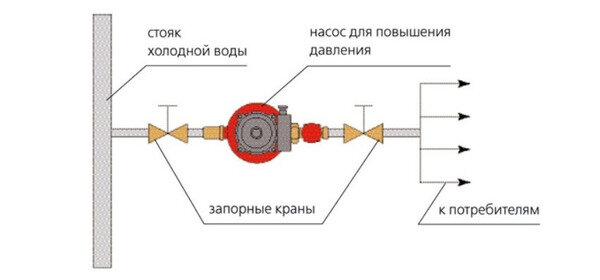
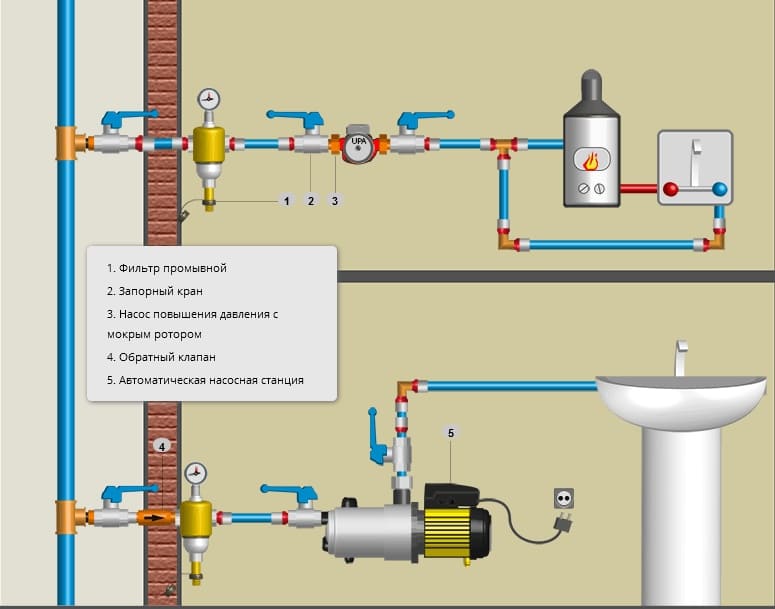
- What pressure should be?
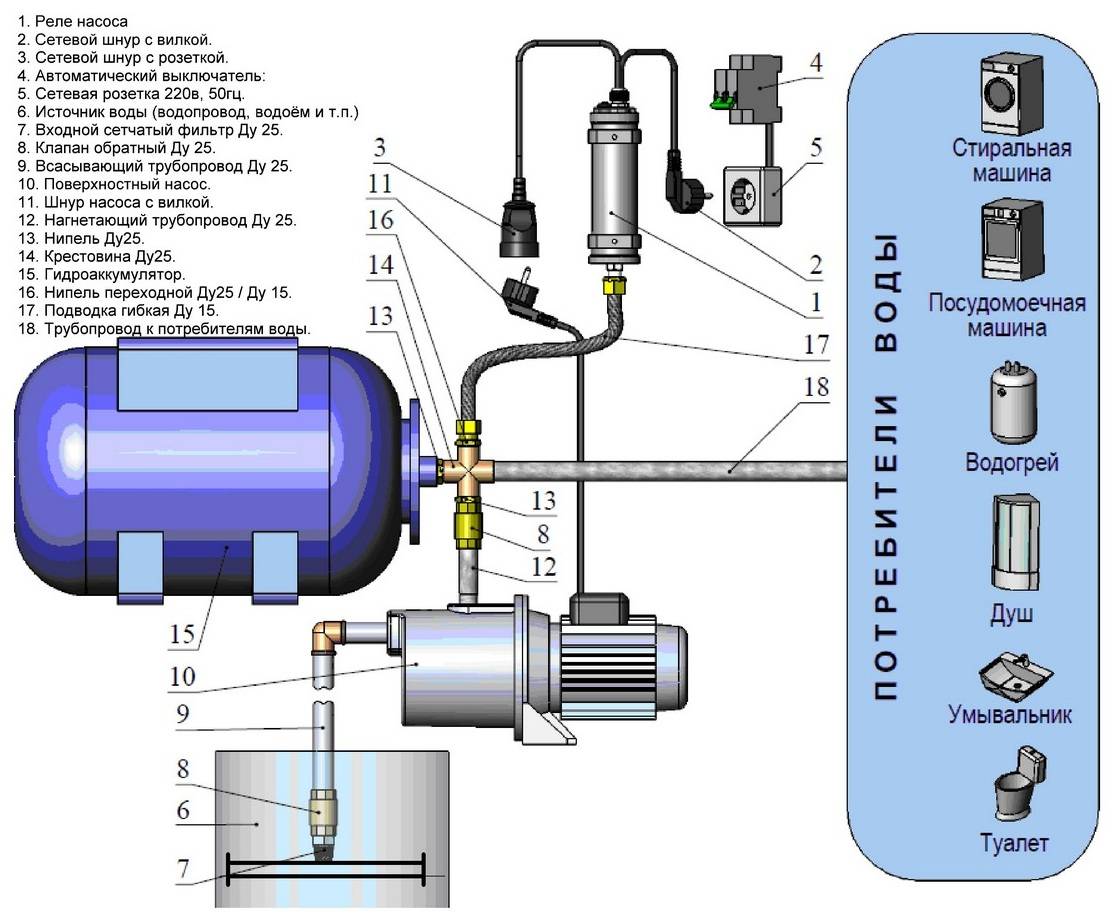
- In an apartment building
- In a private house
- Is assembly required
- prefabricated models
- Rules for constructing closed contours
- DHW
- Types of pressure in heating systems
- Why does pressure drop
- There is air in the system
- Air comes out of the expansion tank
- Flow
- Why does power drop when hot water is turned on?
- Preventive actions
- How to place batteries
- Optimal values in an individual heating system
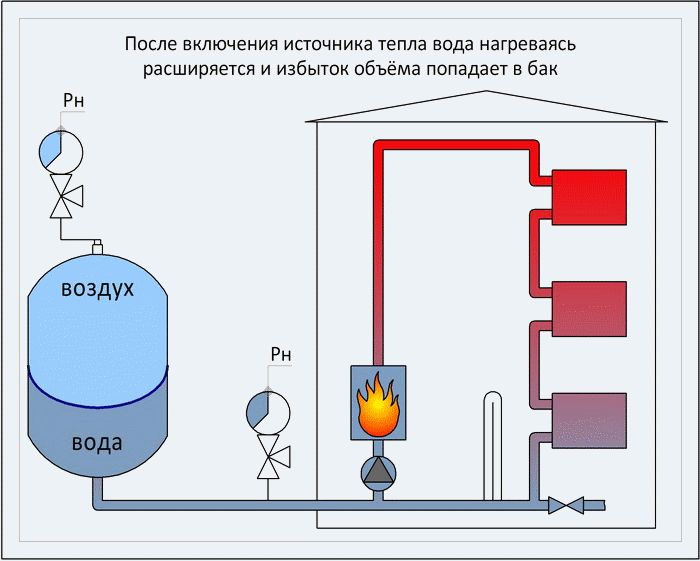
- Pressure increase due to expansion vessel
- Pressure increase in closed heating systems
- Pressure force on the bottom of the vessel
What pressure should be?
The pump must raise the coolant to the highest point and move it to the return pipeline, overcoming the hydraulic resistance of the heating system. To do this, he must create a certain pressure.
It is determined by the formula:
P=Hheating +Presist +PminVT (bar), where:
- Hheating - static pressure equal to the pressure (height in meters) from the lower heating point to the upper point (bar);
- Rresist - hydraulic resistance of the heating system (bar);
- RminVT - the minimum pressure at the highest point of heating, to ensure stable circulation, PminVT ≥ 0.4 (bar).
- Rresist determined by the calculation method.Depends on the diameter and length of the pipes, the heating configuration and the sum of the resistance of all fittings and valves in the system.
- RminVT equal to 0.4 bar is taken for the minimum allowable pressure. Ideally, it should be at least 1.0 bar. The maximum pressure is limited by the strength of the elements of the heating system and cannot exceed more than 80%, taking into account possible water hammer.
In an apartment building
 The static pressure, that is, with the pumps turned off and there is no external pressure from the boiler room, at the lowest point will be determined by the head (height) of the pressure system in the building.
The static pressure, that is, with the pumps turned off and there is no external pressure from the boiler room, at the lowest point will be determined by the head (height) of the pressure system in the building.
In a ten-story building, 32 meters high, it will be 3.2 bars.
When the valves from the boiler room are opened and the network pump is turned on, it will increase to 7.0 bar. The difference of 3.8 bar is conditionally the resistance of the system when working with this pump.
In a private house
If the tank has a direct connection with the atmosphere, such a heating system is called open. Its advantage is a constant pressure, which does not change during heating and cooling of the coolant. This means that the heating elements will experience a load equal to the pressure.
It is determined by the height of the water mirror in the expansion tank above the lower heating point. For example, the height of a one-story house to the attic, where the tank is installed, is 3.5 meters. The difference between the lower and upper heating points is 3.2 meters. The pressure will be 0.32 bar.
A closed system does not have an outlet to the atmosphere, but it has its drawbacks. When water is heated, it expands and pressure increases, and this requires the installation of safety valves.
 And the pumps need to be more powerful. Instead of expansion tanks in the attic, storage tanks are used.
And the pumps need to be more powerful. Instead of expansion tanks in the attic, storage tanks are used.
They can be placed anywhere and are easy to maintain.
For modern heat supply of private properties, up to 3 floors, the power is selected at about 2.0 bar, in the absence of heating.
With heating to 90 C, it will increase to 3.0 bar. Based on these parameters, for private buildings, a safety valve is set to 3.5 bar.
Is assembly required
If the radiators are supplied assembled, it is enough to install the plugs and the Mayevsky crane. Most models have four holes located at the four corners of the case. They are used to connect heating lines. In this case, any scheme can be implemented.
Before the installation of the system begins, it is necessary to close the extra holes using special plugs or air vent valves. The batteries are supplied with adapters that must be screwed into the manifolds of the product. Various communications should be connected to these adapters in the future.
prefabricated models
Assembling the batteries should begin with laying the entire product or its sections on a flat surface. Best on the floor. Before this stage, it is worth deciding how many sections will be installed. There are rules that allow you to determine the optimal amount.
The sections are connected using nipples having two external threads: right and left, as well as a turnkey ledge. The nipples should be screwed into two blocks: at the top and at the bottom.
When assembling the radiator, be sure to use the gaskets supplied with the product.
It is necessary to ensure that the upper edges of the sections are correctly located - in the same plane. The tolerance is 3 mm.
Rules for constructing closed contours
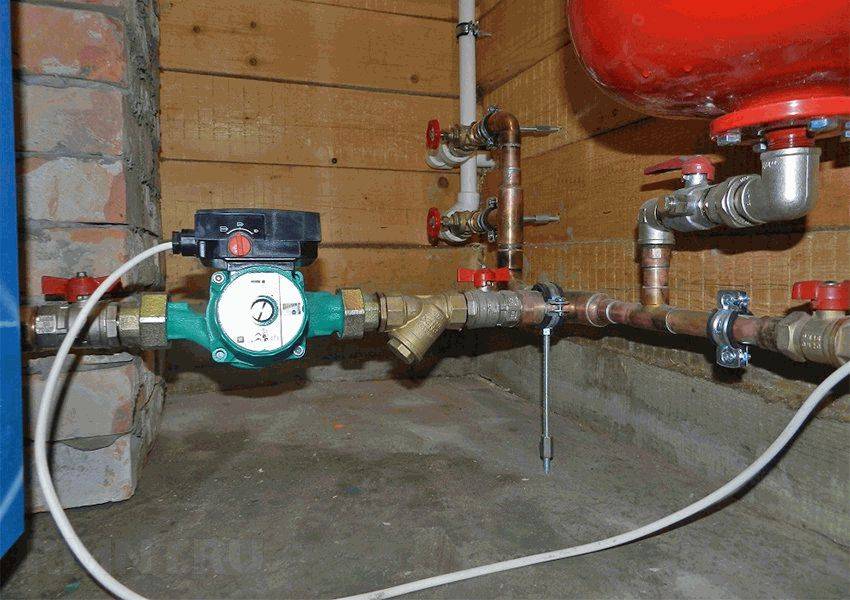
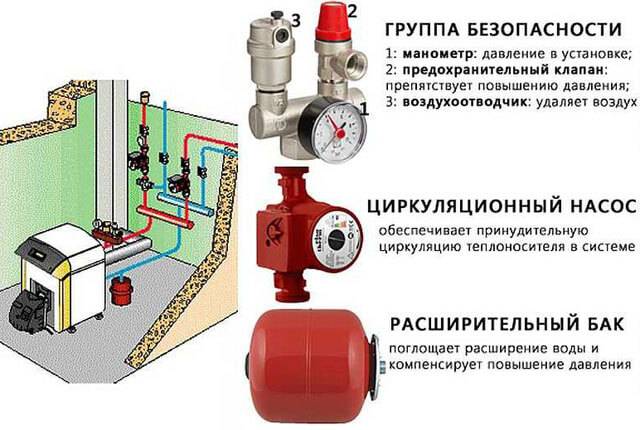
For open-type hydraulic systems, the issue of pressure regulation is irrelevant: there simply are no adequate ways to do this. In turn, closed heating systems can be configured more flexibly, including in relation to the coolant pressure. However, first you need to provide the system with measuring instruments - pressure gauges, which are installed through three-way valves at the following points:
- in the collector of the security group;
- on branching and collecting collectors;
- directly next to the expansion tank;
- on mixing and consumable devices;
- at the outlet of circulation pumps;
- at the mud filter (to control clogging).
Not every position is absolutely mandatory, much depends on the power, complexity and degree of automation of the system. Quite often, the piping of the boiler room is arranged in such a way that the parts important from the point of view of control converge in one node, where the measuring device is installed. So, one pressure gauge at the pump inlet can also serve to monitor the condition of the filter.

Why do you need to monitor pressure at different points? The reason is simple: the pressure in the heating system is a collective term, which in itself can only indicate the tightness of the system. The concept of the worker includes static pressure, formed by the effect of gravity on the coolant, and dynamic pressure - oscillations that accompany the change in operating modes of the system and appear in areas with different hydraulic resistance. So, the pressure can change significantly when:
- heat carrier heating;
- circulation disorder;
- turning on the power supply;
- clogging of pipelines;
- the appearance of air pockets.
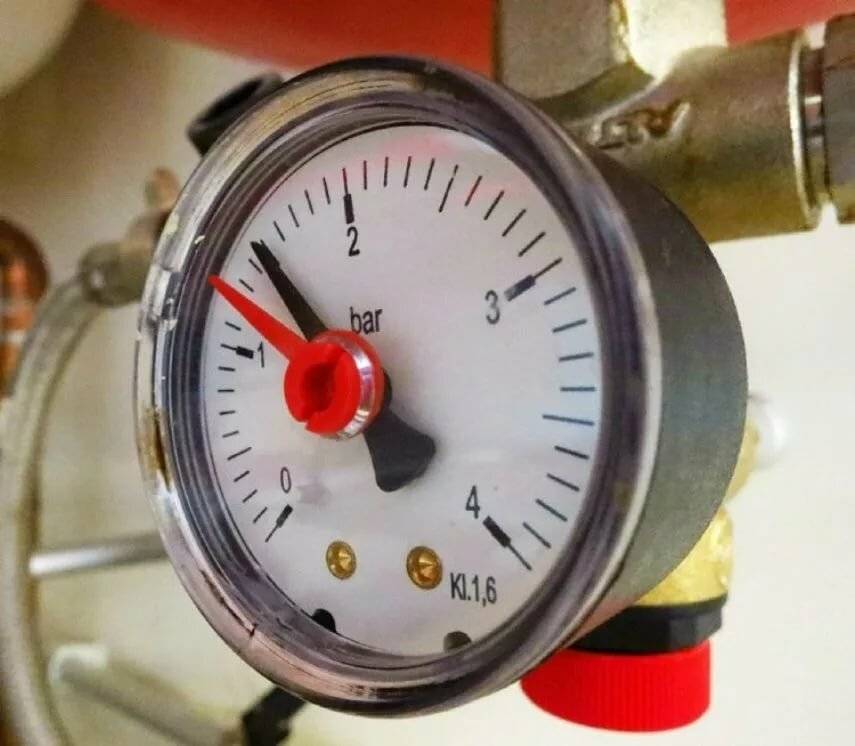
It is the installation of control pressure gauges at different points in the circuit that allows you to quickly and accurately determine the cause of failures and begin to eliminate them. However, before considering this issue, you should study: what devices exist to maintain the working pressure at the desired level.
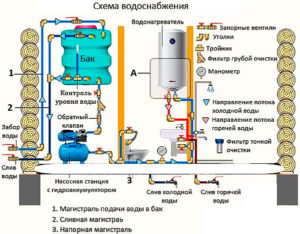
DHW
What pressure should be in the heating system - we figured it out.
And what will the pressure gauge show in the DHW system?
- When cold water is heated by a boiler or instantaneous heater, the pressure of warm water will be exactly equal to the pressure in the cold water main, minus losses to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the pipes.
- When DHW is supplied from the return pipeline of the elevator, there will be the same 3-4 atmospheres in front of the mixer as on the return.
- But when connecting hot water from the supply, the pressure in the mixer hoses can be about an impressive 6-7 kgf / cm2.
Practical consequence: when installing a kitchen faucet with your own hands, it is better not to be lazy and install several valves in front of the hoses. Their price starts from one and a half hundred rubles apiece. This simple instruction will give you the opportunity, when the hoses break, to quickly turn off the water and not suffer from its complete absence in the entire apartment during the repair.

Types of pressure in heating systems
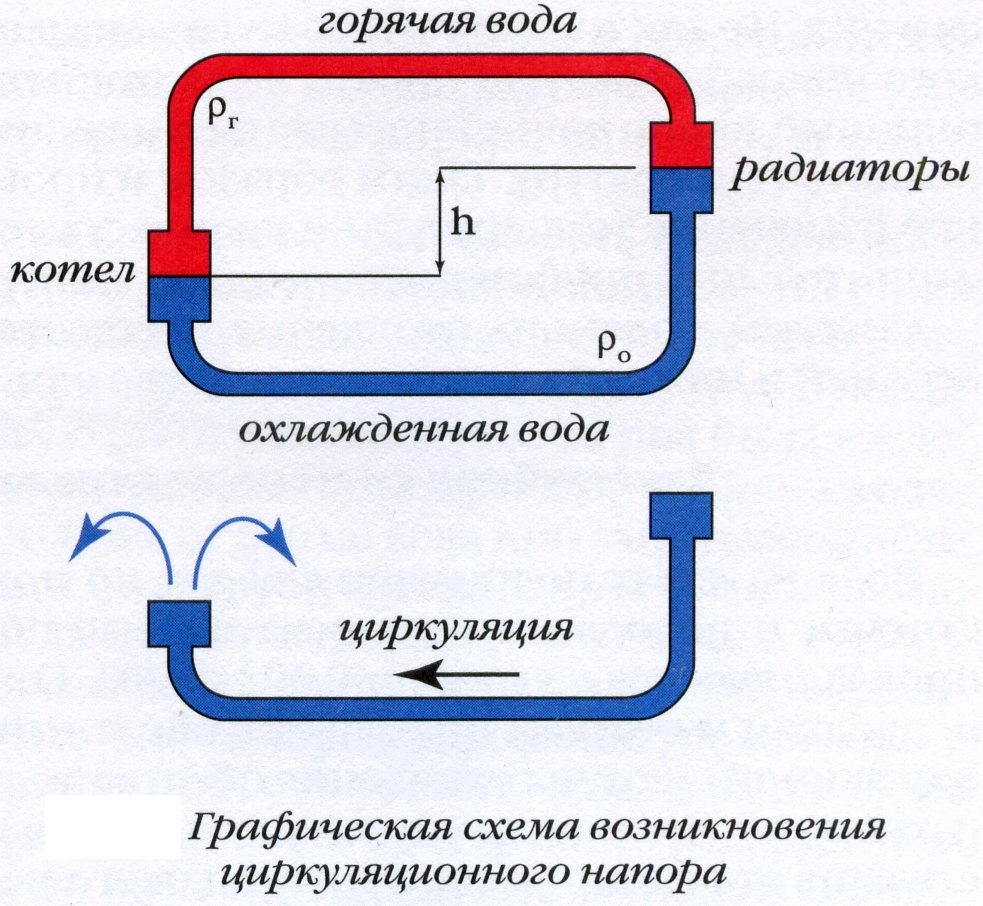
Depending on the current principle of the movement of the coolant in the heat pipe of the circuit, in heating systems the main role is played by static or dynamic pressure.
Static pressure, also called gravitational pressure, develops due to the force of gravity of our planet. The higher the water rises along the contour, the stronger its weight presses on the walls of the pipes.
When the coolant rises to a height of 10 meters, the static pressure will be 1 bar (0.981 atmospheres). Designed for static pressure open heating system, its largest value is about 1.52 bar (1.5 atmospheres).
Dynamic pressure in the heating circuit develops artificially - using an electric pump. As a rule, closed heating systems are designed for dynamic pressure, the contour of which is formed by pipes of a much smaller diameter than in open heating systems.
The normal value of dynamic pressure in a closed-type heating system is 2.4 bar or 2.36 atmospheres.
Why does pressure drop
A decrease in pressure in the heating structure is observed very often. The most common causes of deviations are: the discharge of excess air, the release of air from the expansion tank, the leakage of the coolant.
There is air in the system
Air has entered the heating circuit or air pockets have appeared in the batteries. Reasons for the appearance of air gaps:
- non-compliance with technical standards when filling the structure;
- excess air is not forcibly removed from the water supplied to the heating circuit;
- enrichment of the coolant with air due to leakage of connections;
- malfunction of the air bleed valve.
If there are air cushions in the heat carriers, noises appear. This phenomenon causes damage to the components of the heating mechanism. In addition, the presence of air in the units of the heating circuit entails more serious consequences:
- vibration of the pipeline contributes to the weakening of welds and the displacement of threaded connections;
- the heating circuit is not vented, which leads to stagnation in isolated areas;
- the efficiency of the heating system decreases;
- there is a risk of "defrosting";
- there is a risk of damage to the pump impeller if air enters it.
To exclude the possibility of air entering the heating circuit, it is necessary to correctly start the circuit into operation by checking all the elements for operability.
Initially, test with increased pressure is carried out. When pressure testing, the pressure in the system should not fall within 20 minutes.
For the first time, the circuit is filled with cold water, with the taps for draining the water open and the valves for de-airing open. The mains pump is turned on at the very end. After eliminating air, the amount of coolant necessary for operation is added to the circuit.
During operation, air may appear in the pipes, to get rid of it you need:
- find an area with an air gap (in this place the pipe or battery is much colder);
- having previously turned on the make-up of the structure, open the valve or tap further downstream of the water and get rid of the air.
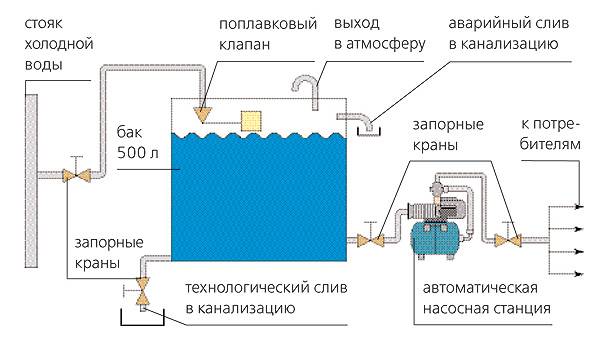
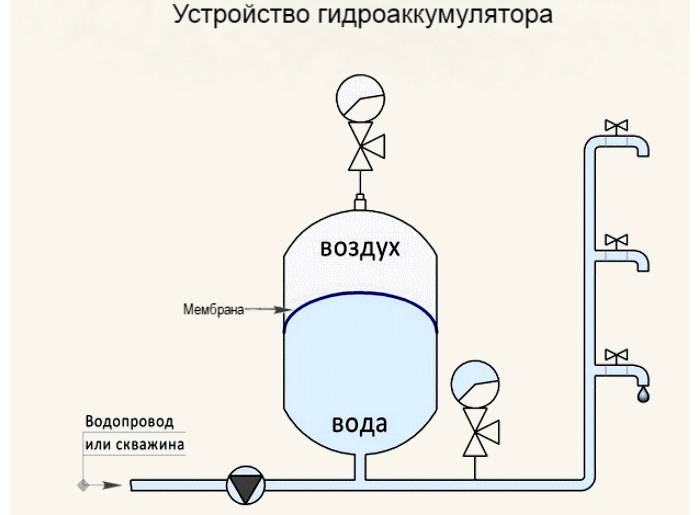
Air comes out of the expansion tank
The causes of problems with the expansion tank are as follows:
- installation error;
- incorrectly selected volume;
- nipple damage;
- membrane rupture.
Photo 3. Scheme of the expansion tank device. The appliance may release air, causing the pressure in the heating system to drop.
All manipulations with the tank are carried out after disconnecting from the circuit. Requires complete removal for repair. water from the tank. Next, you should pump it up and bleed a little air. Then, using a pump with a pressure gauge, bring the pressure level in the expansion tank to the required level, check the tightness and install it back on the circuit.
If the heating equipment is incorrectly configured, the following will be observed:
- increased pressure in the heating circuit and expansion tank;
- pressure drop to a critical level at which the boiler does not start;
- emergency releases of coolant with a constant need for make-up.
Important! On sale there are samples of expansion tanks that do not have devices for adjusting pressure. It is better to refuse to purchase such models.
Flow
A leak in the heating circuit leads to a decrease in pressure and the need for constant replenishment. Leakage of liquid from the heating circuit most often occurs from connecting joints and places affected by rust. It is not uncommon for fluid to escape through a torn expansion tank membrane.
You can determine the leak by pressing on the nipple, which should only allow air to pass through. If a place of loss of coolant is detected, it is necessary to eliminate the problem as soon as possible in order to avoid serious accidents.
Photo 4. Leak in the pipes of the heating system. Due to this problem, the pressure may drop.
Why does power drop when hot water is turned on?
Each heating system may differ from the other, even those made according to a single project. This is especially true in private buildings.
Rules, SanPiN, SNiP and others prohibit the use of a heating system to supply hot water to a dwelling. However, when there is heating but no hot water, the temptation to use heating water is great.
And people screw, instead of air vents, taps. There are cases when even a shower is connected to the heating. When the coolant is taken for domestic needs, and there is no automatic make-up, the pressure will decrease.
What is the risk of low blood pressure? Let's briefly list the possible consequences:
- it is possible to air the system;
- airing can lead to a cessation of circulation;
- in the absence of circulation, heat will cease to flow into the premises;
- in the absence of circulation, overheating of the coolant in the boiler is possible, up to boiling and vaporization;
- boiling and steam formation in the boiler can lead to a sharp increase in pressure with a possible rupture of the boiler elements;
- ingress of water or steam into the boiler, if the heat exchanger breaks, it can lead to an explosion of gaseous or liquid fuel;
- overheating of the boiler elements can cause their deformation, which will be impossible to correct, the boiler will become unusable;
- leaking coolant can cause property damage and even personal injury from burns.
This is not a complete list, but it is enough to understand the danger of lowering the pressure in heating.
Preventive actions
Sometimes regular system maintenance is enough to avoid such situations. The installation of pressure gauges on all important sections of the pipeline will help: at the entrance to the house and in front of plumbing fixtures. Periodically checking the filters and cleaning them will eliminate at least these "suspects" in case of problems.

Insufficient pressure in the pipeline is a problem that appears not only in suburban housing, but also in apartments located on the last floors of high-rise buildings.How to create water pressure in a private house? In most cases, the correction of low pressure does without serious work, and the most common reason is incorrect installation of the pipeline.
Therefore, it is better to entrust the design of the system, the search for the optimal configuration, to a competent specialist, since many troubles can be easily avoided. The minimum number of bends, control and stop valves - a chance to significantly reduce the resistance of the line.
At the end of today's topic - a popular video:
How to place batteries
First of all, the recommendations relate to the installation site. Most often, heating devices are placed where heat loss is most significant. And first of all, these are windows. Even with modern energy-saving double-glazed windows, it is in these places that the most heat is lost. What can we say about the old wooden frames.
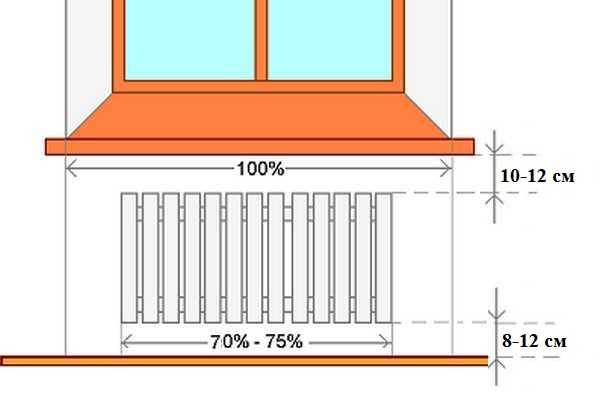
It is important to correctly place the radiator and not make a mistake in choosing its size: not only power is important
If there is no radiator under the window, then cold air descends along the wall and spreads across the floor. The situation is changed by installing a battery: warm air, rising up, prevents cold air from “draining” onto the floor. It must be remembered that in order for such protection to be effective, the radiator must occupy at least 70% of the width of the window. This norm is spelled out in SNiP. Therefore, when choosing radiators, keep in mind that a small radiator under the window will not provide the proper level of comfort. In this case, there will be zones on the sides where cold air will go down, there will be cold zones on the floor. At the same time, the window can often “sweat”, on the walls in the place where warm and cold air will collide, condensation will fall out, and dampness will appear.
For this reason, do not seek to find a model with the highest heat dissipation. This is justified only for regions with a very harsh climate. But in the north, even of the most powerful sections, there are large radiators. For central Russia, an average heat transfer is required, for the south, low radiators are generally needed (with a small center distance). This is the only way you can fulfill the key rule for installing batteries: block most of the window opening.

The battery installed near the doors will work effectively
In cold climates, it makes sense to arrange a thermal curtain near the front door. This is the second problem area, but it is more typical for private houses. This problem may occur in the apartments of the first floors. Here the rules are simple: you need to put the radiator as close to the door as possible. Choose a place depending on the layout, also taking into account the possibility of piping.
Optimal values in an individual heating system
Autonomous heating helps to avoid many problems that arise with a centralized network, and the optimal temperature of the coolant can be adjusted according to the season. In the case of individual heating, the concept of norms includes the heat transfer of a heating device per unit area of the room where this device is located. The thermal regime in this situation is provided by the design features of the heating devices.
It is important to ensure that the heat carrier in the network does not cool below 70 °C. 80 °C is considered optimal. It is easier to control heating with a gas boiler, because manufacturers limit the possibility of heating the coolant to 90 ° C
Using sensors to adjust the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be controlled
It is easier to control heating with a gas boiler, because manufacturers limit the possibility of heating the coolant to 90 ° C. Using sensors to adjust the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be controlled.
A little more difficult with solid fuel devices, they do not regulate the heating of the liquid, and can easily turn it into steam. And it is impossible to reduce the heat from coal or wood by turning the knob in such a situation. At the same time, the control of heating of the coolant is rather conditional with high errors and is performed by rotary thermostats and mechanical dampers.
Electric boilers allow you to smoothly adjust the heating of the coolant from 30 to 90 ° C. They are equipped with an excellent overheating protection system.
Pressure increase due to expansion vessel
Increased pressure in the circuit can be observed due to various problems with the expansion tank. Among the most common causes are the following:
- incorrectly calculated tank volume;
- membrane damage;
- incorrectly calculated pressure in the tank;
- improper installation of equipment.
 Most often, a drop or increase in pressure in the system is observed due to a too small expansion tank. When heated, water increases in volume by about 4% at a temperature of 85-90 degrees. If the tank is very small, then the water completely fills its space, the air is completely bled through the valve, while the tank no longer performs its main function - to compensate for the thermal increase in the volume of the coolant. As a result, the pressure in the circuit is greatly increased.
Most often, a drop or increase in pressure in the system is observed due to a too small expansion tank. When heated, water increases in volume by about 4% at a temperature of 85-90 degrees. If the tank is very small, then the water completely fills its space, the air is completely bled through the valve, while the tank no longer performs its main function - to compensate for the thermal increase in the volume of the coolant. As a result, the pressure in the circuit is greatly increased.
To solve this problem, it is necessary to correctly calculate the volume of the tank, which should be at least 10% of the total water volume in the gas boiler circuit and at least 20% if a solid fuel boiler is used for heating. In this case, for every 15 liters of coolant, a power of 1 kW is used. When calculating the power, it is necessary to determine the volume of the heating surfaces, for each individual circuit, which allows you to get the most accurate values.
The cause of the pressure drop may be a damaged tank membrane. At the same time, water fills the tank, the pressure gauge shows that the pressure in the system has dropped. However, if the make-up valve is opened, the pressure level in the system will be much higher than the calculated working one. Replacing the membrane of the balloon tank or completely replacing the equipment if a diaphragm tank is installed will help to correct the situation.
A malfunction of the tank becomes one of the reasons why a sharp drop or increase in operating pressure is observed in the heating system. To check, it is necessary to completely drain the water from the system, bleed the air from the tank, then start filling the coolant with pressure measurements in the boiler. At a pressure level of 2 bar in the boiler, the pressure gauge installed on the pump should show 1.6 bar. At other values, for adjustment, you can open the shut-off valve, add water drained from the tank through the make-up edge. This method of solving the problem works for any type of water supply - upper or lower.
Improper installation of the tank also causes a sharp change in pressure in the network.Most often, of the violations, the tank is installed after the circulation pump, while the pressure rises sharply, and a discharge is immediately observed, accompanied by dangerous pressure surges. If the situation is not corrected, then a water hammer may occur in the system, all elements of the equipment will be subjected to increased loads, which adversely affects the performance of the circuit as a whole. Reinstalling the tank on the return pipe, where the laminar flow has a minimum temperature, will help to solve the problem. The tank itself is mounted directly in front of the heating boiler.
There are many reasons why there are sharp pressure surges in the heating system. Most often, these are incorrect installation and errors in calculations when choosing equipment, incorrectly made system settings. High or low pressure has an extremely negative effect on the general condition of the equipment, so measures should be taken to removing the cause of the problem.
Pressure increase in closed heating systems
 Causes of pressure increase due to the formation of an air lock in a closed system:
Causes of pressure increase due to the formation of an air lock in a closed system:
- Quick filling of the system with water at start-up;
- The contour is filled from the top point;
- After the repair of heating radiators, they forgot to bleed air through Mayevsky's taps;
- Malfunctions of automatic air vents and Mayevsky taps;
- Loose circulation pump impeller through which air can be sucked.
It is necessary to fill the water circuit from the lowest point with the air bleed valves open. Fill slowly until water flows from the air vent at the highest point of the circuit.Before filling the circuit, you can coat all the air vent elements with soapy foam, so their performance is checked. If the pump sucks in air, then a leak will most likely be found under it.
Pressure force on the bottom of the vessel
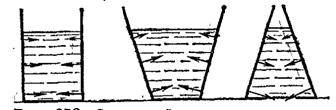
Let's take
a cylindrical vessel with a horizontal bottom and vertical walls,
filled with liquid to a height (Fig. 248).
Rice. 248. In
in a vessel with vertical walls, the pressure on the bottom is equal to the weight of the whole
liquids
Rice. 249. In
all the depicted vessels, the pressure force on the bottom is the same. In the first two vessels
it is greater than the weight of the poured liquid, in the other two it is less
hydrostatic
the pressure at each point of the bottom of the vessel will be the same:
If a
the bottom of the vessel has an area , then the pressure force of the liquid on the bottom
vessel,
i.e., equal to the weight of the liquid poured into the vessel.
Consider
now vessels that differ in shape, but with the same bottom area (Fig. 249).
If the liquid in each of them is poured to the same height, then the pressure on
bottom . in
all vessels are the same. Therefore, the pressure force on the bottom, equal to
,
also
the same in all vessels. It is equal to the weight of a liquid column with a base equal to
area of the bottom of the vessel, and a height equal to the height of the poured liquid. On fig. 249 this
the pillar is shown beside each vessel with dashed lines
Please note that
that the force of pressure on the bottom does not depend on the shape of the vessel and can be as much as
and less than the weight of the poured liquid
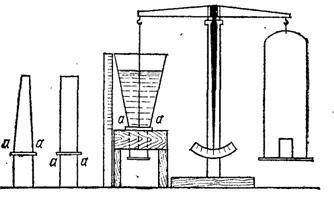
Rice. 250.
Pascal's apparatus with a set of vessels. The cross sections are the same for all vessels
Rice. 251.
Experience with Pascal's barrel
This
the conclusion can be verified experimentally using the device proposed by Pascal (Fig.
250). Vessels of various shapes that do not have a bottom can be fixed on the stand.
Instead of the bottom from below, the vessel is tightly pressed against the scales, suspended from the balance beam.
plate. In the presence of liquid in a vessel, a pressure force acts on the plate,
which tears off the plate when the pressure force begins to exceed the weight of the weight,
standing on the other pan of the scales.
At
vessel with vertical walls (cylindrical vessel) the bottom opens when
the weight of the poured liquid reaches the weight of the kettlebell. Vessels of a different shape have a bottom
opens at the same height of the liquid column, although the weight of the poured water
it can be more (a vessel expanding upward), and less (a vessel narrowing)
kettlebell weight.
This
experience leads to the idea that with the proper shape of the vessel, it is possible with the help of
a small amount of water get a huge pressure force on the bottom. Pascal
attached to a tightly sealed barrel filled with water, a long thin
vertical tube (Fig. 251). When a tube is filled with water, the force
hydrostatic pressure on the bottom becomes equal to the weight of the water column, the area
the base of which is equal to the area of the bottom of the barrel, and the height is equal to the height of the tube.
Accordingly, the pressure forces on the walls and the upper bottom of the barrel also increase.
When Pascal filled the tube to a height of several meters, which required
only a few cups of water, the resulting pressure forces broke the barrel.
How
explain that the force of pressure on the bottom of the vessel can be, depending on the shape
vessel, more or less than the weight of the liquid contained in the vessel? After all, the strength
acting from the side of the vessel on the liquid, must balance the weight of the liquid.
The fact is that not only the bottom, but also the walls act on the liquid in the vessel.
vessel. In a vessel expanding upwards, the forces with which the walls act on
liquid, have components directed upwards: thus, part of the weight
liquid is balanced by the pressure forces of the walls and only a part should be
balanced by pressure forces from the bottom. On the contrary, in the tapering upward
the bottom of the vessel acts on the liquid upwards, and the walls - downwards; so the pressure force
the bottom is more than the weight of the liquid. The sum of the forces acting on the fluid
from the side of the bottom of the vessel and its walls, is always equal to the weight of the liquid. Rice. 252
clearly shows the distribution of forces acting from the side of the walls on
liquid in vessels of various shapes.
Rice. 252.
Forces acting on the liquid from the side of the walls in vessels of various shapes
Rice. 253. When
pouring water into the funnel, the cylinder rises.
AT
in a vessel tapering upwards, a force acts on the walls from the side of the liquid,
upward. If the walls of such a vessel are made movable, then the liquid
will lift them up. Such an experiment can be made on the following device: a piston
fixed, and a cylinder is put on it, turning into a vertical
tube (Fig. 253). When the space above the piston is filled with water, the forces
pressure on the sections and walls of the cylinder raise the cylinder
up.