- How does a refrigerator work
- Refrigerator diagram: device drawing and working unit
- Smart refrigerators with electronic control
- The electrical circuit of the refrigerator and the principle of its operation
- Device
- Compressor
- Wiring diagram
- Schematic diagram of the refrigerator device
- Inverter and conventional refrigerators
- How to connect a start relay
- Oil cooler diagram
- The principle of operation of the absorption refrigerator
- Refrigerator without electricity - fact or fiction?
- Conclusion
- Video: compressor operation experiment with a short circuit
How does a refrigerator work
Let's start a discussion of the principles of operation of the refrigerator compressor. Heart! The main thing is here. The refrigerator motor is usually asynchronous, so a start-up relay is often required for operation. The responsibilities of the device include connecting the starting winding, only at the time of start. The internal bimetallic plate heats up, the capacitor is disconnected from the starting winding, the only working one functions. Protection against overheating works according to a similar system: the refrigerator motor runs for too long, the thermal effect of the current unbends another bimetallic plate, breaking the contact, allowing the windings to rest.
Such a scheme will allow the refrigerator to work efficiently, provide a good starting moment.It is clear that inside the device there is freon, which is not exactly circulating around the circuit with pleasure, the piston requires some effort. Remember here:
Refrigerator motors have individual starting requirements. The power is also different, therefore, the type, heating of the bimetal relay does not remain constant. Special reference books have been written, where we will see what refrigerator engines are, what types of relays correspond. By the way, a list was posted on the site, we hope it pleased readers. Modern refrigerator motors are inverter controlled and no longer contain crankshafts. The movement of the shaft is linear, the wits have stuck an epithet called the compressors.
Inside is a coil equipped with a core that moves forward according to the law of alternating current applied to the wire. Despite the apparent absurdity (resemblance to electric shavers), motors, as practice shows, satisfy the goals to the maximum. In addition, inverter control is most effectively implemented, helping to reduce noise levels and extend life. No wonder Samsung gives a 10-year warranty on refrigerator motors. Recall:
- Asynchronous motors with a squirrel-cage rotor are capable of changing the speed, including those controlled by changing the frequency of the supply voltage.
-
Collector motors, which are rarely used in refrigerators, are deprived of this ability.
- The new type of coil and oscillating core motors is also easily controlled by changing the pulse repetition rate.
The result is the following diagram:
- The input voltage is rectified.
- It is cut with a power key to the required durations.
- The work is run by a clock generator.
The simplest circuit, rather related to a switching power supply, the essence remains the same: there is a voltage of 50 Hz, then becoming a voltage of a different frequency. As a result, we see a change in the speed of the piston, which is why freon begins to move faster, slower. What does it give?
Refrigerator diagram: device drawing and working unit
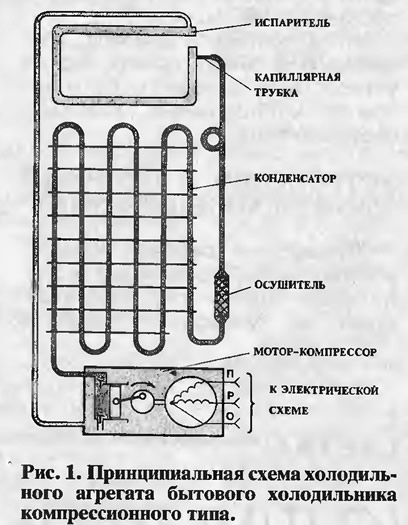
Not a single cold-producing structure could work without a properly designed scheme, which defines all the elements and the sequence of their interaction.
In fact, the cooling process is not at all the way we used to think. Refrigerators do not produce cold, but absorb heat, and because of this, the space inside the device is devoid of high temperatures. The refrigerator circuit includes all the elements of the device that are involved in providing air cooling inside the device, and the sequence of actions of this mechanism.
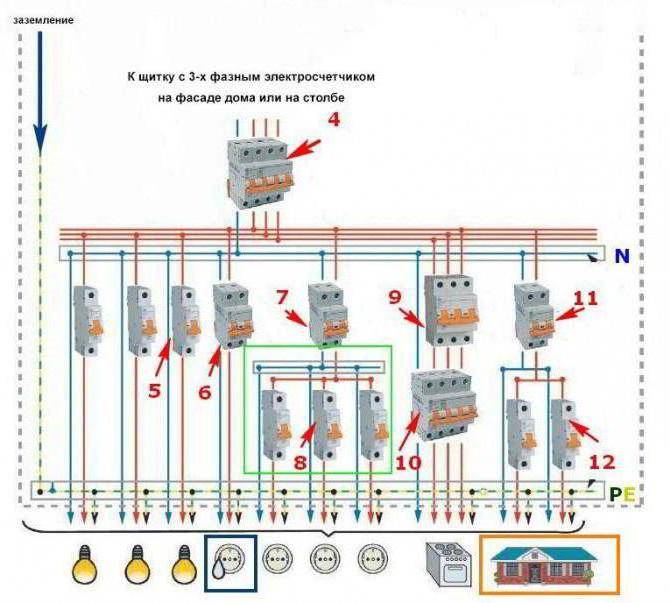
 Basically, the reliability of the refrigerator depends on the quality of the compressor.
Basically, the reliability of the refrigerator depends on the quality of the compressor.
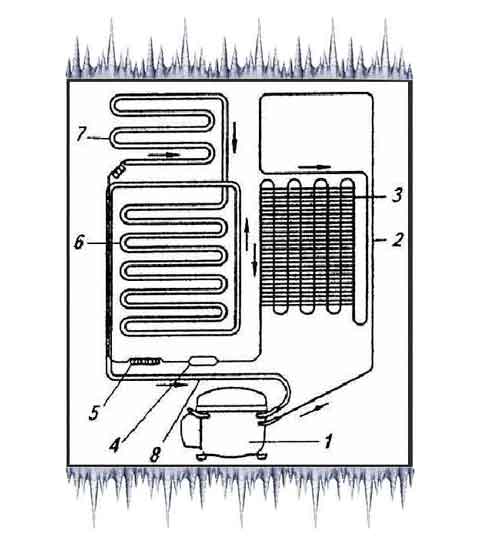
From the image in the diagram, you can understand the following:
- Freon enters the evaporation chamber, and passing through it takes heat from the refrigeration space;
- The refrigerant moves to the compressor, which, in turn, distills it into the condenser;
- Passing through the above system, the freon in the refrigerator cools down and turns into a liquid substance;
- The cooled refrigerant enters the evaporator, and during the passage into a larger diameter tube, it turns into a gaseous mixture;
- After that, it absorbs heat from the refrigerator again.
This principle of operation is inherent in all compression-type refrigeration units.
Smart refrigerators with electronic control
Classic thermostats, with a mechanical rotary knob and a bellows inside, are becoming increasingly rare in modern refrigerators. They are giving way to electronic boards capable of managing an ever-increasing variety of operating modes and additional options for the refrigerator.
Instead of a bellows, the function of determining the temperature is performed by sensors - thermistors. They are much more accurate and compact, often installed not only in each compartment of the refrigerator, but also on the evaporator body, in the ice maker and outside the refrigerator.
Many modern refrigerators have an electric air damper, which makes the No Frost system as efficient, convenient and accurate as possible.
The control electronics of many refrigerators is made on two boards. One can be called user: it is used to enter settings and display the current state. The second one is a system one, it controls all refrigerator devices through the microprocessor to implement a given program.
A separate electronic module allows the use of an inverter motor in refrigerators.
Such motors do not alternate cycles of operation at maximum power and idle time, as usual, but only change the number of revolutions per minute, depending on the required power. As a result, the temperature in the refrigerator chambers is constant, energy consumption is reduced, and the compressor life is increased.
The use of electronic control boards incredibly expands the functionality of refrigerators.
Modern models can be equipped with:
- control panel with or without a display, with the ability to select and set the operating mode;
- many NTC temperature sensors;
- FAN fans;
- additional electric motors M - for example, for crushing ice in an ice generator;
- HEATER heaters for defrost systems, home bar, etc.;
- solenoid valves VALVE - for example, in the cooler;
- S/W switches to control the closing of the door, the inclusion of additional devices;
- Wi-Fi adapter and remote control.
The electrical circuits of such devices are also repairable: even in the most complex system, a failed temperature sensor or a similar trifle often becomes the cause of a malfunction.
 Side-by-side refrigerators with touch screen controls, ice maker, built-in cooler and many customization options are controlled by a rather extensive and complex electronic board
Side-by-side refrigerators with touch screen controls, ice maker, built-in cooler and many customization options are controlled by a rather extensive and complex electronic board
If the refrigerator is “buggy” and refuses to correctly execute the specified program, or does not turn on at all, most likely the problem concerns the board or the compressor, it is better to entrust the repair to a specialist.
The electrical circuit of the refrigerator and the principle of its operation
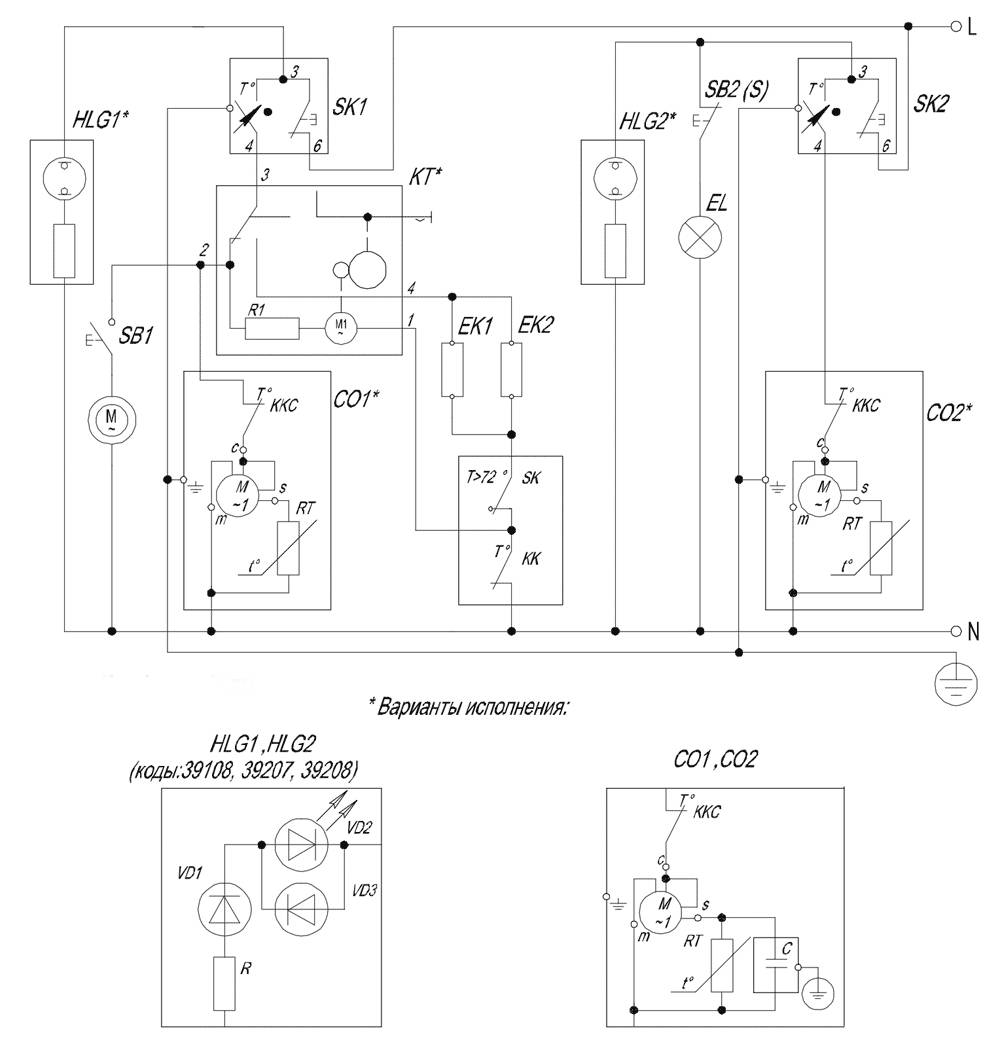
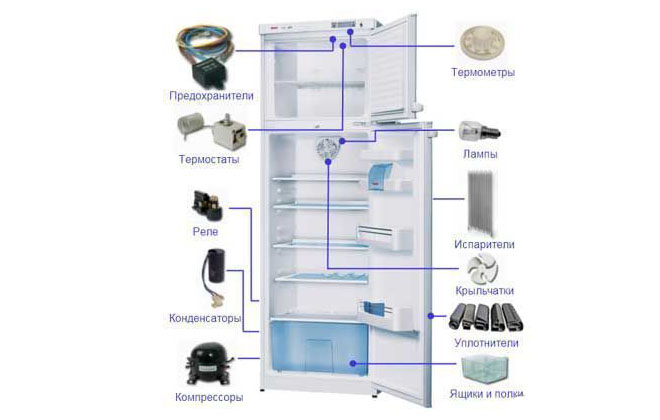
After connecting the device to the power supply, the current flows through the contact group of the thermostat, the protective relay, the inductive coil of the starting relay and the main winding of the electric motor.
As long as the rotor is stationary, the current is substantially greater than usual. After the start relay is activated, the starting inductance winding is connected to the circuit. The armature turns, the current decreases, the relay opens, and the electric motor runs normally.
After the chamber has cooled to the required temperature in the refrigerator chamber, the thermal relay is activated and breaks the power supply circuit of the electric motor.The temperature in the compartment starts to rise, and when it exceeds the set value, the motor is switched on again. The main work cycle is repeated.
The protective relay reacts to the current flowing in its circuit. If the motor is overloaded, the current in its circuit increases. When it reaches the limit values, the protective relay breaks the circuit. After the motor and relay have cooled down, it closes the circuit again, starting the motor. The system protects the engine from premature wear and the room from fire. The sensor in the relay is a bimetallic plate welded from strips of metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion. When heated, the plate changes its shape, bends and breaks the chain. After cooling the plate, it takes the initial odds, closing the contacts of the circuit.
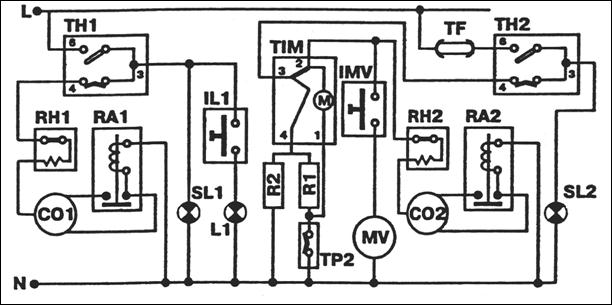
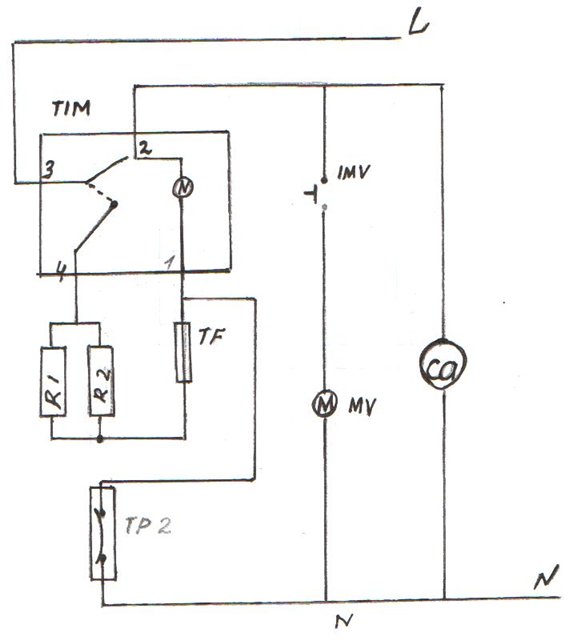
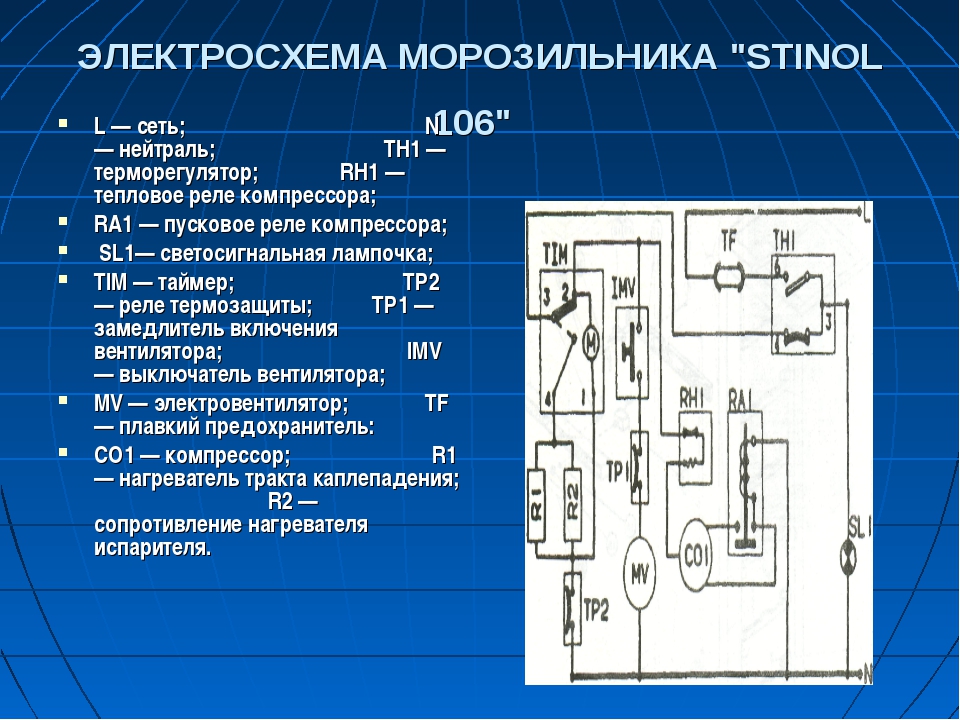
Below is a diagram of a compression refrigerator brand Stinol.
Electrical diagram of the compression refrigerator
Device
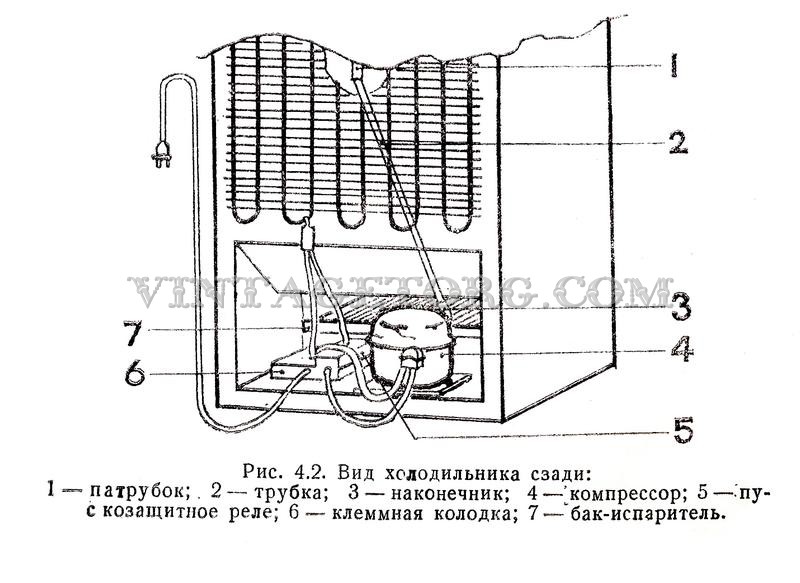
The Atlant refrigerator device includes the following components:
- housing equipped with double stacks with a layer of insulating material;
- front doors with the possibility of hanging on the left or right wall of the case;
- piston compressor with an electric motor (made as a single unit);
- evaporator radiator located inside the working chambers of the equipment;
- condensation unit mounted on the outer part of the housing (on the rear wall);
- thermostat with temperature sensors to maintain the set parameters;
- an electronic control unit and relays that ensure the operation of electrical components.
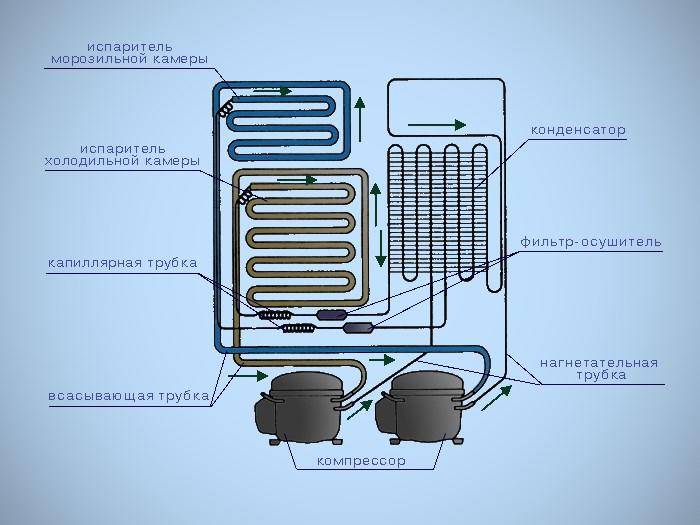
The radiators and the compressor are interconnected into a single block by copper and steel tubes; solder is used to ensure tightness.The design provides for additional elements that separate water or oil vapor, as well as correcting the pressure of the refrigerant. On some of the refrigeration units, an additional liquid crystal display and a block of control indicators are used. There are refrigerators with a special compartment for cooling water and with heat exchangers of the No Frost standard.
Compressor
The refrigerator compressor includes an AC electric motor with a vertically mounted rotor. A crank mechanism is mounted on the front toe of the motor, connected to a piston that compresses the refrigerant. All units are mounted on spring supports in a metal case consisting of 2 halves. The parts of the casing are welded together by arc welding; during operation, maintenance and replacement of components are not provided.
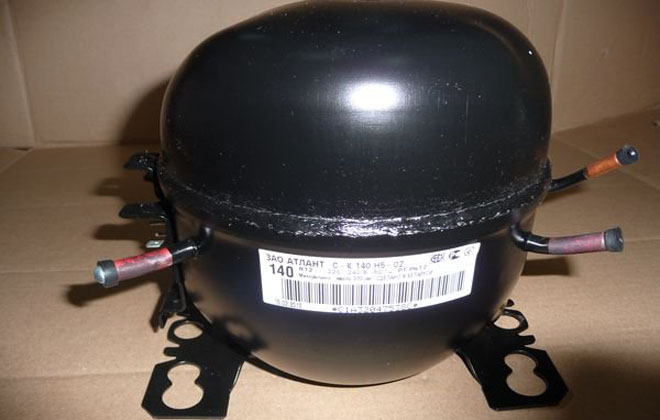

An oil bath is located in the lower part of the body and power cables are entered. The motor is equipped with a double winding, the working part is used when operating the motor. An additional starting winding is used at the moment of spinning the rotor, and then it is disconnected from the power circuit by a special relay installed on the outer part of the housing. A refrigerator with one compressor serves the freezer and the refrigerator at the same time. The two-compressor Atlant is distinguished by the installation of separate heat exchangers and temperature controllers for 2 chambers.
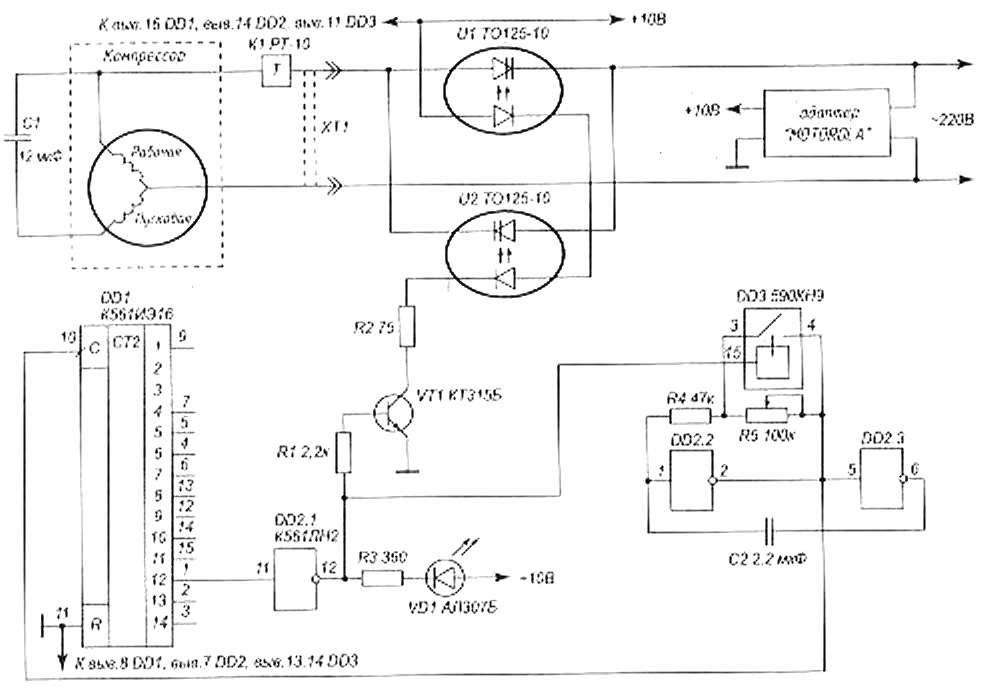
Wiring diagram
The electrical circuit diagram is based on a 2-wire concept, the equipment is connected to a household single-phase current network using a plug. The electrical circuit includes an additional ground loop (only for some modifications of refrigeration equipment).A relay with a built-in air temperature sensor is used to control the operation of the compressor. The device automatically supplies power when the chamber warms up to the set temperature, after the air cools, a signal to stop the rotor of the electric motor is transmitted.
Schematic diagram of the refrigerator device
Even 30 - 40 years ago, household refrigerators had a rather simple structure: the motor-compressor was started and turned off by 2 - 4 devices, there was no question of using electronic control boards.
Modern models have many additional options, but the principle of operation as a whole remains unchanged.
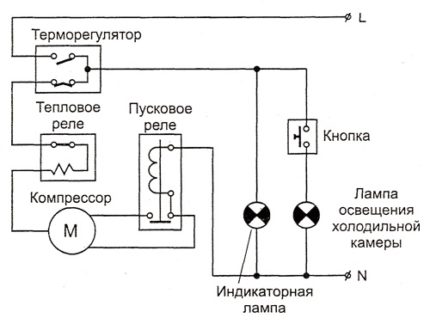 In older refrigerators, all additional equipment comes down to a power indicator and a light bulb in the refrigerator compartment, which is turned off by a button when the door is closed
In older refrigerators, all additional equipment comes down to a power indicator and a light bulb in the refrigerator compartment, which is turned off by a button when the door is closed
The thermostat is the main and only control element with which the user can adjust the operation of the old refrigerator, usually located inside the refrigerator compartment. The bellows spring is hidden under the power lever - a rotating handle. It contracts when the chamber is cold, thereby opening the electrical circuit and turning off the compressor.
As soon as the temperature rises, the spring straightens and closes the circuit again. The handle with indicators of the freezing force of the refrigerator regulates the allowable temperature range: the maximum at which the compressor starts and the minimum at which cooling is suspended.
The thermal relay performs a protective function: it controls the temperature of the engine, therefore it is located directly next to it, often combined with a starting relay.If the permissible values \u200b\u200bare exceeded, and this can be 80 degrees or more, the bimetallic plate in the relay bends and breaks the contact.
The motor will not receive power until it cools down. This protects against both compressor failure due to overheating and a fire in the house.
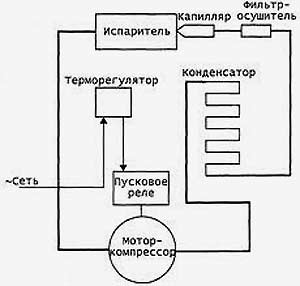
The motor-compressor has 2 windings: working and starting. The voltage to the working winding is supplied directly after all previous relays, but this is not enough to start. When the voltage on the working winding rises, the starting relay is activated. It gives an impulse to the starting winding, and the rotor begins to rotate. As a result, the piston compresses and pushes freon through the system.
The motor-compressor compresses and pumps freon through the tubes of the system, which ensures the transfer of heat from the refrigerator chambers to the outside, cooling the products
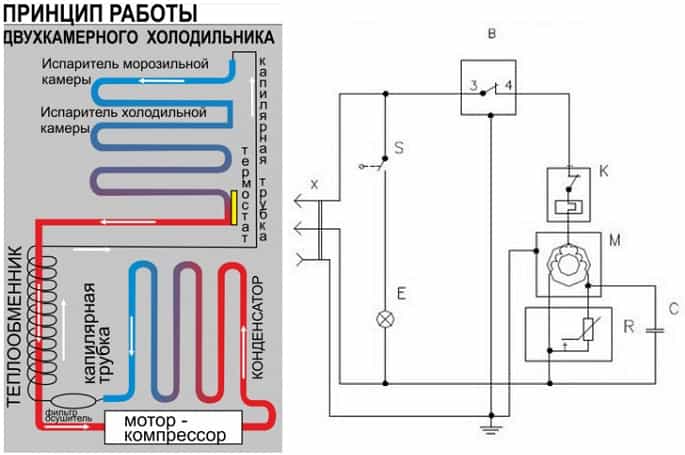
In general, the cycle of operation of the refrigerator can be described as follows:
- Connecting to the network. The temperature in the chamber is high, the thermostat contacts are closed, the motor starts.
- Freon in the compressor is compressed, its temperature rises.
- The refrigerant is pushed into the condenser coil located behind the back or in the refrigerator tray. There it cools, gives off heat to the air and turns into a liquid state.
- Through the dryer, freon enters a thin capillary tube.
- Getting into the evaporator located inside the refrigerator chamber, the refrigerant expands sharply due to an increase in the diameter of the tubes and the transition to a gaseous state. The resulting gas has a temperature below -15 degrees, absorbs heat from the refrigerator chambers.
- Slightly heated freon enters the compressor, and everything starts anew.
- After some time, the temperature inside the refrigerator reaches the set values, the thermostat contacts open, the motor and freon movement stop.
- Under the influence of the temperature in the room, from new warm products in the chamber and opening the door, the temperature in the chamber rises, the thermostat closes the contacts and a new cooling cycle begins.
This diagram exactly describes the operation of old single-chamber refrigerators, in which there is one evaporator.
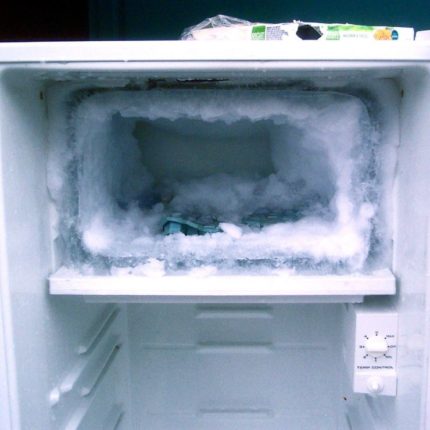 Single-chamber refrigerators have a small freezer, not separated by thermal insulation from the main one, with one door. Food in the front of the freezer may thaw
Single-chamber refrigerators have a small freezer, not separated by thermal insulation from the main one, with one door. Food in the front of the freezer may thaw
As a rule, the evaporator is the freezer housing at the top of the unit, not isolated from the refrigerator compartment. We will consider the differences in the device of other models below.
Inverter and conventional refrigerators
There are two types of compressors - conventional and inverter. They differ in internal structure and mode of operation. Previously, all refrigerators were equipped with linear ones, but now inverter ones are gaining popularity.
A conventional compressor operates in start-stop mode. For example, when the temperature in the chamber rises 1 degree above the desired temperature, the compressor turns on and the refrigerator starts to cool. As soon as the temperature has reached the desired, it turns off.
The inverter compressor runs constantly, but with low power. It maintains the temperature at a given level. At the same time, its total energy consumption is lower than that of a conventional one.
The advantage of a linear compressor is that it is not stressed when switched on and off. Accordingly, its service life is much longer.But inverter equipment is more expensive than usual.
In this article, we described the principle of operation of the refrigerator and touched on other topics. We hope it was helpful to you. Don't forget to share the post with your friends!
How to connect a start relay
Self-installation of a new mechanism must be combined with a certain level of knowledge, otherwise you should call the wizard. If the refrigerator arrived without a starting relay, there was no visual inspection of its correct location, then it is recommended that you read the manufacturer's instructions.

The starting relay connection diagram is standard:
- disconnect the appliance from the network;
- wait a few minutes for a complete de-energization of the equipment;
- unfasten the water supply hose from the back wall and move it away so as not to accidentally damage it;
- unscrew the fasteners fixing the protective panel, remove to the side;
- remove the old start relay, if not, find the location on the compressor;
- connect the connector to a new device;
- insert into place;
- connect the wires according to the marking;
- fix the trigger mechanism with screws, latches;
- put the back panel in place, screw it;
- attach the water supply hose, fix;
- connect to the mains for testing.
Professionals recommend the use of protective gloves to prevent injury to the hands. Independent connection of modern varieties of the starting relay can cause a number of difficulties that are not always possible to fix on your own.
The start relay is an important part of the refrigerator that starts the electric motor and protects equipment from breakdowns. The failure of the element leads to the appearance of uncharacteristic noise, not turning on the equipment.You can identify a malfunction, repair, replace it yourself, but in the absence of certain knowledge, it is better to contact specialists.
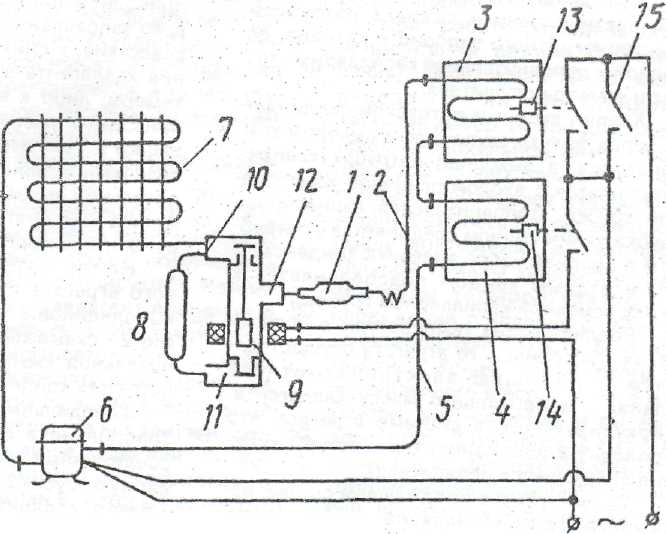
Oil cooler diagram
The oil cooler works in conjunction with a fan in the diffuser socket. The hot oil enters the lower manifold and travels up and down the refrigerator tubes, being cooled by the airflow generated by the fan.
During normal operation, the temperature of the oil leaving the refrigerator should be 18-20 degrees lower than the temperature of the incoming hot oil. The cooled liquid is discharged through an opening in the upper manifold.

The fan creates a stream of air that passes through the core of the oil cooler and removes heat from its tubes. Station fans are arranged similarly to rotary, screw and reciprocating compressors. The air collector, which is a container for compressed air and oil, also performs the function of separating them from each other.
Inside the air collector, consisting of a steel shell and two bottoms, there is an oil separator - a pipe with filter bags, closed with a steel cover. Oil is poured through the neck, its level is determined with a dipstick. A drain pipe with a cock is provided to drain the condensate accumulated in the sump or drain the oil from the oil sump.
The oil-air mixture enters the air collector at high speed, where, due to its large volume, its speed is sharply reduced, and the oil drops are cooled in its lower part. After pre-cleaning, the compressed air passes through the filter bags of the oil separator, where it is finally cleaned of oil.The oil accumulated in the lower part of the oil separator is sucked off by the pump and returned to the oil sump for reuse.
When the outer surface of the tubes and cooling plates is contaminated, the core of the oil cooler is blown with compressed air in the direction opposite to the air flow generated by the fan. When oiling the outer surface of the refrigerator, the tubes and plates are washed with white spirit or other special liquids.
If the inner surface of the tubes is contaminated with oil oxidation products, the core of the oil cooler is removed and immersed in kerosene for 24 hours, after which the tubes are cleaned by repeatedly pushing a rag swab into the tubes.
The oil cooler is made of aluminum alloy and has external cooling fins. The oil cooler and oil filter are mounted on the flywheel side of the engine. The refrigerator consists of sections, each of which is a set of brass radiator tubes soldered to the base. The pipes are ribbed to increase the cooling surface. The sections are installed between the plates, which are connected by racks. Side covers are attached to the plates, and the left one is divided inside by a rib into two halves, each of which has a flange for connecting a pipeline.
The radiator-type oil cooler is located in front of the main water-cooled radiator. Oil filters are pre-filters of the Kuno type (lamellar, cleanable) and fine filters (double with cartridges made of cotton ends).
The principle of operation of the absorption refrigerator
Absorption is the process of absorption of a substance by another substance.So, moisture can absorb ammonia, which is why ammonia is formed, while moisture absorbs, for example, salt. Absorption refrigerators work on the same principle. While this type of refrigeration plant originally appeared due to the study of the possibility of using liquid fuels, with the development of industry, compression plants have practically forced them out of the market. However, then more and more new technologies appeared, and today both principles of work are used on an equal footing in the production of refrigeration machines.
Instead of a compressor, absorption refrigerators use a kind of "boiler" that is heated by the action of an electric current. The boiler contains ammonia, which turns into steam due to heating, and, accordingly, increases the pressure in the device. Under the influence of simple laws of physics, ammonia vapor moves to the condenser, where it cools down and again turns into a liquid state. The very same scheme of operation is almost identical to the scheme of a compression refrigerator. The absorption refrigerator is much quieter than its compression "colleague", does not depend on power surges in the network and does not have moving parts that easily fail. But it also has its drawbacks: the consumption of electrical energy increases somewhat, which leads to financial costs.
Morozko refrigerators work according to this principle of operation.
Refrigerator without electricity - fact or fiction?
A resident of Nigeria, Mohammed Ba Abba, in 2003 received a patent for a refrigerator without electricity. The device is clay pots of various sizes. The vessels are stacked into each other according to the principle of the Russian "matryoshka".
Refrigerator without electricity
The space between the pots is filled with wet sand. A damp cloth is used as a lid. Under the action of hot air, the moisture from the sand evaporates. Evaporation of water leads to a decrease in temperature inside the vessels. This allows you to store food for a long time in a hot climate without using electricity.
Knowledge of the device and the principle of operation of the refrigerator will allow you to perform a simple repair of the device with your own hands. If the system is configured correctly, then the device will work for many years. For more complex malfunctions, you should contact the specialists of the service centers.
Conclusion
When choosing a refrigerator, you should pay attention to models with an inverter compressor. They are characterized by low power consumption, as well as silent operation.
The design of the device helps to maintain a constant temperature in the freezer. The purchase of such a chiller requires a large investment, but the safety and good performance of inverter compressors justify the price of the models.
Video: compressor operation experiment with a short circuit
Inverter Compressor Experiment Short Circuit Operation
 Watch this video on YouTube
Watch this video on YouTube
I recommend to read:
- Inverter compressor in the LG refrigerator - what is it - An inverter compressor is also an electric motor with a pump, but only with an adjustable shaft speed. Adjustment allows you to smoothly adjust the engine speed and ...
- Linear Inverter Compressor in LG Refrigerator - What it is - The linear inverter compressor does not have an electric motor and can change the speed of the pump piston. This type of compressor is the quietest and most economical to date. Principle…
- Refrigerator inverter compressor - An inverter compressor is also an electric motor with a pump, but only with an adjustable shaft speed. Adjustment allows you to smoothly adjust the engine speed and ...
- Pros and cons of a built-in refrigerator - When choosing a built-in refrigerator, you need to carefully read the advantages and disadvantages of this type of equipment. Despite the large parameters of refrigeration equipment, its ...
- Smart inverter in the LG refrigerator - what is it - An inverter compressor is also an electric motor with a pump, but only with an adjustable shaft speed. Adjustment allows you to smoothly adjust the engine speed and ...
- The principle of operation of a car refrigerator - Departure for a picnic or just out of town is almost always accompanied by a collection of food and drinks. But in summer, chilled food in a car heats up quickly, and in winter it cools ....
- By what principle does a compressor work in a domestic refrigerator - Refrigerator Compressor - what is a Compressor called a device that compresses a substance (in our case, it is a refrigerant in the form of freon), as well as its ...