- The positive aspects of a one-pipe system
- Cons of a single pipe system
- Features of the installation of a single-pipe system
- Which boiler is better to choose
- Principle of operation
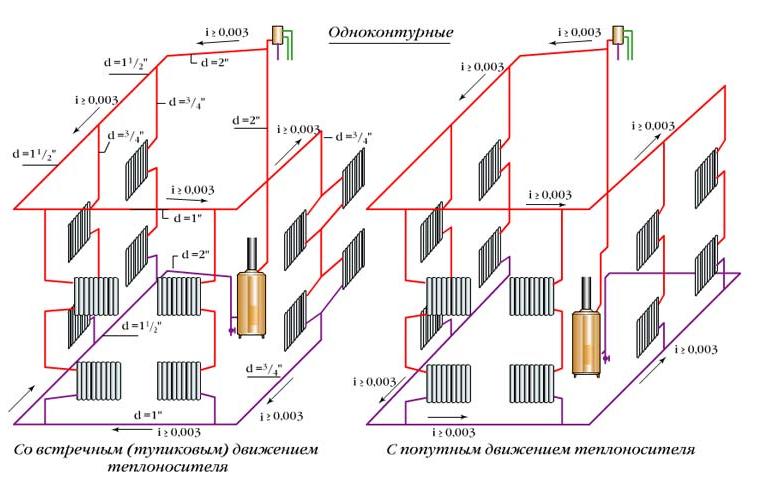
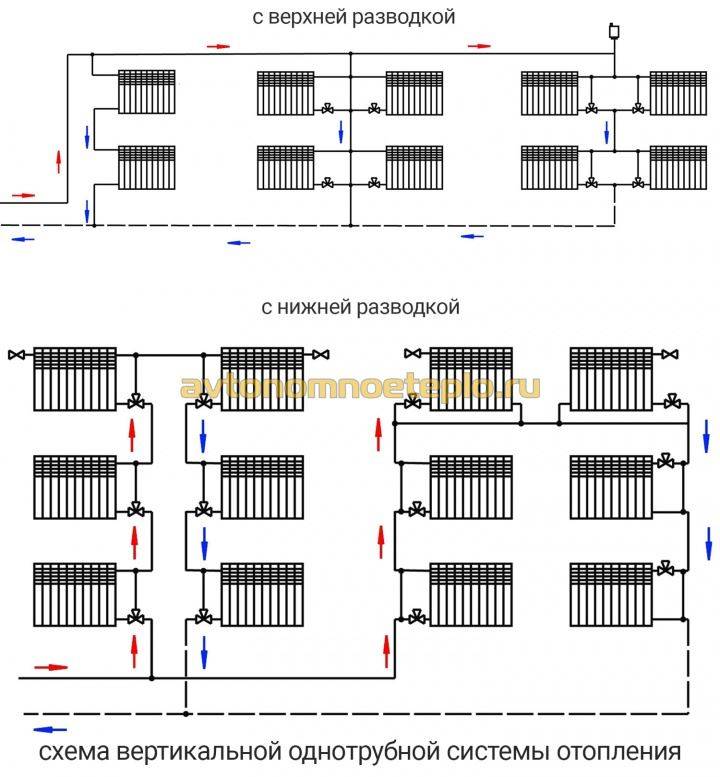
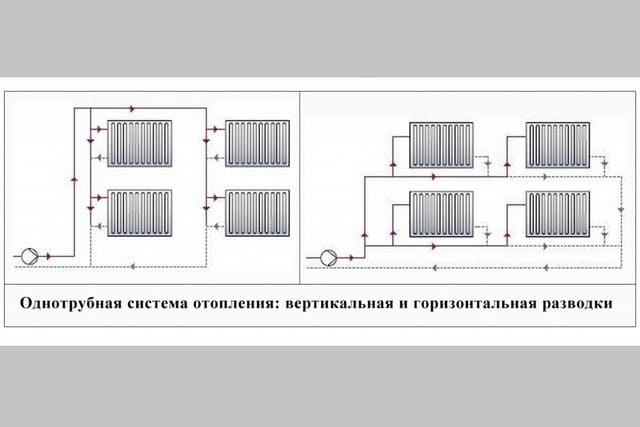
- Types of single-pipe system wiring
- Horizontal wiring
- Vertical wiring
- Schemes for installing a heating system in a private house
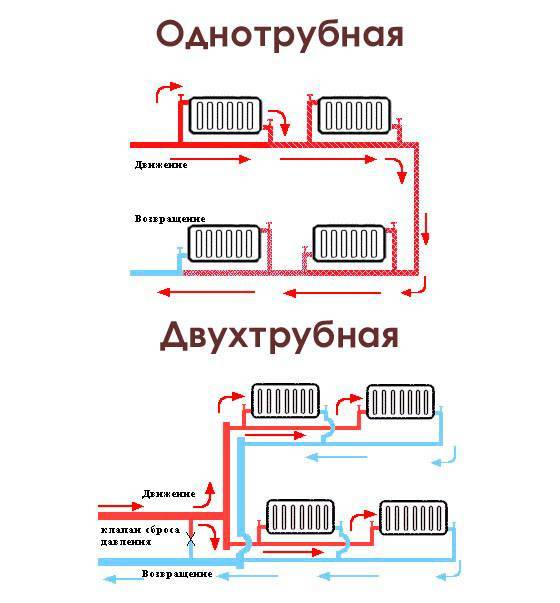
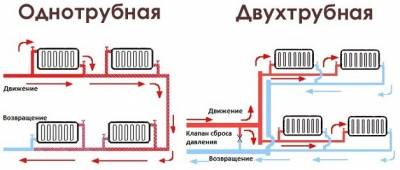
- Single pipe system
- Two-pipe system
- The principle of operation of a one-pipe system
- Feature of the horizontal pipe laying scheme
- Central horizontal heating
- Autonomous horizontal heating
- Single pipe system
- A few extra tips
- Conclusion
- Number of speeds
- Types of heating systems
- Single pipe
- Two-pipe
- Comparison of one-pipe and two-pipe systems
The positive aspects of a one-pipe system
Advantages of a one-pipe heating system:
- One circuit of the system is located around the entire perimeter of the room and can lie not only in the room, but also under the walls.
- When laying below floor level, pipes must be thermally insulated to prevent heat loss.
- Such a system allows pipes to be laid under doorways, thus reducing the consumption of materials and, accordingly, the cost of construction.
- The phased connection of heating devices allows you to connect all the necessary elements of the heating circuit to the distribution pipe: radiators, heated towel rails, underfloor heating. The degree of heating of the radiators can be adjusted by connecting to the system - in parallel or in series.
- A single-pipe system allows you to install several types of heating boilers, for example, gas, solid fuel or electric boilers. With a possible shutdown of one, you can immediately connect a second boiler and the system will continue to heat the room.
- A very important feature of this design is the ability to direct the movement of the coolant flow in the direction that will be most beneficial for the residents of this house. First, direct the movement of the hot stream to the northern rooms or those located on the leeward side.
Cons of a single pipe system
With a large number of advantages of a single-pipe system, some inconveniences should be noted:
- When the system is idle for a long time, it starts up for a long time.
- When installing the system on a two-story house (or more), the water supply to the upper radiators is at a very high temperature, while the lower ones are at a low temperature. It is very difficult to adjust and balance the system with such a wiring. You can install more radiators on the lower floors, but this increases the cost and does not look very aesthetically pleasing.
- If there are several floors or levels, one cannot be turned off, so when carrying out repairs, the entire room has to be turned off.
- If the slope is lost, air pockets may periodically occur in the system, which reduces heat transfer.
- High heat loss during operation.
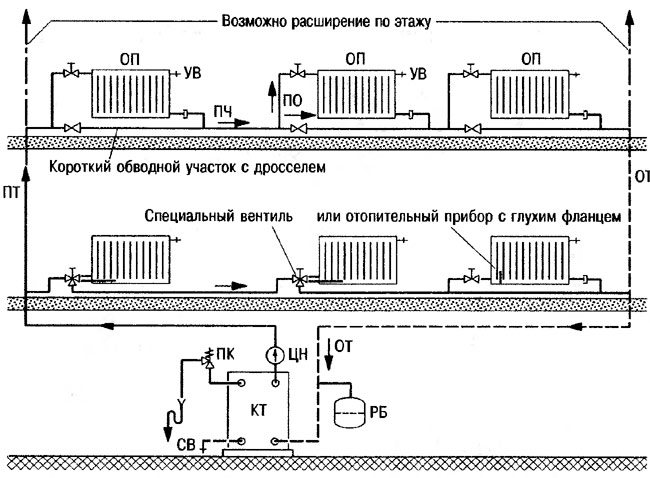
Features of the installation of a single-pipe system
- Installation of the heating system begins with the installation of the boiler;
- Throughout the entire length of the pipeline, a slope of at least 0.5 cm per 1 linear meter of pipe must be maintained. If such a recommendation is not followed, air will accumulate in the elevated area and prevent the normal flow of water;
- Mayevsky cranes are used to release air locks on radiators;
- Shut-off valves should be installed in front of the connected heating devices;
- The coolant drain valve is installed at the lowest point of the system and serves for partial, complete draining or filling;
- When installing a gravity system (without a pump), the collector must be at a height of at least 1.5 meters from the floor plane;
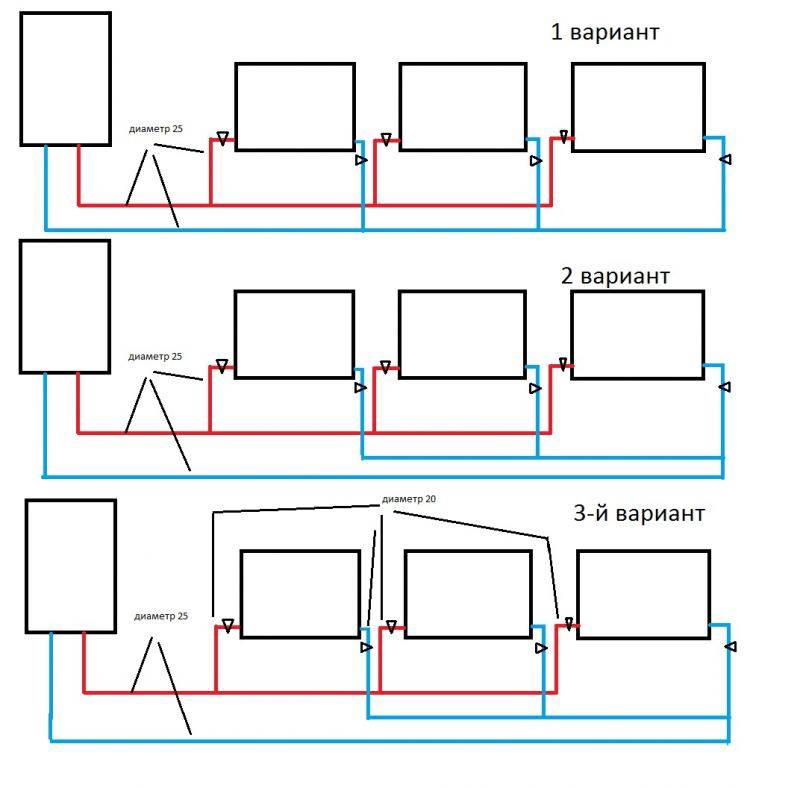
- Since all wiring is made with pipes of the same diameter, they should be securely fastened to the wall, avoiding possible deflections so that air does not accumulate;
- When connecting a circulation pump in combination with an electric boiler, their operation must be synchronized, the boiler does not work, the pump does not work.
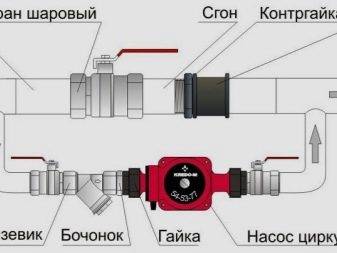
The circulation pump must always be installed in front of the boiler, taking into account its specifics - it works normally at a temperature not exceeding 40 degrees.
The wiring of the system can be done in two ways:
- Horizontal
- Vertical.
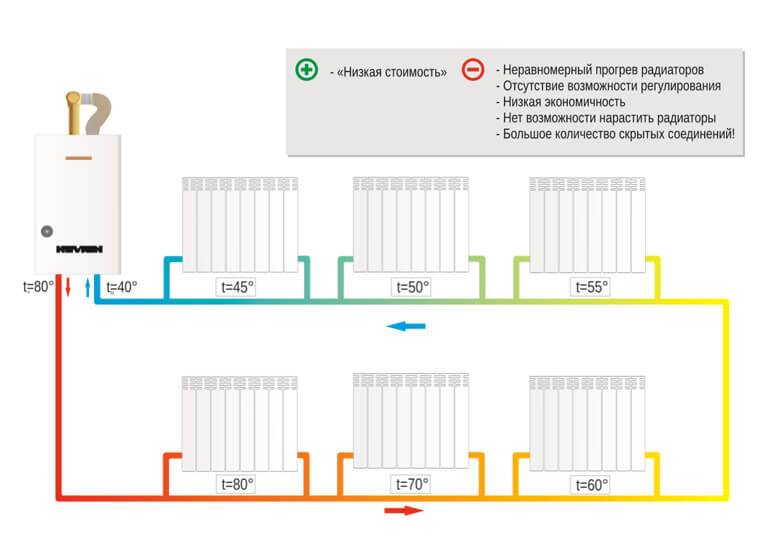
With horizontal wiring, a minimum number of pipes is used, and the devices are connected in series. But this method of connection is characterized by air congestion, and there is no possibility of regulating the heat flow.
With vertical wiring, pipes are laid in the attic and pipes leading to each radiator depart from the central line. With this wiring, water flows to radiators of the same temperature. Such a feature is characteristic of vertical wiring - the presence of a common riser for a number of radiators, regardless of the floor.
Previously, this heating system was very popular due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, but gradually, given the nuances that arise during operation, they began to abandon it and at the moment it is very rarely used for heating private houses.
Which boiler is better to choose
The best option for a single-pipe Leningrad system is a gas boiler. Despite the fact that specialized services should install it, it is small, equipped with automation, and fuel is one of the cheapest. There are other options:
| Type of equipment | Characteristic |
| Drovyanoy | It has large dimensions, requires a separate room for installation. Fuel must be periodically loaded manually |
| Carbonic | It has the same characteristics as the previous type. In addition, there is the problem of ash disposal. But coal burns out for a long time, so you don’t have to load it often |
| pellet | It has a high efficiency (up to 90%), has a small size, and practically does not form soot. Fuel is environmentally friendly, so not very cheap. The bunker is loaded every few days |
| liquid fuel | The device is economical, automatic, but expensive to maintain. It requires an additional installation of a tank or pipeline with fuel |
| Electric | This type of energy is expensive, but does not require the arrangement of a chimney, compact.The disadvantage is a break in work in the absence of power supply |
You also need to pay attention to the direction of movement of the coolant
Principle of operation
Standard heating is based on physical laws: thermal expansion, convection, gravity. Heating up from a source of thermal energy, the coolant expands, and pressure is created in the pipeline. Moreover, it becomes less dense and naturally lighter. Heavier and denser cold liquid pushes the heated up. This is connected with the fact that the pipe that comes out of the boiler is mounted at the maximum height. It is the water heating boiler that is the central element of the entire scheme located in a private house.
The created pressure, convection, as well as gravity make the water move towards the radiator elements, where they are heated and cooled in parallel. As a result, thermal energy is given off by the heat carrier, which heats the room. Then the liquid returns to the boiler in a cold state, and the process is repeated again.

However, this structure has its own characteristics: the smallest temperature indicator of the coolant (40-50 degrees Celsius) is fixed before returning to the boiler, hitting the most remote (last in the circuit) radiator. This is not enough to warm the room normally.
In order to avoid a decrease in temperature indicators on the extreme radiator components, it is necessary to increase the heat capacity of the battery or heat the liquid in the boiler longer. However, these solutions will require additional costs.
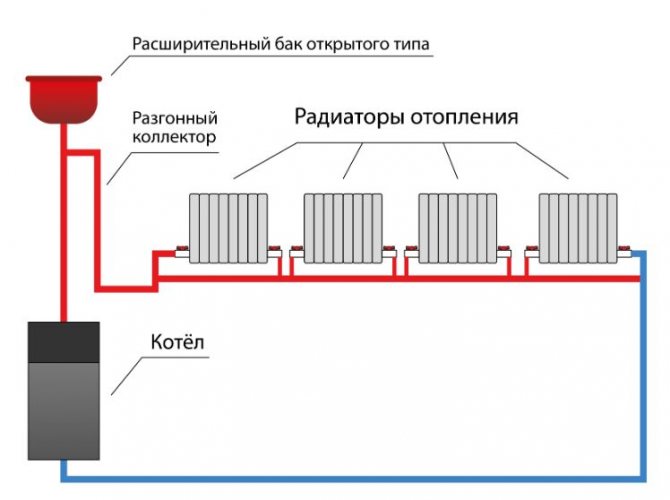
As an alternative solution, another method of supplying hot water is used, which consists in placing a circulation pump in a pipe circuit.She will be able to disperse the coolant throughout the circuit.
The performance of this technology will be better compared to the two previous methods. However, in a suburban environment, a pump-based approach may not be effective due to the likelihood of power failures.

The problem of delivering hot liquid to all radiators of the circuit in this case can be solved by an accelerating collector after its installation. The device appears in the form of a straight high pipe, through which the heated liquid leaving the boiler accelerates to such a speed that it will not allow it to cool in the intermediate radiator before entering the last section.
As a result, a characteristic feature of a single-pipe scheme is the absence of a reverse-action pipe (return pipe) necessary to return the cooled liquid to the boiler. The second part of the only main pipeline will be considered a return.
When choosing a heating scheme, keep in mind that a single-circuit model will not work if the last radiator section is below the level of 2.2 meters. It is suitable for use in two-level buildings.

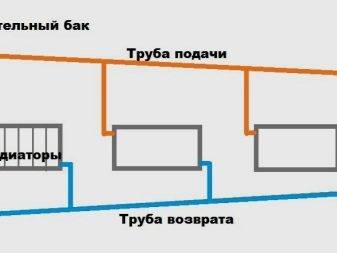
Types of single-pipe system wiring
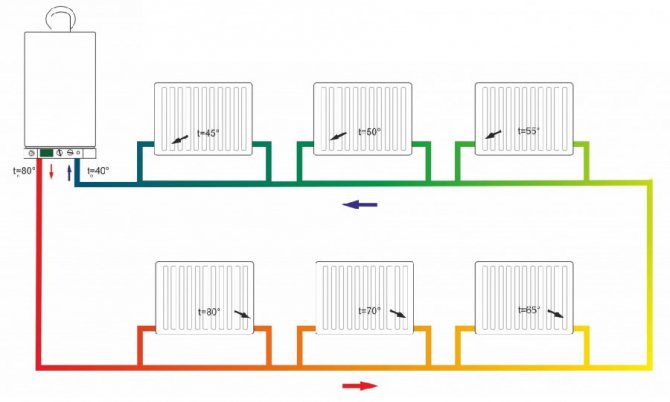
In a single-pipe system, there is no separation between a direct and a return pipe. The radiators are connected in series, and the coolant, passing through them, gradually cools down and returns to the boiler. This feature makes the system economical and simple, but requires setting the temperature regime and correctly calculating the power of the radiators.
A simplified version of a one-pipe system is only suitable for a small one-story house. In this case, the pipe passes through all radiators directly, without temperature control valves.As a result, the first batteries along the coolant turn out to be much hotter than the last ones.
For extended systems, such wiring is not suitable, because the cooling of the coolant will be significant. For them, they use the Leningradka single-pipe system, in which the common pipe has adjustable outlets for each radiator. As a result, the coolant in the main pipe is more evenly distributed throughout all rooms. The layout of a single-pipe system in multi-storey buildings is divided into horizontal and vertical.
Horizontal wiring
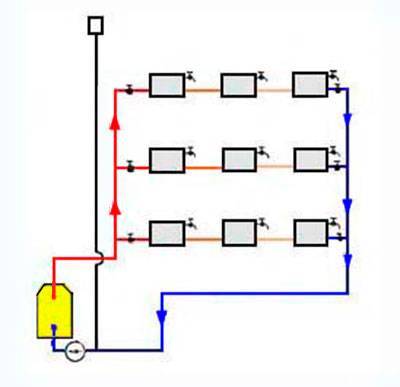
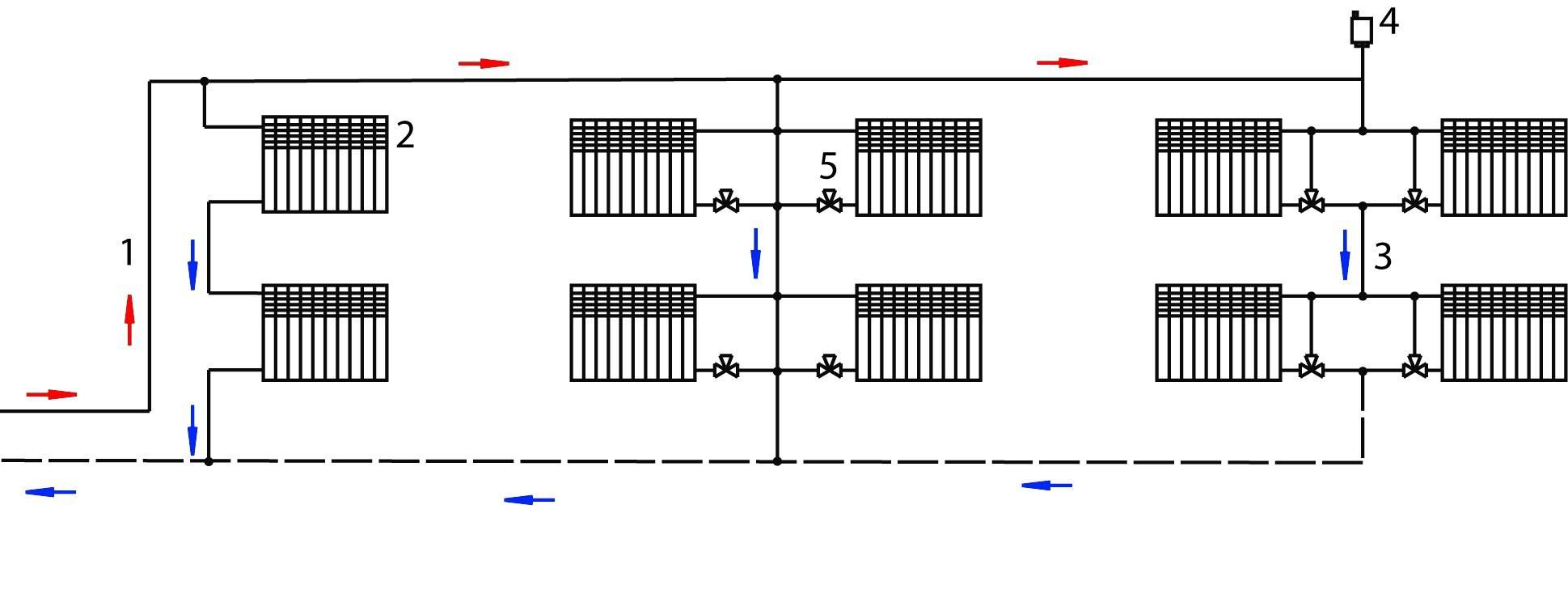
They are combined into a riser of the return line and fed back to the boiler or boiler. Temperature control taps are located on each floor, and Mayevsky taps are on each radiator. Horizontal wiring can be performed both by flow and by the Leningradka system.
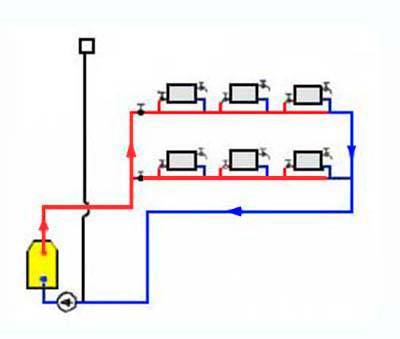
Vertical wiring
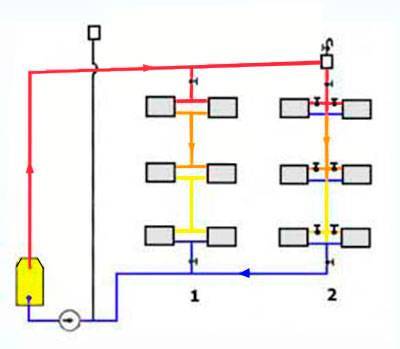
The choice of wiring system for a private house depends mainly on its layout. With a large area of \u200b\u200beach floor and a small number of storeys of the house, it is better to choose vertical wiring, so you can achieve a more even temperature in each room. If the area is small, it is better to choose horizontal wiring, as it is easier to adjust. In addition, with a horizontal type of wiring, you do not have to make extra holes in the ceilings.
Video: one-pipe heating system
Schemes for installing a heating system in a private house
In practice, two types of systems are used - schemes (or types of piping), namely:
- single-pipe;
- two-pipe.
Each of them has its own advantages, disadvantages and is used in different cases.
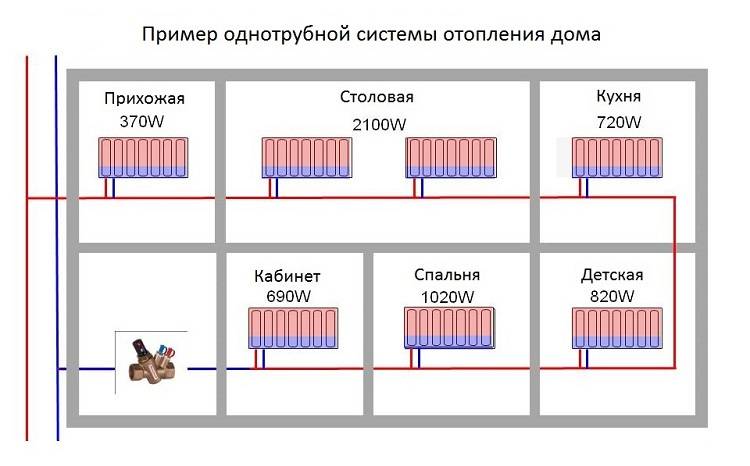
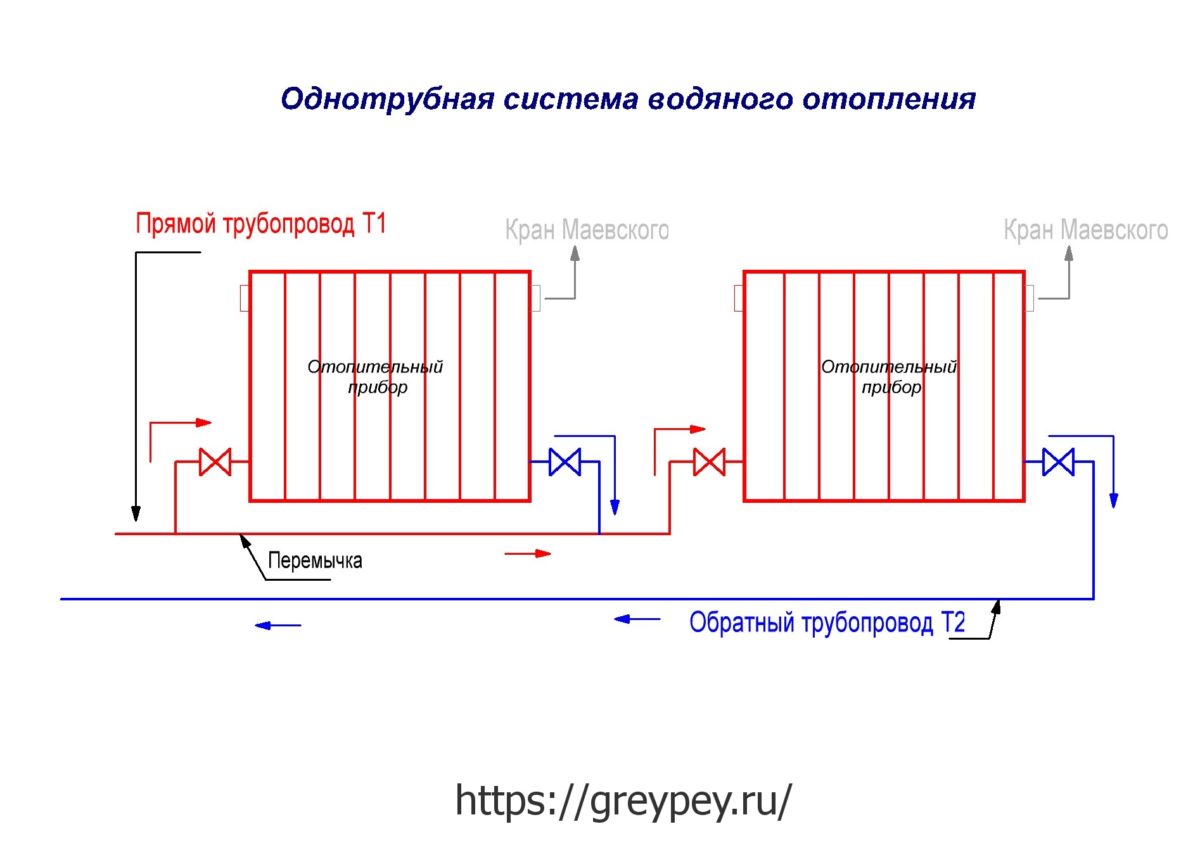
Single pipe system
This type of wiring is cheaper and simpler.The system is built in the form of a ring - all batteries are connected in series with each other, and hot water moves from one radiator to another, then enters the boiler again.
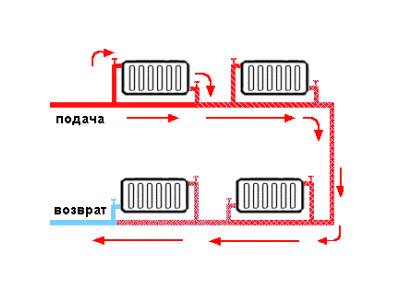
As can be seen in the figure, all batteries are connected in series, and the coolant passes through each of them.
This heating scheme is very economical in its design, it is easy to install and design. But it has one significant drawback. It is so weighty that many refuse such wiring and prefer the more expensive and complex - two-pipe. The problem is that as the coolant advances, it will gradually cool down. Until the last battery, the water will flow a little warm. If you increase the boiler power, then the first radiator will heat the air too much. Such an uneven distribution of heat makes it necessary to abandon a simple and cheap one-pipe system.
You can try to get out of a difficult situation by increasing the number of sections of the last radiator, but this is not always effective. This suggests the conclusion that single-pipe wiring can be used when the number of batteries connected in series is no more than three.
Some get out of the situation as follows: they connect a pump to the boiler, thereby forcing the water to move forcibly. The liquid does not have time to cool down and passes through all the radiators, almost without losing temperature. But in this case, you are waiting for some inconvenience:
- the pump costs money, which means that the cost of installing the system is growing;
- electricity consumption increases, since the pump is powered by electricity;
- if the electricity is cut off, there will be no pressure in the system, which means there will be no heat.
Conclusion.A single pipe system is only effective for small houses with 1-2 rooms, where a small number of radiators are used. Despite its simplicity and reliability, it does not justify itself in country houses, where you need to install more than three radiators for the entire living area.
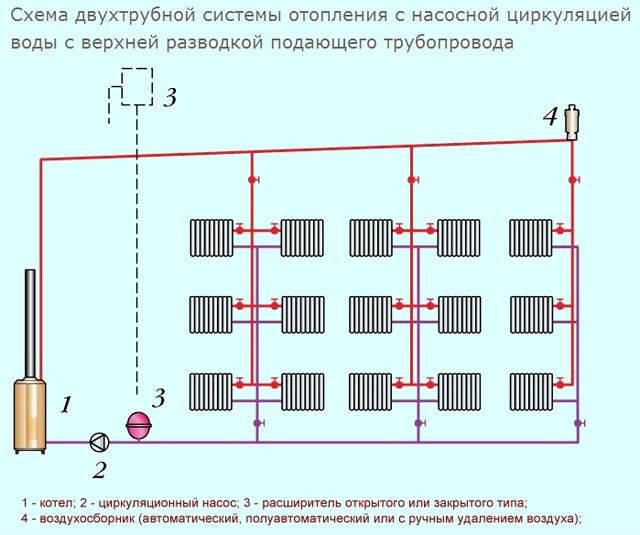
Two-pipe system
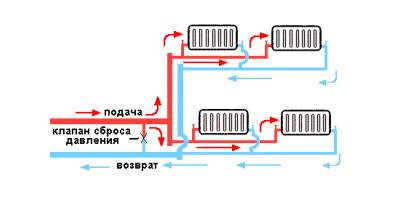
Hot water is supplied through one pipeline, and cooled water through another. This ensures even distribution of heat throughout the batteries.
Such a heating distribution in a private house will be much more efficient and better than a single-pipe one. Although it is more expensive to perform and more difficult to install, it allows you to evenly distribute heat across all batteries, which will help create comfortable conditions. Unlike a single-pipe, in this wiring, a pipe with hot water is supplied under each radiator, and the cooled liquid descends through the return line into the boiler. Since the coolant is supplied immediately to all batteries, the latter are heated equally.
This system is not much more complicated than the first one, you will have to buy more materials, since you will have to bring pipes to each radiator.
A two-pipe system can work in two ways:
- collector;
- ray.
The beam version of the wiring is older. In this option, the supply pipe is installed at the top of the house, after which the pipes are routed to each battery. Thanks to this design, the circuit got the name - beam.
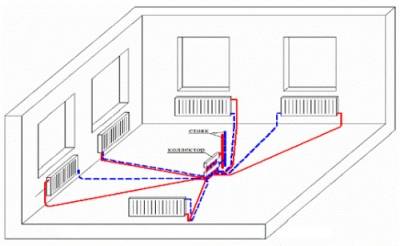
The first scheme works as follows: in the attic it is necessary to install a collector (a special device consisting of many pipes), which distributes the coolant through the heating pipes. In the same place, you need to install shut-off valves, which will cut off the contours.This design is quite convenient, it facilitates the repair of the entire line and even a separate radiator. Although the circuit is reliable, it has one significant drawback - complex installation with a large number of materials (stop valves, pipes, sensors, control devices). The collector wiring diagram for heating pipes is similar to the radial one, but more complex and efficient.
Unlike a single-pipe system, a two-pipe system does not require additional forced circulation of the coolant. It shows high efficiency even without a pump.
The principle of operation of a one-pipe system

solid fuel gas boiler
When assembling this system, it should be understood that, getting into the first radiator, the temperature of the coolant has a high indicator, then it gets into the second, third, etc. Once in the last radiator, the temperature is in the range of 40-50 ° C, and when This temperature does not heat up the room.
There are two ways to overcome such fluctuations in incoming water:
- Increase the heat capacity of the last radiators, thereby increasing its heat transfer;
- Or increase the temperature of the leaving water from the boiler.
These methods in themselves are costly and economically unprofitable, they lead to an increase in the cost of the heating system.
There is another more economical way to distribute hot water through pipes:
- Install a circulation pump that will increase the speed of water movement through the pipes and the efficiency of the system will increase significantly. Such devices are powered by the mains and for suburban villages, where shutdowns are quite frequent, they are not a good option.
- The prudent installation of an accelerating collector - a high straight pipe, the water passing through it picks up speed and moves faster through the radiators.
Collector installation also has its own characteristics. When conducting a heating system in a one-story house, where the ceilings are not very high, it will not work, and all efforts to install it will be in vain, this applies to a height of less than 2.2 meters.
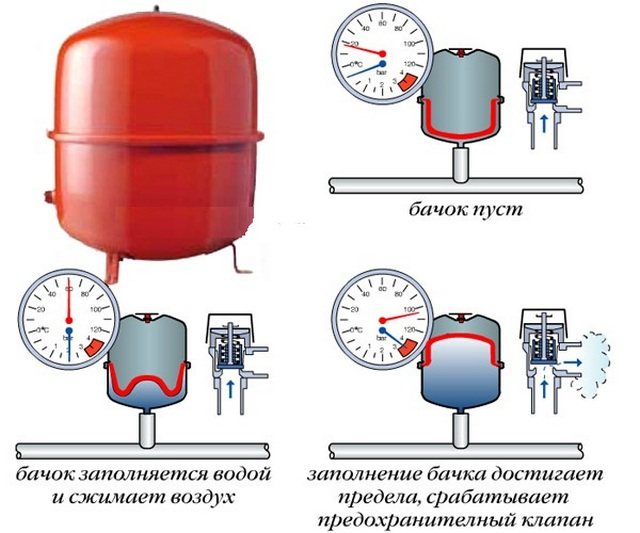
An expansion tank should also be connected to the top point. It is used as a stabilizer and controls the increase in the volume of the coolant. The increased volume of water, when heated, enters the expansion tank and the problem of overflow is solved, when the temperature drops, the volume of water decreases and falls into the system.
The specificity of this design lies in the fact that a single-pipe system does not have a reverse-action pipe through which water would return to the boiler. The return line for such a wiring is considered the second half of the main and only pipe.
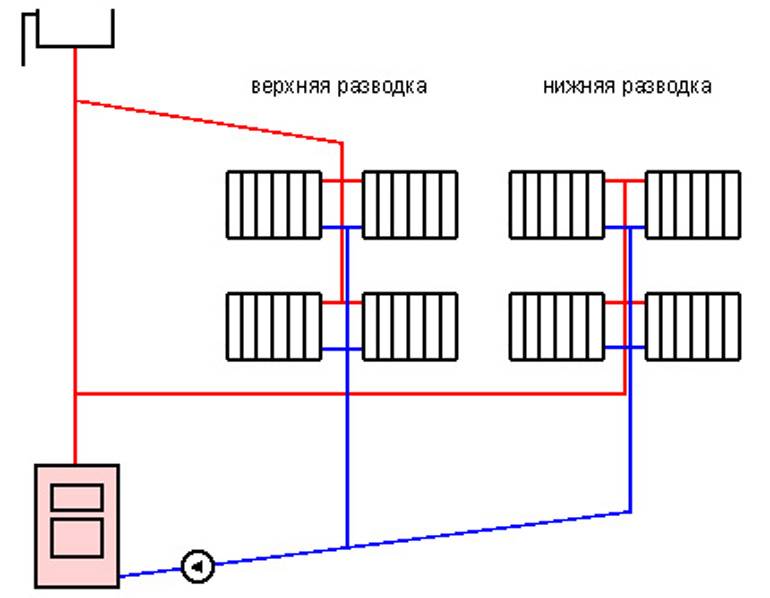
Feature of the horizontal pipe laying scheme
Scheme of horizontal heating in a two-story house
In the vast majority of cases, a horizontal two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring is installed in one or two-story private houses. But, besides this, it can be used to connect to centralized heating. A feature of such a system is the horizontal arrangement of the main and return (for a two-pipe) line.
When choosing this piping system, it is necessary to take into account the nuances of connecting to various types of heating.
Central horizontal heating
To draw up an engineering scheme, one should be guided by the norms of SNiP 41-01-2003.It says that the horizontal wiring of the heating system should ensure not only proper circulation of the coolant, but also ensure its accounting. To do this, two risers are equipped in apartment buildings - with hot water and for receiving cooled liquid. Be sure to calculate a horizontal two-pipe heating system, which includes the installation of a heat meter. It is installed on the inlet pipe immediately after connecting the pipe to the riser.
In addition, hydraulic resistance is taken into account in certain sections of the highway.
This is important, since the horizontal wiring of the heating system will only work effectively while maintaining the appropriate pressure of the coolant.
In most cases, a single-pipe horizontal heating system with a lower wiring is installed for apartment buildings. Therefore, when choosing the number of sections in radiators, one must take into account their distance from the central distribution riser. The further the battery is located, the larger its area should be.
Autonomous horizontal heating
Heating with natural circulation
In a private house or in an apartment without a central heating connection, a horizontal heating system with a lower wiring is most often chosen. However, it is necessary to take into account the mode of operation - with natural circulation or forced under pressure. In the first case, immediately from the boiler, a vertical riser is mounted to which horizontal sections are connected.
The advantages of this arrangement for maintaining a comfortable temperature level include the following:
- The minimum cost for the purchase of consumables.In particular, a horizontal single-pipe heating system with natural circulation does not include a circulation pump, a membrane expansion tank and protective fittings - air vents;
- Work reliability. Since the pressure in the pipes is equal to atmospheric pressure, the excess temperature is compensated with the help of an expansion tank.
But there are also disadvantages to be noted. The main one is the inertia of the system. Even a well-designed horizontal single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation will not be able to provide rapid heating of the premises. This is due to the fact that the heating network begins its movement only after reaching a certain temperature. For houses with a large area (from 150 sq.m.) and with two floors or more, a horizontal heating system with lower wiring and forced circulation of the liquid is recommended.
Heating with forced circulation and horizontal pipes
Unlike the above scheme, for forced circulation, it is not necessary to make a riser. The pressure of the coolant in a horizontal two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring is created using a circulation pump. This is reflected in the improvement of performance:
- Rapid distribution of hot water throughout the line;
- The ability to control the volume of coolant for each radiator (only for a two-pipe system);
- Requires less space for installation as there is no distribution riser.
In turn, the horizontal wiring of the heating system can be combined with a collector. This is true for long pipelines.Thus, it is possible to achieve an even distribution of hot water throughout all rooms of the house.
When calculating a horizontal two-pipe heating system, it is necessary to take into account the rotary nodes, it is in these places that the greatest hydraulic pressure losses are.
Single pipe system
A similar line scheme is mounted from series-connected heaters. The passage of the liquid occurs through each element of the system in turn, slightly heating them, because of this, it reaches the extreme section with a slightly lower temperature. If there are more sections in the last radiator in the circuit, this will not adversely affect the temperature inside the room.
Now there are technologies that help improve the functioning of a single-pipe heating circuit, this is the presence of:
- on batteries of special regulators;
- valves for balancing the incoming liquid;
- thermostatic or ball valves.
Such equipment is used to maintain the required temperature in the room.
Often they install a separate heating, its installation is carried out according to the following schemes:
- horizontal, with the presence of a pump, it distills the coolant by injection, ensuring its circulation;
- vertical - fluid flows naturally in it;
- vertical, using the injection method, with natural distillation or a combined type.
A horizontal system, so that hot water flows naturally, is designed at a slight slope. The installation of radiators is carried out at the same level. Radiators must be equipped with air vent valves.A pump is not installed in this line, because the coolant flows naturally.
A few extra tips
Longevity is largely affected by what materials the main parts are made of.
Preference should be given to pumps made of stainless steel, bronze and brass.
Pay attention to what pressure the device is designed for in the system
Although, as a rule, there are no difficulties with this (10 atm
is a good indicator).
It is better to install the pump where the temperature is minimal - before entering the boiler.
It is important to install a filter at the entrance.
It is desirable to have the pump so that it "sucks" the water out of the expander. This means that the order in the direction of water movement will be as follows: expansion tank, pump, boiler.
Conclusion
So, in order for the circulation pump to work for a long time and in good faith, you need to calculate its two main parameters (pressure and performance).
You should not strive to comprehend complex engineering mathematics.
At home, an approximate calculation will suffice. All resulting fractional numbers are rounded up.
Number of speeds
For control (shifting speeds) a special lever on the body of the unit is used. There are models that are equipped with a temperature sensor, which allows you to fully automate the process. To do this, you do not need to manually switch speeds, the pump will do this depending on the temperature in the room.
This technique is one of several that can be used to calculate the pump power for a particular heating system.Specialists in this field also use other calculation methods that allow you to select equipment according to power and pressure generated.
Many owners of private houses may not try to calculate the power of the circulation pump for heating, since when buying equipment, as a rule, the help of specialists is offered directly from the manufacturer or the company that has entered into an agreement with the store.
When choosing pumping equipment, it should be taken into account that the necessary data for making calculations should be taken as the maximum that, in principle, the heating system can experience. In reality, the load on the pump will be less, so the equipment will never experience overloads, which will allow it to work for a long time.
But there are also disadvantages - higher electricity bills.
But on the other hand, if you choose a pump with a lower power than the required one, then this will not affect the operation of the system in any way, that is, it will work in normal mode, but the unit will fail faster. Although the electricity bill will also be less.
There is another parameter by which it is worth choosing circulation pumps. You can see that in the assortment of stores there are often devices with the same power, but with different dimensions.
You can calculate the pump for heating correctly, taking into account the following factors:
- 1. To install the equipment on ordinary pipelines, mixers and bypasses, you need to choose units with a length of 180 mm. Small devices with a length of 130 mm are installed in hard-to-reach places or inside heat generators.
- 2. The diameter of the nozzles of the supercharger should be selected depending on the cross-section of the pipes of the main circuit.At the same time, it is possible to increase this indicator, but it is strictly forbidden to decrease it. Therefore, if the diameter of the pipes of the main circuit is 22 mm, then the pump nozzles must be from 22 mm and above.
- 3. Equipment with a 32 mm nozzle diameter can be used, for example, in natural circulation heating systems for its modernization.
Types of heating systems
Installation of heating systems is carried out in different ways. But the main node is the installation that produces heat. With its help, the temperature regime of the heat carrier is formed, which is transferred to thermal devices by natural or forced circulation.
Conventionally, such a network is divided into two types, since it is assembled using a single-pipe or two-pipe interchange
The first option can be mounted independently, and for the second type you will have to perform complex calculations, taking into account the mass of operating parameters of all technical units
Single pipe
This type of installation has been used for a long time. Significant savings result from the absence of coolant return risers.
The principle of operation is simple. The coolant is transferred through one closed system, which includes a heating installation and appliances. The binding is made in one common contour. A hydraulic pump is used to ensure the transfer of the coolant.
What does a single-pipe heating system look like?
Schematically, a single-pipe heating system is divided into:
- vertical - used in multi-storey buildings;
- horizontal - recommended for private houses.
Both types do not always give the desired effect in the work. Radiators connected in series cannot always be adjusted so that all rooms are equally warm.
No more than a dozen batteries are connected along the vertical riser. Failure to comply with this rule leads to the fact that the lower floors in the house will not warm up well.
A serious disadvantage is the need to install a pump. It is he who is the source of leaks and forces him to periodically replenish the heating network with water.
For the normal operation of such a network, an expansion tank will have to be installed in the attic.
Despite the negative aspects, there are also positive aspects of such heating, which perfectly compensate for all the shortcomings:
- new technologies have made it possible to solve the problem of uneven heating of the premises;
- the use of devices for balancing and high-quality shutter equipment allows you to perform repair work without shutting down the overall system;
- installation of a single-pipe system will be much cheaper.
Two-pipe
In such a network, the coolant moves up the riser and is fed into each battery. After that, he goes back to the heating boiler.
With the help of such a system, it is possible to organize uniform heating of all radiators. During the circulation of water, large losses in pressure do not occur, the liquid moves by gravity. It is possible to repair the heating network without stopping the supply of heat to the facility.
Two-pipe heating system
If we compare the systems, then the two-pipe one will be much more effective. But it has a major drawback - the assembly requires twice as many pipes and component materials, which affects the final cost.
Comparison of one-pipe and two-pipe systems
We have already figured out how to calculate pipes for heating, and what diameter is needed for both types of systems.For closed circuits, with a room area of 120 m2, this figure is 32 mm for polypropylene.
In this case, the nominal passage for products with a nominal pressure of 20 and 25 atmospheres is 21.2 mm. For products with a nominal pressure of 10 atmospheres, the nominal bore is 20.4 mm, and the outer diameter is 25 mm.
- Efficiency - unequivocally, "rides" heat the room more efficiently than single-pipe ones;
- cost savings - all that can be saved at Leningradka is some section of the contour and that's it.
The number of tees will be the same, the taps too, but more adapters may be required. Imagine a circuit from which two branch pipes leave with a small gap.
One of them goes to the radiator inlet, and the second returns the coolant back to the system. It turns out that the segment between the nozzles is a bypass. In order for the circulation in the battery to be better, the bypass must be made of a smaller diameter than the main heating circuit.
From this it follows that a couple more pieces of fittings will be required. It turns out that we spend less money on pipes and more on fittings, as a result, there is no savings, while the efficiency is lower.
As a result, from this we can conclude that the stories about what a good and cheap one-pipe heating system is simply untenable.