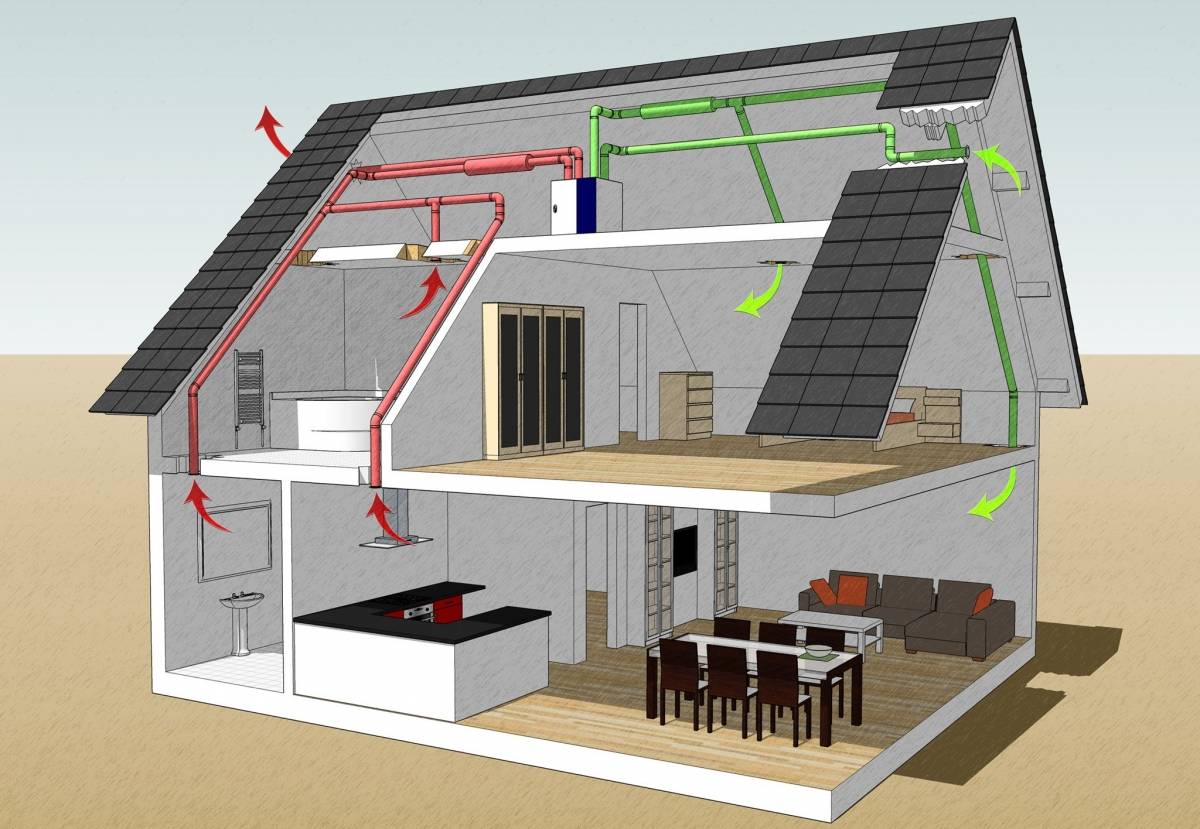
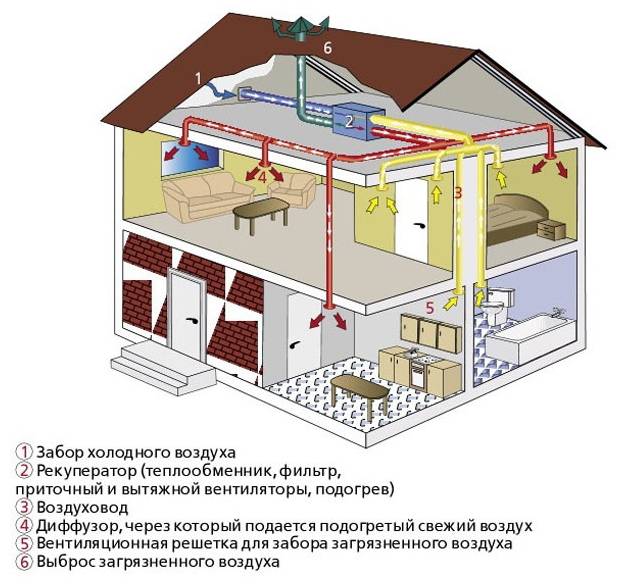
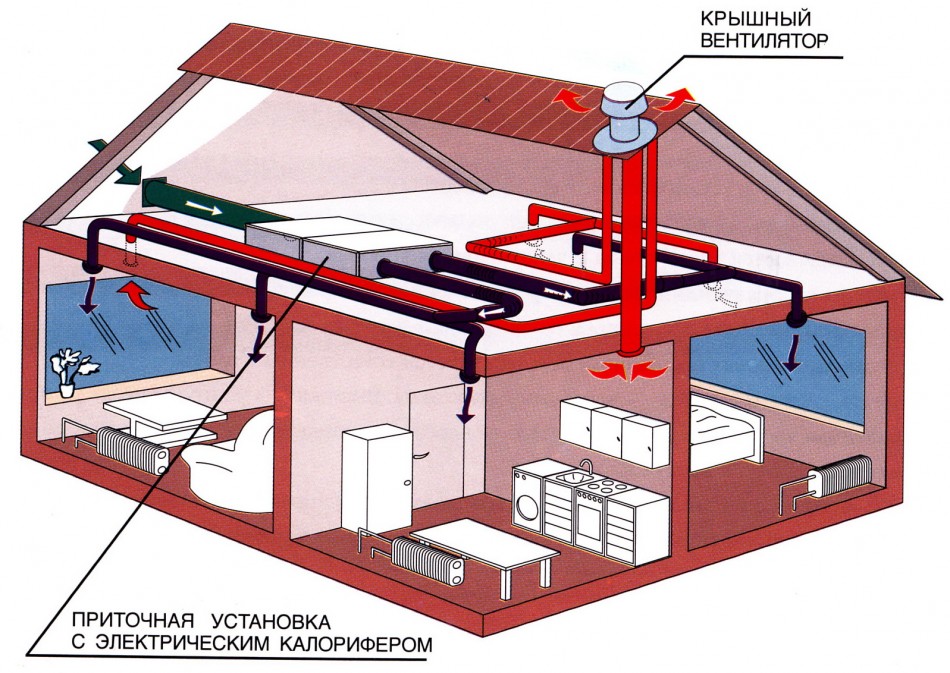
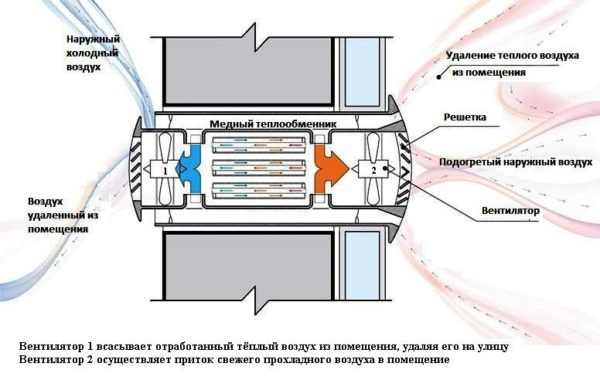
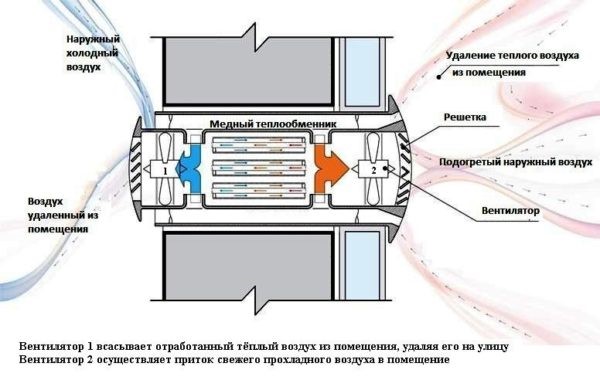
Supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery
For a basement floor where permanent residence is planned, it is not enough to simply install a forced ventilation system. The room must be insulated and waterproofed. The issue of heating and heating is also solved.
Increasingly, supply and exhaust with heat recovery is built into such schemes.
Already well-heated air enters the exhaust pipe, and in order not to throw ready-made calories into the atmosphere, the air is passed through a special ceramic heat exchanger. When heated, it gives off heat to fresh air. The air streams do not intersect. The efficiency of such a device is 50-90%, depending on the design of the heat exchanger. All heat recuperators are very reliable, do not require additional maintenance and can serve for decades.
It is equipped with moisture traps, dust filters, sensors that control humidity and air temperature. For a residential area, these figures lie in the range of 50-65% relative humidity and 18-220C. Such systems are most often found in "smart homes", and their installation is complicated and should only be carried out by professionals.
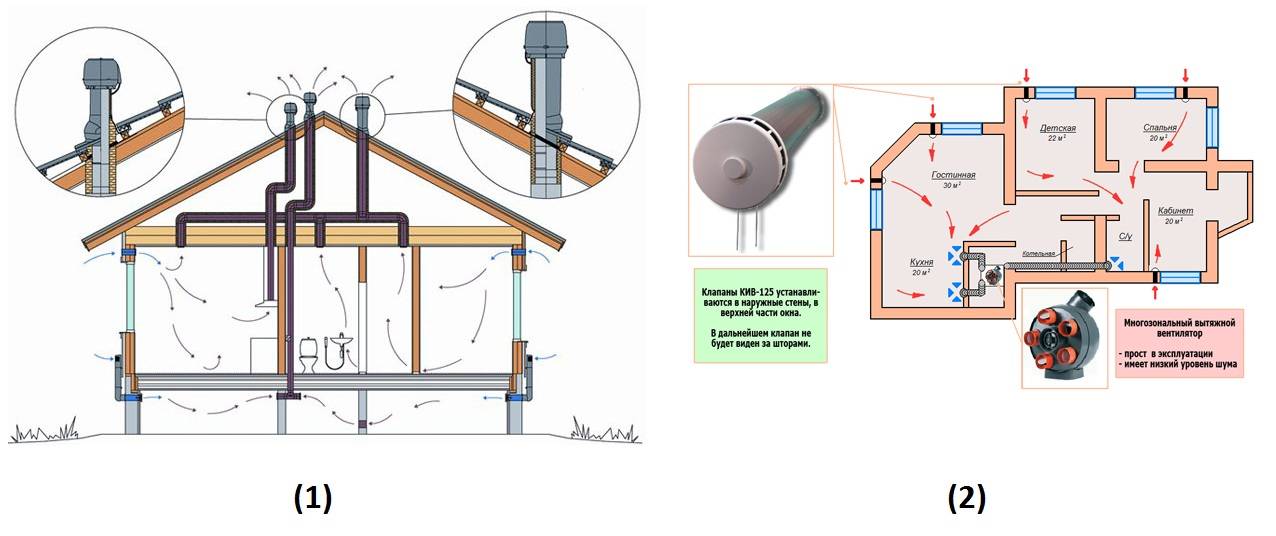
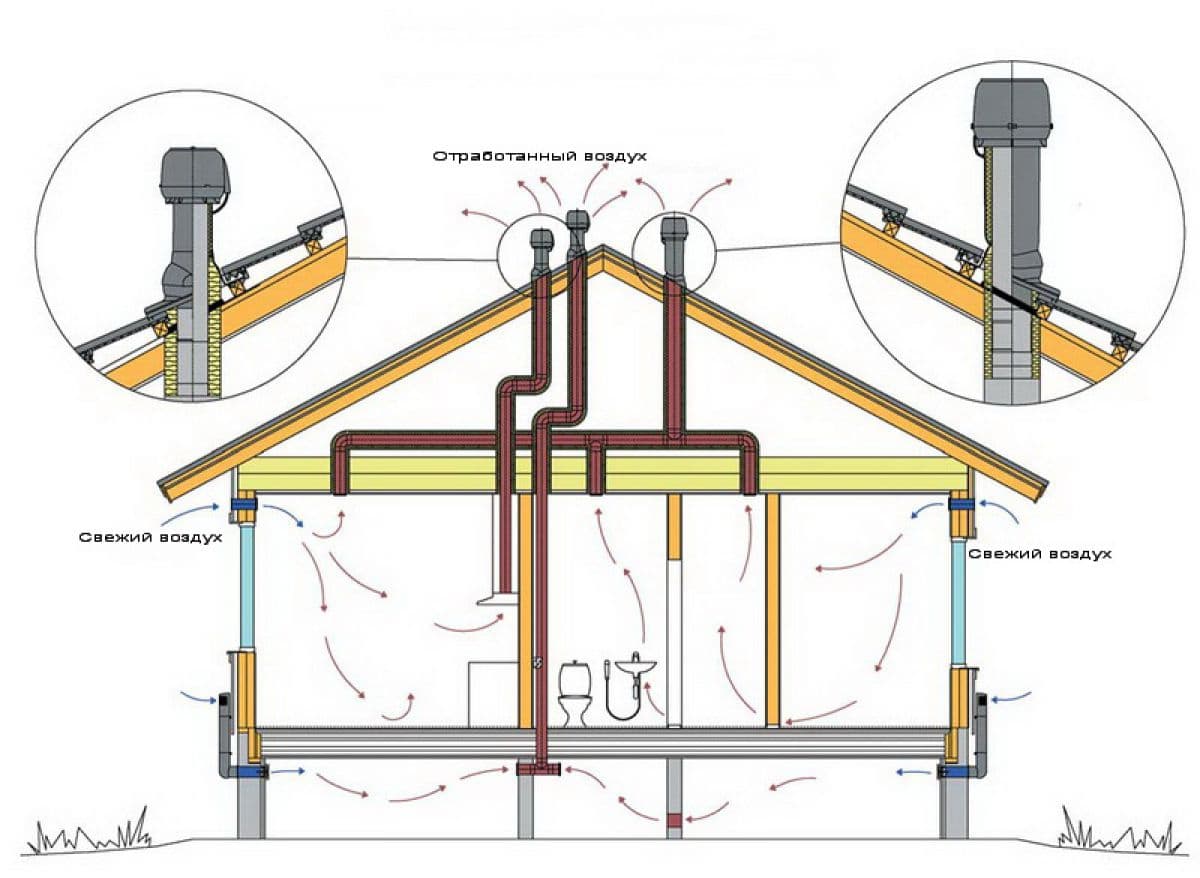
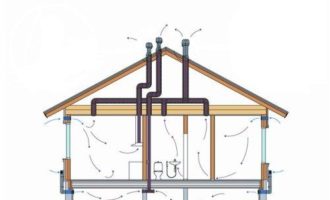
Do-it-yourself ventilation in a private house: some features
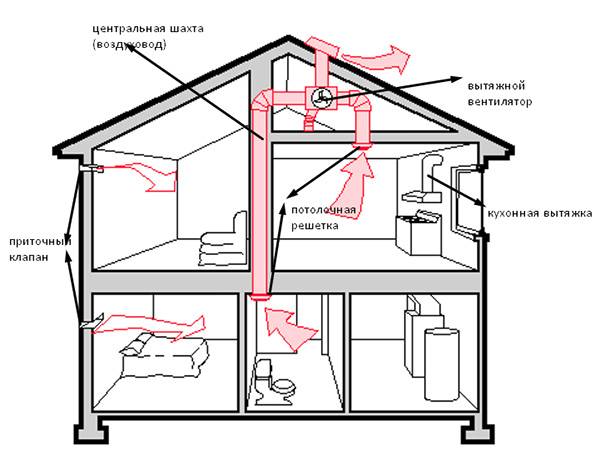
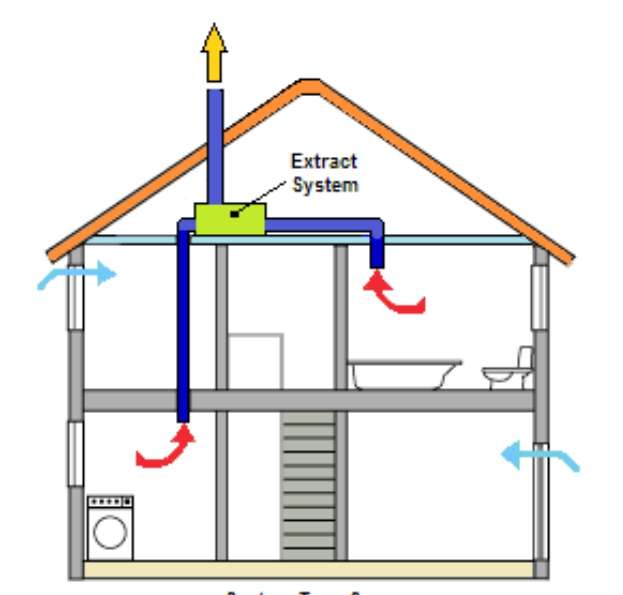
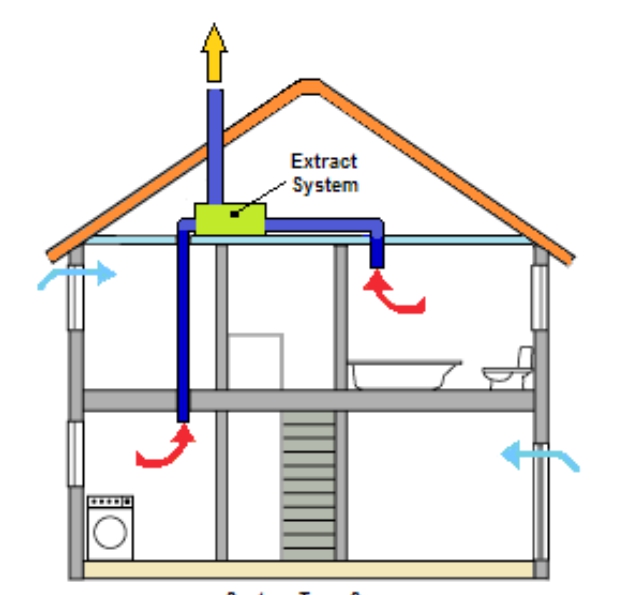
 Scheme of organizing air exchange in the house
Scheme of organizing air exchange in the house
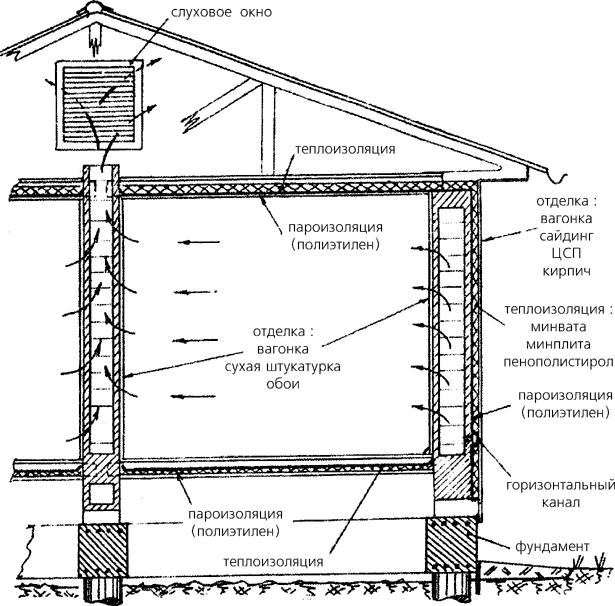
Delivery of air flows to all rooms and their removal into the atmosphere is carried out by an air duct network. Its components: air ducts, adapters, turns, tees. Characteristic features: cross-sectional area; the form; rigidity (rigid, flexible, semi-flexible). The flow rate must be adjusted. If the allowable values are exceeded, a strong noise is created. The material for the manufacture of the air duct network is galvanized steel or plastic.
Insulating material is selected at will, but not less than 10 mm thick. The inflow pipe from the outer grille to the heating section (recuperator) is subjected to insulation, the hood is in the attic. Thermostats, hydrostats, pressure sensors are used as sensors.
For proper operation of external ventilation in a private house, you must comply with the requirements.Firstly, the part of the exhaust pipe passing through the cold attic must be insulated. Insulation choose waterproof. Secondly, the outgoing pipe should be 0.5 m above the level of the ridge. Thirdly, it is advisable to mount a deflector at the end of the pipe. It will improve the performance of the entire system by 15-20% by drawing in exhaust air and passing it through special openings. In addition, it will protect the pipe from snow, rain, birds, debris, and in winter from freezing.
If you decide to make ventilation with your own hands, remember that air ducts, ducts and other elements of the system should not be conspicuous. If the system is mounted after finishing work, then it will be almost impossible to hide them. Therefore, ventilation must be invested in design work. Installation of the system requires the conduct of commissioning.
Do-it-yourself ventilation
To do natural ventilation system with your own hands, you need to pay attention to important points
- The material of the house - for example, wood is great for such a ventilation system, since this material itself “breathes” and actively passes air, creating a comfortable microclimate in the house. But in concrete and brick houses, you will have to create additional ventilation holes through which air will enter the premises.
- The number of people in the room - the more people are constantly in the house, the more work the supply and exhaust air ducts, the more air they must pass through themselves in a minimum period of time.
- The type of activity that takes place indoors – for example, a kitchen or gym needs a more powerful extractor fan than a storage room.
In addition, for the successful design of a natural exhaust system, it is necessary to take into account the requirements for air exchange rates. They are 60 cubic meters per hour per person in the room. And in order to determine how many times the air should change, you just need to multiply the volume of the room by the multiplicity, the value of which can be found in the relevant regulatory tables. The calculation is done separately for each room, and then the resulting figures are simply summed up. If we are talking about the air circulation system in an apartment building, then each system of a single apartment must have access to a common one.
Being engaged in ventilation, it is also worth considering the cross section and length of the air ducts. The shorter the pipe, the faster air will move through it. Please note that with natural exhaust, the greatest efficiency is achieved when the difference between the temperature in the house and outside is maximum, that is, in winter.
In a step-by-step execution, the arrangement of ventilation with a natural impulse is:
- creation of two holes - for air inlet and outlet, the supply air ducts should be located approximately 10 cm from the floor, and the exhaust vents should be under the very ceiling, ideally they should be located in opposite corners of the room;
- air ducts are inserted into the holes: the optimal height of the supply and exhaust is 30 and 50 cm, respectively;
- the openings are closed with special gratings and visors - this is done so that insects, debris and moisture from the street do not get into them.
Natural supply ventilation is far from always effective, therefore, in some cases, it is worth equipping mechanically driven supply and exhaust ventilation instead.
2 id="prinuditelnaya-ventilyatsiya">Forced ventilation
The principle of forced ventilation in a private house is used in those rooms where natural ventilation is not able to fully provide fresh air. Such premises are in constant contact with a large amount of moisture, where fungus and mold can form - these are the kitchen, bathroom, basement and boiler room. Such ventilation is installed to remove unpleasant odors and excess moisture from the premises with the help of fans and forced exhaust hoods.
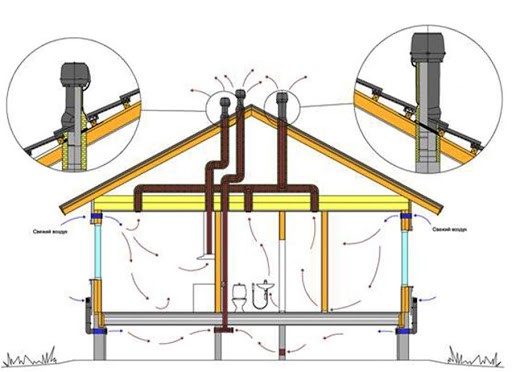
You can regulate the flow of fresh air using a special device called an inlet valve. In addition to the main function, it has the following advantages:
- Minimizes noise from the outside world;
- Provides air filtration;
- Provides thermal insulation of the body, which reduces the likelihood of freezing and condensation;
- The ability to control the process of the device with your own hands.
Each ventilation duct for the home will require additional installation of this device. In extreme cases, you can get by with one valve, provided that there is centralized ventilation.
The function of the valve depends on the temperature difference between the room and the outside world. During the period of forced exhaust operation, the adjustment is carried out in manual mode.
To install a forced ventilation system with your own hands, you will need:
- Calculate the required air exchange. The air exchange rate is taken at the rate of 10 m³ per hour per person;
- Determine the installation location of the equipment (dry utility room);
- Mark the location of the air inlet and outlet openings.
For air ducts, flexible, usually plastic pipes are used, but aluminum pipes are also suitable. With the help of fasteners, the channels are bred through the rooms of the whole house above the suspended ceilings. And the place where the duct pipes exit is closed with ventilation grilles.
Openings for air inflow and exhaust are arranged in opposite corners of the room. A pipe is inserted inside the hole and covered with bars from the outside. A non-return valve is installed from the inside. In the selected place, the air handling unit is fixed, ventilation ducts are attached to it using metal clamps.
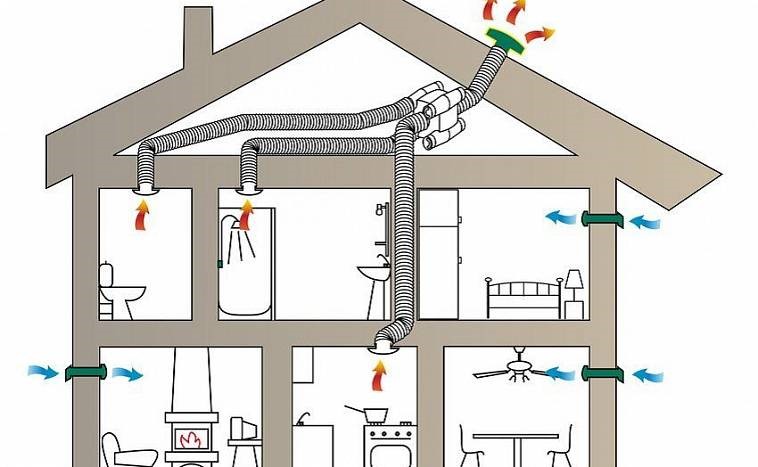
If a supply and exhaust ventilation scheme is used in a private house, its operation can be improved by installing a heat exchanger. Recuperator systems immediately, through one hole in the wall, remove the exhaust air and supply fresh air. This is an ideal solution if ventilation is taken care of after renovation or if it is necessary to solve the problem only in some rooms. The main thing is that these rooms have at least one wall facing the street.
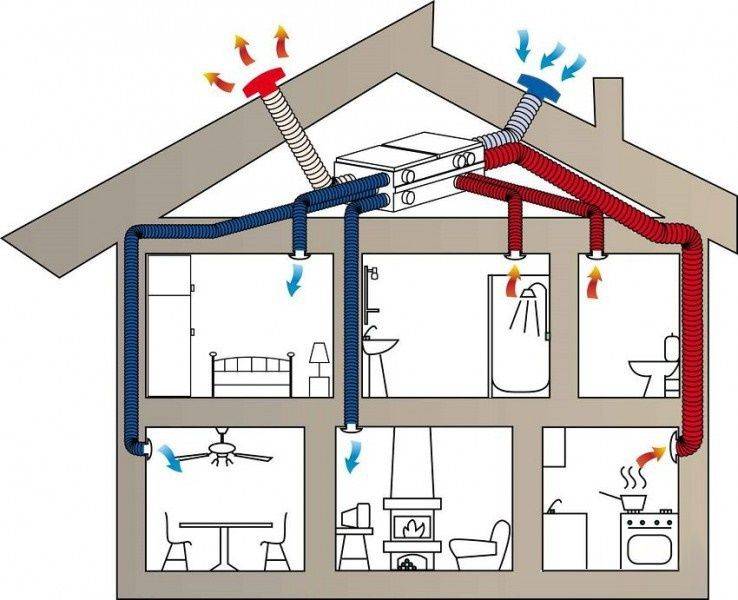
The most suitable system ventilation for a private house is considered a supply-exhaust ventilation
Where air supply and exhaust is carried out by force. A house with an efficient ventilation system will ensure long-term operation of the housing structure and maintain a healthy microclimate for the whole family
Therefore, it is important to make the correct calculation of the project and select reliable materials.
For more than 10 years, UralSibMet has been supplying high-quality building materials and metal-roll at competitive prices and with the possibility of delivery in the Irkutsk Region, Buryatia and the Trans-Baikal Territory. Rolled metal products and building materials from UralSibMet will become a guarantee of the reliability of your home.
Choosing the optimal ventilation system
Each house is unique. And the ventilation system suitable in a particular case will be different. Of great importance when choosing a system is the area of \u200b\u200bthe house, the number of floors, materials of walls and roofs.
You should also take into account the amount allocated for this
The larger the area of the house and the more airtight materials used in its construction, the more complex the system will be required. Another point - additional climate control options. The cost of ventilation directly depends on this parameter.

The arrangement of the ventilation ducts themselves is inexpensive - you can pick up inexpensive pipes, valves, grilles, additional parts that are needed for installation
The more functions a ventilation system can perform, the more expensive it will cost. But with a modest budget, you can do without additional features - the flow of fresh air into the house does not depend on this.
To organize the flow of air use:
- windows with micro-ventilation;
- wooden windows. They have natural micro-ventilation, which provides an influx of fresh air from the outside;
- supply valve.
Inlet valves can be of various shapes and sizes. The materials from which they are made are metal and plastic. As for micro-ventilation in windows, this option is the most convenient - you do not have to additionally make holes in the walls and buy valves.
To remove air from the premises of a private house, ventilation shafts are used in the wall or separate air ducts are laid in the kitchen, pantry, boiler room and bathroom. It is convenient to install a fan in such channels, which will forcibly rid the room of polluted air.

Mechanical ventilation systems use filters that need to be changed periodically. Their service life is indicated in the manufacturer's instructions.
If the area of \u200b\u200bthe house is small, then it is enough to install windows with micro-ventilation, an extractor hood in the kitchen and ventilation ducts from the boiler room and bath. Such a seemingly modest system will completely cope with the ventilation of all the premises of a country house.
Units for local exhaust system
Existing shelters, which are equipped with exhaust ventilation systems, are divided into several specialized categories:
- units installed at the source of pollution;
- solutions that block the source of pollution;
- reblowing products.
In practice, units with the help of which the source of the spread of hazardous substances is localized in a certain area are very popular. However, such solutions are not always convenient and appropriate to apply. They were replaced by more modern hoods with ventilation:
- metal and polycarbonate umbrellas with hood function;
- local suction units;
- powerful fume hoods;
- encapsulated solutions;
- removal of secretions from the body of machine tools and working units;
- showcase, shaped and board solutions.
Local ventilation systems are very common in places where it is necessary to ensure the required standards for air exchange in a specific, local area.
Exhaust hoods are the most popular and common suction designs. They equip small working areas (tables for soldering, cooking). Dangerous impurities are quickly collected and redirected upwards, after which they are discharged. Ventilation for the hood functions both through natural draft and forced draft.
Specialized suction - draw out unwanted and potentially dangerous substances with a minimum consumption of oxygen. Industrial exhaust ventilation is often represented by several local units. Their main feature is that they do not interfere with work.
Fume hoods are one of the most effective solutions for the forced removal of harmful fumes, substances, while forming a minimum level of air exchange. There are several types of such cabinets on sale:
- with an upper outlet device, through which hot and humid air is removed;
- with the removal of contaminated streams of the side structure - we are talking about some analogue of a "snail", for collecting residual products;
- with diverting solutions of the combined type located at the bottom of the unit.
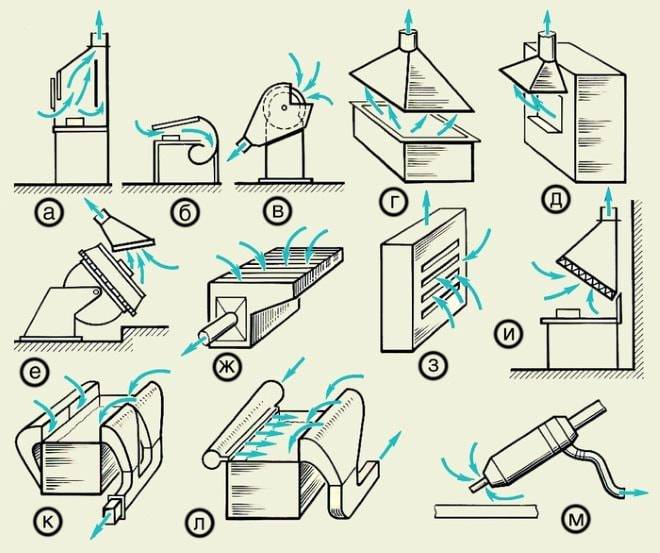
Local hoods: a - fume hood; b - display case; c - shelter-casing for a grinding machine; g - exhaust hood; e - umbrella-visor over the open opening of the furnace; e - exhaust funnel when welding large-sized products; g - lower suction; h - lateral suction; and - inclined exhaust panel; j - double-sided suction from the galvanic bath; l - single-side suction with blowing; m - annular suction for a manual welding gun
The fan, located in the air exchange system, creates a swirl in the flow so that the dust is localized in a small area, and does not spread throughout the room. An example of such an installation is a welding post, where forced exhaust ventilation is represented by a small cabinet. The suction in them is located at the top of the structure.
If we are talking about the removal of non-hazardous substances, then the speed of movement is allowed within the following limits:
- 0.5 – 0.7 m/s;
- 1.1 - 1.6 m / s - for those cases when toxic impurities, metal fumes are removed from the room.

Fume hoods are installed in chemical laboratories
As for the suction panels, they are used in cases where the air in a confined space is saturated with toxic gases, dust and heat. The panel is positioned so that the toxic compounds are at the maximum distance from the worker. Exhaust pipes for ventilation complement the built-in motor and quickly remove dangerous suspensions. The installations under consideration are used at welding posts, when processing large products. From welding, they are located at a distance of up to 3.5 m, equipped with fans with one or two motors.
The speed of movement of air masses must meet the following criteria:
- from 3.5 to 5 m / s, when it comes to the release of hot dust;
- from 2 to 3.5 m / s, if toxic or non-dusty suspensions are released during operation.
Experts focus on one important point - the installation of exhaust ventilation is carried out on the condition that 1 m2 of the panel removes 3.3 thousand m3 of air hourly

Onboard suctions are relevant for cases when the source of pollution is held in a vertical position using special lifts.Such installations are widely used in the shops where the galvanic processing of metals is carried out, in which hazardous substances are poured into a special container and then sucked in through a small hole.
From a constructive point of view, exhaust ventilation of industrial premises consists of several air ducts, the inlets of which have a narrow shape (up to 10 cm), they are located at the edges of the bath.
Advantages and disadvantages of natural and forced ventilation systems
The table shows the main advantages and disadvantages of different systems ventilation in a private house.
| Type of ventilation | Natural | Forced | Mixed (combined) |
| Installation and maintenance cost | Minimum | Maximum | Medium |
| heating costs | Maximum | Minimum | Medium |
| Dependence on weather conditions | Maximum | Minimum | Medium |
| Difficulty of installation | Medium, only the correct laying of air ducts and air intake and exhaust points is necessary. In the presence of non-hermetic building structures and combustion heaters, the minimum | Maximum, requires competent design and placement of all elements of the system, accurate calculation of volume, heating / cooling level and air velocity | Average, provided that forced air extraction is installed only in significant places of housing (kitchen, bathroom) |
| Cost and complexity of maintenance | Minimal, taking into account small periodic costs for the replacement and cleaning of air intake and exhaust points, air ducts | Maximum, it is necessary to replace filters in the PPVV, individual elements of the system with the required frequency, clean the air ducts | Medium |
| The level of purification and air preparation | Minimal, cleaning possible only with coarse filters at the sampling points | Depending on the complexity and direction of the system | Average, depending on the type of system and the number of elements |
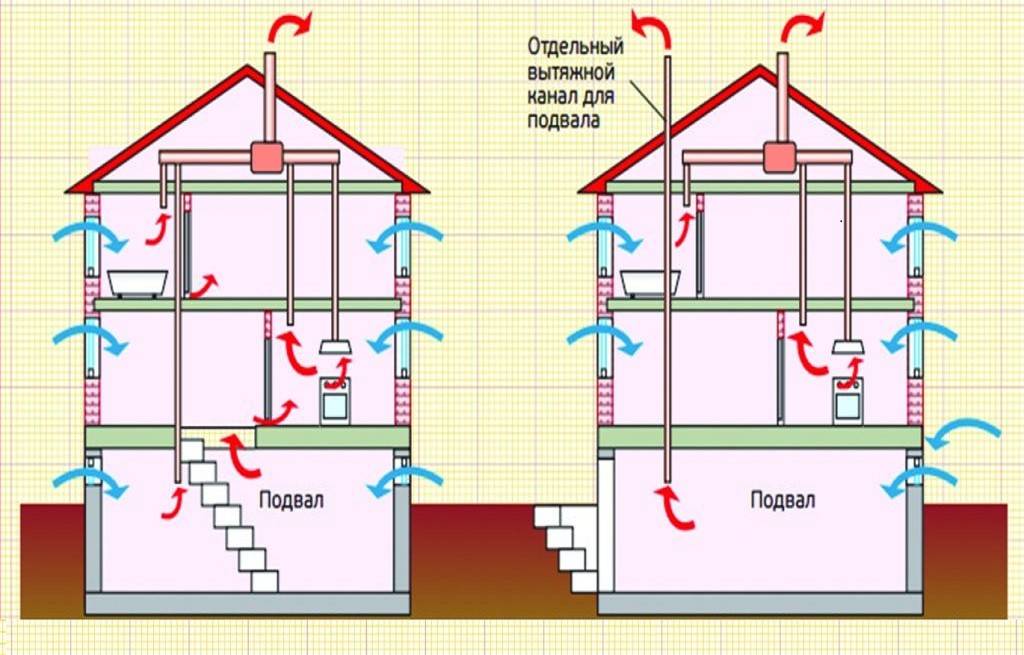
Thus, for private houses (except for hermetic ones), the combined scheme is the most rational: forced ventilation of the basement, bathroom and kitchen, natural supply ventilation in a private house, other rooms.
Ventilation schemes for a private house and apartment
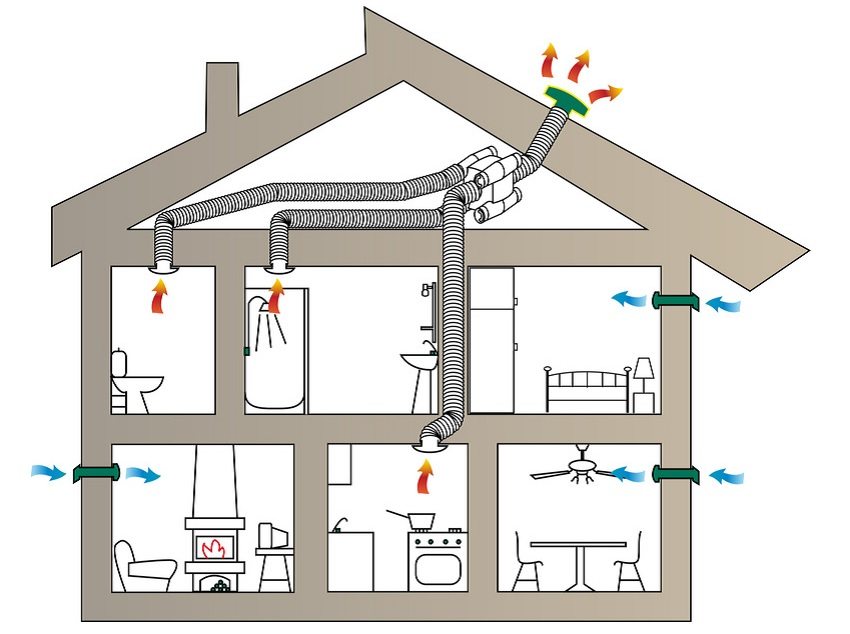
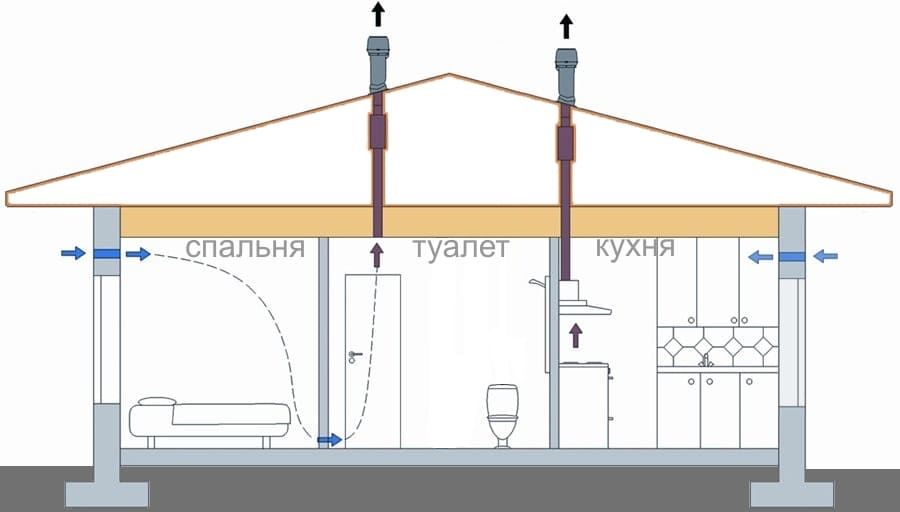
The simplest option is implemented in small houses and apartments. Supply air openings are located in the living rooms, hoods - in the kitchen and bathroom. The air entering the premises through the cracks under the doors enters the kitchen and bathroom, where it is removed. This scheme works with an area of \u200b\u200bnot more than 100 squares.
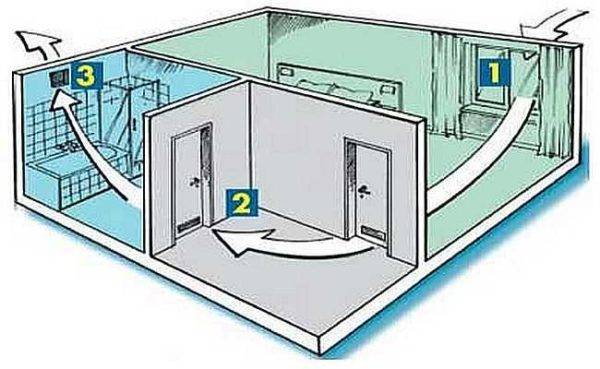
When supply ventilation - separate devices in each room, exhaust - through the kitchen or bath
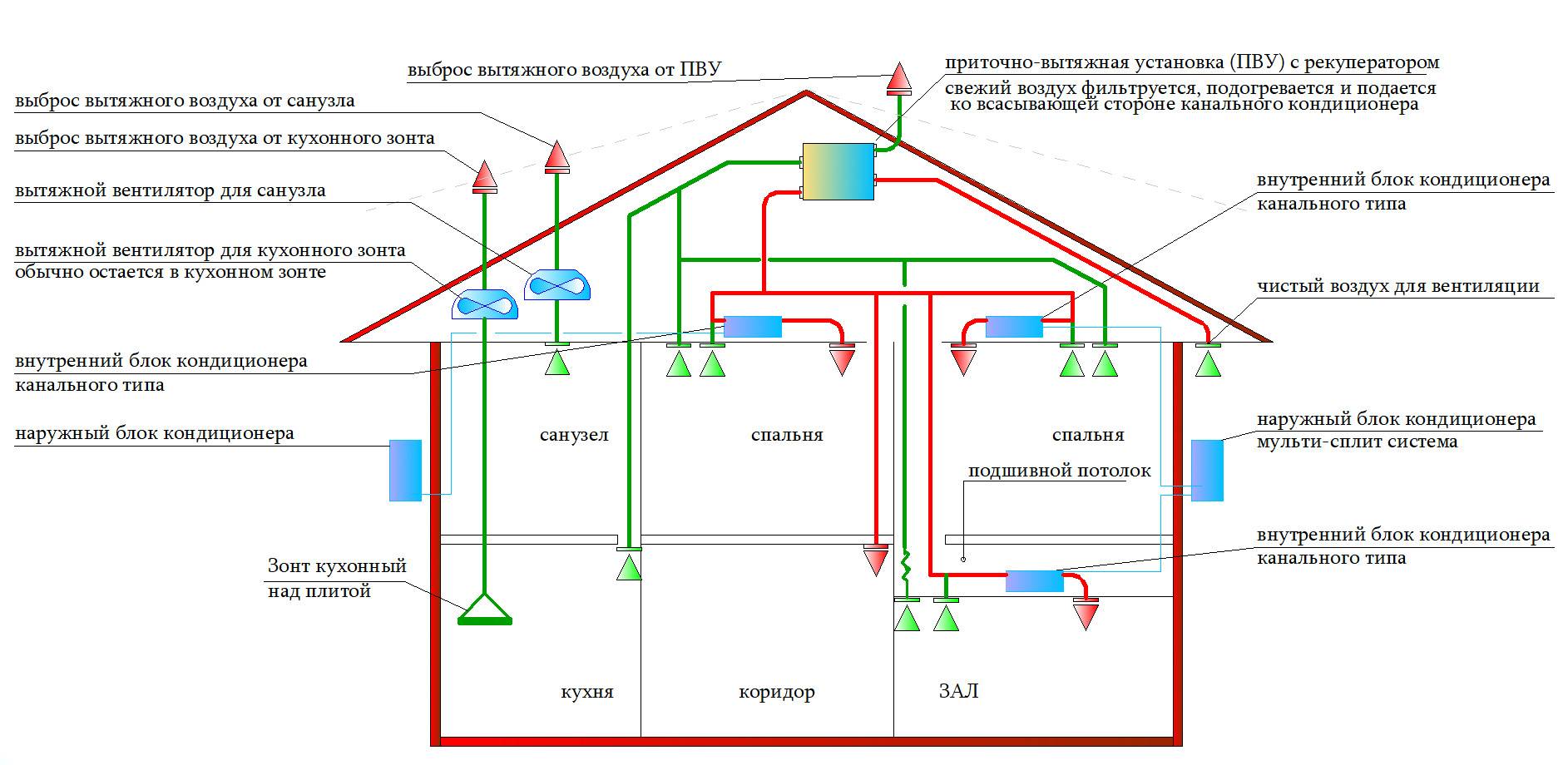
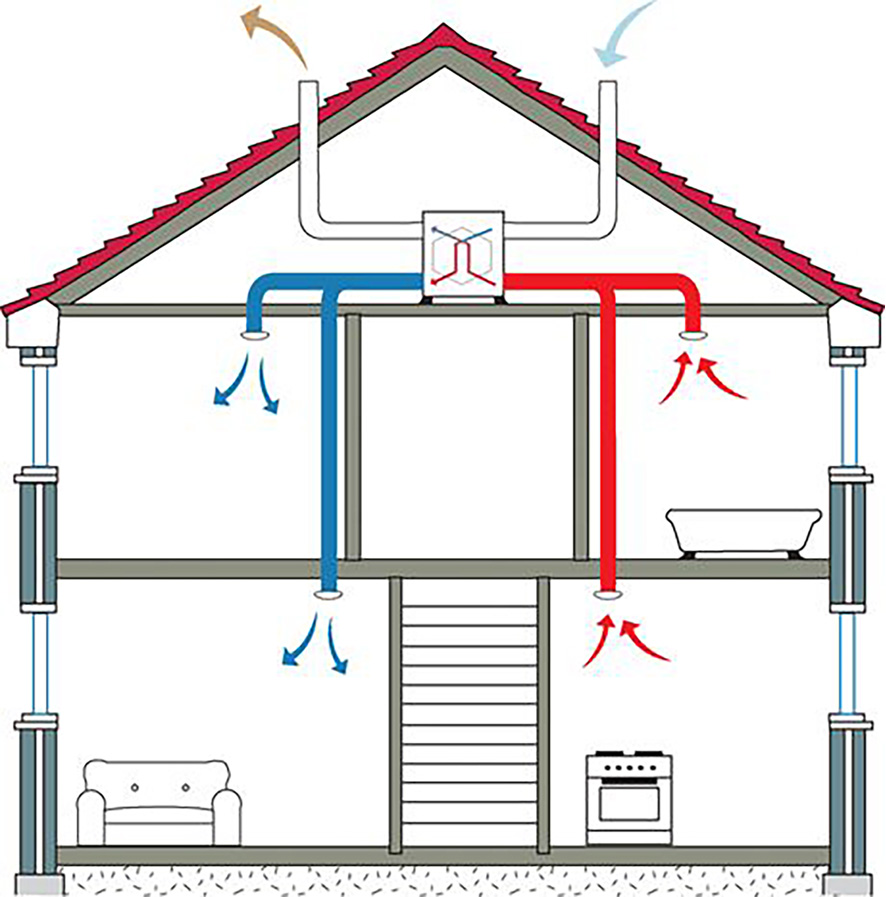
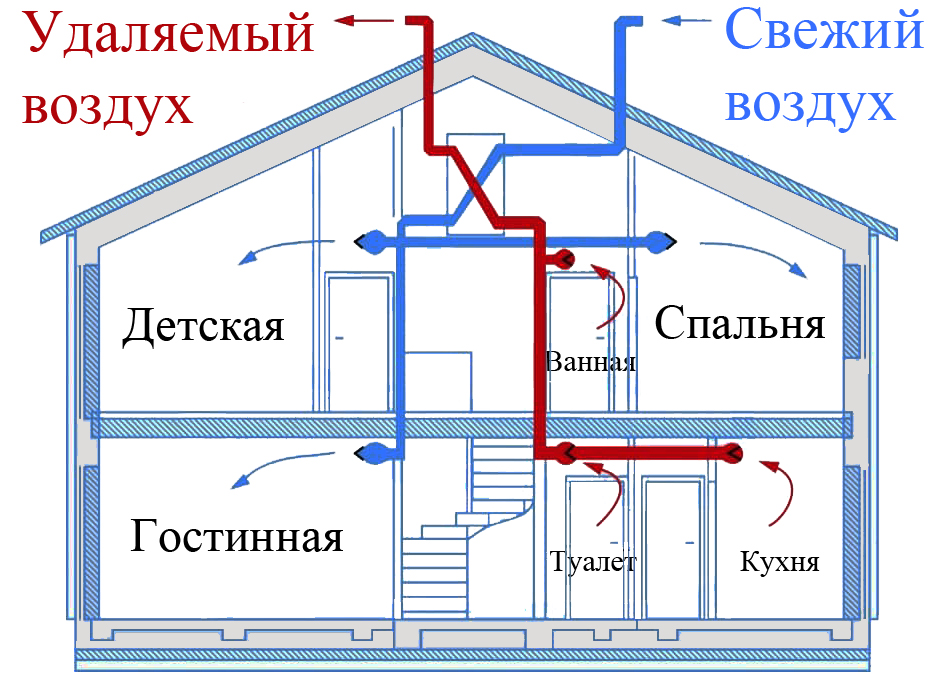
In houses with a total area of more than one hundred and fifty squares, organizing two separate systems - supply and exhaust. Each of them has its own duct system. With such a device in each room there are exhaust and supply openings in each of the rooms. In this case, the intensity of air inflow and outflow can be adjusted in each room - you can adjust the atmosphere to the requirements of its inhabitants.
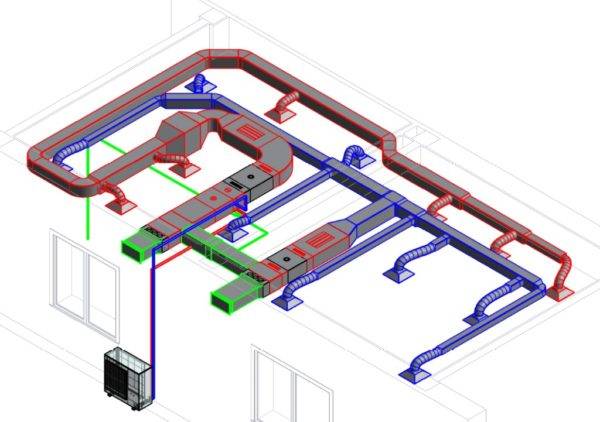
With centralized supply and exhaust ventilation, heating or air conditioning can be arranged
With a centralized supply ventilation system, it is easier to prepare the air taken from the street - you can make a single cleaning and heating system. Prepared air can already be diluted throughout the premises. In this case, each room has two ventilation openings - one supply, one - exhaust.They are located in opposite corners, closed with grilles or diffusers.
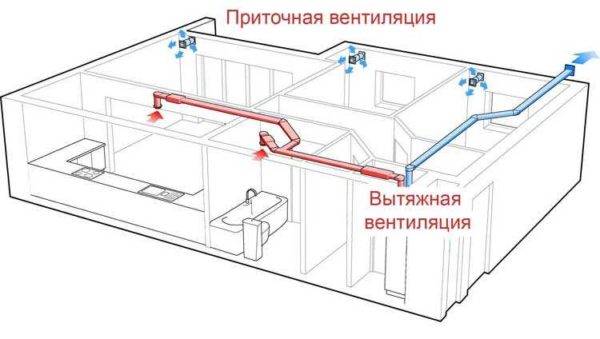
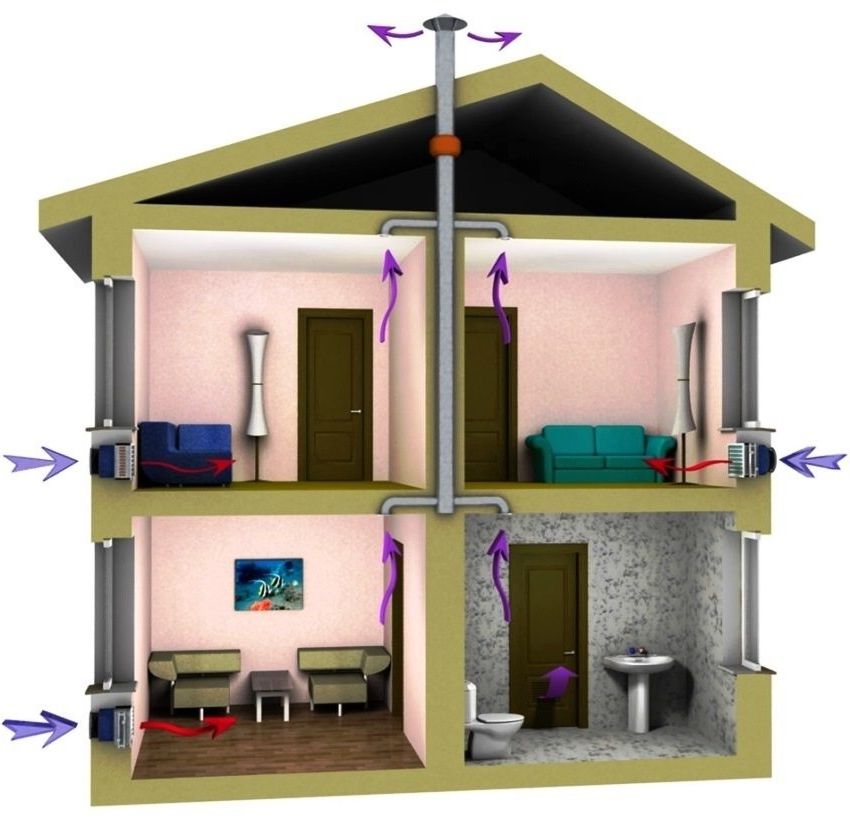
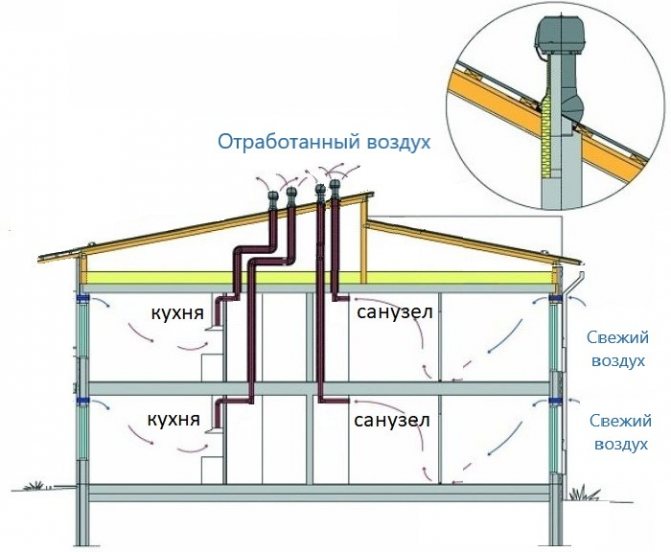
Supply and exhaust ventilation in a private house can be organized in this way: the supply is decentralized, the exhaust is centralized
Even with a large area of \u200b\u200bthe house, the supply ventilation system can be made decentralized, as in the first scheme. With the right selection of equipment, it will work no less efficiently. The question is what will be economically more profitable, since it will be necessary to solve the problem of air preparation for each supply channel. And the equipment is not cheap.