- The principle of operation of the RCD (UZO-D)
- Principle of operation
- Examples of using the device in everyday life
- Full decoding of marking values
- Reasons for automatic shutdown of the RCD
- The principle of operation of the device
- The purpose of the RCD
- Choices
- Additional RCD functions
- Power calculation for RCD
- Calculating power for a simple single-level circuit
- We calculate the power for a single-level circuit with several protection devices
- We calculate the power for a two-level circuit
- RCD power table
- Lineup, manufacturers and prices of RCDs
- The principle of operation of the RCD
- RCD characteristics
- How to provide quality protection
- At the end
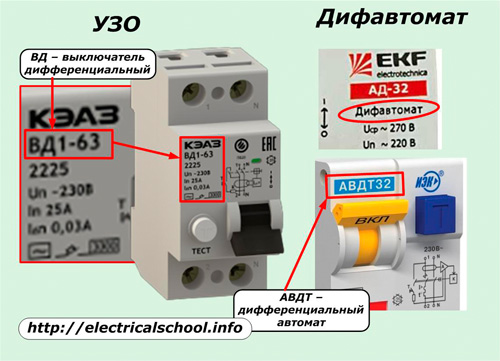
- Types of RCDs and difavtomatov by the nature of the leakage current
- RCD connection diagram, RCD designation on the diagram, single-phase and three-phase RCD connection diagram
- RCD trips
- RCD calculation example
- RCD connection diagram
- RCD scheme in the apartment
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The principle of operation of the RCD (UZO-D)
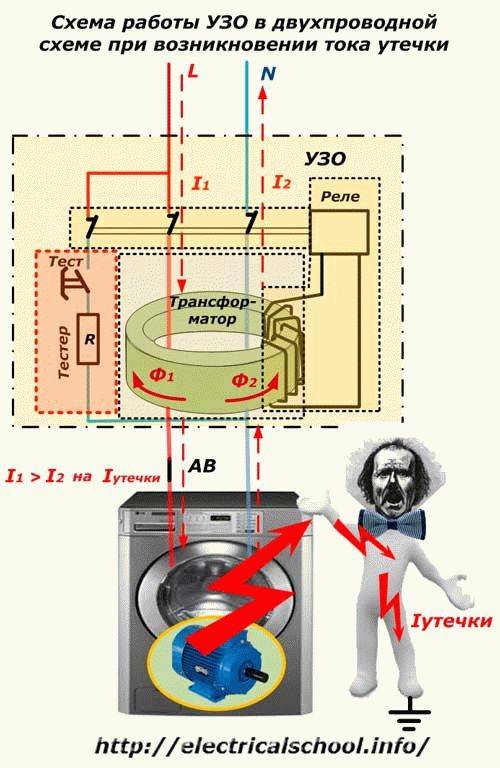
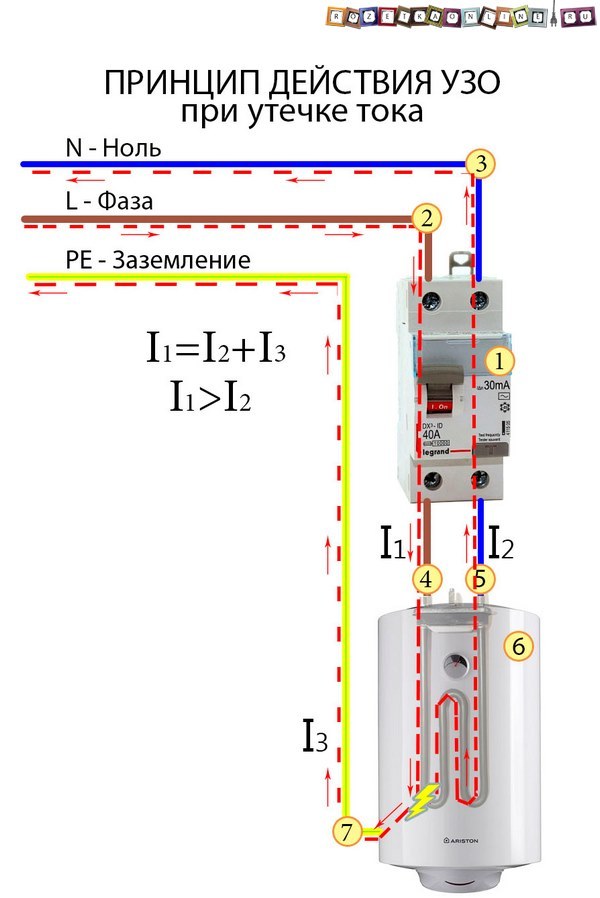
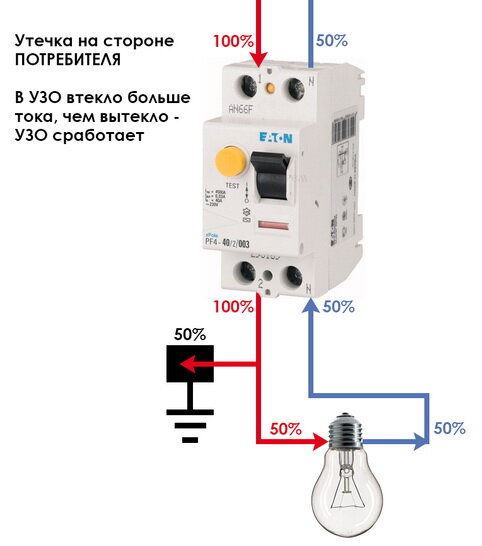
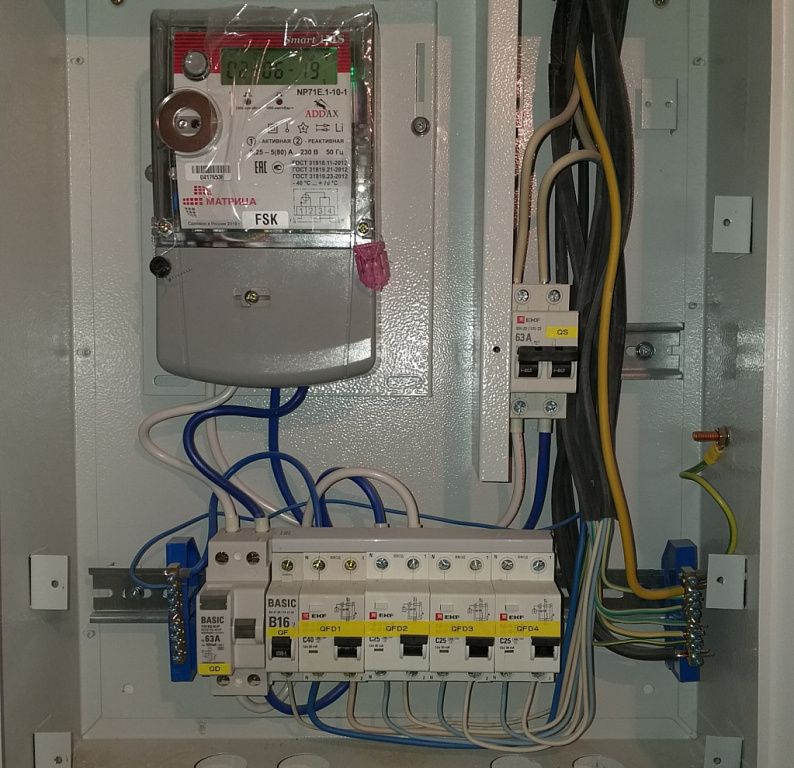
The operation of the RCD-D is based on fixing the leakage current to the "ground" and turning off the network when it appears. The fact of leakage is detected by the difference between the currents: leaving the RCD and returning to it through the neutral.
If the network is in order, then they are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.When a leak occurs, for example, a person touches a wire, part of the current will go through his body “to the ground” along a different circuit, and as a result, the current returning to the RCD through the neutral will be less than the output.
The same situation will arise if the insulation is broken in some electrical load device and the case or other part is under voltage. A person, hitting them, will create an additional circuit “to the ground”, part of the current will go through it and the balance will be disturbed (this situation is shown in the figure).
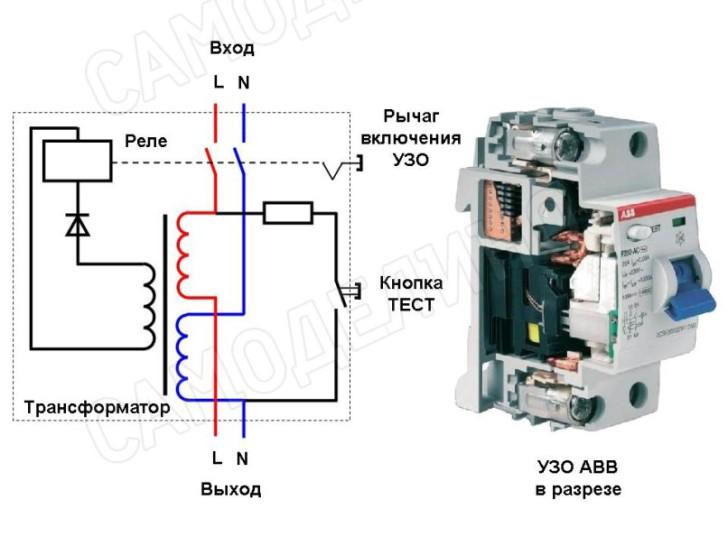
The difference between the outgoing and incoming currents is detected by a transformer with a core in the form of a ring. The phase conductor and neutral N pass inside it and serve as the primary winding. The secondary winding is connected to an actuator that opens the contacts.
Of course, if the insulation is damaged, a branch circuit can be formed without the “participation” of a person, but in this case, the RCD will also work and protect the network section from dangerous consequences (for example, heating and fire). The symbol "T" in the figure indicates a button that includes a device testing circuit - RCD-D should work when it is pressed.
The same principle is used for three-phase protection devices, however, in them, the differential current in the secondary winding appears not only during leakage, but also during “phase imbalance” (unevenly distributed between the phases of the load), therefore, additional circuits have been developed that exclude operation due to violation symmetry.
Principle of operation

To protect the network from short circuits, circuit breakers are used, which should always be installed together with the RCD
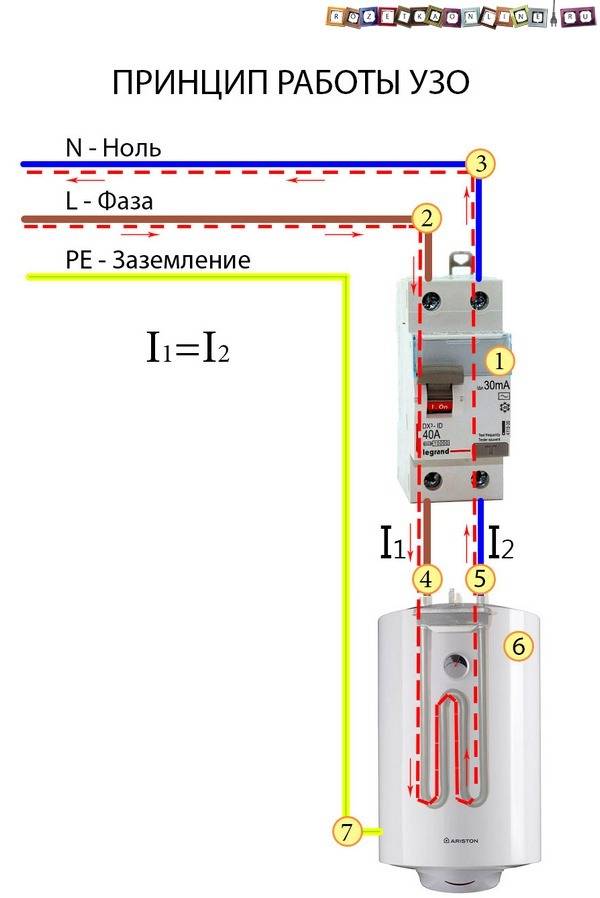
Mains voltage is supplied to electrical appliances through two wires, one of which is neutral, and the second is phase.The neutral wire is connected to the ground, and the phase wire has an alternating voltage of 220 V. During normal operation of the equipment, a current of the same magnitude flows in each wire, but in a different direction.
If a person touches a bare phase wire, then a current will begin to flow through his body, which closes to the ground. This current is called leakage current. In the phase wire, the total current immediately increases by the value of the leakage current, and in the zero wire it remains at the same level.
The RCD, using a differential transformer, captures the difference that has arisen and instantly breaks the network contacts. Shutdown occurs very quickly, in a fraction of a second, and there is no critical defeat.
Such RCDs are called "protective type" and are available for different leakage currents: 6, 10, 30 mA. For normal premises, 30 mA devices provide reliable human protection. In rooms with increased danger (bathrooms, damp basements), devices with a lower leakage current are more suitable.
Leakage currents occur over time and in the wiring due to the deterioration of the insulation. They can reach significant levels, especially in large houses with a distributed electrical network, and cause a fire. To prevent fires, an RCD of 100-300 mA is installed, which they call “firefighters”.
It must be taken into account that all these devices react only to the occurrence of a leakage current. They do not protect the network from a short circuit, because during a short circuit there is no current imbalance in the neutral and phase conductors, although it increases by unacceptable thousands of times. To protect the network from short circuits, circuit breakers are used, which should always be installed together with the RCD.
Examples of using the device in everyday life
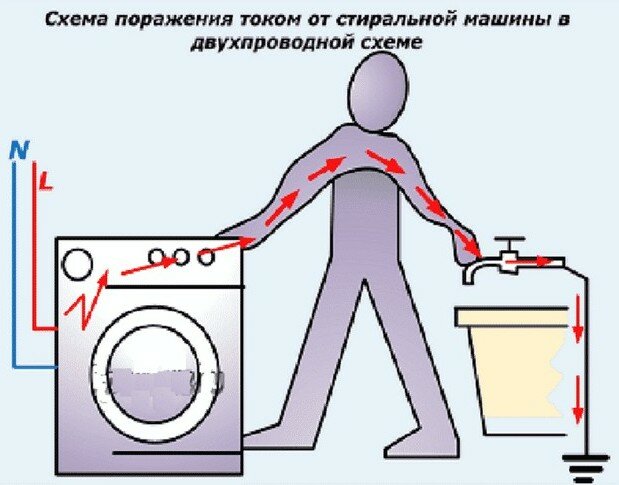
The first, vivid example, is the case with damage to the electrical wiring.Here is an example with a washing machine:
- The insulation near the phase is damaged, the wire touched the housing. The device immediately blocks electricity.
- The current that went through the electrical circuit went to the apartment, but did not return. The guard block is immediately triggered because it has lost control of the flow.
- The current in this case went through the ground wire into the shield, bypassing the protection device, the system reacted to the difference in incoming and outgoing flows.
Let's describe another example, this is careless handling of electrical wiring:
- There are cases during repair work, for example, drilling a wall surface.
- An inexperienced master rests his foot on the radiator, while falling into the phase wiring.
- Passing current through such a circuit can hit a person and cause heart failure.
- In the presence of an RCD, the voltage will turn off very quickly and there will be no trouble. A person can be electrocuted, but not to death.
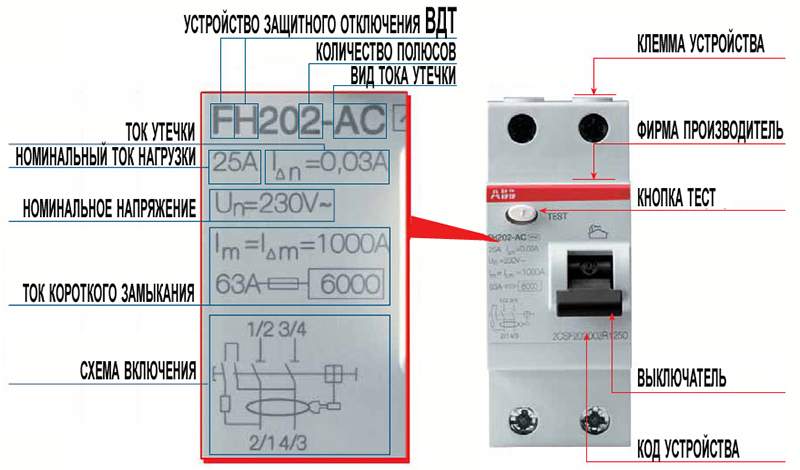
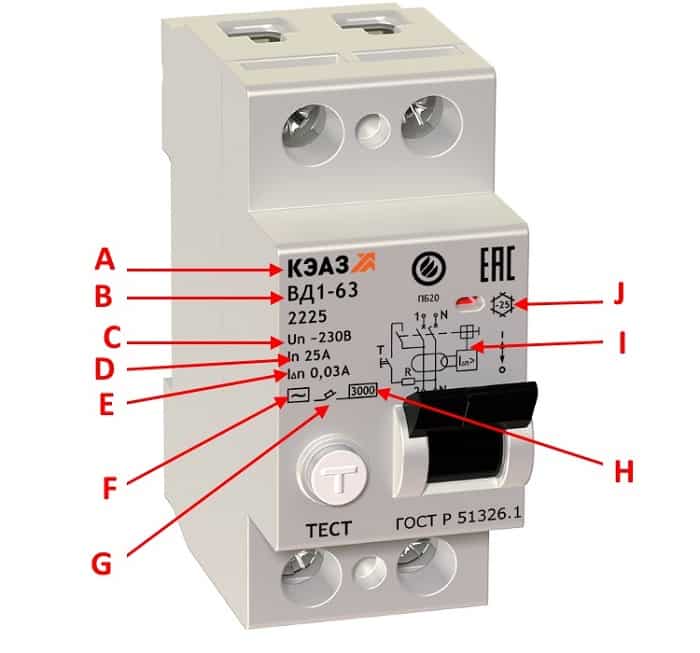
Full decoding of marking values
Without fail, the name of the developer company is present on the body of the device. This is followed by a standardized marking with a serial number designation.
To decipher the abbreviation, we will use the following example 00-:
- – protective shutdown device;
- – performance format;
- 00 - numeric or alphanumeric designations of the series;
- – number of poles: 2 or 4;
- - characteristics by type of leakage current: AC, A and B.
Also, the nominal parameters of the device will be indicated here, which, when choosing, must be paid special attention.Abbreviation decoding: 1 - brand; 2 – device type; 3 – selective view; 4 - compliance with European standards; 5 - rated operating current and setting; 6 - maximum alternating operating voltage; 7 - rated current that the device can withstand; 8 - differential making and breaking capacity; 9 - wiring diagram; 10 – manual performance check; 11 - marking of the switch position
Abbreviation decoding: 1 - brand; 2 – device type; 3 – selective view; 4 - compliance with European standards; 5 - rated operating current and setting; 6 - maximum alternating operating voltage; 7 - rated current that the device can withstand; 8 - differential making and breaking capacity; 9 - wiring diagram; 10 – manual performance check; 11 - marking of the switch position
The maximum parameters for which the devices are designed include: voltage Un, current In, differential value of the opening current IΔn, making and breaking capacity Im, switching capacity at short circuits Icn.
The main marking values must be located in such a way that they remain visible after the appliance has been installed. Some parameters may be applied on the side or on the rear panel, visible only before the installation of the product.
Outputs intended only for connecting a neutral wire are indicated by the Latin symbol "N". The disabled mode of the RCD is indicated by the symbol “O” (circle), the enabled mode is indicated by a short vertical line “I”.
Not every product is labeled with optimum ambient temperatures.In those models where there is a symbol, this means that the operating mode range is from -25 to + 40 ° C, if there are no symbols, it means standard indicators from -5 to +40 ° С.
Reasons for automatic shutdown of the RCD
Before proceeding with the repair, it is worth finding out why does the RCD work. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon, and the method and cost of repair depends on them.
- Current leakage in the network. This problem is often found in buildings with old wiring. The insulating coating loses its elasticity over time, cracks, and the wiring is exposed in some areas. If the wiring was recently laid, it is worth checking the quality of the wire connection. Sometimes an accidentally hammered nail can break the insulation layer.
- Malfunction of the device to which the RCD is connected. Among the damages, the most common failure is the cord, motor winding or water heater heating element.
- Installation error. If the device is installed incorrectly, then the automation may periodically work for no reason. Before installing the device, you should carefully study the instructions or use the services of a specialist.
During installation, it is important not to make mistakes, otherwise the device will turn off for no apparent reason.
Wrong device selection
When buying a unit, it is important to consider all its characteristics and purpose. Failure to comply with these parameters may result in a false shutdown.
Human touch on a wire without insulation
In fact, this device is designed specifically to protect a person in such situations.
Damage to the mechanism itself.Sometimes the trigger mechanism is damaged, and at the slightest vibration, an automatic shutdown is triggered.
Incorrect placement of the device in the wiring. To avoid such a problem, it is worth mounting the device after the meter and in front of the machine. If the house has a lot of electrical appliances with high power, then you should use several devices for each group. This will allow, in case of malfunctions, not to turn off the electricity throughout the house, but only in certain areas.
According to the rules of the PUE, grounding and working zero cannot be combined
But, sometimes electricians do not take this prohibition into account. A short circuit of these two lines may occur, which will cause the RCD to automatically turn off.

During installation, all safety requirements must be observed.
- Weather conditions. A device that is installed outdoors is susceptible to moisture. As a result, moisture accumulates in the internal mechanism, a leak occurs, and the machine operates. If there are minor current leaks in the house, then lightning during a thunderstorm can amplify them. This is also the reason for the automatic shutdown. At very low temperatures, the microcircuits of the device can fail, and the RCD simply will not work in cases of current leakage.
- High humidity level in the room. If they tried to hide the installed wiring with putty, then the electricity should be connected after drying, otherwise the protective automation may work.

To ensure safety, all wires must be connected correctly.
The principle of operation of the device
When installing an RCD, two conductors are connected to it - working zero and phase. If the electrical appliance operates without leakage, then the current strength in the conductors should be the same.In emergency situations, when a current leakage occurs, the device turns off. As a result, the electrical device is de-energized and stops working. Thus, RCD helps to preserve the health and life of ordinary users.

RCD protects the house from fire and controls electrical wiring and equipment from leakage
All equipment has a slight current leakage. But usually its level is insufficient to cause harm to human health. All RCDs are set to a level of electrical energy that poses a danger to people or will lead to a malfunction of electrical appliances.
The speed of automatic shutdown is such that a child who puts a nail into the socket will not even experience discomfort - the device will automatically turn off the power throughout the house.

After the automatic shutdown of the device, it is necessary to detect the current leakage
The purpose of the RCD
Most current protection devices (fuses, circuit breakers, etc.) protect electrical wiring and electrical receivers connected to it from overload currents and short circuits. Residual current devices perform other functions. Depending on the tripping current, they protect people from electric shock or prevent fires.
Every electrician knows that the power frequency alternating current flowing through the human body becomes hazardous to health if its value exceeds 0.01 ampere. Currents over 0.1 A are deadly. Therefore, the threshold operating current (setting) of the RCD protecting a person from electric shock is usually selected from the ratings of 10 mA or 30 mA. The first setting is used for damp rooms, children's rooms, and so on. The 30 mA setting applies for normal conditions.
To prevent fires, devices are installed that are tuned to differential currents exceeding 300 mA.
Choices
Capacitive RCDs are considered the first household models. Their principle of operation is similar to that of a capacitive relay that responds to a reactive type bias current. Their sensitivity is extremely high - a fraction of µA, they work almost instantly and do not respond to grounding factors. But at the same time, they react very strongly to interference and cannot differentiate the causes of an emergency.


Differential electromechanical models are now popular for electrical work of various levels of complexity. When a leakage occurs, one and the currents increase, as a result of which a magnetic flux occurs. It is born on the ferrite, which leads to the induction of the EMF in the second winding. The latch is pulled by an electromagnet, opening the contacts.
UZO-DE related to electronic modifications are also known. They have a sensor and are built directly into the operating plant. Such products are characterized by high sensitivity and the ability to open the circuit in response to bias currents.

And, of course, they have a high reaction rate. But at the same time, their cost is an order of magnitude higher than analogues, and electronics can fail.

If you want to know how to choose an RCD, then it is advisable to solve several questions:
- install a set of RCDs and an automatic machine or a separate difautomatic device;
- estimate by calculation the required cut-off current at the moment of overload;
- calculate the operating current of the device;
- set the desired leakage current.

Additional RCD functions
To protect human life and health, devices are used that detect current leakage of 30 mA and 10 mA.All RCDs that have the highest indicators do not provide protection for human life. Very often, in multi-stage circuits, fire protection RCDs are used as the first stage of protection. These are fire protection RCDs that are set to leak current from 100 mA to 300 mA.
They are installed in switchboards on each floor, or in accounting boards. They perform the function of protecting the input cable and consumer lines that do not have separate protection. Also, these devices are additional protection in case of failure of the downstream device.
RCD in switchboard
In order for fire-fighting devices to successfully perform their function, it is necessary to install devices with different sensitivity to current and unequal response times of automatic protection.
Power calculation for RCD
Each individual device has its own threshold current load, at which it will work normally and will not burn out. Naturally, it must be higher than the total current load of all devices connected to the RCD. There are three types of RCD connection schemes, for each of which the calculation of the power of the device is different:
- A simple single-level circuit with one protection device.
- Single-level scheme with several protection devices.
- Two-level trip protection circuit.
Calculating power for a simple single-level circuit
A simple single-level circuit is characterized by the presence of one RCD, which is installed after the counter. Its rated current load must be higher than the total current load of all consumers connected to it. Suppose the apartment has a boiler with a capacity of 1.6 kW, a washing machine for 2.3 kW, several light bulbs with a total of 0.5 kW and other electrical appliances for 2.5 kW.Then the calculation of the current load will be as follows:
(1600+2300+500+2500)/220 = 31.3 A
This means that for this apartment you will need a device with a current load of at least 31.3 A. The nearest RCD in terms of power is 32 A. It will be enough even if all household appliances are turned on at the same time.
One such suitable device is the RCD ERA NO-902-126 VD63, designed for a rated current of 32 A and a leakage current of 30 mA.
We calculate the power for a single-level circuit with several protection devices
Such a branched single-level circuit assumes the presence of an additional bus in the meter device, from which wires depart, forming into separate groups for individual RCDs. Thanks to this, it is possible to install several devices on different groups of consumers or on different phases (with a three-phase network connection). Usually a separate RCD is installed on the washing machine, and the rest of the devices are mounted for consumers, which are formed into groups. Suppose you decide to install an RCD for a washing machine with a power of 2.3 kW, a separate device for a boiler with a power of 1.6 kW and an additional RCD for the rest of the equipment with a total power of 3 kW. Then the calculations will be as follows:
- For a washing machine - 2300/220 = 10.5 A
- For a boiler - 1600/220 = 7.3 A
- For the rest of the equipment - 3000/220 = 13.6 A
Given the calculations for this branched single-level circuit, three devices with a capacity of 8, 13 and 16 A will be required. For the most part, such connection schemes are applicable for apartments, garages, temporary buildings, etc.
By the way, if you don’t want to bother with installing such a circuit, then pay attention to portable RCD adapters that can be quickly switched between sockets. They are designed for one appliance.
We calculate the power for a two-level circuit
The principle of calculating the power of a residual current device in a two-level circuit is the same as in a single-level one, with the only difference being the presence of an additional RCD located at the entrance to the apartment, up to the meter. Its rated current load must correspond to the total current load of all devices in the apartment, including the meter. We note the most common RCD indicators for current load: 4 A, 5 A, 6 A, 8 A, 10 A, 13 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A, etc.
The RCD at the input will protect the apartment from a fire, and the devices installed on individual groups of consumers will protect a person from electric shock. This scheme is the most convenient in terms of repairing electrical wiring, as it allows you to turn off a separate section without turning off the whole house. Also, if you need to repair cable systems at the enterprise, you will not have to turn off all office premises, which means there will be no massive downtime. The only drawback is the considerable cost of installing an RCD (depending on the number of devices).
If you need to choose an RCD for a group of machines for a single-phase network, then we can advise the ERA NO-902-129 VD63 model with a rated current load of 63 A - this is enough for all electrical appliances in the house.
RCD power table
If you are thinking about how to easily and quickly select an RCD by power, the table below will help you with this:
| Total load power kW | 2.2 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 7 | 8.8 | 13.8 | 17.6 | 22 |
| RCD type 10-300 mA | 10 A | 16 A | 25 A | 32 A | 40 A | 64 A | 80 A | 100 A |
Lineup, manufacturers and prices of RCDs
The table shows the products of the most common manufacturers of UDT and shows the market prices they offer:
| product name | Trademark | price, rub. |
| RCD IEK VD1-63 single-phase 25A 30 mA | IEK, China | 442 |
| RCD ABB single-phase 25A 30 mA | ABB, Italy | 536 |
| RCD ABB 40A 30 mA single-phase | ABB, Italy | 740 |
| RCD Legrand 403000 single-phase 25A 30 mA | Poland | 1177 |
| RCD Schneider 11450 single-phase 25A 30 mA | Schneider Electric, Spain | 1431 |
| RCD IEK VD1-63 three-phase 63A 100 mA | IEK, China | 1491 |
| Automatic switch IEK BA47-29 25A | IEK, China | 92 |
| Circuit breaker Legrand 404028 25A | Poland | 168 |
| Circuit breaker ABB S801C 25A single-pole | ABB, Italy | 441 |
| RCBO IEK 34, three-phase C25 300 mA | IEK, China | 1335 |
As can be seen from the comparative table, the price of RCD 25A 30 mA (the most demanded on the market) depends on the manufacturer. So the price of RCD ABB 25A 30 mA is higher than Chinese counterparts, but lower than that of such manufacturers as Legrand or Schneider Electric. Taking into account such criteria as quality and cost, it is preferable to buy an RCD 25A 30 mA from ABB, and you can buy the necessary circuit breaker made in China or Legrand.
Summing up this excursion into the world of differential current devices, in particular, the residual current device (RCD), we will focus on the important points considered.

Range of RCDs and circuit breakers manufactured by ABB
One of the most effective means of protecting humans and animals from the damaging effects of electric current is the installation of residual current devices (RCDs) in the power supply network.
The RCD has the function to respond to the differential leakage current that appears when a person comes into contact with a bare part of the wiring or the body of any electrical equipment. It may be under phase voltage due to damage to the insulation of the phase wire and its contact with the housing. The RCD also responds to current leakage in places where the wiring insulation is damaged, when this can lead to heating and fire.
However, the RCD does not respond to short circuit phenomena in the wiring circuit and to excess current in the circuit. In this regard, it is necessary to install the device in tandem with a circuit breaker ("automatic"), which responds to a short circuit and power overload.
Most importantly, always follow the safety rules and caution when working with electrical appliances and machinery. As often as possible, visually inspect open current-carrying elements of electrical wiring and connected elements of current collectors.
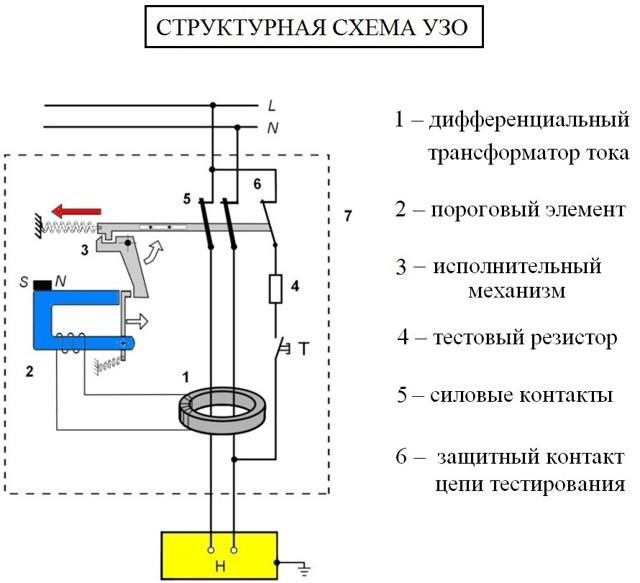
The principle of operation of the RCD
To prevent accidental electric shock when in contact with household and industrial electrical appliances, a residual current device was invented.
It is based on a transformer with a toroidal core, which monitors the current strength on the "phase" and "zero". If its levels diverge, then the relay is activated and the power contacts are disconnected.
You can check the RCD by pressing the special "TEST" button. As a result, a current leakage is simulated, and the device should disconnect the power contacts
Normally, any electrical device has a leakage current. But its level is so small that it is safe for the human body.
Therefore, RCDs are programmed to operate at a current value that can cause electrical injury to people or lead to equipment breakdown.
For example, when a child sticks a bare metal pin into a socket, electricity will leak through the body, and the RCD will turn off the light in the apartment.
The speed of operation of the device is such that the body will not experience any negative sensations at all.

The RCD adapter is convenient for the ability to quickly move between outlets. It is suitable for people who do not want to install fixed protective devices.
Depending on the power of the connected equipment, the presence of intermediate protective devices and the length of the wiring, RCDs with different limit values of differential currents are used.
The most common in everyday life protective devices with a threshold level of 10 mA, 30 mA and 100 mA. These devices are sufficient to protect most residential and office premises.
It should be remembered that the classic RCD does not protect the electrical wiring from a short circuit and does not turn off the power contacts when the network is overloaded. Therefore, it is desirable to use these devices in combination with other electrical protection mechanisms, such as circuit breakers.
RCD characteristics
RCD connection diagram
Rated current
Specifies the trigger threshold of the device: 6, 10, 16, 25, 50, 63, etc. (amps). The rated current is the same for both RCDs and automata.
Performance
RCD distribution
In the marking of difavtomatov, an index of electrical action is used, which is marked with the letter "B", "C" or "D". It stands in front of the rated voltage, as in standard machines
Speed of action is an important variable characteristic of an emergency vehicle
Breaking current (leakage)
Usually this is a number from a set: 10, 30, 100, 300 or 500 mA. This characteristic is indicated by a triangle (letter "delta"), which stands in front of a number characterizing the value of the rated leakage current in milliamps, at which the protection is activated.
Rated voltage
The most important operating indicator of automata and RCDs is the voltage rating (220 volts for one phase or 380 volts for three) - this is the usual operating voltage.
How to provide quality protection
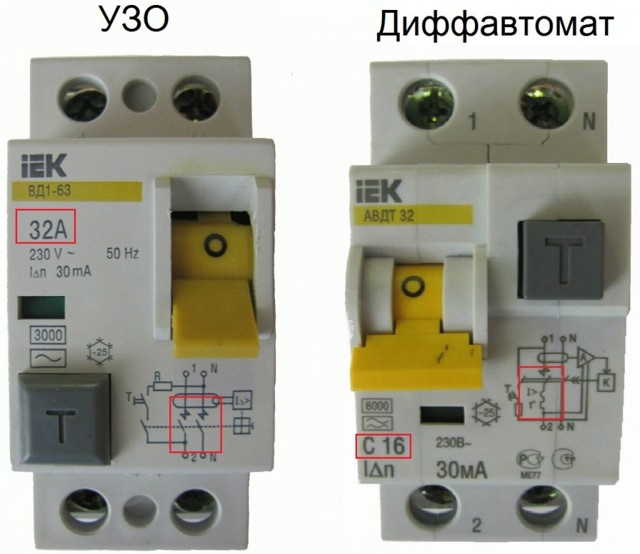
Despite the obvious benefits of RCDs, it is impossible to do without a circuit breaker. The RCD does not respond to overcurrents (short circuits) or overloads. It only monitors the leakage current. So for the safety of the wiring, an automatic machine is also needed. This pair - automatic and RCD - is placed at the entrance. The machine usually stands before the counter, leakage protection - after.
Instead of a pair - RCD + automatic, you can use a differential automatic. These are two devices in one case. The difavtomat immediately monitors both the leakage current, and the short, and the overload. It is put if there is a need to save space in the shield. If this is not necessary, they prefer to install separate devices. It is easier to determine damage, cheaper replacement in case of failure.
At the end
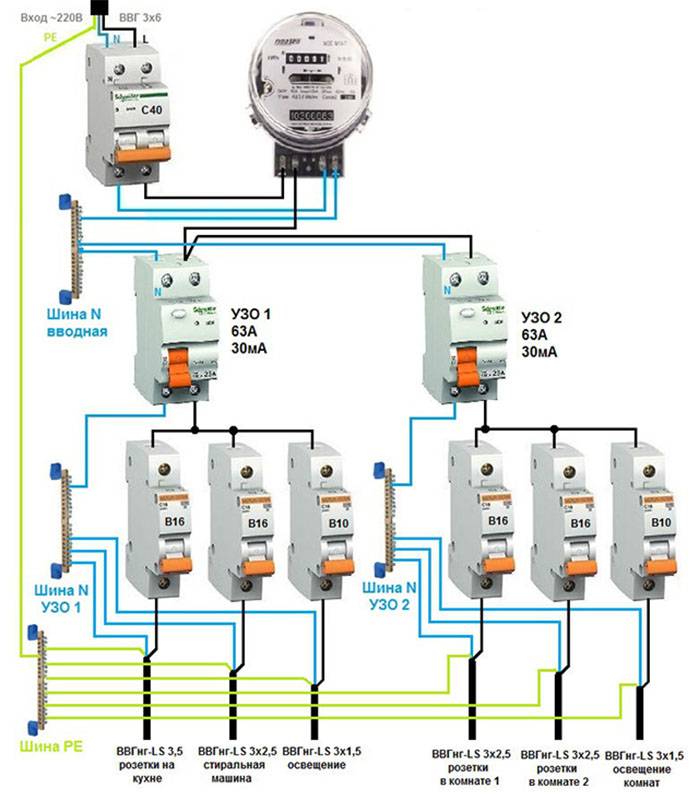
 Connection diagram for a multi-storey building
Connection diagram for a multi-storey building
- In mansions and country cottages, it is best to install four-pole devices from 3-phase DT switches so that the protection is really reliable.
- For large facilities, it is best to install several reliable devices for all groups of equipment.
- For houses with more than one floor, the power scheme has a cascading look and many branches.
- In this case, a protective device must be installed on each branch, on all floors, together with an electrical panel.
- For the home, it is recommended to choose a residual current switch of about 100 mA or more.
- It is necessary to install a VDT of type S. It has a long delay in tripping time.
Note! It is not recommended to install a protective device in a room with old faulty electrical wiring. It will constantly work.
In this case, it is best to change sockets already with a built-in protection system. For more information on what RCD is, we recommend that you watch the video below:
Types of RCDs and difavtomatov by the nature of the leakage current
The circuits use different types of currents, and therefore RCDs come in different classes:
- AC type. They are still most common in residential buildings and are cheaper than analogues. They are designed for AC sinusoidal current leakage. Most household electrical receivers operate on this current. The designation "~" is applied to the case of RCD class AC;
- type A. Recognizes leakage not only of alternating sinusoidal, but also of pulsating direct current. AC class analogs do not respond to such leaks. Recently, pulsating direct current has been used in an increasing number of household appliances: washing machines, induction cookers and hobs, computers, TVs, DVD players, new models of power tools, dimmable lamps. They use switching power supplies (computers, etc.) or power adjustment is carried out by cutting off part of the sinusoid with a thyristor or triac converter (lamps, power tools).Due to the increase in the number of such consumers, it is recommended to use class A devices instead of class AC in household electrical networks. In addition, they are more reliable, and cost only 20-30% more;
- type B. Able to respond to current leakage of all forms: sinusoidal, rectified pulsating and constant. Such devices are used in industrial enterprises; it is not advisable to purchase them for installation in an apartment or a private house.
In the instruction manual for washing machines and induction cookers, manufacturers directly indicate that the device must be connected through an RCD of type A.
RCD connection diagram, RCD designation on the diagram, single-phase and three-phase RCD connection diagram
The installation of an RCD significantly increases the level of safety when working on electrical installations. If the RCD has a high sensitivity (30 mA), then protection against direct contact (touch) is provided.
However, the installation of an RCD does not mean that you should not take the usual precautions when working on electrical installations. Mount the RCD on a panel or enclosure
Connect the equipment exactly as shown in the diagram. Turn on all loads connected to the protected network
Mount the RCD on a panel or housing. Connect the equipment exactly as shown in the diagram. Turn on all loads connected to the protected network.
RCD trips
If the RCD trips, find out which device is causing the trip by successively disconnecting the load (we turn off the electrical equipment in turn and look at the result). If such a device is found, it must be disconnected from the network and checked.
If the electrical line is very long, the normal leakage currents can be quite large.In this case, there is a possibility of false positives. To avoid this, it is necessary to divide the system into at least two circuits, each of which will be protected by its own RCD.
You can calculate the length of the electrical line.
If it is impossible to determine in a documentary way the sum of leakage currents of wiring and loads, you can use an approximate calculation (in accordance with SP 31-110-2003), assuming the load leakage current is 0.4 mA per 1A of the power consumed by the load and the mains leakage current is 10 μA per meter the length of the phase wire of the electrical wiring.
RCD calculation example
For example, let's calculate the RCD for an electric stove with a power of 5 kW, installed in the kitchen of a small apartment.
The approximate distance from the shield to the kitchen can be 11 meters, respectively, the estimated wiring leakage is 0.11mA. The electric stove, at full power, draws (approximately) 22.7A and has a rated leakage current of 9.1mA.
Thus, the sum of the leakage currents of this electrical installation is 9.21mA. To protect against leakage currents, you can use an RCD with a leakage current rating of 27.63mA, which is rounded up to the nearest higher value of the existing ratings according to the differential.
current, namely RCD 30mA.
Important
The next step is to determine the operating current of the RCD. With the above maximum current consumed by the electric stove, you can use the nominal (with a small margin) RCD 25A, or with a large margin - RCD 32A.
Thus, we calculated the value of the RCD that can be used to protect the electric stove: RCD 25A 30mA or RCD 32A 30mA. (you must not forget to protect the RCD with a 25A circuit breaker for the first rating of the RCD and 25A or 32A for the second rating).
RCD connection diagram
Let's consider the RCD connection diagram with an example. On the picture. 1 shows a fragment of a switch cabinet.
A photo. 1 Connection diagram of a three-phase RCD with a circuit breaker (in the photo, number 1 RCD, 2 is a circuit breaker) and single-phase RCDs (3).
RCD does not protect against short circuit currents, so it is installed in tandem with a circuit breaker. What to put before an RCD or a circuit breaker in this case is not important. The rating of the RCD should be equal to or slightly larger than the rating of the circuit breaker. For example, a circuit breaker is 16 Amperes, which means that we set the RCD to 16 or 25 A.
As seen in the photo. 1 on a three-phase RCD (number 1), three phase and neutral conductors are suitable, and after the RCD a circuit breaker is connected (number 2). The consumer will connect: phase conductors (red arrows) from the circuit breaker; neutral conductor (blue arrow) - with RCD.
Under the number 3 in the photo shows differential automata connected by a busbar, the principle of operation of the differential. the machine is the same as that of the RCD, but it additionally protects against short-circuit currents and does not require additional short-circuit protection.
And the connection, that of the RCD, that of the differential. machines are the same.
We connect the phase to the L terminal, zero to the N (the designations are printed on the RCD case). Consumers are also connected.
RCD scheme in the apartment
Below is a diagram of the use of an RCD in an apartment for additional protection against electric shock.
Rice. 1 Scheme of RCD in the apartment.
In this case, the RCD is installed before the meter, on the entire group of circuit breakers, which provides additional protection against electric shock and fire.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video material with a detailed overview of all the constituent elements of review protection mechanisms, their purpose and the principle of interaction with each other:
Description of all types of circuit breakers, as well as tips on how to make your choice:
The answer to the age-old question, what to choose - on a differential machine, or on an RCD + installation secrets:
The use of RCDs is a profitable and correct solution not only from the side of economy, but from the point of view of fire safety and human protection. It is recommended to maximize its potential in domestic conditions, installing it on all groups of electrical engineering to ensure complete isolation from the effects of electricity.