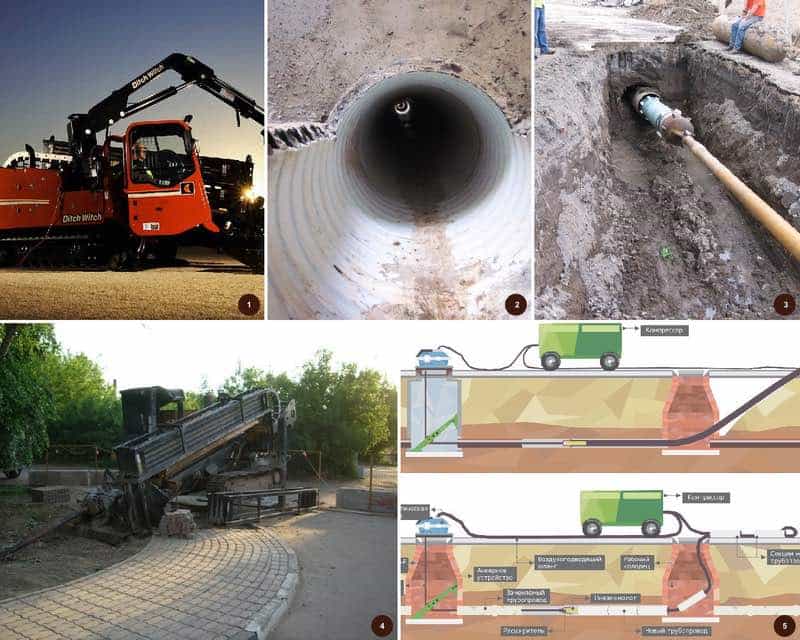
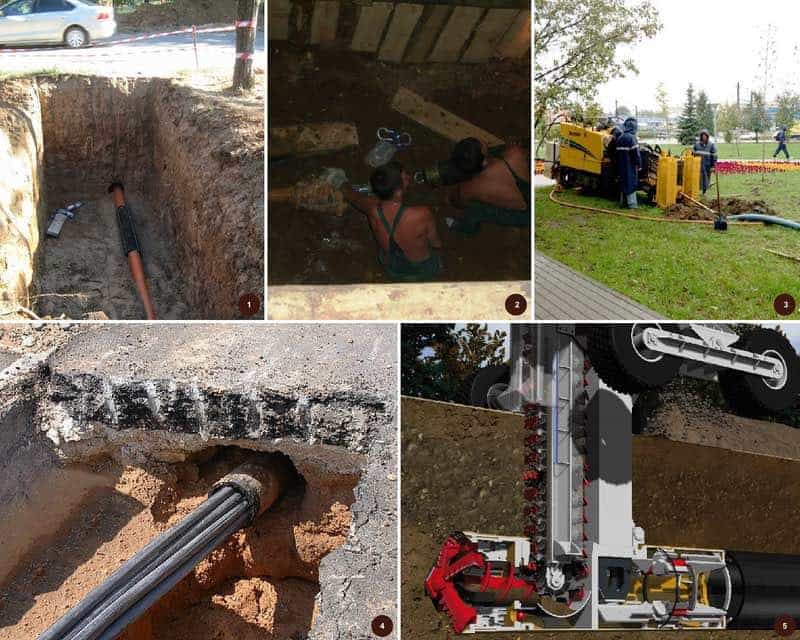
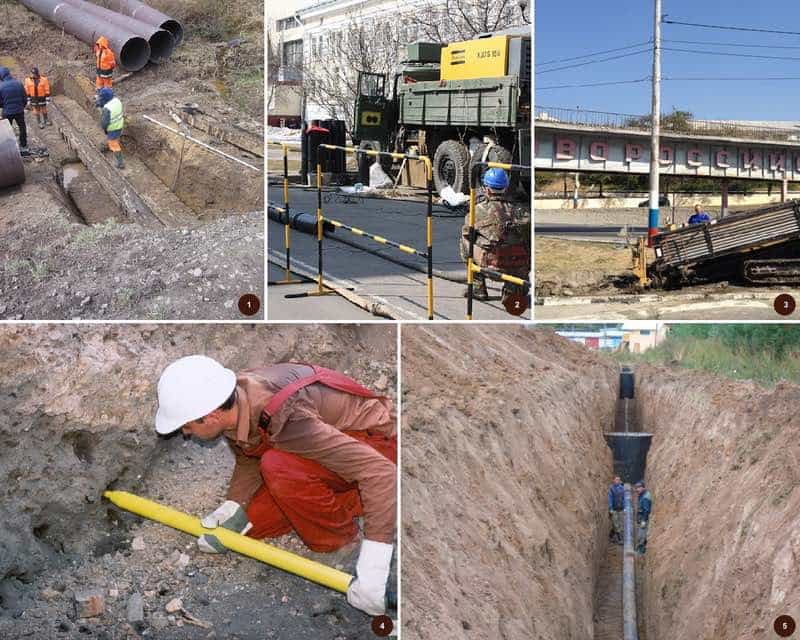
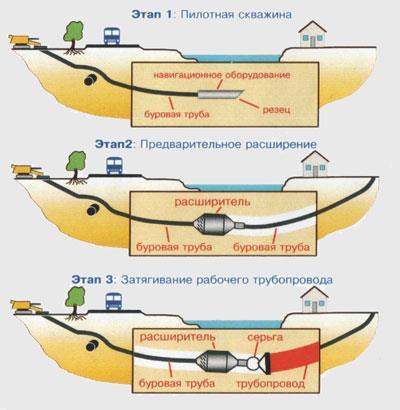
- Trenchless laying methods
- The nuances of trenchless sewerage
- Trenchless pipe laying methods
- What pipes to use for sewerage under the road?
- Trenchless repair of engineering networks
- Trenchless Pipeline Replacement Technology
- Piping Methods
- Information about ensuring the security of personal data
- A bit about history: how the HDD method originated
- Features of trenchless pipe laying
- Advantages of the method
- Scope of use
- Special equipment
- Advantages of the method and cooperation with our company
Trenchless laying methods
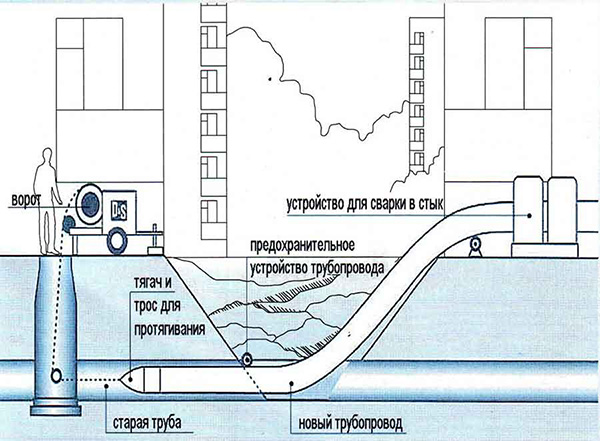
The trenchless method of laying called refurbishment combines a number of different methodologies that allow you to build a new line by updating the old one. At the same time, depending on what will be done with the old line, 2 groups of methods are distinguished:
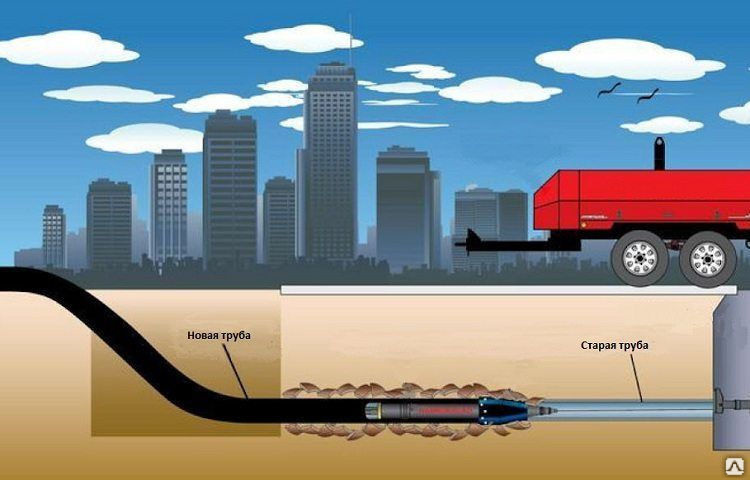
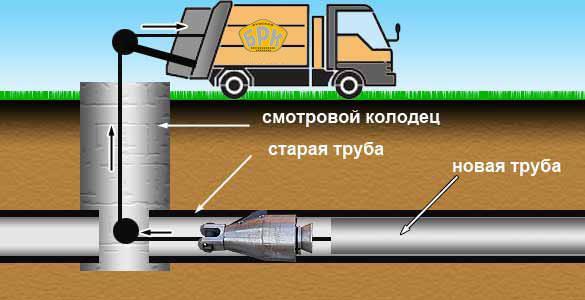
The first option involves keeping the old line. It is cleaned from foreign objects and all kinds of obstacles manually or using various techniques. And then a new line of smaller diameter is laid inside it from new materials that have a longer service life and improved characteristics.
Relining involves a lot of implementation options.Trenchless laying of communications can be carried out in this case both by pulling pipes from the opposite end of the path, and by pushing them from the starting point of construction (repair). At the initial stage, it is required to disconnect the repaired area from the water supply or sewerage system, with a parallel change in the flow route through temporary pipes. The introduction of new pipes can be carried out directly from the starting point or at any other point of the repaired pipeline with its partial destruction for the introduction of a new pipe. At the end of the installation, the flow is reconnected from the temporary pipes to the permanent updated paths.
The second option - Renovation, implies a complete renewal of the line with a possible decrease or increase in the flow diameter due to the static destruction of the previous structure. At the same time, its fragments are not brought to the surface, but remain inside, creating a compacted shell around the new structure.
Sanitation allows you to replace almost all old types of pipes from ceramic and concrete structures to metal variations.
The nuances of trenchless sewerage
Trenchless installation of sewerage has the following nuances:
- Before starting the laying, the craftsmen must study the scheme for the passage of underground communications - water pipes, drain systems, storm trays, gas supply pipes. If the work is carried out within the boundaries of settlements, then you need to find out at what level the foundations of buildings and structures, the bottom of ponds and lakes, tunnels and metro lines are. This will help to calculate the drilling depth and the trajectory of the route with an accuracy of up to a centimeter.
- For the manufacture of underground wells, modern equipment is used, which is operated by professionals with extensive experience. Depending on the volume of construction, mobile equipment on a caterpillar or wheeled chassis, stationary modular equipment is rented. To ensure its effective operation, it will be necessary to equip access roads and parking spaces for auxiliary mechanisms.
- For each type of soil, the right type of drilling fluid is selected. The correct choice depends on how strong the walls of the well will be, its stability and durability.
- When laying a gas pipeline, pipes of different diameters are pulled into the channel. The outer shell performs the function of protecting internal communications from contact with moisture and soil pressure.
- In the process of drilling a pilot well and its subsequent expansion, a large volume of water contaminated with bentonite and earth is formed. For its pumping and subsequent cleaning, a pumping station and an artificial settling pond will be required.
- Depending on the characteristics of the soil and the substances transported through the pipes, a material is selected that has the best resistance to the effects of internal and external factors.
Trenchless pipe laying methods
This method has become widespread in Europe. This comes with many benefits:
- Profitability. Unlike classical earthworks, trenchless laying is several times cheaper.
- The speed of work. According to this indicator, the classical method loses twice.
- Depth. The pipeline can be laid at a depth of up to 25 meters.
- The use of this method does not require road closures, does not prevent residents from moving freely around the yard area, and does not destroy the microclimate in the soil.
Either method also depends on the type of soil, the diameter of the pipe being laid, and where it needs to be laid. There are several basic options for performing such work:
- Ground breaking. When pipes need to be laid on clay or loamy soil, this method is chosen. With it, you can lay a pipeline with a diameter of up to 15 cm.
- Sanation. This method can be divided into renovation and relining. Relining is a method of installing a new plastic pipe into an old metal one. Therefore, polypropylene should be smaller in diameter than the old one. It is used in cases of minor damage to the pipeline. If its certain section is completely out of order, the renovation method is used. It involves the complete replacement of a node or section. When there are no other solutions than replacing part of the pipeline, renovation is carried out.
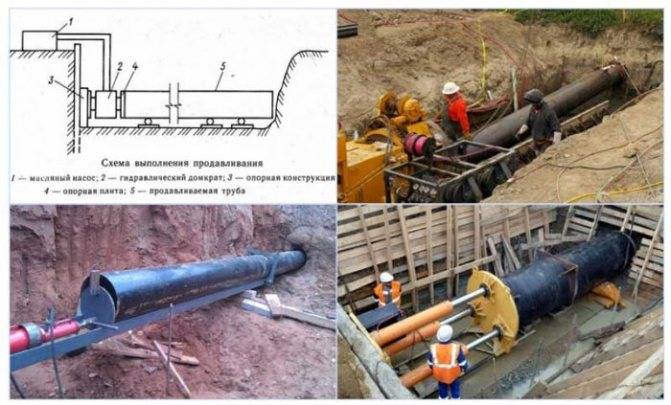
- Soil extrusion. This method is used on sandy and loose soils. With it, you can lay pipes of large diameter.
- Horizontal directional drilling. Universal method. Used on all types of soil. It is carried out with the help of drilling machines.
What pipes to use for sewerage under the road?
For sewerage, pipes with welded links are used, since other docking options are not suitable for a structure that is subjected to high tensile loads when pulled into the channel.
The diameter of the products is selected based on the specifics of the structure. So, for a private house, sewage from pipes of 100-110 mm is enough, and a highway with a cross section of 200 mm is laid for a nine-story house.To divert wastewater from the microdistrict, products of 300-400 mm are selected, with a length of 1 link of 12 m. The slope of the pipe should be 2-3º to ensure effective drainage and prevent blockages.
Cross-linked polyethylene is considered the best material for arranging sewer systems. Products have a diameter of 110-1420 mm, with a length of 1 section of 2-12 m. Docking is carried out by welding, the seams are durable and solid.
Steel has high strength and flexibility. Steel pipes are welded as they are pulled into the well. The disadvantage of the material is the instability to corrosion. The service life of black iron sewage is 25-50 years, depending on its quality and operating conditions.
Trenchless repair of engineering networks
The best method of restoring the operability of pipeline systems and preventing the subsequent creation of emergencies in urban environments is currently the use of trenchless repair technologies.
Trenchless technologies make it possible to reduce capital costs by an average of 30-50% in comparison with traditional excavation technologies and do not require many and often expensive approvals for repair work. Also, the use of such technologies reduces the consumption of electricity by pumping and power equipment by an average of 25-40%, and through the use of polyethylene and other inert materials, it stabilizes the throughput of pipelines.
For trenchless repair of water supply networks, pipes made of polyethylene, polypropylene or a composite - polyethylene plus polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are used.
The main advantages of such pipes are:
- lengthiness;
- elasticity;
- range of pipe diameters (up to 1600 mm inclusive);
- low coefficient of hydraulic resistance;
- equal strength of the butt joint and the pipe body;
- ease of installation;
- long service life of pipes (50 years).
In world practice, six main methods of trenchless repair of underground pipelines are used:
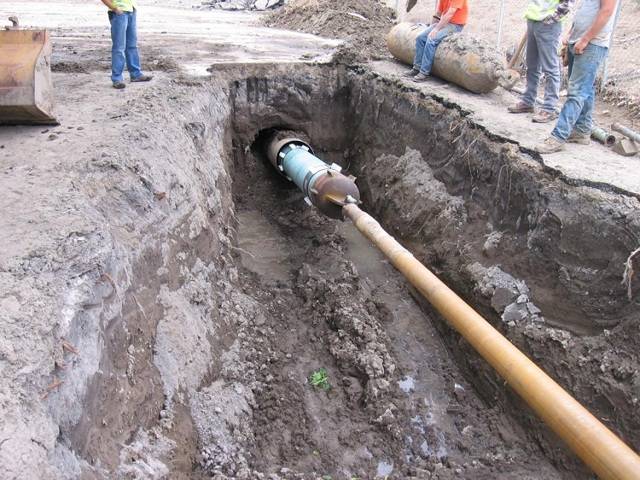
- "pipe in pipe" - pulling a new string of polyethylene pipes into the internal cavity of the repaired section. In this case, the outer diameter of the pipeline made of polyethylene is slightly less than the inner diameter of the repaired pipeline. The old pipeline is pre-washed with a high pressure jet. This technology is suitable for repairing both water and sewer networks.
- “breaking” is a special case of the “pipe in pipe” technology, with an increase in diameter by one standard size with the destruction of the old pipeline with a special pneumatic punch, which makes it possible to drag or push a new polyethylene lash of a relatively large length (> 100m) depending on the diameter;
- "stocking technologies" - dragging a special synthetic stocking inside the repaired pipeline, previously cleaned with a high-pressure jet. After pulling through, the pre-prepared stocking is polymerized in hot water at a certain temperature or irradiated with ultraviolet light, which ensures the formation of a strong inert layer of a pipe of adjustable thickness on the inner surface of the repaired pipeline;
- applying a cement-sand layer of various thicknesses to the inner surface of the repaired section of the network, previously cleaned with a high-pressure jet, followed by smoothing with a special cone.The technology is applicable only for the repair of water supply networks;
- "U-liner" technology, in which a U-shaped polyethylene lash is pulled inside the previously cleaned repaired pipeline, followed by its straightening with the help of a coolant of a certain temperature, followed by the formation of a new one-piece polyethylene pipeline;
- this technology is a local repair using self-propelled robots using various methods and materials.
The choice of the composition of technological equipment should be reduced to solving the problem associated with obtaining a minimum set of technical means that ensure the implementation of the technological process of trenchless repair of pipelines of a specific diameter, made of specific materials, at reasonable competitive prices.
Mandatory (initial) composition of technological equipment for all repair methods includes:
- a machine for hydrodynamic cleaning of the network (except for method 2);
- equipment for mechanical cleaning of pipes (except for method 2);
- equipment for TV - network diagnostics;
- equipment for butt welding of plastic pipes (except methods 3, 4, 6);
- equipment for tightening a whip of plastic pipes (except for methods 3, 4, 6).
Trenchless Pipeline Replacement Technology
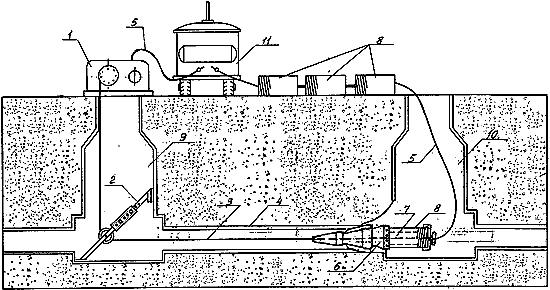
1 - pneumatic winch
2 - anchor
3 - winch cable
4 - replaceable pipeline
5 - air hose
6 - expander
7 - pneumatic hammer
8 - sections (modules-pipes)
new pipeline
9 - receiving well
10 - working well
11 - compressor
for Diakan LLC for the repair of sewer pipelines in St. Petersburg or Leningrad region.
Piping Methods


Underground pipes are laid in two main ways - open and closed.
The open method involves opening the soil and includes the following steps:
- - digging a trench to a depth regulated by GOSTs;
- - leveling the bottom and strengthening the walls of the trench;
- - backfilling of the sand cushion;
- — pipeline installation;
- — protection of pipes with inert materials;
- - trench backfilling;
- - Carrying out restoration work.
Cons of the trench method of laying communications:
- - high cost and labor intensity of work;
- — long terms of project implementation;
- - destruction of road surfaces, landscaped areas;
- - destruction of the natural landscape, fertile soil.
In some places it is generally impossible to lay pipes in an open way. It:
- - highways and railways that cannot be blocked;
- - individual industrial facilities and residential buildings;
- - insurmountable natural obstacles (ravines, reservoirs, swamps).
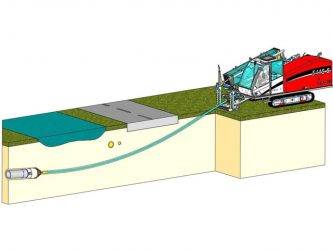
In such cases, the construction of pipelines is carried out in a trenchless way using special HDD equipment - drilling equipment, controlled puncture installations and hydraulic breakers, pneumatic punches.
In addition, if a company has trenchless equipment in its arsenal, it is sometimes advisable to carry out work with its help even in cases where open laying of communications is possible.
Information about ensuring the security of personal data
9.1. The operator appoints a person responsible for organizing the processing of personal data to fulfill the obligations stipulated by the Federal Law "On Personal Data" and the regulatory legal acts adopted in accordance with it.
9.2. The operator applies a set of legal, organizational and technical measures to ensure the security of personal data to ensure the confidentiality of personal data and protect them from illegal actions:
9.2.1 provides unlimited access to the Policy, a copy of which is posted on the website
9.2.2 in pursuance of the Policy approves and enforces internal local acts;
9.2.3 familiarizes employees with the provisions of the legislation on personal data, as well as with the Policy and internal local acts;
9.2.4 provides employees with access to personal data processed in the information system of the Operator, as well as to their material carriers only for the performance of work duties;
9.2.5 establishes the rules for access to personal data processed in the information system of the Operator, and also ensures registration and accounting of all actions with them;
9.2.6 makes an assessment of the harm that may be caused to the subjects of personal data in case of violation of the Federal Law "On Personal Data";
9.2.7 determines threats to the security of personal data during their processing in the information system of the Operator;
9.2.8 applies organizational and technical measures and uses information security tools necessary to achieve the established level of personal data security;
9.2.9 detects the facts of unauthorized access to personal data and takes measures to respond, including the restoration of personal data modified or destroyed due to unauthorized access to them;
9.2.10 exercises internal control over the compliance of the processing of personal data with the Federal Law "On Personal Data", the regulatory legal acts adopted in accordance with it, the requirements for the protection of personal data, the Policy, the Regulations and other local acts, including control over the measures taken to ensure the security of personal data and their level of security during processing in the information system of the Operator.
A bit about history: how the HDD method originated
Appearing in America almost thanks to the observation, enthusiasm and engineering talents of Martin Cherrington (Martin Cherrington), HDD technology has greatly developed, improved and gone far ahead, having won the recognition of builders around the world.
Today, Martin Cherrington is unequivocally recognized as the main inventor of the technology and is sometimes even called the "grandfather of directional drilling." And then, almost 50 years ago, the horizontal drilling industry was developing on several fronts, construction contractors were trying ways to overcome the problems of lack of control and the inability to make trenchless drilling for long distances. It was Cherrington who came up with the idea of combining two already used technologies - directional controlled drilling (it was used in the oil and gas industry) and horizontal drilling (already quite actively used in construction, but was uncontrolled). After several drilling trials, he successfully applied the new idea for the first time to drill a well for a gas pipeline under the Pajero River, which had very high banks with difficult rocky soil.Thus, the solution found was the beginning of a new technique: drilling along a given trajectory, and, if necessary, curvilinear.
BENEFITS AND ADVANTAGES of using HDD as a trenchless method of laying pipes; Areas of use.
The main features of horizontal directional drilling methods are that it allows in cramped urban conditions, or in the presence of highways on the construction path, to carry out trenchless (not damaging the surface) laying of pipes and communications for various purposes. and also solve the problem of overcoming natural barriers in the form of rivers. For clarity, we list the industries in which HDD capabilities have been used for a long time and with great success:
Trenchless pipe laying for transporting liquids and gases at construction of a water pipeline; sewers; heating networks; gas pipeline and oil pipeline, as well as other product pipelines.
Trenchless laying of communications all types: pulling an electric cable, laying communication and data cables; other types of communications.
Moreover, pipes are used in almost a variety of ways: from steel, cast iron, concrete, polyethylene, ceramics.
Due to its very essence, the idea of this technique, Trenchless technologies and in particular, HDD technology, contain a whole range of advantages. Let's list them point by point.
The method of HDD implementation does not damage the surface. The integrity of the road pavement is fully preserved and the traffic is not disturbed in any way;
accordingly, coordination with the traffic police, city public transport organizations is dramatically simplified and minimized and their terms are reduced;
The presence of natural barriers, such as rivers, ceases to be a problem for builders, and at the same time, it is not necessary to roughly disturb the landscape with bulky earthworks:
since no tangible harm is done to the ecology of the territory, coordination with environmental organizations also becomes minimal.
In turn, all this significantly reduces the overall time for preparing the construction of networks and communications.
With the trenchless method, the volume of earthworks is significantly reduced, there is no need to remove the soil, as with "ground" technologies for laying trenches;
the amount of equipment and labor required is also decreasing.
Will not affect the landscape - and, therefore, there are no costs for its restoration (including the cost of time)
The accuracy of the gait controlled from the surface makes it possible to exclude “erroneous” exits of the drill at an off-design point and damage to neighboring utilities, which is extremely important in a modern city.
Minimal risks of any emergency situations.
As a result of all of the above, the total financial costs can be reduced in general from 30% and up to 3 times, depending on the object and methodology.
The reduction of construction time is very significant: from 2 to 20 times.
— So, we objectively see a number of undeniable benefits. Thanks to all this, trenchless technology for laying pipes, pipelines and communications has become so popular in all developed countries as a highly efficient, cost-effective, and in a number of complex cases - simply irreplaceable technology.And that is why it is actively developing, conquering new markets.
Features of trenchless pipe laying
For many years, laying the pipeline in a trench has remained a common method of arranging urban communications. The consequences of these works are dug up sidewalks and green areas, damaged roadbeds, changed public transport routes and constant indignation of citizens. Although all this nightmare can be avoided if you use trenchless pipe laying technologies.
This is a closed method of arranging and repairing engineering communications, in which underground work is carried out without opening the soil. In this case, there is no need to build additional crossings, change traffic routes, and carry out a large number of agreements with other utilities.
 With trenchless laying of pipelines, 90% of the work is done underground.
With trenchless laying of pipelines, 90% of the work is done underground.
Compared with laying a sewer pipe in a trench, the trenchless method involves the construction of engineering networks by horizontal directional drilling, pipe punching, soil puncture, sanitation. This is the most promising way to build new and repair or replace old water and sewer networks in a big city.
Advantages of the method
The main advantages of the method are clear even to the average man in the street, who is not indifferent to the appearance of his native city.
- All communications that pass near the pipeline remain intact. Indeed, when digging a trench, gusts of neighboring networks very often occur.
- The economic benefit is that there is no need to connect additional equipment and labor for earthworks, backfilling of the pipeline trench.
- There is no need to make subsequent repairs of damaged asphalt, paving slabs.
- Speed of work.
- Possibility to work in winter.
- Preservation of the landscape, roadway, green areas.
- Minimal harm to the environment.
- There are almost no emergencies.
The advantage of using the trenchless method is that special preparatory earthworks are not required. For example, laying polyethylene pipes in a trench involves the use of an excavator, a sand or gravel cushion at the bottom. After laying, backfilling of the pipeline trench follows (SNiP imposes special requirements on this stage of earthworks), compaction and compaction of the soil. And in the case of a closed method of laying pipes, only a well-designed project of work, a well-thought-out optimal route without bends and turns, a calculated depth and slope of the pipeline are required.
Scope of use
The trenchless method of laying pipes is universal, since it can be used for various types of communications. It is indispensable for the construction of pipelines under a busy highway, railway tracks, subway lines, a river, as well as in conditions of dense laying of other networks. These communications may include:
- water pipes,
- sewer,
- electrical cables,
- pipeline,
- pipeline,
- communication cables.
Special equipment
Such work requires special equipment. Depending on which method of trenchless pipe laying is used for a particular engineering communication,
- drilling,
- hydraulic,
- location installations,
- generators,
- welding machines for plastic pipes,
- mortar mixing units,
- automanipulators.
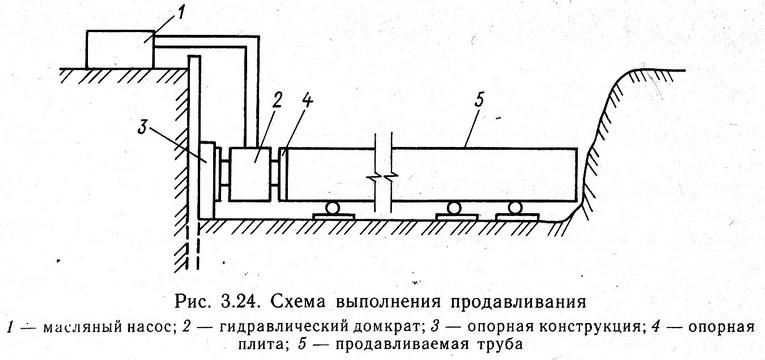
 The punching of the soil occurs with the help of a powerful hydraulic installation.
The punching of the soil occurs with the help of a powerful hydraulic installation.
Advantages of the method and cooperation with our company
Key benefits of the trenchless method:
- lower cost of work in comparison with other technologies;
- minimal damage to the environment and road surface;
- minimized risks of emergency situations on the laid pipelines;
- fast execution of work;
- trenchless technology makes it possible to perform punctures under the railway in the Moscow region, loaded highways and buildings;
- performed with the help of one drilling complex, managed by just a few specialists.
Compared to trenching, where the soil is removed along the entire length, in the case of horizontal drilling, only one entry and exit point is needed. As a result of the work, the road surface and landscape, laid networks and infrastructure are not disturbed. Also, the HDD method does not cause inconvenience to citizens, since with this method there are no torn sidewalks, ditches and mountains of garbage, there is no need to remove the soil. At the same time, the trenchless technique allows several times to speed up the process compared to the standard technique by digging ditches and pits.
Trenchless technique can significantly save finances and time. The question of how much a puncture under the road costs, you can check with our managers by calling the indicated numbers. They will also advise you on the features and other nuances of the work.