- Gas distribution networks
- Main gas pipelines and their protected zones
- What should be in an apartment and a private house according to the standard?
- The difference between gas pipelines by type of laying
- Converting pressure values from millimeters of water column to pascals
- In the same section:
- Main gas pipelines. High, Medium and Low Pressure Gas Pipelines - Glossary
- Gas pipeline classification by pressure
- Location of gas pipelines (classification)
- Materials for gas pipelines
- The principle of construction of distribution systems of gas pipelines
- Natural gas supply
- Unit ratio tables
- Requirements for the selection of pipes
- Types of gas supply systems
- Gas veins - how does gas circulate through the system?
- Classification of gas pipelines in the gas distribution system.
Gas distribution networks
A gas distribution network is a system of pipelines and equipment that serves to transport and distribute gas in settlements. At the end of 1994, the total length of gas networks in our country was 182,000 km.
Gas enters the gas distribution network from the main gas pipeline through the gas distribution station. Depending on the pressure, the following types of gas pipelines of gas supply systems are distinguished:
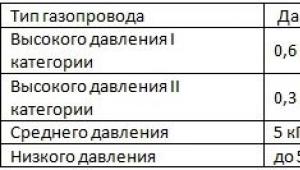
- high pressure (0.3. 1.2 MPa);
- medium pressure (0.005. 0.3 MPa);
– low pressure (less than 0.005 MPa).
Depending on the number of stages of pressure reduction in gas pipelines, the gas supply systems of settlements are one-, two- and three-stage:
1) single-stage (Fig. 16.5 a) - this is a gas supply system in which gas is distributed and supplied to consumers through gas pipelines of only one pressure (usually low); it is used in small towns;
2) a two-stage system (Fig. 16.5 b) ensures the distribution and supply of gas to consumers through gas pipelines of two categories: medium and low or high and low pressures; it is recommended for settlements with a large number of consumers located over a large area;
Figure 16.5 - Schematic diagrams of gas supply to settlements:
a - single-stage; b - two-stage; c - three-stage; 1 - branch from the main gas pipeline; 2 – low pressure gas pipeline; 3 – medium pressure gas pipeline; 4 – high pressure gas pipeline; GDS - gas distribution station; GRP - gas distribution point; PP - industrial enterprise
When using two- and three-stage gas supply systems, additional gas reduction is carried out at gas control points (GRP).
Low pressure gas pipelines are mainly used to supply gas to residential buildings, public buildings and utilities. Gas pipelines of medium and high (up to 0.6 MPa) pressure are designed to supply gas to low-pressure gas pipelines through urban hydraulic distribution stations, as well as for gas supply to industrial and large municipal enterprises.Through gas pipelines of high (more than 0.6 MPa) pressure, gas is supplied to industrial consumers, for which this condition is necessary according to technological requirements.
According to the purpose in the gas supply system, distribution gas pipelines, gas pipelines-inlets and internal gas pipelines are distinguished. Distribution gas pipelines provide gas supply from gas supply sources to gas pipelines-inlets. Gas pipelines-inputs connect distribution gas pipelines with internal gas pipelines of buildings. The internal one is the gas pipeline running from the gas pipeline-inlet to the place of connection of the gas appliance, heat unit, etc.
By location in settlements, there are external (street, intra-quarter, yard, inter-shop, inter-settlement) and internal (intra-shop, intra-house) gas pipelines.
By location relative to the surface of the earth, underground and aboveground gas pipelines are distinguished.
According to the material of the pipes, metal (steel, copper) and non-metallic (polyethylene, asbestos-cement, etc.) gas pipelines are distinguished.
Connecting and disconnecting individual sections of gas pipelines and gas consumers is carried out using shut-off valves - valves, taps, valves. In addition, gas pipelines are equipped with the following devices: condensate collectors, lens or flexible compensators, control and measuring points, etc.
Main gas pipelines and their protected zones
Combustible gases are transported through the main gas pipelines from the places of their extraction or production to the places of application.
Main gas pipelines
There is such an indicator as the performance of the gas pipeline. This is the annual amount of gas that has passed through it.
During the design of gas pipelines, the probable performance is calculated.It depends on the fuel and energy balance of the area where the pipeline will run. During the year, the performance indicator may vary, as the use of gas is affected by the season and temperature.
There are several ways to improve the performance of a structure. To do this, sections called loopings are laid parallel to the main pipeline. Their use increases the capacity of the structure.
Gas security zone, what restrictions
At compressor stations, centrifugal blowers are installed, which work thanks to turbines or electric motors.
The state of the gas pipes is usually controlled by a state-owned company. She must also ensure that the workers involved in the inspection and repair of the highway, regularly raised their qualifications.
Security zone of the main gas pipeline - this is the area around the structure defined by two lines. Since the gas main is a potentially explosive structure, the presence of a security zone on both sides of it is mandatory.
According to the requirements, the security zone should be:
- for high-pressure pipes of category I - at least 10 meters;
- for highways of category II - at least 7 meters;
- for category III pipes - 4 meters;
for a class IV pipeline - more than 2 meters.
What should be in an apartment and a private house according to the standard?
The main documents regulating the supply of gas to an apartment or a private house are:
- Law No. 69-FZ "On gas supply in the Russian Federation" dated 31.03.1999.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 549 “On the procedure for supplying gas to meet the domestic needs of citizens” dated 21.07.2008.
- Government Decree 1314 “On Approval of the Rules for Connecting Facilities to Gas Distribution Networks” dated 12/30/2013.
- Specific norms for the main parameters and rules for the arrangement of gas systems are subject to SNiPs, in particular, SNiP 42-01-2002.
Legislatively, for domestic consumption, the gas pressure standard is set at 5 kPa (0.05 atm). Deviations upwards or downwards of no more than 10% are allowed, i.е. 0.5 kPa. The maximum allowable pressure in the system of private houses is 3 kPa.
Compliance with the norms is ensured by special gas distribution substations.
The difference between gas pipelines by type of laying
The gas pipeline can be laid in different ways. Most often today they use the ring method of laying and dead-end. In the case of a dead-end network, gas enters the user from only one side, while in a ring main, gas enters from two sides and moves further like a closed ring.

Laying a gas pipeline in an annular way
There is a big drawback in the dead-end system - when gas services carry out repair or maintenance work, they are forced to disconnect a huge number of consumers from gas. If you live in such a zone, then when choosing a gas boiler, you should take into account the automatic shutdown of the equipment in the absence of pressure, otherwise the unit will run idle.
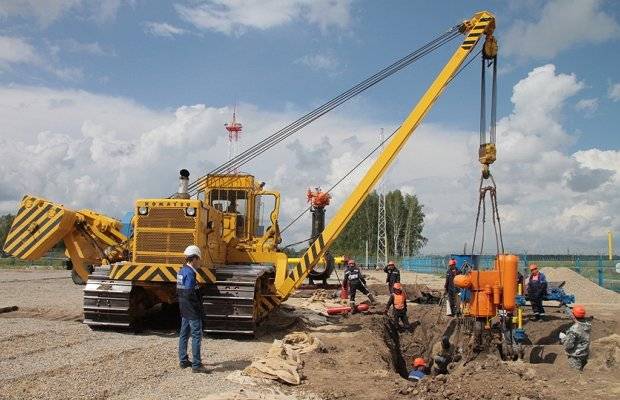

Repair work of the gas service
There is no such drawback in the ring system - gas flows from two sides.Due to this, the pressure is evenly distributed among all consumers, while in a dead-end system, the farther the house is from the hydraulic fracturing, the less pressure will be in the pipe. Again, this factor should be taken into account when buying a house - the farther the house is from the gas control point, the more the quality of gas supply is leveled.
Converting pressure values from millimeters of water column to pascals
| Pressure, mm of water. Art. | millimeters of water column | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Pressure values in pascals | ||||||||||
| 10 | 20 | 29 | 39 | 49 | 59 | 69 | 79 | 89 | ||
| 10 | 98 | 108 | 118 | 127 | 137 | 147 | 157 | 167 | 176 | 186 |
| 20 | 196 | 206 | 216 | 225 | 235 | 245 | 255 | 265 | 274 | 284 |
| 30 | 294 | 304 | 314 | 324 | 333 | 343 | 353 | 363 | 372 | 382 |
| 40 | 392 | 402 | 412 | 422 | 431 | 441 | 451 | 461 | 470 | 480 |
| 50 | 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 529 | 539 | 549 | 559 | 569 | 578 |
| 60 | 588 | 598 | 608 | 618 | 627 | 637 | 647 | 657 | 667 | 676 |
| 70 | 686 | 696 | 706 | 716 | 725 | 735 | 745 | 755 | 765 | 774 |
| 80 | 784 | 794 | 804 | 814 | 823 | 833 | 843 | 853 | 863 | 872 |
| 90 | 882 | 892 | 902 | 921 | 912 | 931 | 941 | 951 | 961 | 970 |
Example: 86 mm w.c. Art. = 843 Pa; 860 mm w.c. Art. = 8430 Pa; 1860 mm w.c. Art. = 1000 mm w.c. Art. + 860 mm w.c. Art. \u003d 9800 Pa + 8430 Pa \u003d 18 230 Pa. To get the pressure in bar, it is necessary to divide its value in pascals by 10 5 .
In the same section:
2007–2020 HC Gazovik. All rights reserved. The use of site materials without the permission of the owner is prohibited and will be prosecuted.
Source
Main gas pipelines. High, Medium and Low Pressure Gas Pipelines - Glossary
The gas pipeline is an important element of the gas supply system, since 70.80% of all capital investments are spent on its construction. At the same time, 80% of the total length of distribution gas networks falls on low pressure gas pipelines and 20% on medium and high pressure gas pipelines.
Gas pipeline classification by pressure
In gas supply systems, depending on the pressure of the transported gas, there are:
- high-pressure gas pipelines of category I (operating gas pressure over 1.2 MPa);
- high-pressure gas pipelines of category I (operating gas pressure from 0.6 to 1.2 MPa);
- high-pressure gas pipelines of category II (operating gas pressure from 0.3 to 0.6 MPa);
- medium pressure gas pipelines (operating gas pressure from 0.005 to 0.3 MPa);
- low pressure gas pipelines (operating gas pressure up to 0.005 MPa).
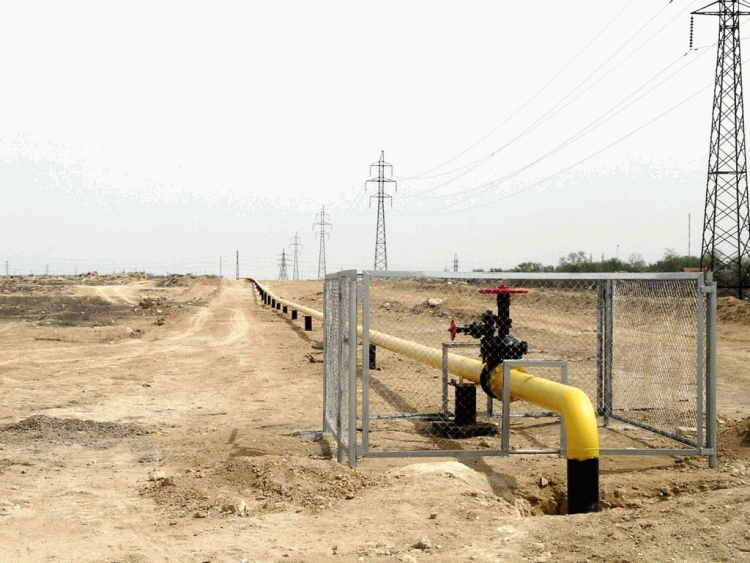 Low pressure gas pipelines are used to supply gas to residential buildings, public buildings and public utilities.
Low pressure gas pipelines are used to supply gas to residential buildings, public buildings and public utilities.
Medium pressure gas pipelines through gas control points (GRP) supply gas to low pressure gas pipelines, as well as industrial and municipal enterprises. Through high-pressure gas pipelines, gas flows through hydraulic fracturing to industrial enterprises and medium-pressure gas pipelines. Communication between consumers and gas pipelines of various pressures is carried out through hydraulic fracturing, GRSH and GRU.
Location of gas pipelines (classification)
Depending on the location, gas pipelines are divided into external (street, intra-quarter, yard, inter-workshop) and internal (located inside buildings and premises), as well as underground (underwater) and above-ground (above-water). Depending on the purpose in the gas supply system, gas pipelines are divided into distribution, gas pipelines-inlets, inlet, purge, waste and inter-settlement.
Distribution pipelines are external gas pipelines that provide gas supply from main gas pipelines to gas input pipelines, as well as high and medium pressure gas pipelines designed to supply gas to one object.
The inlet gas pipeline is considered to be the section from the point of connection to the distribution gas pipeline to the disconnecting device at the inlet.
The inlet gas pipeline is considered the section from the disconnecting device at the entrance to the building to the internal gas pipeline.
Inter-settlement pipelines are distribution gas pipelines located outside the territory of settlements.
The internal gas pipeline is considered to be the section from the gas pipeline-inlet (inlet gas pipeline) to the place of connection of a gas appliance or a thermal unit.
Materials for gas pipelines
Depending on the material of the pipes, gas pipelines are divided into metal (steel, copper) and non-metallic (polyethylene).
There are also pipelines with natural, liquefied hydrocarbon gas (LHG), as well as liquefied natural gas (LNG) at cryogenic temperatures.
The principle of construction of distribution systems of gas pipelines
According to the principle of construction, distribution systems of gas pipelines are divided into ring, dead-end and mixed. In dead-end gas networks, gas flows to the consumer in one direction, i.e. consumers have a one-way supply.
Unlike dead-end networks, ring networks consist of closed loops, as a result of which gas can be supplied to consumers through two or more lines.
The reliability of ring networks is higher than dead-end networks. When carrying out repair work on the ring networks, only a part of the consumers connected to this section is turned off.
Of course, if you need to order gas supply to the site or perform gasification of an apartment building, instead of memorizing the terms, it is more profitable and more efficient to turn to reliable certified contractors. We will carry out work on conducting gas to your facility with high quality and within the agreed time frame.
LLC "GazComfort"
Office in Minsk: Minsk, Pobediteley Ave. 23, bldg. 1, office 316АOffice in Dzerzhinsky: Dzerzhinsk, st. Furmanova 2, office 9
Natural gas supply
Household and industrial equipment operating on a natural mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons is well known to everyone. Boilers, gas stoves and water heaters are installed in residential buildings. Many enterprises have boiler equipment and fenced "houses" of the GRU at their disposal.
And on the streets there are gas distribution points, attracting attention with a yellow color and a bright red inscription “Gas. Flammable." Everyone knows that gas flows through pipes
But how does it get into these same pipes? The path traveled by natural gas to each apartment, each house is truly enormous. After all, from the field to end consumers, fuel follows branched sealed channels stretching for thousands of kilometers.
Everyone knows that gas flows through pipes. But how does it get into these same pipes? The path traveled by natural gas to each apartment, each house is truly enormous. After all, from the field to the final consumers, the fuel follows through branched sealed channels stretching for thousands of kilometers.
Immediately after production at the field, the gas mixture is cleaned from impurities and prepared for pumping. Compressed by compressor stations to high pressure values, natural gas is sent through the main pipeline to the gas distribution station.
Its installations lower the pressure and odorize the gas mixture with methane, ethane and pentane with thiols, ethyl mercaptan and similar substances to give it an odor (in its pure form, natural gas has no odor). After additional purification, gaseous fuel is sent to the gas pipelines of settlements.

The natural gas is then delivered to gas distribution points within urban areas.Before being sent to the gas pipeline network of the quarter, the pressure of the transported gas is reduced to the required minimum. Finally, the gas follows the intra-house gas supply network - to a gas stove, boiler or water heater.
Each gas processing plant is equipped with a special burner that mixes the main fuel with air before combustion. In its pure form (i.e. without access to oxygen), the combustibility of natural gas is zero.

Unit ratio tables
A more visual and detailed concept of the categories of gas pipelines will be obtained from Table 1.
Table 1.
| unit of measurement | Gas pressure indicators | |||
| Low | Average | High 2 cat. | High 1 cat | |
| MPa | up to 0.005 | from 0.005 to 0.3 | from 0.3 to 0.6 | from 0.6 to 1.2 |
| kPa | up to 5.0 | from 5 to 300 | from 300 to 600 | from 600 to 1200 |
| mbar | up to 50 | from 50 to 3000 | from 3000 to 6000 | from 6000 to 12000 |
| bar | up to 0.05 | from 0.05 to 3 | 3 to 6 | 6 to 12 |
| atm | up to 0.049 | from 0.049 to 2.96 | from 2.960 to 5.921 | from 5.921 to 11.843 |
| kgf/cm2 | up to 0.050 | from 0.5 to 3.059 | from 3.059 to 6.118 | from 6.118 to 12.236 |
| n/m2 (Pa) | up to 5000 | from 5000 to 300000 | from 300000 to 600000 | from 600000 to 1200000 |
Here are indicators in various measurement systems that are often used in technical and regulatory literature.
Requirements for the selection of pipes

Pipelines made of HDPE, steel, copper and polypropylene are used for gas transportation. Specifications for their manufacture are specified in the relevant GOST. The most used materials for a domestic gas pipeline are water and gas pipes. Designed for internal and external networks with compression up to 1.6 MPa, nominal bore 8 mm. It is possible to use metal-plastic products made of PE-RT polyethylene.
Underground gas pipelines are allowed to be made of polyethylene materials with a frame made of metal mesh and synthetic fibers, metal-plastic products.
The material of the pipes and fittings is selected taking into account the gas pressure, the outdoor temperature at the installation sites, the presence of groundwater and vibrations.
Types of gas supply systems
The gas supply system can be of the following types:
1. Single-level, where gas is supplied to consumers only through a gas pipeline product of the same pressure indicators (either with low indicators or with average ones);
2. Two-level, where gas is supplied to the circle of consumers through a gas pipeline structure with two different types of pressure (indicators of medium-low or medium-high 1 or 2 level, or high indicators of category 2 low);
3. Three-level, where the passage of a gaseous substance is carried out through a gas pipeline with three pressures (high first or second level, medium and low);
4. Multilevel, in which gas moves along gas lines with four types of pressure: high 1 and 2 levels, medium and low.
Gas pipeline systems with different pressures, which are included in the gas supply system, must be connected through hydraulic fracturing, KDD.
Gas pressure in supply lines for different consumers
For industrial heat installations and boiler equipment that are separate from gas pipelines, it is acceptable to use a gas substance with an available pressure within 1.3 MPa, provided that such pressure indicators are necessary for the specifics of the technical process.It is impossible to lay a gas pipeline system with a pressure index of more than 1.2 MPa for a multi-storey residential building in a populated area, in areas where public buildings are located, in places where a large number of people are located, for example, a market, a stadium, a shopping center, a theater building.
The current distribution systems of the gas supply line consist of a complex complex composition of structures, which, in turn, take the form of basic elements such as gas ring, dead-end and mixed networks with low, medium and high pressure indicators. They are laid in urban areas, other settlements, in the heart of neighborhoods or buildings. In addition, they can be placed on the routes of a gas distribution station, gas control point and installation, a communication system, a system of automatic installations and telemechanical equipment.
The whole structure must ensure the supply of consumer gas without problems. The design must have a disconnecting device, which is directed to its individual elements and sections of the gas pipeline for repair and elimination of emergencies. Among other things, it ensures trouble-free transportation of gaseous substances to gas consuming persons, has a simple mechanism, safe, reliable and convenient operation.
It is necessary to design the gas supply of the entire region, city or village on the basis of schematic drawings and the layout of the area, the general plan of the city, taking into account the long-term development. All elements, devices, mechanisms and key parts in the gas supply system should be used the same.
It is worth choosing a distribution system and principles for constructing a gas pipeline (ring, dead-end, mixed) based on technical and economic settlement operations, taking into account the volume, structure and density of gas consumption.
The selected system must be of the highest efficiency, from an economic point of view, and must include construction processes and be able to put the gas supply system into operation partially.
Gas classification. Gas of medium pressure, low, high 1 and 2 categories
Gas veins - how does gas circulate through the system?
Before the gas ignites with a blue flame on your stove, it travels hundreds and thousands of kilometers through gas pipelines. The most important artery of the gas transmission system is the gas pipeline. The pressure in such lines is very high - 11.8 MPa, and is completely unsuitable for private consumption.

Blue gas flame on the stove
However, already in gas distribution stations (GDS), the pressure drops to 1.2 MPa. In addition, additional gas purification takes place at the stations, it is given a specific smell, which is perceptible by the human sense of smell. Without odorization, as the process is called, we would not sense the presence of gas in the air when it leaks, since methane itself has neither color nor smell. Ethanthiol is often used to give a smell - even if there is one part of this substance in several tens of millions of parts of air in the air, we will feel its presence.
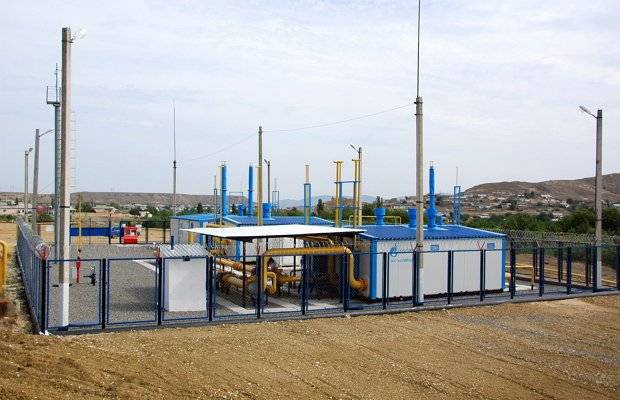

gas distribution station
From gas distribution stations, the gas path runs to gas control points (GRP).These points are actually the point of distribution of blue fuel between consumers. At hydraulic fracturing, automatic equipment monitors the pressure and recognizes the need to increase or decrease it. Also, at the gas control points, another stage of gas filtration takes place, and special devices register the degree of its pollution before and after cleaning.
Classification of gas pipelines in the gas distribution system.
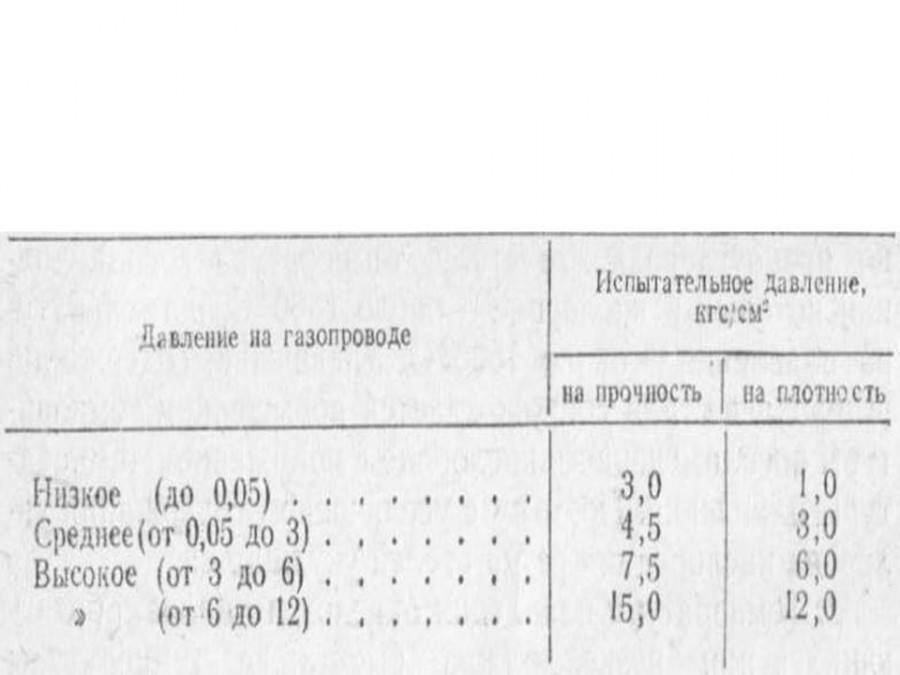
Depending on the maximum gas pressure, gas pipelines are divided into the following groups:
Table 1 - Classification of gas pipelines by gas pressure
Classification of gas pipelines by pressure
Type of transported gas
Working pressure in
according to GOST on the drawings
Low
Natural and LPG
up to 0.005 MPa ( 5 kPa)
Medium
Natural and LPG
from 0.005 MPa to 0.3 MPa
High
II category
Natural and LPG
from 0.3 to 0.6 MPa
I category
from 0.6 to 1.2 MPa
from 0.6 to 1.6 MPa
low gas pipelines serve to supply gas to residential buildings, public buildings and public utilities; medium-pressure gas pipelines supply gas to low-pressure gas pipelines through gas control points, as well as industrial and municipal enterprises; High-pressure gas pipelines are used to supply gas to hydraulic fracturing of industrial enterprises and medium-pressure gas pipelines.
Depending on the location relative to the surface of the earth:
Depending on the material of the pipes, gas pipelines are divided into:
metal (steel, copper); non-metallic (polyethylene).
According to the principle of constructing a gas supply system, they are divided into:
ring; dead ends; mixed.
In dead-end gas networks, gas flows to the consumer in one direction, i.e.consumers have a one-way supply, and difficulties may arise during repair work. The disadvantage of this scheme is the different values of gas pressure at consumers. Moreover, as the distance from the source of gas supply or hydraulic fracturing, the gas pressure drops. These schemes are used for intra-quarter and intra-yard gas pipelines.
Ring networks represent a system of closed gas pipelines, which achieves a more uniform gas pressure regime for consumers and facilitates repair and maintenance work. The reliability of ring networks is higher than dead-end networks. A positive feature of ring networks is that in the event of failure of any gas control point, the load on supplying consumers with gas is taken over by other hydraulic distribution stations.
The mixed system consists of ring gas pipelines and dead-end gas pipelines attached to them
When studying the issues of tracing networks of low and high (medium) pressure, you need to pay attention to the nature of the industrial facility or city development
By purpose, urban gas networks are divided into the following groups:
gas distribution pipelines through which gas is transported through the supplied territory and supplied to industrial consumers, public utilities and residential areas.They are of high, medium and low pressure, ring and dead ends, and their configuration depends on the nature of the layout of the city or settlement; subscriber branches supplying gas from distribution networks to individual consumers; intra-house gas pipelines transporting gas inside the building and distributing it to individual gas appliances; inter-settlement gas pipelines laid outside the territory of settlements.
According to the number of pressure stages used in gas networks, gas supply systems can be divided into:
single-stage, providing gas supply to consumers through gas pipelines of the same pressure, usually low; The main drawback of this system is the rather large diameters of gas pipelines and the uneven gas pressure at various points in the network. two-stage, consisting of networks of low and medium or medium and high (up to 0.6 MPa) pressures; three-stage, including gas pipelines of low, medium and high (up to 0.6 MPa) pressure); multistage, in which gas is supplied through low, medium and high pressure gas pipelines of both categories.
Purpose, classification and composition of oil product pipeline structures. Their role in ensuring the stability and reliability of the supply of petroleum products to consumers of various types.