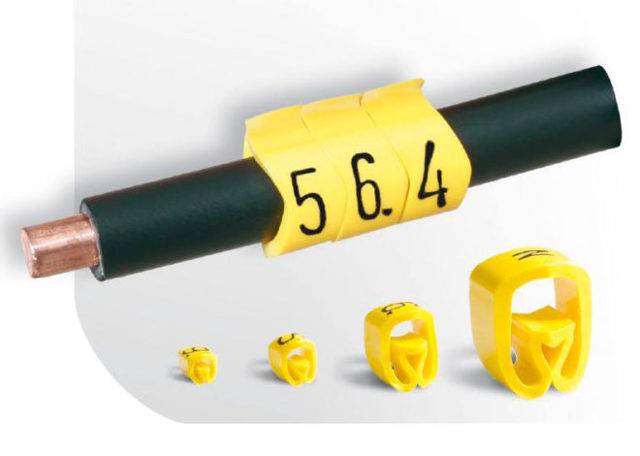
- The main types of marking cable tags
- Form of marking tags
- Dimensions of marking tags
- Color coding of wires and cables
- Afterword
- Purposes of wire marking
- Cable marking with tags according to PUE - Security Portal
- Forward and reverse phase sequence
- Color zero, neutral
- How to find ground, neutral and phase in the absence of a designation
- Letter and number wire markings
- Wire colors abroad
- Specification marking
- Wire colors
- DC network - what color are the plus and minus wires
- Purpose of marking
- Main differences
- Letter marking of electrical cables
- First letter
- Second letter
- Third letter
- What is color coding for?
- Core marking for electrical installation solutions
The main types of marking cable tags
A marking tag in accordance with international standards should be installed on open cable routes and power plants. If the wire is laid in structures specially designed for this, then the distance between the markers can be 50-70 m. You cannot do without them in a number of other cases:
- when the route crosses various obstacles that make visual inspection difficult (interfloor ceilings, walls, partitions), then the tags are placed on each side of the passed obstacle (for example, on both sides of the wall);
- at points where the direction of the cable line changes;
- in places where input or output from other structures is carried out.

Many manufacturers and electricians prefer plastic cable tags, since such material is able to withstand moisture for a long time without changing its properties.
Form of marking tags
The rules and regulations indicate information on the forms of tags, which was described above:
- triangular - installed in cable lines for control or signal purposes;
- square - for power lines with voltage up to 1 kV;
- round - over 1 kV.
Dimensions of marking tags
The most common brands of cable tags are U-134, U-135, U-136 and U-153. Let's compare their sizes and, depending on the data obtained, draw conclusions on their possible application in systems:
- U-134 is used to designate a power line with a voltage not exceeding 1000 V. A square tag with an area of 55 × 55 mm is equipped with two grooves 11 × 3.5 mm for fixing with a cable binder.
- U-135 is suitable for indicating information on electrical circuits with a voltage of more than 1000 V. Round products with a diameter of 55 mm and similar grooves for a cable binder.
- U-136 is used for marking signal and control wires. The triangular product has equal sides 62 mm long each. There are two slots for a cable binder of the same size.
- U-153 is used for power lines with voltage up to 1000 V.A square product with a length of 28 mm and a hole of 5 mm is attached using a special wire.
Important! Many organizations either ignore the cable tagging process or do it using freeform tags. The consequences of both decisions can cause frequent emergencies and injury to operating personnel.
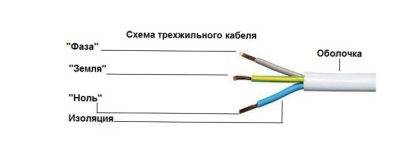
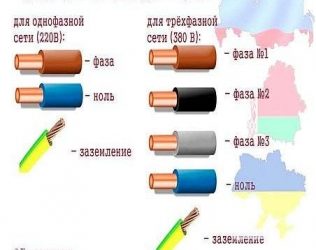
Color coding of wires and cables
The generally accepted standards and rules for color marking the insulating sheath of wires allow you to quickly and accurately determine the operating parameters of the cable, understand in which systems and devices it can be used. The color marking regulation is prescribed by the PUE and GOST.
It is noteworthy that the notation will be different for cable networks with alternating or direct current. Often the cable is made multi-colored. Instead of a sheath, color marking can be done using heat shrink tubing (cambric). Another option is colored tape. The choice of color for phase and neutral wires should always be different!
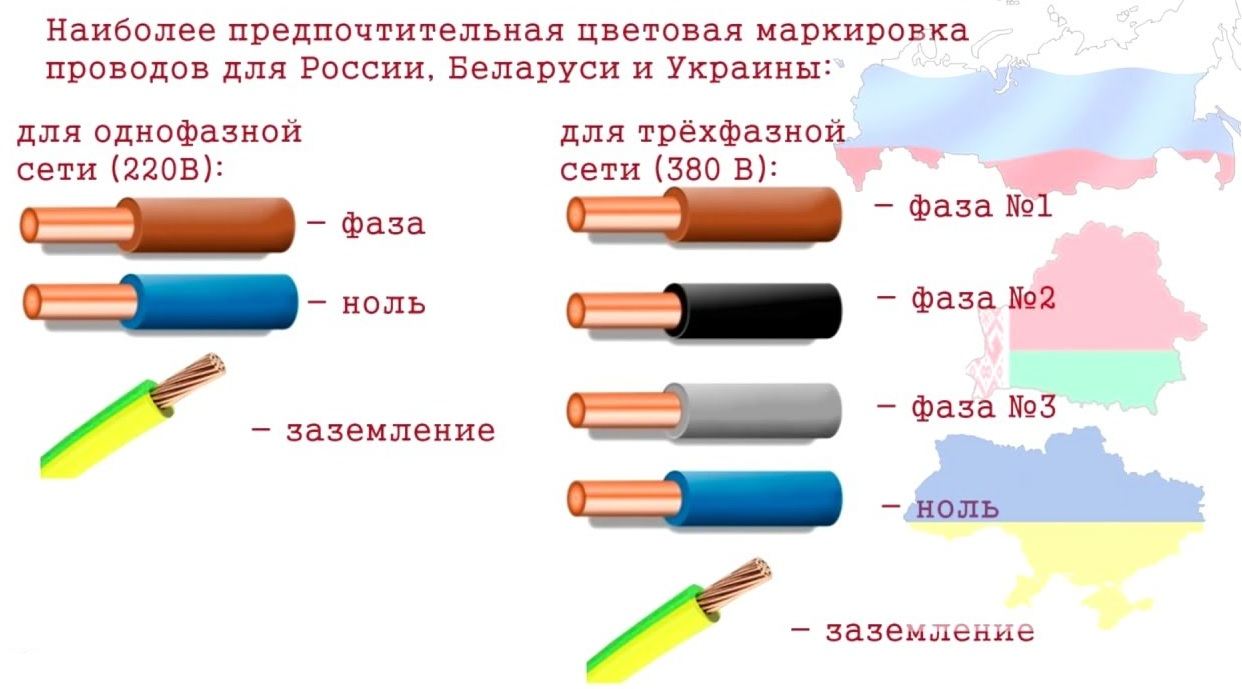
For three-phase variable power lines, the tires should be marked as follows:
- the first phase is yellow;
- the second is green;
- the third is red.
In DC cable runs, colors are chosen according to the charge, which can be positive or negative. In the first case, a wire in a red braid is selected, in the second - in blue. The system does not support phase and neutral wires, and for the middle one they usually take a light blue conductor.
For power plants with voltage up to 1 kV and neutral, the following marking is performed:
- working neutral wire - blue;
- grounding - yellow-green;
- combined zero - yellow-green with blue markers (or blue with yellow-green markers);
- phases - red, black and other colors depending on the quantity.
It is noteworthy that the wiring inside electrical appliances is made red, in sockets - brown.
Afterword
If it suddenly turned out that during installation a violation of color marking was noticed, there is no need to repeat other people's mistakes and continue wiring not according to the established rules. It is better to correctly mark the incoming veins, and then lead it according to the necessary colors. This method will save, subsequently, from the troubles and inconveniences associated with the revision, repair of wiring in the apartment and will significantly reduce the time spent on these actions. After all, it is much more convenient when the fitter knows what this or that designation means and is sure that you can not be afraid of the colors that mean grounding and zero, but you should be more careful with the red wire.
Purposes of wire marking
This process allows you to significantly simplify electrical work, scheduled or emergency repairs, maintenance of facilities and cable lines during operation. Another functional purpose is to reduce the likelihood of emergencies and the resulting injury to workers.

The cable is marked already in the manufacturing process. The manufacturer must choose a color for the insulating sheath of the wire in accordance with international or domestic standards prescribed in the PUE, PTEEP, GOSTs and other documentation. The data displayed on the outer sheath of the cable indicates information on several parameters:
- number of wires;
- cross-sectional area of the entire cable;
- applied insulating materials;
- wire materials, etc.
Such marking, although necessary, is not sufficient to improve safety during the operation of cable lines. Focusing on it, maintenance specialists will not be able to draw unambiguous conclusions about the purpose of the entire system or a specific section of electrical wiring. Therefore, when performing electrical work, additional abbreviations are applied to the cable, adding information about the purpose of the circuit to the characteristics.
Thanks to this, tags with the following data appear on the insulation:
- cable brand;
- purpose;
- the object associated with it;
- line length and other information, if necessary.

Cable tags greatly simplify such marking, make it convenient and as fast as possible. They are selected depending on the diameter, characteristics and insulating materials on the wire. They may differ in a number of parameters, but they have a common purpose and are able to store inscriptions for a long period of operation.
Cable marking with tags according to PUE - Security Portal
> Theory > Cable tags
For the correct installation and operation of electrical wiring and other devices, it is necessary to have at least minimal knowledge in the field of standards for the installation of cable lines and electrical installations.
There are many provisions and instructions that regulate the actions of an electrician and an installer when working on electrical lines of various voltages. Such documents include the Rules for marking wires on the highway and in the switch cabinet.
This article discusses the types of tags for cable marking, as well as the conditions under which the label should be on the surface of the wire.
Forward and reverse phase sequence
Three-phase AC graphically represents three phases in the form of alternating sinusoids on the X axis, shifted relative to each other by 120 °. The first sine wave can be represented as phase A, the next sine wave as phase B, shifted 120° from phase A, and the third phase C, also shifted 120° from phase B.
Graphical display of phase shift by 120° of a three-phase network
If the phases have the order ABC, then such a sequence of phases is called direct alternation. Therefore, the order of the CBA phases will mean reverse alternation. In total, three direct phase sequences ABC, BCA, CAB are possible. For reverse phase sequence, the order would be CBA, BAC, ACB.
You can check the phase sequence of a three-phase network with a phase indicator FU - 2. It is a small case on which there are three clamps for connecting the three phases of the network, an aluminum disk with a black dot on a white background and three windings. Its principle of operation is similar to that of an asynchronous electric motor.
If you connect the phase indicator to three phases and press the button on the case, the disk will begin to rotate in one direction. When the rotation of the disk coincides with the arrow on the housing, then the phase indicator shows a direct phase sequence, the rotation of the disk in the opposite direction indicates a reverse phase sequence.
The electrical circuit of the phase indicator FU-2
In what cases it is necessary to know the order of phase sequence. Firstly, if the house is connected to a three-phase network and an induction electricity meter is installed, then a direct phase sequence must be observed on it.If such an electric meter is connected incorrectly, its self-propelling is possible, which will give incorrect readings in the direction of increasing electricity consumption.
Also, if asynchronous electric motors are used in the house, then the direction of rotation of the rotor will depend on the order of the phase sequence. By changing the phase sequence on an asynchronous electric motor, you can change the direction of rotation of the rotor in the desired direction.
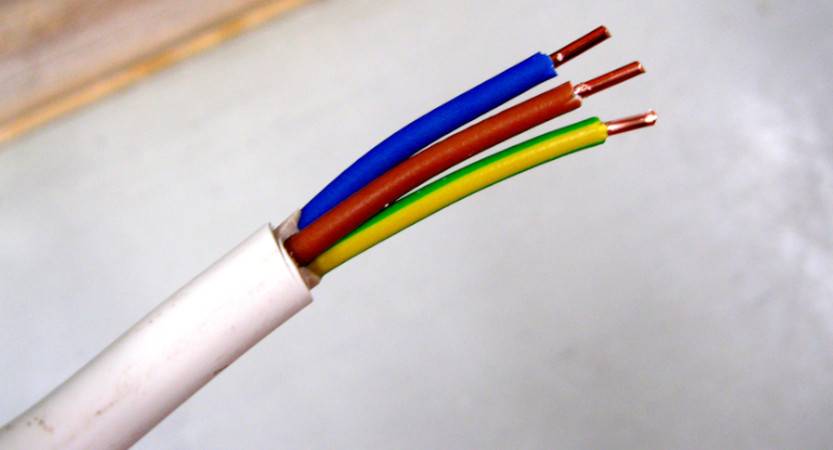
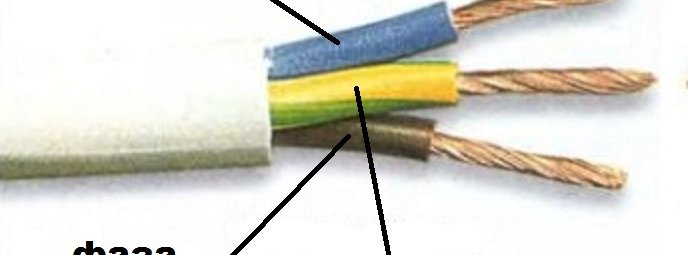
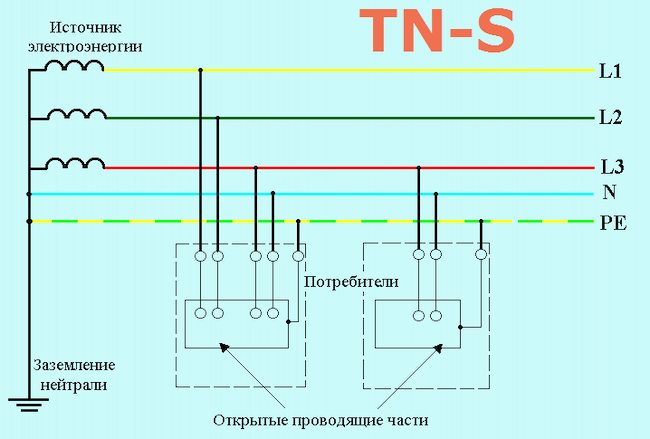
Color zero, neutral
Zero wire - should be of blue color. In the switchboard, it must be connected to the zero bus, which is indicated by the Latin letter N. All blue wires must be connected to it. The bus is connected to the input by means of a meter or directly, without additional installation of the machine. In the distribution box, all wires (with the exception of the wire from the switch) of blue color (neutral) are connected and do not participate in switching. To the sockets, the blue “zero” wires are connected to the contact, which is indicated by the letter N, which is marked on the back of the sockets.
The designation of the phase wire is not so clear. It can be either brown, or black, or red, or other colors. Besides blue, green and yellow. In the apartment switchboard, the phase wire coming from the load consumer is connected to the lower contact of the circuit breaker or to the RCD. In the switches, the phase wire is switched, during shutdown, the contact closes and voltage is supplied to consumers. In phase sockets, the black wire must be connected to the contact, which is marked with the letter L.
How to find ground, neutral and phase in the absence of a designation
If there is no color marking of the wires, then you can use an indicator screwdriver to determine the phase, upon contact with it, the screwdriver indicator will light up, but not on the neutral and ground wires.
You can use a multimeter to find ground and neutral. We find the phase with a screwdriver, fix one contact of the multimeter on it and “probe” the other contact of the wire, if the multimeter showed 220 volts, this is neutral, if the values \u200b\u200bare below 220, then grounding.
Letter and number wire markings
The first letter "A" denotes aluminum as the core material, in the absence of this letter, the core is copper.
The letters "AA" denote a multi-core cable with an aluminum core and an additional braid from it.
"AC" is indicated in the case of an additional lead braid.
The letter "B" is present if the cable is waterproof and it has an additional braid of two-layer steel.
"Bn" cable braid does not support combustion.
"B" polyvinyl chloride sheath.
"G" does not have a protective shell.
"g" (lowercase) naked waterproof.
"K" control cable wrapped with wire under the top sheath.
"R" rubber shell.
"HP" non-flammable rubber sheath.
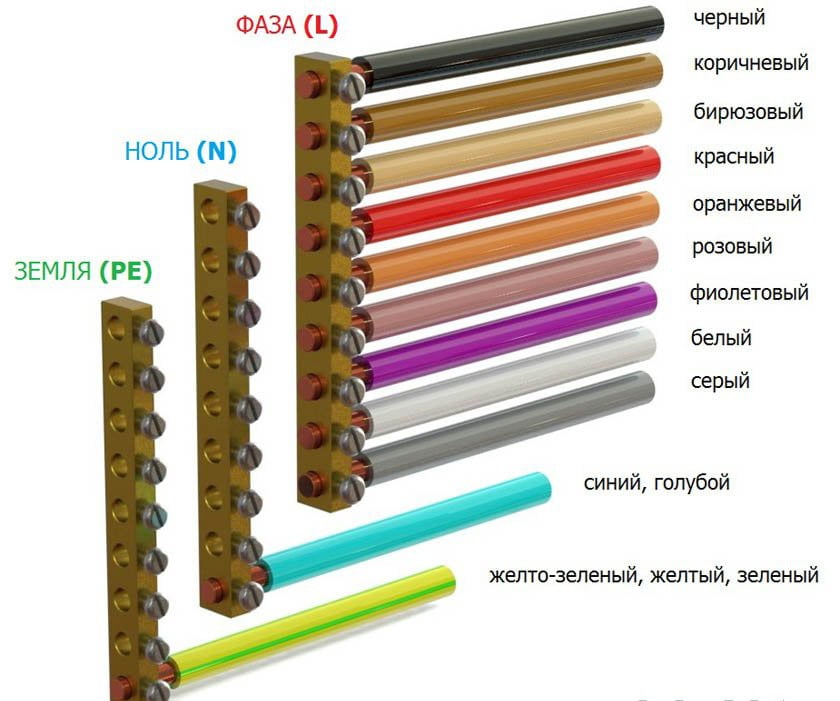
Wire colors abroad


The color marking of wires in Ukraine, Russia, Belarus, Singapore, Kazakhstan, China, Hong Kong and in the countries of the European Union is the same: Ground wire - Green-yellow
Neutral wire - blue
phases are marked with different colors
The neutral designation is black in South Africa, India, Pakistan, England, but this is the case with old wiring.
currently neutral blue.
In Australia, it can be blue and black.
In the USA and Canada it is designated as white.Also in the USA you can find gray markings.
The ground wire is yellow, green, yellow-green everywhere, and in some countries it may be without insulation.
Other wire colors are used for phases and may be different, except for the colors indicating other wires.
13 ways to save electricity
Specification marking
Cables and wires are marked not only for their intended purpose. An alphanumeric designation is usually indicated on the cable sheath, by which its technical characteristics can be determined.
Letter designations of domestic products:
1 - core material (A - aluminum);
2 - type of wire (M - mounting, K - control, etc.);
3 - insulation material (R - rubber, P - polyethylene, etc.);
4 - protective structure (B - armored with metal tapes, T - for laying in pipes, etc.).
Digital designations of domestic products:
1 - number of cores (there is no first digit on a single-core wire);
2 - section;
3 - maximum voltage.
Designations according to European standards:
N - VDE standard;
Y - PVC insulation;
M - mounting cable;
RG - armored protection;
C - shielded cable;
SL - control cable;
05 - voltage up to 500 V;
07 - voltage up to 750 V.
This is the most common and well-known marking of cable products.
Wire colors
PVC or polyethylene insulation can be painted in any color, chemists have selected all the necessary dyes for this. The most relevant color marking was first in telephone cables, there are still rules for counting pairs and fours by color.They use a thin copper core covered with multi-colored plastic insulation. Later, color standards came to power electrical engineering.
For example, aluminum and copper busbars in power cabinets used to be colored yellow, green, and red to represent phases A, B, and C.
Phase rotation is very important in many cases, for example, the direction of rotation of electric motors depends on it.
There are simple rules that allow you to confidently determine the purpose of the conductor by color. The protective earth (PE conductor) is always colored yellow-green or yellow or green. This is the color of the ground wire - no other can be this color.
Neutral N (this is the common connection point of the generator windings connected in a star pattern) is always blue or light blue. All other colors are used for marking phases, provided that they cannot be confused with zero and ground wires even in poor lighting conditions. That is, contrasting colors are most preferred:
Most often, a phase conductor in a single-phase circuit is indicated in brown. A three-phase three-core wire is marked with colors: brown, black, gray. Such cables are usually connected to electric motors on a metal frame when the windings are connected in a triangle (cranes, loaders, industrial equipment).
A few words must be said about DC circuits. In such cases, colors are used to indicate polarity: plus - preferably brown (or red), minus - gray. If any of the conductors of the DC circuit is connected to the neutral of the AC, then blue is used for it.
The colors of the wires in the electrics must be observed in all cases (GOST R 50462 - 2009).Electrical wires are live and color coded for added safety. This in no way overrides the rest of the security rules. Even after removing the voltage from the circuit, you should use the phase indicator, produced in the form of a small screwdriver.
Installation wires (for the installation of electrical installations and equipment) are almost always located in such a way that they necessarily require dialing before connecting: either there are a lot of them in a bundle, or they come from nowhere. Multi-core cable can be used for various needs, not only for power supply, but also in control and automation circuits.
In the past, the installation wires were often white aluminum wire with no difference between phase and neutral. If it was necessary to install, for example, a push-button station with several buttons, there were difficulties with dialing and frequent errors. Sometimes it was too costly.
DC network - what color are the plus and minus wires
In addition to AC networks, the national economy uses DC circuits, which are used in the following areas:
- • in industry, construction, storage of materials (loading equipment, electric carts, electric cranes);
- • in electrified transport (trams, trolleybuses, electric locomotives, motor ships, mining dump trucks);
- • at electrical substations (for supplying automation and operational protection circuits).
The DC network uses only two wires. In such networks, there is no phase or neutral conductor, but there is only a positive bus (+) and a negative bus (-).
By regulation, wires and rails of positive charge (+) must be colored red, and wires and rails of negative charge (-) must be blue. The middle conductor (M) is indicated in blue.
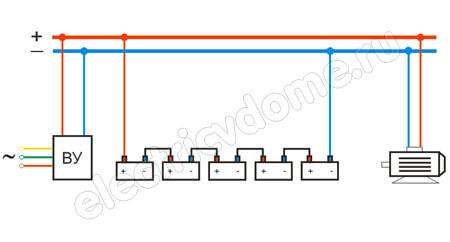
If a two-wire DC electrical network is created by branching off a three-wire DC circuit, then the positive conductor of the two-wire network is indicated by the same color as the positive conductor of the three-wire circuit with which it is connected.
Purpose of marking
Most beginners, when faced with the very concept of marking for the first time, are wondering what the letters and numbers that make up it mean. Despite the wide variety of both domestic and foreign products, cable marking contains information about:
- the material of the cores and their number, in most cases, current-carrying elements are made of copper or aluminum with monolithic or stranded conductors, but there are also specific models with steel or composite cores;
Rice. 1: type and material of conductors
- type of insulation - provides information on what the insulating sheath is made of, both the cores themselves and other layers in the cable (rubber, polyvinyl chloride, fluoroplast, etc.);
- section of conductors - indicates the area of current-carrying elements in the cross section, which determines the resistance to electric current and varies from 0.35 to 240 mm2;
- nominal electrical values - may contain the value of the operating voltage for which the insulation is designed, in the marking most often there are ratings of 0.23; 0.4; 6; ten; 35 kV;
- areas of application - indicates resistance to aggressive environmental influences;
- design features - in the marking indicates the presence of additional elements or the use of specific technologies in the manufacture;
- degree of flexibility - indicates how well this cable model can bend, the flexibility of the core in the marking can be indicated by numbers from 1 to 6, where 1 is the least flexible and 6 is the most flexible brand.
Main differences
It should be noted that the purpose of marking cables and conductor products may also include an indication of specific design features corresponding to its type (cable, wire or cord). So a wire is a product made of a monolithic or multi-wire current-carrying element, which can either contain insulation or be made without it.
Electric cord - includes several insulated wires with a multi-wire structure and is used to connect various devices to the power supply.
Cable - can include both single-core and multi-core wires, several layers of insulation, screen armor and other structural elements (power, communication, control, control and radio frequency cables are distinguished by purpose).
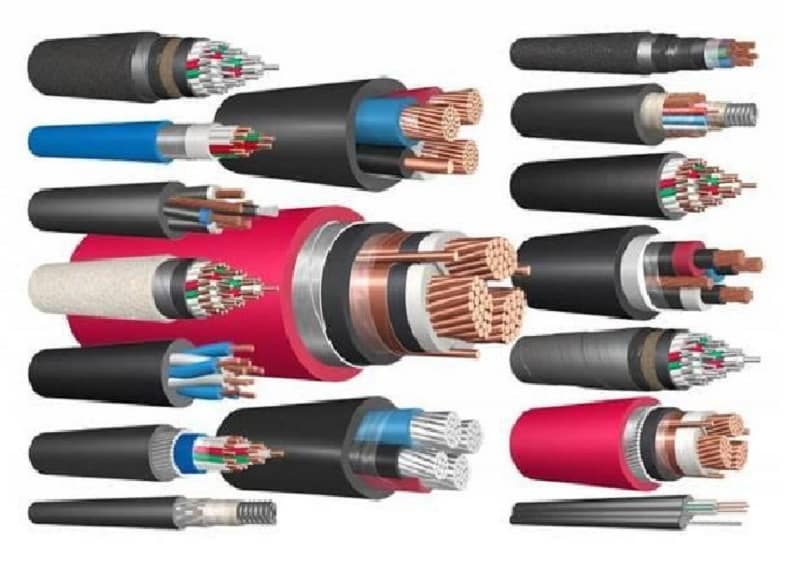

Figure 2: different types of cables
Thanks to the above division, from the marking you can immediately determine what is in front of you (cable, wire or cord), as well as establish its role in a particular electrical installation. To do this, we will analyze the marking options for the most common brands used in domestic devices, and the principle of their compilation.
Letter marking of electrical cables
The letter part of the cable marking consists of several letters, each of which carries a specific semantic load.
First letter
There are only two options in this part of the marking.
- The letter , which means that the cable cores are made of aluminum (example, BUTVVG).
- The absence of a letter means that the conductors are made of copper (for example, VVG).
Second letter
The 2nd letter of the marking indicates the purpose of the cable.
The absence of the second letter in the cable marking means that the cable is power.
- K - control (ToGVV, ToGVV-KhL, KGVVng(A), KGVEV,);
- M - mounting (MKSh, MKESH, MKEShvng, MKEShvng-LS);
- MG - mounting flexible (MGShV);
- P (U) - installation wire (PAT 3, PuGV);
Third letter
The third letter in the marking of electrical cables indicates the material from which the core insulation is made. If there are several layers of insulation, list the layers from the top layer to the bottom layer. For example isolation.
- B - PVC insulation (example, -BATG);
- P - electrical rubber (example, RPSh);
- HP - non-flammable rubber;
- P (Pv) - cross-linked polyethylene (-PvVG).
The following capital letters denote special design features:
- P - flat wire or cable armored with flat wires (SHVVP);
- B - cable armored with tapes (ABBbShv, VBbShv);
- G - for a power cable, it means without a protective cover (VVG); for wire, it is flexible wire (PUGAT)
- Shv - protective hose made of polyvinyl chloride composition (example VBbShv).
Fifth, additional part of the letter marking of cables:
Usually these are small letters used by manufacturers for specific cable design features.
- ng - non-combustible;
- LS - low smoke and gas emission;
- h - filled.
I will give a few examples of marking cables used for wiring in an apartment and a house.
VVG cable. This marking is deciphered as follows:
VVG. There are no first and second letters, so this is a power cable with copper conductors. PVC core insulation. PVC cable sheath. The letter G means that the cable does not have a protective cover.
VVGng - non-flammable cable VVG.
Armored cable VBbShv (AVBShv)
- B - Vinyl insulation;
- B - Armored;
- b - bitumen;
- Shv - vinyl hose;
- A - aluminum wires.
What is color coding for?
Wires must be connected to each other only in strict accordance. If mixed up, a short circuit will occur, which can lead to equipment failure or the cable itself, and in some cases even a fire.
Standard wire colors
Marking allows you to correctly connect the wires, quickly find the right contacts and work safely with cables of any type and shape. Marking, according to the PUE, is standard, so knowing the principles of connection, you can work in any country in the world.
Note that the old cables produced under the USSR had one conductor color (usually black, blue or white). In order to find the desired contact, they had to ring or apply a phase to each wire in turn, which led to unreasonable waste of time and frequent mistakes (many people remember freshly built Khrushchev houses, in which when the bell was pressed at the front door, the light in the bathroom turned on, and when the switch was pressed in the bedroom power was lost in the outlet in the hallway).
Core marking for electrical installation solutions
No wonder at the beginning of the article the idea was voiced that the color designation of conductors greatly simplifies the installation process.
If you are independently engaged in wiring electricians in an apartment or a private house, select wires according to the standards, when connecting electrical devices, installing automatic protection, distributing cores in junction boxes, you do not need to double-check where the phase, zero, earth are - this will tell the color of the insulation.
A few examples of wiring where marking is important:
There are cables with a large number of cores, the coloring of which does not seem appropriate. An example is SIP, which uses a different way to define conductors. One of them is marked with a small groove along its entire length. The embossed core usually performs the function of a neutral conductor, the rest play the role of linear ones.
To distinguish the cores, they are marked with tape, heat shrink, lettering, which are applied with multi-colored markers. And in the process of electrical installation work, a ringing is sure to be done - additional identification.





















![Choosing the Best Water Towel Warmers [Our Top 8] | engineer will tell you how to do it](https://fix.housecope.com/wp-content/uploads/2/e/c/2ec9bd33db262982410ba1db2395e9fa.jpeg)
