- Advantages of pump heating
- The best premium pumps for home heating systems
- ESPA RE1-F SAN SUP 40-80-B 230 50
- AQUARIO AC 14-14-50F
- ZOTA RING 65-120F
- The design and principle of operation of the pump
- What are circulation pumps and how do they differ
- Equipment performance
- Where to put
- forced circulation
- natural circulation
- Mounting Features
- Manufacturers and prices
- Selection of a circulation pump for a heating system
- Design features of a pump for heating a private house
- wet rotor
- Dry Rotor
- Features of circulation pumps for heating
- Calculation of the pressure and performance of the circulation pump
- Why do you need a circulation pump for heating
- Main technical parameters in marking
- Which manufacturers to choose
- The principle of operation of the system with coercion
- Conclusion
Advantages of pump heating
Not so long ago, almost all private houses were equipped with steam heating, which worked from a gas boiler or a conventional wood burning stove. The coolant in such systems circulated inside the pipes and batteries by gravity. transfer pumps water was completed only by centralized heating systems. After the appearance of more compact devices, they were also used in private housing construction.

This solution provided a number of advantages:
- The coolant circulation rate has increased. The water heated in the boilers was able to flow much faster to the radiators and heat the premises.
- Significantly reduced the time for heating homes.
- The increase in the flow rate resulted in an increase in the throughput of the circuit. This means that smaller pipes can be used to deliver the same amount of heat to the destination. On average, the pipelines were reduced by half, which was facilitated by the forced circulation of water from an embedded pump. This made the systems cheaper and more practical.
- For laying highways in this case, you can use the minimum slope, without fear of complex and lengthy water heating schemes. The main thing at the same time is to choose the right pump power so that it can create optimal pressure in the circuit.
- Thanks to household circulation pumps, it became possible to use underfloor heating and closed systems of high efficiency, which require increased pressure to operate.
- The new approach made it possible to get rid of a lot of pipes and risers, which did not always fit harmoniously into the interior. Forced circulation opens up opportunities for laying the circuit inside walls, under the floor and above suspended ceiling structures.

A minimum slope of 2-3 mm per 1 m of the pipeline is necessary so that in the event of repair measures, the network can be emptied by gravity. In classical systems with natural circulation this figure reaches 5 or more mm/m. As for the disadvantages of forced systems, the most significant of them is the dependence on electrical energy.Therefore, in areas with unstable electricity supplies, when installing a circulation pump, it is necessary to use uninterruptible power supply units or an electric generator.
You should also be prepared for an increase in bills for consumed energy (with the right selection of unit power, costs can be minimized). In addition, leading equipment manufacturers for heating systems modern modifications of circulation pumps have been developed that can operate in the mode of increased economy. For example, the Alpfa2 model from Grundfos automatically adjusts its performance, depending on the needs of the heating system. Such equipment is quite expensive.
The best premium pumps for home heating systems
Models in this category are distinguished by high performance and power. They are used in multi-storey residential buildings or in enterprises.
Such pumps are very expensive, but they have flexible settings, easy control and are extremely reliable.
ESPA RE1-F SAN SUP 40-80-B 230 50
5.0
★★★★★editorial score
100%
buyers recommend this product
The device has a lightweight design and is easy to install. It is equipped with an LED display and a three-stage electronic power regulator, which simplifies the control of operating modes and all main parameters.
The automatic setting function sets the most suitable pressure according to current needs. Thanks to the use of a permanent magnet motor, energy savings of up to 70% are achieved.
Advantages:
- flexible setting;
- informative screen;
- saving electricity;
- quiet work;
- remote control.
Flaws:
high price.
ESPA RE1-F SAN SUP 40-80-B 230 50 has a capacity of up to 35 cubic meters per hour. Such a pump can be installed in industrial buildings or large residential buildings with a multi-stage heating system.
AQUARIO AC 14-14-50F
4.9
★★★★★editorial score
94%
buyers recommend this product
A feature of the model is the high value of the pressure indicator. Robust cast iron housing, technopolymer impeller, natural lubrication and cooling of the components contribute to extending the life of the device.
The maximum performance of the pump is 466 liters per minute, the pressure is 10 atmospheres. The device is silent during operation and easy to install due to its compact size and simple threaded connection.
Advantages:
- long service life;
- high performance;
- small dimensions;
- silent operation.
Flaws:
no speed controller.
Aquario AC 14-14-50F will be an excellent purchase for installation in a multi-storey building. Head up to 16 meters guarantees stable operation of the pump in a branched system.
ZOTA RING 65-120F
4.8
★★★★★editorial score
86%
buyers recommend this product
This unit can be connected to pipes of small diameter, as well as used in heating systems with non-freezing coolants. The main components of the apparatus are made of materials resistant to high temperature and wear.
The maximum productivity is 20 cubic meters per hour, the pressure is 15 meters. With a power of 1300 W and electronic status monitoring, high efficiency and easy control of the pump are achieved.
Advantages:
- ease of installation;
- durability;
- powerful engine;
- high performance.
Flaws:
resistant to moisture and dust.
ZOTA RING 65-120F will circulate the coolant in low-rise residential buildings. An excellent choice for residents of cottages or summer residents.
The design and principle of operation of the pump
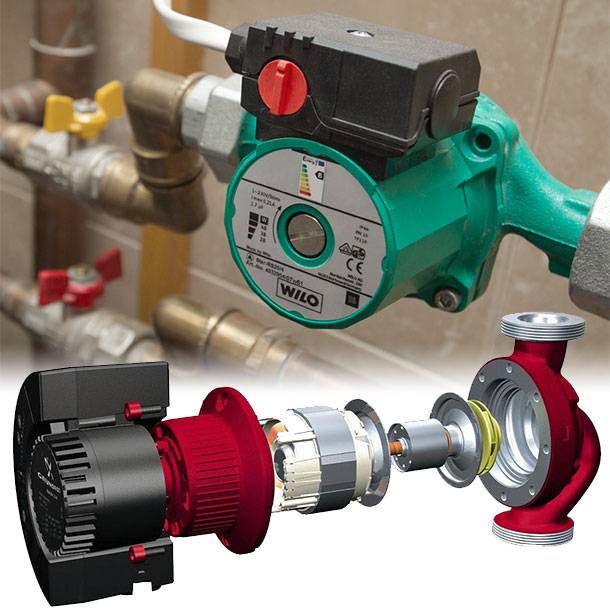
By design, the circulation pump resembles a drainage installation. The pump consists of a robust housing made of stainless steel/cast iron/aluminum and an electrical part which includes a stator winding with an integrated ceramic/steel rotor.
 Installation of a pumping device for forced circulation significantly increases the efficiency of systems hot water supply and autonomous heating
Installation of a pumping device for forced circulation significantly increases the efficiency of systems hot water supply and autonomous heating
The impeller is fixed on the shaft of the rotating part of the electric motor.
The impeller consists of two parallel disks connected by radially curved blades. On one of them there is a hole for the flow of the coolant fluid, on the other there is a small hole for fixing the impeller on the shaft of the electric motor.
 The body parts of circulation pumps are made of steel and durable alloys. Under the walls of the housing is a hidden rotor with a fixed impeller
The body parts of circulation pumps are made of steel and durable alloys. Under the walls of the housing is a hidden rotor with a fixed impeller
The motor itself is equipped with a special control board and terminals for connecting wires. For circulation pumps without electronics, a capacitor is installed instead of a board, and a speed switch is located on the terminal box.
When electricity is supplied, the wheel with blades rotates, creating a vacuum in the pipe and forcing the coolant. The rotor creates the movement of the working fluid in the direction from the inlet to the outlet valve.
The pump constantly takes water from one side and pushes it into the heating system from the other. Centrifugal force contributes to the transport of fluid throughout the line.
The pressure created overcomes the resistance in different parts of the circuit and ensures the circulation of the coolant.
Judging by the intensity of sales, the most popular in the domestic market are devices from the following manufacturers:
What are circulation pumps and how do they differ
The device and principle of operation of all circulation pumps are similar. The devices consist of a durable stainless steel housing, a single or three-phase electric motor, a rotor and a rotating impeller. When the electric motor is turned on, it rotates the rotor with the impeller, due to which a reduced pressure is created and water enters the device, and the impeller ejects liquid through the outlet pipe into the heating system.
There are "dry" and "wet" designs. In the first, the rotor is closed from water by a special sealing ring, and in the second, it is in contact with the coolant. "Dry" pumps are more difficult to install, require regular inspection and maintenance, but are more productive and durable. "Wet" ones do not need to be maintained, they are more durable, but their efficiency is about 20% lower.
In private homes, “wet” pumps are usually installed, paying tribute to their silent operation. And in boiler rooms designed for heating large buildings or several buildings, “dry” appliances are more often used due to higher productivity.

Equipment performance
To calculate it, a simple formula is used: G \u003d Q / (1.16 x ΔT), where Q is the heat demand found earlier; ΔT is the difference between two temperatures: supply and return. For a conventional two-pipe system, this is 20 degrees C, and for a warm floor - 5 degrees C.
For a house with an area of 100 sq.m, the calculation will be as follows:
Q \u003d 173 x 100 \u003d 17300 kW.
G \u003d 17300 / 1.16 x 20 \u003d 745.689 \u003d 746 cubic meters / h.
For a new one, this value is calculated according to certain formulas using the values specified for fittings, pipes, etc.
For an already mounted system, the exact value of this parameter is difficult to find, it is calculated approximately:
- for the passage of 1 m of the heating pipeline, 0.01-0.015 m of pressure is needed;
- heat loss in fittings - approximately 30% of the previous parameter;
- the check valve, as well as the three-way valve, prevent the normal circulation of the coolant, therefore they are estimated at 20%;
- thermostatic valves installed to control the room temperature.
The value is calculated as follows: H = R x L x ZF, where:
R is the resistance of straight sections (it is better to take into account the maximum value of 0.015 m);
L - the length of the pipes that form the heating system (two-pipe - the return is also taken into account);
ZF is a coefficient: if conventional ball valves and fittings are installed, it will be 1.3 (the indicated 30% loss), and if a thermostatic valve or throttle that breaks the circuit, it will be 1.7.
Where to put
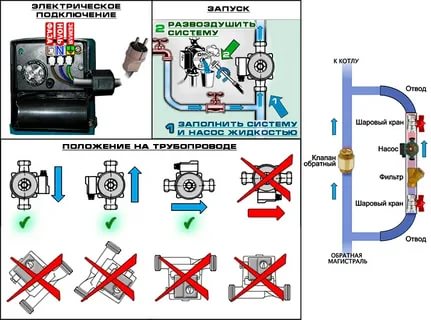
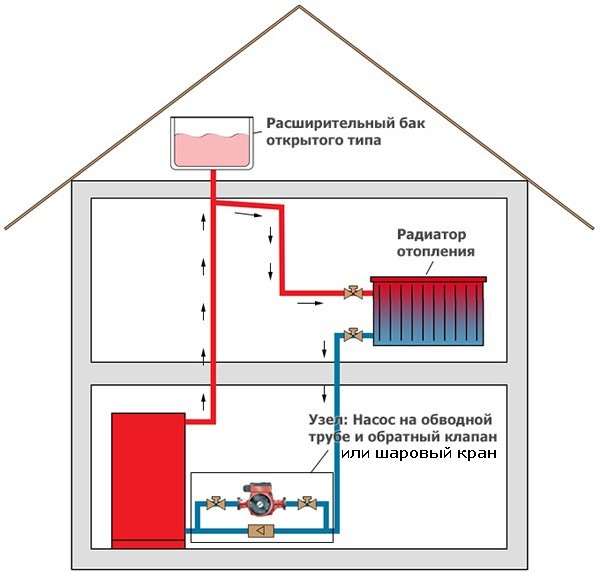
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but it does not matter on the supply or return pipeline. Modern units are made from materials that normally tolerate temperatures up to 100-115 ° C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, therefore considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you are so calmer, put it in the return line.
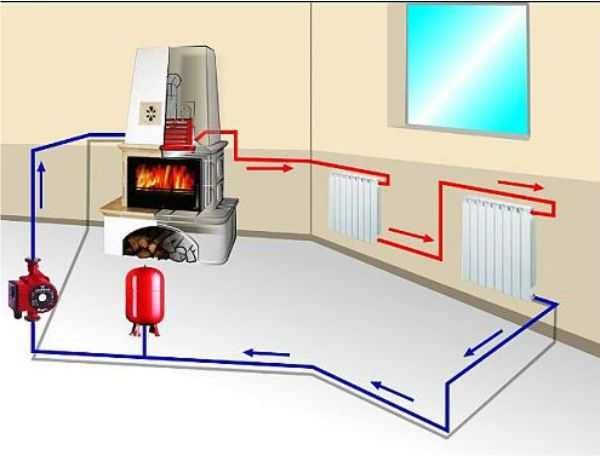
Can be installed in return or forward pipeline after/before boiler until the first branches
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system, it does not matter whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in the sense of tying, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point at the installation site. If there are two separate branches in the heating system - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floors - it makes sense to put a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule is preserved on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal regime in each of the parts houses independently of the other as well as in two-story houses to save on heating. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of the coolant is set much less, and this allows you to burn less fuel, and without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - with forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump, with natural circulation they work, but in this mode they have a lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is slammed into it. This gives high efficiency and reliability of heating. It is clear that circulation pump installation these systems are different.

All heating systems with underfloor heating are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
forced circulation
Since the forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap supply or return pipe (of your choice).
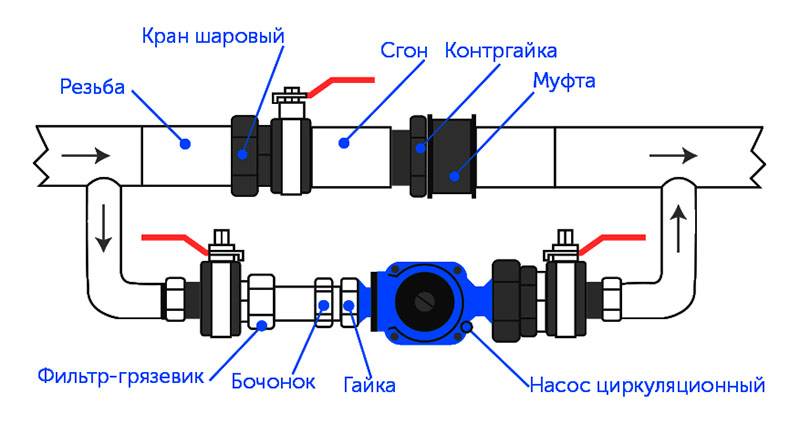
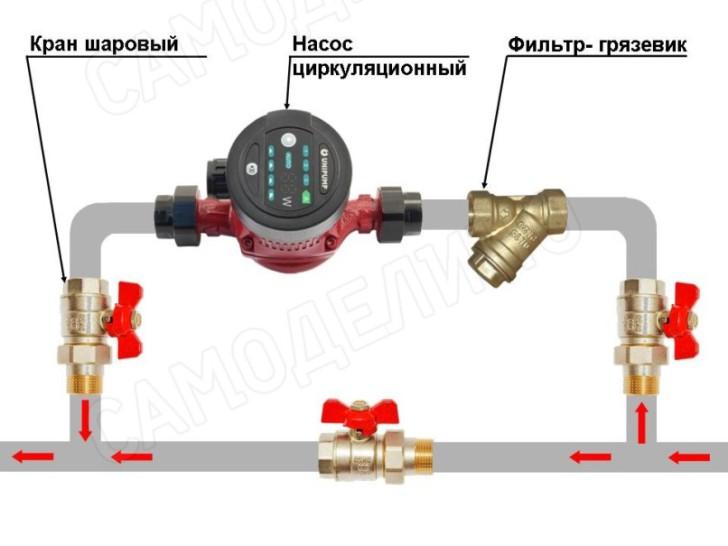
Most problems with circulation pump arise from- due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They are able to jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a strainer must be placed in front of the unit.

Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
Also preferably on both sides installation of ball valves. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps, remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not running. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed all the time while pumping is in operation. In this mode, the system works as a forced one.
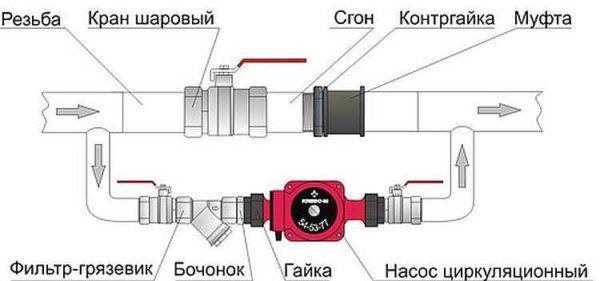
Scheme of installation of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When electricity fails or the unit fails, the faucet on the jumper is opened, the faucet leading to the pump is closed, the system works like a gravitational one.
Mounting Features
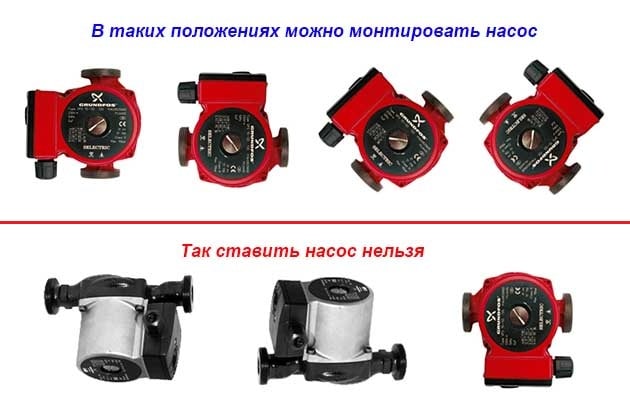
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require alteration: it is required to turn the rotor so that it is directed horizontally.The second point is the direction of the flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating in which direction the coolant should flow. So turn the unit around so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, only when choosing a model, see that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (created pressure) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Manufacturers and prices
When choosing manufacturers of a circulation pump, the approach is the same as when choosing any arc equipment. If possible, it is better to take equipment from European manufacturers that have been on the market for a long time. The most reliable circulation pumps in this sector are Willo (Willo), Grundfos (Grundfos), DAB (DAB). There are other good brands, but you need to read reviews on them.
| Name | Performance | pressure | Number of speeds | Connecting dimensions | Max working pressure | Power | Housing material | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grundfos UPS 25-80 | 130 l/min | 8 m | 3 | G 1 1/2″ | 10 bar | 170 W | Cast iron | 15476 rub |
| Caliber NTs-15/6 | 40 l/min | 6 m | 3 | external thread G1 | 6 atm | 90 W | Cast iron | 2350 rub |
| BELAMOS BRS25/4G | 48 l/min | 4.5 m | 3 | external thread G1 | 10 atm | 72 W | Cast iron | 2809 rub |
| Gileks Compasses 25/80 280 | 133.3 l/min | 8.5 m | 3 | external thread G1 | 6 atm | 220 W | Cast iron | 6300 rub |
| Elitech NP 1216/9E | 23 l/min | 9 m | 1 | external thread G 3/4 | 10 atm | 105 W | Cast iron | 4800 rub |
| Marina-Speroni SCR 25/40-180 S | 50 l/min | 4 m | 1 | external thread G1 | 10 atm | 60 W | Cast iron | 5223 rub |
| Grundfos UPA 15-90 | 25 l/min | 8 m | 1 | external thread G 3/4 | 6 atm | 120 W | Cast iron | 6950 rub |
| Wilo Star-RS 15/2-130 | 41.6 l/min | 2.6 m | 3 | internal thread G1 | 45 W | Cast iron | 5386 rub |
Please note that all specifications are for moving water. If the coolant in the system is a non-freezing liquid, adjustments must be made
For relevant data for this type of coolant, you will have to contact the manufacturer. Similar characteristics could not be found in other sources.
Selection of a circulation pump for a heating system
Sometimes a person who has already planted a tree and raised a son is faced with the question - how to choose circulation pump for heating system of the house under construction? And a lot depends on the answer to this question - whether all radiators will be evenly heated, whether the coolant flow rate will be in
the heating system is sufficient, and at the same time not exceeded, whether there will be a rumble in the pipelines, whether the pump will consume excess electricity, whether the thermostatic valves of the heating devices will work correctly, and so on and so forth. After all, the pump is the heart of the heating system, which tirelessly pumps the coolant - the blood of the house, which fills the house with warmth.
 Choosing a circulation pump for the heating system of a small building, checking whether the pump is correctly selected by the sellers in the store, or making sure that the pump in the existing heating system is selected correctly is quite simple if you use the enlarged calculation method. The main selection parameter circulation pump is his performance, which must correspond to the thermal power of the heating system served by it.
Choosing a circulation pump for the heating system of a small building, checking whether the pump is correctly selected by the sellers in the store, or making sure that the pump in the existing heating system is selected correctly is quite simple if you use the enlarged calculation method. The main selection parameter circulation pump is his performance, which must correspond to the thermal power of the heating system served by it.
The required capacity of the circulation pump can be calculated with sufficient accuracy using a simple formula:
where Q is the required pump capacity in cubic meters per hour, P is the thermal power of the system in kilowatts, dt is the temperature delta - the difference coolant temperature in the supply and return pipeline. Usually taken equal to 20 degrees.
So let's try. Take, for example, a house with a total area of 200 square meters, the house has a basement, 1st floor and an attic. The heating system is two-pipe. The required thermal power required to heat such a house, let's take 20 kilowatts. We make simple calculations, we get - 0.86 cubic meters per hour. We round up and accept the performance of the required circulation pump - 0.9 cubic meters per hour. Let's remember it and move on. The second most important characteristic of the circulation pump is the pressure. Every hydraulic system has resistance to the flow of water through it. Each corner, tee, reducing transition, each rise - all these are local hydraulic resistances, the sum of which is the hydraulic resistance of the heating system. The circulation pump must overcome this resistance, while maintaining the calculated performance.
The exact calculation of hydraulic resistance is complex and requires some preparation. To approximately calculate the required pressure of the circulation pump, the formula is used:
where N is the number of floors of the building, including the basement, K is the average hydraulic loss per one floor of the building. The coefficient K is taken as 0.7 - 1.1 meters of water column for two-pipe heating systems and 1.16-1.85 for collector-beam systems. Our house has three levels, with a two-pipe heating system.The K coefficient is taken as 1.1 m.v.s. We consider 3 x 1.1 \u003d 3.3 meters of water column.
Please note that the total physical height of the heating system, from the bottom to the top point, in such a house is about 8 meters, and the pressure of the required circulation pump is only 3.3 meters. Each heating system is balanced, the pump does not need to raise water, it only overcomes the resistance of the system, so there is no point in getting carried away with high pressures
So, we got two parameters of the circulation pump, productivity Q, m / h = 0.9 and head, N, m = 3.3. The point of intersection of the lines from these values, on the graph of the hydraulic curve of the circulation pump, is the operating point of the required circulation pump.
Let's say you decide to go for the excellent DAB pumps, Italian pumps of excellent quality at a perfectly reasonable price. Using the catalog, or managers of our company, determine the group of pumps, the parameters of which include the required operating point. We decide that this group will be the VA group. We select the most appropriate hydraulic curve diagram, the best suited curve is the pump VA 55/180 X.

The operating point of the pump should be in the middle third of the graph - this zone is the zone of maximum efficiency of the pump. For selection, choose the graph of the second speed, in this case you insure yourself against insufficient accuracy of the enlarged calculation - you will have a reserve for increasing productivity at the third speed and the possibility of reducing it at the first.
Design features of a pump for heating a private house
Basically, circulation heating pump is no different from other types of water pumps.

It has two main elements: an impeller on a shaft and an electric motor that rotates this shaft. Everything is enclosed in a sealed case.
But there are two varieties of this equipment, which differ from each other in the location of the rotor. More precisely, whether the rotating part is in contact with the coolant or not. Hence the names of the models: with a wet rotor and dry. AT this case means motor rotor.
wet rotor
Structurally, this type of water pump has an electric motor in which the rotor and stator (with windings) are separated by a sealed glass. The stator is located in a dry compartment, where water never penetrates, the rotor is located in the coolant. The latter cools the rotating parts of the device: the rotor, impeller and bearings. Water in this case acts for bearings, and as a lubricant.
This design makes the pumps quiet, because the coolant absorbs the vibration of the rotating parts. A serious drawback: low efficiency, not exceeding 50% of the nominal value. Therefore, pumping equipment with a wet rotor is installed on heating networks of small length. For a small private house, even 2-3 floors, this would be a good choice.
The advantages of wet rotor pumps, in addition to silent operation, include:
- small overall dimensions and weight;
- economical consumption of electric current;
- long and uninterrupted work;
- Easy to adjust rotation speed.
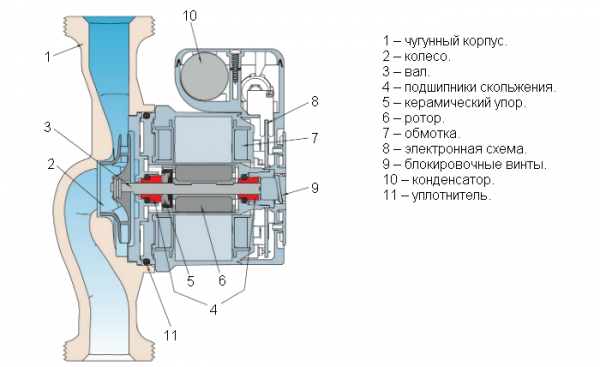
Photo 1. Scheme of the device of a circulation pump with a dry rotor. Arrows indicate parts of the structure.
The disadvantage is the impossibility of repair. If any part is out of order, then the old pump is dismantled, installing a new one.There is no model range in terms of design possibilities for pumps with a wet rotor. All of them are produced of the same type: vertical execution, when the electric motor is located with the shaft down. The outlet and inlet pipes are on the same horizontal axis, so the device is installed only on a horizontal section of the pipeline.
Important! When filling the heating system, the air pushed out by water penetrates into all voids, including the rotor compartment. To bleed the air plug, you must use a special bleed hole located at the top of the motor and closed with a sealed rotating cover. To bleed the air plug, you must use a special bleed hole located in the upper part of the electric motor and closed with a sealed rotating cover
To bleed the air plug, you must use a special bleed hole located at the top of the motor and closed with a sealed rotating cover.
Preventive measures for "wet" circulation pumps are not required. There are no rubbing parts in the design, cuffs and gaskets are installed only on fixed joints. They fail due to the fact that the material has simply grown old. The main requirement for their operation is not to leave the structure dry.
Dry Rotor
Pumps of this type do not have a separation of the rotor and stator. This is a normal standard electric motor. In the design of the pump itself, sealing rings are installed that block the access of the coolant to the compartment where the elements of the engine are located. It turns out that the impeller is mounted on the rotor shaft, but is in the compartment with water.And the entire electric motor is located in another part, separated from the first by seals.
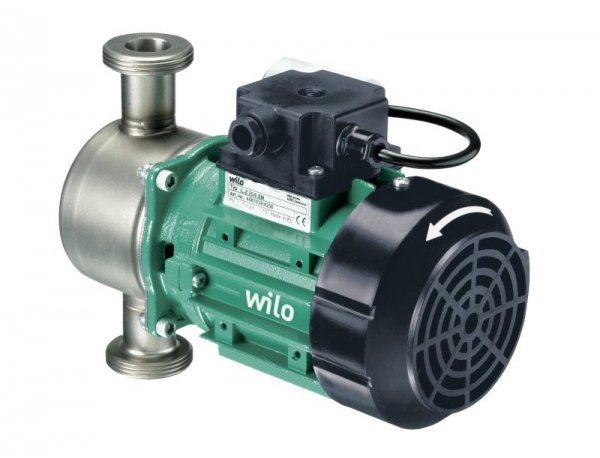

Photo 2. A circulation pump with a dry rotor. There is a fan at the back to cool the device.
These design features have made dry rotor pumps powerful. The efficiency reaches 80%, which is quite a serious indicator for equipment of this type. Disadvantage: the noise emitted by the rotating parts of the device.
Circulation pumps are represented by two models:
- Vertical design, as in the case of a wet rotor device.
- Cantilever - this is a horizontal version of the structure, where the device rests on the paws. That is, the pump itself does not press on the pipeline with its weight, and the latter is not a support for it. Therefore, a strong and even slab (metal, concrete) must be laid under this type.
Attention! O-rings often fail, becoming thin, which creates conditions for the penetration of the coolant into the compartment where the electrical part of the electric motor is located. Therefore, once every two or three years, they carry out preventive maintenance of the device, inspecting, first of all, the seals
Features of circulation pumps for heating
The main purpose of circulation pumps (pumps) installed in heating systems is to ensure the constant movement of the coolant through the pipeline without increasing the pressure in it. Heated water, moving along the circuit at a certain speed, evenly gives off heat to all elements of the system. Due to this, space heating occurs quickly and with less gas required for heating the coolant.
If a heating system is installed, for example, for a private house, which will work on the principle of forced circulation, then you cannot do without installing a circulation pump. Also, these pumps can be installed in heating systems operating according to the principle of natural circulation. Installing a pump increases the efficiency of the heating circuit and helps save gas.

You should buy circulation pumps for heating after studying the full range of this type of product, which is widely represented on the Internet, since the devices can differ not only in design (“dry” and “wet”), but also in power, installation method. In addition, some models of circulation units are equipped with operating mode switches that change the speed of rotation of the apparatus shaft.
Calculation of the pressure and performance of the circulation pump
How to choose a pump for heating a private house? For this, it is important to calculate the performance and pressure of the device. Under the performance of the device, we mean the amount of liquid (in our case, water) pumped in 1 hour
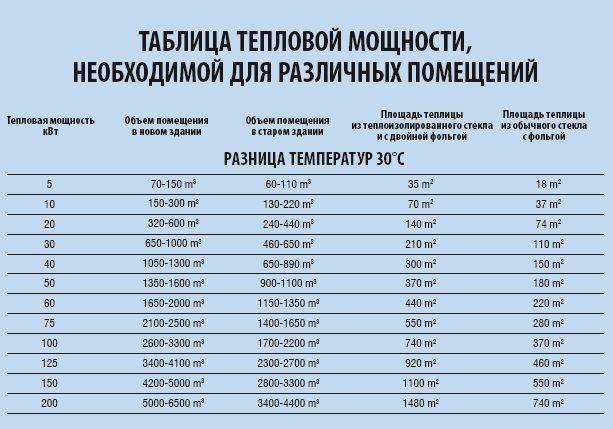
We need to choose a device that pumps water at a sufficient speed so that the farthest radiator is warm, but at the same time, so that the performance margin is small, as this affects the price of the pump. Suppose we have a newly built house with an area of 100 m2 with a ceiling height of 2.7 m. Then the heated volume will be equal to 100 * 2.7 = 270 m3. Now we need to find out the power of the heat source Qn - we take it from the table. It is 10 kW
By the performance of the device, we mean the amount of liquid (in our case, water) pumped over in 1 hour. We need to choose a device that pumps water at a sufficient speed so that the farthest radiator is warm, but at the same time, so that the performance margin is small, as this affects the price of the pump. Suppose we have a newly built house with an area of 100 m2 with a ceiling height of 2.7 m. Then the heated volume will be equal to 100 * 2.7 = 270 m3. Now we need to find out the power of the heat source Qn - we take it from the table. It is 10 kW.
 Now we calculate the pump performance using the formula: Qpu = Qn / 1.163 * dt, where 1.163 is the specific heat capacity of water; dt is the calculated difference between the supply and return temperatures equal to 15°. So, the performance of the device is equal to:
Now we calculate the pump performance using the formula: Qpu = Qn / 1.163 * dt, where 1.163 is the specific heat capacity of water; dt is the calculated difference between the supply and return temperatures equal to 15°. So, the performance of the device is equal to:
Qpu = 10/1.163 * 15 = 0.57 m3/h
Now we consider the head of the unit. It is calculated according to the following formula: Hpu = R*L*ZF/10000, where R is the friction loss in pipes equal to 150 Pa/m; L is the length of the supply and return in the longest heating branch (if it is unknown, then we take (house length + width + height)*2); ZF - stop valve resistance coefficient equal to 2.2 (with thermostatic valve); 10000 is the conversion factor for pascals to meters. So the pressure is:
Hpu \u003d 150 * 45 * 2.2 / 10000 \u003d 1.485 m
Please note that our calculations are very average, since everyone may have a different maximum supply and return length in the longest branch or the resistance of valves. We also made calculations for the second or average speed of the pump (there are three in total)
Why do you need a circulation pump for heating
This is a household appliance for pumping liquid, in the body of which an electric motor and a working shaft are installed.When turned on, the rotor begins to rotate the impeller, which creates a reduced pressure at the inlet and an increased pressure at the outlet. The device speeds up the movement of hot water through the pipes, and the owner receives the benefit of reducing the cost of heating the house.
Main technical parameters in marking
There are designs with a dry and wet rotor. Despite the relatively low efficiency (50-60%), models of the second type are most often used, because. they are compact and do not make noise during operation. When mounting such a device, it is advisable to install a mud filter in front of the inlet so that pieces of scale from the radiators do not get inside the case and jam the impeller.
The device works from a conventional power supply with a voltage of 220 watts. Power consumption may vary depending on the model and mode of operation. Usually it is 25-100 W / h. In many models, the possibility of adjusting the speeds is provided.
When choosing, special attention should be paid to performance, pressure, diameter of the connection to the pipe. The data are indicated in the technical documentation and marking. The first digit of the marking determines the connecting size, and the second indicates the power
For example, the Grundfos UPS 25-40 model is suitable for connection to an inch (25 mm) pipe, and the water lifting height (power) is 40 dm, i.e. 0.4 atmospheres
The first digit of the marking determines the connecting size, and the second indicates the power. For example, the Grundfos UPS 25-40 model is suitable for connection to an inch (25 mm) pipe, and the water lifting height (power) is 40 dm, i.e. 0.4 atmospheres.

Which manufacturers to choose
The list of the most reliable brands is headed by Grundfos (Germany), Wilo (Germany), Pedrollo (Italy), DAB (Italy).The equipment of the German company Grundfos is always high quality, functionality, long service life. The company's products rarely cause inconvenience to the owners, the percentage of marriage is minimal. Wilo pumps are slightly inferior in quality to Grundfos, but they are cheaper. "Italians" Pedrollo, DAB also please with high quality, good performance, durability. Devices of these brands can be bought without fear.

The principle of operation of the system with coercion
The circulation pump is a small electrical device that is extremely simple in design. Inside the housing there is an impeller, it rotates and gives the coolant circulating through the system the necessary acceleration. The electric motor that provides rotation consumes very little electricity, only 60-100 watts.
The presence of such a device in the system greatly simplifies its design and installation. Forced circulation of the coolant allows the use of heating pipes of small diameter, expands the possibilities when choosing a heating boiler and radiators.
Very often, a system originally created with the expectation of natural circulation does not work satisfactorily due to the low speed of the coolant through the pipes, i.e. low circulation pressure. In this case, installing a pump will help solve the problem.
However, one should not get too carried away with the speed of the water in the pipes, since it should not be excessively high. Otherwise, over time, the structure may simply not withstand additional pressure for which it was not designed.

If in systems with natural circulation of the coolant it is possible to use an open expansion tank, then in forced circuits, preference should be given to a closed sealed container
For residential premises, the following limiting norms for the speed of movement of the coolant are recommended:
- with a nominal pipe diameter of 10 mm - up to 1.5 m / s;
- with a nominal pipe diameter of 15 mm - up to 1.2 m / s;
- with a nominal pipe diameter of 20 mm or more - up to 1.0 m / s;
- for utility rooms of residential buildings - up to 1.5 m / s;
- for auxiliary buildings - up to 2.0 m/s.
In systems with natural circulation, the expansion tank is usually placed on the supply. But if the design is supplemented with a circulation pump, it is usually recommended to move the drive to the return line.
 The device of the circulation pump is very simple, the task of this device is to give the coolant an acceleration sufficient to overcome the hydrostatic resistance of the system
The device of the circulation pump is very simple, the task of this device is to give the coolant an acceleration sufficient to overcome the hydrostatic resistance of the system
In addition, instead of an open tank, a closed one should be put. Only in a small apartment, where the heating system has a small length and a simple device, you can do without such a rearrangement and use the old expansion tank.
Conclusion
What kind of pump do you have at home?
Wet RotorDry Rotor
Circulation pumps are necessary and important elements of the heating system of a private house. The best installation method is the return line, where the temperature of the coolant is much lower than at the outlet of the boiler.
When choosing a pump, you should pay attention to its parameters:
- Performance
- pressure
- Power
- Maximum temperature
First of all, you should consider the products of well-known and reliable companies. They are more expensive, but these costs are always justified.According to experts and ordinary users, a properly selected circulation pump is practically maintenance-free and provides a long service life without failure.
- Pumping station for a summer residence. How to choose? Model overview
- How to choose a generator for a summer residence. Main criteria and review of the best models
- Surface pumps for wells. Overview and selection criteria
- Pumps for watering the garden. How to choose, rating models