- Laying methods
- open position
- hidden option
- underground location
- Features of wire marking
- Mounting
- Self-supporting
- How to use the marking cable VVG-Png(A)
- How to choose
- Service life of VVG cable
- Types of wires
- flat
- with jumpers
- Single core
- For the manufacture of electrical cords
- Cable decoding VVG 3x1.5 (VVGng 3x1.5 and VVGng (A) 3x1.5 and others)
- Varieties of electrical cables
- Execution under the VVG brand
- Power flexible cable type KG
- Armored cable VBbShv
- Cable testing and production
- Types of cable marking
- The difference between cables and wires depending on the core material
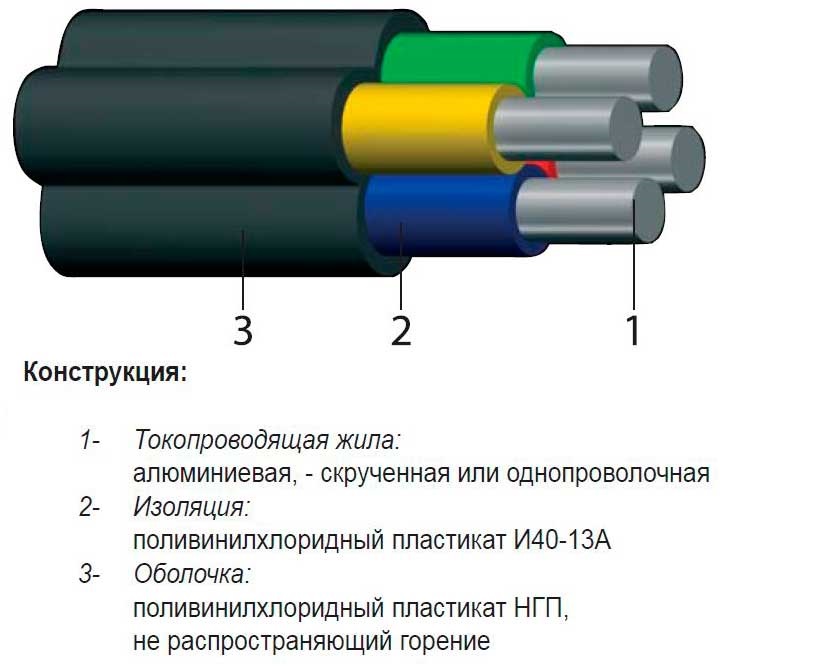
- Aluminum conductors
- Copper conductors
- Wire test
- Structural basis of the cable product
- What does VVG mean by spelling
Laying methods
VVG cable can be used in the construction of various facilities, as well as in underground trenches. The laying method directly depends on the specific purpose. It is possible to lay the conductor on various surfaces consisting of non-combustible materials. These include concrete, plaster, brick or plaster. The VVG cable can be laid in an open way under a variety of suspended structures. Reception of scrap cable .
A prerequisite is the exclusion of any mechanical influences.If there is a possibility of damage to the conductor, you need to think about additional protection. Often, special channels, tubes, metal or corrugated sleeves are used for this.
The most popular is the hidden method. Often it is used in residential areas, when the cable is laid under the plaster. First you need to make grooves in the walls, and then process the product with cement plaster. In such situations, the possibility of mechanical impacts is excluded, so there is no need to use additional protection. The only exception is when the wire is laid in wooden buildings. This option can be used in structures made of non-combustible materials, for example, in pipes.
There is no wire that can be laid underground without the use of special protective elements. This is due to the fact that the cable needs to be stored for a long period, but it itself is not equipped with built-in protection. Because of this, certain elements of protection against mechanical damage are used. In most cases, they are sealed boxes.
open position
If you study the technical parameters of the cable, then we can conclude that it is allowed to lay it in surfaces made of slow-burning or non-combustible materials, such as brick, concrete, gypsum or plaster. In an open way, the VVG wire can be laid under various suspended structures, such as a cable and the like. In this case, the gasket must be very reliable.
Any mechanical influences should be excluded. If the cable can be damaged, then additional protection must be taken into account.Usually, special channels, metal hoses, corrugated hoses or tubes are used for this purpose. Protection is installed if the open laying method is carried out on flammable objects, built, for example, from wood.
hidden option
This method of laying the most popular - is used in residential premises. The wire is usually laid under the plaster. Up to this point, furrows are made in the walls, and after that the cable is covered with plaster and cement. In this case, mechanical damage is excluded, and therefore there is no need to apply additional protection. An exception is when the cable is laid in wooden houses. Concealed gasket can be used in various non-combustible materials such as pipes.
underground location
No type of cable can be laid underground without the use of special protection. This is because the wire needs to be stored for a long time, but it itself is not equipped with built-in protection. That is why protective measures against various mechanical damages are applied. For laying underground, sealed boxes are used.
Features of wire marking
The range of cable and wire products also includes wires. How are they different from cables? As a rule, they have a smaller cross section, they can be insulated or without it. There are wires consisting of one core, there are several.

The wire has a smaller cross-section of cores, usually soft
In order to distinguish them from cables by name, the letter “P” is put in the name at the beginning of the marking. It is in first place if the conductors are copper and their designation is simply not put (example 1), or in second place if the conductors are made of aluminum and are indicated by the letter A (example 2).
- PBPPG - wire (P), domestic and industrial use (BP), flat shape (P), flexible (G).
- APPV - aluminum conductors (A), flat wire (PP), in a PVC sheath.
Marking wires for various purposes
Wires can be of two sections:
- round - this is not displayed in the marking:
- flat, then the letter P is placed.
Mounting
If the wire has a specific purpose - mounting - instead of the letter "P" put "M". For example, MGShV. It stands for installation (M) stranded (G) wire in a sheath made of polyamide silk and PVC.
The purpose of the mounting wires is to connect parts of devices, electronic and electrical equipment.
Decoding in the marking of mounting wires
Wires with PVC insulation (marked with the letter B) are designed for operation at temperatures not exceeding 70 ° C, from cross-linked polyethylene (PV) - up to 100 ° C. To work in an environment heated to a temperature of 200 ° C, wires of the MS and MGTF types are used.
Self-supporting
Wires that are installed on power lines or used in the air method of connecting electricity from the pole to the house are called self-supporting - they do not need a support. They have enough rigidity to support their own weight.
There are not so many products in this group, you can remember their decoding:
- SIP - self-supporting insulated wire in a sheath made of cross-linked polyethylene. It is applied at air connection to a column.
- SIP-1 also with uninsulated neutral;
- SIP-2 - the same, but the neutral is isolated;
- SIP-4 - insulated conductors of the same section.
- A - a wire twisted from several aluminum wires without insulation. It used to be quite widely used, now it is less and less common.
- AC - aluminum conductors twisted around a steel core.Pretty specific product.
There is a separate group - heating cables. They have their own label. After the letter "P" is "H" as a display of destination. For example, PNSV - wire (P), heating (H), steel single-wire core, PVC insulation.
How to use the marking cable VVG-Png(A)
An open method of laying the VVG cable is allowed. According to the technical characteristics of this cable, its open laying is allowed on structures and surfaces made of slow-burning or non-combustible materials, such as concrete, plastered surface, brick, gypsum, etc.
Open laying of the VVG cable is not excluded along suspended structures, for example, a cable, etc. In the case of laying wire along suspended structures, the possibility of mechanical action on the cable (stretching or sagging) must be excluded.
 Proper use of conductor
Proper use of conductor
It is required to install additional protection if there is a threat of mechanical damage to the cable product. When laying the conductor in an open way on wooden combustible surfaces, additional protection must also be used.
Note! Installation in this case should be carried out using a pipe, metal hose, corrugated hose, cable channel and other types of protection
How to choose
The first step is to choose a suitable wire section. There are special tables that indicate which section of the aluminum / copper core is necessary for a particular load. Masters use the usual formula:
- for example, a load of 8 kW is taken. The cross section of a copper wire of 1 mm2 passes through itself 10A or 2.2 kW;
- therefore, a load of 8 kW in amperes will equal 36 A (load = 8kW / 220V), so a cable with a cross section of 4mm2 can be used.
This formula is most suitable for wires whose cross section does not exceed 6 mm2. For thicker cables, you need to use the "permissible current loads" table.
With the same load, the cross section of the copper wire should be approximately 30% smaller than that of aluminum.
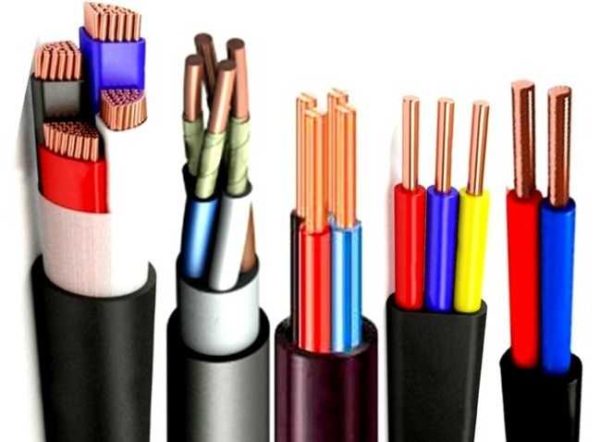
 Aluminum conductors
Aluminum conductors
Service life of VVG cable

It is believed that the service life of the VVG cable is quite long. However, it all depends on whether it is the result of production in accordance with GOST or compliance with TU.
The cable produced according to the requirements of GOST has a service life of up to 30 years.
Similar wires manufactured according to specifications have an officially declared service life of 10 years.
The conditions of use also play a decisive role. For example, staying in a humid room, constant exposure to too high or low temperatures can also negatively affect the life of the wire, reducing it proportionately.
The period of operation of the cable purchased in the store will also directly depend on the conditions of its storage.
Unfortunately, if they are not respected, then the cable may either be completely inoperative, or it will greatly disappoint you.
It is allowed to place the cable on special drums or open platforms.
If storage is carried out in closed premises, then the period will be about 30 years. Outdoors or indoors, the term is reduced to 20 years.
If the wire was manufactured in accordance with the specifications, it is necessary to make a request for production in case of purchasing a large batch. Most likely, the information specified in the documentation is not the most detailed, and therefore cannot be fully accepted as reliable.
Types of wires
The selection of the desired wire largely depends on the power of the electrical appliances that will be powered through it. Next, consider the various types of wires that are most often used for domestic use.
flat
1. PBPP (PUNP).
Flat protected wire with single-wire copper conductors, cross-section from 1.5 to 6 mm², located in the same plane. The material of external and internal insulation is PVC. It can be used at temperatures in the range of -15/+50, during installation it is allowed to bend in a circle with a radius of at least 10 diameters (since the wire is flat, the width is measured - the larger side). Designed to transmit current with voltage up to 250 Volts, frequency 50 Hertz. It is mainly used to connect lighting or sockets.
2. PBPPg (PUGNP).
The letter "g" in the name indicates a distinctive feature of the wire - the flexibility that the use of stranded wires gives. This also reduces the bending radius during installation, which is 6 diameters. All other characteristics are the same as for single-wire PBPP (PUNP).
3. APUNP.
The same PUNP wire, but with a single-wire aluminum core, with a cross section of 2.5 to 6 mm². The rest of the characteristics are unchanged.
with jumpers
1.PPV.
The wire is easy to recognize thanks to the characteristic jumpers between the cores, which are made of the same material as their insulation - PVC. The number of cores themselves is 2-3, they are single-wire, with a cross section of 0.75-6 mm².The wire can be used to transmit current with a voltage of 450 volts and a frequency of up to 400 hertz. Insulation does not burn, resistant to acids and alkalis - after installation, the wire can be used at temperatures of -50/+70 °C and in conditions of 100% humidity (characteristic for 35 °C). During installation, a bend with a radius of 10 diameters is allowed.
2. APPV.
The same characteristics as for PPV, but taking into account aluminum conductors - the cross section starts from 2.5 mm². Purpose - installation of open wiring - lighting and power.
Single core
1. AR.
Separate aluminum single core wire. A core with a cross section of 2.5-16 mm² is single-wire, and 25-95 mm² is multi-wire. Insulation material - PVC, resistant to chemically aggressive compounds, allows the wire to be used at a humidity of 100% (tests at 35 °C), in a temperature regime of -50/+70 °C. When mounting, observe a bending radius of 10 diameters. There are no special restrictions for use.
2. PV1.
The same APV, only with a single-wire copper core, with a cross section of 0.75-16 mm² and a stranded one of 16-95 mm².
3. PV3.
The number in the name of the wire indicates the class of flexibility - here it is much higher, since it is multi-wire for any section of the core. It is used for mounting lines where frequent transitions and bends are needed. The radius of the latter should not be less than 6 diameters.
Wires PV1, PV3 and APV are made with multi-color insulation, which increases the convenience of their use for the installation of switchboards without the use of additional marking.
For the manufacture of electrical cords
1. PVA.
Copper stranded wire, with 2-5 stranded wires with a cross section of 0.75-16 mm². The insulation of all cores is of different colors, the sheath is plain white. The purpose of the wire is to transmit current with a voltage of 380 volts at a frequency of 50 hertz.Due to its high flexibility, it is most often used for connecting electrical equipment - it is designed for at least 3000 bends.
It is not recommended for laying inside walls - in such conditions, after 4-5 years, the external insulation will begin to collapse. It can be used at temperatures of -25/+40 °С, and in the modification of PVSU - from -40 to +40 °С.
2. ShVVP.
Copper stranded wire, with 2-3 stranded conductors of increased flexibility with a cross section of 0.5-0.75 mm². It is used for the manufacture of power cords for lamps or low-power electrical devices that require voltage up to 380 Volts and a frequency of 50 Hertz. Not suitable for laying inside walls.
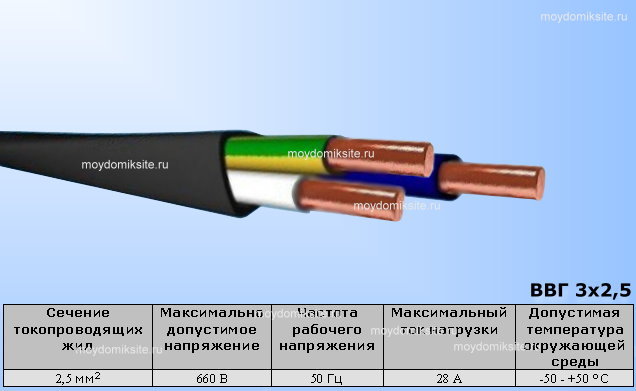
Cable decoding VVG 3x1.5 (VVGng 3x1.5 and VVGng (A) 3x1.5 and others)
Its marking indicates the presence of polyvinyl chloride insulation material for three copper conductors and a common sheath made of it. It is also about the lack of additional protective cover.

- B - PVC compound as an insulating material.
- B - PVC sheath.
- G - no protective armored shell.
- ng - insulation with an increased level of fire safety.
- (A) - when laid in a group, they do not ignite, the index means "not propagating combustion according to category A".
- 3 - the number of lived.
- 1.5 - cross-section of conductors, mm2. It means the cross section of a copper core, and it is this value that is the most popular, but there are others, up to 240 square millimeters.
- ls - means Low Smoke, prevents the spread of smoke.
- fr - means Fire Resistance, the presence of a thermal barrier in the form of a conductor winding with two mica tapes
- hf - no halogens
- frls - the abbreviation means Fire Resistance Low Smoke and says that when ignited, the wire emits a minimum amount of gas and smoke, and also does not spread fire during group laying.
- frhf - fire-resistant cable products that do not spread combustion during group laying and do not emit corrosive gaseous products during combustion and smoldering;
Additionally, the following indices are possible in the designation:
- "ok", "ozh" - single-wire (monolithic) design;
- "mk", "mzh" - multi-wire design.
- 0.66 - operating voltage, kV.
- 1.0 – operating voltage, kV.
Varieties of electrical cables
If we consider only cables for power electrical circuits, here the main types are the following power cables:
- VVG;
- KG;
- VBbShv.
Of course, this is not a complete list of all existing cable products. Nevertheless, using the example of technical characteristics, one can form a general idea of \u200b\u200bthe cable for electrical purposes.
Execution under the VVG brand
Widely used, popular and reliable brand. The VVG cable is designed to transmit current with a voltage of 600 - 1000 volts (maximum 3000 V).
The product is manufactured in two modifications, with current-carrying conductors of a solid structure or a beam structure.
A product from the category of electrical cables, noted as popular and often chosen as a material for building electrical power lines
According to the product specification, the core cross-section range is 1.5 - 50 mm. Polyvinyl chloride insulation allows the use of the cable at temperatures of -40 ... + 50 ° С.
There are several modifications of this type of cable products:
- AVVG
- VVGng
- VVGp
- VVGz
Modifications are distinguished by a slightly different design of insulation, the use of aluminum conductors instead of copper conductors, and the shape of the cable.
Power flexible cable type KG
The design of another popular cable, characterized by a high degree of flexibility, due to the use of a beam structure of current-carrying conductors.
Execution of a power flexible cable of the KG brand for four working current-carrying conductors. The product is of high quality insulation, shows good technical characteristics
The execution of this type provides for the presence of up to six current-carrying conductors inside the sheath. Operating temperature range -60…+50°С. Mostly, a type of KG is used to connect power equipment.
Armored cable VBbShv
An example of the design of special cable products in the form of a product under the brand name VBbShv. Conductive elements can be bundled or solid conductors. In the first case, the cross section range is 50-240 mm2, in the second case it is 16-50 mm2.
The cable insulation is built with a complex structure, including belt insulation, tape screen, steel armor, bitumen and PVC.
The structure of the power cable for high voltage and significant power. This is one of those cable products, the use of which guarantees the reliability of the circuit.
There are several modifications of this type:
- VBBShvng - non-combustible insulation;
- VBbShvng-LS - does not emit harmful substances during combustion;
- AVBbShv - the presence of aluminum conductors.
The ability to read the marking of cable products is useful when choosing products and wiring electrical networks.
Alphanumeric marking of the cable product: 1) letter 1 - core metal; 2) letter 2 - purpose; 3) letter 3 - insulation; 4) letter 4 - features; 5) number 1 - the number of cores; 6) number 2 - section; 7) number 3 - voltage (nominal) (+)
Features of the core material type - Letter 1: "A" - aluminum core. In any other case, copper lived.
As for the purpose (Letter 2), here the decoding is as follows:
- "M" - for installation;
- "P (U)", "MG" - flexible for installation;
- "Sh" - installation; "K" - for control.
The designation of insulation (Letter 3) and its decoding is as follows:
- "V(BP)" - PVC;
- "D" - double winding;
- "N (NR)" - non-combustible rubber;
- "P" - polyethylene;
- "R" - rubber;
- "C" - fiberglass;
- "K" - capron;
- "Sh" - silk polyamide;
- "E" - shielded.
The features that Litera 4 testifies to have their own decoding:
- "B" - armored;
- "G" - flexible;
- "K" - wire braid;
- "O" - the braid is different;
- "T" - for pipe laying.
The classification also provides for the use of lowercase letters and letters indicated in Latin:
- "ng" - non-flammable,
- "z" - filled,
- "LS" - without chemical. combustion emissions,
- "HF" - no smoke when burning.
Markings, as a rule, are applied directly to the outer shell, and along the entire length of the product at regular intervals.
Table of symbols for the most used types of wires and their compliance with standards. It is always possible to determine the brand by simply reading directly from the product shell (+)
On our website there are articles on the choice of cable products for arranging electrical networks in an apartment and a house, we advise you to read:
- Which cable to use for wiring in an apartment: an overview of the wires and choosing the best option
- Which wire to use for wiring in the house: recommendations for choosing
- What cable to use for wiring in a wooden house: types of non-combustible cable and its safe installation
Cable testing and production
 Manufacturers, before marking the conductor as non-flammable, test products using various methods. For testing in the laboratory, the situation of a real fire is simulated. Then a specialist using certain equipment measures the transparency of the air inside the room with fire. All measurements should be done twice: initially, and then after ignition.
Manufacturers, before marking the conductor as non-flammable, test products using various methods. For testing in the laboratory, the situation of a real fire is simulated. Then a specialist using certain equipment measures the transparency of the air inside the room with fire. All measurements should be done twice: initially, and then after ignition.
The smoke reduces the light penetration inside the room and this fixes the device. Then the specialist calculates the ratio of the values before and after the experiment. For the cable to successfully pass the test, the transparency in the room should not change by more than 40%. Only then is the appropriate marking applied to the product.
To date, several domestic companies are engaged in the production of VVG wire. Among them:
- "Sevkabel" (St. Petersburg).
- "Concord" (Smolensk).
- Moskabelmet (Moscow).
- "Podolskkabel" (Podolsk).
Types of cable marking
Due to its availability and reasonable price, the conductor of the VVG brand has become widespread in the installation of electrical wiring in private construction. The marking of this product is presented in several forms:
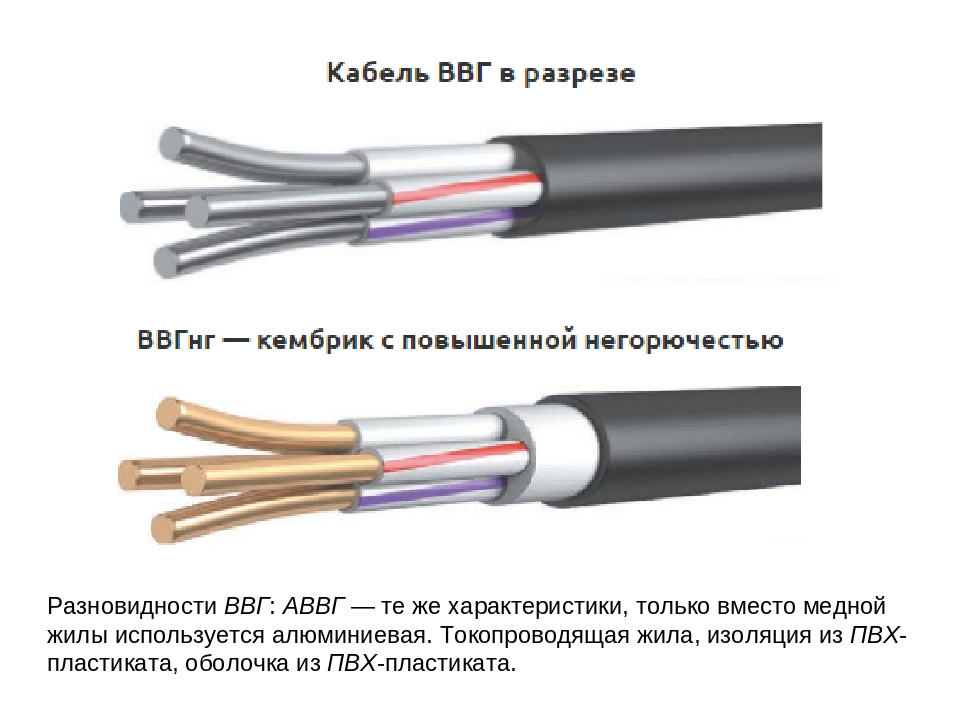
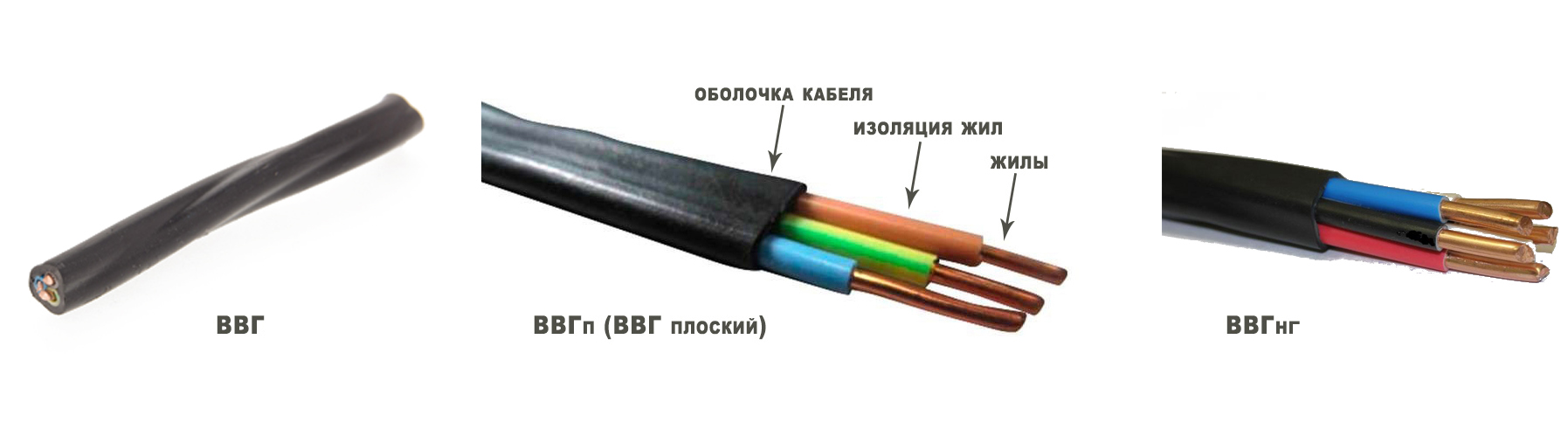
- A standard cable of the VVG brand consists of a round-shaped wire made of copper and protected by double insulation made of PVC or plastic. It is used in premises for permanent residence.
- The VVGP cable is a copper wire (“P” stands for flat), which is used in places with variable temperature conditions. It has a flat cross-sectional shape and is equipped with an additional insulating layer, and is also more durable in use.
- Copper cable VVGng is a wire with a round cross section. The central core has a special flexible mesh winding. The outer insulating layer is made of polyvinyl chloride. Even large industrial enterprises do not refuse to use this product, since it is made of non-combustible materials and, due to its flexibility, is less prone to fracture.
- Features of flat copper wire, abbreviated VVGP ng, are the presence of double insulating protection, which uses polymers. Polymers perform a protective role and provide an extension of the service life of the cable.
- Marking VVGng-ls indicates an obstacle to combustion and does not emit soot and smoke with an open flame. The presence of plastic compound in the winding does not allow installation outdoors or in rooms with temperatures below +5 °C.
- For industrial use, a product with the abbreviation VVGP ng-ls is suitable, which has increased strength and flexibility, the outer insulating layer of which is made of non-combustible polymers with a high degree of wear resistance.
Non-combustible conductors also include products VVGng-LSLTx and VVGng-HF.
The difference between cables and wires depending on the core material
Cores of wires and cables for specialized purposes can be made of various metals, but aluminum and copper are mainly used in electrical engineering.Each of them has its own specific properties, advantages and disadvantages, which must be taken into account when selecting a core material for a specific purpose.
Aluminum conductors
The invention of a relatively inexpensive way to extract aluminum made a revolution in the global development of electrification, because in terms of electrical conductivity, this metal is in fourth place, skipping ahead only silver, copper and gold. This allowed the production of wires and cables to be as cheap as possible and made universal electrification a reality.
Such electrical wires and their types are distinguished by their low cost, chemical resistance, high level of heat transfer and low weight - they have determined the mass character of electrification in industrial and domestic conditions for more than half a century.
In the light of the relatively recent dominance of aluminum in the wire market, it may seem strange to the uninitiated that the provisions of the PUE prohibit the use of this material in everyday life. More precisely, you can not use aluminum wires with a cross section of less than 16 mm², and these are the most common ones for installing home electrical wiring. To understand why there is a ban on the use of these wires, you can familiarize yourself with their advantages and disadvantages.
+ Advantages of aluminum wires
- Lighter than copper.
- Significantly cheaper.
- Cons of aluminum wires
- Aluminum conductors with a cross section of up to 16 mm² can only be single-wire, which means that they can only be used for laying fixed wiring and without bending at an acute angle. All flexible wires and cables have always been made of copper.
- The chemical resistance of aluminum is determined by the oxide film that forms when it comes into contact with air.Over time, with constant heating of the contact due to the flow of electric current through it, this film worsens the electrical conductivity, the contact overheats and fails. That is, aluminum wires require additional maintenance, and contacts through which powerful currents pass are coated with a special lubricant.
- Amorphousness of the material - if you clamp two aluminum wires together, then over time the contact will weaken, since the aluminum will partially “leak out” from under the yoke.
- Soldering can only be carried out using special tools, and welding can be done in an inert gas chamber.
- Good electrical conductivity is observed only in pure aluminum, and impurities that inevitably remain during production worsen this indicator.
As a result, aluminum is a good choice if you need to save money here and now, but in the long run it will cost more due to the relatively short service life and the need for regular maintenance. For this reason, and for additional security reasons, the PUE categorically prohibits using it for laying new power lines.
Copper conductors
In terms of electrical conductivity, copper is in second place, only 5% inferior to silver in this indicator.
Compared to aluminum, copper has only 2 significant drawbacks, due to which it was used much less frequently for a long time. Otherwise, copper wins in all respects.
+ Advantages of copper wires
- The electrical conductivity is 1.7 times higher than aluminum - a smaller wire section will pass the same amount of current.
- High flexibility and elasticity - even single-core wires can withstand a large number of deformations, and cords for electrical appliances of increased flexibility are obtained from stranded wires.
- Soldering, tinning and welding are carried out without the use of additional materials.
- Cons of copper wires
- The cost is several times more expensive than aluminum.
- High density - a coil of copper wire, the same length and cross section as aluminum, will weigh 3 times more.
- Copper wires and contacts oxidize in the open air. However, this practically does not affect the contact resistance and, if necessary, is “treated” by lubricating the surface of an already tightened contact.
As a result, although copper is a more expensive material, in general its use is more cost-effective, as it is more durable, requires less effort during installation and attention during maintenance.
Wire test
In order to label a wire as flame retardant, the wire must be tested in various ways. Real fire conditions are recreated for laboratory testing. After that, the laboratory assistant, using special equipment, measures the transparency of the air inside the fire room. These measurements must be carried out both under normal conditions and after a fire.
Smoke will reduce the light transmission of the room, and this will fix the device. As a result, a trained worker will calculate the ratio of light transmission before the experiment, as well as after ignition. In order for the wire to successfully pass the test, the change in transparency inside the room should be no more than 40%. Only in this case it will be possible to put the appropriate designation on the cable.
Structural basis of the cable product
The performance of the cable or electrical wires determines the technical and operational characteristics of the product. Actually, the execution of cable or wire products is, in most design variations, a fairly simple technological approach.
Classic performance:
- Cable insulation.
- Core insulation.
- Metal core - solid/beam.
A metal core is the basis of a cable / wire through which an electric current flows. The main characteristic, in this case, is the throughput, determined by the cross section of the core. This parameter is influenced by the structure - solid or beam.
Such a property as flexibility also depends on the structure. Stranded (beam) conductors in terms of the degree of “softness” of bending are characterized by better properties than single-core wires.
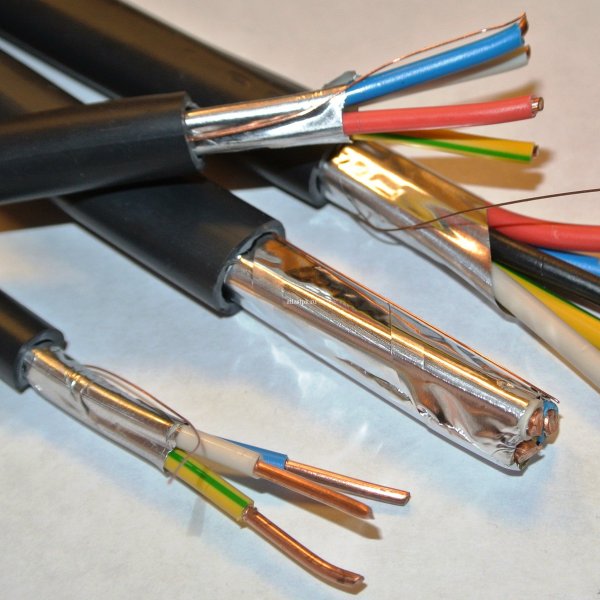
 The structural design of the current-carrying part is traditionally represented by "beam" or "solid" (monolithic). This matters, for example, in relation to the properties of flexibility. The picture shows stranded/bundle wire type
The structural design of the current-carrying part is traditionally represented by "beam" or "solid" (monolithic). This matters, for example, in relation to the properties of flexibility. The picture shows stranded/bundle wire type
The cores of cables and wires in electrical practice, as a rule, have a cylindrical shape. However, rarely, but there are somewhat modified forms: square, oval.
The main materials for the manufacture of conductive metal conductors are copper and aluminum. However, electrical practice does not exclude conductors in the structure of which there are steel cores, for example, a "field" wire.
If a single electrical wire is traditionally built on a single conductive core, a cable is a product where several such cores are concentrated.
What does VVG mean by spelling
In the instructions for electrical work, the non-combustible cable VVGng can be seen most often.In terms of price / quality - this is the best option. This conductor is indeed quite versatile, as it can be used in flammable buildings and in structures with high humidity. Below are the technical characteristics of this product, as well as its purpose, disadvantages and advantages.

What can the label say? First, let's see what conductor markings are. Knowing the decoding of each letter in the marking, you can easily determine what properties the cable has.
We list the main features by which conductors can be divided.
1. The material used to make the conductive core:
- - the letter A, if it is aluminum;
- - no designation if it is copper.
2. The material from which the insulation of conductive conductors is made:
- - the letter P - polymer insulation;
- - letters Pv - polyethylene;
- - the letter B - polyvinyl chloride.
3. Cable armor:
- - the letter G - there is no armor, the cable is bare;
- - armored (B).
4. Sheath, outer insulation:
- - the letter B - polyvinyl chloride;
- - letters Shv - has a protective hose;
- - letters Shp - has a protective hose made of polyethylene;
- - the letter P - a polymeric outer shell.
5. For fire safety:
- - if there is no designation, then with a single laying, the cable does not spread combustion;
- - if the designation is ng, then during group laying the cable does not spread combustion;
- - if the designation is ng-ls, smoke and gas emission is reduced, during group laying the cable does not spread combustion;
- - if the designation is ng-hf, during group laying the cable does not spread combustion, during smoldering and burning corrosive gaseous substances are not emitted;
- - if the designation is ng-frls, with group laying it does not spread combustion, the emission of gas and smoke is reduced;
- - if the designation ng-frhf, during group laying, the cable does not spread combustion, during smoldering and burning, corrosive gaseous substances are not emitted.
Based on the above, we can decipher the VVGng abbreviation as follows: the insulation of the conductive cores is made of polyvinyl chloride (B), the insulation of the outer sheath is also made of polyvinyl chloride (B), there is a special protective layer, there is no armor (G).
| Friends, all VVG cables and their varieties are manufactured in accordance with the standard - GOST 31996-2012. I post a selection of decoding markings from this GOST |
In the language of VVG electric motorists, the decoding sounds something like this: V - vinyl, V - vinyl, G - naked. In addition, the letters ng mean that this cable does not support combustion during group laying. This is a very important parameter if you want to lay the cable in places with a fairly high probability of fire. Safety comes first. Since there is no letter A in the described marking, the cable consists of copper conductors. Table 1. Cable VVG marking decoding
| Lived | core insulation | Shell insulation | Armor | fire safety | |
| VVG | copper | polyvinyl chloride | polyvinyl chloride | missing | Yes - single gasket only |
| VVG ng | — | — | — | — | Yes |
| VVG ng-ls | — | — | — | — | Yes + with reduced smoke and gas emission |
| VVG ng-hf | — | — | — | — | Yes + does not emit corrosive products |
| VVG ng-frls | — | — | — | — | Yes + fire-resistant, + with reduced smoke and gas emission |
| AVVG | aluminum | polyvinyl chloride | polyvinyl chloride | missing | Yes - single gasket only |
| AVBShvng | aluminum | polyvinyl chloride | PVC protective hose | there is | Yes |
This conductor has two modern modifications: with the prefix ng-hf - when the cable burns, there is no release of corrosive gaseous substances; with the prefix ng-ls - during combustion, the emission of gas and smoke is reduced. These two modifications, in turn, also have their own improvement - fr (fire resistance). As a result, the product may be marked VVGNG-FRLS. Deciphering this marking is quite simple once you have mastered the principle.
Along with the usual VVG, there are often cables with the letter "P" at the end of the marking. In terms of technical characteristics, these two subspecies are no different, but there is a slight difference in structure - it is flat, i.e. VVG p decoding sounds like: V-vinyl, V-vinyl, G-naked, P-flat.