- How justified is the price of the boiler?
- Factors affecting the formation of condensate
- Condensate and chimney types
- brick
- Asbestos-cement
- Steel and galvanized
- Furanflex
- stainless steel
- How does a thermostatic control valve work?
- Condensation in chimneys
- What is condensate and how does it form in a chimney?
- Is it possible to drain condensate into the sewer?
- What is harmful condensate
- Determination of the probability of condensation formation
- Causes of condensation in the chimney pipe
How justified is the price of the boiler?
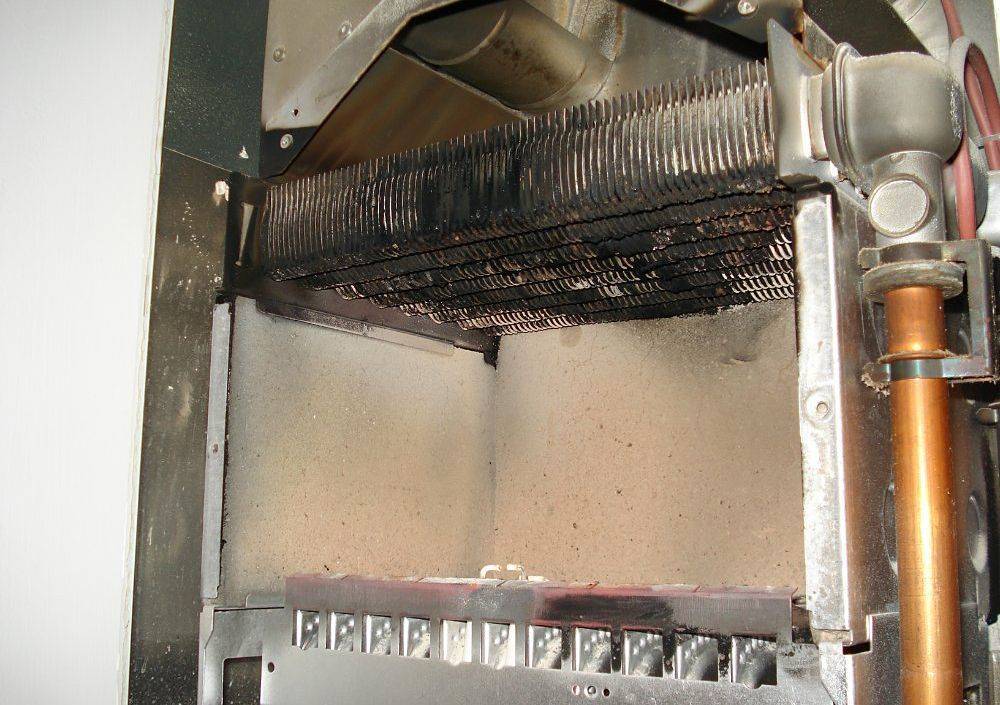
A quality boiler is never cheap.
Only very highly qualified welders and locksmiths are allowed to manufacture START boilers. Many welders have been working for over 15 years and value their work. Each weld is of very high quality and carefully checked.
The seams of the combustion chamber of the chamber are always welded on both sides
for maximum reliability, and for welding the outer seams, a KUKA welding robot is used, which ensures a perfect, even seam due to the fact that it is inherently a ROBOT and due to drip mode welding arc with deep welding.
We do not apply no cheap parts
, gearbox - the best German, engine - high-quality Spanish, fan - a leading manufacturer from Poland, metal - 6mm thick MMK (Russia), iron casting - very high-quality Russian (indistinguishable from Finnish casting), even sealing cords are used not cheap fiberglass, but very high-quality high-temperature mulite-silica.
Factors affecting the formation of condensate
The process of formation of condensate in the chimney channel depends on several factors:
- Humidity of the fuel used by the heating system. Even seemingly dry firewood contains moisture, which turns into steam when burned. Peat, coal and other combustible materials have a certain percentage of moisture content. Natural gas, burning in a gas boiler, also releases a large amount of water vapor. There is no absolutely dry fuel, but poorly dried or damp material increases the condensation process.
- Traction level. The better the draft, the faster steam is removed and less moisture settles on the pipe walls. It simply does not have time to mix with other combustion products. If the draft is bad, a vicious circle is obtained: condensate accumulates in the chimney, contributing to clogging and further worsening the circulation of gases.
- The temperature of the air in the pipe and the gases leaving the heater. The first time after kindling, smoke moves along an unheated channel, also having a low temperature. It is at the start that the greatest condensation occurs. Therefore, systems that operate constantly, without regular shutdowns, are least susceptible to condensation.
- Temperature and humidity of the environment.In the cold season, due to the temperature difference inside the chimney and outside, as well as increased air humidity, condensate forms more actively on the outer and end parts of the pipe.
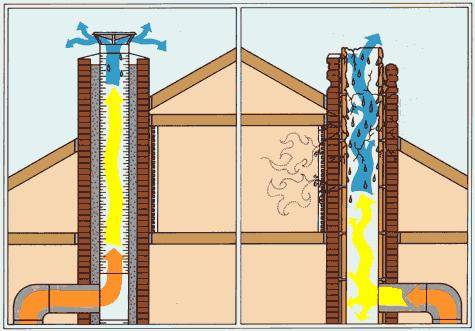
- The material from which the chimney is made. Brick and asbestos cement prevent the dripping of moisture drops and absorb the resulting acids. Metal pipes can be prone to corrosion and rust. Chimneys made of ceramic blocks or stainless steel sections prevent chemically aggressive compounds from catching on a smooth surface. The smoother, smoother the inner surface and the lower the moisture absorption capacity of the pipe material, the less condensate is formed in it.
- Integrity of the chimney structure. In case of violation of the tightness of the pipe, the appearance of damage on its inner surface, traction worsens, the channel becomes clogged faster, moisture from the outside can get inside. All this leads to increased steam condensation and deterioration of the chimney.
Modern man is very thermophilic. If you, our dear reader, have your own house, then you have to solve the problem of heating it yourself. But modern heating equipment is different from the fireplaces of the past; along with an increase in efficiency, the complexity of the design increases and the maintenance of the units becomes more complicated.
During the operation of modern boilers, stoves and fireplaces, condensation is necessarily formed in the chimney.
Whatever type of fuel you use, you are burning hydrocarbons. Coal, coke, firewood, fuel oil, gas, pellets - everything consists of hydrogen and carbon with small impurities of sulfur and some other chemical elements. Any fuel also contains a small amount of water - it is impossible to completely remove it.During combustion, they are oxidized by atmospheric oxygen and the output is water, carbon dioxide, and other oxides.
Sulfur oxides react with water at high temperatures and form very aggressive acids (sulphuric, sulphurous, etc.), which also enter the condensate. A few other acids are also formed: hydrochloric, nitric.
Condensate and chimney types
To know how to avoid condensation in the chimney, you need to know what type it is. It also depends on how much condensate will form during the furnace. It must be chosen carefully even before construction, otherwise the failed system will have to be completely changed later. In this situation, serious repairs will be required.
brick
Such a system has a number of advantages:
- excellent traction;
- high quality heat storage;
- heat is retained for a very long time.
But this system also has a number of disadvantages. If brick is used as the main material, then the chimney will no longer be very good. In such systems, condensate is already formed due to the low temperature and because the pipe warms up for a very long time. The situation can be saved if you think about the removal of condensate from the chimney.
Particularly influenced by the large formation of condensate, certain climatic conditions. These include periodic freezing and thawing of pipes in winter.
In this system, there is still an important disadvantage from the formation of condensate - the system itself will quickly collapse. Brick absorbs moisture very well. The walls are constantly getting wet, the interior decoration is destroyed. This will cause the pipe head to simply crumble.
Advice! If, nevertheless, it is decided to make a chimney out of brick, it will be necessary to use a liner.
That is, a stainless steel channel is built into the chimney system.
Asbestos-cement

For a long time, this type of chimney was the most popular. They are cheap. But the price is not the main indicator. Such chimneys have a lot of disadvantages that can cause a large amount of condensate.
Cons are as follows:
- joints are very difficult to close hermetically;
- installation work can only be carried out in vertical sections;
- it is difficult to carry out installation work due to the large length and weight of the structure;
- unstable to high temperatures, easily burst and explode;
- the boiler itself is very difficult to connect, you will need a tee, a steam trap and a cleaning hatch.
Of all the shortcomings, not only a lot of condensate is formed on the inner surface, but it is still very quickly and easily absorbed into the walls of the chimney. Therefore, it is necessary to clean such a system in a timely and frequent manner. All preventive work can be done by hand.
Steel and galvanized
This type is short lived. You need to constantly monitor the condensate. It is he who is the main reason for the failure of a steel or galvanized chimney. For example, the service life of steel is about three years, galvanized is no more than four years.
Furanflex
This type of chimney is the most resistant to condensation. The disadvantage is that they have low thermal conductivity. Made from special plastic. Additionally, the plastic is reinforced with high-strength fibers. Thanks to this solution, the products are durable and withstand condensate well.
Chimney pipes made of this material are used at temperatures not exceeding 200 degrees.
We must remember! If you plan to make a chimney from furanflex, you must take into account the fact that at a temperature of more than 200 degrees their strength is lost, they can melt and fail.
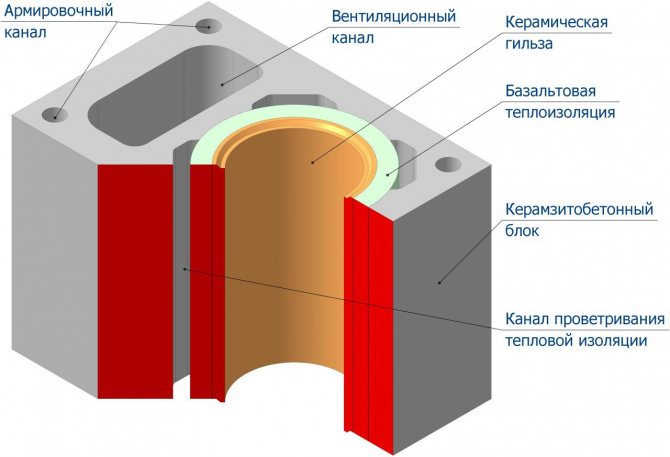
stainless steel
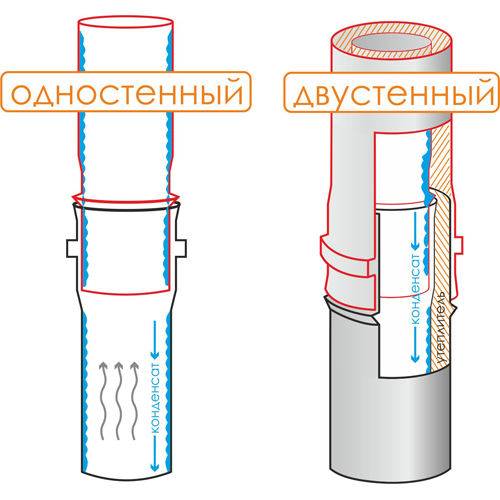
Chimney systems of this type can be:
- single-walled;
- double-walled or insulated.
Basalt fiber is used as a heater. In order to protect the system from condensate, the same steel is used. In combination with a heater, the chimney becomes more resistant to condensation and, therefore, the entire system will last a long time.
Chimneys made of stainless steel have a number of advantages. These are such as:
- fireproof, if everything is done according to the rules, the system will be completely fireproof;
- tight;
- easy to use;
- excellent traction, all thanks to the round section and smooth surface.
How does a thermostatic control valve work?
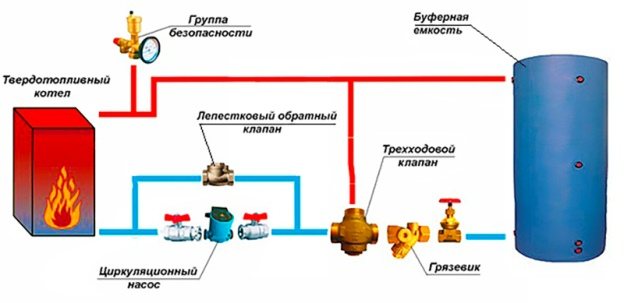
The thermostatic valve is installed on the supply in front of the bypass section (section of the pipeline) connecting the supply and return of the boiler in close proximity to the boiler. In this case, a small coolant circulation circuit is formed. The thermoflask, as mentioned above, is installed on the return pipeline in close proximity to the boiler.
At the time of boiler start-up, the coolant has a minimum temperature, the working fluid in the thermoflask occupies a minimum volume, there is no pressure on the thermal head rod, and the valve passes the coolant only in one direction of circulation in a small circle.
As the coolant heats up, the volume of the working fluid in the thermoflask increases, the thermal head begins to put pressure on the valve stem, passing the cold coolant to the boiler, and the heated coolant into the common circulation circuit.
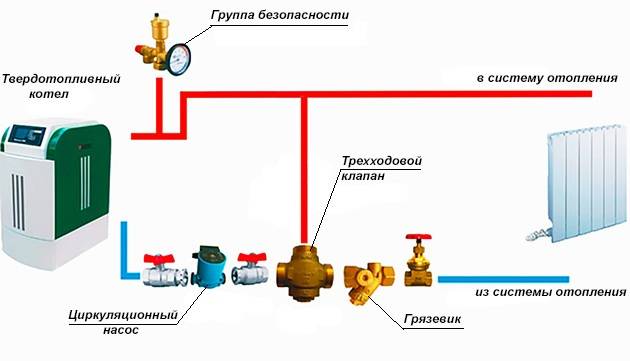
As a result of mixing cold water, the return temperature decreases, which means that the volume of the working fluid in the thermoflask decreases, which leads to a decrease in the pressure of the thermal head on the valve stem. This, in turn, leads to the cessation of the supply of cold water to the small circulation circuit.
The process continues until the entire coolant is heated to the required temperature. After that, the valve blocks the movement of the coolant along the small circulation circuit, and the entire coolant begins to move along the large heating circle.
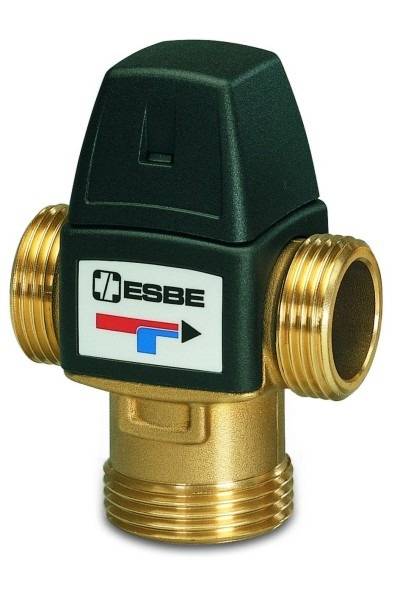

The mixing thermostatic valve works in the same way as a control valve, but it is not installed on the supply pipe, but on the return pipe. A valve is located in front of the bypass, which connects the supply and return and forms a small circle of coolant circulation. The thermostatic bulb is fixed in the same place - on the section of the return pipeline in close proximity to the heating boiler.
While the coolant is cold, the valve passes it only in a small circle. As the coolant heats up, the thermal head begins to put pressure on the valve stem, passing part of the heated coolant into the common circulation circuit of the boiler.
As you can see, the scheme is extremely simple, but at the same time effective and reliable.
The operation of the thermostatic valve and thermal head does not require electrical energy, both devices are non-volatile. No additional devices or controllers are needed either. It takes 15 minutes to heat the coolant circulating in a small circle, while heating the entire coolant in the boiler can take several hours.
This means that using a thermostatic valve, the duration of condensate formation in a solid fuel boiler is reduced by several times, and with it, the time for the destructive effect of acids on the boiler is reduced.
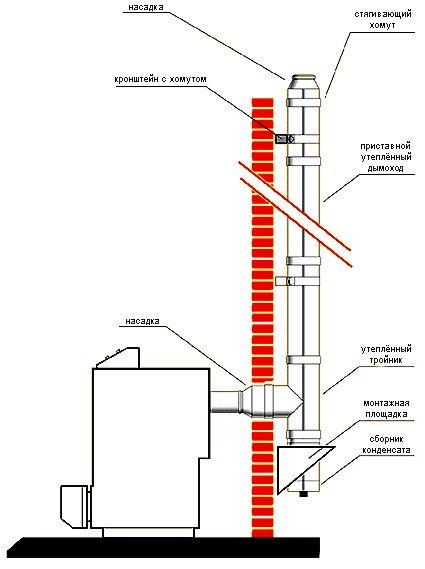
For solid fuel boiler protection from condensate, it is necessary to properly piping it, using a thermostatic valve and creating a small coolant circulation circuit.
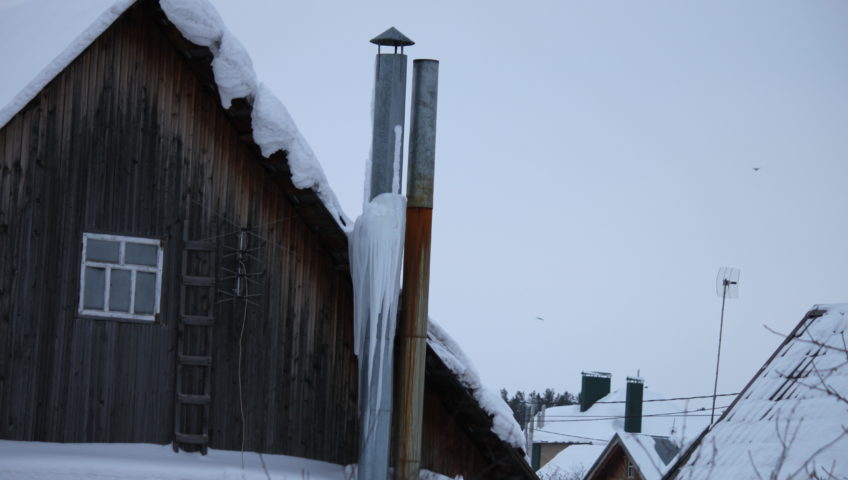
Condensation on the pipe of a gas boiler is formed due to the difference in ambient temperatures and the walls of the flue channel. In winter, the condensate freezes, and icicles form on the head of the pipe, and ice plugs form in the chimney. Over time, the ice thaws, moisture flows down the pipe, the chimney and adjacent structures get wet and gradually collapse.
Condensation in the gas boiler pipe also leads to negative consequences. Water vapor, which is contained in the products of combustion of fuel, condenses on the cold walls of the chimney. As a result, moisture is formed, which combines with the salts of flue gases. In this case, aggressive acids are formed that destroy the chimney and other surfaces.
Condensation in chimneys
Flue gases, rising through the chimney, are gradually cooled. When cooled below the dew point, condensation begins to form on the walls of the chimney. The cooling rate of the DG in the chimney depends on the flow area of the pipe (the area of its inner surface), the material of the pipe and its planting, as well as the intensity of combustion. The higher the burning rate, the greater the flow of flue gases, which means that, all other things being equal, the gases will cool more slowly.
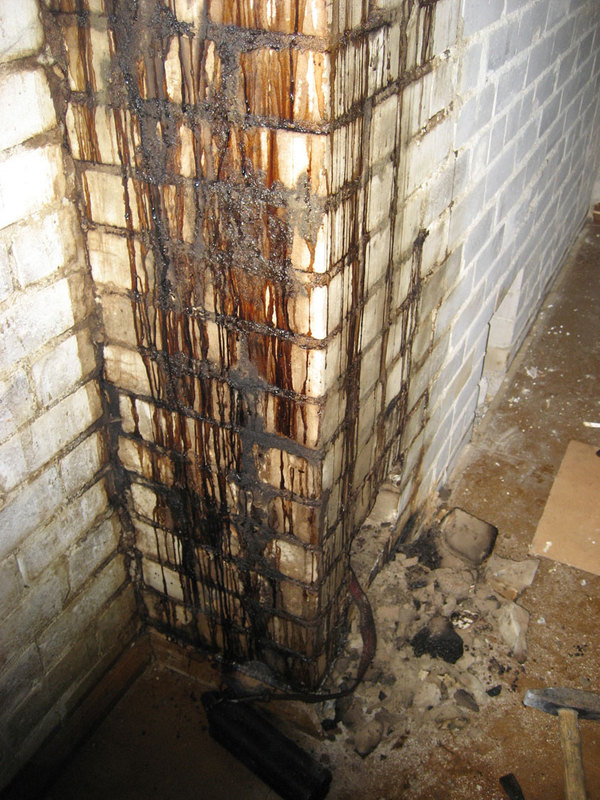
The formation of condensate in the chimneys of stoves or intermittent fireplace stoves is cyclical.At the initial moment, while the pipe has not yet warmed up, condensate falls on its walls, and as the pipe warms up, the condensate evaporates. If the water from the condensate has time to evaporate completely, it gradually impregnates the brickwork of the chimney, and black resinous deposits appear on the outer walls. If this happens on the outer section of the chimney (on the street or in a cold attic), then the constant wetting of the masonry in winter will lead to the destruction of the stove brick.
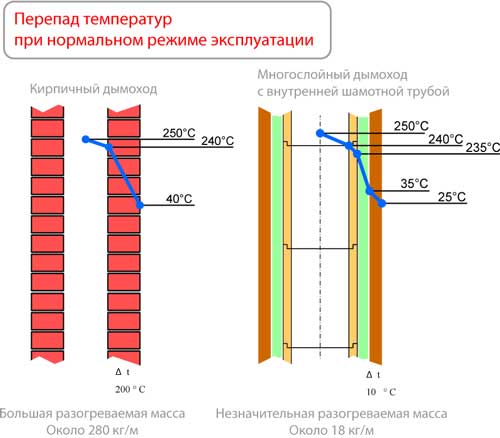
The temperature drop in the chimney depends on its design and the amount of DG flow (fuel combustion intensity). In brick chimneys, the drop in T can reach 25 * C per linear meter. This justifies the requirement to have a DG temperature at the outlet of the furnace (“on the view”) of 200-250*C, in order to make it 100-120*C at the pipe head, which is obviously higher than the dew point. The temperature drop in insulated sandwich chimneys is only a few degrees per meter, and the temperature at the outlet of the furnace can be reduced.
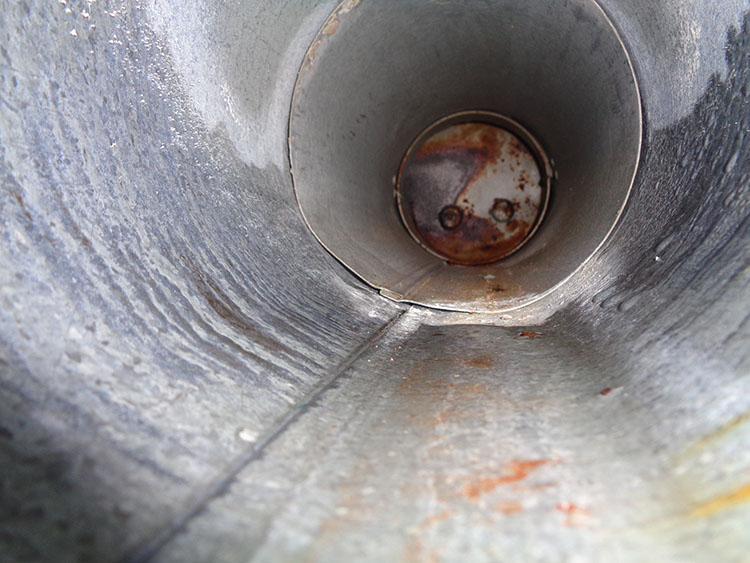
Condensate, forming on the walls of a brick chimney, is absorbed into the masonry (due to the porosity of the brick), and then evaporates. In stainless steel (sandwich) chimneys, even a small amount of condensate formed in the initial period immediately begins to flow down. "for condensate".
Knowing the rate of burning wood in the stove and the cross section of the chimney, it is possible to estimate the decrease in temperature in the chimney per linear meter using the formula:
where
The coefficient of heat absorption of the walls of the chimney is conditionally taken as 1500 kcal / m2 h, because for the last gas duct of the furnace, the value of 2300 kcal/m2h is given in the literature. The calculation is indicative and is intended to show general patterns. On fig. 5 shows a graph of the dependence of the temperature drop in chimneys with a section of 13 x 26 cm (five) and 13 x 13 cm (four) depending on the speed of burning wood in the firebox of the stove.
 Rice. 5.
Rice. 5.
The temperature drop in a brick chimney per linear meter, depending on the rate of burning wood in the stove (flue gas flow). The coefficient of excess air is taken equal to two.
The numbers at the beginning and at the end of the graphs indicate the speed of the DG in the chimney, calculated based on the DG flow, reduced to 150 * C, and the cross section of the chimney. As can be seen, for recommended GOST 2127-47 speeds of about 2 m/s, the DG temperature drop is 20-25*C. It is also clear that the use of chimneys with a cross section larger than necessary can lead to strong cooling of the DG and, as a result, condensation.
As follows from Fig. 5, a decrease in the hourly consumption of firewood leads to a decrease in the flow of exhaust gases, and, as a result, to a significant drop in temperature in the chimney. In other words, the temperature of the exhaust gases, for example, at 150 * C for a brick oven of periodic action, where firewood is actively burning, and for a slow-burning (smoldering) oven is not at all the same thing. Somehow I had to observe such a picture, fig. 6.
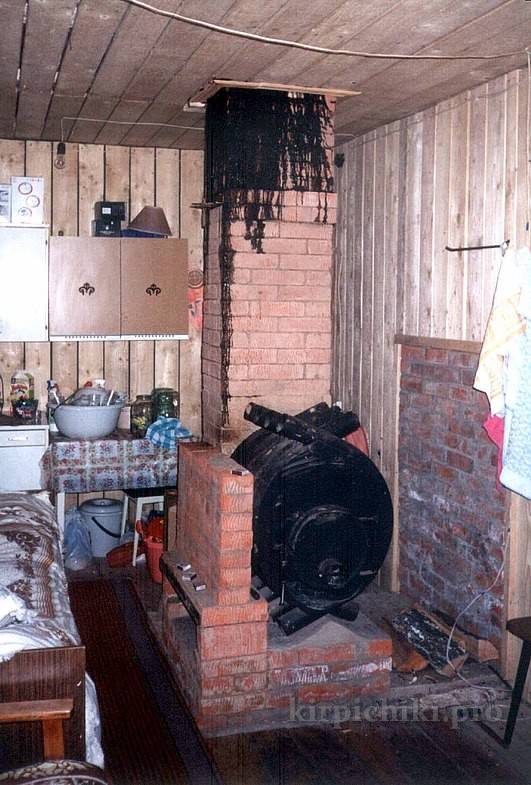 Rice. 6.
Rice. 6.
Condensation in a brick chimney from a long burning stove.
Here the smoldering furnace was connected to a brick pipe with a cross section of a brick. The burning rate in such a furnace is very low - one bookmark can burn for 5-6 hours, i.e. the burning rate will be about 2 kg/h.Of course, the gases in the pipe cooled below the dew point and condensate began to form in the chimney, which soaked the pipe through and dripped onto the floor when the stove was fired. Thus, long-burning stoves can only be connected to insulated sandwich chimneys.
14.02.2013
What is condensate and how does it form in a chimney?
Breathe on the cold window glass - it will immediately be covered with fog and. the smallest droplets of steam (condensate) will merge into a stream. Under certain conditions, condensate also forms on the inner surface of the chimney. From the breath of firewood burning in the firebox.
True, under optimal conditions for the operation of the furnace (the temperature of the gases released during combustion at the exit from the mouth of the pipe is 100-110 C), water vapor will not cling to the inner masonry of the brick pipe and will be carried away with the smoke to the outside, but if the temperature of the inner surface of the walls of the chimney falls below the point dew for gases (44-61 C), then condensate will sit on them and create a lot of problems. Having accumulated and dissolved soot, in which a mass of unburned organic residues of fuel has been preserved, the condensate will turn into sulfurous acid - a black liquid with a disgusting odor.
In the end, the brickwork is corroded and soaked through with it, and black resinous stains appear on the walls. But that's not all. The draft weakens sharply, a stench arises in the bathhouse, the pipe (and then the stove) will begin to collapse. The temperature of the exhaust gases can be determined in a simple way. A dry splinter is placed across the opening of the view during the firebox. After 30-40 minutes, the splinter is removed and the sooty surface is scraped off.
If its color does not change, then the temperature is within 150 C, and if the splinter turns yellow (to the color of a white bread crust), then it reaches 200 C, turned brown (to the color of a rye bread crust), rose to 250 C. A blackened splinter indicates a temperature З00С, when it turns into coal, then 400 С. When the furnace is fired, the temperature of the gases must be regulated so that it is within 250 С at the view.
The cooling of gases and the formation of condensate are also facilitated by cracks and holes in the pipe and furnace, through which the furnace sucks in cold air. It weakens the draft (hence, again, heat is taken away from the inner surface of the pipe) and an excessively large cross section of the pipe or chimney channel. Contribute to the slow passage of smoke and condensate in the pipe and various roughness of the walls.
But the most important role in the formation of condensate is played by the combustion process itself. Wood ignites at a temperature not lower than 300 C, coal - at 600 C. The combustion process proceeds at an even higher temperature: wood - 800-900 C, coal - 900-1200 C. This temperature ensures continuous combustion, provided that air (oxygen) is supplied without interruption in sufficient quantities.
If it is supplied in excess, the firebox cools and combustion worsens, since a high temperature is needed. Do not heat the stove with the firebox open. When the fuel is completely burned, the color of the flame is straw-yellow, the smoke is white, almost transparent. There is no doubt that soot will not be deposited on the walls of the furnace channels and pipes under such conditions.
The formation of condensate also depends on the wall thickness of the chimney.Thick walls warm up slowly and retain heat well. Thinner ones do not retain heat well (although they heat up quickly). mm (one and a half bricks).
Chimneys made of asbestos-cement or pottery pipes have a small wall thickness, so they must be thermally insulated throughout the masonry. Outside air temperature has a great influence on the condensation of water vapor contained in gases. In the summer, when it is warm outside, it is insignificant on the inner surfaces of the chimneys, since moisture evaporates instantly from the well-heated surfaces of the chimney.
In the winter season, when the outside temperature is negative, the walls of the chimney cool down strongly and the condensation of water vapor increases. Of particular danger are ice plugs in the chimney.
Is it possible to drain condensate into the sewer?
During operation of the gas boiler, oxides are formed that react with water vapor. As a result, carbonic and sulfuric acids are formed, the average pH of which is 4. For comparison, the pH of beer is 4.5.
The acidic solution is so weak that there are no restrictions on discharge into the public sewer. This rule applies if the formation of condensate has occurred on the pipe of a gas boiler operating in an apartment.
The only condition is that the condensate must be diluted with sewage 1 to 25. If the boiler power is more than 200 kW, a condensate neutralizer must be installed.This requirement is indicated by the manufacturer in the equipment passport.
It is not possible to collect condensate into an autonomous sewer that discharges effluents into a septic tank with anaerobic bacteria or into a deep cleaning station using anaerobes and aerobes. It will destroy the biological environment involved in the cleaning process.
What is harmful condensate
At first glance, there is nothing wrong with the fact that a certain amount of water appears inside the boiler. Sooner or later, it will still evaporate under the influence of high flue gas temperatures. However, everything is not so simple here. In fact, the condensate contains not pure water, but a weak solution of acids. In addition, the complete evaporation of condensate may not happen if it appears in too large quantities.
Despite the low concentration, acids in the composition of the condensate can corrode the metal body of the boiler even in one season of active operation of the unit. In a properly configured heating system, this will never happen. But the piping of the heat generator, performed with errors, leads to the fact that condensate is formed during the entire time of operation of the boiler. As a result, it accumulates and continuously acts on metal surfaces, gradually destroying them.
The second problem associated with the appearance of condensate is that soot particles begin to stick to it. In the process of fuel combustion, a certain amount of soot is emitted into the flue gases, most of which exits the boiler through the chimney to the street. However, if there is any amount of condensate on the surface of the heat exchanger, then a small percentage of soot constantly sticks to these droplets.
As a result, over time, a fairly dense layer appears on the heat exchanger.If, in addition, wet firewood is used during the operation of the heat generator, this plaque also contains various combustible resins. The gradual thickening of such a crust leads to a drop in the efficiency of the boiler, since it isolates the metal body of the heat exchanger from the heat of the heated gases. The temperature from the furnace to the coolant is transferred worse and worse with each subsequent inclusion of the heat generator.
In the maintenance of the heat generator, there is one feature that is not so obvious at first glance, but becomes the main reason for the too infrequent cleaning of the boiler. We are talking about the fact that modern solid fuel units have a rather complex structure, which is specially calculated to increase the efficiency of the device.
As a result, a large number of intricate ornate passages inside the boiler greatly complicates the process of cleaning it. From which, over time, any desire to perform this procedure with the necessary regularity disappears. For the same reason, it is completely impossible to access some places of the structure, which once again confirms the need to solve the problem with condensate.
Determination of the probability of condensation formation
Calculations can be carried out if condensate is formed as a result of a large release of steam and overheating of the chimney walls, and the power of the operating equipment is known. The average rate of heat release is 1 kW per 10 square meters. m.
The formula is relevant for rooms with ceilings below 3 m:
MK = S*UMK/10
MK - boiler power (kW);
S is the area of the building where the equipment is installed;
WMC is an indicator that depends on the climatic zone.
Indicator for different climatic zones:
- south - 0.9;
- north - 2;
- middle latitudes - 1.2.
When operating a double-circuit boiler, the resulting MK indicator should be multiplied by an additional coefficient (0.25).
Causes of condensation in the chimney pipe
The formation of condensate in the chimney of the furnace is influenced by many factors. The main ones are:
- Incomplete combustion of fuel
Every combustible fuel used by humans has an efficiency below a hundred percent. Those. the fuel does not burn completely, and during its combustion carbon dioxide and water vapor are formed. Due to the release of these carbon dioxide and water vapor, condensate is formed.
- Insufficient draft in the chimney
If the chimney has low draft, then the smoke, not having time to cool, turns into steam and settles on the walls.
- Large temperature difference
This problem is especially relevant during winter. It is characterized by different temperatures inside the chimney and in the external environment.