- The difference between cast iron and bimetallic batteries
- Bimetallic heating radiators which is better selection instructions
- The positive aspects of using bimetallic radiators
- The negative aspects of using bimetallic radiators
- Varieties and design features of cast iron radiators
- The main differences between batteries
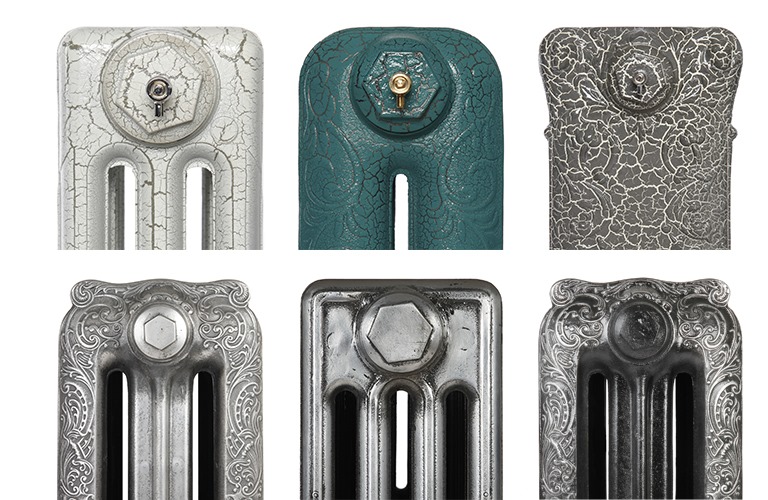
- Features of decorative radiators
- Disadvantages of cast iron radiators
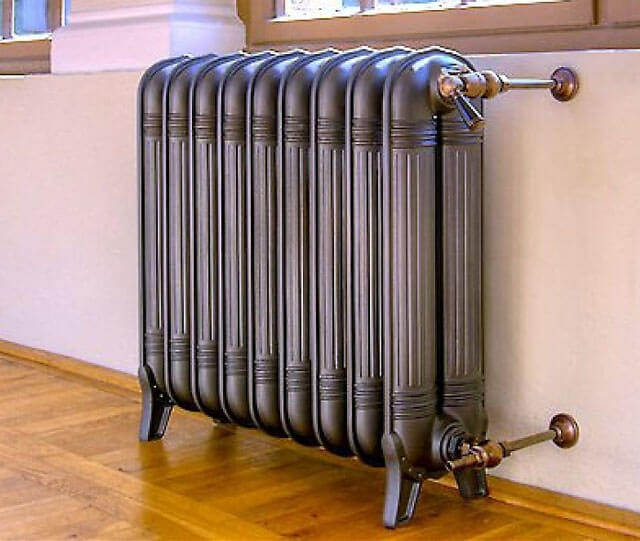
- Modern design cast iron radiators
- Retro Style Cast Iron Radiators
- Installing the battery in the system
- Varieties and their characteristics
- Bimetallic
- Cast iron
- Aluminum
- Steel
- Which steel radiators are better to buy
- Steel panel or tubular radiators
- Radiators with bottom or side connection
- An example of calculating the required radiator power
- Why Radiator Certification Is So Important
- Conclusion on the topic
The difference between cast iron and bimetallic batteries
Radiators, consisting of two types of metals at once, came to the domestic market from Italy and quickly won the hearts of consumers, despite their high cost. This can be summed up in one word: reliability. If you choose which is better, cast iron or bimetallic batteries, then you should refer to a comparison of their technical indicators:
- Structure:
- Cast iron structures now look stylish, but are also assembled from sections equipped with a fairly wide channel for the coolant. Their weight has become much less (3.5 kg compared to 8 kg before), the appearance is presentable, and the reliability is the same. There are classic sectional models and artistic, retro-style models on the market. The latter are very expensive, and mostly imported.
- Bimetal constructions consist of a steel or copper core with aluminum fins and casing. The coolant comes into contact exclusively with stainless steel, which protects the device from corrosion, and the casing provides high heat transfer. Such a heater weighs a little, it is easy to install, and additional thermostats allow you to monitor the heating of the coolant.
- Heat dissipation level:
- If you decide whether cast-iron radiators or bimetallic ones heat better, then their performance will be approximately equal. So the heat transfer of a cast iron section ranges from 100 W to 160 W. Many consumers feel that they take too long to warm up, and they are right. At the same time, everyone forgets that these batteries also take a very long time to cool down.
- The heat output of one section of a bimetallic radiator is 150-200 W, which, with instant heating, brings this type of heater to a leading position.
- Operating pressure:
- Although many years of experience in the operation of cast iron batteries suggests that they are strong and reliable, this is not entirely true when it comes to high-rise buildings. Even in five-story buildings, water hammer can occur in the heating system, which is quite strong, to say nothing of buildings of 16 floors and above. The working pressure of cast iron batteries is 9-12 atmospheres, which may not be enough with a sharp rise in pressure, for example, up to 15 atmospheres.In this case, the cast iron sections will simply burst.
- Bimetallic radiators are more reliable, since their operating pressure is 25-40 atmospheres, and in some models even 100 atmospheres. At this point, designs of two types of metal are also in the lead.
- Heat transfer resistance:
- Cast iron is absolutely "indifferent" to the quality of water and its acidity. It does not affect him and her complete drain for the summer, but the pebbles that sweep through the system gradually weaken the cast iron, exude it and disable it. This process is lengthy, and if the radiator walls are of sufficient thickness, then it is completely endless.
- The bimetallic radiator is weaker in this respect. He is not afraid of the level of acidity of the water as long as it is in the system, but as soon as it is drained, corrosion begins to appear after 2-3 weeks of contact with air. In this indicator, bimetal loses to cast iron.
- According to the temperature regime, both types of radiators tolerate its differences well. For cast iron, the maximum water heating is +110, and for bimetal - +130 degrees.
- Today you can find cast-iron batteries, the age of which has exceeded the mark of 100 years, but on average they have a service life of 50 years. Manufacturers set a limit for bimetallic radiators of 25-30 years, which is less than that of cast iron.
Bimetal heaters are the best option for replacing old batteries. In the main indicators, they are superior to cast iron devices, which guarantees their efficient operation in an unfriendly district heating environment. In addition, they are much easier to install, they are light and do not require additional care.
If the question is whether to change cast-iron radiators to bimetallic ones or not, then residents of five-story buildings do not have to do this, especially since the latest devices are twice as expensive. Here, residents of high-rise buildings will have to abandon cast-iron batteries, as they will not withstand the load of the system and will leak. In this variant, there is definitely nothing better than bimetallic structures.
Bimetallic heating radiators which is better selection instructions
The first heating radiators made from two metals (bimetallic) appeared in Europe more than sixty years ago. Such radiators quite coped with the assigned function of maintaining a comfortable temperature in the room during the cold season. At present, the production of bimetallic radiators has been resumed in Russia, while the European market, in turn, is dominated by various aluminum alloy radiators.
Bimetal heating radiators which are better
Bimetallic radiators are a frame made of steel or copper hollow pipes (horizontal and vertical), inside which the coolant circulates. Outside, aluminum radiator plates are attached to the pipes. They are attached by spot welding or special injection molding. Each section of the radiator is connected to the other by steel nipples with heat-resistant (up to two hundred degrees) rubber gaskets.
The design of the bimetallic radiator
In Russian city apartments with centralized heating, radiators of this type perfectly withstand pressures up to 25 atmospheres (when pressure tested up to 37 atmospheres) and, due to their high heat transfer, perform their function much better than their cast-iron predecessors.
Radiator - photo
Externally, it is quite difficult to distinguish bimetallic and aluminum radiators. You can verify the correct choice only by comparing the weight of these radiators. Bimetallic because of the steel core will be heavier than its aluminum counterpart by about 60% and you will make an error-free purchase.
The device of a bimetallic radiator from the inside
The positive aspects of using bimetallic radiators
- Bimetal panel-type radiators fit perfectly into the design of any interior (residential buildings, offices, etc.), without taking up much space. The front side of the radiator can be one or both, the size and color scheme of the sections are varied (self-coloring is allowed). The absence of sharp corners and too hot panels makes aluminum radiators suitable even for children's rooms. In addition, there are models on the market that are installed vertically without the use of brackets due to the additionally present stiffeners.
- The service life of radiators made of an alloy of two metals reaches 25 years.
- Bimetal is suitable for all heating systems, including central heating. As you know, low-quality coolant in municipal heating systems adversely affects radiators, reducing their service life, however, bimetal radiators are not afraid of high acidity and poor quality of coolants due to the high corrosion resistance of steel.
- Bimetallic radiators are the standard of strength and reliability. Even if the pressure in the system reaches 35-37 atmospheres, this will not damage the batteries.
- High heat transfer is one of the main advantages of bimetal radiators.
- The regulation of the heating temperature using a thermostat occurs almost instantly due to the small cross section of the channels in the radiator. The same factor allows you to halve the amount of coolant used.
- Even if it becomes necessary to repair one of the radiator sections, thanks to the well-thought-out design of the nipples, the work will take a minimum of time and effort.
- The number of radiator sections needed to heat a room can be easily calculated mathematically. This eliminates unnecessary financial costs for the purchase, installation and operation of radiators.
The negative aspects of using bimetallic radiators
- As mentioned above, bimetallic radiators are suitable for operation with a low-quality coolant, but the latter significantly reduces the life of the radiator.
- The main disadvantage of a bimetallic battery is the different expansion coefficient for aluminum alloy and steel. After prolonged use, creaking and a decrease in the strength and durability of the radiator may occur.
- When operating radiators with low-quality coolant, steel pipes may quickly become clogged, corrosion may occur, and heat transfer may decrease.
- The contested disadvantage is the cost of bimetal radiators. It is higher than that of cast iron, steel and aluminum radiators, but considering all the advantages, the price is fully justified.
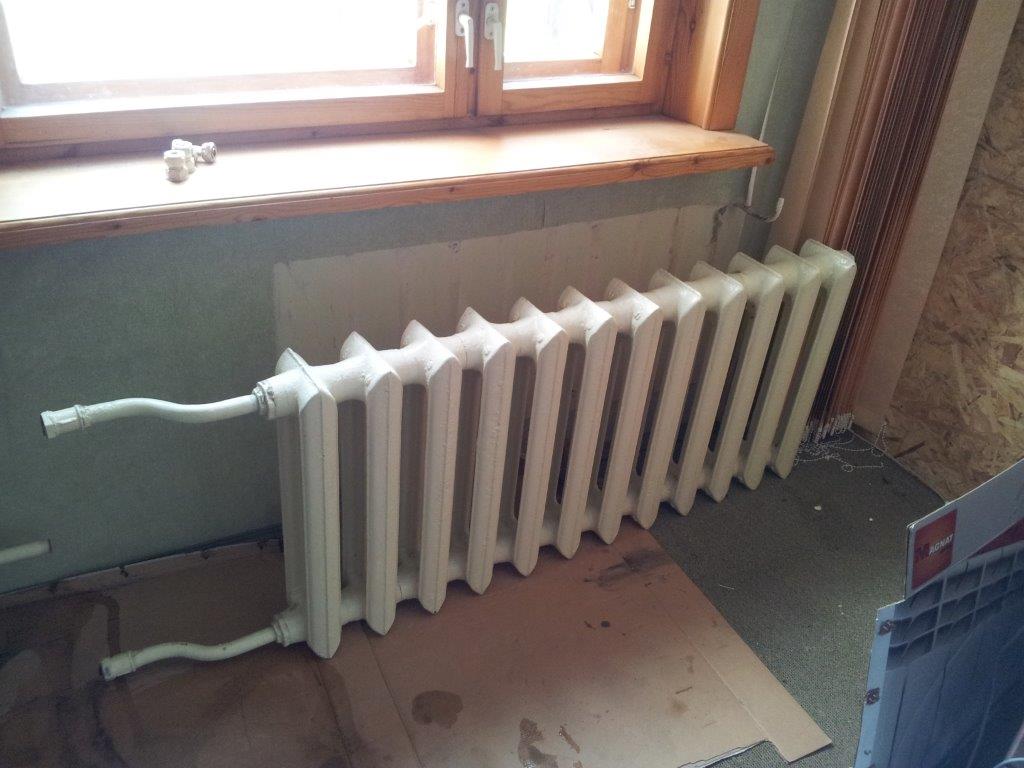
Varieties and design features of cast iron radiators
Each battery consists of several cast sections. They are made from gray cast iron. Inside the sections there are channels through which the coolant moves. The cross section of the channels is round or elliptical.The sections are interconnected by nipples. So that the joints do not leak, they are additionally sealed with special gaskets - usually paronite or rubber.
Depending on the number of channels inside the sections, several types of batteries are distinguished:
- single-channel;
- two-channel;
- three-channel.
Manufacturers produce heaters of various sizes, with a different number of sections. The main technical characteristic - power - depends on the parameters of the radiators. The height of the instruments ranges from 35 to 150 cm, the depth is 50-140 cm.
As for the location and type of fastening, the cast-iron radiators are mostly wall-mounted, they are mounted under the window sills on powerful brackets. But in recent years, manufacturers are increasingly supplying the market with floor models that are equipped with legs. This is a convenient option, because cast iron is very heavy, it can not be mounted on all types of walls.
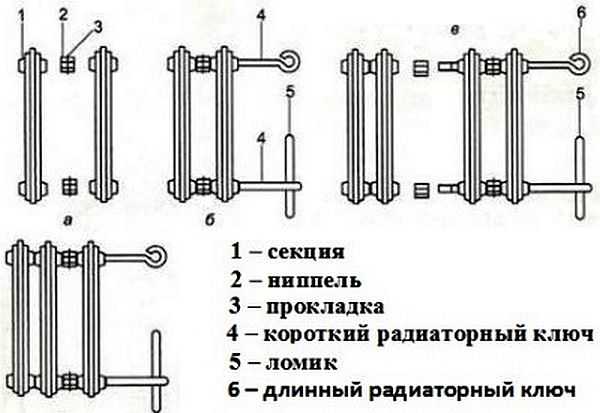
Construction of cast iron radiators
The main differences between batteries
There are two types of pressure in district heating plants:
- Working.
- Crimping.
The latter is always higher. For aluminum radiators, the working pressure is considered to be up to 16 atmospheres, which corresponds to the performance in thermal networks. Sometimes the pressure can reach up to 28 atmospheres, which is a critical value for aluminum radiators. Experts do not recommend using them in apartment buildings. Not only because of the pressure, but also because of the characteristics of the coolant. In private households, the pressure in the boiler usually does not exceed 1.5 atmospheres, so aluminum radiators are more preferable.
Crimping pressure is more relevant, it is necessary to know about its existence.Before the start of the heating season, it is recommended to test the tightness of the entire system. In professional language, this process is called: pressing. That is, at a higher pressure (1.5-2 times), water will be driven through the radiators.
In private houses, the pressure in the heating system is objectively lower. In high-rise buildings, in order for water to rise to a height of ten meters (three-story building), a pressure of one atmosphere is required.
Utilities do not always adhere to GOSTs, sometimes the pressure “jumps” in large ranges, so it’s better to buy batteries with a margin
Manufacturers often indicate different units of measurement in performance characteristics. One bar corresponds to one atmosphere, if the calculation is in megapascals, then in order to convert them into familiar atmospheres, you need to multiply by a factor of 10. Example: 1.3 megapascals corresponds to 13 atmospheres.
Half of the heat that aluminum radiators give off is the so-called heat rays. The rest of the heat is convection currents, they are generated when air masses move from bottom to top. This design effectively enhances heat dissipation.
Heat dissipation is measured in watts, for an aluminum battery with an axis of up to half a meter, heat dissipation can be up to 155 watts. Aluminum batteries have a high heat transfer, according to this indicator they are ahead of cast iron ones.
Cast iron radiators largely depend on the battery model. During the Soviet Union, cast iron batteries occupied up to 90% of the market, the design was especially popular: P140.
- The power of such a product ranged from 0.122 to 0.165.
- Average weight within 7.5 kg.
- Surface area 0.25 sq. meters
- Functional pressure 9.2 atm.
In order for the room to have an acceptable temperature in winter, it should be borne in mind that 140 watts of power is required per square meter (if there is one window and one outer wall). The temperature of the battery must be at least 65 degrees. If the room is too large, then ten square meters will require about 1.5 kW of power. All figures are given for guidance. More accurate you can get with the help of heat calculations.
Old cast-iron batteries work properly, but they look outdated. Often, heating devices are covered with special gratings or screens. There are also modern modifications that have a modern appearance. Particularly interesting are the products of the World Cup factory in the city of Cheboksary.
Example:
- ChM-1: depth up to 72 cm, power 0.076 to 0.12 kW, weight of one section 4.2 kg. Withstands pressure up to 9 atm.
- ChM - 2 also withstands pressure of nine atmospheres. Depth up to 1.1 meters, power 0.1082-0.143 kW. One section weighs up to approximately 6 kg.
Interesting models (MC-110) are produced by the Setehlit plant, the radiators are compact and easily fit into various openings.
Cast iron radiators are produced in Turkey, the Czech Republic and China. There are very attractive models that look ultra-modern. Example: Conner makes the Modern model: it has a depth of only 82 cm, withstands pressure up to 12.2 atm., and power from 0.122 to 1.52 kW. The weight of one section does not exceed 5.5 kg.
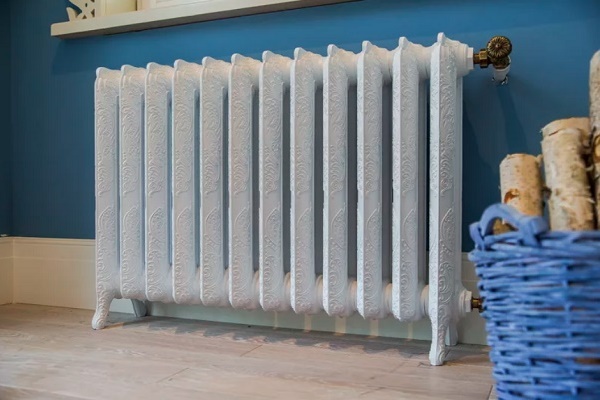
Features of decorative radiators
Designer products do not have such good technical performance:
- The heat transfer is somewhat lower, which is associated with an additional layer of paint, in some cases - with an ornament.
- The average power is less, because the dimensions are often cut.This helps to create an interior, but interferes with the direct purpose of the battery.
- The hydraulic resistance drops as the pipes are made small, neat.
- Unlike simple radiators, decorative ones are much more expensive.
These features look negative, but beauty requires sacrifice. Problems can be easily solved by minor design changes or by combining radiator heating with another.
Disadvantages of cast iron radiators
Modern model
Large radiator weight. If we take into account how much one section of a cast-iron heating radiator weighs (7.12 kg MS-140, the Soviet version), then a radiator of seven sections, together with water, will pull 60 kg. In addition, they are bulky, often protrude beyond the window sill, which spoils the appearance of the room.
The high thermal inertness of the cast iron alloy may not always be considered an advantage, since this property makes the radiator inefficient for use in an automatic thermal control system.
Less heat transfer surface area compared to other types of radiators. In addition, the thermal conductivity of cast iron is less than that of aluminum, bimetallic, steel counterparts.
If heating devices are installed near walls made of lightweight structures, then they are mounted on special brackets and stands.
Care comes down to removing dust not only from the rough surface of the product, but also between the sectional gaps, which is not very convenient. However, this must be done, otherwise the dust will be carried by warm air around the apartment.
Outdated design. The old design of radiators does not fit into the European renovations of recent years.The way out is to hide them behind decorative screens, make niches for them, change them to more modern ones.
Modern design cast iron radiators
New radiator model
Progress does not mark time, and manufacturers have developed new models that are significantly superior in design to their predecessors.
Having considered the advantages and disadvantages of cast iron radiators, adherents of cast iron do not take into account the disadvantages and want to install only cast iron in their apartment, but of a new generation. Some of today's models are close in design to aluminum and bimetallic counterparts.
They have a beautiful modern look, the facade part is made of a flat panel.
Some of today's models are close in design to aluminum and bimetallic counterparts. They have a beautiful modern look, the facade part is made of a flat panel.
If earlier an improved version was supplied from Turkey, China, Italy and other countries, today they are launched in Russia, Belarus, Ukraine.
When comparing our batteries and products from far abroad, we lose to them in terms of quality and some technical characteristics. This affects the price accordingly - it is much higher for foreign manufacturers.
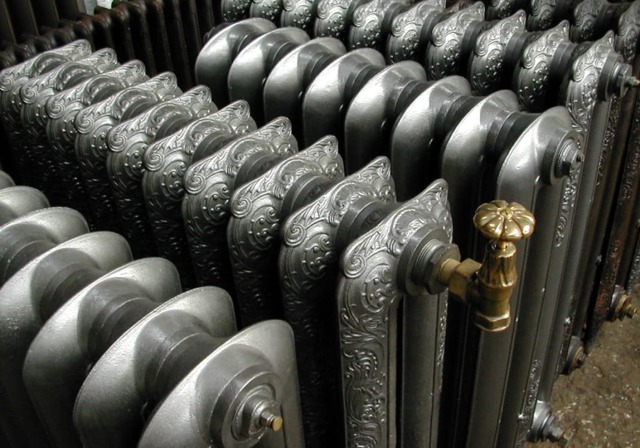
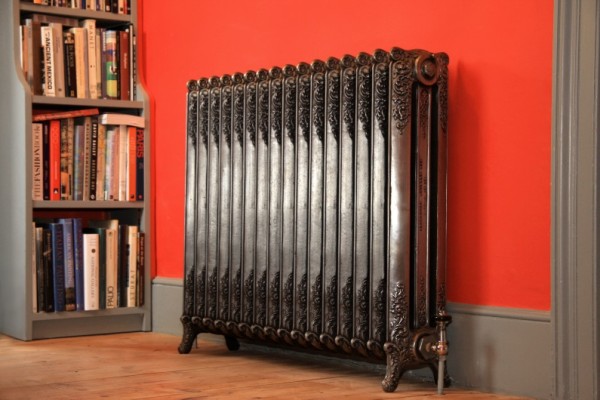
Retro Style Cast Iron Radiators
Retro style
For lovers of exclusivity, manufacturers can offer a retro-style option. This is not only a radiator, but also a decorative decoration for your home, that is, as they say, two in one.
They are produced in different geometric sizes, heat transfer, capacity, mass, design, painted in any color. The surface is covered with molded patterns, retro-installed on legs cast together with the radiator.
If you want to buy retro, it will harmoniously fit into any interior with its original design and become an exclusive warming decor in your home.
Perhaps the only drawback can be considered its cost, but a small compensation may be that the radiator does not need to be hidden and covered with protective screens, curtains, as it is beautiful.
You can still consider the advantages and disadvantages of cast iron radiators for a long time and compare them with modern bimetallic, aluminum and other counterparts. To summarize the above - as long as the heating networks and equipment remain in their current state, cast-iron batteries can be considered the best option.
Installing the battery in the system
When choosing one or another type of low radiator, it is necessary to determine its parameters, based on the size of the window and the required heat transfer. The length of the heat exchanger must be equal to the width of the opening or exceed it by 200-300 mm.
Having the skill of owning the necessary tool, it is not difficult to connect the radiator to the system with your own hands.
The following guide will help you with this:
- determine the type of system - one- or two-pipe;
- determine the most optimal connection scheme - diagonal, one-sided or lower;

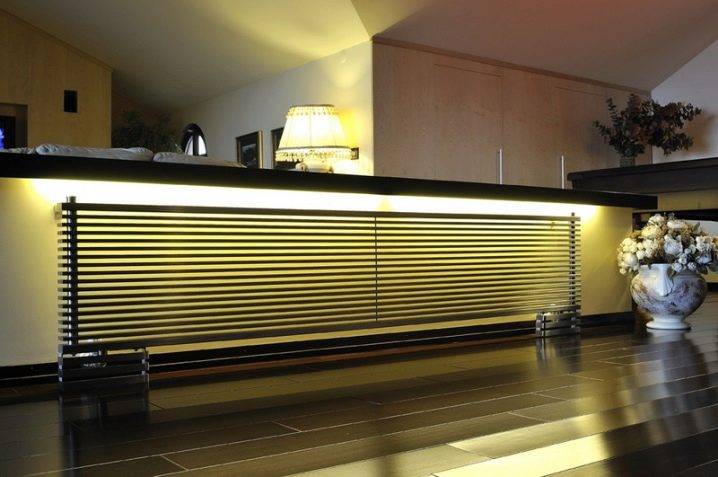
Inconspicuous element of the interior
- then we install taps on the inlet and outlet pipes. allowing to shut off the coolant supply in case of emergency;
- in the remaining holes we screw in the Mayevsky crane (top) and the plug (bottom).
- pre-assembly can be carried out dry, the final connection is made using linen winding and sanitary paste;
- it is possible to attach batteries from various metals to heating systems made of metal, metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes.
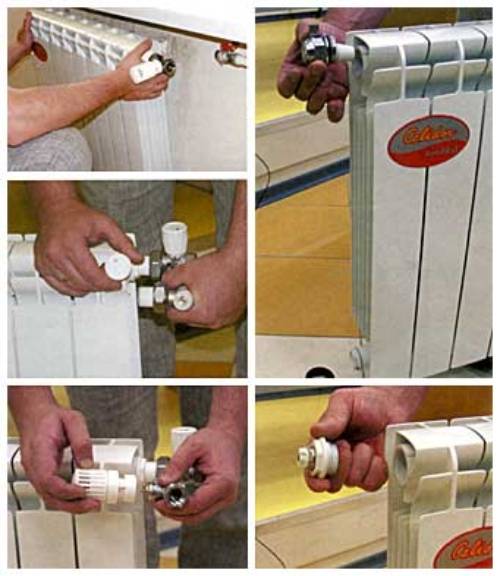

Picture montage
Varieties and their characteristics
Before deciding which radiators are better for heating: cast iron or bimetallic, or maybe aluminum type or steel, you need to figure out what the peculiarity of each of the materials is.
Bimetallic
If you have a question about how to choose the right bimetallic radiators for heating an apartment, you need to find out what the features of this product are. Firstly, bimetallic models have a modern appearance, as well as high-quality filling from the inside. Secondly, equipment made of this material should not be installed in production, as the resulting pressure surges can disable it or internal corrosion of the metal will appear.
Bimetallic radiators are distinguished by their long-term operation, as well as stability and the ability to withstand pressures up to 50 atmospheres.
They tend to warm up quickly and at the same time have a beautiful design.
But also bimetallic models have minor drawbacks, which include slag deposits and a decrease in heat transfer due to the use of various material options.
Cast iron
This material is different in that it is familiar to many, since earlier cast iron radiators were installed in almost every apartment. Now, modern models have practically nothing in common with their predecessors, except for the material, and differ from them both in appearance and in power and efficiency.
It is cast iron that differs from others in the best thermal conductivity.
Despite the fact that it tends to heat up for a long time, it does not cool down for a long time. Even after turning off the heating, the batteries continue to keep warm for some time. Residual retained heat can be up to 30%, which is twice that of steel and aluminum options.
The cast iron radiator is distinguished by its strength and durability, due to which the pressure indicator reaches 30 atmospheres. Batteries will not be afraid of either water hammer or accidents in the central heating system.
The advantage of cast iron models is that they have a universal connection. They are unpretentious during operation, corrosion does not form inside, and the smooth outer surface does not require special care. Various types of cast-iron heating radiators allow you to choose the right option for any requirements.

Advantages of cast iron radiators:
- low cost;
- strength and reliability;
- well compatible with any pipe materials;
- simplicity and ease of use;
- corrosion does not appear;
- long term use.
In addition, there are several disadvantages of such products: it is a difficult installation, since they are quite heavy, and weak inertia.
If you mount this radiator yourself, then you should adhere to all the points indicated in the instructions.
Aluminum
Cast iron or aluminum radiators, which is better for heating. In answering this question, the following should be noted. Despite the rather attractive appearance, it is better not to purchase this option for a centralized heating network.
They are more suitable for rooms with autonomous heating.
A few advantages that can be distinguished from an aluminum radiator:
- it is light in weight;
- ease of installation;
- has a stylish design;
- the price category is low;
- increased heat dissipation.
But at the same time, it is worth considering several disadvantages that may appear when installing the product in a central heating network:
- cannot withstand water hammer;
- has a short service life;
- pressure in the system is allowed up to 12 atmospheres.
It is best to choose an aluminum model based on the type of building heating system.
Steel
Steel batteries from a modern manufacturer can be distinguished both in design and construction. That is why the types of steel radiators are divided into two types: panel and tubular.
The advantages of this option include light weight, simple installation, a wide variety of different models, as well as absolutely not overstated requirements for the heating system.
Which steel radiators are better to buy
Steel radiators are divided into two types: panel and tubular. The former are cheaper and lighter, but less durable. The latter are more expensive and heavier, but withstand increased pressure and last longer. Models differ in design and principle of operation. Let's consider these two types in more detail to understand which radiators are best for specific operating conditions.
Steel panel or tubular radiators
Panel steel radiators
The design is a panel filled with a coolant and a corrugated metal sheet in contact with it for accelerated heat removal (the metal sheet increases the heat transfer area). The device works in two ways, combining them.Heat from the panel is given off to the surrounding air, and its passage through the fins starts natural convection in the room.
Sectional steel panel heating radiator.
Panel radiator - type 11.
Panel radiator - type 22.
Panel radiator - type 33.
Advantages of steel panel radiators
- light weight;
- good heat dissipation;
- affordable cost.
Cons of steel panel radiators
- low resistance to hydraulic pressure shocks;
- low inertia (quickly cool down after the boiler is turned off);
- the appearance of dust in the air from convection.
Tubular steel radiators
This category is visually similar to cast-iron batteries, but since the walls here are 1.2-1.5 mm thick, they are much thinner and more aesthetically pleasing, unlike bulky heavy metal radiators. The design is based on the lower and upper collectors, connected by vertical steel pipes. There can be two, three or four of them in each section, which increases the volume of the coolant and the area for heat exchange.
Steel tubular radiator.
Often the design can be expanded by adding additional sections if the current number is not enough to heat a particular room. This cannot be done in panel types. This type of battery does not create strong convection.
Advantages of tubular steel radiators
- resistance to water hammer;
- long service life;
- more attractive look;
- less hull depth;
- the possibility of growing or shortening.
Cons of tubular steel radiators
- higher cost;
- increased weight;
- may leak between sections.
Radiators with bottom or side connection
Lateral connection implies the supply of coolant to the upper fitting of the radiator, and the exit of water through the lower one, located on the left or right side of the body. This allows the fluid to pass through all internal channels faster and more efficiently in heat transfer. But with this installation, more pipe will be required for supply to the upper fitting, which can be located at a height of 300-850 mm. Still, such communications can spoil the interior, and you will have to think about how to hide them behind false panels.
Panel radiator with side connection.
The bottom connection involves the supply and removal of water through the fittings from the bottom of the radiator. When the panel is located close to the floor at a distance of 50 mm, such communications are not visible at all. This helps to make hidden wiring around the room without the cost of decorative materials. But the lower connection is less efficient in terms of the mixing speed of the hot and cold coolant, so the heating efficiency is reduced by 2-7%.
Panel radiator with bottom connection.
An example of calculating the required radiator power
In order not to miscalculate with the efficiency of heating, it is important to calculate in advance how much power the radiator should be, so that this is enough to heat a particular room. Here is the calculation formula:
Here is the calculation formula:
P=V*B*40+To+Td.
Let's take a look at these values:
- P is the power of the radiator, which we need to determine by substituting other values.
- V is the area of the room.
- B is the height of the ceilings in the room.
- 40 kW is the approximate heating power required to heat 1 m³.
- That is the inevitable heat loss on the windows, where one standard opening takes about 100 watts.
- Tg - similar losses occurring on the doors. Up to 150-200 watts can be lost on one leaf.
Now we count. There is a bedroom with an area of 15 m², in which there is one standard window and one door. Which radiator to buy for such a room?
15 m²*2.5 m (ceiling height)*40+100+200=1800 W. It is with such a minimum power that it is necessary to look for a radiator among panel or tubular options. If there is no exact value, then the choice is given in favor of a larger one.
Why Radiator Certification Is So Important
When certifying radiators, the following is checked:
- compliance with the declared heat transfer in terms of power;
- thickness of steel walls (should be at least 1.2 mm);
- maintaining nominal and maximum pressure.
Conclusion on the topic
Radiator taps Carlo Poletti
So, it's too early to say goodbye to cast-iron radiators, especially since it has become possible to purchase high-class appliances - beautiful and stylish. Of course, novelties will force traditional products out of the market, but until the heat carriers in the networks rise to a certain quality level, it is not necessary to talk about the departure of cast iron from the sphere of heating systems.
Let's add a low price and a long service life of cast iron products - and these two indicators for the mass consumer are still in the first place. Therefore, cast iron batteries will be present in our houses and apartments for a long time to come.