- The specifics of the production of briquettes for heating
- Types of briquettes for heating
- Recommendations for choosing fuel briquettes
- Comparative characteristics of briquettes
- wood briquettes
- Prices for Eurowood Briquettes
- coal briquettes
- Prices for coal briquettes WEBER
- Peat briquettes
- Husk briquettes
- Types of briquettes for heating according to the composition of raw materials
- What are charcoal briquettes made of?
- How are fuel briquettes prepared and transported?
- Coal for a good boiler
- Fuel briquettes or ordinary firewood: what to choose?
- Why compare cheap firewood with expensive briquettes
- Which briquettes are better
- Manufacturing technology and scope
- Main advantages
- Briquetted coal - what is it?
- Varieties
The specifics of the production of briquettes for heating
The peculiarity of the production of Eurowood is the use of waste from the woodworking industry, agriculture and coal mining. The production of briquettes for heating can be organized on the basis of any of the above enterprises.
For manufacturing, it is necessary to choose the right source material. Proper production of briquettes for heating starts from the preparatory stage. Depending on the available raw material base, several types of materials are distinguished:
- Agricultural waste - seed husks, straw.The first has the largest energy capacity. However, it is also characterized by a high purchase cost;
- Wood sawdust. The most suitable option, since it is from them that do-it-yourself briquettes for heating are most often made;
- Peat. Needs a complex preparatory process, as it initially has high humidity;
- Coal. In fact, they use the so-called coal dust, which is a by-product of mining.
Preparation of feedstock includes preliminary grinding and further drying. This is necessary to reduce humidity, since heating with sawdust briquettes will be beneficial only if the water content is not more than 10% of the total volume. Then fixatives and modifiers can be added to the resulting material to increase heat transfer.
Types of briquettes for heating
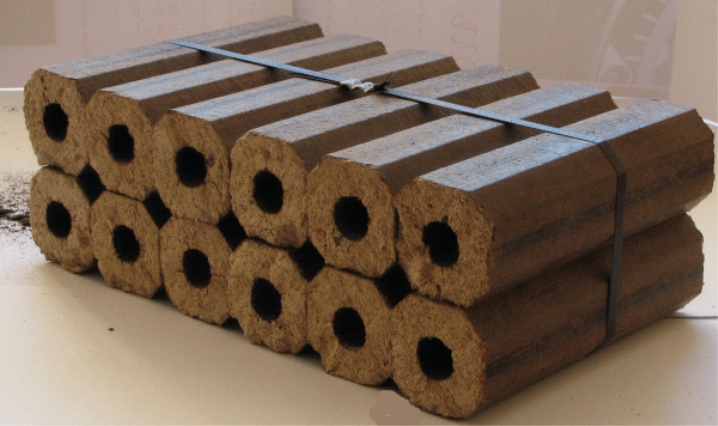
In fact, eurofirewood differs not only in the feedstock, but also in the way it is processed. The simplest manufacturing method is pressing. For the production of briquettes for heating RUF, a special belt press of the RUF company of the same name is required. It was from him that the naming of Eurowood of this type came.
The advantage of this technological process lies in the speed of production. The pre-prepared raw material is loaded into the receiving chamber, and then, with the help of augers, enters the pressing zone. Those. in fact, the production of briquettes of this type will require a minimum of investment and effort.
However, the final product has a number of features:
- Almost all reviews of peat briquettes for heating note their susceptibility to moisture absorption. Therefore, you need to take care of the appropriate storage location;
- Eurowood, made on original equipment, have a letter imprint on the surface. In most cases, this indicates compliance with the manufacturing technology. But it all depends on the quality of the raw material.
To improve performance, it is best to choose a different production method. Peat briquettes for heating, in addition to pressing, go through the stage of surface firing. In this way, a moisture-resistant outer shell is formed, which in addition contributes to an improvement in mechanical resistance.
Additionally, the equipment has a heating zone, which is located around the feeding pressing screw. This manufacturing technology is called Pini Kay. Its feature is relatively low performance compared to RUF. However, wood briquettes for heating Pini Kay have a much longer shelf life. In addition, their increased density has a positive effect on heat transfer.
Recommendations for choosing fuel briquettes
To choose the best fuel briquettes for home use that will burn well and efficiently, adhere to the following principles:
Give preference to sawdust wood briquettes. In terms of combustion quality, they are as close as possible to firewood, burn well, have low ash content and high heat transfer. Seed husk briquettes also give a lot of heat, but due to oil, they more intensively pollute the chimney and heater with soot.
Calorific value fuel briquettes from solid and coniferous woods is the same, because they are based on the same woody substance. But softwood briquettes contain resin, which pollutes the chimney more with soot.
Do not believe in the calorific value, humidity and ash content of briquettes in words. Ask the seller for test reports, which indicate the main characteristics of the briquettes. But be prepared for the fact that they may not be.
Choose briquettes with maximum density. The higher the density, the more evenly and longer the briquettes burn, and also do not crumble and leave a lot of hot, long-burning coals. The highest density is in pinikey briquettes, the average is in Nestro, and the minimum is in Ruf.
Before buying a large number of briquettes, take 10-20kg samples from different places. Check them for strength: if the briquette breaks easily and crumbles, then it is poorly compressed or contains a lot of moisture. Burn each sample in the heater
Pay attention to the heat, how long and at what thrust do the briquettes burn? The lower the thrust at which the briquettes are able to burn, the better. Look what coals they leave
Do they hold their shape or break up into small embers? This is the only sure way to choose high-quality briquettes for heating.
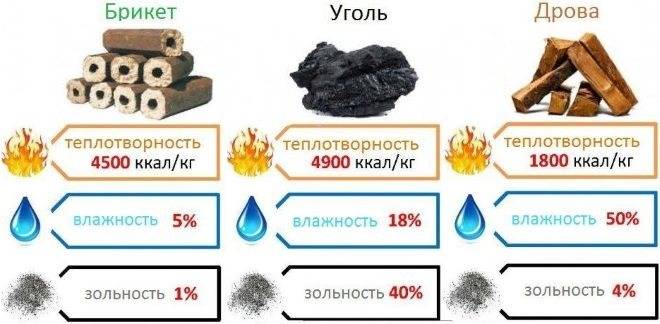
Comparative characteristics of briquettes
| Type of fuel | Calorific value, MJ/kg |
|---|---|
| Anthracite | 26,8-31,4 |
| Brown coal | 10,5-15,7 |
| Coal | 20,9-30,1 |
| Gas | 27 |
| Peat (moisture content 20%) | 15,1 |
| Diesel fuel | 42,7 |
| Wood (moisture 40%) | 6-11 |
| Briquettes (from sawdust) | 16-29,5 |
Each type of briquettes has its own characteristics and advantages. And although they are all great for domestic heating, it is still worth familiarizing yourself with their characteristics in more detail in order to choose the best option.
Forms of fuel briquettes
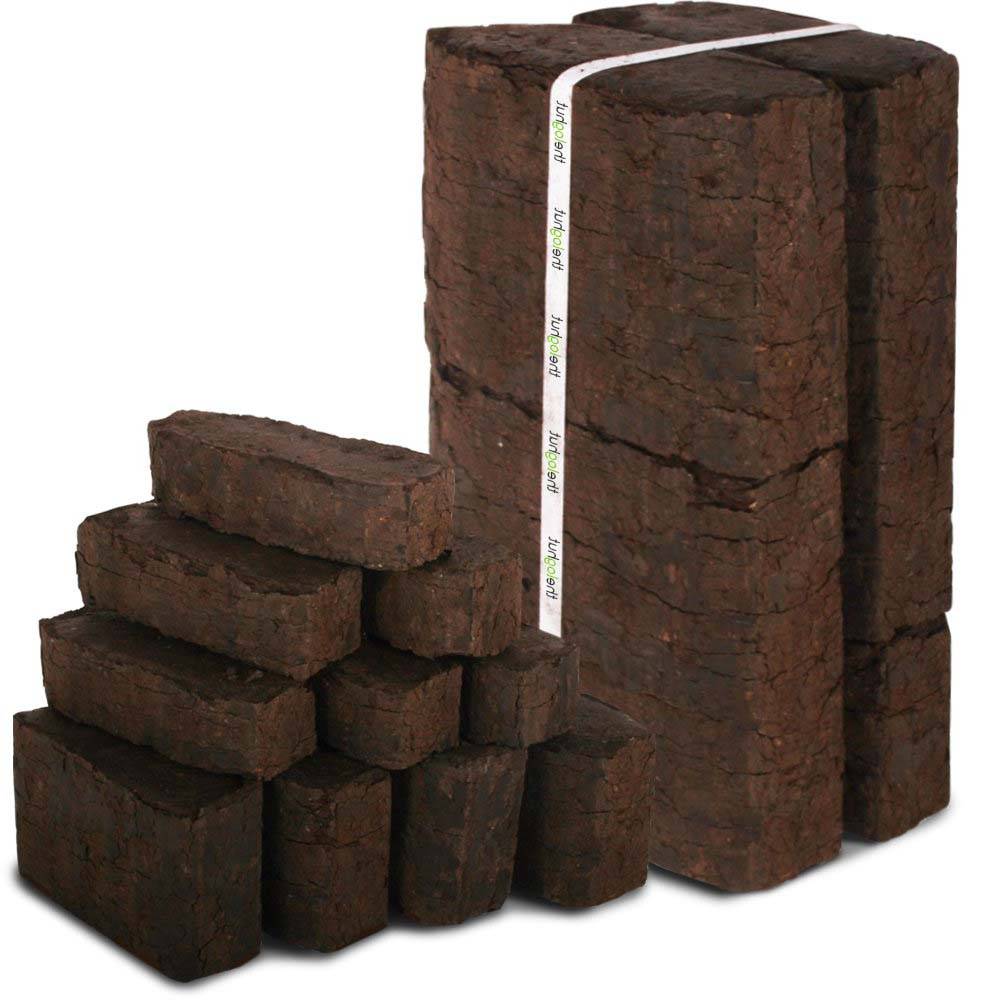
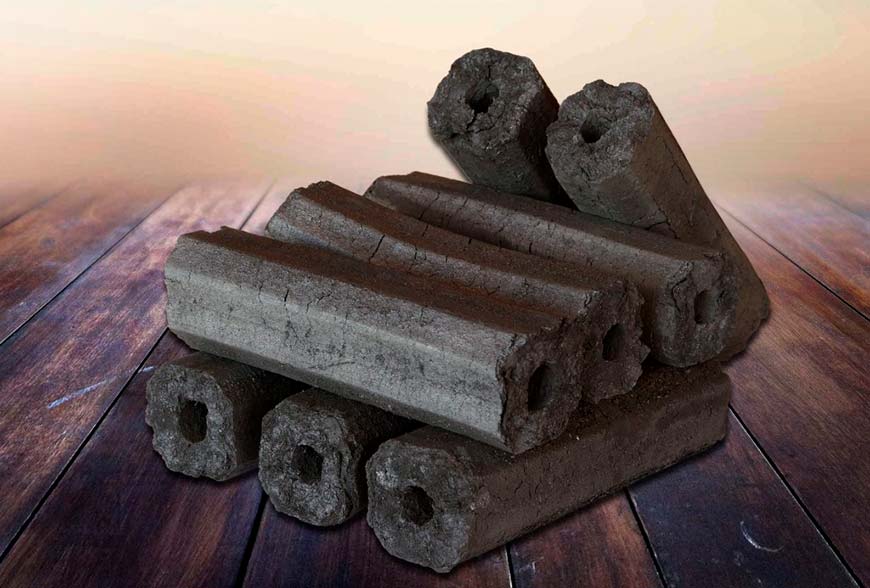
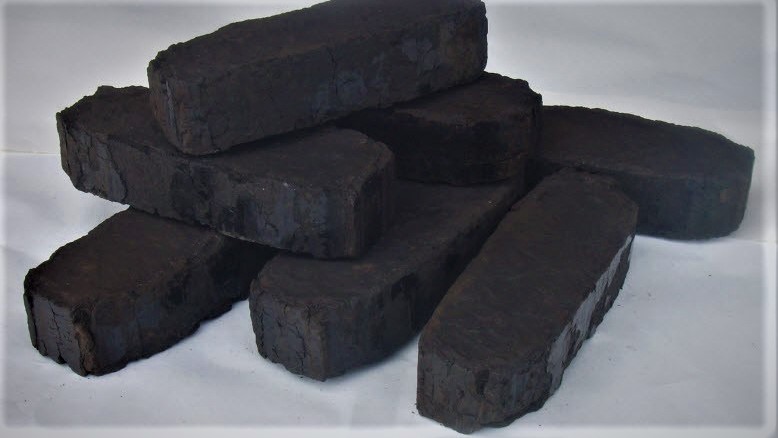
wood briquettes
This type of briquettes is obtained by pressing various wood waste - deadwood, sawdust, shavings, substandard wood.Before pressing, the waste is heated to a certain temperature, as a result of which an adhesive substance, lignin, is released from the cells. Thanks to lignin, briquettes acquire high strength and retain their shape during transportation and storage.
wood briquettes
The advantages of briquettes over solid wood are obvious:
- the density of the briquettes is constant and amounts to 1240 kg/m³, the density of the wood depends on the species and ranges from 150-1280 kg/m³;
- maximum humidity of briquettes is 10%, wood - from 20 to 60%;
- when burning a briquette, the volume of ash is 1% of the total mass, wood - 5%;
- when burning, a briquette releases 4400 kcal/kg, a tree - 2930 kcal/kg.
wood briquettes
In addition, wood briquettes have other advantages:
- pressed wood does not spark during combustion and emits very little smoke;
- the boiler is maintained at a constant temperature;
- briquette burning time 4 hours;
- the remaining coals after combustion are great for cooking on an open fire;
- the correct form of briquettes simplifies their transportation and storage.
Such fuel is sold not in cubic meters, like wood, but in kilograms, which is much more profitable.
Prices for Eurowood Briquettes
Eurowood Pini-kay
coal briquettes
coal briquettes
This type of briquettes is obtained from the elimination of hard coal. The screenings are first crushed, mixed with a binder, and then pressed under high pressure.
The main properties of such fuel:
- coal briquettes do not smoke;
- do not emit carbon monoxide;
- burning time in conventional boilers from 5 to 7 hours, with adjustable air supply - 10 hours;
- suitable for domestic use;
- have a compact shape;
- during combustion, 5200k / cal is released and a constant temperature is maintained;
- maximum ash volume - 28%;
- have a long shelf life.
Coal briquettes are the most optimal fuel in severe winters, when pressure drops in domestic gas systems due to low temperatures. Briquettes burn at any temperature, the main thing is that there is a constant flow of air.
Prices for coal briquettes WEBER
Coal briquettes WEBER
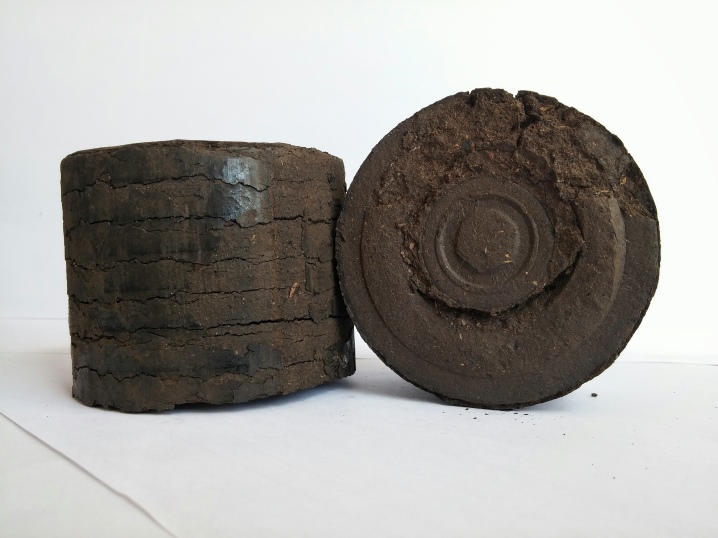
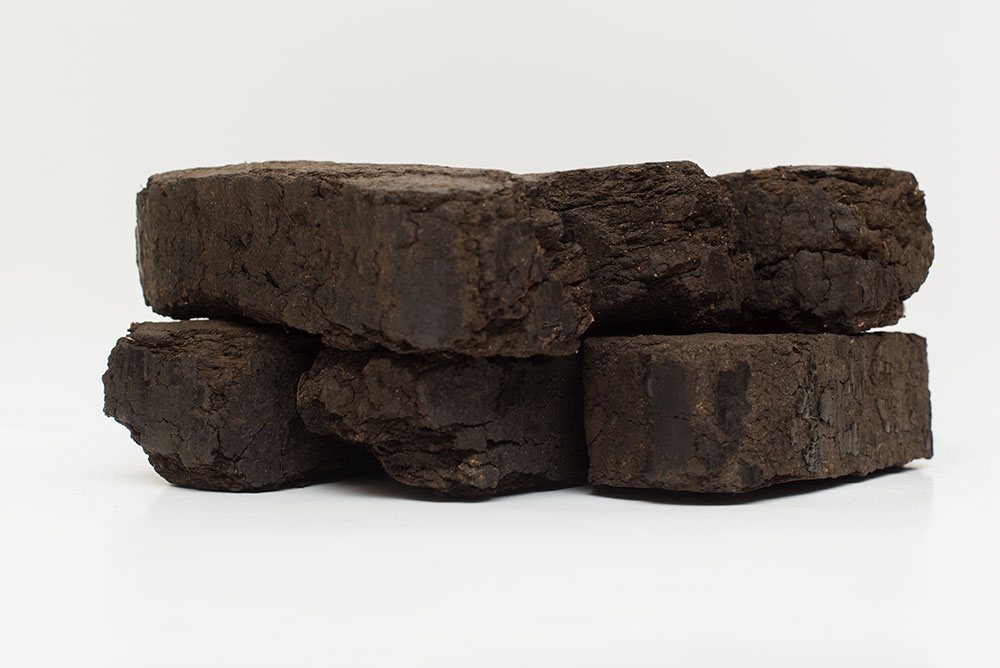
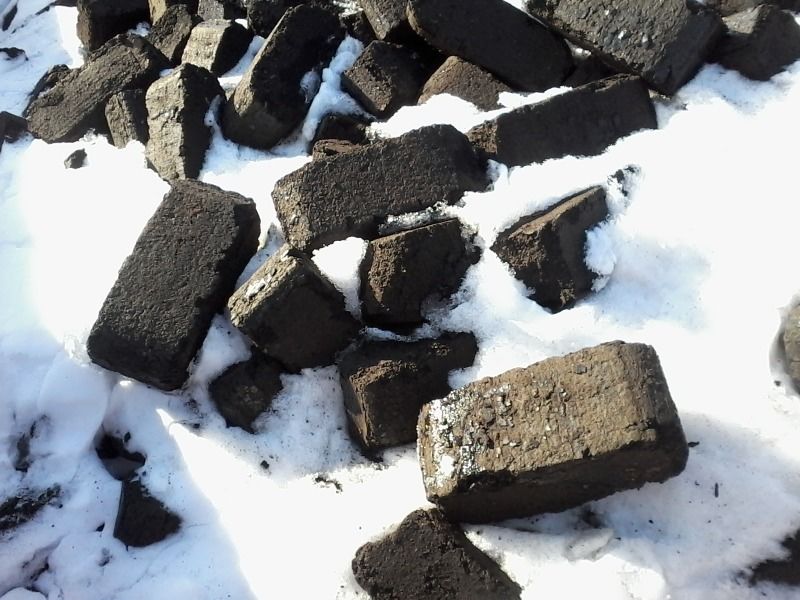
Peat briquettes
Peat briquettes
To make briquettes, peat is dried, heated and pressed under high pressure. The result is neat light bricks of dark color. With adjustable air supply, peat briquettes maintain the temperature for 10 hours, which is very convenient for heating the house at night.
Basic properties:
- suitable for all types of ovens;
- heat transfer is 5500-5700 kcal / kg;
- the volume of ash is 1% of the total volume of the briquette;
- affordable price;
- the minimum amount of impurities in the composition.
Peat briquettes
The ash that remains after the combustion of fuel can be used as an effective lime and phosphorus fertilizer. For many owners of private households, this factor is decisive when choosing heating briquettes. Since peat is a flammable substance, it should be stored at a safe distance from open flames and heating appliances. Even dust spilled from the packaging can ignite and cause a fire, so you need to handle the briquettes correctly.
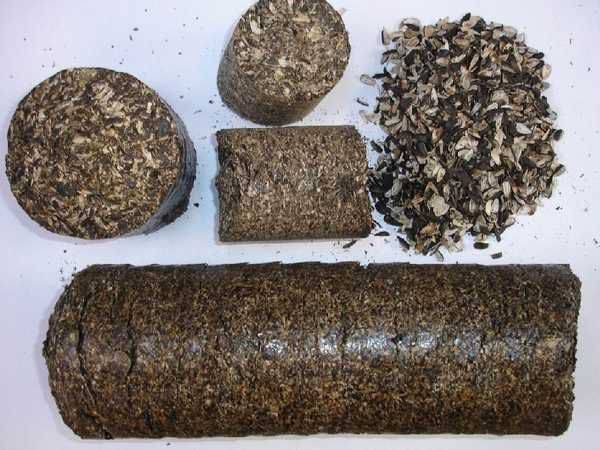
Husk briquettes
Husk briquettes
Sunflower husks, buckwheat and rice husks, rye, oats and even straw waste are widely used for production of fuel briquettes. The most common are sunflower husk briquettes, since a large percentage of waste remains during the production of oil. The maximum moisture content of the pressing husk is 8%, which increases the heat transfer and reduces the ignition time.
Sunflower briquettes
Specifications:
- the density of briquettes is 1.2 t/m³;
- heat transfer - 5200 kcal / kg;
- the volume of ash is from 2.7 to 4.5%.
Additional benefits:
- no harmful impurities;
- affordable price;
- long burning time;
- ease of storage and transportation.
Types of briquettes for heating according to the composition of raw materials
Classification according to the material of manufacture is the most common. Briquettes are created from various remnants of natural raw materials. Each type of fuel has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
Types of briquettes for heating:
- Coal;
- woody;
- Peat;
- From the husk.
Coal varieties are produced in the form of tablets or cylinders from the waste of the coal industry. Coal screenings are additionally crushed, binders are added, and then the material is pressed. Such fuel is excellent for both stoves and barbecues.
The advantages of coal briquettes include reduced carbon monoxide emissions. Such briquettes are often used by restaurant enterprises. Such material burns for a long time. If desired, this time can be up to 10 hours.

Wood briquettes are created from lignin. They are durable, easy to transport, but while the heat transfer of the material significantly less than other analogues. Briquettes are made from any tree species.
Although the structure changes during processing, but after combustion, wood briquettes leave coals.Due to this, such fuel is often used for cooking. It is considered the most environmentally friendly material.
Peat briquettes are characterized by a number of advantages. Take at least a high heat transfer of the material. But there are also negative points. After burning briquettes, a lot of waste remains. Resourceful gardeners use ash as fertilizer. The disadvantages include high smoke.
Sunflower husk briquettes characterize waste-free production. What used to go in the trash is now working for good. Husk briquettes can be recognized by the characteristic smell during combustion. In addition, due to the oils in its structure, this fuel is characterized by high heat transfer. This material is environmentally friendly and cheap.
What are charcoal briquettes made of?
Such fuel briquettes are becoming increasingly popular and widespread due to their relatively low cost, efficiency, simplicity of the production process and, of course, availability. However, this type of fuel is divided into several varieties in accordance with the type of raw material used, as well as according to the form of the final product.
So, today these briquettes can be produced from several types of coal - in particular, it can be:
- brown (this is the most common, since the cheapest type of raw material);
- anthracite (the most efficient, but at the same time the most expensive coal, characterized by excellent heat transfer performance);
- woody (the production technology in this case is more complex than that of brown coal, since it requires the use of additional equipment).
We also note that for the manufacture of briquetted fuel there is no need to use high-quality raw materials, because coal fines and dust are quite suitable for this, as well as waste (the latter can fall through the grate, sinter badly, therefore, they are simply unsuitable for use in furnaces or for making coke ).

How are fuel briquettes prepared and transported?
As you can see, during the production of briquette fuel, combustion rates increase, which makes artificial fuel a good alternative to coal.
To kindle the stove with peat, it should be dehydrated and thoroughly crushed. The production of briquettes for heating and peat processing is located next to its deposit. Hence the low cost, since there is no need to transport it from the deposits to the place of processing. The production costs of peat briquettes are low, and therefore the retail price is low. The cost of transport services affects the price. In the entire production scheme, this stage is the most expensive. As you can see, the convenient form of the finished material allows you to transport large volumes compared to their original sources.
It is interesting: Energy saving heating systems private home - technology overview
Coal for a good boiler
The combustion temperature of coal can reach 1400 ° C, the ignition temperature - 600 ° C - these properties are used in energy-intensive processes in ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, where coal and anthracite are traditionally used. The combustion of coal (brown) is accompanied by increased heat transfer to heat metals up to 1200 ° C.At the same time, studies show that during the combustion of coal, up to 40% of volatile gases are released, and after their combustion, up to 14% of ash remains.
Coal briquettes for heating have significantly lower values for these indicators, while maintaining high performance by calorific value (up to 5500 kcal). A briquette is a compressed mixture of crushed coal fractions and fixatives-fillers with a density of 1.4 g/cm3. High calorific value, absence of coal dust have made coal in briquettes a popular type of fuel used in private households and in enterprises where there is no centralized heating supply. Coal slag, formed during the combustion of fuel, can serve as fertilizer for plants in the area adjacent to the house.
Fuel briquettes or ordinary firewood: what to choose?
What to give preference to: ordinary firewood or fuel briquettes? To answer this question, it is necessary to study the advantages and disadvantages of both.
We list the most important advantages of fuel briquettes:
- A fuel briquette, when compared with ordinary firewood, burns 4 times longer than the latter, which contributes to the economical consumption of such fuel.
- After the combustion of pellets, very little ash remains - about 1% of the total mass of used fuel. When using conventional firewood, this figure can reach up to 20% of the total mass of fuel used. The ash left after the combustion of wood briquettes or any other type can be used as a fertilizer containing a large amount of potassium.
- The amount of thermal energy released during the combustion of eurofirewood is almost twice as much as when using ordinary firewood.
- During combustion, fuel briquettes emit heat almost all the time, which cannot be said about ordinary firewood, the heat output of which decreases rapidly as it burns.
- During combustion, fuel briquettes practically do not spark, emit a minimum amount of smoke and smell. Thus, this type of fuel does not create discomfort and does not harm the environment. In addition, when burning firewood infected with mold or fungus, toxic smoke is formed, which is excluded when using eurofirewood, for the production of which carefully dried sawdust or shavings are used.
- When using wood briquettes as fuel, much less soot is deposited on the walls of chimneys than when using conventional firewood.
- The compact dimensions that distinguish eurofirewood allow more economical use of the area for storing such fuel. Moreover, when storing fuel briquettes, usually placed in a neat package, there is no garbage and wood dust, which are necessarily present in places where ordinary firewood is stored.

Compact storage is an indisputable advantage of fuel briquettes
Naturally, this type of fuel has certain disadvantages:
- Due to the high density of the internal structure, fuel briquettes flare up for a long time, it will not be possible to quickly warm up the room with the help of such fuel.
- The low moisture resistance of eurofirewood can cause them to simply deteriorate if the required storage conditions are not provided.
- Fuel briquettes, which are compressed sawdust, are characterized by a rather low resistance to mechanical damage.
- When burning fuel briquettes, there is no such beautiful flame as when using ordinary firewood, which somewhat limits the use of pellets as fuel for fireplaces, where the aesthetic component of the combustion process is also very important.
Comparison of the main parameters various types of solid fuel
To make a choice between fuel briquettes and ordinary firewood, the advantages of the latter should also be taken into account.
- When burning ordinary firewood, as mentioned above, more heat is generated, respectively, with the help of such fuel it is possible to quickly warm up the heated room.
- The cost of ordinary firewood in comparison with fuel briquettes is much lower.
- Firewood is more resistant to mechanical damage.
- When burning firewood, a beautiful flame is formed, which is an especially important quality for fireplace fuel. In addition, when burning firewood, essential oils contained in wood are released into the surrounding air, which has a beneficial effect on the nervous and respiratory systems of a person who is in a heated room.
- The characteristic crackle that firewood emits during combustion also has a beneficial effect on the nervous system.
- The ash left after burning ordinary firewood does not have such a tart smell as the product of burning pellets.
Why compare cheap firewood with expensive briquettes
For residents of regions rich in forests, where woodworking enterprises are located, such a comparison is irrelevant. Firewood and sawdust in those parts are inexpensive or donated. But we decided to compare them with briquettes for the following reasons:
- There are practically no forests in the southern and desert regions. Hence the higher price of firewood bought by the owners of country houses and summer cottages.
- In these areas, it is advantageous to press any kind of combustible mass - coal dust, agricultural waste and peat. Thanks to the development of such industries, the cost of briquettes is reduced and they become an alternative to firewood.
- It is more comfortable to heat with pressed products than with wood raw materials, which our experiment will show.

The last reason is the conflicting reviews of homeowners about various fuels on thematic forums. A user who does not understand this issue is hardly able to figure out which types of briquettes are best used for a stove, fireplace or boiler. We will present the conclusions and opinion of the expert on this matter.
Which briquettes are better
Which briquettes are better
Comparison of the characteristics of heating briquettes and traditional fuels shows that pressed materials are still more efficient. If you choose between the briquettes themselves, you should take into account their features and properties.
Calorific value of different briquettes
Wood fuel briquettes (euro firewood) - economical and most environmentally friendly fuel
| Type of fuel | Average weight of fuel for the production of 16,000 MJ of energy | Comparative price of obtaining energy for a consumer on average in Russia, rub. |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel briquettes | 1000 kg | 2000 |
| Wood | 1600 kg | 2200 |
| Gas | 478 cubic meters | 3500 |
| Diesel fuel | 500 l | 8000 |
| fuel oil | 685 l | 5500 |
| Coal | 1000 kg | 2800 |
Manufacturing technology and scope
After the processing of natural raw materials, a large amount of waste remains. For example, in the woodworking industry, these are shavings, sawdust, and wood chips. Each production strives for a waste-free scheme of work, therefore, even the remnants of raw materials have long been learned to be used for the manufacture of the necessary products, for example, chipboard.With the rise in price of solid fuels, waste began to be pressed into briquettes that are convenient for use and transportation - and they immediately became in demand.
The technology for manufacturing wood briquettes for heating is simple: the waste is crushed, pressed, and simultaneously subjected to heat treatment. To bond the particles, a natural component of lignin or synthetic solutions are used. Lightly melt the surface to keep the shape.
To improve combustion efficiency, some types have through holes. Then the small-sized products are packed in a film. or paper bags, more protected briquettes are left unpacked. In this form, products are sold for private and industrial needs.
By purchasing briquettes at retail or, which is much more profitable, in bulk, pay attention to the shape and dimensions - they must match your boiler, stove or barbecue
The heat transfer of the fuel is sufficient to be successfully used for heating completely different rooms, such as:
- production shops, warehouses up to 200 m²;
- utility rooms, boiler rooms;
- private property: cottages, country houses, dachas;
- Russian baths, saunas.
Small-sized briquettes and granules can easily be placed in furnaces of any size; for volumetric solid fuel boilers, "euro-firewood" of increased length or diameter is provided. One example: 30-35 kg of fuel from sawdust is needed per day to heat a large warehouse hangar with an area of 180-200 m², that is, 3-3.5 standard ten-kilogram packages will be needed.
Light and compact briquettes are convenient for transportation in the trunk of a car, they burn beautifully in the open air, so they are preferred by lovers of outdoor recreation for making fires, barbecues or cooking on the grill. For summer residents, briquetted products are a universal remedy - they are successfully used both for heating houses and for making a fire on the site.
Main advantages
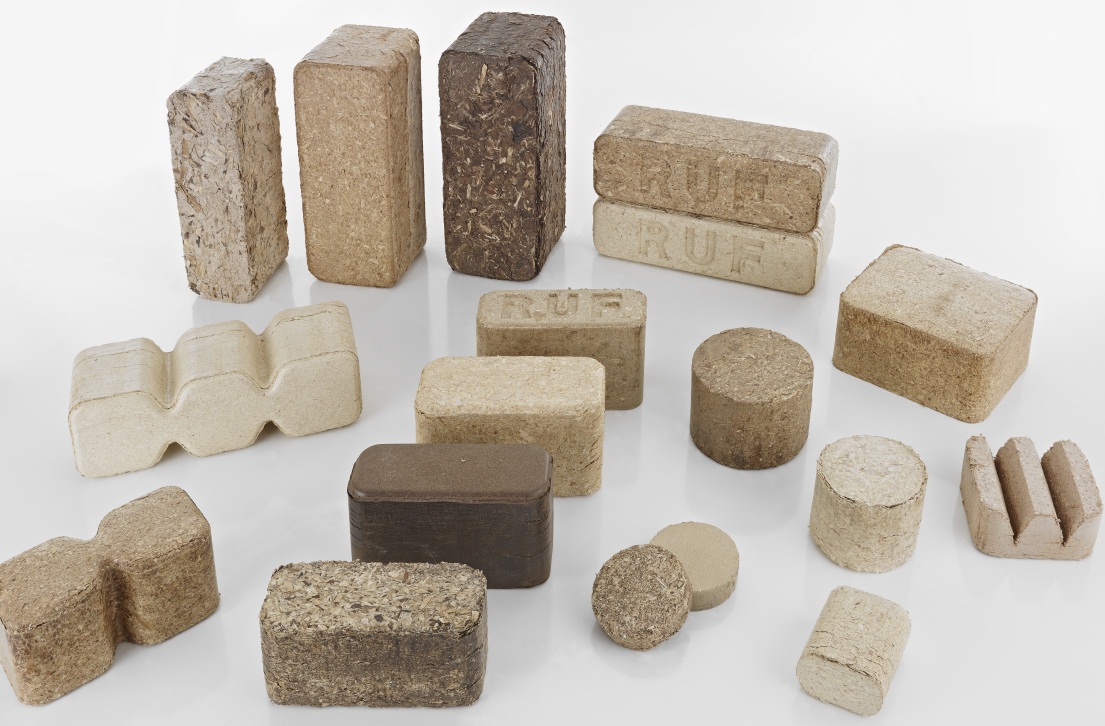
Fuel briquettes are modern type of alternative fuel. They can be used in any stoves, fireplaces, boilers, barbecues, barbecues. Eurobriquettes are cylindrical blanks resembling firewood, or rectangular bricks. Small dimensions allow to place them in furnaces of any size.
What are briquettes made of? Most often, wood is used (sawdust, shavings, dust), but straw, paper, peat, coal, seed or nut husks, and even manure are also used. The composition of the eurobriquette can vary significantly, depending on which technology is used in the production.
A home-made eurobriquette can be used to kindle a sauna stove or heat a house. Since the raw material is compressed quite strongly and the amount of moisture is minimal, the fuel briquette burns for a long time, constantly releasing a large amount of heat. An interesting point was noticed by people who are already actively using such fuel: if you melt your barbecue with eco-wood and fry food on it, it does not ignite if it gets on the briquettes of fat.

For solid fuel stoves, boilers and fireplaces, sawdust briquettes are an excellent option. They slowly flare up, but after burning for a long time and emit a large amount of heat.This is explained by the high density of the pressed wood product. The heat transfer from briquettes significantly exceeds the level of heat obtained by burning even the driest firewood, the storage and drying of which took at least a year.
Humidity of fuel briquettes is 8-9%, dry firewood, in turn, has an indicator of 20%. It turns out that a briquette made from the same wood burns better than the wood itself. This effect is formed due to the fact that during combustion, fuel briquettes do not need to evaporate a large amount of moisture.
The briquette burns with a stable fire, without splashes, sparks, cod, and the amount of smoke emitted during combustion can be described as small. It is extremely convenient to lay such fuel in the furnace, since all products have the same regular shape.

Like any product, fuel briquettes are not without disadvantages:
- First of all, it is worth noting that they are very vulnerable to moisture, therefore they are sold in cellophane packaging.
- Briquettes are not able to withstand mechanical stress, especially products made using the RUF technology that are not fired on the outside.
- If you want to set up the manufacture of such things at home, it will cost you a pretty penny, although there will certainly be a benefit in the long run. The fact is that you will have to purchase a grinding plant, a dryer and a press machine in order to carry out the entire cycle of work with raw materials. With the right equipment, it will be possible to set up handicraft production of fuel briquettes even in your own garage.
Briquetted coal - what is it?
Such briquettes are, in fact, a solid fuel product, which is produced in bars of various sizes and configurations.Such bars are produced by pressing at high temperature and under considerable pressure. To connect the particles of raw materials to each other, as well as to improve the strength characteristics of products, special binders are used (the latter can be of both organic and inorganic origin).
The efficiency of coal briquettes depends, first of all, on the duration of their burning and heat transfer properties - these indicators are significantly higher than those of traditional hard coal. No less important here is the density / shape of the bars - these characteristics contribute to uniform combustion and constant maintenance of the required temperature regime throughout the entire process of fuel combustion. The waste that remains after the extinction of the flame (ash) is only 3 percent. For comparison: for coal, this figure is 10 (!) Times higher. Finally, the briquettes do not fall apart in the furnace until they are completely burned out.

Varieties
As a solid fuel, peat is used by humans in three different forms:
- loose peat (crushed) is burned in suspension;
- lumpy fuel material, which has a low degree of compression;
- peat briquette (peat briquette), made on modern technological equipment, a product of a fairly high degree of pressing, has maximum useful characteristics.
Peat briquettes themselves are classified according to the type of mechanisms and equipment that are used in their production. The shape of the products will depend on this. There are several varieties.
Rectangle (or brick). Products have rounded corners. The homeland of this product is Germany. Produced using shock-mechanical and hydraulic presses.