- Features of heating an apartment in a multi-storey building
- Two-pipe dead-end heating system: diagrams and description
- What is
- Types of dead-end systems
- Characteristics of one-pipe and two-pipe systems
- Why choose such a system?
- Classification of one-pipe heating systems
- Bottom and horizontal wiring of the system and its diagrams
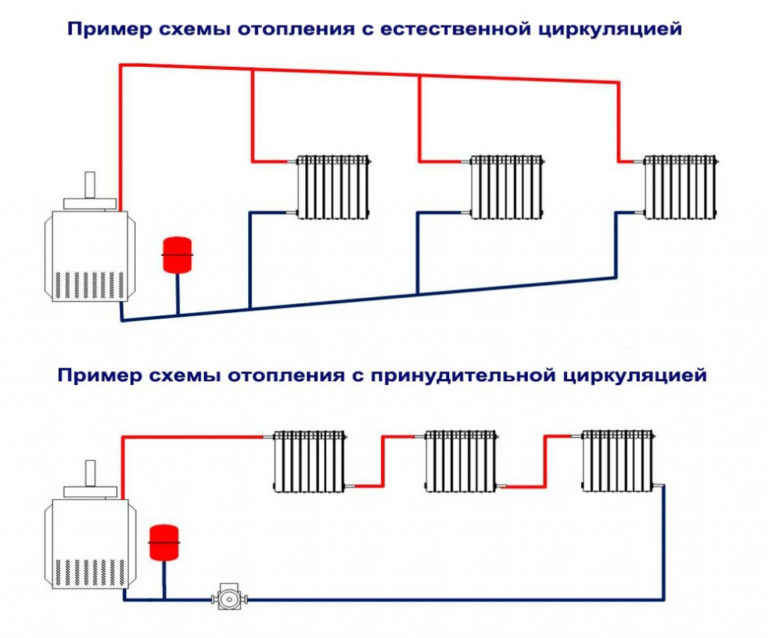
- Scheme with natural circulation
- Scope and disadvantages of gravity
- Design Tips
- Two-pipe heating system with top wiring
- Selection of pipes by diameter
- Two-pipe system with bottom wiring
- Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
- Features of mounting a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
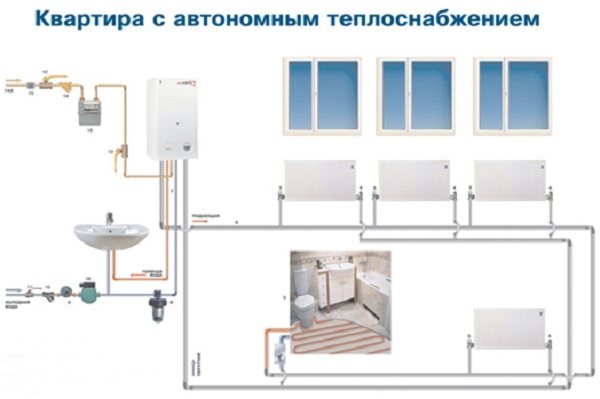
Features of heating an apartment in a multi-storey building
After carefully reading the instructions for the heating scheme of a multi-storey building, you can make sure that all norms and requirements must be observed without fail.
The scheme of the heating system of an apartment building provides for its competent installation, thanks to which it is possible to achieve such a temperature and humidity.
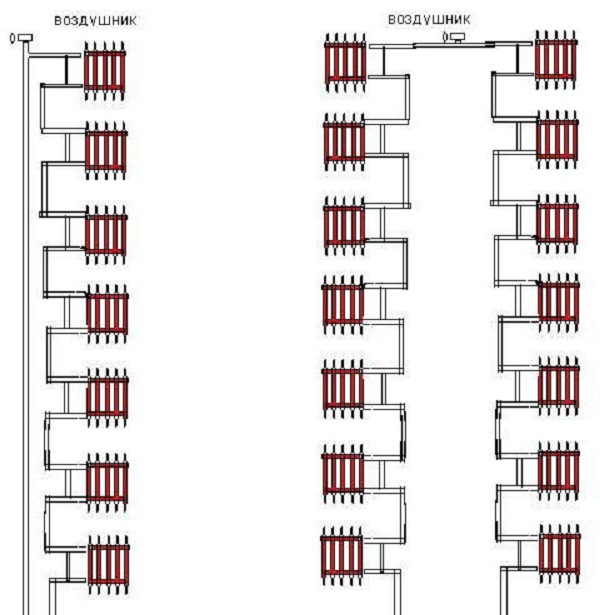
In the process of designing such a heating scheme, highly qualified specialists should be invited who will be able to qualitatively calculate all the necessary aspects for work.They must also ensure that uniform pressure of the coolant is maintained in the pipes. Such pressure should be the same both on the first and on the last floor.
The main feature of the modern multi-storey building heating system is manifested in work on superheated water. This coolant comes from the CHP and has a very high temperature - 150C with a pressure of up to 10 atmospheres. Steam is formed in the pipes due to the fact that the pressure in them rises greatly, which also contributes to the transfer of heated water to the last houses of the high-rise building. Also, the heating scheme of a panel house assumes a considerable return temperature of 70C. In the warm and cold seasons, the water temperature can vary greatly, so the exact values \u200b\u200bwill depend solely on the characteristics of the environment.
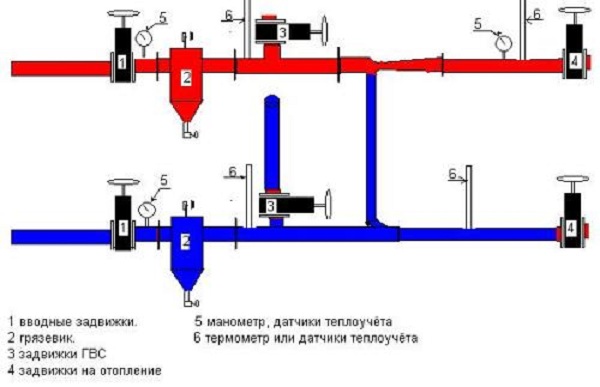
As you know, the temperature of the coolant in the pipes that are installed in a multi-storey building reaches 130C. But such hot batteries in modern apartments simply do not exist, and all due to the fact that there is a supply line through which heated water passes, and the line is connected to the return line using a special jumper called "elevator node".
Such a scheme has many features, since such a node is designed to perform certain functions. The coolant with a high temperature must enter the elevator unit, which performs the main function of heat exchange. The water reaches a high temperature and with the help of high pressure passes through the elevator to inject the coolant from the return. In parallel, water is also supplied from the pipeline for recirculation, which occurs in the heating system.
Such a heating scheme for a 5-storey building is the most efficient, therefore it is actively installed in modern multi-storey buildings.
This is how heating in an apartment building looks like, the scheme of which provides for the presence of an elevator unit. On it you can see many valves that play an important role in heating and uniform heat supply.
When installing heating in an apartment building, the scheme should also provide for the presence of such valves at all possible points so that in the event of an accident it is possible to shut off the flow of hot water or reduce pressure. This is also facilitated by various collectors and other equipment that operates in automatic mode. Therefore, this technique provides greater heating performance and efficiency of its supply to the last floors.
Depending on these aspects, the coolant can be supplied both from top to bottom and from bottom to top. Some houses have special risers that act as a supplier of hot water up and cold down. Therefore, in many apartments, cast-iron batteries are installed, which are very resistant to temperature extremes.
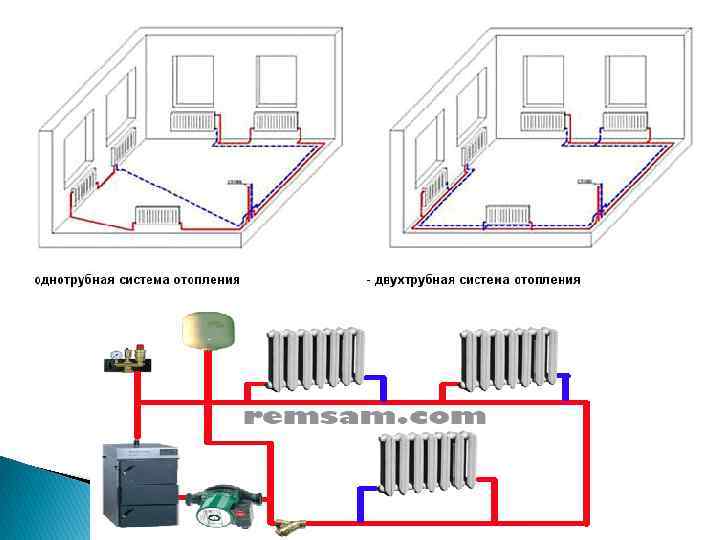
Two-pipe dead-end heating system: diagrams and description
 Heating schemes in residential buildings of the private sector of housing construction are dead-end two-pipe heating systems, single-pipe systems are rarely used.
Heating schemes in residential buildings of the private sector of housing construction are dead-end two-pipe heating systems, single-pipe systems are rarely used.
In practice, there are several variants of schemes. Each of them is mounted in accordance with the specific conditions of the dwelling.
What is
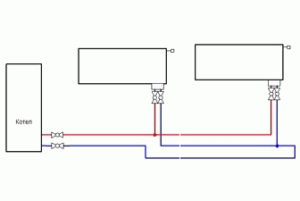 A heating system mounted in such a way that the rings through which the coolant passes are not equal to each other is called a dead end.
A heating system mounted in such a way that the rings through which the coolant passes are not equal to each other is called a dead end.
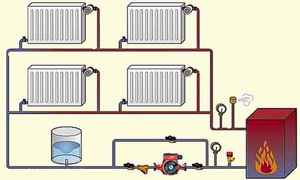
The figure shows a general diagram of such a system, where there are two pipelines:
- With heated coolant. The supply line is marked in red in the diagram.
- With cooled coolant. The return line is marked in blue on the diagram.
According to this scheme, the flow of heated coolant after leaving the gas boiler flows through the supply pipeline towards the radiator system. When it enters the radiator, in the process of passing through it, the heated flow of the coolant gives off heat. After cooling, the coolant flow immediately goes into the return line, moving towards the gas boiler.
An alternative to a dead-end system is an associated heating system, but the so-called associated heating system has a different scheme for the passage of the coolant through the system.
Types of dead-end systems
There are two options for such systems:
- horizontal, where horizontal piping is used;
- vertical, where vertical piping is used.
horizontal layout
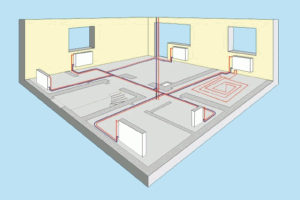 According to this scheme, the supply and return pipelines are horizontal until they are connected to the radiators.
According to this scheme, the supply and return pipelines are horizontal until they are connected to the radiators.
In this case, the diameters of the pipelines are the same, and the standard sizes of the mounting components are the same as the diameters of the pipelines. This greatly simplifies the installation of these systems and, accordingly, saves both money and time.
During operation of this heating system, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet of the radiators is approximately the same. But there is a drawback. The fact is that with large areas and long pipelines it is difficult to balance individual radiators.
A type of two-pipe dead-end horizontal system is a scheme with a central line
It is important to know that it is most expedient to mount such a wiring in a hidden version either in the floor during its concreting, or in the wall under a layer of plaster. Then the design of the living space will not be violated
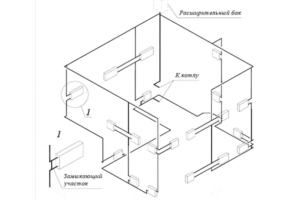
 This technology is a connection without rubber seals. The pipe material itself is a sealant.
This technology is a connection without rubber seals. The pipe material itself is a sealant.
However, when mounted to radiators, there is a problem with crossing pipelines, since the pipelines will protrude from the screed.
It is important to know that the solution to this problem is the use of a cross. When exiting to the radiator, the crosspiece makes it possible, without going beyond the mounting plane, to bypass the main pipeline
This system allows you to connect:
These circuits are connected using a mixing module, which consists of:
- circulation pump, which gives the dynamics of movement to the coolant;
- mixing valve with temperature sensor.
This module makes it possible for circuits to operate independently from the main system. In this mode, they themselves do not affect the operation of the overall system.
Heating scheme in vertical design
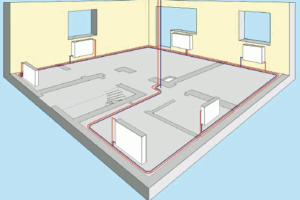
 This scheme is used in houses with more than one floor.
This scheme is used in houses with more than one floor.
From the gas boiler at the same time there is a division into two branches:
- the first passes through the first floor;
- the second one passes through the vertical riser along the second floor.
There are certain conditions that ensure the reliability and stability of the shoulder circuit:
- the number of radiators - on each floor should be within ten pieces;
- pipelines must be installed with those diameters that are suitable for this particular system;
- must be mounted on each floor of a two-story house, both on the lower and on the upper, balancing valves with automatic pressure control.
The fact is that the vertical circuit cannot be made so that the coolant passes by gravity, when the movement is exclusively under pressure from the hot coolant to the cold one, so a pump must be used.
The scheme of a two-pipe dead-end heating system is quite common, as it is easy to install and easy to operate. This scheme is quite economical from a financial point of view. For these reasons, the private sector of households willingly uses it.
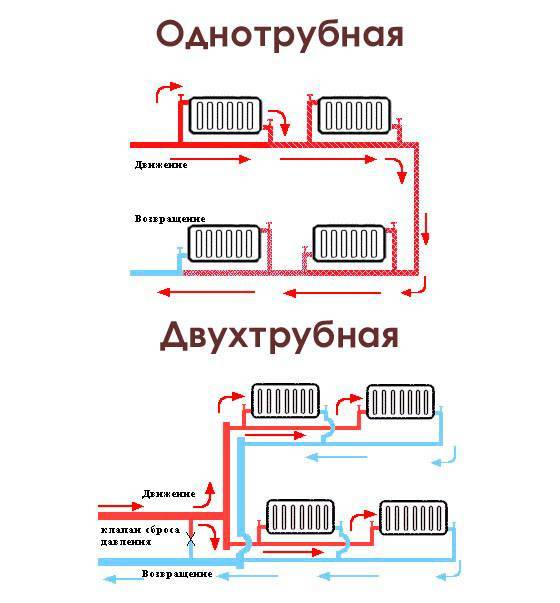
Characteristics of one-pipe and two-pipe systems
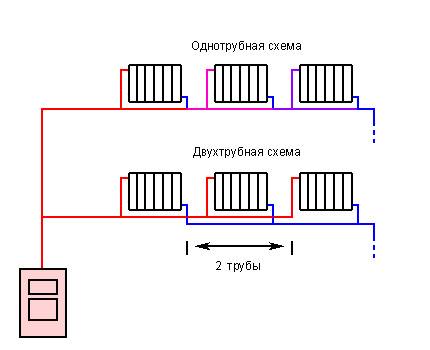
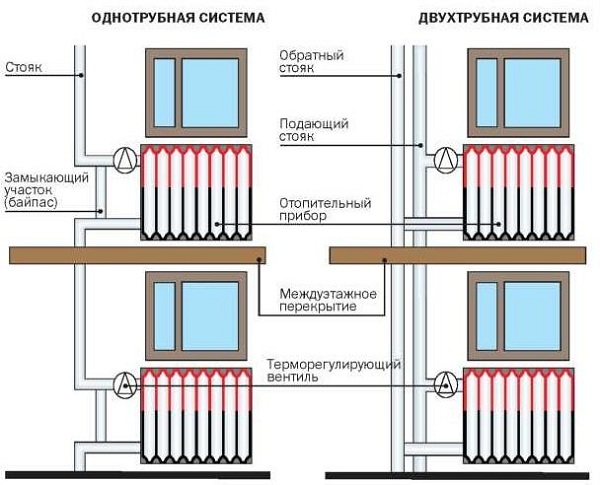
The water heating system is one-pipe and two-pipe. Consider the features of each option.
In a single pipe system, radiators are connected in series to the supply pipe. Its advantages include a simple design and low material consumption, as it requires a minimum of pipes to be installed.. But when connected in series to heating devices remote from the boiler, the coolant enters already cooled down, and in order to provide the necessary level of air heating in the room, it is necessary to install radiators of higher power, which increases the cost of the project. The disadvantages should also include:
- complexity of hydraulic calculation;
- limitation on the number of heating devices;
- the criticality of errors made at the stage of design and installation;
- the inability to regulate the temperature of heating devices separately, depending on the requirements for the microclimate of the premises;
- the impossibility of shutting off the flow of water to a separate radiator (for repair or replacement, etc.) without stopping the operation of the entire system;
- high heat losses.

A 2-pipe heating system, unlike a single-pipe one, provides for a parallel arrangement of the supply and return pipelines to which radiators are connected. This option has the following advantages:
- allows you to deliver liquid of the same temperature to all radiators (it is not necessary to increase the number of sections for batteries farthest from the boiler);
- a thermostat can be installed on each heating device;
- additional heating devices can be added to the mounted line;
- there are no restrictions on the length of the contour.
Two-pipe heating also has some disadvantages, including the complexity of the connection scheme, increased consumption of materials and labor-intensive installation, when compared with a single-pipe option.
It is also worth noting the radial (collector) connection of heating devices - separate supply and return pipes are mounted for each radiator. The advantages of independent connection of heating devices include the maintainability of the system - turning off any of the circuits will not affect the performance of other radiators. The main disadvantage is the need for laying a large number of pipes.
Usually, water heating of a private house comes down to arranging a two-pipe system, since this is the most efficient and cost-effective option.
Why choose such a system?
Two-pipe water heating is gradually replacing traditional single-pipe designs, since its advantages are obvious and very significant:
- Each of the radiators included in the system receives a coolant with a certain temperature, and for all it is the same.
- Possibility to make adjustments for each battery. If desired, the owner can put a thermostat on each of the heaters, which will allow him to get the desired temperature in the room. At the same time, the heat transfer of the remaining radiators in the building will remain the same.
- Relatively small pressure losses in the system. This makes it possible to use an economical circulation pump of relatively low power for operation in the system.
- If one or even several radiators fail, the system can continue to operate. The presence of shutoff valves on the supply pipes allows you to carry out repair and installation work without stopping it.
- Possibility of installation in a building of any height and area. It will only be necessary to choose the optimally suitable type of two-pipe system.
The disadvantages of such systems usually include the complexity of installation and the high cost compared to single-pipe structures. This is due to the double number of pipes that have to be installed.
However, it should be borne in mind that for the arrangement of a two-pipe system, pipes and components of small diameter are used, which gives certain cost savings. As a result, the cost of the system is not much higher than that of a single-pipe counterpart, while it provides much more advantages.

One of the significant advantages of a two-pipe heating system is the ability to effectively control the temperature in the room.
Classification of one-pipe heating systems
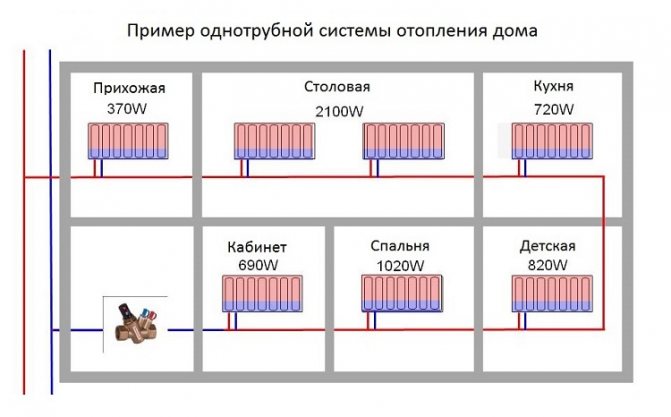
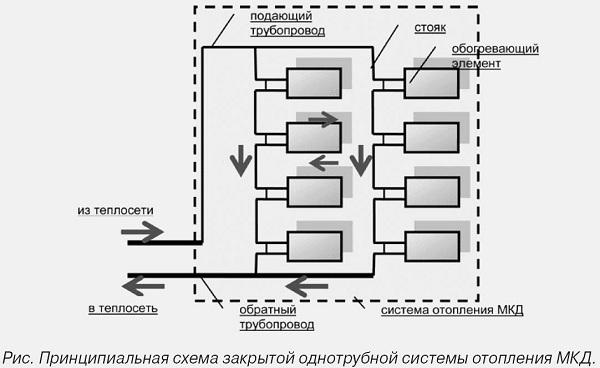
In this type of heating, there is no separation into return and supply pipelines, since the coolant, after leaving the boiler, goes through one ring, after which it returns to the boiler again. Radiators in this case have a serial arrangement. The coolant enters each of these radiators in turn, first into the first, then into the second, and so on. However, the temperature of the coolant will decrease, and the last heater in the system will have a temperature lower than the first one.
The classification of single-pipe heating systems looks like this, each type has its own schemes:
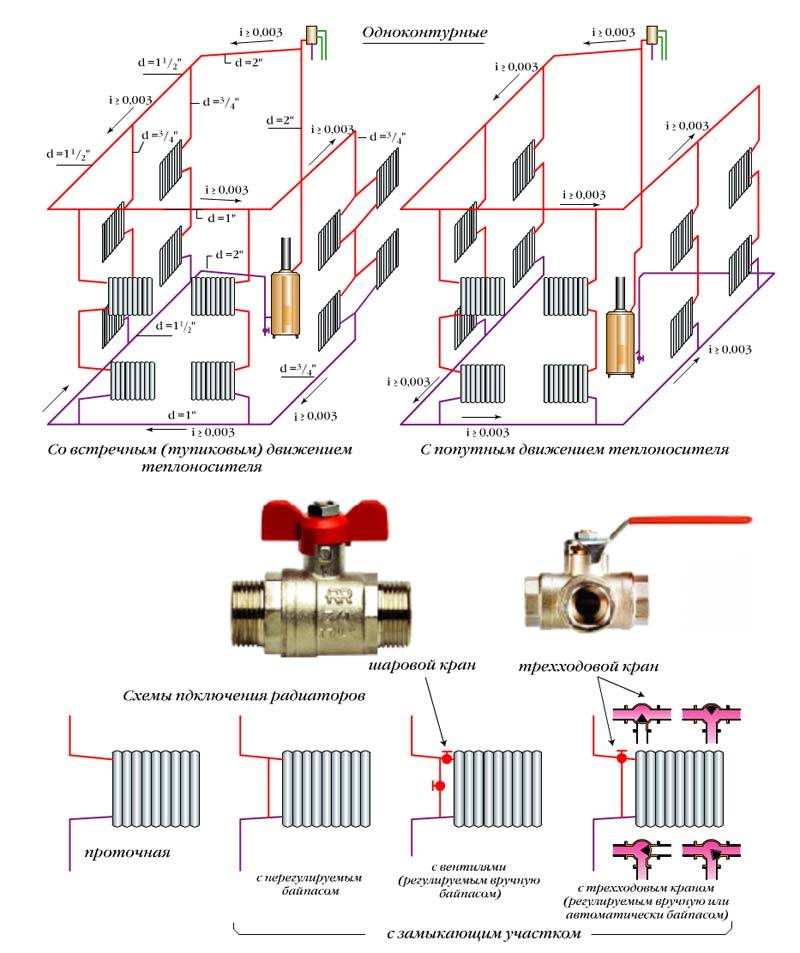
- closed heating systems that do not communicate with air. They differ in excess pressure, the air can only be discharged manually by means of special valves or automatic air valves. Such heating systems can work with circular pumps. Such heating may also have a lower wiring and a corresponding circuit;
- open heating systems that communicate with the atmosphere using an expansion tank to release excess air. In this case, the ring with the coolant should be placed above the level of the heating devices, otherwise air will collect in them and the water circulation will be disturbed;
- horizontal - in such systems, the coolant pipes are placed horizontally. This is great for private one-story houses or apartments where there is an autonomous heating system. Single-pipe type of heating with lower wiring and the corresponding scheme is the best option;
- vertical - the coolant pipes in this case are placed in a vertical plane.Such a heating system is best suited for private residential buildings, consisting of two to four floors.
Bottom and horizontal wiring of the system and its diagrams
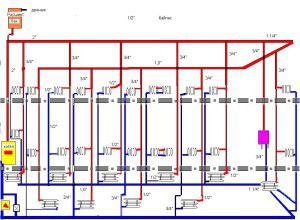
The circulation of the coolant in the horizontal piping scheme is provided by a pump. And the supply pipes are placed above or below the floor. A horizontal line with a lower wiring should be laid with a slight slope from the boiler, while the radiators must be placed all on the same level.
In houses with two floors, such a wiring diagram has two risers - supply and return, while the vertical circuit allows for more. During forced circulation of the heating agent using a pump, the temperature in the room rises much faster. Therefore, to install such a heating system, it is necessary to use pipes with a smaller diameter than in cases of natural movement of the coolant.
On the pipes that enter the floors, you need to install valves that will regulate the supply of hot water to each floor.
Consider some wiring diagrams for a single-pipe heating system:
- vertical feed scheme - can have natural or forced circulation. In the absence of a pump, the coolant circulates by means of a change in density during the cooling down of the heat exchange. From the boiler, water rises to the main line of the upper floors, then it is distributed through the risers to the radiators and cools in them, after which it returns to the boiler again;
- diagram of a single-pipe vertical system with bottom wiring. In the scheme with the lower wiring, the return and supply lines go below the heating devices, and the pipeline is laid in the basement.The coolant is supplied through the drain, passes through the radiator and returns down to the basement through the downcomer. With this method of wiring, heat loss will be much less than when the pipes are in the attic. Yes, and it will be very simple to maintain the heating system with this wiring diagram;
- scheme of a single-pipe system with an upper wiring. The supply pipeline in this wiring diagram is located above the radiators. The supply line runs under the ceiling or through the attic. Through this line, the risers go down and radiators are attached to them one by one. The return line goes either along the floor, or under it, or through the basement. Such a wiring diagram is suitable in the case of natural circulation of the coolant.
Remember that if you do not want to raise the threshold of the doors in order to lay the supply pipe, you can smoothly lower it under the door on a small piece of land while maintaining the general slope.
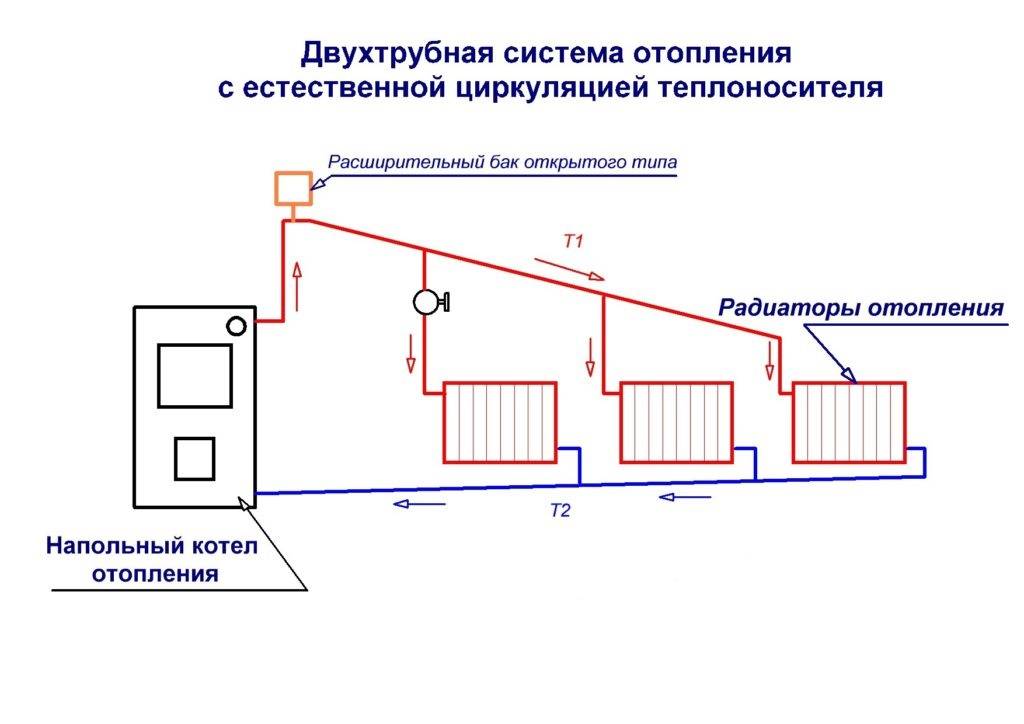
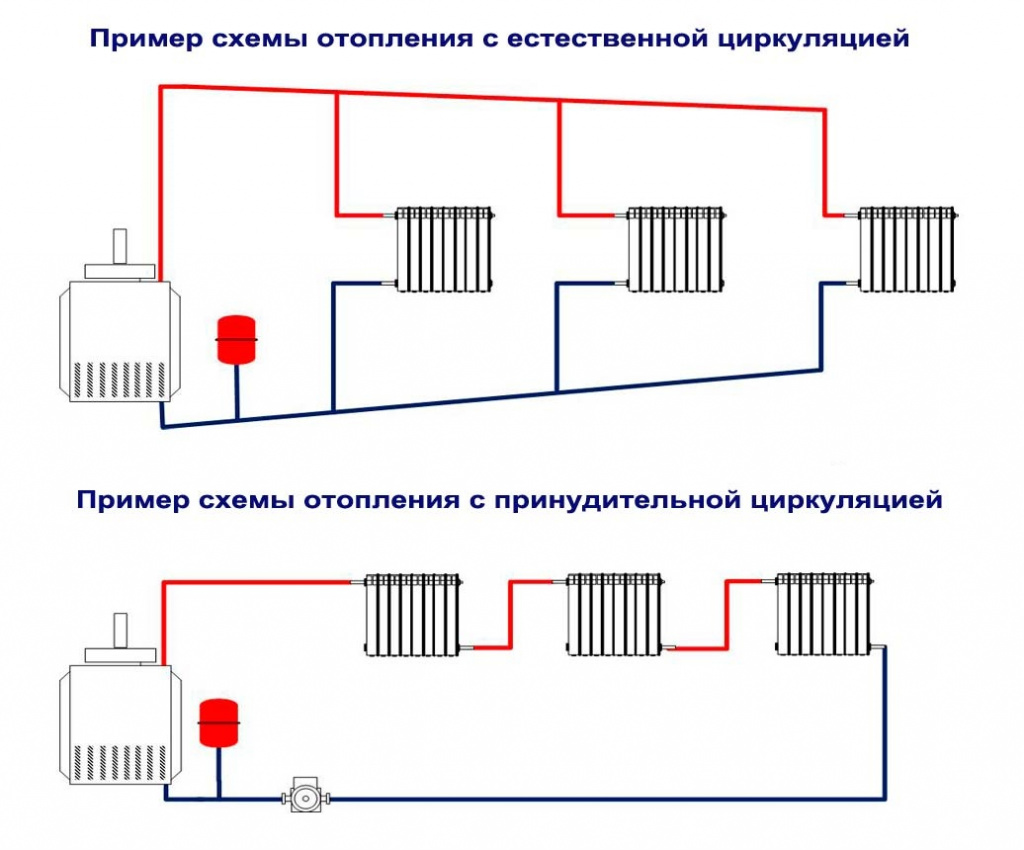
Scheme with natural circulation
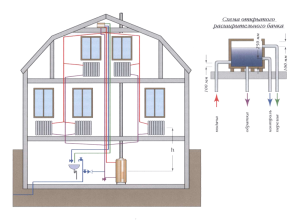
To understand the principle of operation of the gravity system, study the typical scheme used in two-story private houses. Combined wiring is implemented here: the supply and return of the coolant occurs through two horizontal lines, united by single-pipe vertical risers with radiators.
How gravity heating of a two-story house works:
- The specific gravity of the water heated by the boiler becomes smaller. A colder and heavier coolant begins to displace hot water up and take its place in the heat exchanger.
- The heated coolant moves along a vertical collector and is distributed along horizontal lines laid with a slope towards the radiators. The flow velocity is low, about 0.1–0.2 m/s.
- Diverging along the risers, the water enters the batteries, where it successfully gives off heat and cools. Under the influence of gravity, it returns to the boiler through the return collector, which collects the coolant from the remaining risers.
- The increase in water volume is compensated by an expansion tank installed at the highest point. Typically, the insulated container is located in the attic of the building.
Schematic diagram of gravity distribution with a circulation pump
In the modern design, gravity systems are equipped with pumps that accelerate the circulation and heating of the premises. The pumping unit is placed on the bypass parallel to the supply line and operates in the presence of electricity. When the light is turned off, the pump is idle, and the coolant circulates due to gravity.
Scope and disadvantages of gravity
The purpose of the gravity scheme is to supply heat to dwellings without being tied to electricity, which is important in remote regions with frequent power outages. A network of gravity pipelines and batteries is able to work together with any non-volatile boiler or from furnace (formerly called steam) heating.
Let's analyze the negative aspects of using gravity:
- due to the low flow rate, it is necessary to increase the coolant flow rate through the use of large diameter pipes, otherwise the radiators will not warm up;
- in order to “spur” natural circulation, horizontal sections are laid with a slope of 2-3 mm per 1 m of the main;
- healthy pipes running under the ceiling of the second floor and above the floor of the first floor spoil the appearance of the rooms, which is noticeable in the photo;
- automatic regulation of air temperature is difficult - only full-bore thermostatic valves should be purchased for batteries that do not interfere with the convective circulation of the coolant;
- the scheme is unable to work with underfloor heating in a 3-storey building;
- an increased volume of water in the heating network implies a long warm-up and high fuel costs.
In order to fulfill requirement No. 1 (see the first section) in conditions of unreliable power supply, the owner of a two-story private house will have to bear the cost of materials - pipes of increased diameter and lining for the manufacture of decorative boxes. The remaining disadvantages are not critical - slow heating is eliminated by installing a circulation pump, lack of efficiency - by installing special thermal heads on radiators and pipe insulation.
Design Tips
If you took the development of a gravity heating scheme into your own hands, be sure to consider the following recommendations:
- The minimum diameter of the vertical section coming from the boiler is 50 mm (meaning the internal size of the nominal bore of the pipe).
- The horizontal distributing and collecting manifold can be reduced to 40 mm, in front of the last batteries - up to 32 mm.
- A slope of 2-3 mm per 1 meter of pipeline is made towards the radiators on the supply and the boiler on the return.
- The inlet pipe of the heat generator must be located below the batteries of the first floor, taking into account the slope of the return line. You may have to make a small pit in the boiler room for installing a heat source.
- On the connections to the heating appliances of the second floor, it is better to install a direct bypass of small diameter (15 mm).
- Try to lay the upper distribution manifold in the attic so as not to lead under the ceilings of the rooms.
- Use an open-type expansion tank with an overflow pipe leading to the street, and not to the sewer. So it is more convenient to monitor the overflow of the container. The system will not work with a membrane tank.
The calculation and design of gravity heating in a complex-planned cottage should be entrusted to specialists. And the last thing: lines Ø50 mm and more will have to be made with steel pipes, copper or cross-linked polyethylene. The maximum size of metal-plastic is 40 mm, and the diameter of polypropylene will come out simply menacing due to the wall thickness.
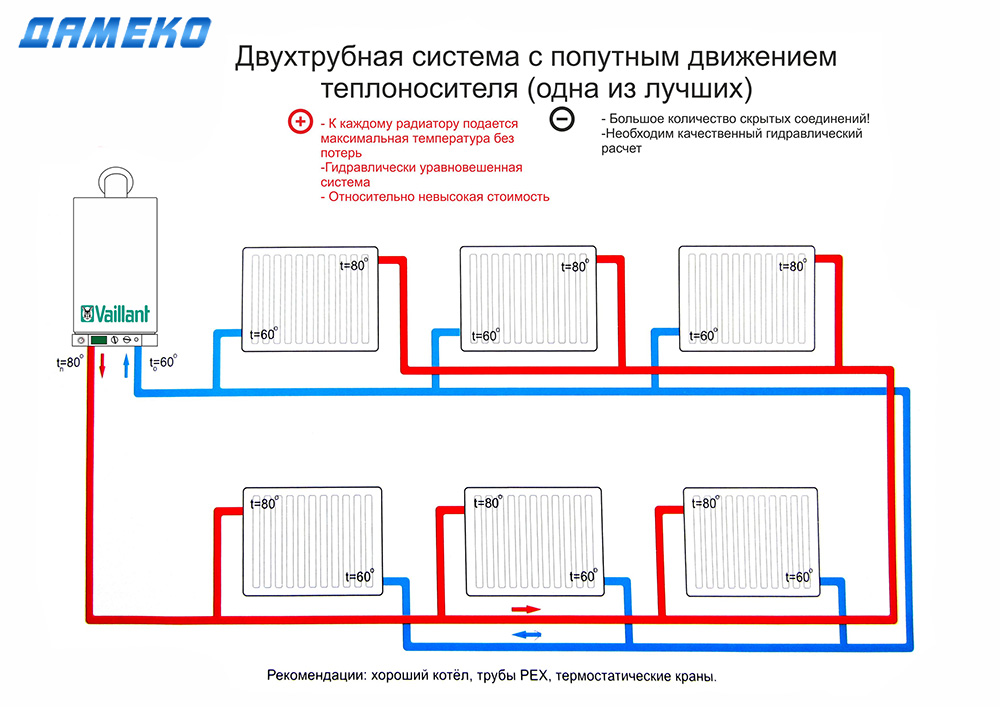
Two-pipe heating system with top wiring
Installing a two-pipe heating system with top wiring minimizes or completely eliminates many of the above disadvantages. In this case, the radiators are connected in parallel.
For its installation, much more materials are needed, since two parallel lines are installed. A hot coolant flows through one of them, and a cooled coolant flows through the other. Why is this overflow heating system preferred for private houses? One of the significant advantages is the relatively large area of the room. The two-pipe system can effectively maintain a comfortable temperature level in houses with a total area of up to 400 m².
In addition to this factor, for a heating circuit with top filling, the following important performance characteristics are noted:
- Uniform distribution of hot coolant over all installed radiators;
- The possibility of installing control valves not only on the battery piping, but also on separate heating circuits;
- Installation of water floor heating system.A collector hot water distribution system is only possible with two-pipe heating.
To organize forced top filling in the heating system, it is necessary to install additional units - a circulation pump and a membrane expansion tank. The latter will replace the open expansion tank. But the place of its installation will be different. Membrane sealed models are mounted on the return line and always on the straight section.
The advantage of such a scheme is the optional observance of the slope of the pipelines, which is characteristic of the upper and lower distribution of heating with natural circulation. The required pressure will be created by the circulation pump.
But does a two-pipe forced heating system with an upper wiring have any disadvantages? Yes, and one of them is dependence on electricity. During a power outage, the circulation pump stops working. With a large hydrodynamic resistance, the natural circulation of the coolant will be difficult. Therefore, when designing a scheme for a single-pipe heating system with an upper wiring, all the required calculations must be performed.
You should also take into account the following features of installation and operation:
- When the pump stops, reverse movement of the coolant is possible. Therefore, in critical areas, it is necessary to install a check valve;
- Excessive heating of the coolant can cause the critical pressure indicator to be exceeded. In addition to the expansion tank, air vents are installed as an additional protection measure;
- To increase the efficiency of the heating system with the upper piping, it is necessary to provide for automatic replenishment with coolant.Even a slight decrease in pressure below normal can lead to a decrease in radiator heating.
The video will help you visually see the difference for various heating schemes:
Most of the heating systems of multi-apartment and private houses are built according to this scheme. What are its advantages and are there any disadvantages?
Can a do-it-yourself two-pipe heating system be installed?

Convector in a two-pipe heating system
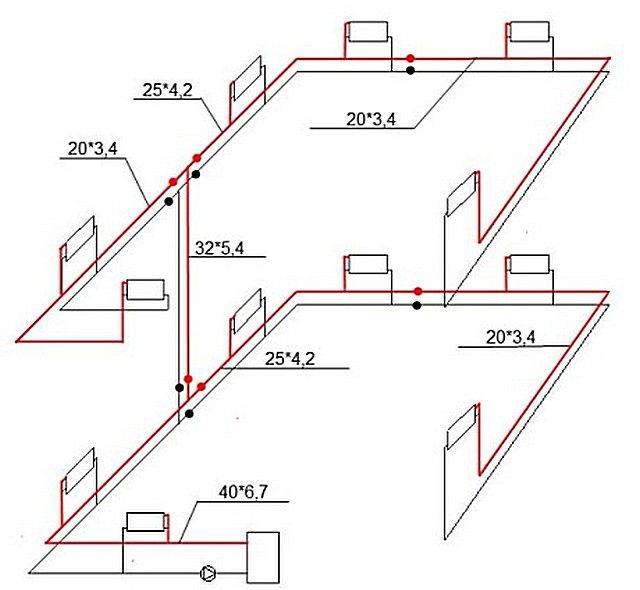
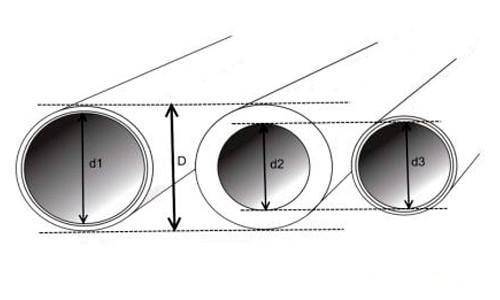
Selection of pipes by diameter
You can ensure good heating of the room if you choose the right pipe section. Thermal power is taken as the basis here. It determines how much water should move in a certain time. To calculate the thermal power, the following formulas are used: G=3600×Q/(c×Δt), where: G is the liquid consumption for heating the house (kg/h); Q - thermal power (kW); c is the heat capacity of water (4.187 kJ/kg×°C); Δt is the temperature difference between the heated and cooled liquid (standard value is 20 °C).
In order for the system to work in a balanced way, it is necessary to calculate the cross section of the pipes. For this, the following formula is needed: S=GV/(3600×v), where: S – pipe cross-section (m2); GV - water flow (m3/h); v is the speed of the coolant (0.3−0.7 m/s).
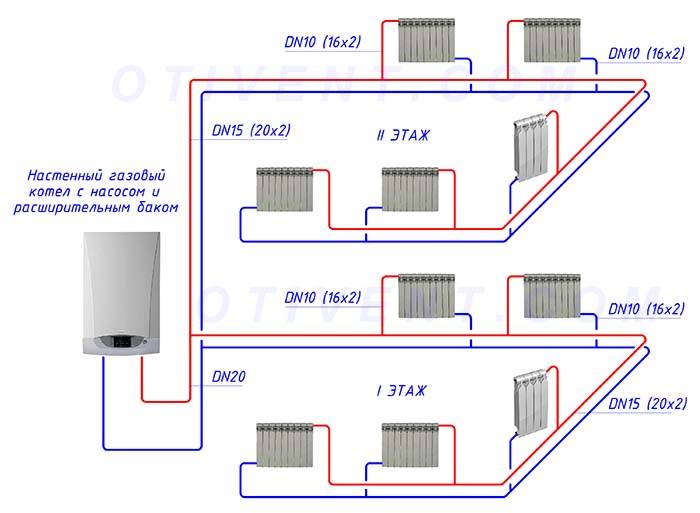
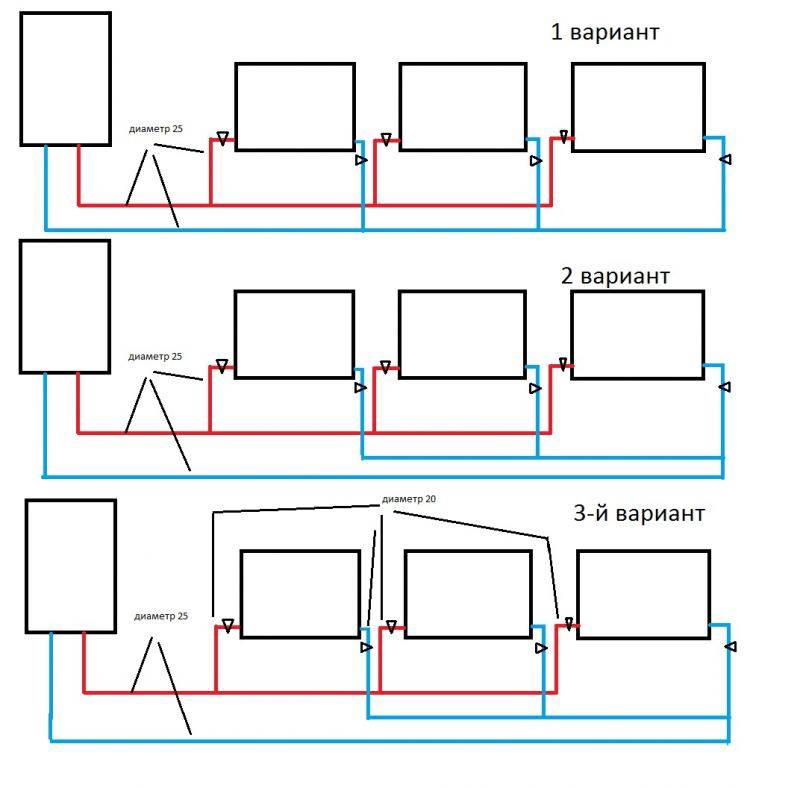
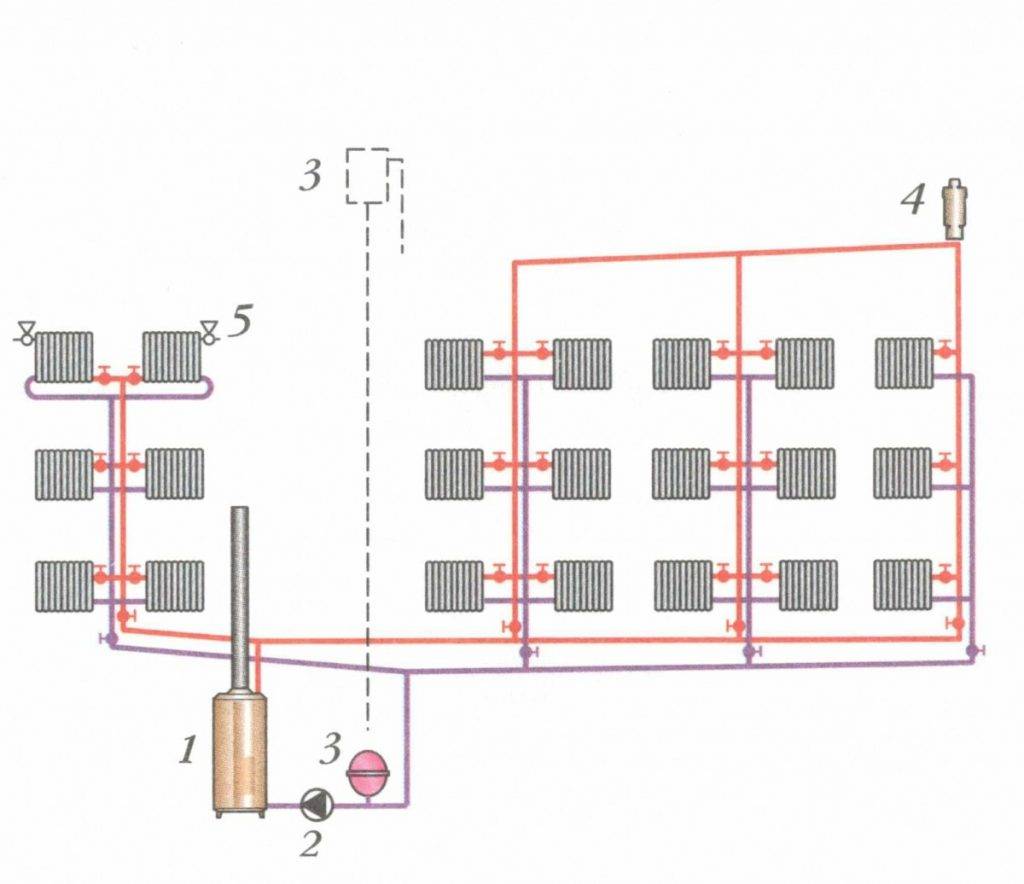
Two-pipe system with bottom wiring
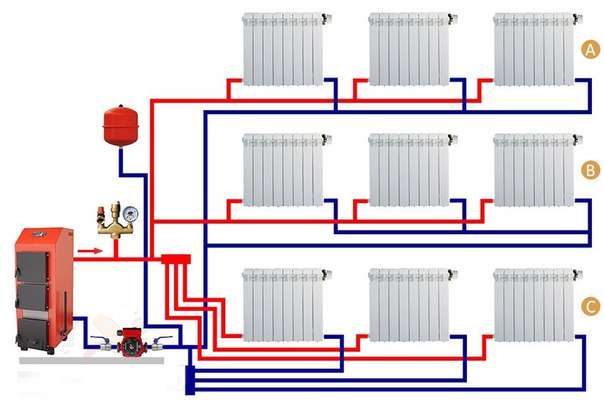
Next, we will consider two-pipe systems, which are distinguished by the fact that they provide an even distribution of heat even in the largest households with many rooms. It is the two-pipe system that is used to heat multi-storey buildings, in which there are a lot of apartments and non-residential premises - here such a scheme works great. We will consider schemes for private houses.
Two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring.
A two-pipe heating system consists of a supply and return pipes. Radiators are installed between them - the radiator inlet is connected to the supply pipe, and the outlet to the return pipe. What does it give?
- Uniform distribution of heat throughout the premises.
- Possibility to regulate the temperature in the rooms by completely or partially blocking individual radiators.
- Possibility of heating multi-storey private houses.
There are two main types of two-pipe systems - with lower and upper wiring. To begin with, we will consider a two-pipe system with a bottom wiring.
Lower wiring is used in many private homes, as it allows you to make heating less visible. The supply and return pipes pass here next to each other, under the radiators or even in the floors. Air is removed through special Mayevsky taps. Heating schemes in a private house made of polypropylene most often provide for just such a wiring.
Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
When installing heating with a lower wiring, we can hide the pipes in the floor.
Let's see what positive features two-pipe systems with bottom wiring have.
- The possibility of masking pipes.
- The possibility of using radiators with a bottom connection - this somewhat simplifies installation.
- Heat losses are minimized.
The ability to at least partially make heating less visible attracts many people. In the case of the bottom wiring, we get two parallel pipes running flush with the floor. If desired, they can be brought under the floors, providing for this possibility even at the design stage of the heating system and the development of a project for the construction of a private house.
If you use radiators with a bottom connection, it becomes possible to almost completely hide all the pipes in the floors - the radiators are connected here using special nodes.
As for the disadvantages, they are the need for regular manual removal of air and the need to use a circulation pump.
Features of mounting a two-pipe system with bottom wiring
Plastic fasteners for heating pipes of different diameters.
In order to mount the heating system according to this scheme, it is necessary to lay the supply and return pipes around the house. For these purposes, there are special plastic fasteners on sale. If radiators with side connection are used, we make a tap from the supply pipe to the upper side hole, and take the coolant through the lower side hole, directing it to the return pipe. We put air vents next to each radiator. The boiler in this scheme is installed at the lowest point.
It uses a diagonal connection of radiators, which increases their heat transfer. Lower connection of radiators reduces heat output.
Such a scheme is most often made closed, using a sealed expansion tank. The pressure in the system is created using a circulation pump. If you need to heat a two-story private house, we lay pipes on the upper and lower floors, after which we create a parallel connection of both floors to the heating boiler.