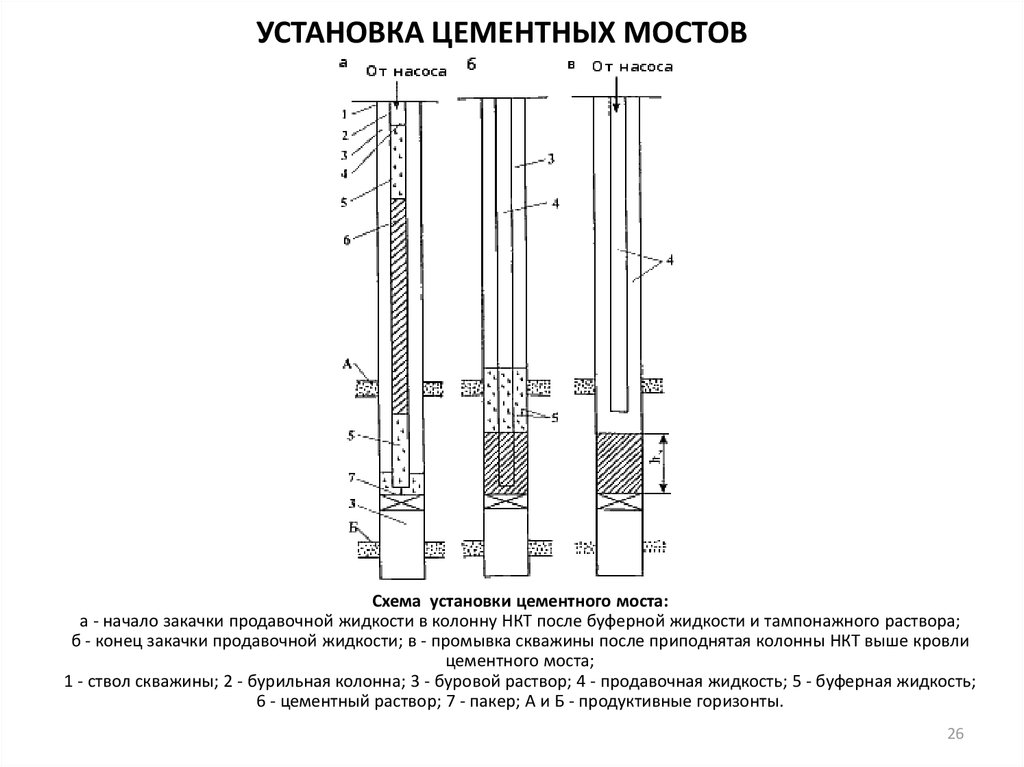
- The choice of cementing method is determined by a number of conditions.
- WELL CEMENTING TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESS
- CEMENTING PROCESS
- DISCHARGE FEATURES
- TOOLS AND MATERIALS:
- CEMENTING TECHNOLOGY
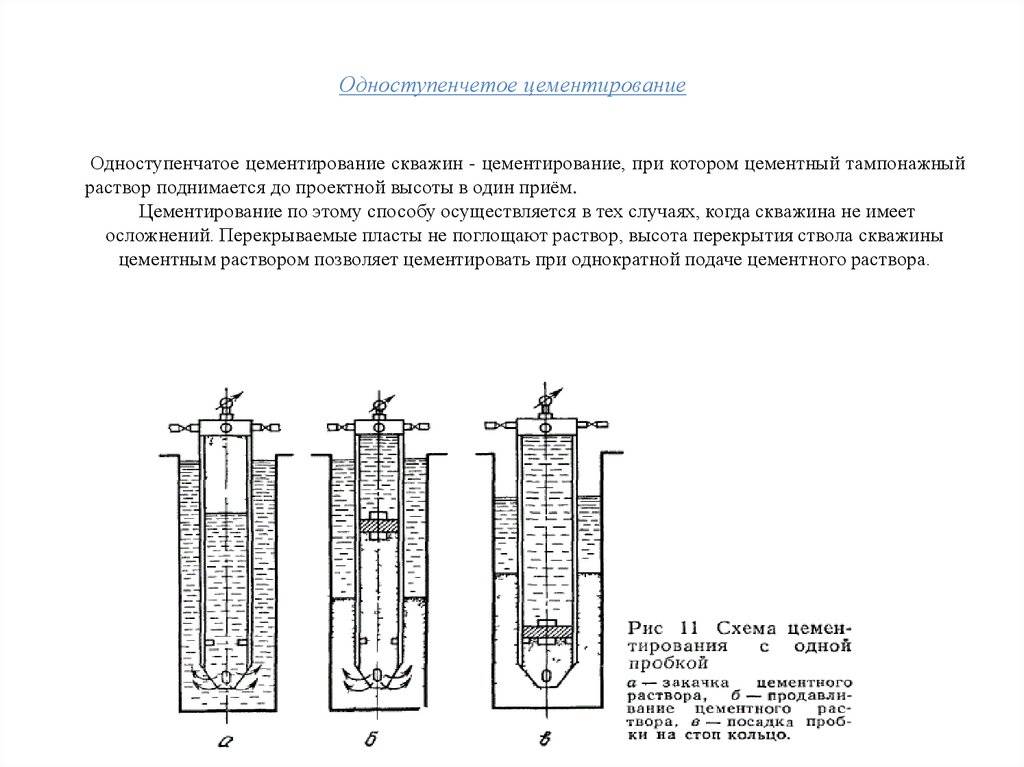
- Single stage (continuous) cementing system
- Types of well plugging.
- Why is it necessary to cement wells
- Description of the carburizing process
- How is the quality of cemented wells assessed?
- Well cementing methods
- The process of formation of cement stone
- The duration of hardening of the protective layer and checking its quality
- Safety measures for killing wells.
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The choice of cementing method is determined by a number of conditions.
Rating: / 0
The first condition determining the choice of cementing method is the appointment of insulation work. When fixing the cement sheath, isolating the influx of high-pressure water into the well, and when returning to the underlying formation, cementing is used through special holes with poker or cementing under pressure with drilling out the cement plug. When returning to the overlying formation, cementing without pressure is used.
The second condition that determines the choice of cementing method is the absorption capacity of the well.In this case, the expression “well absorption capacity” is conditional, it means the absorption capacity for water and cement slurry of any holes through which the injection of an insulating substance behind the production string is planned.
According to their absorption capacity, the wells are divided into three groups. The first group includes wells that have an absorption capacity of not more than 0.1 m3/min at a wellhead pressure of more than 50 at. The static level in such wells is at the wellhead, and sometimes there is even an overflow of fluid from the wellbore. When flushing wells with low absorption capacity, flushing water is not absorbed. In the wells of the second group, the static level is usually below the wellhead; when they are flushed, flushing water is partially absorbed. Absorption wells are characterized by the following features. They have a low static level, corresponding to a liquid column 50–200 m high, and have a high absorption capacity for water, clay and cement mortars. As a result, flushing units with a capacity of up to 100 l / s cannot cause circulation during forward and reverse flushing. When water, clay and cement slurries are injected, the level in absorbing wells rises, but then within a short time (0.5–1 h) it decreases to a static level. These features of absorbing wells require the use of specific cementing methods.
With a high water cut, it is necessary to apply cementing through the filter holes, with a low water cut - cementing through special holes or use oil-cement mortars.
The fourth condition that determines the choice of cementing method is the possibility of cleaning the behind-the-casing circulation channels, through which extraneous water enters, from rock particles, clay and unhardened cement mass. The study of the process of restoration of the cement sheath, carried out at the TatNII on a device simulating a section of the wellbore, showed that reliable isolation of the behind-the-casing circulation channels is achieved if these cracks are pre-flushed with water at a flow rate of at least 10 m/sec. This flow rate is provided under the condition:
where : q—water flow rate during reservoir drainage, m3/day;
D—diameter of the wellbore during drilling, m;
h is the length of the crack in the cement ring, m,
B is a constant value, at • day2/m6.
After intensive well drainage with water withdrawal of at least q, cementing is applied through the filter holes.
In case of insufficient water inflow from the formation, cementing is used through special holes with preliminary flushing of the behind-the-casing circulation channels using a packer.
The fifth condition determining the choice of cementing method is the depth of the well. With an increase in depth, the time of lowering and raising the pouring pipes increases, the hydraulic resistance during flushing increases, as well as the temperature and pressure at the bottomhole. These factors limit the possibilities of using one or another cementing method.
The sixth condition, which is taken into account when choosing a cementing method, is the technical condition of the production string. In many cases, it limits the value of the maximum possible displacement pressure and determines the degree of pressure reduction in the column.
< НазадВперёд >
WELL CEMENTING TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESS
The final stage of drilling operations is accompanied by a process that involves well cementing. The viability of the entire structure depends on how well these works are carried out. The main goal pursued in the process of carrying out this procedure is to replace the drilling fluid with cement, which has another name - cement slurry. Cementing wells involves the introduction of a composition that must harden, turning into stone. To date, there are several ways to carry out the process of cementing wells, the most commonly used of them is more than 100 years old. This is a single-stage casing cementing, introduced to the world in 1905 and used today with only a few modifications.
CEMENTING PROCESS
Well cementing technology involves 5 main types of work: the first is mixing the cement slurry, the second is pumping the composition into the well, the third is feeding the mixture into the annulus by the selected method, the fourth is the cement mixture hardening, the fifth is checking the quality of the work performed.
Before starting work, a cementing scheme should be drawn up, which is based on technical calculations of the process.
It will be important to take into account the mining and geological conditions; the length of the interval that needs strengthening; characteristics of the design of the wellbore, as well as its condition. Should be used in the process of carrying out calculations and experience in the implementation of such work in a particular area
DISCHARGE FEATURES
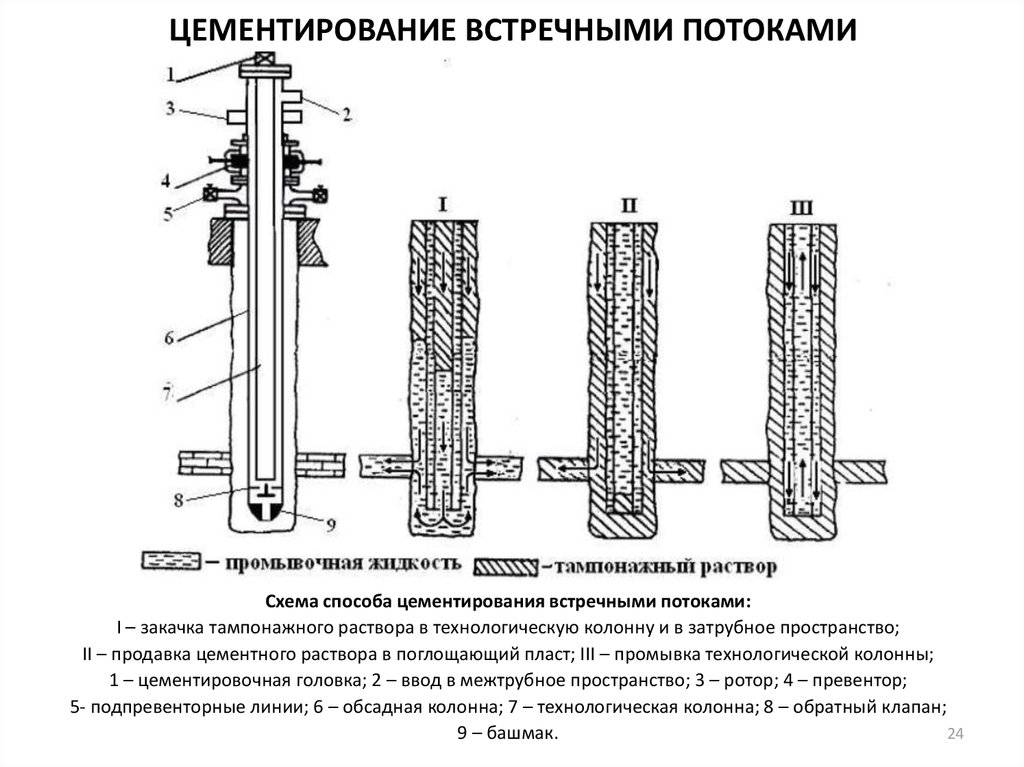
Cementing can be done by different methods of supplying the mixture into the annulus, moreover, various devices can be used in the process of work. Cementing wells may involve the direct supply of the mixture, such a scheme involves the flow of cement into the internal space of the casing string, followed by its passage directly to the shoe and further entry into the annulus, while the flow of the solution is made from the bottom up. With the reverse scheme, the injection is performed in the reverse order, from top to bottom.
In this case, well cementing can be carried out in one approach, during which the required volume for plugging the mixture is forced through at a time.
Two-stage cementing is used when the well has a significant depth. The technological process is divided into sequential filling of individual intervals through the use of equipment. Collar cementing, in contrast to the above methods, involves protecting a part of the wellbore from the passage of the cement mixture. The cuff allows you to isolate the area located along the length of the reservoir. The well may have hidden columns and sections, their cementing can be classified as a separate group.
The implementation of well cementing, regardless of the chosen method of work, pursues the goal of expelling the solution formed by drilling from the annulus, which is possible by placing a cement slurry there.Cementing ensures complete filling of the wellbore interval with cement mixture; elimination of the drilling fluid by penetration of the cement mixture within the interval intended for cementing; protection of the cement mixture from the penetration of flushing fluid; the formation of cement stone, which is characterized by significant resistance to various kinds of influences in the form of deep loads; excellent adhesion of cement stone to the walls of the well and to the surface of the casing.
TOOLS AND MATERIALS:
- cementing units designed for mixing the mixture and its subsequent punching under significant pressure;
- cement-mixing equipment;
- cementing head for flushing the wellbore and further cementing its walls;
- filling plugs for two-stage cementing;
- high pressure taps;
- steel flexible hoses;
- devices designed to carry out the distribution of the solution.
CEMENTING TECHNOLOGY
Turbulator
Lecture 14
Cementing is the process of filling a given interval of a well with a suspension of binders, capable of thickening at rest and turning into a solid, impermeable body.
Cementing O.K. - one of the most critical stages of well construction. High quality cementing of any wells includes: and cement stone behind the column.
The main goals of cementing are:
one). Isolation of permeable horizons from each other after they are opened by the well, and prevention of formation fluid overflows through the annulus;
2). Suspended casing string;
3).Protection of the casing string from the impact of aggressive formation fluids;
four). Elimination of defects in the lining of the well;
5). Creation of dividing screens that prevent watering of productive horizons;
6). Creation of high-strength bridges in the well, capable of absorbing sufficiently large axial loads;
7). Isolation of absorbing horizons;
eight). Strengthening of the walls of the well;
9). Wellhead sealing in case of well abandonment.
-implementation of the developed norms and rules of work in order to most completely fill the annular space of the well with cement slurry of a certain quality (instead of drilling slurry) in a given area, ensuring contact of the cement slurry - stone with the surface of OK. and well wall while maintaining the integrity of the layers.
The technological process of cementing is determined by geological and technological factors.
These factors are:
1. Setting time and thickening time of the cement slurry, its rheological characteristics, sedimentation stability, water loss and other properties.
2. Compatibility and relationship between drilling and cement slurries in the annulus.
3. Mode of movement of drilling and cement slurries in the annulus.
4. The volume of the injected cement material, the time of its contact with the well wall.
5. Quality and quantity of the buffer liquid.
7. Cementing the column.
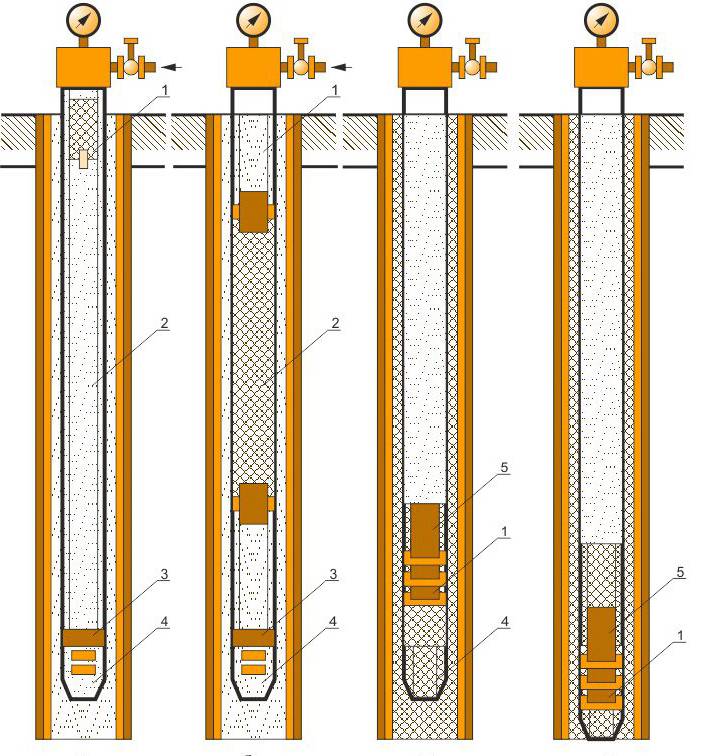
There are several cementing methods:
– methods of primary cementing (single-stage, multi-stage, reverse, sleeve);
– methods of secondary (repair and correction) cementing;
— Methods for installing dividing cement bridges.
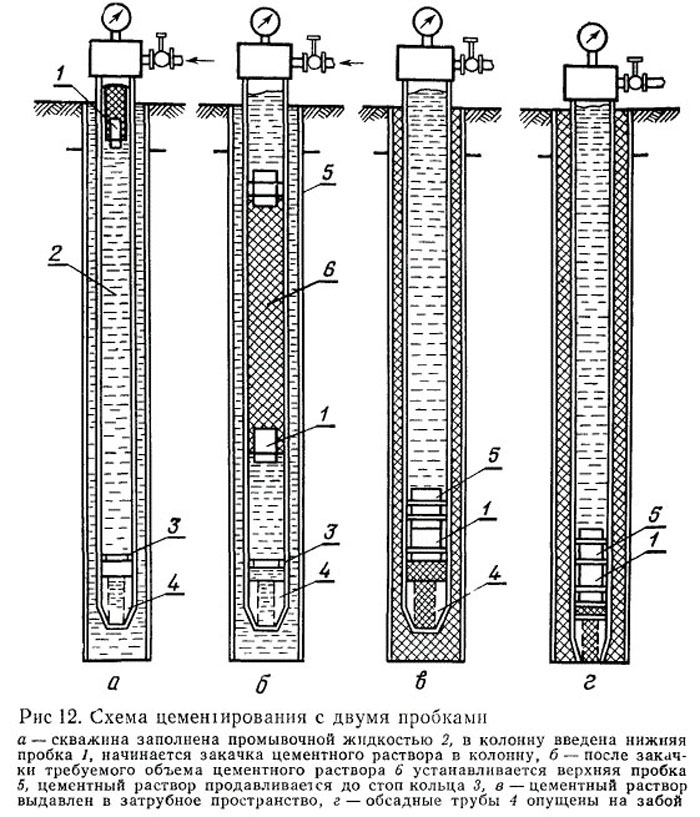
Single-stage cementing - the cement slurry is pumped in the volume necessary to fill the specified interval of the well annular space and the O.K. section. below the check valve, and the squeezing liquid - in the amount necessary to fill the internal cavity of the column above the check valve. The density of the cement slurry must be greater than the density of the drilling fluid.
Types of primary cementing:
The opposite is true when cement slurry is immediately pumped into the annulus.
Direct, when the cement slurry is pumped into the O.K., and only then it is pressed into the annulus. It is subdivided into:
A) One-stage (used most often).
B) Two-stage (used on long intervals or with ANPD). It can be with a time gap and without a time gap.
Step cementing (with a break in time). It is used in cases:
1. If it is impossible to cement this interval at one time due to the danger of rock rupture;
2. If there is a danger of GNVP during the setting and hardening of the cement slurry;
3. If cementing the upper section of a long interval, a cement slurry must be used that cannot be exposed to the high temperatures typical of the lower section.
Sleeve cementing. Applicable if the lower section casing string made up of pipes with pre-drilled holes. At the end of flushing, a ball is dropped into the well. With the flow of the pancreas, the ball goes down and sits on the saddle of the lower sleeve of the cementing sleeve.As the pump continues to pump the pancreas, the pressure in the string rises sharply, the sleeve cuts off the pins that hold it in the coupling body, goes down to the limiter and opens the windows for the fluid to exit into the annulus. From this point on, the process proceeds in the same way as with two-stage cementing.
93.79.221.197 Not the author of the materials posted. But it provides free access. Is there a copyright infringement? Write to us | Feedback.
Disable adBlock! and refresh the page (F5)very necessary
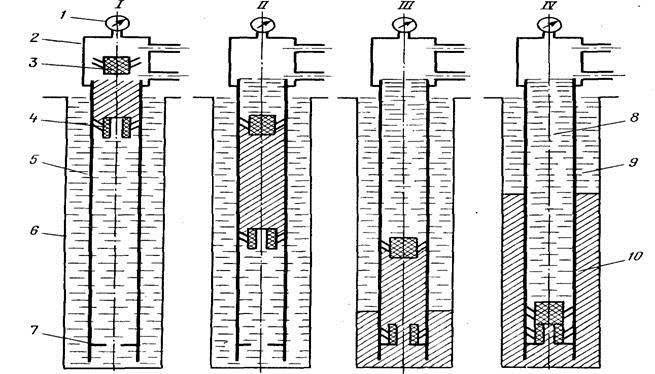
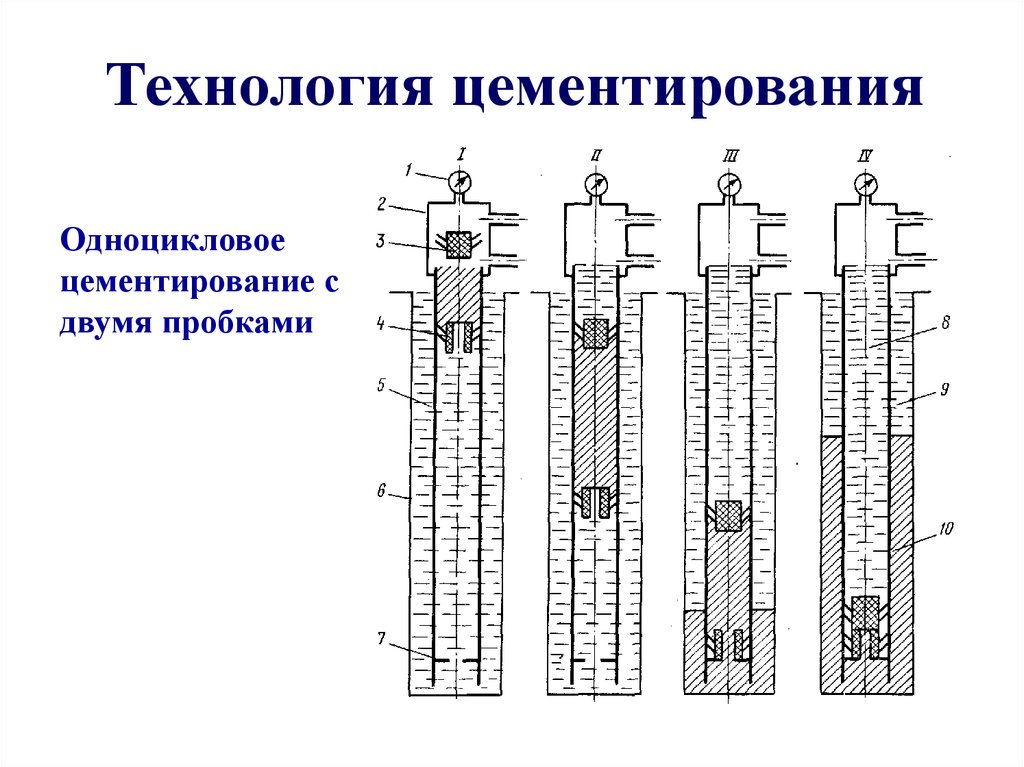
Single stage (continuous) cementing system
For fast and reliable strengthening of casing shafts of private hydraulic structures, a continuous mixture supply system is used. Single-stage cementing of wells involves the injection of a cement composition into the space around the pipe under high pressure using special equipment installed on the base of the vehicle or near the structure.
The grouting solution, under its own weight, is directed to the shoe base of the column, thereby filling all the existing cavities.
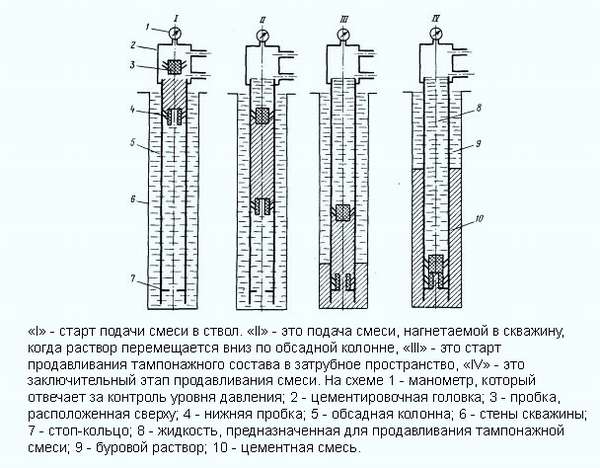
Before starting work, a thorough washing of the intake shaft is carried out, then a special plug is installed - a limiter. The concrete pump supplies the mixture, under the weight of which the plug is lowered onto the shoe base.
After the cement is pumped, another plug is placed and the mixture is compacted until both plugs abut against each other. This ensures that the space around the pipe is completely filled with mortar.
For tamping the mixture, a concrete pump equipped with a vibropress is used. Complete hardening of the cement occurs after 48 hours.
Solid cementing is used for small wells of the correct configuration. The disadvantage can be considered the complexity of monitoring the quality of the tamping of the poured cement mixture.
Types of well plugging.
The first type of tamponage is temporary and consists in the use of clay and various tampons. Temporary well plugging is applicable when the well is being tested and it is required to completely isolate aquifers or their individual fragments.
The second type of well plugging can be called permanent, in this case, the well is filled with cement mortar. Permanent plugging of the well is carried out for a long period of time
It is important to know that clay plugging of a well is applicable if a shallow well with free-flowing aquifers is liquidated, and when drilling fluid is lost. If it is necessary for a limited time to divide the wells into separate sections, then special tampons are used, which are called packers. In the study of porous rocks and rocks that have cracks for water abundance, as well as high, specific water absorption, packers are also used.
With the help of packers, it is possible to check the quality of cementation of rock-type rocks, in cases where it is required to give them additional strength.
In the study of porous rocks and rocks that have cracks for water abundance, as well as high, specific water absorption, packers are also used. With the help of packers, it is possible to check the quality of cementation of rock type rocks, in cases where it is required to give them additional strength.
Why is it necessary to cement wells
- First, the overall strength of the structure is increased.
- Secondly, grouting protects the surface of the pipe, which is made of metal, from corrosion, which may occur due to subsoil moisture.
- Thirdly, if the well is built in such a way that connects different oil and gas spaces, then after cementing they will definitely be isolated from each other.
Description of the carburizing process
Not surprisingly, grouting technology has undergone major changes. It is completely different from the old one. Now they use computerized technological calculations for the correct ratio of water in cement mortars and use special additives for them.
Additives to cement mortars can be in the form of:
- Quartz sand - it allows you to reduce shrinkage and maximize strength
- Fibrous cellulose, which does not allow leakage of liquid cement anywhere, especially the most porous rocks
- Priming polymers - during solidification, they expand and compact the soil
- Pozzolanov. This is a special crumb - ultralight minerals, they are waterproof and are not afraid of aggressive chemicals. Oil wells during cementation require a special multi-stage quality control of the plug made.
How is the quality of cemented wells assessed?
Perform special procedures:
- Thermal - determine the level of maximum rise of cement
- Acoustic - detects possible internal empty spaces in the cement
- Radiological - it is a kind of x-ray during this procedure
Well cementing methods
At the moment, there are four main methods of cementing:
- Single step method.The cement mixture is poured into the casing string and plugged with a plug. Washing solution is applied to the plug. Such actions lead to the fact that the cement is displaced into the annulus
- Two-stage. According to technology, it is exactly the same as the single-stage one. The difference is that actions are performed first with the lower part, and then with the upper. A special ring is used to separate the two departments.
- Cuff. Cementing is used with a solid collar to cement only the top of the well.
- Back. Cement slurry is poured immediately into the space behind the pipe, drilling and cleaning solutions are forced out into the cavity of the columns.
The MosOblBureniye company performs well drilling with high quality. You will be satisfied with the cooperation with our specialists.
The process of formation of cement stone
The process of formation of cement stone begins immediately after the injection of plugging solution and lasts from 12 to 36 hours. The main factors affecting the duration of the mortar hardening to the state of cement stone:
- properties of the components that make up the solution;
- soils, casing material;
- hydrogeological and climatic conditions at the site;
- injection density, correct implementation of the plugging process.
During the solidification period, it is necessary to leave the well at rest. It is forbidden to use cables, crowbars, wire to assess the quality of cementing, because. this may compromise the integrity of the resulting cement stone.
If you do not know how long it takes for the cement to fully set, wait three days and proceed with the control measurements
It is interesting: How to clean a well or cleaning the well hands step by step
The duration of hardening of the protective layer and checking its quality
The formation of cement stone begins immediately after the completion of the pouring of the mixture. The process of complete hardening depends on the ambient temperature, the composition and moisture content of the soil, the material of the casing elements, as well as the characteristics and list of components of the solution itself. If it is not possible to determine when the protective layer has fully formed, wait at least 48 hours before taking any action.
After two days, it is recommended to check the obtained protective layer. More accurate results can only be obtained using special professional equipment. There are three ways to check the integrity of a solution:
- Acoustic. The technique is based on tapping casing pipes along the entire length of the shaft and processing the results obtained through a computer program.
- Radiological. The measurement is carried out by special radio devices.
- Thermal. The temperature is measured during the solidification of the layer.
If it is not possible to invite specialists to evaluate the work performed, you can check the readiness of the cement layer using a simplified thermal method. To do this, during the period of solidification of the mixture, the temperature at the walls of the casing is measured. It should first be equal to the ambient temperature, and then become 1-1.5 degrees lower.
The final step is to clean the barrel from the remnants of the mixture. When doing work with your own hands, cleaning can be done with a bailer. Before putting the source into operation, the shaft is checked for tightness. To do this, water is pumped into the barrel under pressure for 20-30 minutes.If during this time the water pressure decreased by no more than 0.5 MPa, the work was done with high quality.
Safety measures for killing wells.
6.1. Well killing can be
started only after the execution of a bilateral act on the acceptance of the well for repair
(foreman of the KRS brigade and representative of PDNG, TsPPD).
6.2. well killing
produced on the instructions of the KRS master. Killing a well without a plan
PROHIBITED.
6.3. well killing
usually done during daylight hours. In special cases, jamming
can be carried out at night when the illumination of the well is not
less than 26 hatch.
6.4. Playground size
40x40 m, on which the units are installed, must be freed from
foreign objects, in winter from snow.
6.5. Before jamming
it is necessary to check: the serviceability of all gate valves and flange connections on
wellhead equipment; the presence of a duct
liquid along the flow line from the well to the metering unit and at its
stop working at the well until the causes are clarified and eliminated.
6.6. washing unit and
tank trucks should be located on the windward side at a distance of at least
10 m from the wellhead. At the same time, the cabin of the unit and tankers must be
facing away from the wellhead, the exhaust pipes of the unit
and tank trucks must be equipped with spark arresters, the distance between them
must be at least 1.5 m.
flushing unit, except
In addition, it must be equipped with safety and non-return valves.
6.7. In the process of silencing
well DO NOT mount any nodes assembly or piping
wells and pipelines. There must be constant monitoring of:
readings of pressure gauges, behind the piping line, behind the location of people. Pressure gauges
must be installed on the pumping unit and the flow line of the well.
6.8. When killing wells
the pumping pressure of the killing fluid must not exceed the pressure of the pressure test
production string of this well.
6.9. Disassembly of the flushing
lines should only be started after the pressure in the discharge line has been reduced to
atmospheric. At the same time, the gate valve on the X-mas tree from the side of the well
should be closed.
6.10. After graduation
of well killing operations, valves must be closed, the area around
the well has been cleaned, the dead well must be awaiting repair
over 36 hours.
With a longer
downtime of the well in anticipation of repair, the well must be killed again before
start of repair work.
6.11. After the end of all
well killing operations, a “Well killing act” is drawn up.
AT act of suppression
wells should be indicated:
- date of well killing;
- specific gravity of the kill fluid;
- the volume of killing fluid by cycles;
- the time of the beginning and end of the jamming cycles;
- the initial and final pressure of pumping the killing fluid.
6.12. “Act to kill the well” signed (with
indicating the specific gravity and volume of the killing fluid), the person who produced
well killing, by the foreman of the workover team and the machinist of the unit.
Responsibility for Compliance instructions.
7.1. For preparation
the territory of the pad and the well to kill the well is the responsibility of the foreman of the TsDNG, TsPPD.
7.2. For authenticity
data on the current reservoir pressure, at the time of killing the well, corresponds to
geological service TsDNG, TsPPD.
7.3. For compliance
the specific gravity of the killing fluid to the calculated value - specified in the task plan
to kill the well, perform the entire range of work to prepare the well for
killing, compliance with well killing technology and safety measures when
killing the well is the responsibility of the workover team foreman.
Attachment 1
R A S X O D
materials
necessary for cooking one cubic meter of killing fluid relevant
density.
Solution liquid
– Cenomanian water with a density of 1.01 g/cm3.
| Density | Amount of NaCl, kg | Density | Amount of NaCl, kg |
| 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 | 19 38 56 75 94 113 132 151 170 | 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 | 188 207 226 245 264 283 302 321 |
| Killing liquid density, g/cm3 | The amount of CaCl2, kg | ||
| Fresh | Cenomanian | Commercial | |
| 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 |
Appendix 2
VOLUME
ring
space depending
from the diameter of production strings
and
Tubing lowered into the well.
| Volume | |||
| Descent depth Pump (tubing), m | NKT-60 | NKT-73 | NKT-89 |
| At | |||
| 800 1 000 1 200 1 400 | 8.68 10.85 13.02 15.19 | 7.50 9.38 11.26 13.13 | 5.86 7.32 8.78 10.25 |
| At | |||
| 800 1 000 1 200 1 400 | 12.25 15.31 18.37 21.43 | 11.06 13.83 16.60 19.36 | 9.42 11.73 14.11 16.49 |
| At | |||
| 800 1 000 1 200 1 400 | 4.27 5.34 6.41 7.48 | — — — — | — — — — |
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
In the videos below, we are talking about wells in the oil and gas industry, but the principle of work technology is the same as for aquifers.
One-stage well cementing procedure:
Specifics of sleeve cementing production:
Technological features of two-stage cementing:
Cementing is a complex process that requires the use of specialized equipment. However, this does not mean that it is impossible to carry it out on your own.Having chosen and properly prepared the cement slurry, using a minimum set of units, it is quite possible to cope with the work on your own.
In any case, the operation of a well without strengthening the wellbore with cement will not be long, and the cost of drilling a new water source will be no less.
If after studying the material you still have questions about how to properly cement a well after drilling, or you have valuable knowledge on this issue, please leave your comments in the block below.