- open tank
- Installation of heating radiators
- The nuances of calculating the installation scheme of a heating system with forced circulation
- Top and bottom wiring
- Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
- System characteristics, pros and cons
- Planning and calculation
- Choosing a circulation pump
- Other Tips
- Pros and cons of two-pipe wiring
- How does it work
- Comparison with other types
- Roof and floors - meaning
- How to choose the diameter of pipes for heating
- Types of two-pipe systems
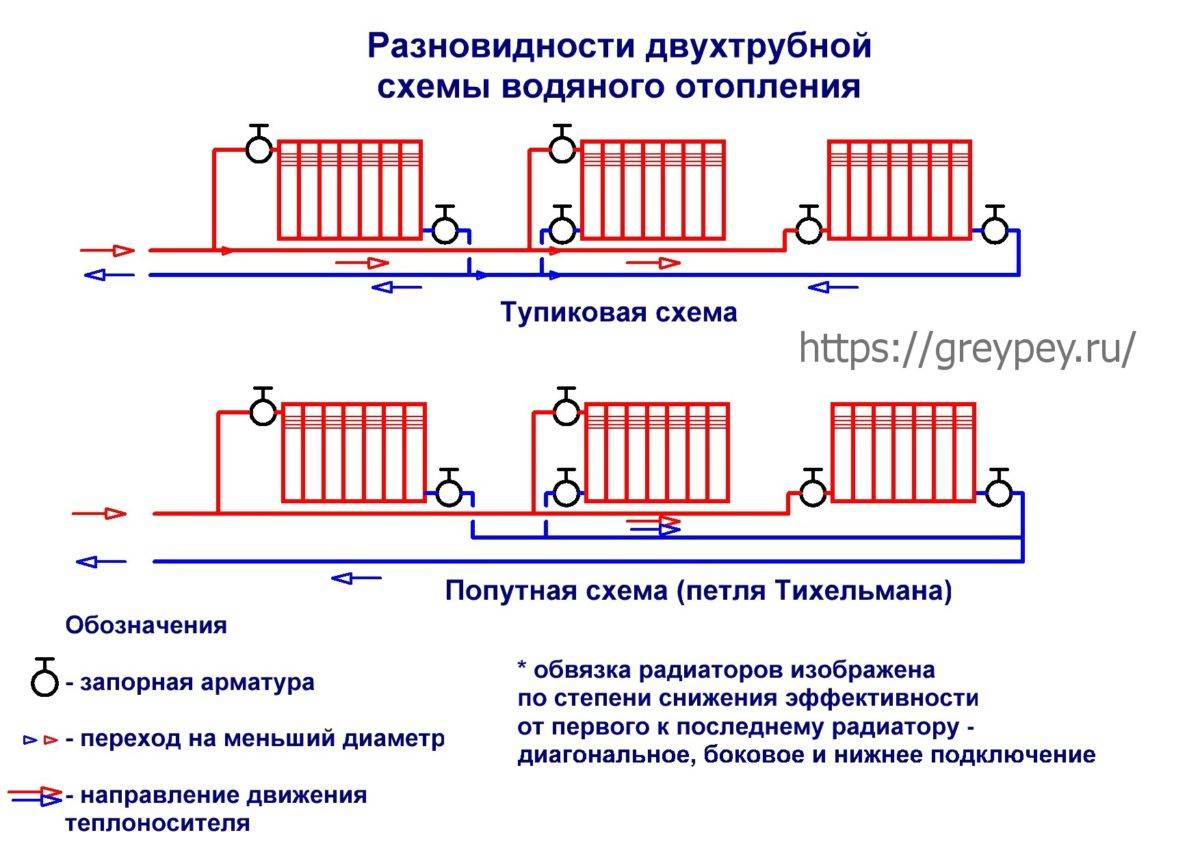
- Dead-end and flow-through
- open and closed
- Gravity and forced circulation
- Color combinations
open tank
An open expansion tank is a partially or completely open tank connected to the circuit in its highest section, immediately after the boiler. To prevent the liquid from overflowing over the edges of the vessel, there is a special pipe closer to the top: it serves to drain excess water into the sewer or into the street. When organizing the heating of one-story buildings, the compensating capacity is mainly installed in the attic. In order to avoid freezing of water in winter, the walls of the tank are additionally insulated.
Such heating systems are called open. Most often we are talking about non-volatile or combined heating.In this case, the coolant comes into direct contact with air: this leads to its natural evaporation and enrichment with oxygen.
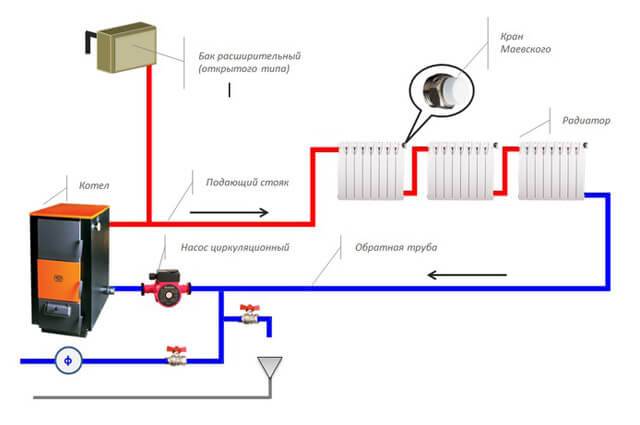
Open circuits are characterized by the following disadvantages:
- Precise observance of slopes (if gravity systems are used). This will allow the air seeping into the pipes to exit through the tank into the atmosphere.
- The need for constant monitoring of the water level in the tank. From time to time, the volume of the coolant has to be replenished, since part of it evaporates through the open top.
- Do not use non-freezing fluids that release toxic substances when evaporating.
- Oxygen saturation of the circulating fluid provokes corrosion processes inside metal steel heating radiators.

Strengths of open systems:
- It is possible not to carry out regular checks of the pressure level in the pipeline.
- Small leaks in the circuit will not prevent him from properly heating the home. The main thing is that there is enough liquid in the pipes.
- To make up for the loss of coolant, it is allowed to use a simple bucket. This is done by simply adding water to the expansion tank to the required level.
Installation of heating radiators
The next stage in the assembly of such a structure as a two-pipe heating system for a private house is the installation of radiators. They are usually hung on brackets under the windows. When installing them, observe the following rules:
- The distance from the bottom edge of each battery to the floor should be approximately 10 cm.
- The distance from the radiator to the window sill should be the same.
- The gap between the wall and the battery should not be less than 5 cm.
Radiators should not be mounted horizontally, but with a slight slope (no more than one degree).This will prevent stagnation of air in them. In the event that it is mounted horizontal two-pipe system heating, a Mayevsky crane will need to be attached to each radiator. It is necessary in order to remove air from the equipment during pressure testing and filling the system.
The nuances of calculating the installation scheme of a heating system with forced circulation
It depends on the competent installation of the heating circuit how long and trouble-free the heating in the house will work. Since the liquid in a closed system does not come into contact with the environment, it cannot evaporate. When heated, the coolant expands, thereby increasing the pressure inside the system. Since a closed heating system with forced circulation does not imply the possibility of water leaving the circuit, an expansion tank is needed that will take over the excess volume.
The tank is connected to the return pipeline, in the same way as the circulation pump, because. it is in this area that the heating of the coolant is minimal. Since hot liquid shortens the life of the pump, it is best to install it in a location where the water temperature is at its lowest.
Due to the fact that the pipes in the system with a pump have a smaller cross-sectional diameter, the volume of coolant circulating through them is less than the volume of liquid required for heating a similar at home without a pump. This factor has a positive effect on the operating conditions of the expansion tank; in a system with a pump, the tank does not fail longer. A forced circulation heating system does not cause as much inconvenience as natural circulation.
Also, modern models of heating boilers often have mechanisms for regulating the water temperature depending on the time of day, which work automatically. This nuance allows you to make the circuit work more economical.
A modern heating boiler has great potential and various adjustments, which facilitates its operation.
In order to increase the heating surface, a finned heating tube can be installed in the circuit. The well-known cast iron radiators are a type of finned tubes. Such designs, by increasing the surface of the heater, provide more uniform and high-quality heating of the room. Finned tubes are best installed in non-residential premises, because. due to their complex shape, they easily accumulate dust.
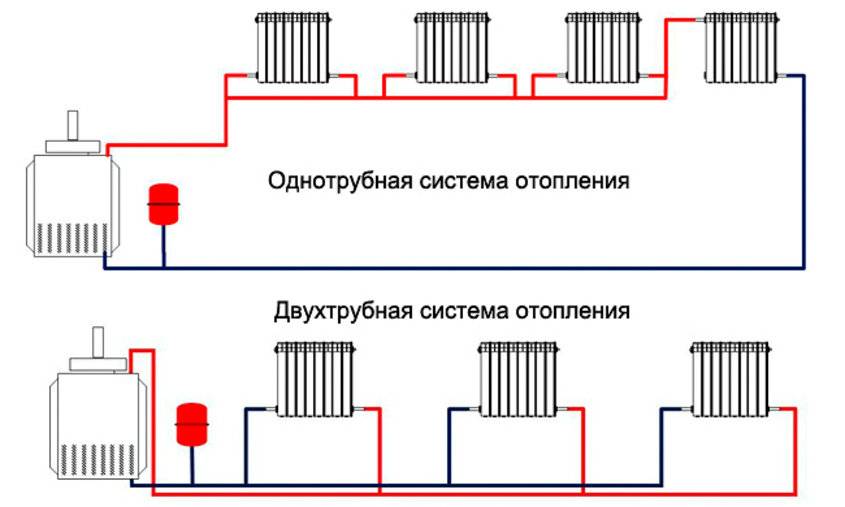
Unlike a gravity circuit, where there is no circulation in the heating system, a design with a pump requires a careful approach. One of the primary tasks that needs to be solved when designing is whether it will be a one-pipe forced circulation heating system or a two-pipe one. The first option is more economical and easier to install, but a two-pipe forced circulation heating system is more productive.
The heating scheme of a three-story house with gravity circulation is easily converted into a circuit with forced water circulation. To do this, attach a water pump and an expansion tank to it. Thus, they modernize the heating scheme and maintain a comfortable temperature in the home, regardless of the weather outside the window.
Choosing a circulation pump
When buying a circulation pump, take into account its reliability, the amount of electricity consumed and the clear principle of operation.Forced heating depends on the power of the unit and the pressure that it is able to create. When evaluating these characteristics, they start from the size of the room for which the pump is purchased for heating. So, for a private house with an area of 250 sq.m. you will need a pump with a pressure of 0.4 atmospheres and a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters. m/hour. If the house is spacious and its area exceeds 500 sq. m, then the required pump power is 11 cubic meters. m / h, and the pressure is 0.8 atmospheres. When buying a pump for a particular room, it is advisable to carry out an individual calculation that will take into account individual characteristics: the length of the circuit, the number of heating batteries, the diameter of the pipeline, the material of the pipes, the type of fuel.
WATCH VIDEO
Heating with forced circulation reduces heat transfer when air pockets form inside the pipeline. The movement of the coolant along the circuit is difficult. Air congestion occurs near radiators, in vertical sections of the circuit. To avoid this problem, a Mayevsky crane and automatic air vents are installed on each radiator. This is an effective way to eliminate system malfunctions associated with air entering the pipes. The forced circulation heating system is always on top.
Top and bottom wiring
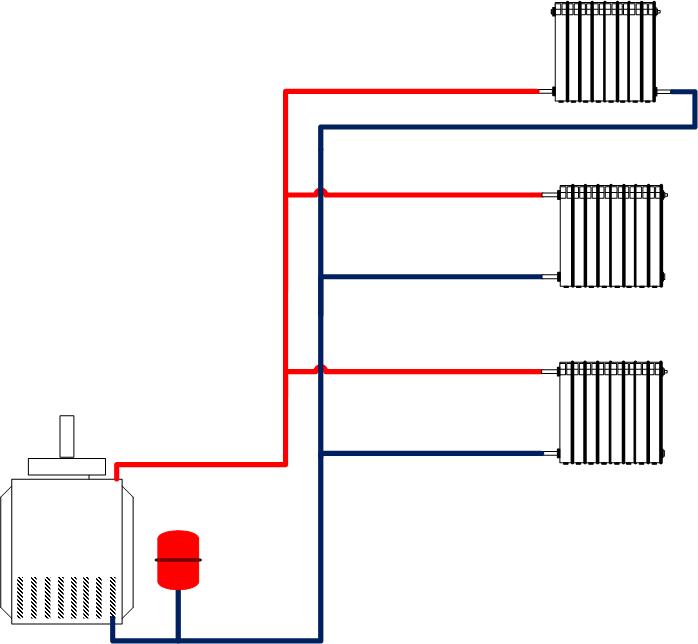
According to the method of distributing the supply, a system with an upper and lower supply is distinguished. With the upper wiring, the pipe goes under the ceiling, and from it the supply pipes go down to the radiators. The return line runs along the floor. This method is good in that you can easily make a system with natural circulation - the difference in height creates a flow of sufficient force to ensure a good circulation rate, you just need to observe the slope with a sufficient angle.But such a system is becoming less and less popular due to aesthetic considerations. Although, if you hide the pipes at the top under false or stretch ceiling, then only pipes to the devices will remain in sight, and they, in fact, can be monolithic into the wall. Upper and lower wiring are also used in vertical two-pipe systems. The difference is shown in the figure.
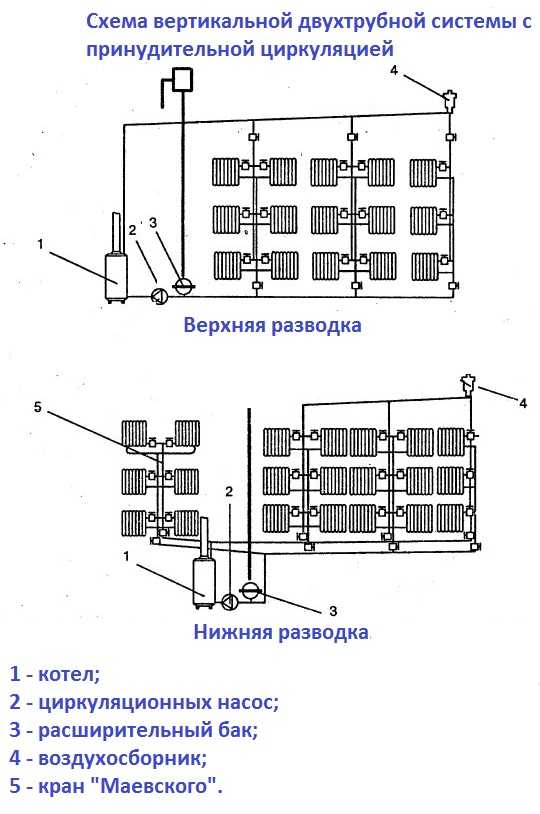
Two-pipe system with top and bottom coolant supply
With bottom wiring, the supply pipe goes lower, but higher than the return line. The supply tube can be located in the basement or semi-basement (the return line is even lower), between the rough and finish floors, etc. It is possible to supply / discharge coolant to radiators by passing pipes through holes in the floor. With this arrangement, the connection is the most hidden and aesthetic
But here you need to select the location of the boiler: in systems with forced circulation, its position relative to the radiators is unimportant - the pump will “push”, but in systems with natural circulation, the radiators must be above the level of the boiler, for which the boiler is buried
Two-pipe system different radiator connection scheme
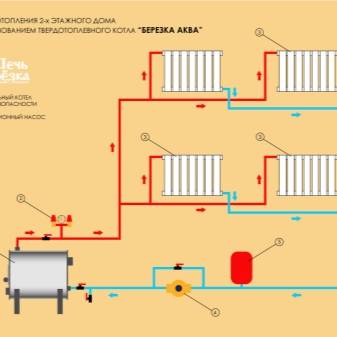
The two-pipe heating system of a two-story private house is illustrated in the video. It has two wings, the temperature in each of which is regulated by valves, the lower type of wiring. System with forced circulation, because the boiler hangs on the wall.
Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m).This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid of the circuit. It is mounted at the inlet to the heater, where the coolant temperature is the lowest.
With a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of storeys and the area of \u200b\u200bthe building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, therefore, when passing through the pipeline lines, the coolant does not cool down much. This contributes to a more even distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a sparing mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the scheme, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it. Now, if there is a power outage and the subsequent stop of the pump, the system will continue to work in convection mode.
- with one pipe
- two;
- collector.
Each can be mounted by yourself or invite specialists.
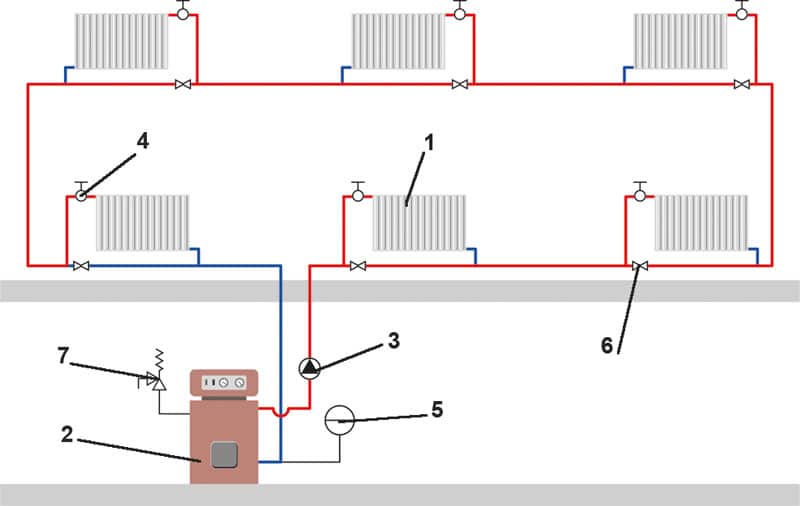
Variant of the scheme with one pipe
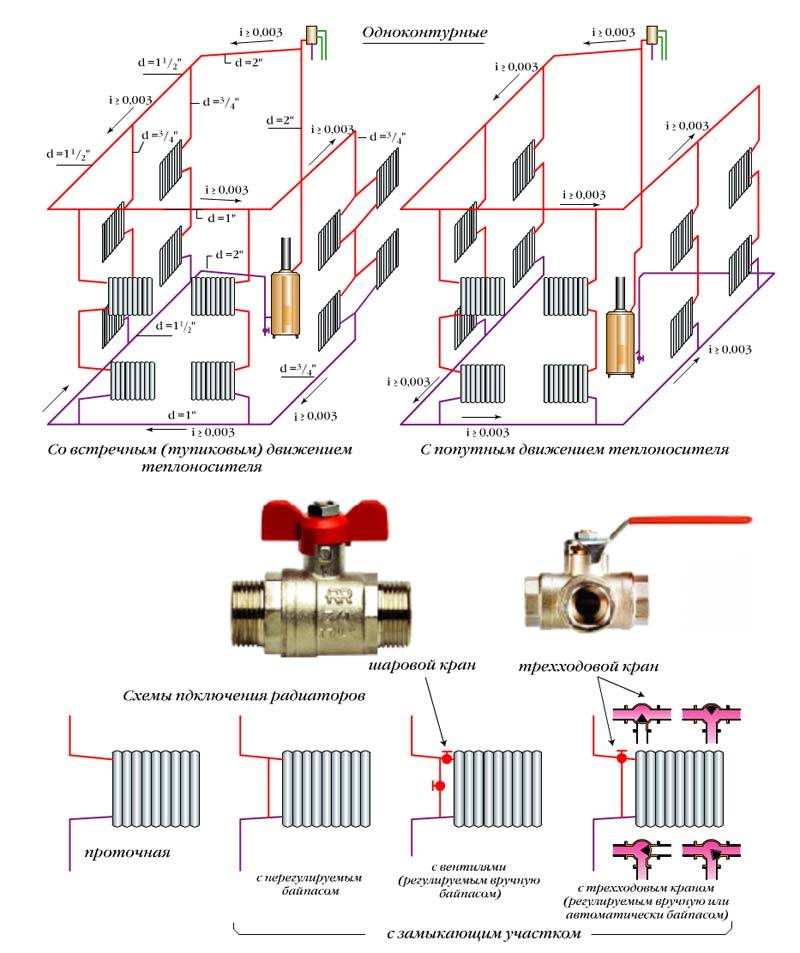
Shutoff valves are also mounted at the battery inlet, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. An air bleed valve is installed on top of the radiator.
Battery valve
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of heat carrier, that is, the farther from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is optional, but without it, the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
To get away from the uneven distribution of the heat carrier, schemes with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector.
Options for dead-end and passing schemes
The associated option makes it easy to control the level of heat, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
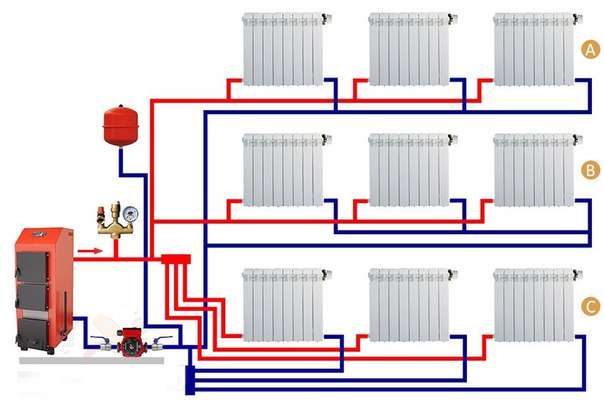
The collector circuit is recognized as the most effective, which allows you to bring a separate pipe to each radiator. Heat is distributed evenly. There is one minus - the high cost of equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
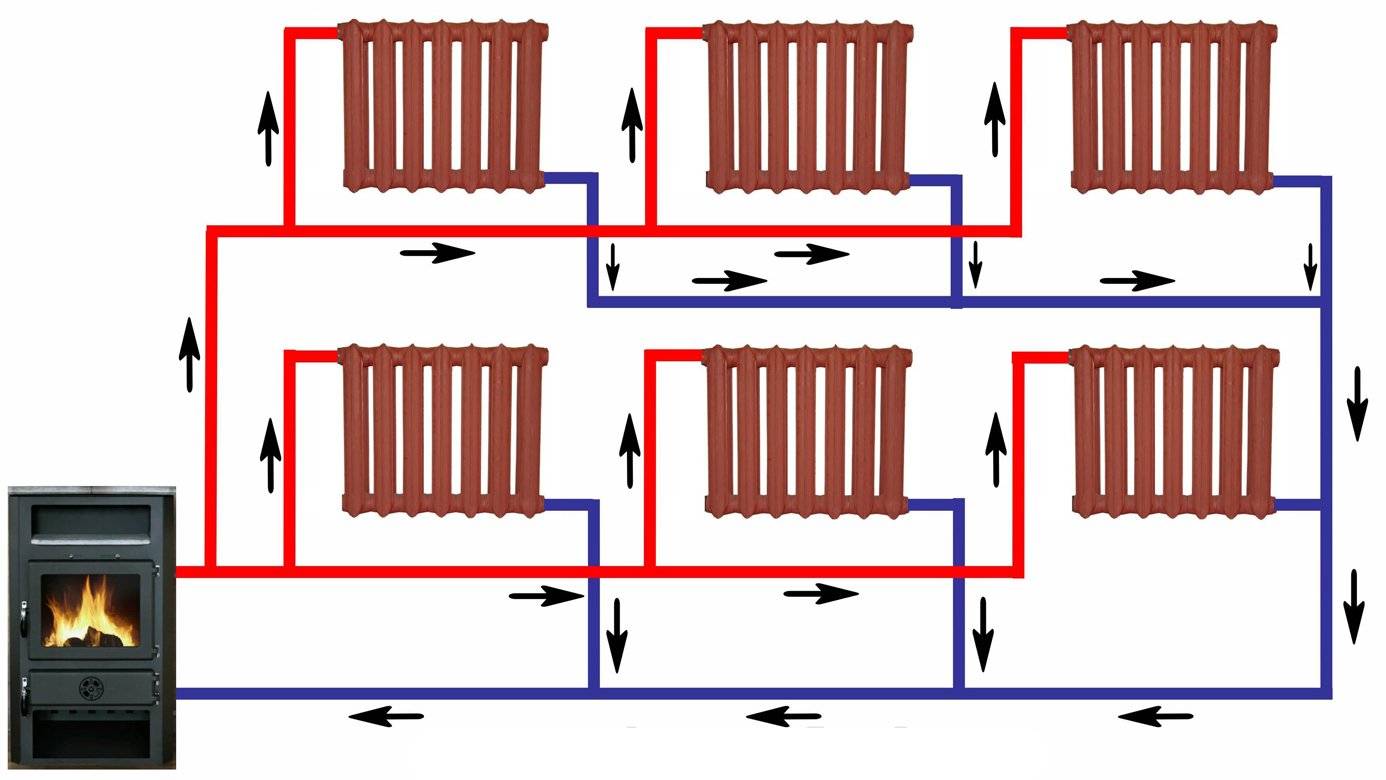
There are also vertical options for supplying heat carrier, which are found with the lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of a heat carrier passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical layout
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from a few tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of outbuildings and heated verandas, the position to the cardinal points. Focusing on these and many other factors, you should decide on the natural or forced circulation of the coolant.
A simple scheme of coolant circulation in a private house with a natural circulation heating system.
Heating schemes with natural coolant circulation are distinguished by their simplicity. Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat, it rises up, enters the pipes, is distributed over the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to go back to the boiler.That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly longer horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, diagonally);
- Possibility of mounting additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure drop below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses, it is best to use heating systems with forced circulation. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems, as more effective.
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - this is the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
System characteristics, pros and cons
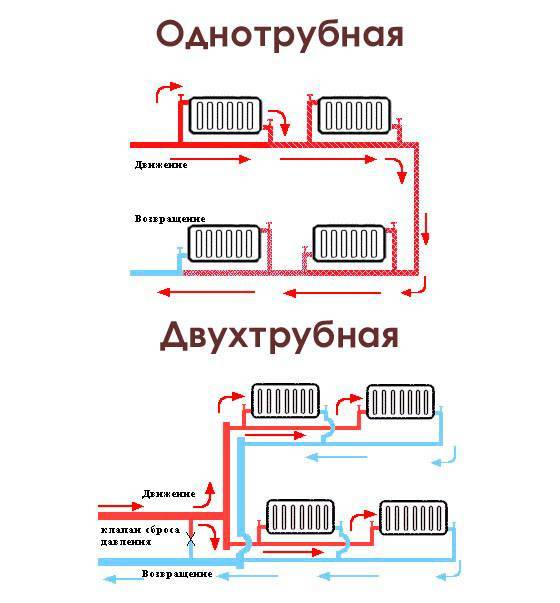
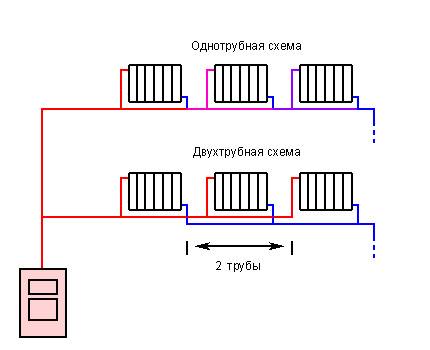
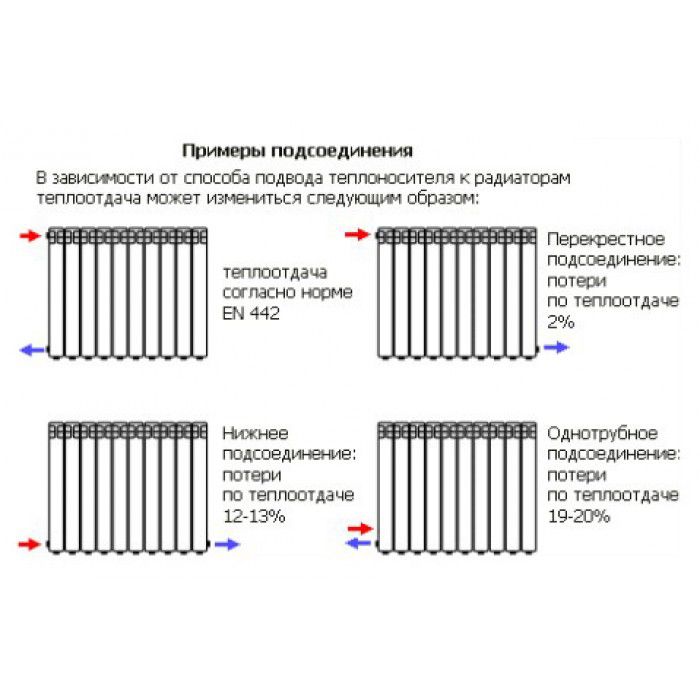
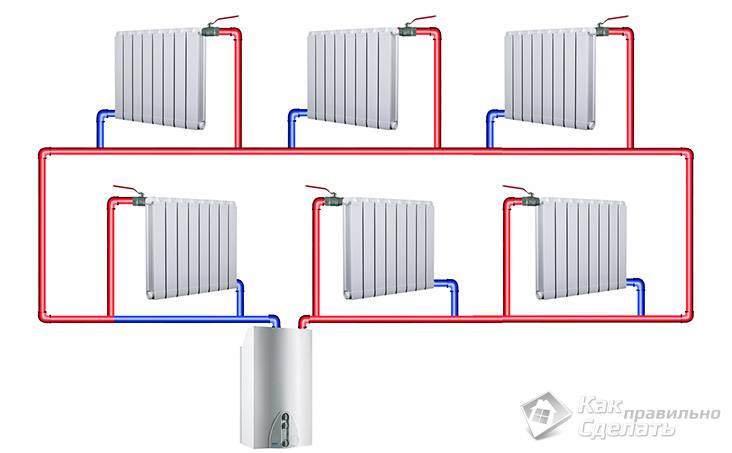
This kind of heating systems are distinguished by the fact that they contain two branches of the pipeline at once. The first one transfers the heated coolant through all elements of the system, and when it (the coolant) cools down, the second branch transports it back to the boiler. A significant advantage compared to a single pipe design is that the coolant is supplied to all elements at the same temperature, without losing heat when it reaches the most distant point in the system.
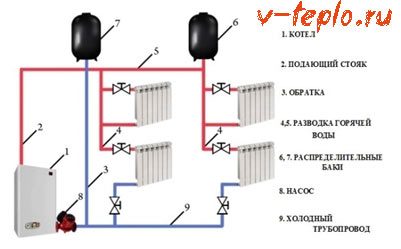
Important! It cannot be said that a double pipeline is the purchase of a double number of pipes.The fact is that in this case a large diameter of these pipes is not needed, and the dimensions of the valves and fasteners will also be smaller.
It turns out that the price difference between the two systems is insignificant.
Planning and calculation
When choosing the most optimal type of heating system for a private house, cottage, it is imperative to take into account the area of \u200b\u200bthe house
This is important, since, for example, a single-pipe scheme with natural circulation performs excellently only in houses with an area not exceeding 100 m2. And in a house with a significantly larger quadrature, it will not be able to work due to a sufficiently large inertia. It follows that the primary calculation of the pressure in the heating system and the design of the heating system are needed in order to find out and design a system whose use in the house will be more rational
At the stage of preliminary drawing up a plan, one should try to take into account all the specifics of the architecture of the building. For example, if the house is quite large and, accordingly, the area of the rooms to be heated is also large, the most rational would be to introduce a heating system with a pump that will circulate the heat carrier
It follows that the primary calculation of the pressure in the heating system and the design of the heating system are needed in order to find out and design a system whose use in the house will be more rational. At the stage of preliminary drawing up a plan, one should try to take into account all the specifics of the architecture of the building.For example, if the house is quite large and, accordingly, the area of the rooms to be heated is also large, it would be most rational to introduce a heating system with a pump that will circulate the heat carrier.
In this case, there are certain characteristics that the circulation pump must meet:
- long period of service;
- low level of electricity consumption;
- high power;
- stability;
- ease of operation;
- absence of mechanical vibrations and noiselessness during operation.
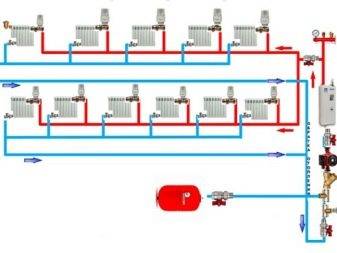

When planning a heating system, whether it is a private or multi-storey building, the most difficult and critical phase is the hydraulic calculation, in which it is necessary to establish the resistance of the heating system.
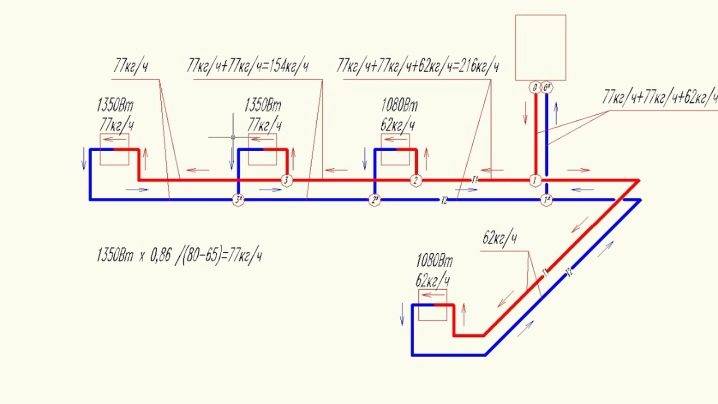
Calculations are made according to a previously created heating scheme, on which all the components in the system are marked. Implement hydraulic calculation of a two-pipe heating system using axonometric projections and formulas. The design object is taken as the busiest ring of the pipeline, divided into segments. As a result, the acceptable cross-sectional area of the pipeline, the required surface area of the radiators, and the hydraulic resistance in the heating circuit are established.
Calculations of hydraulic characteristics are carried out according to various methods.
The most common:
- calculations by the method of specific linear pressure losses, providing for equivalent changes in the temperature of the coolant in all components of the wiring;
- calculations on resistance parameters and conductivity indicators, providing for variable temperature fluctuations.
The result of the first method is a clear physical picture with a specific distribution of all observed resistances in the heating circuit. The second calculation method makes it possible to obtain clear information about water consumption, about the temperature values in each element of the heating system.
Choosing a circulation pump
The two-pipe heating system of a private house is usually supplemented by another important element - a circulation pump. In fact, water can move through pipes in a natural way - due to the temperature difference in the supply and return lines. However, for buildings of a large area, such systems are not very suitable. The inclusion of a pump in the design allows you to distribute heat throughout the rooms much more evenly.
Of course, you need to choose this equipment correctly. When buying, you should pay attention mainly to two important parameters:
- pump performance. Calculated by the formula Q = N /
- (t 2- t 1) (where Q is the actual performance, N is the boiler power, t1 is the return water temperature, t2 is the supply water).
- Diameter of connected pipes. This information is indicated on the label by the manufacturer.
- If the boiler is located not in the basement, but right in the house, it is worth considering such an indicator as the noise of the pump.
Other Tips
The living room with the kitchen can be combined and decorated with various shortcomings.
It is important to calculate and anticipate everything in advance.
Designers and craftsmen share tips that will help you avoid problems during repairs and arrangements:
The result depends on how detailed the project will be.Oddly enough, it is worth considering the growth of loved ones and relatives. It is also advised to calculate the approximate number of possible guests.
You can get rid of the smell of food if you install a strong hood or ventilation system.
Small models are more suitable for housewives who cook little.
If a sleeping place is planned in the living room, then it is important that the ringing of appliances and other kitchen utensils is not heard. Silent dishwashers and other appliances will come in handy.
In addition, you can install a sliding door and install a soundproof partition. If there is sensitivity to ultraviolet light, the owners hang thick curtains made of opaque fabric.
If household appliances do not fit the direction of the interior, they are hidden behind furniture or put away in kitchen cabinets.
When installing fixtures and lamps are guided by several criteria
It is important that the light falls evenly throughout the space. Particularly bright lighting is preferred in the kitchen area and where the dining table is installed
In the living room, designers create a subdued atmosphere using wall lights and table lamps. Multi-level stretch ceilings with LED strip also look good in this room.
Moisture-resistant finishing materials are more durable and easy to clean. Thus, they retain their appearance for a long time.
The kitchen, combined with the living room, combines:
- personal tastes of the owners;
- reliable finishing materials;
- current design ideas;
- convenience;
- trends. The best photos of living room kitchen design































Pros and cons of two-pipe wiring
For ease of perception, we have combined the advantages and disadvantages of all the above systems into one section.First, let's list the key positives:
- The only advantage of gravity over other schemes is independence from electricity. Condition: you need to select a non-volatile boiler and make the piping without connecting to the house electrical network.
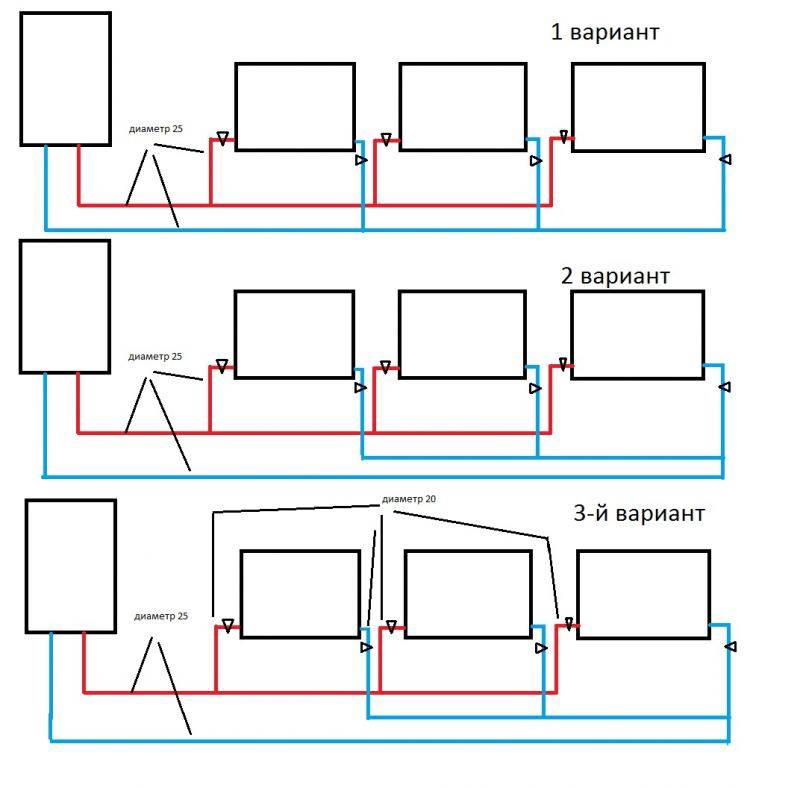
- The shoulder (dead-end) system is a worthy alternative to the "Leningrad" and other single-pipe wiring. The main advantages are versatility and simplicity, thanks to which the two-pipe heating scheme of a house of 100-200 m² is easily mounted by hand.
- The main trump cards of the Tichelman loop are hydraulic balance and the ability to provide a large number of radiators with coolant.
- Collector wiring is the best solution for hidden pipe laying and full automation of heating operation.

The best way to hide pipes is to lay them under the floor screed
- small sections of distributing pipes;
- flexibility in terms of laying, that is, the lines can run along various routes - in floors, along and inside walls, under ceilings;
- various plastic or metal pipes are suitable for installation: polypropylene, cross-linked polyethylene, metal-plastic, copper and corrugated stainless steel;
- all 2-pipe networks lend themselves well to balancing and thermal regulation.
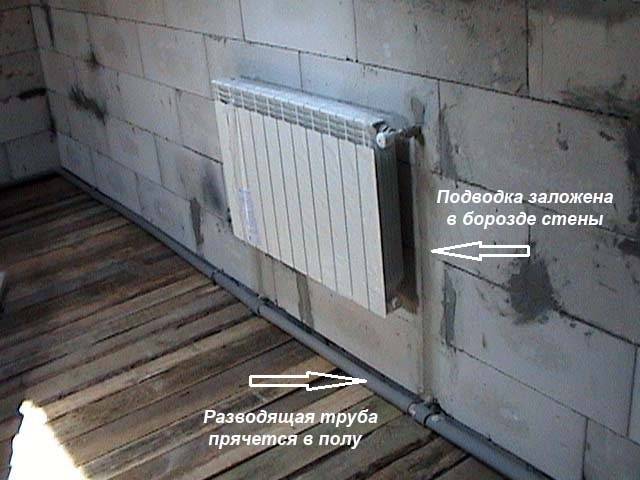

To hide pipe connections, you need to cut grooves in the wall
We note a secondary plus of gravity wiring - the ease of filling and removing air without the use of valves and taps (although it is easier to vent the system with them). Water is slowly supplied through the fitting at the lowest point, air is gradually forced out of the pipelines into an open-type expansion tank.
Now for the major drawbacks:
- The scheme with natural water movement is cumbersome and expensive.You will need pipes with an inner diameter of 25 ... 50 mm, mounted with a large slope, ideally steel. Hidden laying is very difficult - most of the elements will be in sight.
- No significant disadvantages were found in the installation and operation of dead-end branches. If the arms are very different in length and number of batteries, balance is restored by deep balancing.
- Tichelman's ring wiring lines always cross doorways. You have to make bypass loops, where air can subsequently accumulate.
- Beam-type wiring requires financial costs for equipment - manifolds with valves and rotameters, plus automation equipment. An alternative is to assemble a comb from polypropylene or bronze tees with your own hands.
How does it work
 Principle of operation
Principle of operation
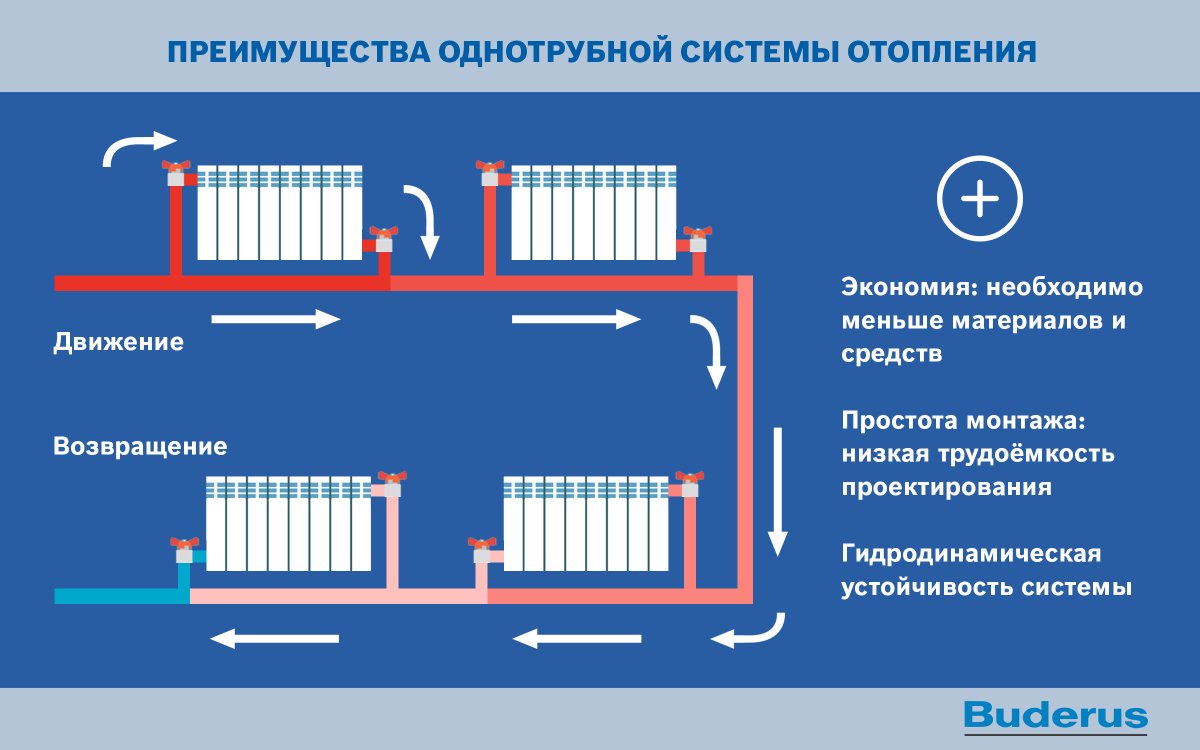
The scheme of such a heating system is quite simple. At the heart of everything is any boiler. It heats the coolant supplied through the pipe coming from the boiler. Why is such a scheme called one-pipe? Because one pipe is laid along the entire perimeter, which comes from the boiler and enters it. In the right places, radiators are installed on the brackets and connected to the pipe. The coolant (most often water) moves from the boiler, filling the first radiator in the node, then the second one, and so on. At the end, the water returns to the starting point and the cycle repeats. There is a continuous circulation process.
It should be noted that by assembling such a scheme, one may encounter one difficulty. Since the rate of advance of the coolant can be small, temperature losses are possible. Why? If we talk about a two-pipe system, then the principle of its operation is as follows: water enters the battery through one pipe, and leaves it through the other.In this case, its movement passes immediately through all the radiators, and there is no heat loss.
In a single-pipe system, the coolant enters all batteries gradually and, passing through them, loses temperature. So, if the temperature of the carrier was 60˚C when leaving the boiler, after passing through all pipes and radiators, it can drop to 50˚C. What to do in this case? To overcome such fluctuations, it is possible to increase the heat capacity of the batteries at the end of the chain, increasing their heat transfer, or to increase the temperature in the boiler itself. But all this will lead to additional costs that are unprofitable and make the cost of heating more expensive.
To get rid of such a problem without high costs, you need to increase the speed of the coolant through the pipes. There are 2 ways to do this:
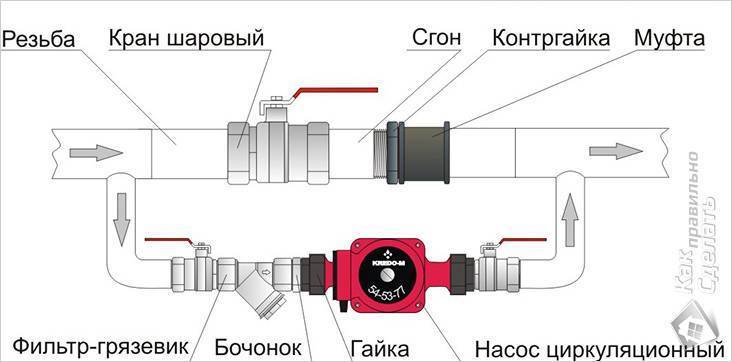 Pump installation technology in the heating system
Pump installation technology in the heating system
Install a circulation pump. So you can significantly increase the speed of movement of water in the system. In this case, the heat loss at the outlet will be significantly reduced. The maximum loss can be several degrees. These pumps are powered by electricity. It should be noted that for country houses where electricity is often cut off, this option will not be ideal.
Installing a collector directly behind the boiler
Install the booster manifold. This is a high straight pipe, thanks to which the water, passing through it, gains high speed. Then the coolant in the natural circulation system makes a full circle faster, which also solves the problem of heat loss. It is especially good to use this method in a multi-storey building, since work will be inefficient in a one-story building with low ceilings.For normal functioning of the collector, its height must be more than 2.2 m. You should know that the higher the accelerating collector is, the faster, more efficient and quieter the movement in the pipeline will be.
In such a system, there must be an expansion tank, which is best installed at the top point. It acts as a stabilizer, controlling the increase in the volume of the coolant. How does he work? When heated, the volume of water increases. These excesses enter the tank, preventing overpressure from occurring. When the temperature drops, the volume decreases and from the expansion tank goes back to the heating network.
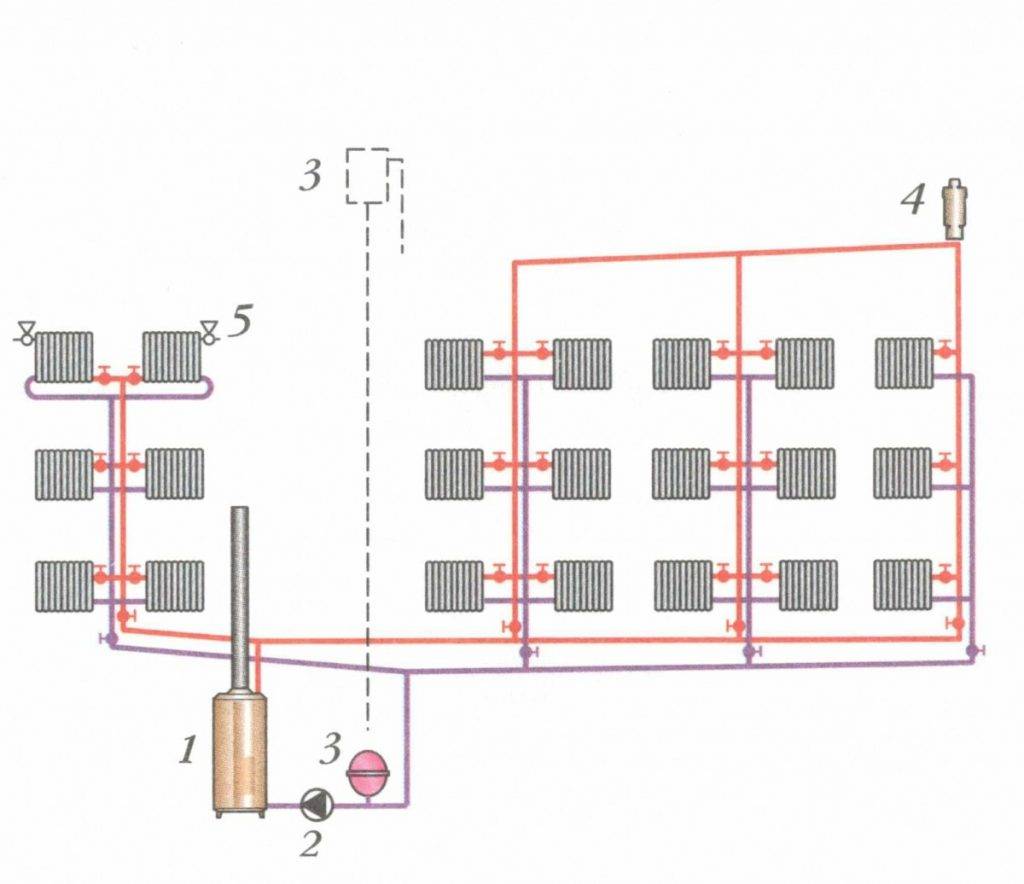
That's all principle of operation of a one-pipe system heating. This is a closed circuit, which includes a boiler, main pipes, radiators, an expansion tank and elements that provide water circulation. Distinguish forced circulation, when all the work is done by the pump, and natural, in which the accelerating manifold is mounted. The difference of this design is that it does not provide a reverse-action pipe through which the coolant returns to the boiler. The second half of this wiring is called the return line.
Comparison with other types
In the lower tie-in, the supply line is laid from below, next to the return line, therefore the coolant is directed upwards along the supply risers. Both types of wiring can be designed with one or more circuits, dead-end and associated water flow in the supply pipe and return.
Natural circulation systems with bottom connections are very rarely used, since they require a large number of risers, and the point of such a tie-in of pipes is to minimize their number.With this in mind, such designs most often have forced circulation.
Roof and floors - meaning
In the upper connection, the supply line is above the level of the radiator. It is mounted in the attic, in the ceiling. The heated water comes up, then - through the supply risers it evenly spreads over the batteries. Radiators must be above the return. To exclude air accumulation, a compensating tank is installed at the topmost point (in the attic). Therefore, it is not suitable for houses with a flat roof without an attic.
The wiring from the bottom has two pipes - supply and discharge - radiators must be above them. It is very convenient for removing air congestion with Mayevsky cranes. The supply line is located in the basement, in the basement, under the floor. The supply pipeline must be higher than the return. An additional line slope towards the boiler minimizes air pockets.
How to choose the diameter of pipes for heating
In the article we will consider systems with forced circulation. In them, the movement of the coolant is provided by a constantly operating circulation pump.
When choosing the diameter of pipes for heating, they proceed from the fact that their main task is to ensure the delivery of the required amount of heat to heating devices - radiators or registers. For the calculation, the following data will be needed:
- General heat loss of a house or apartment.
- The power of heating devices (radiators) in each room.
- Pipeline length.
Method of distributing the system (single-pipe, two-pipe, with forced or natural circulation).
That is, before proceeding with the calculation of pipe diameters, you first calculate the total heat loss, determine the boiler power and calculate the radiator power for each room.
It will also be necessary to decide on the method of wiring. Based on these data, draw up a diagram and then only proceed with the calculation.
What else you need to pay attention to. On the fact that the outer diameter is marked for polypropylene and copper pipes, and the inner diameter is calculated (subtract the wall thickness)
For steel and metal-plastic, when marking, the internal size is affixed. So don't forget this little thing.
Types of two-pipe systems
Two-pipe systems are classified according to several criteria:
- the direction of movement of the liquid medium (dead-end or flow-through);
- type of circuit (open or closed);
- the principle of fluid movement (natural or forced circulation).
Dead-end and flow-through
In a flow type system, the direction of fluid movement does not change in the supply and return pipes. The dead-end scheme is different in that the coolant moves in opposite directions in the supply and discharge pipes. Radiators are mounted on the supply and return pipes after the bypass (jumper), which allows, if necessary, to turn off a separate heating device without disturbing the operation of the entire heating circuit.
open and closed
Expansion tank (thermal expansion compensation tank) is an open tank or a sealed tank equipped with an elastic membrane. An open container is installed at the top of the circuit, water must be added to it regularly.The membrane tank is designed to work under pressure, its use reduces the risk of corrosion of metal elements, since the coolant does not come into contact with air.
Gravity and forced circulation
Gravity (with natural circulation) systems ensure the movement of the coolant through the pipes due to a change in the density of the liquid with increasing temperature and due to the action of gravity. To ensure efficient circulation, it is necessary to correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes in all sections of the circuit and mount them at a certain slope. The composition of such a system usually includes an open expansion tank.
Forced circulation of fluid in the circuit is provided by a special pump. The energy-dependent system operates under increased pressure and requires the installation of a membrane tank, air vents. The popularity of this option is based on the high efficiency and ease of use of the system.
Color combinations
Stylists are advised to take into account such nuances:
- direction in the interior;
- combination of shades;
- illumination.

It is much easier to choose a palette if the style for the kitchen with the living room is already chosen. For example, neoclassicism and Provence are characterized by their own combinations. In a classic interior, designers combine pastel colors, pale colors, which are slightly diluted with dark shades.
In French country houses, you can often see soft blue, pink, pistachio colors. Art Deco designers make up objects and finishing materials in black and white, sometimes beige and brown or silver and black. The main thing is to choose a shade for the walls. White will become universal, it will expand the space, and later you can paint over them with any paint.
However, in the cooking area, the whiteness ceases to look fresh. Beige or gray shades will be more practical. This background will accentuate other colors. In a monochrome interior, designers advise to glue wallpapers of an unusual color or with a photo print.