- Commissioning of gas pipelines
- Kinds
- 3 Calculation of the residual life of the gas pipeline by changing the impact strength of the metal
- black steel
- Standard service life
- Destructive factors
- Real life
- 2 Calculation of the residual life of the gas pipeline by changing the ductility of the metal
- Service life extension
- General requirements for the operation of gas facilities
- When to calculate the residual life of the equipment
- DETERMINATION OF THE OPERATION LIFE OF A GAS PIPELINE BEFORE ITS DIAGNOSIS
- How to extend?
- What is the service life of a product: the concept of the term
- 3 Calculation of the residual life of the gas pipeline by changing the impact strength of the metal
- 5.2 Analysis of the initial data required to assess the technical condition and calculate the actual values of the safety factors of the gas pipeline section
Commissioning of gas pipelines
 The gas pipeline is put into operation after checking the materials, the quality of installation, the location of devices
The gas pipeline is put into operation after checking the materials, the quality of installation, the location of devices
Gas supply to residential buildings is carried out through fan-type pipelines. On the gas supply route to the settlement, several distribution substations are installed, the last of which is mounted inside or outside the building.Further, gas is supplied to apartments through risers, where branches go from them to meters, and from them to consumers (stoves, columns, boilers). Wiring and connection schemes are carried out in accordance with established norms and rules. Checking compliance with the technology is carried out by special control services.
Commissioning of gas pipelines is permitted subject to the following parameters:
- pipe wall thickness - 3 mm for underground and 2 mm for external;
- diameter - 15-100 mm;
- design pressure - 3-12 atmospheres;
-
ceiling height - from 220 cm;
- the gasket is separate, not in the air ducts or next to the heating riser;
- not opposite windows and doors;
- free access for inspection and repair;
- the presence of effective natural ventilation;
- lack of combustible materials in the composition of the finish;
- the connection is only welded using couplings;
- use of special devices for fastening to walls.
The reception of intra-house communication consists of checking the status of the following criteria:
- welding of joints;
- staining (for iron);
- material of manufacture;
- system tightness.
Kinds
There are several types that are established by the technical and other accompanying documentation attached to the product:
- normative - the service life in which the equipment remains operational, but reimburses the cost through depreciation (established in regulatory documents for buildings, structures or equipment);
- assigned — a calendar date after which the operation must be terminated regardless of the product's operability;
- minimum - the minimum allowable service period during which the product can be operated without loss of quality and characteristics;
- maximum - the full service life during which the product is operated without performance degradation, subject to strict observance of the instructions;
- average - the mathematical expectation of the service life, based on statistical indicators and calculations;
- limit - the limit state, after which the further service of the product is unprofitable or unsafe;
- residual - the estimated duration of service before repair or replacement based on an assessment of the state of the product or forecast;
- unlimited - the absence of a certain service life, suggesting the possibility of operating an unlimited amount of time;
- actual - the actual service life, which is calculated taking into account the actual factors of impact or operation;
- useful - the period of service during which the product is able to generate income or other benefits from use;
- long - the life of durable goods;
- guaranteed - the period of operation during which the manufacturer or seller fulfills its warranty obligations;
- recommended - the period established by the technical documentation, after which a decision is made on the further operation of the product, taking into account its condition and other factors.
Each of these types can be used in technical documentation depending on the type of object, device or product.
3 Calculation of the residual life of the gas pipeline by changing the impact strength of the metal
3.1
Correction factor for operating conditions when changing data on
temperature
where , are the parameters that take into account the influence
temperature changes on impact strength (Table 4).
3.2 Actual
the value of the impact strength of the material at the measuring point, taking into account the influence of temperature
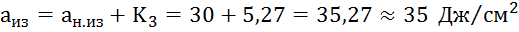
where is the actual measured value
impact strength of the material at the measuring point, .
3.3 Decline
crack resistance (impact strength) of pipe metal as a result of aging
where are the parameters reflecting the process
aging relative to the initial value of impact strength (Table 4); - the initial value of impact strength, (Table 2).
results
calculations are given in table. 3.
3.4 Meaning
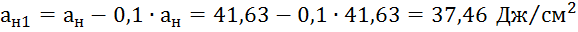
For
other time of operation of the gas pipeline, the calculation is carried out similarly
way. The results of the calculation are given in table. 3.
3.5
Calculation results table
Table
3
results
calculation
| 5 | 41,63 | 37,46 |
| 10 | 22,12 | 19,91 |
| 15 | 11,75 | 10,57 |
| 20 | 6,23 | 5,61 |
| 25 | 3,30 | 2,97 |
| 30 | 1,75 | 1,57 |
| 35 | 0,92 | 0,83 |
| 40 | 0,49 | 0,44 |
3.6
Plotting

Picture
2. Graph for determination of residual life in terms of toughness
black steel
Steel rusts. Especially quickly it rusts with prolonged contact with water. That is why the resource of steel risers and liners laid down in the regulatory documents, frankly, is not striking in duration.
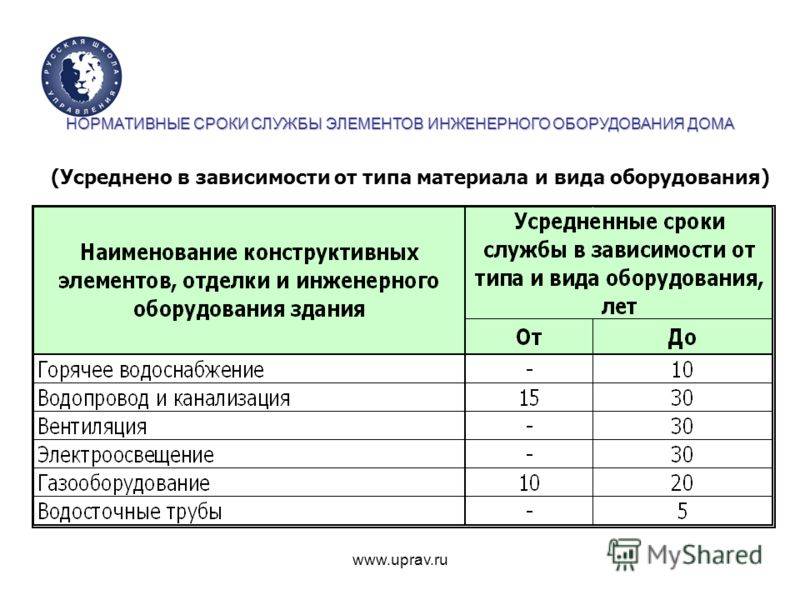
Standard service life
The main document establishing the normative service life of utilities in a residential building is VSN (departmental building codes) No. 58-88, adopted in 1988. They regulate the terms of maintenance, reconstruction and repair of buildings.
The document regulates the procedure for the repair and reconstruction of buildings
Appendix No. 3 to the document contains the following figures:
| Engineering system element | Standard service life, years |
| Riser or cold water supply from gas pipes | 15 |
| A riser or hot water supply from gas pipes in a building with a closed heat supply system (without hot water extraction from the heating system) | 10 |
| The same, in a building with an open heating system (DHW is taken from the heating circuit) | 15 |
| Towel dryers in the DHW system | 15 |
Destructive factors
What factors limit the service life of VGP pipes without anti-corrosion coating:
| Image | Description |
| Steel water risers. The first fistula that made the ceiling wet appeared in the ceiling | Corrosion. Pipe rusting is accelerated by a broken outer layer of paint, frequent water supply shutdowns (in this case, the unpainted inner surface of the pipe is in contact with air with high humidity) and poor ventilation in the bathroom (read - consistently high humidity). The first fistulas appear on longitudinal welds (VGP pipes GOST 3262 - electric welded), on threads where the thickness of the pipe walls is minimal, and in ceilings where the surface of the pipes is not ventilated and (in the case of cold water risers) is continuously wetted by condensate falling on them. |
| Lime deposits and rust have almost completely blocked the gap in the water pipe | Overgrowing of pipes with deposits (primarily lime salts) and rust. The overgrowth rate is directly proportional to the hardness of the water in the region: where it erodes sedimentary rocks on the way to the consumer, the gap in the water supply decreases much faster. The narrowing of the clearance leads to a drop in water pressure on plumbing fixtures connected to the water supply. |
| The diameter of the steel risers is selected, adjusted for a decrease in pipe throughput due to deposits | Pipeline diameter. The larger the internal section of the pipe, the longer it maintains an acceptable throughput. |
| The thicker the wall, the longer the pipe can resist corrosion. | Wall thickness. According to GOST 3262, ordinary, reinforced and lightweight pipes are produced. It is clear that those reinforced before the appearance of the first through fistulas will last longer. |
Chemical flushing can transform old plumbing
Real life
In the memory of the author, the minimum period of trouble-free service of the cold steel water supply system in the new building was only 10 years. The house was built and rented shortly before the collapse of the Soviet Union, in conditions of austerity on building materials and the actual inoperability of Soviet norms and standards. Lightweight VGP pipes, purchased for reasons of economy, quickly and massively began to leak on welded joints and threads.
In the photo - a typical condition of the cold water riser after 20 years of service
The oldest engineering systems made of black steel have been serving for more than half a century.
In addition to the large thickness of the walls of pipes, their longevity is facilitated by:
- Low humidity level;
- Lack of condensate on cold water pipes;
- Periodic painting of risers and eyeliners;
- Low content of mineral salts in water.
2 Calculation of the residual life of the gas pipeline by changing the ductility of the metal
2.1 Difference
average annual soil temperature at the level of the gas pipeline from the baseline
values
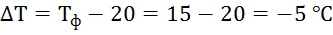
2.2 Corrective
operating conditions coefficient for changing temperature data
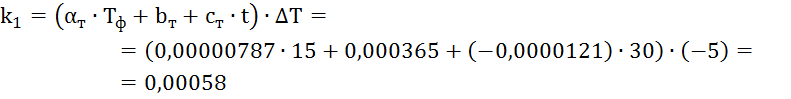
where — parameters taking into account the influence
temperature changes on plasticity (Table 3); — time of operation of the gas pipeline, years.
For
other time of operation of the gas pipeline, the calculation is carried out similarly
way. The results of the calculation are given in table. 2.
2.3 Decline
metal ductility due to aging
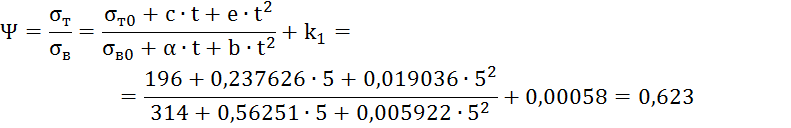
where is the yield strength for steels of group B,
MPa (Table 2); — tensile strength for steels
group B, MPa (Table 2); , - parameters reflecting the process
aging (Table 3).
For
other time of operation of the gas pipeline, the calculation is carried out similarly
way. The results of the calculation are given in table. 2.
2.4
Meaning
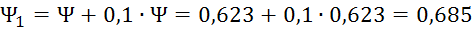
For
other time of operation of the gas pipeline, the calculation is carried out similarly
way. The results of the calculation are given in table. 2.
2.5
Calculation results table
Table
2
results
calculation
| 5 | -0,00093 | 0,623 | 0,685 |
| 10 | -0,00063 | 0,625 | 0,687 |
| 15 | -0,00033 | 0,629 | 0,692 |
| 20 | -0,00002 | 0,636 | 0,700 |
| 25 | 0,00028 | 0,645 | 0,709 |
| 30 | 0,00058 | 0,656 | 0,721 |
| 35 | 0,00088 | 0,669 | 0,735 |
| 40 | 0,0011853 | 0,683 | 0,752 |
| 45 | 0,00149 | 0,700 | 0,770 |
| 50 | 0,00179 | 0,718 | 0,789 |
| 55 | 0,00209 | 0,737 | 0,811 |
| 60 | 0,00240 | 0,758 | 0,834 |
| 65 | 0,00270 | 0,780 | 0,858 |
| 70 | 0,00300 | 0,803 | 0,883 |
| 75 | 0,00330 | 0,827 | 0,910 |
| 80 | 0,00361 | 0,852 | 0,938 |
| 85 | 0,00391 | 0,878 | 0,966 |
| 90 | 0,00421 | 0,905 | 0,995 |
| 95 | 0,00451 | 0,932 | 1,025 |
2.6
Plotting
Picture
1. Graph for determining the remaining service life by ductility
2.7 Residual life of the gas pipeline by change in plasticity
metal
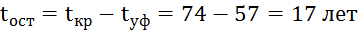
Service life extension
After diagnostics, gas equipment can be operated if it complies with the standards
Service life is not a constant category, it is calculated on the basis of calculations, tests and generalization of data obtained from the results of statistics from previous years. The operational period can be extended if the security of facilities where communications are installed is ensured. Experts evaluate the conditions for the use of pipes, after which they issue forecasts, which are scientifically based conclusions and suggestions.
The gas pipeline can be operated after the expiration of the warranty period, if the results of the diagnostics do not reveal any serious defects in the system, as well as the tendency to their occurrence.
There are the following rules for extending the operational life of a gas pipeline:
- regular inspection of communications;
- use of high-quality shut-off valves and control equipment;
- do not use the pipeline as a support under furniture or for attaching clotheslines.
General requirements for the operation of gas facilities
Everything related to the use of gas is clearly regulated by the state. household operation of gas communications must be carried out in strict accordance with the rules specified in the regulations approved by the government of the Russian Federation.
One of the fundamental documents is Federal Law No. 184 - FZ "On Technical Regulation". The chapters of this law define the principles of technical regulation, the procedure for carrying out various kinds of routine maintenance and checking for compliance with standards, the procedure for state control over the operation of gas equipment.
 In addition to the requirements for the operation of gas equipment, there are established technical standards for gas supplied for domestic use. Its characteristics must comply with current standards
In addition to the requirements for the operation of gas equipment, there are established technical standards for gas supplied for domestic use. Its characteristics must comply with current standards
Another document that gas communications must comply with is the National Standard of the Russian Federation (GOST R 54961-2012), which directly considers everything related to gas distribution systems and networks. It describes in detail the general requirements and standards for the operation of gas equipment systems, and establishes the life of gas pipelines.
The requirements specified in the National Standard must be observed by persons operating gas equipment. This applies to both legal entities and individuals, owners of private property and renters of premises, residents of apartment buildings, owners of hotels, restaurants, technical industries, etc.
So, in the course of constant use of the gas pipeline and gas equipment, it is necessary to perform the following types of work:
- Maintenance;
- current and major repairs in accordance with the plan;
- emergency repairs in case of disruption of the stable operation of the gas supply system;
- shutdown and dismantling of unused gas systems.
Work with gas equipment must be carried out with strict compliance with all safety requirements and recommendations specified in the technical documentation, which are developed in accordance with the specifics of the operation of each individual gas supply system.
It should be noted that in multi-apartment buildings, such processes as commissioning, reorganization of gas supply systems and decommissioning should be provided by special organizations accredited to carry out this kind of work.
 Everything related to gas distribution networks operated in production (operation, maintenance, repair and liquidation) is regulated by the Federal Law "On Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities" (N116-FZ) and technical regulations. They regulate the use and security of gas distribution networks
Everything related to gas distribution networks operated in production (operation, maintenance, repair and liquidation) is regulated by the Federal Law "On Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities" (N116-FZ) and technical regulations. They regulate the use and security of gas distribution networks
Living in residential and multi-apartment buildings, as well as in public and administrative buildings in which a gas supply system is installed, must have the following documents:
- executive and design documentation for the construction of gas networks;
- act of acceptance into operation of the gas consumption network;
- permission to launch gas equipment and put gas networks into operation.
If these documents are lost, they are restored by visual inspection, actual measurements and technical surveys, which will provide complete information on the operated gas equipment and pipelines.
When to calculate the residual life of the equipment
The need to determine the residual life of the equipment arises under the following circumstances:
1. Extension of the standard service life of equipment.
In the case when the technical documentation for the equipment (design, executive and operational) establishes a standard period of safe operation, and this period has come to an end, it is possible to extend the standard period of safe operation by calculating the residual life. Work to extend the service life of technical devices (equipment) is recommended to be planned and carried out in such a way that the appropriate decision is made before they reach the normatively established service life.
IMPORTANT: If the equipment is supervised by Rostekhnadzor and there is no standard operating life in the documentation, then the standard operating life is set to 20 years.
2. Determination of the market value of the equipment.
When it is necessary to carry out an assessment of the cost of equipment, the person interested in this assessment decides. In this case, the calculation of the remaining life can show a real picture of the state of the equipment and possible future expenses. Residual resource calculation identifies equipment that is not advisable to use and repair. It must be emphasized that the standard service life is determined during operation under certain conditions and may not reflect the actual condition of the equipment.
Example: For example, the enterprise has pressure equipment (boilers), due to circumstances, they are often operated in the limit mode, or their operating conditions are violated, leading to general and local overheating. Possible consequences of such exploitation will be as follows (Fig. 1,2).
 | |
| Fig.1. Crack in the coil of a convective superheater | Rice. 2. Changing the cross section of the pipe |
Taken together, the operation of boilers in extreme operating conditions or with violations (overheating) leads to significant wear and tear of equipment and an increase in depreciation costs. This will affect the market value of the equipment.
3. Use of equipment in extreme conditions.
Equipment manufacturers indicate in the documentation which operating conditions are acceptable. If the equipment is operated beyond the limits of permissible conditions, excess wear of the equipment occurs, which reduces the standard operating life. The actual wear of the equipment and its residual resource can be determined only by calculating the residual resource.
4. At the request of a representative of Rostekhnadzor.
A representative of Rostechnadzor, when conducting a scheduled or unscheduled inspection of a hazardous production facility, in accordance with Part 1 of Article 9 of Federal Law No. 116-FZ, has the right to issue an order from Rostechnadzor, which obliges to conduct an industrial safety review, and therefore to calculate the residual life. The decision is made on the basis of a visual and documentary check of the technical device.
5. In the event of an accident and damage to the technical device.
When an accident occurs at a hazardous production facility and the technical device is damaged as a result of the accident, it is required to conduct an industrial safety examination, and therefore to calculate the residual life. This norm is established by clause 2 of Article 7 of Federal Law No. 116-FZ.
DETERMINATION OF THE OPERATION LIFE OF A GAS PIPELINE BEFORE ITS DIAGNOSIS
According to, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2010 N 870, the duration of operation of gas pipelines, technical and technological devices is established during design based on the condition of ensuring the safety of objects of technical regulation with predicted changes in their characteristics and guarantees of the manufacturer of technical and technological devices.
To establish the possibility of operation of gas pipelines, buildings and structures and technological devices of gas distribution and gas consumption networks after the deadlines specified in the project documentation, their technical diagnostics should be carried out.
Deadlines for the further operation of objects of technical regulation of this technical regulation should be established based on the results of technical diagnostics.
Similar requirements are contained in, approved. by order of Rostekhnadzor N 542 dated November 15, 2013. Thus, technical diagnostics (industrial safety examination) of gas pipelines, technical and technological devices of gas distribution networks and gas consumption of TPPs should be carried out in order to determine and predict their technical condition in accordance with Federal Law dated July 21, 1997 N 116 -FZ "On industrial safety of hazardous production facilities".The service life of gas pipelines, technical and technological devices of gas distribution networks and gas consumption of TPPs are established on the basis of calculations and are indicated in the project documentation.
How to extend?
The extension of the assigned indicators of service time is carried out for certain types or groups of objects, taking into account their physical condition, maintaining safety requirements, environmental protection. The increase in service time is carried out in order to save material resources.
The procedure for extending the operating time for machinery and equipment is regulated by GOST 33272-2015 and assumes:
- determination of the need for extension work, submission and consideration of the relevant application;
- development, coordination and approval of relevant works;
- carrying out work according to the developed program, evaluating the results, developing technical solutions;
- preparation and execution of a decision on the possibility of extension, adjustment of the program;
- production control over the implementation of the adjustment.
Works are carried out taking into account the state of objects, components, components, materials and substances
This takes into account:
- the severity of the consequences in case of an error;
- actual technical condition;
- residual operating values;
- possible technical or economic limitations.
Attention! The request for the extension of the assigned indicators is submitted to specialized accredited organizations that are authorized to assess the object and develop adjustment programs.
What is the service life of a product: the concept of the term
In accordance with the terminology of GOST 27.002-2015, the service life is the calendar duration of product operation, starting from the first day of use until the transition to the limit state.
According to ch. VI Order of the Ministry of Antimonopoly Policy of the Russian Federation dated 05.20.1998 N 160, its establishment is mandatory for durable goods contained in the list of Government Decree No. 720, as well as other goods and components that, after a certain period of service, may pose a threat to life and safety.
In other cases, the service life can be set at the request of the manufacturer. The law emphasizes that the manufacturer is interested in this, because otherwise, he is liable for causing harm due to product defects for 10 years.
The service life is assigned units of time (years, months, hours, etc.). For individual products, it can be measured in other units of outcome (kilometers, meters, etc.).
Important! In accordance with Art. 5 of the RFP, service life - the period during which the manufacturer undertakes to be responsible for product defects, as well as to ensure that it can be used for its intended purpose.
3 Calculation of the residual life of the gas pipeline by changing the impact strength of the metal
3.1
Correction factor for operating conditions when changing data on
temperature
where , are the parameters that take into account the influence
temperature changes on impact strength (Table 4).
3.2 Actual
the value of the impact strength of the material at the measuring point, taking into account the influence of temperature
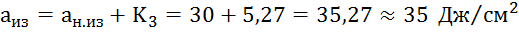
where is the actual measured value
impact strength of the material at the measuring point, .
3.3 Decline
crack resistance (impact strength) of pipe metal as a result of aging
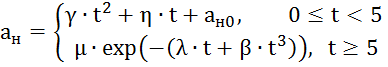
where are the parameters reflecting the process
aging relative to the initial value of impact strength (Table 4); - the initial value of impact strength, (Table 2).
results
calculations are given in table. 3.
3.4 Meaning
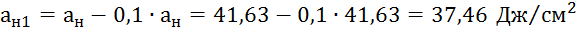
For
other time of operation of the gas pipeline, the calculation is carried out similarly
way. The results of the calculation are given in table. 3.
3.5
Calculation results table
Table
3
results
calculation
| 5 | 41,63 | 37,46 |
| 10 | 22,12 | 19,91 |
| 15 | 11,75 | 10,57 |
| 20 | 6,23 | 5,61 |
| 25 | 3,30 | 2,97 |
| 30 | 1,75 | 1,57 |
| 35 | 0,92 | 0,83 |
| 40 | 0,49 | 0,44 |
3.6
Plotting

Picture
2. Graph for determination of residual life in terms of toughness
5.2 Analysis of the initial data required to assess the technical condition and calculate the actual values of the safety factors of the gas pipeline section
5.2.1 Actual ratio
bearing capacity is one of the main parameters of the technical
condition of the operated section of the gas pipeline, which determines its design
reliability (probability of failure-free operation).
5.2.2
The general algorithm for assessing the technical condition of gas pipelines, necessary for
calculation of the actual safety factor, as a rule, provides for
sequential implementation of the following steps:
— collection and analysis of the original
technical information about the section of the gas pipeline where the evaluation is to be carried out
actual values of the safety factor;
— establishing patterns of change
determining parameters of the technical condition, limit states and their
criteria;
– damage analysis,
establishment of their mechanism and defining parameters of the technical condition
object;
— analysis of failures and limit
conditions, assessment of the consequences and criticality of failures in accordance with GOST
27.310;
— processing of received data and
assessment of the parameters of the stress-strain state of this section
gas pipeline;
— substantiation of solutions
about the possible modes of further operation of this section.
Note -
Additional information about the technical condition can be obtained from
the results of a diagnostic examination of the gas pipeline section with
involvement of a specialized organization in accordance with STO
Gazprom 2-2.3-095.
5.2.3 Mandatory
element of initial information for assessing the technical condition of the site
gas pipeline, in relation to which the coefficient values are calculated
reserve, is the design of the gas pipeline, including:
— pipe size (diameter, thickness
walls, steel grade, pipe manufacturing technology, specifications for
pipes);
- technological scheme
gas pipeline;
— specifications for pipes and
technological equipment used;
- pipe laying along the route
gas pipeline.
5.2.4 Considerations
the following information about the laying region:
- geographic information about
region (location, climate, terrain);
- gas pipeline location
regarding settlements and individual industrial facilities;
- gas pipeline location
regarding other communications (gas and oil pipelines and product pipelines,
power grids, railways and roads, etc.).
5.2.5 If necessary,
be collected and reviewed data on accidents and failures that occurred on
gas pipeline during construction and operation.
Note - The necessary information can be obtained
based on the information provided in the accident investigation reports. In acts
information about the place and time of the accident, the cause
occurrence, the scale of damage and the priority measures taken to
localization of the accident.
5.2.6 If necessary,
be collected and reviewed data on repair and repair
work performed on the pipeline.
Note - Data on performed on the gas pipeline
repair and restoration works are presented in the acts drawn up on the basis of
their implementation.
5.2.7 Consideration should be given to
analyze materials containing the results of surveys carried out
earlier on the gas pipeline. It is necessary to take into account the results of the current
operational monitoring performed by the regular services of the operating
organization, as well as the results of specialized surveys (if any
took place) carried out on the basis of additional agreements and programs
regular services and involved third-party organizations.
5.2.8 The received data should
be processed in order to identify the following parameters and groups of data on
gas pipeline, which must be taken into account when calculating the safety factors:
- characteristic types of damage
and mechanisms of degradation of the properties of the object;
- characteristic and maximum
the size of the damage;
— data on development kinetics
defects and damage;
- actual (available)
physical and mechanical properties of pipe metal in comparison with the initial indicators,
fixed at the time of delivery.